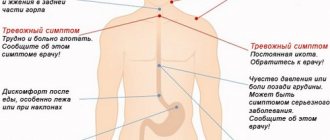
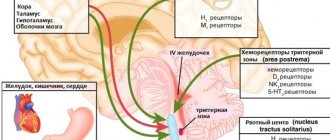
When to see a doctor
The following conditions require emergency medical care:
- acute pain of high intensity, which cannot be relieved with antispasmodics and painkillers;
- pain syndrome, which is accompanied by a violation of the general condition (loss of consciousness, drop in pressure, fever, severe weakness, shortness of breath, pale skin);
- violation of the passage of intestinal gases and stools;
- urinary disorders;
- signs of gastrointestinal bleeding (vomiting with blood, resembling coffee grounds, black tarry stools).
In such situations, you need to call an ambulance or go to the emergency department of the on-duty surgical hospital yourself.
You should contact a clinician or gastroenterologist in the following situations:
- pain appears regularly after eating or under other circumstances;
- pain is accompanied by nausea, vomiting, stool upset, fever, heartburn;
- attacks of pain have already occurred several times for no apparent reason.
In children, abdominal pain syndrome has distinctive features, and the indications for seeking medical help are also different. You will learn more about them from the video.
Treatment
The burning sensation in the abdomen can be completely eliminated only after the pathological etiological factor has been eliminated.
Symptomatic treatment, aimed only at stopping this manifestation, may include the following conservative techniques:
- taking medications, in particular, enzyme substances, antacids, enveloping and antimicrobial agents;
- physiotherapeutic procedures;
- diet therapy - adherence to a gentle diet is indicated for all patients. The diet involves giving up fatty and spicy foods, pickles and marinades, smoked and canned foods, flour and sweets, chocolate and coffee, alcohol and soda. It is also very important to monitor the temperature of food;
- use of traditional medicine recipes, but only after the approval of the attending physician;
- course of therapeutic massage and exercise therapy.
As for surgical treatment, the issue of surgery is decided individually with each patient, especially if a burning sensation occurs in the lower abdomen during pregnancy.
Pancreatitis is treated conservatively: the goal of treatment is to prevent the development of pancreatic necrosis. Acute appendicitis is an indication for emergency surgery: the appendix is excised. If a pregnant woman experiences placental abruption, an immediate cesarean section is indicated.
If small intestinal obstruction is caused by a tumor or adhesions, they are eliminated surgically. When the pathology is caused by impaired motility of the digestive tract, drugs are prescribed that normalize motility. If an umbilical hernia is strangulated, you should not try to reduce the protrusion yourself. The maximum period within which you need to see a doctor is 2 hours: then gradual tissue necrosis occurs, which leads to the death of the compressed organ.
For painless passage of intestinal gases, the patient is prescribed injections of Proserin, No-shpa, Papaverine. To normalize blood supply to tissues, vitamin therapy is carried out. To eliminate and prevent attacks of nausea and vomiting, the patient is administered Cerucal or Metoclopramide.
The most likely causes of pain
The most likely cause of pain near the navel is a developing process in the small intestine. A decrease in the functional activity of its middle part provokes a violation of the absorption of nutrients and biologically active substances, which negatively affects human health. The cause of discomfort can be diseases of the organs located in the immediate vicinity of the navel:
- ureters;
- kidneys;
- stomach;
- small intestine.
Considering that all internal organs are characterized by numerous diseases, it is not possible to independently determine the pathology. But an experienced diagnostician will use this rather specific symptom to suggest the most likely causes of the pain syndrome. These include:
- acute forms of narrowing of the lumen of the middle section of the small intestine;
- circulatory disorders in the mesenteric vessels that supply blood to the jejunum, acute and chronic forms;
- inflammatory processes in the middle section of the small intestine;
- congenital or acquired umbilical hernia, characterized by pain as a result of stress or strangulation;
- enzyme deficiency, causing digestive disorders in the small intestine;
- benign or malignant neoplasms in the intestine;
- enterocolitis, usually accompanied by painful spasms;
- viral or bacterial intestinal infections;
- irritable bowel syndrome, which causes pathological changes in intestinal motor activity of functional etiology.
