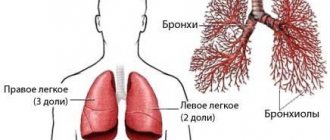
Brown urine with blood
Brown urine mixed with blood may indicate the presence of kidney stones. Stones, moving along the urinary tract, damage them, and blood appears, which also turns the urine brown. If brown urine appears for several days, you should consult a doctor for a detailed examination.
Sometimes brown urine can appear due to the consumption of foods and a number of medications. Thus, brown urine may appear due to frequent consumption of strong black tea, beef and legumes. But after eliminating these foods from the diet, the color returns to normal.
How to determine the cause of pain when urinating based on symptoms
Pain when emptying the bladder may be sudden and severe. The urge becomes more frequent, and the process of emptying itself causes painful sensations. Most often, the pain radiates to the urethral canal, but the lower back, lower abdomen, and groin area can be affected.
Pathologies of the urinary system are determined by the following criteria:
| Symptoms | Description |
| Lower abdomen hurts | In addition to frequent urges, aching pain and cramping caused by cystitis are observed in the lower abdomen. Discomfort also occurs in the presence of urolithiasis. Crystallization of minerals in the urinary bladder leads to pain in the perineum and genitals, which manifests itself when walking and defecating. |
| Blood and pain | Blood cells in urine occur during the acute stage of cystitis, bacterial infection of the urethral canal, and the presence of kidney stones. |
| Pain and burning | Painful urination in women occurs when there is an infection in the reproductive system. Accompanying symptoms are pain in the groin, burning, itching of the external and internal genital organs. |
| Cutting pain | Sudden eruption pain most often occurs with cysts in the ovary or interstitial cystitis. There are pain sensations in the pelvis, chest, and vagina. |
| Itching and pain | Itchy and painful sensations are caused by candida infection. The genitals swell, itch, and a white discharge resembling cottage cheese may appear. |
| Frequent urination and pain | Cutting pain and burning indicate the presence of an infection transmitted through sexual contact. Penetration of bacteria into the urethra is possible due to reduced immunity and improper hygiene. |
| Cutting in the urethra | A pathology affecting the urinary canal is called urethritis. Inflammation begins as a result of infectious diseases, allergies or trauma to the urethra. |
| Pain during pregnancy | During pregnancy, women's hormonal levels change, and the volume and speed of blood circulation increases. The uterus begins to grow, putting pressure on the urine bladder. |
Frequent bowel movements can also be a signal of pregnancy, especially in the early stages. Only a doctor can rule out the presence of other pathologies in the body.
Cloudy urine with blood
Cloudy urine may be due to dehydration. It is possible that a person is not drinking enough fluid. This is often observed in pregnant women.
Most often this happens during prolonged exposure to the sun or in a bath. But cloudy urine with traces of blood has nothing to do with the weather and liquid; it signals serious problems with the kidneys or the presence of a tumor in the organs of the genitourinary system. You must ask your doctor to prescribe tests for tumor markers. This analysis can be done independently in any private laboratory.
One of the reasons may be pyelonephritis or cystitis. These diseases lead to the appearance of traces of blood in the urine. The presence of stones in the kidneys or ureter may also be diagnosed. In order to understand the correct diagnosis, the doctor will prescribe several urine tests. It is necessary to determine the number of red blood cells and white blood cells in the urine.
Indications for the study
If blood is found in the urine, this is a direct indication for examination of the body. You should immediately determine whether the blood flow is caused by a disease or taking medications. As soon as blood is detected in the urine after the process of emission of urine is completed, contact a specialist to get the necessary advice and undergo additional examination.
The presence of blood in the urine requires prompt diagnosis, especially when this sign is accompanied by additional symptoms:
- pain in the kidneys and lumbar region;
- burning in the urethra;
- increase in body temperature;
- increased frequency of urination;
- pain and delay during urine output.
It is necessary to constantly undergo follow-up examinations, including general tests and urine culture.
Pus and blood in urine
The presence of blood and pus in the urine may indicate an infection. It can be located in the bladder, urethra, or descend from the kidneys. In men, pus and blood in the urine are often a manifestation of prostatitis.
Also, do not exclude the presence of malignant tumors in the kidneys or bladder.
