Every woman should take care of her health. But this should be done not when anxiety pains begin to bother you, but constantly.
Women's health is very fragile and vulnerable, and taking care of it should be one of the main priorities in the life of any woman.
During the period of the most active sexual life, many representatives of the fairer sex may be bothered by gynecological diseases. Our women are not used to going to doctors.
And as long as they don’t feel unwell or have any signs, women ignore preventive visits to the gynecologist, postponing this procedure until last.
For some, women's diseases are just a bad dream, while others have real health problems that arose due to simple oversight.
Today we will tell you what the most common female diseases affect the health of millions of women.
To prevent these common female diseases from becoming a horror for you, visit your gynecologist regularly and monitor your well-being without putting off your health for later.
Symptoms of female inflammatory diseases
Symptoms depend on the organ affected. The following manifestations are considered common:
- redness, swelling, itching of the mucous membrane of the vulva and vagina;
- pain in the lower abdomen, in the area of the external genitalia, in the pelvic area, sometimes radiating to the lower back;
- discomfort and pain during sexual intercourse, decreased libido;
- pathological discharge from the vagina - mucous or mucopurulent, cloudy, cheesy, with gas bubbles, with an unpleasant odor and a yellowish tint;
- menstrual irregularities (scanty, heavy, painful, irregular periods);
- painful and frequent urination;
- increased body temperature, general weakness, digestive disorders;
- infertility.
All these symptoms are considered good reasons to consult a gynecologist.
Treatment Options
Whatever the discharge, the slightest deviation from the norm indicates a disorder or disease. Depending on which group of pathologies the identified disorder belongs to, various treatment methods are used. These include medications, physiotherapy and surgery.
Medicines
During infectious attacks, inflammation is relieved with anti-inflammatory and painkillers in the form of suppositories and tablets. They can be either general or local. Preference is given to the latter.
To stop the disease at its root, agents are used that directly destroy its causative agent. This includes antibiotics, antiseptics, antiviral and antifungal medications. They can also exert their effect through a general action, or they can also influence locally with the help of ointments and suppositories.
Hormonal medications are used for disorders caused by hormonal imbalance.
Physiotherapy
For pathological disorders and inflammation, physiotherapy is successfully used. It is mainly prescribed in combination with medications.
- Electrotherapy stimulates normal blood circulation in the pelvic organs, reduces pain and spasms.
- Ultrasound enhances microcirculation, stimulates the hormonal activity of the ovaries, softens scars and adhesions.
- Magnetic therapy comes to the rescue in case of swelling and inflammation.
- Laser, radio wave, and chemical therapies are effective alternatives to surgery. Surgical intervention is used in cases of benign tumors, oncological diseases and advanced pathologies.
Causes of development of inflammatory gynecological diseases in women
Most often, the inflammatory process develops against the background of tissue infection by pathogenic or opportunistic bacteria. The following reasons increase the likelihood of developing female inflammation:
- infection with sexually transmitted infections. Occurs during unprotected sexual contact (chlamydia, trichomoniasis, ureaplasmosis, syphilis, gonorrhea, candidiasis, human papillomavirus, etc.);
- uncontrolled use of antibacterial drugs, disrupting the normal microflora of the genital organs;
- hypothermia, failure to comply with personal hygiene rules, weakened immunity;
- hormonal and metabolic disorders in the body;
- difficult childbirth, abortion, surgical interventions in the genital area;
- controlling the urge to urinate and defecate;
- heavy physical exertion, prolapse of the internal genital organs.
Accurate determination of the cause of the development of the inflammatory process allows you to select effective treatment.
Vaginal candidiasis
Vulvovaginal candidiasis, or as it is popularly called thrush, is an inflammation in the vagina that is formed as a result of a fungal infection.
The disease gets its name from thrush because it provokes a mucous discharge that is somewhat reminiscent of milk-based products. Many women experience this disease several times in their lives, especially during childbearing years. The fungus is found in the body of every woman. Some of them have thrush several times, while others are not even familiar with this problem.