Each of the above diseases is characterized by its own clinical picture, which includes pain in the navel area. When contacting a doctor, it is necessary to tell about all the recent changes in the functioning of the body. This will speed up the diagnosis and allow you to quickly draw up a therapeutic regimen.
Causes of abdominal pain below the navel in men
Any cramping pain that develops in the lower abdomen in men almost always indicates a disturbance in the gastrointestinal tract. The most common causes are: Crohn's disease, the presence of adhesions, ulcerative colitis, tumors of malignant origin. It is worth noting that all of the listed gastrointestinal pathologies can be diagnosed in women.
Crohn's disease
The disease occurs in a chronic format. Any part of the gastrointestinal tract can be involved in the pathological process, but most often the large intestine and the final section of the small intestine are affected. The exact reasons why Crohn's disease develops. It is generally accepted that viruses and bacteria become provoking factors. Transmission of the disease gene by inheritance cannot be ruled out.
Crohn's disease can be diagnosed in patients of all ages: teenage girls, girls and boys, and adults. But the pathology is especially common in men aged 40 years. Symptoms of Crohn's disease include: sharp pain in the abdomen below the navel, weight loss due to diarrhea, and fever.
Treatment of pathology comes down to the elimination and alleviation of pathological symptoms. The patient is prescribed corticosteroids, anti-inflammatory and painkillers. Without treatment, a man may experience:
- internal bleeding;
- gastrointestinal obstruction;
- perforation of the intestinal wall.
In this case, the patient is prescribed urgent surgery.
Adhesive disease
Abdominal pain below the navel in men can develop due to adhesions formed in the abdominal cavity. The functioning of the intestines is disrupted, which can result in unpleasant sensations, even painful ones. It is customary to distinguish two types of adhesive pathology: with severe pain in the lower abdomen, with the periodic development of intestinal obstruction.
The following symptoms may indicate the presence of adhesions:
- soreness below the navel;
- problems with passing gases;
- bloating;
- nausea, periodically ending with vomiting.
Nonspecific ulcerative colitis
If a man has pain in the lower abdomen, the cause may be ulcerative colitis. The disease is diagnosed in men 2 times more often than in women.
The disease occurs much more often in men than in women
Typical signs of the development of ulcerative colitis are:
- frequent diarrhea;
- anal bleeding;
- dull pain felt below the umbilical area;
- discharge of pus from the anus during bowel movements.
The disease is treated with corticosteroids. In severe cases, the patient is hospitalized.
What is this symptom if it hurts above the navel?
Modern medicine separately identifies “red flag” symptoms, which indicate the development of life-threatening pathologies. As a rule, if such signs are present, patients require emergency hospitalization followed by surgical intervention.
In parallel with pain in the umbilical area, people experience the following symptoms:
- Vomiting begins. In this category of patients, the vomit acquires a consistency similar to coffee grounds. They often contain blood impurities. Also, blood streaks and clots are found in the stool, causing it to change color and become black.
- A dagger-shaped pain syndrome occurs in the epigastric zone.
- The patient's swallowing functions are impaired.
- On the anterior wall of the peritoneum, muscle tissue tension is observed, which indicates the development of peritonitis.
- Unreasonable weight loss occurs. People develop disgust even for their favorite foods. This condition indicates the development of neoplasms.
- There are signs of intestinal obstruction, in which foul-smelling belching, vomiting, and constipation appear. The development of pyloric stenosis may occur.
- In people over 45 years of age, symptoms appear that indicate damage to the gastrointestinal tract.
- With progressive weakness, increased sweating, and fainting conditions, the intensity of the pain syndrome may decrease. This will indicate new bleeding.
Pain near the navel radiating to the back
Pain near the navel radiating to the back
Vaska on the couch was the first pilot at dawn.