It is difficult not to notice pus and blood in the urine, since they usually appear along with cutting pain and severe discomfort when urinating. In rare cases, pus and blood may appear without pain. This does not mean that you can ignore such symptoms.
Diagnosis and treatment
Any person should know that any disruption of the body’s functioning is a reason to consult a specialist.
Especially if the pain has been tormenting for some time, and there is blood in the urine, which is very dangerous. First, the doctor prescribes an examination that will rule out an infectious cause. Next, an examination is carried out.
- Examination by a gynecologist (urologist), proctologist, infectious disease specialist.
- Study of patient complaints.
- Urine and blood analysis.
- Analysis for sexually transmitted diseases.
- Studying strokes.
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs.
Since the causes of pain and blood during urination can be very different, appropriate treatment is prescribed based on the examination.
Mucus with blood in urine
Mucus and blood in urine are associated with inflammatory processes in the genitourinary system due to infections. If only mucus is present, then the rules of general hygiene may have been violated when donating urine. The genitals should be clean before taking the test.
Sometimes the presence of mucus indicates a long period of abstinence before urinating.
Mucus along with blood indicates a serious inflammatory process. In women, such symptoms may indicate gynecological problems. For example, endometriosis, cervical erosion. In men, the presence of mucus can provoke prostatitis or venereal diseases.
Why do women experience painful urination with blood?
The causes of bleeding and pain during urination in women vary, so it is necessary to quickly determine the source of the problem, because the success of the treatment course will depend on this. The most common causes of hematuria include:
- Inflammatory processes in the bladder, cystitis, during which infectious bacteria infect the mucous membrane, causing swelling and fragility in the vessels located in the tissue of the bladder. If the disease is not treated, the amount of blood in the fluid secreted by the body will increase and will begin to affect the general condition of the woman and the functionality of the organs of the ureteric system.
- When the mucous membrane of the ureteral canal becomes inflamed, urethritis can develop. Dangerous microflora will quickly multiply along the mucous membrane of the passage, thin it, form ulcers and erosions. With this disease, blood begins to flow after the end of urination.
- With the presence of stones in the kidneys, blood appears in the urine as a result of tissue injury from the salt edges of the deposits. An unresolved problem can lead to inflammatory processes occurring in the areas of wounds and erosions, which later develop into bacterial infections. The woman begins to urinate at the wrong time, thereby complicating the problem and provoking more severe consequences.
- Neoplasms of a malignant nature are also considered to be the cause of blood clots. This symptomatology often manifests itself in the later stages of oncology, reducing hope for a successful outcome of therapy. For this reason, you should constantly visit a doctor in order to promptly treat diseases of the urinary and reproductive systems.
Bloody urine with odor
Urine with blood and odor indicates a bladder infection. Most likely, this is cystitis or pyelonephritis. It spreads to the kidneys. It is also worth paying attention to the smell itself. If it resembles acetone, then diabetes may be the cause.
An unpleasant and pungent smell of fish may indicate problems with the liver. Most likely there are fermentation disorders.
But, despite the smell, the presence of blood already indicates pathologies in the genitourinary system. The doctor will check the condition of this part of the body first.
An unpleasant smell of urine without blood may indicate the presence of thrush in women and sexually transmitted infections in men. A man should remember that blood in the urine and an unpleasant odor are sometimes symptoms of prostatitis. Therefore, it would not be a bad idea to visit a urologist’s office.
Urine truly reflects many processes that occur in the body. No matter how strange it may sound, you need to constantly monitor the condition, color and smell of urine. These observations will help describe the situation in the doctor’s office in more detail and detail. A complete picture of symptoms will help the doctor prescribe exactly the tests that are needed.
What does it mean if there is blood in the urine of women? More than 100 nosologies are known in medicine, accompanied by hematuria (blood in the urine). Some of them relate to urgent conditions requiring emergency medical care, others are a sign of chronic diseases. Hematuria can also be transient.
Normally, urine does not contain blood. Hematuria indicates a number of surgical or therapeutic diseases.
Therapeutic pathologies accompanied by hematuria:
- glomerulonephritis;
- infectious and inflammatory diseases of the urinary tract (pyelonephritis, cystitis, urethritis);
- Berger's disease;
- amyloidosis;
- multiple myeloma;
- pathology of the renal vessels.
