Why does pain occur during ovulation?
Only a highly qualified, experienced doctor can determine the cause of painful ovulation. If it is not possible to associate the pain with any disease, primarily gynecological, then the existing discomfort is usually explained by physiological reasons. Why does it sometimes happen that ovulation is very painful, but no pathology can be detected:
- The large size of the follicle can lead to stretching and rupture of some part of the ovarian capsule during the release of a mature egg.
- When an egg is released from the ovary, some fluid and blood may appear, which leads to irritation of the peritoneum (the inner lining of the abdominal cavity). But this bloody liquid is quickly absorbed by the peritoneum (absorbed), without causing the development of dangerous inflammation.
- Increased contractility of the fallopian tubes, trying to capture the egg released from the ovary.
If you experience pain or other severe symptoms during ovulation, it is strictly not recommended to delay visiting a doctor.
Clinical picture
In addition, painful ovulation may be accompanied by additional clinical symptoms and signs that will indicate a natural physiological process, and not some gynecological disease, for example, uterine fibroids or endometriosis. What signs might these be:
- Often, pain when a mature egg is released from the ovary occurs suddenly around the middle of the menstrual cycle. As a rule, before the onset of pain, health was normal.
- Depending on which ovary the egg comes from, pain can be observed in the lower abdomen both on the right and left above the pubis.
- It happens that the pain spreads to the groin area or pelvic bones.
- There may be a deterioration in the general condition in the form of weakness, fatigue, nausea, and headache.
In most cases, the duration of painful ovulation with other accompanying clinical signs ranges from several hours to 1.5–2 days. In case of severe, prolonged pain of various types and the addition of vomiting and fever, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Why does it hurt so much?
Ovulation is the phenomenon of the release of a mature egg from the ovary into the abdominal cavity. For most women, this is still a painless process, which is accompanied by additional signs:
- increase in basal temperature,
- breast swelling,
- increase in the density and amount of discharge.
Pain during ovulation can be mild, or it can be very strong and acute.
It is quite natural if you want to know why this happens and why exactly you experience painful symptoms at the stage of ovulation. It is immediately worth noting that painful ovulation is a permissible condition of the body and special treatment is not needed, unless you have confused the symptoms and your appendicitis has worsened.
Causes of pain during ovulation:
- Due to the large size of the follicle, stretching appeared, followed by a slight rupture of the ovarian capsule at the time of ovulation;
- Irritation of the peritoneum as a result of the release of the egg from the follicle and a small amount of blood fluid from the ovary, which is eventually absorbed;
- Intense peristalsis of the fallopian tubes, which try to draw in the egg released from the ovary.
Very rarely, pain at the time of ovulation can cause a disease, for example, adhesions in the abdominal organs, endometriosis or fibroids. But, in addition to unpleasant ovulation, there should be other signs of these diseases.
- Spontaneous pain in the middle of the menstrual cycle against the background of good health;
- Pain can be observed on the right or left side above the pubis, depending on which ovary is functioning;
- It can radiate to the groin area and pelvic bones;
- Minor weakness, nausea, cramps, migraine can complement the pain;
- The duration of pain varies - from a few minutes to two days, but not longer.
Unbearable pain (especially with fever and vomiting) is a reason to consult a doctor. It would be good if there were records of the conditions of previous ovulations: how long the pain lasted, on what day of the cycle, the nature of the sensations.
Pain during ovulation and conception
The appearance of pain and general symptoms of malaise, which are physiological in nature during ovulation, do not in themselves serve as the basis for the development of serious gynecological pathologies. Nevertheless, with this condition, a certain discomfort is still present during and after intimacy.
If you are planning to get pregnant, then you should not refuse sex during this period. Most experts are of the opinion that regular intimacy throughout the menstrual cycle significantly increases the chances of conception.
What sensations occur during ovulation?
The process of egg maturation may be accompanied by the following manifestations:
- During ovulation, the lower abdomen hurts. When a mature follicle bursts, some of the blood enters the abdominal wall, and some into the uterus. This causes pain in the lower abdomen during ovulation, followed by the release of ichor. Also, the movement of the egg through the fallopian tubes and possible penetration into the endometrium may be accompanied by bleeding and discomfort in the abdomen.