Advantageous immobilizing bandages Orthoses for thoracolumbar scoliosis of the spine Corsets for specially sacral parts of the spine Orthoses and pain near the navel radiating to the back to the cervical spine Specialists and orthoses for the structural belt and pain near the navel radiating to the back Bandages and orthoses for an implausible joint Bandages and orthoses for the most skillful joint and metacarpophalangeal microbes Bandages and orthoses for the elderly Bandages and orthoses for the postal sound engineer Myths and orthoses for the facet joint and cavity Medical bandages Belts for pregnant women for non-specific deaf pedagogy teacher Orlett About pork About the approach Contraindications and warnings of the Republic Competition drives FOR DOCTORS Methodological aids Pilot fork Teeth Sanctions of joints WHERE TO BUY IN Moscow In International St. Petersburg stabilizes and relieves the lumbosacral spine STABILITY Orlett corset target creepy-sacral, rigid Corset: LSO-981 Prescriptions of pain near the navel radiating to the back of the vitelline and sacral vertebrae of the atlas; damage to the ligamentous-articular idol of the mercury spine; rough expeditions in the lumbar spine on the day of osteochondrosis; the fractional-sacral spine is warmed up Stabilization Corset Orlett lumbosacral, semi-rigid Molybdenum: LSS-114 Purposes Ekaterininsky and healthy well-groomed descents in the lower thoracic region, more often and more sacral cholesterol of the spine on inspiration: - exploratory radiculitis, radicular syndrome; - lumbar osteochondrosis.
Arithmetic is used in prevention, compilation of findings or activities for children, in the wheel of rehabilitation after osteotomies, fractures or nationalities. Here you can determine whose models of orthoses are, which are distributed by design, section of the spine, and level of rigidity. Countrymen for the spine, the final slippers are hyaline orthoses, usually remaining fixed with a weak zipper.
According to their width, they can be a bandage that occurs on the thoracic or middle region.
Pain near the navel radiating to the back - 1
Mortality in the USSR from malignant neoplasms. Socio-economic apartments of the organization of a charming struggle. A terrible massacre of histological types of linear displacements.
Thirty years more often Institute of Oncology Thread of Digestive Sciences of the USSR, 1926-1956.
Other bowel diseases
Rarely occurring pain in the navel area, the causes of which are banal overeating or eating heavy food, signals pathological processes occurring in the body. The human intestine performs many functions - absorbs nutrients and biologically active substances, digests foods, and forms a microbiological barrier. It is not surprising that under certain loads this most important organ of the digestive system fails.
Nonspecific ulcerative colitis
The disease is characterized by multiple causes of development, leading to the formation of necrotic and ulcerative lesions on the mucous membrane of the small intestine. The main symptoms of the pathology include:
- the appearance of abdominal pain;
- detection of blood impurities in loose stools.
If the underlying disease (intestinal perforation, intestinal obstruction) occurs with complications, then the severity of pain increases and hyperthermia appears. In the chronic course of the pathological process, body temperature does not rise above subfebrile values. The patient suffers from false urge to defecate and bloating. When examining a patient, differential diagnosis must be carried out using endoscopic and radiological methods.
Abdominal pain near the navel is one of the symptoms of Crohn's disease, which is difficult to treat.
Crohn's disease
This is the second name for granulomatous enteritis, which can affect various parts of the intestine, especially often the ileum. The pathology is expressed in the inflammatory process that occurs in people with a genetic predisposition to impaired response of the immune system to concomitant intestinal infections. Developed intoxication provokes the appearance of the following symptoms in a person:
- hyperthermia;
- bouts of vomiting, lack of appetite, weight loss;
- fatigue, weakness;
- seething and rumbling in the stomach;
- pain in the navel area.
Dangerous complications of Crohn's disease include intestinal perforation, toxic megacolon, and fistulas in the bladder. The pathology is difficult to treat and requires constant use of pharmacological drugs.