Among surgical pathologies, the most common are tumors of the urogenital tract, anomalies in the development of renal vessels, injuries of the pelvic organs and urolithiasis.
The hemorrhagic form of cystitis is accompanied by severe hematuria. Usually the disease occurs with pain, pain when urinating and symptoms of general intoxication.
Hematuria is often accompanied by pain. Based on the projection of pain, the expected location of the lesion can be determined.
Most often, intense pain is accompanied by surgical pathologies. However, discomfort is also typical for infectious and inflammatory diseases of the urinary tract. Oncopathology, on the contrary, is not accompanied by pain.
For the differential diagnosis of hematuria, the portion of urine in which red blood cells appear is important. If the presence of blood is noted in the first portion, then the urethra is probably affected. When blood appears in the last portion, the suspected lesion is located at the entrance of the urethra to the bladder. With uniform hematuria (in all portions), the pathological process involves the kidneys, ureters or bladder.
There are two types of hematuria:
Microhematuria is not characterized by a visual change in the color of urine. However, a laboratory test detects red blood cells. With gross hematuria, diffuse staining of the biological material is noted. From a prognostic and diagnostic point of view, the value of this classification is low. There is no direct relationship between the severity of the condition and the volume of blood released. But this test allows you to detect the disease at an early, preclinical stage.
Pathological reasons for the appearance
Most often, an admixture of blood is a consequence of pathologies such as urethritis, cystitis, endometriosis, pathologies of pregnancy, and diseases of the reproductive system. It is important to pay attention to the following aspect: if the process of urination is painless, but there is blood in the urine, there is a high probability of developing malignant tumors or receiving mechanical injuries. Each of the above ailments is also characterized by additional symptoms, which should be discussed in more detail.
Urethritis
One of the common causes of blood in the urine is urethritis, characterized by a violation of the anatomical integrity of the mucous tissues of the urethra. Various factors can lead to damage, including inflammatory processes, the release of stones against the background of urolithiasis, and surgical interventions.
Additional symptoms of this disease are: painful sensations when urinating, the appearance of itching, burning sensations, and mucus in the urine. Often the discomfort increases significantly during menstruation. What to do in such situations? To restore mucous tissue, both physiotherapeutic procedures and medication may be recommended. The treatment regimen is selected individually according to the reasons that led to the release of bloody urine.
Cystitis
The most common pathology leading to the appearance of streaks and blood clots in the urine is called cystitis. This disease is an inflammatory process localized to the mucous tissues of the bladder. The disease can occur due to the influence of a wide range of factors, which include general hypothermia of the body, long-term use of potent medications, violation of a healthy diet, and a cold.
The main symptomatic manifestations of cystitis are the following: a frequent irresistible desire to go to the toilet, even if the patient has recently urinated, the release of a small amount of urine with blood clots. An increase in temperature and the appearance of acute painful sensations in the lower abdomen are also possible.
Prolonged course of cystitis without treatment almost always leads to chronic inflammation, making it extremely difficult to completely eliminate the disease. The treatment regimen for cystitis is developed taking into account the factors that caused the development of the pathology.
Endometriosis
The appearance of blood in the urine before menstruation, as well as after the end of menstruation, may be the result of the development of endometriosis. It is generally accepted that this disease primarily affects the organs of the reproductive system, but this is not entirely true. At the initial stages, the pathology actually leads to modification of the mucous tissue of the uterus. Further, as the disease progresses, damage occurs to the integument lining the walls of the bladder and ureter.
The disease may be asymptomatic or accompanied by pain in the lumbar area and lower abdomen. With significant localization of pathological processes, the disease is almost always associated with pain, which can be nagging, sharp or aching in nature.
If urine with blood is precisely the result of a pathology called endometriosis, you should consult a doctor as soon as possible to select and prescribe adequate therapy. Lack of treatment can cause compression of the ureteral ducts, disruption of urination processes, and general intoxication of the body.
Infectious diseases
Also among the common causes leading to the detection of blood in urine are diseases of infectious and inflammatory origin. Pathologies of this kind lead to damage to mucous tissues, which become more loose and permeable, and damage to small capillaries is also possible. The result is the release of more or less blood.
Treatment of diseases of an infectious or inflammatory nature is a prerequisite. Failure to take them in a timely manner can lead to the development of a number of complications. It should be noted that if blood flowed throughout the entire treatment period, after completion of the treatment course, its release must stop. If a symptom is present, this may mean that the therapeutic tactics were chosen incorrectly.