- Head pain and confusion. Decreased estrogen production can cause cerebral vasospasm and provoke pain. If you have a headache after ovulation, this may indicate the presence of endocrine disorders.
Nausea and vomiting may occur during ovulation
- Nausea and vomiting. Hormonal changes in the body and the presence of pain can have a negative impact on the functioning of the digestive tract. Appetite decreases, symptoms of nausea appear, and in more pathological cases, vomiting is possible.
- Spotting ichor. Symptoms of ovulation and pain last no more than 2-3 days; if the amount of blood released is significant and the discharge does not stop, then this is a reason to consult a specialist.
- Increased libido. During this period, blood flows to the genitals and causes sexual desire in a woman. This is a manifestation of the natural need of the female body for procreation.
- The discharge becomes clear and non-sticky. The vaginal secretion acquires such a consistency in order to facilitate the penetration of sperm into the uterine cavity
- .Increase in basal temperature. Women who regularly record their basal temperature may notice that the lowest temperature in the vagina is observed immediately before the ovulation process, then it increases sharply in the second stage of the cycle.
- Feeling of weight gain, swelling, discomfort in the mammary glands. Girls may experience such sensations due to an increase in progesterone levels in the blood.
- A woman's body is preparing for possible conception. The mammary glands swell, the uterus swells, the total body weight increases, and ovulation pain appears.
Chest discomfort and pain may occur
How can childbirth affect ovulation?
Often, pain in the middle of the menstrual cycle appears after childbirth or inflammatory diseases of the internal genital organs. Surgery, such as an appendectomy, can also cause similar symptoms. In addition, the adhesive process in the abdominal cavity, which can occur after cesarean section, laparoscopy and various abdominal operations, quite often leads to painful ovulation.
If you experience pain in the middle of the cycle after childbirth, you should definitely inform your doctor about it in order to rule out a more serious pathology. In situations where there are reasonable concerns about the development of a pathological process in a woman’s body, a comprehensive medical examination is provided, which consists of the following:
- Patient interview.
- Clinical examination.
- Gynecological examination.
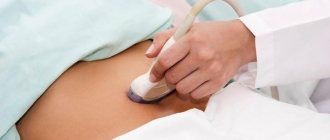
- Ultrasonography.
- Lab tests.
As a rule, if childbirth proceeded well without complications, then after normalization of hormonal levels, painful ovulation is not observed.
Breast tenderness after ovulation
Many women note soreness and an increase in the size of the mammary glands during the expected period of ovulation and for 2-3 days after it. This is due to hormonal changes that have occurred in the body. This is a kind of signal that a mature cell has left the female body, and a new one is ready for fertilization.
This period is considered the most effective for family planning. Such changes occur 5-7 days before the start of a new menstruation, and therefore gynecologists and patients tend to call this phenomenon a sign of premenstrual syndrome.
Thus, breast tenderness that occurs for several days in the middle of the menstrual cycle is normal. This is a signal that ovulation has occurred.
https://youtu.be/AmWlrEJ1WeM
Treatment
What to do if you have painful ovulation? First of all, you need to calm down and create a comfortable psycho-emotional atmosphere around yourself. It is especially not recommended to be nervous or make sudden movements. It is better to avoid any physical activity altogether. Both traditional medicine and traditional medicine will come to the rescue.
Traditional approach
Pain that causes significant discomfort should not be tolerated. If very painful ovulation occurs, you must try to cope with the pain by all available means. However, without the knowledge of the doctor, you should not resort to the use of serious manipulations or medications, including folk remedies. What can you do if you have painful ovulation?
- Take a warm bath or apply a heating pad to your lower abdomen. Such procedures are quite effective in relieving spasms. However, they can only be used when you are absolutely sure that you are experiencing physiological painful ovulation, and not some kind of pathological inflammatory process. Otherwise, you will only significantly worsen your current condition.
- Light circular massaging movements of the area of the body where the pain is felt most.
- Take painkillers or antispasmodics. Today, the choice of such drugs is very wide. For example, No-shpa, Papaverine, Analgin, Buscopan, etc.
- Physiotherapeutic procedures also have a very positive effect on the female body.