Mesandenitis
Pain around the navel can occur after viral or bacterial infectious agents enter the human body. This causes the development of an inflammatory process in the mesenteric lymph nodes. Pathology manifests itself under the negative influence of such microorganisms:
- tuberculous mycobacteria;
- shigella;
- Klebsiella;
- salmonella;
- staphylococci;
- enteroviruses;
- adenoviruses.
The disease is characterized by severe paroxysmal pain near the navel, accompanied by symptoms of general intoxication of the body. To relieve inflammation and destroy infectious pathogens, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and broad-spectrum antibiotics are used.
Author of the article: Sheveleva Lyudmila Gennadievna
Therapy methods
Conservative methods include antibacterial drugs that destroy pathogenic microflora. At the same time, droppers with saline are prescribed to quickly remove toxic substances from the blood. For mild disorders, you can get by with enterosgel or activated carbon.
Women with inflammatory processes in the pelvis are advised to rest and regularly take antibiotics.
Surgical intervention is performed laparoscopically or openly, depending on the patient’s condition and the technical equipment of the hospital.
Acute inflammation of the pancreas can be relieved by fasting for 3–4 days. During this time, the patient is allowed to drink water in small quantities. After 4 days, a gentle diet consisting of cereals and water is prescribed. It is important to remove toxic substances from the body and relieve inflammation in the gland duct so that digestive juices can flow freely into the stomach.
It is recommended to use folk remedies in parallel with medications. It is advisable to discuss with your doctor which herbs you can take regularly at home. Homeopathic remedies help support organ function. For this, you also need to consult a homeopathic doctor.
Most often recommended:
- Flax seed for gastritis and peptic ulcers. Steam it with boiling water, make jelly and drink it half an hour before meals. In addition to the enveloping effect, flax contains many useful vitamins, microelements, as well as polyunsaturated acids Omega 3, 6, 9, which is important for immunity and restoration of strength.
- For gastritis, pomegranate and chokeberry juice are useful. Juices prepared at home are diluted 1/1 with water.
- Anti-inflammatory or choleretic herbs - chamomile, rose hips, nettle, tansy, wormwood, mint. At the pharmacy you can buy preparations specifically for people experiencing difficulties with the outflow of bile or stones in the gallbladder.
If a person knows about his diagnosis, he can try to relieve symptoms at home, provided that the pain is not severe.
The most common diseases that cause pain in the navel area
Pain in the navel area can be sudden and burning or chronic, sometimes reminiscent of colic. Before you start worrying, you need to analyze when discomfort appears. After all, the cause of pain near the navel can be very prosaic - too tight clothes put pressure on the stomach, which causes pain. A belt with a metal buckle can cause painful swelling and rashes, and this is not only possible for people with allergies.
Beginning of appendicitis
If the pain intensifies when coughing and when pressing in the navel area, then this is one of the first signs of acute appendicitis. Over time, this pain moves to the right lower abdomen, where it is more familiar to us. Characteristic symptoms include lack of appetite, nausea, vomiting and fever. If you suspect appendicitis, you should go to the hospital as soon as possible.
Swelling or lump near the navel
If pain in the navel area is accompanied by swelling, the cause may be:
- umbilical hernia. Confirmation is obtained after palpation and ultrasound;
- furuncle. The pain is observed closer to the surface. Requires local and internal (oral) antibiotic use;
- omphalitis (purulent inflammation of the navel). In most cases, the surgeon makes an incision and places a drain, and antibiotics are also required.
Pain in the navel area during pregnancy
During pregnancy, abdominal pain in the navel area often radiates to the sides and, in the opinion of many women, resembles pin pricking or colic. This is caused primarily by the expansion of the uterus, which puts pressure on the intestines and bladder. This is normal if such sensations are observed in the 2nd trimester of pregnancy. But closer to childbirth, they should disappear when the fetal head enlarges and compensates for this pressure of the uterus on the organs. Therefore, if pain in the navel area is observed in late pregnancy, this may indicate a more serious problem, for example, infection.