By about the age of 25, almost every woman experiences this disease, often more than once. The main problem is that in a considerable number of adult women who have suffered from such a disease, it later develops into a chronic form, and they have to fight inflammation at least two, or even four times a year.
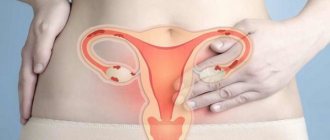
Inflammatory diseases in gynecology
Inflammation can affect different organs of the female reproductive system:
- vulva;
- vagina;
- uterus;
- ovaries;
- fallopian tubes;
- bladder.
The most common inflammatory diseases in gynecology are:
Vulvitis
Vulvitis is an inflammation of the external genitalia in women. The disease is manifested by redness, burning, itching, soreness, and swelling of the mucous membranes of the vulva. The inflammatory process usually involves the labia minora and majora, the vestibule of the vagina, and the clitoris. The disease often develops in girls of preschool and school age, causing fusion of the labia minora (synechia). The cause of vulvitis in children is poor genital hygiene, weakened immune defenses, and infections. At the first signs of discomfort in the genital area, you should consult a gynecologist.
In adult women, vulvitis most often results from sexually transmitted infections. STIs include chlamydia, gonococci, trichomonas, streptococci, yeast, etc. Contributing factors may include:
- hormonal imbalances;
- wearing tight synthetic underwear;
- poor hygiene during menstruation;
- injury to the mucous membrane and skin in the pubic area;
- long-term antibiotic therapy.
Vulvitis often develops as a complication of other female inflammatory diseases - cervicitis, endocervicitis, colpitis.
Treatment of inflammation of the external genitalia begins with taking antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs. Next, the patient is prescribed supportive medications that enhance immunity.
Vaginitis (colpitis)
Vaginitis (colpitis) is an inflammation of the vaginal mucosa. Every second woman experiences vaginitis at least once in her life. Patients are concerned about burning, itching and discomfort during sexual intercourse. In addition, the appearance of pathological vaginal discharge is noted.
The causes of vaginitis are different - failure to comply with personal hygiene rules, allergies to underwear, latex, intimate hygiene products, wearing uncomfortable clothes, hormonal imbalances, abortions, complicated childbirth, diagnostic curettage. The most common cause of vaginitis is infection of the patient with an STI. If left untreated, microorganisms quickly move higher up the woman’s genital tract.
The basis of treatment for colpitis is antibacterial and anti-inflammatory drugs. Physiotherapy, diet therapy, and lifestyle correction are also carried out. If necessary, the patient is prescribed concomitant supportive treatment in the form of hormone therapy, immunostimulation, and fortification of the body.
Bartholinitis
Bartholinitis is an inflammation of the Bartholin gland, which is located in a woman on the vestibule of the vagina. The disease develops when infectious pathogens penetrate the gland duct. These can be staphylococci, streptococci, E. coli, etc. In the initial stages, the pathology is manifested by edema, hyperemia, swelling of the tissues surrounding the vestibule of the vagina. Next, there is a violation of the patency of the gland duct, which leads to the development of stagnant processes that aggravate the situation. Severe forms of bartholinitis are accompanied by tissue suppuration and the development of an abscess.
Treatment of pathology includes taking antibiotics, anti-inflammatory and painkillers. In case of suppuration, an operation to open the abscess is indicated. For rehabilitation after eliminating acute symptoms, physiotherapy is prescribed.
Cervicitis
Cervicitis is an infectious or non-infectious inflammation of the mucous membranes of the cervix. The symptoms of the disease are determined by the form of its course - acute and chronic cervicitis are distinguished. Pathology manifests itself:
- purulent, serous or bloody vaginal discharge;
- discomfort during sex;
- swelling of the cervix;
- increase in body temperature.
Cervicitis can be asymptomatic for a long time.