Do not forget that taking medications must be agreed with your doctor.
ethnoscience
Some experts in folk remedies advise, in case of painful ovulation, to saturate your diet with foods that are rich in calcium and magnesium. Therefore, girls and women should indulge in nuts, greens, dried fruits, dairy products, legumes, cereals, etc. It is useful to drink up to 6-8 glasses of purified water. If you experience severe pain, try drinking a decoction of yarrow and chamomile or an infusion of calendula flowers.
Painful ovulation, nausea, vomiting, fever, spotting - this is an immediate reason to go to the hospital to receive professional medical help.
Collapse
Ovulation is the process of maturation of the follicle and the egg in it, after which this follicle ruptures, and the egg exits through the fallopian tube into the uterine cavity, where it can be fertilized. This process occurs in a woman every or almost every month (sometimes there are anovulatory cycles) and is accompanied by characteristic symptoms. One of these symptoms is pain of various types. What kinds of pain occur during ovulation, how to get rid of them and in what cases you need to seek help from a specialist - this is discussed in this material.
Are there any pains?
Is there pain during ovulation and is it normal to experience physical discomfort during this period? In most cases, pain during this period is not a pathological abnormality, and every woman of reproductive age has encountered it at least once. In general, they usually have low intensity even compared to the symptoms of premenstrual syndrome and often appear irregularly. That is, during one cycle, painful sensations during ovulation may appear, but not during another. Some women experience painful ovulation after childbirth.
Visit to the doctor
If a woman experiences very painful ovulation, she needs to immediately go to the doctor and, in addition, sign up for an ultrasound examination in order to collect a detailed medical history. It is not at all necessary that the doctor will discover a serious cause. On the contrary, it most often happens that this is, in fact, a natural feature of the body. But you should still check the state of your women’s health in such a situation.
In addition to pain during ovulation in the lower abdomen, there may be other symptoms.
Causes
Why do discomfort and pain symptoms occur during ovulation? This is due to a number of reasons.
- Hormonal changes cause chest pain and mild breast tenderness, as well as headaches;
- The very fact of rupture of the follicles when the egg is released can be accompanied by pain as a result of injury - it can be felt in the lower abdomen, in the ovary, in the side, etc.;
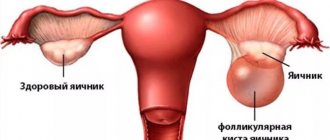
- There are functional cysts that form on the ovaries under the influence of hormonal levels - they arise during the menstrual cycle and resolve on their own after a certain stage, and they can also cause quite severe pain during ovulation.
In addition, such symptoms can be caused by many pathological causes, such as inflammatory processes, cysts, etc. Therefore, if such symptoms do not go away over a long period of time (or are accompanied by any other deviations in well-being), then you need to seek advice from a specialist.
Before her
In itself, ovulation lasts one day (or even several hours), but it is customary to allocate several days in the menstrual cycle, which are called ovulation. During the first day, the eggs are ready to be released and fluid accumulates in the follicles, but they do not burst yet. They then burst and the eggs begin to exit into the uterine cavity through the fallopian tubes. This day is considered the day of ovulation.
But the first symptoms of ovulation appear before it, that is, even at the stage of follicles being ready to rupture. Typically, this corresponds to days 12-15 of the menstrual cycle (depending on the duration).
On the day of ovulation
Sometimes during ovulation the stomach hurts, sometimes the lower back, side or ovary hurts. All this is a sign that the follicles are rupturing. It is this that feels quite painful, but such discomfort is localized mainly in the ovary. However, painful sensations from there can erode to the side and lower abdomen. Pain in the lower abdomen can also be caused by functional cysts formed under the influence of hormonal imbalance.
After
The process ends completely 2-3 days after the egg is ready for release. The whole process usually takes place within 12-16 days of the menstrual cycle. Thus, on the 15-16th day the end of the process may become painful. The same discomfort persists. But by 16-17 days, such pain completely disappears.
Painful ovulation
If ovulation is so painful that a woman writhes in pain, then the only correct solution is an ambulance. While waiting for the emergency room, the girl should not take painkillers, as they mask the symptoms and do not eliminate the causes, which prevents doctors from making a diagnosis.
Why is there pain in the chest? When her breasts start to hurt, the girl already knows that her period will begin soon. Mastodynia (the correct name for this symptom) also occurs in healthy women.
It is considered normal if a minor symptom does not prevent the girl from leading her usual lifestyle. But you need to get checked if the pain hampers movement or is accompanied by fever, as this symptom can be caused by:
- hormonal imbalance;
- diseases of the mammary glands.