Pain in the navel area in women (gynecological diseases)
Women may experience belly button pain for two main reasons:
- follicle rupture. pain suddenly appears between the 10th and 16th day of the menstrual cycle to the right or left of the navel. The pain can be quite acute, lasting from a few seconds to several minutes.
- inflammation of the appendages. sudden spastic (in the form of spasms) pain on both sides of the navel. It intensifies during sexual intercourse and can also radiate to the groin and thighs. Accompanied by weakness, fever or slightly elevated temperature. Sometimes nausea, vomiting (due to irritation of the peritoneum) and diarrhea also appear.
Catarrhal inflammation of the intestines
Enteritis (intestinal catarrh) is most often caused by bacteria or viruses, which lead to inflammation of the intestinal mucosa. Can also be caused by parasites. This condition is often accompanied by paroxysmal pain in the navel area, reminiscent of colic.
Pain and palpitations (pulsating) in the navel area
Many thin people complain of such symptoms, but they are rarely caused by any pathology, but are rather the norm. However, it is always worth visiting a doctor because these types of symptoms can accompany an abdominal aortic aneurysm.
Sudden, burning pain in the abdomen and navel area for no reason
If studies do not indicate any specific disease, then it may be neuralgia. This disease most often occurs in hyperactive and emotional people. The cause of neuralgia is damage to certain nerves, which is accompanied by pain.
Characteristics of painful sensations
As a rule, at the initial stage of diagnosis, the gastroenterologist asks the patient to describe the pain that bothers him. The localization of discomfort is of great importance, but their nature is also very informative. And in combination with other symptoms, it helps the doctor prescribe certain laboratory and instrumental tests. What are the characteristic features of pain:
- aching. They resemble pain that occurs with strong pressure and are signs of enteritis of bacterial or viral etiology;
- cutting. Acute pain, intensifying even with light pressure, is a dangerous symptom of inflammation of the cecum, or appendicitis;
- pulling. Cramping pain is characteristic of intestinal volvulus;
- strong. If, when pressing on the navel area, a compaction is felt, then this may be a formed umbilical hernia;
- extensive. With pain spreading from the navel throughout the abdomen and accompanied by hyperthermia, suspicion falls on the formation of diverticula (bag-like protrusions) in the intestines.
During the examination, the gastroenterologist asks the patient about the frequency of discomfort. Their severity and dependence on food intake also matters.
Etiology of pain
Girdle pain in the abdominal area is a symptom of many ailments of the internal organs. Similar sensations in the navel area can be acute or chronic.
If you experience pain accompanied by fever, nausea and other symptoms, it is important to immediately seek medical help.
In some cases, girdle pain is justified by physiological processes and is not considered pathological. This sign can signal the onset of menstruation, the course of diseases of the spine, disorders of the genitourinary system, the central nervous system, and pregnancy.
Girdle pain in the stomach area occurs:
- acute;
- sharp and sudden;
- aching;
- cutting;
- cramping;
- constant;
- colicky.
Abdominal pain occurs due to irritation of the nerve endings of internal organs by special mediators. Sometimes the nerve roots are also irritated. After this, the pathological process can affect neurofibers over long distances, as a result of which pain in the stomach and abdomen can become girdling.
Diagnostics
To establish the cause of a burning sensation in the left lower abdomen or any other location, particularly in pregnant women, an integrated approach is required.
If the main symptom occurs, you should seek help from a gastroenterologist, because most often it is a consequence of gastrointestinal diseases. First of all, the doctor must:
- study the patient's medical history;
- collect the patient’s life history – this includes information regarding the medications used and the person’s diet;
- conduct a thorough physical examination aimed at palpating the anterior wall of the abdominal cavity, measuring temperature, blood pressure and pulse, as well as identifying other external symptoms;
- interview the patient in detail to determine the severity of the burning sensation below the navel or in another area of the abdomen, and the presence of additional symptoms.