The disease can be caused by chlamydia, herpes simplex virus, trichomonas, mycoplasma. Non-infectious causes of cervicitis:
- gynecological procedures (abortions, curettage, operations);
- the use of local medications that disrupt the microflora of the genital tract;
- rough sex;
- violation of intimate hygiene.
Treatment of cervicitis depends on the cause of its development.
Endometritis
Endometritis is an inflammation of the inner lining of the uterus (endometrium). The disease occurs when an infection enters the uterine cavity. Pathogens can enter the uterine cavity as a result of unprotected sexual intercourse. Sometimes the infection spreads through the bloodstream from other organs. The development of pathology is promoted by:
- failure to comply with personal hygiene rules;
- indiscriminate change of sexual partners;
- weakening of immune defense;
- performing surgical interventions in the uterine area.
Patients complain about:
- severe pain in the lower abdomen;
- bloody or purulent vaginal discharge;
- increased body temperature;
- menstrual irregularities.
The most dangerous complication of endometritis is the spread of infection to healthy tissue. To prevent this process, it is necessary to start treatment as early as possible. This includes taking antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs. Refusal from sexual activity is required for the duration of treatment. If necessary, therapeutic and diagnostic hysteroscopy is performed.
Salpingoophoritis (adnexitis)
Inflammation of the uterine appendages is called salpingoophoritis and adnexitis. The inflammatory process involves tissues of the ovaries and fallopian tubes. Pathology develops as a result of tissue infection. Pathogens can penetrate into the tissue of the appendages from the uterus or through the blood and lymph. Salpingo-oophoritis can be caused by pathogenic and opportunistic microorganisms. Associated factors are abortions, unhealthy lifestyle, intense hypothermia, especially in the legs, pelvis, lower back, and immune deficiency.
Inflammation of the ovaries and fallopian tubes is usually asymptomatic. Sometimes a woman notes:
- nagging pain in the lower abdomen;
- menstrual irregularities;
- systemic malaise with high fever;
- pathological vaginal discharge.
Salpingo-oophoritis in purulent forms can lead to serious complications. After healing, adhesions and scars may form in the tissues of the ovaries and fallopian tubes. This can lead to infertility for the patient. In each case, the treatment regimen is determined individually. It always includes taking antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, and antihistamine drugs.
Urethritis and cystitis
Urethritis affects the urethra, and cystitis affects the bladder. These pathologies are treated jointly by a gynecologist and a urologist. The symptoms of the diseases are similar. These include:
- frequent urination;
- itching;
- discomfort;
- burning sensation when emptying the bladder;
- discomfort during sexual intercourse.
How can a woman become infected with sexually transmitted infections?
Many women are concerned about the ways of contracting sexually transmitted infections in women. As doctors note, there are three most common options in clinical practice.
- Sexual tract
Sexual intercourse always means sexual contact. Moreover, as venereologists say, the likelihood that a sexually transmitted infection will occur in women is slightly higher during unprotected sex than in men. This is tied to the structural features of the genital tract.
First of all, the short urethra plays a role. Through it, it is easier for pathogenic microorganisms to reach organs where they can successfully continue to reproduce. In both men and women, not only classic vaginal sex plays a role in the spread of the disease. Oral and anal sex is also dangerous. And, importantly, lesbian sex, if basic safety rules are not followed, can also lead to infection.
- Vertical path
This spread option occurs when a woman with a sexually transmitted infection gives birth to a child. Moreover, as doctors note, infection mainly occurs during childbirth.
Cases of transplacental transmission of infection are rather rare than a widespread method of infection. In boys, such infection mainly affects the eyes and oropharynx, as well as the lungs. But in girls, the reproductive tract is most often affected.
- Contact and household path
The most rarely implemented option for the spread of sexually transmitted infections is through household contact. It is implemented if a woman or child does not follow the rules of hygiene, sharing a towel, underwear or other personal hygiene items with an infected person. Of course, most STI pathogens do not survive in the environment. However, in some cases, infection through contact is still possible. Any of the routes of spread can play an important role in a woman’s life, leading to infection. But knowing the ways in which STDs spread allows you to take steps to reduce the likelihood of encountering the disease.