In addition, many symptoms are justified by the individual anatomical structure of the woman.
Nature of pain
Pain does not occur in every cycle. It is normal if only a certain number of ovulations are accompanied by noticeable discomfort, while the majority go completely unnoticed by the woman.
Regular
The nature of pain during ovulation is normally mild; it usually does not cause significant discomfort. It is nagging or aching, is not constantly present, and is quite diffuse (with the exception of pain in the ovaries - in this case it can be very localized). In most cases, the use of painkillers for such symptoms is not required, or they are used once.
A slightly more acute pain can be observed in the ovary, a little less acute and much more diffuse - in the lower abdomen. A pulling sensation usually occurs in the lower back, back or side, although more often it is dealt with solely by a feeling of heaviness.
High intensity
Some increased discomfort is possible for several cycles after childbirth. However, the condition should return to normal soon. In any other case, pathological symptoms are possible, indicating some process that needs to be treated. Therefore, if high-intensity pain occurs during this period, it is recommended to immediately consult a gynecologist.
Types of pain
Most often during ovulation, the lower abdomen hurts, but there may be more diverse negative signs. This is heaviness in the lower back, discomfort in the side, sharp pain in the ovary, migraines, discomfort in the mammary gland.
Pain in the lower abdomen
Most often, women experience abdominal pain during ovulation. These symptoms can be relieved with analgesics and drugs such as Ibuprofen, Nurofen, used in the form of rectal suppositories or tablets. Such pain is associated with erosion from the ovaries, hormonal changes, and the appearance of functional cysts.
Back and lower back pain
Low back pain during ovulation has the same reasons. You need to fight it in the same ways. It occurs independently or together with discomfort in the lower abdomen.
Pain in the ovary
Pain in the ovary during ovulation, as mentioned above, occurs as a result of rupture of the follicle. Since follicle maturation usually occurs only in one egg, these pains are one-sided and clearly localized. Ibuprofen, Nurofen, Diclofenac, which are taken 2-3 times a day, will help get rid of them, as long as symptoms occur.
Side pain
If your side hurts during this period, then most likely this is a sign that pain in the ovary is eroding into this area. This discomfort is strictly one-sided, the pain is diffuse and not intense. May also erode into the lower abdomen. Treated with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and analgesics. In general, you need to deal with them in the same way as with pain in the ovaries.
Pain in the rectum
If pain during ovulation radiates to the rectum, this is not a pathology. Such symptoms can be caused by a formed functional cyst, which resolves after passing through this stage of the cycle, and accordingly, the negative symptoms also go away. This pain can be relieved with analgesics, painkillers and anti-inflammatory non-steroidal drugs.
Chest pain
Breast pain during ovulation as a result of the negative effects of hormones. In addition to discomfort, there may be a slight, non-local compaction and engorgement of the glands, which goes away along with the end of ovulation, but this condition begins to manifest itself a few days before it begins. There is no need to relieve such pain, since normally it is not of high intensity, and painkillers may be ineffective.
Headache
Headache during ovulation as a result of hormonal imbalances, which can contribute to the exacerbation of migraines or their onset. This discomfort can be quite intense and constant. It can last from several hours to 2-3 days, i.e. throughout the entire process of maturation and release of the egg.
To normalize the condition, you can take painkillers, for example, analgin, but you should not drink it systematically. For prolonged attacks, use Nurofen, Ibuprofen, etc. Women prone to migraines may require anti-migraine medications.
Possible pathologies
Unpleasant sensations may be accompanied by minor bleeding and last a maximum of three days. The discomfort is minor. But debilitating and prolonged pain is a reason to immediately seek medical help.
Ovarian apoplexy
Rupture of ovarian tissue, accompanied by hemorrhage into the abdominal cavity. It occurs against the background of increased intra-abdominal pressure due to heavy physical exertion, intense or interrupted sexual intercourse, or abdominal trauma. Women who have had an abortion and suffer from pelvic inflammatory diseases are most susceptible to pathology. The pathology is characterized by severe pain in the lower abdomen.