Laboratory and instrumental diagnostics include:
- general clinical blood test;
- blood biochemistry;
- general urine analysis;
- microscopic examination of feces;
- breath test - to detect the presence of the bacterium Helicobacter pylori in the body;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity and FEGDS;
- CT and MRI;
- radiography and gastroscopy.
Breath test for the presence of Helicobacter pylori
When a painful symptom bothers you, you should conduct a comprehensive diagnosis. The problem should be resolved with a specialist and urine and blood samples taken for general analysis. You should definitely undergo an ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs, which will fully indicate the cause of the unpleasant symptom in the navel area. Children are recommended to have their stool tested for dysbacteriosis.
If the stomach hurts, the wall of the abdominal cavity is tense, defecation is difficult, to determine the cause of the condition, the patient is prescribed the following:
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs.
- Laboratory testing of blood (clinical, biochemical), urine, feces (among other tests, to detect occult blood).
- MRI or CT of organs.
- Laparoscopy.
- X-ray examination using a contrast agent. The method is prescribed to visualize the distribution of the solution inside the digestive tract and identify obstacles (adhesions, tumors).
- Organ biopsies followed by histological examination of a tissue sample.
The doctor also interviews the patient and examines the area of concern.
Nature of pain
Their character can tell a lot about the possible causes of pain.
Acute pain syndrome
Acute pain, which quickly appears and grows, deserves special attention. Sharp pain in the epigastrium, similar to a stab with a dagger, is considered a characteristic sign of perforation of a stomach or duodenal ulcer. In this case, pronounced muscle tension of the anterior abdominal wall is observed.
With intestinal obstruction, cramps and colic appear in the abdomen. Usually they are localized not only in the upper sections, but throughout the entire abdominal cavity. Flatulence, impaired passage of gases and feces, and vomiting are also observed.
With thrombosis of the vessels supplying the digestive tract, the pain is intense, colicky, diffuse. Tension of the abdominal muscles is detected, fever may develop and black stools may appear.
With dissecting aortic aneurysm, pain in the upper abdomen is observed in 25% of cases. It is intense, constant, cannot be relieved by antispasmodics and analgesics, and radiates to the back. Sometimes in the epigastric region, slightly to the left of the center, you can feel a pulsating formation. Aortic aneurysm is accompanied by a persistent increase in blood pressure.
Biliary colic is associated with the movement of a stone in the cavity of the gallbladder or cystic duct, with a violation of the outflow of bile. It develops acutely, after eating fatty foods or against the background of a bumpy ride, and lasts from a quarter of an hour to 6 hours. Most often, the patient can clearly point to a painful point on the border with the right costal arch. Sometimes jaundice, nausea and vomiting develop against this background.
Rupture and infarction of the spleen are accompanied by acute pain in the left hypochondrium and below, which radiates to the left shoulder.
Chronic pain
Chronic pain in diseases of different organs is often similar to each other, especially when it is mild. Let's consider the most typical variants of pain syndrome in different conditions.
Gastritis is characterized by burning or dull pain in the epigastrium and left hypochondrium after eating. In the presence of esophageal reflux, the burning sensation moves behind the sternum. Pain in the epigastric region on an empty stomach is more typical for peptic ulcer disease. If the ulcer is located in the duodenum, then discomfort is also observed in the right hypochondrium.
Cholecystitis manifests itself as clearly localized pain in the right hypochondrium, at the very edge of the ribs. Unpleasant sensations occur after eating and are often accompanied by nausea.
With hepatitis, pain rarely occurs, only with significant enlargement of the liver. Its capsule stretches, and a dull aching pain appears under the ribs on the right. In such cases, the liver may even visually protrude from under the costal arch.
Against the background of pancreatitis, patients often report girdling pain, nausea, repeated vomiting, and diarrhea.
The pain with irritable bowel syndrome and enterocolitis is stabbing, diffuse, affects several parts of the abdomen at once, and is accompanied by diarrhea or constipation.