Urolithiasis disease
Urolithiasis can also provoke the appearance of a small amount of blood in urine. This is due to the following aspects: most often, pathological stones form in the kidneys, subsequently moving with urine flow to the lower parts of the excretory system. If the stones have a porous structure and sharp edges, damage to the walls of the mucous tissue occurs.
It is quite difficult to determine urolithiasis in the early stages, since often against the background of this pathology the symptoms are mild. However, it is still recommended to pay attention to some symptoms. These include, for example:
- The urine becomes cloudy and a strong unpleasant odor may appear. This symptom can be characterized as relative, since, provided there is no sand in the urine, the biological fluid may well remain transparent.
- Sharp pain appears in the lumbar area and lower abdomen.
If the above symptoms appear in a complex manner, you should immediately consult a doctor to make a diagnosis and prescribe adequate therapy.
Which doctor should I contact?
The most important thing in diagnosing most diseases is a thorough collection of complaints and medical history. Only by subjective signs can we assume the cause of blood in the urine. For example, hematuria combined with polyuria, thirst, or itchy skin indicates diabetic nephropathy.
If blood appears in the urine, you should consult a physician, who will refer you to a specialist for further diagnosis. A urologist and nephrologist deals with diseases of the kidneys and urinary tract. The latter specializes in pathologies of the renal parenchyma.
To detect hematuria, a clinical urine test is performed. This study allows us to establish the fact of loss of red blood cells, but does not provide information about the true cause of blood in the urine in women.
Algorithm for diagnosing diseases of the urogenital tract:
- Detailed clinical urine analysis.
- Bacterial culture of urine.
- Urine analysis according to Zimnitsky.
- Urinalysis according to Nechiporenko.
- Daily proteinuria.
- Clinical blood test.
- Biochemical blood test.
- Ultrasound examination of the kidneys and bladder.
- Excretory urography.
- Cystoscopy.
- Kidney biopsy.
Having figured out what it is - blood in the urine of women, and the true reasons for its appearance, the doctor begins treatment. Surgical pathology often requires surgical intervention, while therapeutic pathology often requires adequate drug therapy. The kidneys are a very sensitive organ. To preserve their function, it is important to diagnose the disease in a timely manner and begin treatment.
Classification
The urine of a person who does not have any health problems and follows the basic rules of a healthy diet is a liquid colored in various shades of yellow and free of foreign inclusions. At the same time, when performing the act of urination, no unpleasant sensations should appear, including pain, as well as burning and itching.
If blood is found in a woman's urine, this is usually an alarming sign. To determine the severity of the condition, the following classification option is used:
- Microhematuria. In this case, it is almost impossible to determine the presence of blood in the urine visually, since the amount is small. This condition is detectable only during diagnostic procedures.
- Macrohematuria. As the name suggests, in this case the urine takes on a red or pink tint, which is due to a large number of blood streaks or even blood clots. Often this condition is accompanied by pain in the urethra or bladder area and is a consequence of a violation of the integrity of the mucous tissues of the excretory system. If this type of hematuria is detected, you should immediately seek medical help.
Video
We offer you to watch a video on the topic of the article
The phenomenon in which urine with blood appears in women is hematuria. This symptom manifests pathologies that require immediate intervention - therapeutic or surgical. In half of the cases, blood loss must be compensated. Substitution will prevent the development of anemia, avoid hemorrhagic shock and death. Without specialized medical care, it is impossible to determine the cause of hematuria and replenish the volume of lost blood. Calling a doctor is an indispensable condition for maintaining health and life.
Physiological reasons
Urine with blood in women can be the result of not only pathology, but also a completely physiological phenomenon. For example, various foods, medications, and drinks can give urine a red tint. It is possible that a small amount of blood may be released when urinating in women at the beginning or end of menstruation. This is a completely normal occurrence and should not cause concern.
Hematuria in pregnant women
In some cases, blood clots in the urine of women can be the result of so-called hematuria during pregnancy, a condition the causes of which have not been fully studied at present. As a rule, the appearance of blood in urine is almost painless, and most often occurs if a woman has not urinated for a long period of time.