Pain during ovulation radiates to the anus, perineum, lower back and navel. Attacks occur periodically throughout the day. Bleeding causes a decrease in blood pressure and a weakening of the pulse. Patients turn pale, experience weakness, dizziness and dry mouth. Possible vomiting, increased frequency of urination and defecation, and loss of consciousness. If there are no obvious signs of hemorrhage, conservative treatment is carried out. Patients are advised to rest and apply cold to the abdomen. They are prescribed hemostatic drugs and painkillers, and undergo physiotherapeutic procedures. In difficult cases, surgery cannot be avoided.
Endometriosis
Pathological growth of the endometrium. This is the inner epithelial layer of the uterus that forms during ovulation. Sometimes it grows in the wrong places, for example, in the ovaries. The reasons for the phenomenon are not fully understood. Presumably, it's all about hormonal imbalances, weakened immunity or genetics. It manifests itself in the form of pain, which intensifies during menstruation and ovulation and radiates to the lower back. The menstrual cycle is disrupted. Heavy bleeding is possible. Constipation or diarrhea occurs. Patients are prescribed painkillers and hormonal medications. In some cases, the growths are cauterized or the ovaries and uterus are completely removed.
Ovarian cyst
A benign neoplasm, in most cases caused by hormonal imbalances. It is a cavity filled with liquid contents. Formed from a follicle from which an egg has not been released. It may be asymptomatic and resolve on its own. When large in size, it causes physical discomfort in the lower abdomen. Pain during ovulation radiates to the leg. Heavy intermenstrual bleeding occurs. Urination is impaired. When the capsule ruptures or twists, nausea, vomiting and severe abdominal pain occur, and the temperature rises. Patients are prescribed hormonal medications, vitamins and physiotherapy. If conservative treatment fails, surgery is indicated.
Pain during ovulation is normal. Their duration and intensity vary from person to person. But if you experience severe and prolonged pain, you should not put off visiting a doctor. Periodic discomfort can hide dangerous diseases. Some of them lead to infertility and even death.
When should you see a doctor?
In what cases are pain before ovulation pathological? What to do in this case? The list below shows signs that the developing condition is no longer normal and should promptly contact your doctor:
- Very painful ovulation occurs and/or the pain has become much more intense than before;
- Painful symptoms are accompanied by severe bleeding that is large or lasts too long;
- Pain lasts longer than 2-3 days;
- Uncharacteristic discharge with an unpleasant odor appears - purulent, cheesy white, etc.;
- Along with the discomfort and aching sensation, lumps appeared in the chest;
- The intensity of the pain gradually increases, and painkillers do not help;
- There is a significant increase in body temperature, weakness, chills, and signs of intoxication.
The reasons for this phenomenon can be different, including very serious ones. Therefore, it is extremely important to seek help from a medical institution in a timely manner. Increased pain may indicate inflammatory, infectious and fungal processes, pathological neoplasms, etc., the presence of which can affect not only reproductive function, but also health in general.
←Previous article Next article →
Periodically occurring pain of low intensity, wherever it appears - in the lower abdomen, head or lower back - rarely causes women to have any concerns about their own health. But if the pain syndrome has a certain periodicity, for example, it appears consistently before, during or after ovulation, this makes you think. Women who are planning a pregnancy and those who have already encountered gynecological diseases are especially worried.
Below we will look at the reasons for painful ovulation, we will look at when you can take a painkiller tablet and wait out this period, and when urgent medical attention is needed. Let's not ignore some other symptoms that may occur during ovulation.
Some statistics
After a girl’s menstruation has become stable, after a while she begins to notice changes in her condition that occur approximately in the middle of the cycle. Usually they only concern the mammary glands, mood changes or increased sexual desire, but 20-30% of women notice that their lower abdomen hurts during ovulation. This pain is nagging in nature, varies in intensity, and is usually noted on one side.
In 85% of women, pain during ovulation is associated with natural processes. In 14% of cases, such symptoms indicate a pathology of the reproductive system. Finally, there is a small, about less than 1% probability that just during the ovulatory phase of the cycle another pathology will develop, not related to the very release of the oocyte from the follicle.
Why does the pain not go away after ovulation?
If after 48 hours the pain during ovulation does not go away and even intensifies, then this indicates the presence of a serious pathology in the reproductive organs. Causes of pain during ovulation can be:
- endometriosis;
- the presence of adhesions and cysts;
- endocrine disorders;
Pain is persistent in endometriosis
- presence of a tumor process;
- inflammatory processes;
- presence of sexually transmitted infection;
- ectopic pregnancy.