Diagnostics
To identify inflammation of the external genitalia, it is enough for the gynecologist to conduct a survey and examination of the patient. If the inflammatory process affects the internal organs of the reproductive system, additional studies are carried out:
- Microscopic examination
is the study of biological material from a smear under a powerful microscope to identify infectious pathogens; - Bacterioscopic seeding is
based on placing biological tissues in a favorable nutrient medium. This leads to the growth of colonies. Next, a microscopic examination of the colonies is carried out. This helps to accurately determine the type of microorganisms, as well as assess the sensitivity of pathogens to antibiotics. - Serological tests -
detection of specific antibodies to viruses and bacteria in the patient’s blood. One of the most informative methods of this group is enzyme immunoassay. - Molecular genetic methods are
the most accurate method for diagnosing infectious pathogens. It is based on the extraction of DNA of microorganisms from the patient’s biological material. The most common and informative method of this group is PCR diagnostics (polymerase chain reaction). The technique is based on repeated copying of individual sections of the pathogen's DNA for further identification. - Ultrasound of the pelvic organs -
this study allows you to examine the internal organs of the woman’s reproductive system. Using ultrasound, the specialist evaluates the structure of the ovaries, uterus, fallopian tubes, and bladder. Inflammation is manifested by a change in the normal structure of tissues. - Endoscopic studies -
these techniques allow you to examine the tissues of the internal genital organs using high-resolution video cameras and powerful optical equipment. Inflammation is determined during colposcopy, hysteroscopy, cystoscopy, urethroscopy, laparoscopy.
Sexual infections: what tests a woman will have to undergo
Many patients are concerned about the question of when and what kind of blood tests they take for sexually transmitted infections in women. As doctors note, a blood test is not the most important thing in diagnosing various STIs that a patient at a venereology office may suffer from. In most cases, the main diagnostic role is played by a smear from the genital organs.
The smear is performed in the venereologist’s office on a chair designed for gynecological examinations.
The procedure is painless, and is often performed on patients by gynecologists for preventive purposes. During the analysis, the doctor takes material from three points: from the vagina, cervical canal and urethra. It is this material that is being studied. It can be assessed using the following methods:
microscopy, during which a biomaterial is simply applied to glass and examined by a doctor under the magnification of a microscope after staining;
- sowing, which requires the use of nutrient media with subsequent assessment of the colonies growing on them;
- PCR studies are a modern, highly informative method that has high diagnostic accuracy and allows one to assess the patient’s condition even if there is very little pathogen in the body;
- ELISA studies are another popular method that can even be used as a screening method.
In some cases, the smear may not be taken from the genitals. For example, a mouth smear for sexually transmitted infections in women should be performed if there is a suspicion of infection with microorganisms through the oral route.
An anal smear for genital infections in women is effective if contact with a pathogenic microorganism was preceded by anal sexual intercourse.
Diseases of the mammary glands
Diseases of the mammary glands in women occur in the form of inflammation or benign and malignant neoplasms.
The list of the most common ones includes:
- mastitis;
- fibroadenoma;
- mastopathy.
Mastitis
Breast inflammation that occurs as a result of harmful microorganisms entering the mammary glands through cracks in the nipples. The ICD-10 code is N61.
Divided into 2 types:
- Lactational. Occurs during breastfeeding as a result of hypothermia and deterioration of the immune system after childbirth. The main symptoms are fever, purulent discharge from the nipples, severe pain and the appearance of noticeable lumps in the chest.
- Not lactation. The cause of development is a breast cyst. Develops in diseases of the thyroid gland, weakened immunity and hypertension.
With purulent mastitis, it is contraindicated to continue breastfeeding, as this can harm the baby’s health.
Mastitis - inflammation of the mammary glands
Fibroadenoma
A benign tumor manifests itself in the form of breast lumps. The ICD-10 code is N40. It can develop in girls under 30 years of age. The reason lies in the increased production of tarragon.