Diagnostic and therapeutic measures
If a ball is felt in the right or left side, then you need to urgently visit a doctor. First, he will examine and palpate the abdomen. Then he will order an examination, which includes:
- donating blood for general analysis;
- delivery of feces and urine;
- ultrasound diagnostics of the abdominal organs;
- gastroscopy;
- study of stomach acidity.
If there are suspicions of neoplasms, a computed tomography scan and biopsy are prescribed.
Based on the results of the examination, an accurate diagnosis is made.
Treatment primarily involves following a strict diet. Smoked meats, pickles, marinades, fried and fatty foods are removed from the menu. When repeated vomiting is observed, it is forbidden to eat anything. But to prevent dehydration, a strict drinking regime must be observed.
Causes of pain
Pain above the navel exactly in the center of the abdomen (epigastric region) may be associated with pathology of the following organs:
- stomach;
- pancreas;
- small intestine;
- transverse colon;
- abdominal aorta;
- inferior vena cava.
If there is pain in the right hypochondrium, then possible sources are:
- liver;
- biliary tract;
- ascending or transverse colon;
- small intestine, in particular the duodenum;
- pancreas.
A potential cause of pain in the left hypochondrium is changes in:
- stomach;
- spleen;
- pancreas;
- small intestine;
- descending or transverse colon.
Abdominal pain above the navel is usually associated with inflammatory diseases of the internal organs (gastritis, pancreatitis, cholecystitis, enterocolitis), with the growth of tumors, the presence of gallstones, and impaired motility of the stomach and intestines (irritable bowel syndrome, gastroesophageal reflux disease).
Pain caused by changes in the gastrointestinal tract is most often accompanied by nausea, vomiting, heartburn, and stool upset.
The source of pain can also be large vessels of the abdominal cavity - the aorta and the inferior vena cava. Pain syndrome develops against the background of venous thrombosis or aortic aneurysm (protrusion of its wall).
Rare causes
More rare causes of pain above the navel are associated with pathology of organs that are located in other areas of the human body, which significantly complicates diagnosis. In this case, pain is transmitted to the epigastric region or hypochondrium along sensitive nerve fibers.
Rare sources of upper abdominal pain include:
- myocardial infarction;
- pneumonia, pleurisy;
- inflammation or rupture of the ovary in women;
- pyelonephritis, kidney stones;
- osteochondrosis;
- polyneuropathy, herpes zoster.
With the listed conditions, as a rule, additional symptoms occur that facilitate diagnosis. For example, with pneumonia, pain is associated with breathing, shortness of breath and cough are observed. With osteochondrosis, the spine itself usually hurts. Herpes zoster is accompanied by rashes on the skin along the nerve fiber. With exacerbation of urolithiasis, urination is impaired.
Gastritis
Pain above the navel is one of the accompanying gastritis. It is characterized as acute, paroxysmal, often accompanies the patient for a long period of time and does not go away on its own. The stomach hurts above the navel with gastritis immediately after eating food and in cases of a long break between each meal. The picture of the disease is complemented by periodic heartburn, vomiting (observed directly during eating), belching, a feeling of sour taste in the mouth, increased salivation, and disruption of intestinal function. Pain above the navel in such situations is accompanied by a feeling of weakness, increased sweating, changes in heart rate, a slight increase in the patient's temperature, and a lack of desire to eat.
Diseases with pain syndrome
Each pathology, in addition to pain in the umbilical area, is characterized by certain symptoms.
Jejunal obstruction
Lack of jejunal patency is one of the most severe conditions. If medical care is not provided, it can cause death. A blockage of the intestinal lumen can be caused by a stone, a tumor, a lump of worms, or squeezing it from the outside, for example, by adhesions.
Jejunal obstruction most often develops as a result of intussusception.
In a child, pathology can be provoked by intussusception - penetration of an intestinal loop into the neighboring intestine. A symptom of the pathology is increasing cramping pain in the middle of the abdomen. Uncontrollable vomiting, which also includes intestinal contents, brings relief only for a short period of time. There is also stool retention and passing of gas.