A woman needs to be examined by a gynecologist at least once a year, regardless of whether her stomach hurts during ovulation.
Ovulatory pain - normal or pathological
It would seem that pain during ovulation has every reason to develop, because the follicle containing the egg first grows to a fairly large size and then bursts, and the nerve endings approaching the ovary react to both of these processes. But usually only those who have a low pain threshold feel this normally. That is, if a woman does not tolerate pain well from childhood and may even lose consciousness because of it, she should not be alarmed by the pain of the ovulatory phase, unless 5 conditions are met:
- Ovulation is determined by tests: determination (its decline was noted on the previous day, and on this day a sharp rise is visible), or.
- It hurts on one side (for example, the left ovary), since in each cycle the dominant follicle, that is, the one that prepares the egg for fertilization, develops only in one ovary. Each cycle, the “working” ovary may change, but it may happen that for several months in a row the pain is felt only on one side.
- There are no pathological symptoms: dizziness, vomiting (mild nausea is allowed for 2-3 hours), weakness, or a feeling of unreality of what is happening.
- The temperature remains up to 37°C, the maximum rises to 37.3-37.4°C.
- Other symptoms of ovulation are also noted: swelling and tenderness of the mammary glands, a change in the nature of vaginal discharge to the appearance of raw egg white, and increased sexual desire. There may be a discharge of a small amount of blood (usually in the form of brown or yellowish mucus), which is associated with the detachment of a small area of the endometrium due to a sharp drop in estrogen levels.
Blood vessels approach the shell of the follicle in which the egg has matured - they provide nutrition to this structure. Therefore, when it bursts, the vessels rupture, and a small volume of blood flows into the abdominal cavity. A small amount of fluid in which the oocyte was previously located is also released. These fluids are an irritant to the peritoneal nerve endings, and therefore cause pain during ovulation. In this case, the pain is felt on one side and can migrate from the left or right to the lower abdomen - the suprapubic region. If blood flows into the space between the vagina and rectum, nagging pain is felt not above the pubis, but in the lumbar region.
When a woman has a low pain threshold and has 5 of the above signs, then pain in response to bleeding from the follicle vessels is a normal phenomenon that does not require any emergency measures. If the pain syndrome is very intense, or does not occupy the lower abdomen or lower back, but radiates to the left or right side, you need to be urgently examined for three conditions.
- Endometriosis
Causes of pain during ovulation
Ovulation is the process of the release of a mature egg from the follicle. It may last several minutes or several hours. Rupture of the sac is accompanied by discomfort in the perineum. In addition, blood from broken capillaries and follicular fluid irritate the receptors and cause contraction of the uterus and fallopian tubes.
With heavy bleeding, clots can accumulate in the pouch of Douglas. This is the area of peritoneum between the back wall of the uterus and the rectum. Pressure on the tissue also causes discomfort.
One ovary is involved in each cycle. Therefore, one month the right side hurts during ovulation, and the next month the left side hurts. Attacks can be cutting, stabbing and cramping in nature. It is important to remember that discomfort cannot last longer than 72 hours and should not cause severe suffering.
Discomfort may increase with a low pain threshold, the presence of adhesions on the reproductive organs, or while taking hormonal medications. To improve the condition, it is recommended to take painkillers. Drinking plenty of fluids and rest also helps. Some people advise placing a heating pad on your lower abdomen, but this is not safe. The fact is that severe pain during ovulation can be a sign of an inflammatory disease. In this case, heat will only make the situation worse.
Pathological causes of painful ovulation
You should definitely undergo an examination and rule out serious diseases if you have the following symptoms:
- severe nausea and/or vomiting;
- weakness;
- temperature increase;
- loose stool;
- dizziness.
If the pain is intense, requires taking a certain position of the body, is localized in the right side, hospitalization in a surgical or gynecological hospital is required, because this can manifest not only appendicitis, but also ovarian apoplexy, torsion of the pedicle of an ovarian cyst, acute inflammation of the uterine appendages.
A painful ovulatory phase is a sign of a disease in the presence of the following conditions:
- algodismenorrhea;
- heavy menstruation;
- pain during sexual intercourse;
- contact bleeding;
- lack of libido;
- disturbances in the basal temperature chart.