Why does this happen, and is there a threat to the health of the expectant mother and baby? In the early stages of pregnancy, the release of some blood during urination may be the result of hormonal changes in the body. If bloody streaks or particles are released in small quantities and are observed quite rarely, there is no cause for concern.
In the later stages of pregnancy, bloody urine often means a disruption of blood flow in the pelvic organs, the development of which is provoked by the pressure of the growing uterus. This condition can be quite dangerous; the pathology may well lead to premature birth, intrauterine anomalies of fetal development, and hypoxia.
Functional hematuria
In some cases, the appearance of blood in women's urine may be a completely natural physiological factor. As a rule, the appearance of a small amount of red streaks in the urine occurs after prolonged or exhausting physical exertion, when the body is overheated or hypothermic. This also happens quite often during severe infectious or viral diseases, such as influenza.
Also among the relatively safe factors, as a result of which some women bleed, include menstrual irregularities, which are a consequence of hormonal imbalances. More often, this condition is detected in young girls at the stage of puberty. To normalize the functioning of the body, normalize the menstrual cycle and prevent heavy bleeding, patients may be advised to take a course of medications.
Causes
There are over 10 conditions that contribute to the appearance of red blood cells in the urine. These pathologies are associated with disorders of the urogenital tract and dysfunction of the endocrine system. Hematuria can be caused by improper medication use or the presence of a tumor process in the body. Only a doctor can determine the exact cause of the symptom.
Infections of the genitourinary system
In infectious-inflammatory pathologies, the urine is slightly stained with blood. Factors contributing to the development of diseases of the urogenital tract in women:
- systematic exposure to low temperatures on the body
- lack of a regular sexual partner
- introduction of bacterial, fungal or viral microflora from instruments during diagnostic and treatment procedures
- insufficient implementation of hygiene measures
- neglecting to use pads when visiting a public toilet
- overuse of tampons during menstruation
If hematuria is caused by an infection in the genitourinary system, the woman’s body temperature rises and pain occurs. The localization of the unpleasant sensation is the lumbosacral region of the back, vagina, lower abdomen. The process of urine excretion is accompanied by cutting sensations inside the urethra; urine has an unpleasant fishy or acidic odor. At the same time as the woman, her sexual partner should undergo treatment.
Clinical picture of various diseases
Blood in urine also indicates that the female uterus is susceptible to disease. Mechanical damage to the urethra or vagina is possible. When pain is felt during the process of urinating, a burning sensation and discomfort appear, you should contact a gynecologist, because there is a possibility of the onset of infectious inflammation.
If the female body is exposed to heavy physical stress every day, there is a danger of uterine prolapse. Minute tears appear in the tissues, and blood vessels are damaged, which allows blood to enter the urine.
Cervical disease, during which wounds and erosions appear on the tissues, can also cause a pathological problem. If the disease is not detected in a timely manner, blood vessels may become damaged, pain will appear in the abdominal area, and blood will enter the urine.
For older women, the problem of bleeding is primarily associated with a urinary tract infection. The peculiarity is that with age, the muscles of the organs weaken, causing stagnation. From this, inflammatory processes begin to develop, which in acute forms will be accompanied by severe pain, discharge of blood into the urine, and the presence of protein, increased leukocytes, red blood cells and other components in urine analysis that exceed the norm.
Blood clots can be the cause of physiological processes in the form of menstruation. There is nothing wrong with this, but if mucus or pus appears in the urine, it is recommended to go to the hospital, as there is a high probability of complications.
Possible complications
If the disease or condition that caused the development of hematuria is not eliminated for a long period of time, the level of hemoglobin may decrease and the formation of anemia. Other potential risks:
- Miscarriage, premature onset of labor. Develops due to partial or complete detachment of the fertilized egg from the walls of the uterus.
- Hydronephrosis, or dropsy of the kidney, is the expansion of its membranes due to a stone blocking the outflow of urine. If the obstruction is not removed, the risk of organ loss increases.
- Infertility. Occurs due to adhesive disease. It develops against the background of prolonged inflammation in the urogenital tract, endometriosis, or previous trauma to the pelvic or abdominal organs.
In almost 100% of cases, these complications can be avoided.