The leaf-shaped form of fibroadenoma is the most dangerous for a woman’s health; over time, it can develop into cancer.
Fibroadenoma is a benign tumor in the breast
Mastopathy
It occurs as a result of increased production of prolactin in the pituitary gland. Diffuse cystic mastopathy is the most dangerous form of the disease and can develop into a malignant tumor. It is characterized by the presence of multiple formations over a large area of the mammary gland and discharge. The ICD-10 code is N60.1.
Mastopathy is characterized by the appearance of neoplasms in the mammary glands
The development of the disease occurs at the age of 35–50 years, during the period of decline of reproductive function and decrease in hormone production. The main symptom is severe chest pain, which radiates to the shoulder and armpit area, and discharge from the nipples.
A little about the treatment of sexually transmitted diseases
Treatment involves taking immunostimulants, bactericidal, antiviral, antifungal agents, vitamin and mineral complexes. Modern medicine uses laser-magnetic, magnetoacoustic and physiotherapy. Due to the use of medications, therapy can take up to one week.
Therapy should be aimed at both partners to prevent recurrence of the disease:
- for bacterial infection, antibiotics are used;
- fungal disease is eliminated by the use of antifungal drugs;
- viral ones require taking antiviral medications, but it is impossible to completely get rid of them.
Doctors warn that after treatment, symptoms may persist for some time. This is how the human body reacts to therapy. If symptoms do not go away within 1-2 weeks, it makes sense to consult a specialist.
Cervical erosion
Cervical dysplasia is a condition in which the organ is covered with epithelium, the constituent layers and the structure of the cells of which it consists change.
This type of disease is classified as a disease that can lead to the formation of cancer cells in the genital organs. Dysplasia is considered one of the most dangerous complications and one of the most common diseases before cancer.
When it forms, the uterine mucosa changes its structure. It can appear in absolutely different ways, but the most important thing that characterizes it is that along with it the normal structure of epithelial cells is disrupted. In addition to the top layer, it can penetrate the body much deeper.
This type of disease is often called erosion, but this is not entirely accurate. The main difference is that erosion appears after mechanical damage to the genital organs, and dysplasia as a result of disruption of tissue cells.
Cervical erosion (there are other names: ectopia, pseudo-erosion) is a deviation in the structure of the vaginal mucosa or a violation of its integrity. Erosion can occur in any woman, regardless of age.
If this disease is not treated in time, it may lead to the formation of cancer cells in the future. This is especially dangerous for those women who have the papilloma virus, as it leads to an increased risk of tumor formation.
During examination, erosion is reflected in the mirror as a small red area surrounding the external pharynx. Its size ranges from two millimeters to two centimeters. Erosion lasts in the body for several months and even years.
Endometriosis
This disease is observed in women of childbearing age. When present, endometriotic tissue is found in places where it shouldn't be, such as the uterus. If this happens, it has a negative effect, affecting the organs and forming a growth on them, which provokes severe pain and can even lead to infertility and other serious diseases.
The most favorable place for the development of the disease:
- abdomen;
- ovaries;
- uterine area;
- vagina;
- intestines;
- pelvic cavity.
The manifestation of this disease can also be seen on scars formed after surgery on the genitals. These growths themselves are not malignant; this tissue is completely normal.
The exception is that tissue damaged by the growth cannot be naturally excreted from the body. This may lead to the formation of internal bleeding and tissue separation from growths. But this can already lead to the formation of an inflammatory process and scars.
Colpitis
Colpitis is one of the most common diseases that affects exclusively women. Colpitis affects the vagina. According to statistics, an average of 60% of females suffer from this disease.
Vaginitis is the second name for this disease; it can be classified as the most common in gynecology. The inside of a woman's vagina is a cavity and is constantly in a moist state.
Based on this, we can conclude that there is the most suitable environment for the proliferation of various microbes. However, the vagina has protection from pathogenic microorganisms, this is “friendly microflora”, which belongs to the type of lactobacilli.