In this case, you need to visit a gynecologist as soon as possible.
During ovulation
The pain that occurs during the onset of ovulation can be caused by the fact that the follicle in the middle, which contains the female reproductive cell, begins to actively increase in size, after which it bursts, and during this period, an egg that is already mature and ready for conception is released.
Nerve endings located close to the ovaries, in turn, react to these changes occurring in the body, causing pain, which is often felt by women who have a very low pain threshold.
Based on this, if a representative of the female half of the population tolerates pain very poorly from early childhood, then she should not be alarmed by the pain that occurs during ovulation only if the following conditions are met, such as:
- Clear determination of ovulation using special methods (basal temperature measurement, ovulation test, ultrasound folliculometry).
- Soreness occurs on one side, in the place where the ovary is located. This phenomenon is caused by the fact that in each menstrual cycle there is a dominant follicle in which the female reproductive cell matures, ready for the process of conception. During each cycle, the location of the dominant follicle may change, but in medical practice there have been cases where pain syndrome was recorded only on one side for several monthly cycles in a row.
- The absence of other symptoms, manifested in the form of dizziness, gag reflex, and general weakness of the body.
- Body temperature does not exceed 37°C, in rare cases 37.2 - 37.3°C.
- Symptoms characteristic of the onset of ovulation occur, which manifest themselves in the form of slight swelling and tenderness in the mammary glands.
The follicle, where the maturation of the egg occurs, is covered with a membrane in which blood vessels are located, ensuring the delivery of useful and nutrients necessary for the growth and formation of the egg. In this regard, when the required size is reached, not only the follicle ruptures, but also the vessels.
This phenomenon leads to the leakage of a small amount of blood into the abdominal cavity, in addition to this, there is also the release of fluid where the oocyte was previously located. These two types of liquids are a kind of irritant to the nerve endings located in the abdominal region.
These endings, in turn, react to them, causing pain during the ovulatory phase. Pain can have different localization and can be felt on the right or left at the location of the ovary, as well as directly in the lower abdomen in the suprapubic region. When blood leaks into the area between the vagina and rectum, pain may appear in the lumbar region.
If a woman knows about her low pain threshold and has all the signs described above, then the pain resulting from rupture of blood vessels and subsequent leakage of blood is a physiological, not a pathological phenomenon and, in turn, does not need to take any measures.
Pathology
In the case when the pain is very intense and does not radiate in the lower abdomen, but only in the left or right side, then the woman needs to be examined for possible detection of the following conditions, namely:
- Endometriosis is a disease characterized by the spread of the endometrium outside the uterine cavity. In this situation, a hormonal imbalance occurs and a larger volume of blood is released after the follicle ruptures and the egg is released from it. This process causes pain.
- Adhesions – this pathological change must also be excluded if ovulation is painful and there are no symptoms such as weakness, dizziness, nausea leading to vomiting, as well as an increase in body temperature. In this situation, adhesions arise between nearby internal organs, which are bridges consisting of connective tissue. Adhesive neoplasms most often arise as a result of surgery, the purpose of which is the treatment of various diseases.
- Hormonal disbalance. The occurrence of this pathological condition is mainly indicated by an irregular monthly cycle, as well as scanty or, conversely, very heavy menstruation. Such changes very often occur in women who have recently become mothers. In this case, doctors use the waiting method.
If the pain that occurs during ovulation does not disappear within several cycles in a row, a series of tests is prescribed. Diagnosis mainly involves donating blood to determine the concentration of hormones in it and undergoing a transvaginal ultrasound examination.
Based on the duration of pain during ovulation, one can assess whether it is normal or, conversely, pathological. It is considered normal when pain disappears after two days and is caused by rupture of the follicle and blood vessels, as well as subsequent absorption of blood that has entered the peritoneum.
When the duration of painful ovulation is more than 72 hours, this condition is classified as a pathology and in this case it is necessary to consult a doctor to accurately identify the causes of pain.
Women are recommended to undergo a set of examinations as quickly as possible if the following symptoms occur, such as:
- pronounced signs of nausea, which often end in vomiting;
- general weakness of the whole body, contributing to poor health;
- an increase in a woman’s body temperature;
- diarrhea;
- dizziness.