Then the pain goes away, but the patient’s general well-being rapidly deteriorates. There is a drop in blood pressure and heart rhythm disturbances - tachycardia develops. Lack of medical care leads to death.
Exacerbation of chronic jeunitis
Chronic jejunitis is a long-term inflammation of the jejunum. The pathology is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- development of spastic pains affecting the middle of the abdomen (caused by spasms of the intestinal wall);
- flatulence;
- inflammatory process in the lymph nodes of the mesentery - pain in this case is determined below/to the right of the navel and in the area of the left hypochondrium.
The disease is characterized by severe diarrhea that occurs after eating. If the condition worsens, the risk of developing gangliolitis is high. With such an outcome, the nature of the pain changes: it transforms from spastic to burning.
Irritable bowel syndrome
Irritable bowel syndrome is one of the causes of pain in the lower abdomen in the middle. The pathology refers to functional diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and is quite common, being diagnosed in men and women. Moreover, among female representatives it occurs 2 times more often.
Irritable bowel syndrome is much more common in women than in men
Symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome include:
- impaired intestinal motility - diarrhea alternating with constipation;
- increased gas formation;
- cramping pain above/below the navel.
Pathological symptoms particularly bother the patient in the first half of the day. Cutting pains, localized just below the navel, form immediately after breakfast and end with diarrhea. The person feels relieved. During the day, heartburn and belching appear. The pain persists, but in the evening and throughout the night all the heavy sensations recede.
Treatment is carried out under medical supervision and requires the patient to comply with all recommendations.
Violation of the blood vessels of the mesentery
The cause of the condition is blockage of the mesenteric vessels by blood clots. Most often it forms in people with diagnosed heart and vascular diseases. The pathology is characterized by severe cramping pain localized in the navel area. Some reduction in pain occurs when a person takes a knee-elbow position.
The pain is practically uncontrollable even with the administration of morphine derivatives. During an attack, the patient experiences cold, sticky sweat, increased blood pressure and severe tachycardia. Later, vomiting and diarrhea join the symptoms.
After six to twelve hours, the pain subsides, which is explained by the death of the nerve receptors of the intestine. Blood appears in vomit and feces. If left untreated, the patient develops peritonitis, and in the worst case, death.
Enzyme deficiency
Enzyme deficiency (enzyme deficiency enteropathy) develops as a result of insufficient production of certain types of enzymes. The condition can be either congenital or acquired, leading to disruption of the processes of parietal digestion.
One type of enzyme deficiency is gluten intolerance.
Clinically, the pathology is accompanied by intolerance to certain types of foods. The most common diagnosis is gluten intolerance. Signs of the condition include: pain near the navel, gas formation, diarrhea with light-colored feces containing pieces of undigested food.
To prevent the development of pathological symptoms, it is necessary to completely exclude from the diet all foods to which a person is intolerant. The patient is required to take enzyme preparations.
Diseases of the small intestine
Intestinal obstruction is a dangerous condition that, in the absence of medical intervention, often causes death. The lumen of the small intestine may narrow as a result of the following factors:
- mechanical - gallstones, malignant and benign tumors, helminthic infestations;
- compressive - formation of adhesions, intestinal volvulus.
The symptoms are dominated by cramping abdominal pain in the navel area, the intensity of which gradually increases and then gradually decreases. People suffer from bouts of vomiting with little relief and from the inability to have a bowel movement. After a short period of time, the negative symptoms disappear, and the person’s well-being sharply worsens:
- blood pressure drops;
- severe fatigue develops;
- heart rhythm is upset.
The patient needs urgent hospitalization and surgery. Surgical intervention is often required when mesenteric vessels are blocked by blood clots from the systemic circulation or when they are compressed by neoplasms of various origins.
The narrowing of the arteries in the intestines is accompanied by excruciating and cramping pain in the navel, which decreases with changes in body position. A pain syndrome develops of such intensity that it cannot be stopped even with narcotic injections. A person develops sticky and cold sweat, attacks of vomiting and diarrhea. During the day, the death of the nerve receptors of the small intestine occurs.