Ovarian apoplexy
An ovarian cyst is a disease characterized by the presence of a benign formation in a woman’s genital organs, which looks like a cavity completely filled with fluid. This disease is not classified as a tumor, and it is formed as a result of an excessive accumulation of fluid in the follicle (the place where the egg is formed).
The cyst does not belong to any specific age category of women; it can form at any time and no matter how old the patient is, even newborns are not an exception. But still, women of childbearing age most often face this problem.
DETAILS: What group of antibiotics does chloramphenicol belong to?
To the delight of those who are sick, it should be said that the majority of cysts go away on their own and do not require any treatment. It can go away either after the first menstruation or a little later. But this does not mean that everything can be left to chance; during this period, the woman should be under the supervision of a qualified doctor in order to avoid complications of the disease. If the cyst does not come out on its own after three months, then you need to move on to its treatment.
Ovarian apoplexy is the name given to sudden ruptures of tissue in the ovaries; it is impossible to foresee them, and subsequently such ruptures cause hemorrhages in the abdominal organs. This type of abnormality in the ovaries contributes to the manifestation of severe pain.
Quite often, deviations occur in the corpus luteum of the ovary, its integrity is disrupted, and such a deviation can also form in a corpus luteum cyst. Most often, the cause of such deviations is pathologies in the blood vessels, the formation of any inflammatory processes in the body.
In the greatest number of women, such ruptures can occur at the moments of ovulation, as well as when the corpus luteum becomes vascularized. Young girls and young women are most often affected by the disease. The disease has several forms:
- Painful. It is characterized by severe pain and nausea.
- Anemic form. It is characterized by bleeding, along with which the woman becomes dizzy, and fainting is also possible.
- Mixed. Combination of pain and anemic forms.
Salpingo-oophoritis
Salpingo-oophoritis is a female gynecological disease. Inflammation occurs in the tubes and uterus. It can be provoked as a result of infection of the uterus in the following ways:
- from the vagina;
- from the rectum;
- from the abdominal cavity;
- through blood.
Reduced immunity plays an important role in the formation of the disease. Pathology can develop due to various factors: severe hypothermia of the body, due to excessive physical exertion, as a result of stress and for other reasons.
If the organs are constantly in a tight state, for example, in tight clothing, this can also lead to the formation of inflammatory processes in the appendages.
The disease has two forms:
- nonspecific, caused by flora;
- specific, formed due to sexually transmitted infections.
By nature, the disease can be divided into the following forms:
- acute, it initially forms in the fallopian tube, and later begins to affect the ovaries. There is an accumulation of fluid that appears during inflammation. If there is a lot of it, it can lead to the formation of pus and severe abdominal pain;
- subacute form, in which the symptoms are not so pronounced. Inflammatory processes can begin in any part of the abdomen;
- chronic, may appear if treatment of previous forms of pathology is not started.
Infertility
The psychology of women with gynecological diseases plays an important role in their lives. The question of infertility, stress, worries, possible depression and anxiety disrupt the normal course of life and change the response to the question of a woman’s sexual function. This can lead to depression and hysteria. Classification of infertility:
- primary, secondary;
- physiological, voluntary;
- temporary, permanent.
The main sign of infertility is the inability to conceive a child. Further, other causes and treatment of possible concomitant diseases are clarified.
Possible complications
The biggest problem associated with sexually transmitted diseases is the serious consequences and complications. It is worth noting that they pose a threat to both male and female health. These include:
- infertility;
- oncology;
- inflammation;
- heart and vascular diseases;
- damage to internal organs;
- pathology of newborns;
- skin pathology;
- hair loss;
- pathological changes in nails;
- problems in the bone structure;
- tooth loss;
- rotting of the muscle structure;
- brain inflammation;
- development of nervous and mental diseases.
We should not forget that advanced stages of a number of diseases often lead to death, or, to put it simply, to death.