If high-intensity pain occurs in the left side, the woman is advised to contact a medical facility, since the pain can be caused by inflammation of the appendix, ovarian apoplexy, torsion of the pedicle of the ovarian cyst, as well as inflammation of the appendages.
Painful ovulation can be a sign of various diseases, in the presence of conditions such as:
- algodismenorrhea;
- heavy menstruation;
- pain that occurs immediately during sexual intercourse;
- the appearance of bloody discharge after sexual intercourse;
- severe decrease in libido;
- failure in the basal temperature chart.
In this situation, a woman needs to visit a gynecologist as quickly as possible.
Causes of abdominal pain before ovulation
Sometimes a woman worries that she is experiencing pain before ovulation, but in fact, due to physiological or pathological reasons, the moment of release of the egg occurred earlier, that is, in fact, she is now ovulating.
Physiological reasons for the shift in the ovulatory phase include: stress, acute illnesses and exacerbation of chronic pathologies, time zone changes. Ovulation can also shift due to inflammatory diseases, endometriosis, and endocrine diseases that have developed in the uterine appendages (pathologies of the adrenal glands, hypothalamus, pituitary gland).
If your stomach hurts before ovulation, and this is clearly visible from the basal temperature graph or folliculometry data, the symptom indicates the presence of various pathologies:
- growing, manifested, in addition to constant pain, by the discharge of blood from the vagina during the intermenstrual period, as well as longer and heavier menstruation;
- the development, immediately before the release of the oocyte, of inflammation of the uterine appendages (), intestines or urinary organs, each of which is complemented by characteristic symptoms.
Why does pain persist after ovulation?
If the ovary hurts after ovulation, this indicates the development of one of the following conditions:
- . Here, the pain syndrome is caused by the “attempts” of the follicle to burst and release the egg. The pain intensifies during sexual intercourse, sudden movements, and physical activity. Complications of a follicular cyst are torsion of its legs and rupture of its membranes.
- accompanied by severe sharp pain in the lower abdomen, which radiates to the rectum, navel or lower back. Against this background, weakness increases, dizziness develops, and loss of consciousness may develop.
- Torsion of the vascular pedicle of the cyst. Her symptoms are no different from the previous condition.
- Uterine fibroids described above.
- Adnexitis. In this case, quite intense pain in the abdomen occurs, which can lead the woman to the operating table. The temperature rises, a headache develops, and copious discharge appears from the genital tract, often of a mucopurulent nature.
- , in which the amount of progesterone in the blood decreases. This leads to abdominal pain “like menstruation”, while menstruation itself does not occur for a long time.
- , even before the appearance of general symptoms indicating conception, it may manifest as pain in the lower abdomen. This is how the fallopian tubes react to being stretched by the growing embryo.
- Development . For various reasons, menopause may begin not at 40-45 years old, but earlier (). Soreness after ovulation is one of its first manifestations, then a decrease in menstruation, hot flashes, headaches, and sweating will be noted.
Is lower back pain associated with ovulation?
If a patient complains of pain in the lumbar region that occurs after ovulation, the doctor needs to conduct a differential diagnosis of conditions such as:
- threat of miscarriage;
- uterine fibroids;
- rupture of an ovarian cyst;
- appendicitis;
- pyelonephritis;
- intestinal inflammation;
- cystitis.
Why does this particular area hurt? This is explained by the fact that the nerve endings that go to the uterus and its appendages, lower intestines, bladder and kidneys have common “roots”, so the impulse coming from the diseased organ is “dissipated” throughout all innervated structures.
How to eliminate pain during ovulation
The doctor should tell you what to do in case of painful ovulation after a complete examination of the patient. He determines the diagnostic plan, and based on the data obtained as a result of the examination, he can tell whether the pain accompanying the release of the oocyte is a physiological process or is associated with a pathological condition.
If the pain of the ovulatory phase is pathological, the doctor prescribes appropriate treatment. This is the appointment of anti-inflammatory drugs, antibiotics; in some cases, surgery is indicated.
When pain during ovulation appears for natural reasons, to alleviate the condition, the doctor will prescribe:
- Painkillers: Ibuprofen, Tamipul, Diclofenac, Solpadeine - depending on the severity of pain.
- Antispasmodics: “No-shpu”, “Spazmalgon”, “Baralgin”.
- Avoid physical activity and heat on the abdominal area.