Why and from what happens
Bloody discharge during urination most often occurs as a result of inflammatory processes that affect the urinary system. Painful urination with blood indicates an infection or severe physical exertion. The following are the reasons for the appearance of blood in the urine:
- inflammation of the bladder or urethra;
- the presence of stones in the organs of the urinary system;
- malignant or benign tumors;
- inflammatory process in the kidneys;
- taking anticoagulants or hormonal drugs;
- benign growth of the inner layer of the uterus beyond its limits.
Sometimes blood in the urine of women can appear during pregnancy or gynecological problems. In men, this symptom signals urological diseases. The cause of scarlet or burgundy discharge is infection of the urinary system, injury or hypothermia.
Cystitis
Cystitis is inflammation of the bladder. The disease occurs as a result of hypothermia. Against the background of mental stress and weakened immunity, the disease begins to progress. Cystitis can also appear against the background of chronic tonsillitis, furunculosis, caries, intestinal diseases, adenoids, and thrush. The main symptoms are blood from the urethra, painful urination, discomfort in the abdomen and lower back. With cystitis, the urine is cloudy and sometimes pink due to drops of blood. This means that the mucous membrane of the organ is damaged.
Urolithiasis disease
With urolithiasis, stones are found in the urinary tract and kidneys. The disease occurs due to vitamin deficiency, water-electrolyte imbalance, poor nutrition, and a sedentary lifestyle. The first symptoms include pain in the back and lower abdomen, vomiting, nausea, pain when urinating and eventually blood. Bloody urine occurs during an inflammatory process due to damage to the blood capillaries and the advancement of the stone.
Important information: How many days does bleeding last after childbirth and how long should bleeding last in the postpartum period in women
Urethritis
Urethritis is an inflammatory process that affects the urethra. Occurs due to infection, injury, promiscuity, hypothermia, and poor hygiene.
With urethritis, blood appears from the urethra, which means the presence of an inflammatory process.
Urine has an unpleasant odor, there is itching and burning, and there is pain when urinating. The fluid from the urethra may contain pus, blood clots, and mucus.
Oncology
Bladder cancer in adults is a tumor that appears inside the organ. A malignant disease can spread beyond the organ. The first symptoms are blood coming out when urinating in a rusty or red color, as well as pain in the organ, burning sensation. Bloody discharge can only be detected after diagnosis. The risk of developing the disease increases with smoking, long-term use of medications, pelvic irradiation, birth defects, and chronic urinary tract diseases.
Hematuria
Hematuria is a condition in which blood appears at the end of urination. Hematuria is a symptom that may indicate the presence of various diseases of the urinary system. Discharge appears as a result of vascular damage against the background of an inflammatory process, which can be chronic. An alarming symptom should not be ignored. The patient may urinate with pain. The discharge comes with streaks or droplets of blood. It is necessary to consult a specialist to get tested and prescribe appropriate treatment.
Glomerulonephritis
With glomerulonephritis, damage to the renal glomeruli occurs. Bloody urine and pain can occur due to immunoinflammatory diseases. With glomerulonephritis, a person detects traces of blood in the urine. Blood pressure rises and swelling appears. The disease occurs as a result of hypothermia, allergic reactions, exposure to toxic substances, disruption of the immune system, alcohol consumption, and streptococcal infections.
Injuries
If the organs of the genitourinary system are injured, the discharge from the urogenital bladder becomes scarlet. Blood from the urethra can appear when lifting heavy objects, damage to the kidneys or lower back, abdominal tension, sudden turning of the torso, fractures of the pelvic bones, falling, or increased intra-abdominal pressure. In combination with abnormal discharge during urination, painful sensations occur in the lower abdomen or lumbar region, itching in the perineum and burning sensation are felt. When urinating, there is blood with clots.
Pregnancy
Blood after urination during pregnancy indicates infection of the genitourinary system. In this case, other symptoms may occur: frequent urge to go to the toilet, vomiting, fever, burning and itching in the perineum, pain in the lower abdomen. Most often, symptoms indicate the development of pyelonephritis or cystitis. Blood at the beginning of urination can appear with anemia, lupus, diabetes, and sexually transmitted infections. Urine may change color after consuming certain foods and medications. In this case, no treatment is required.
Taking hormonal medications
Hormonal medications are taken to prevent pregnancy. They are not considered safe because they have a number of side effects. Undesirable reactions appear immediately or after a few weeks.
Pills containing large amounts of estrogens most often cause side effects.
One of the symptoms is blood when urinating. After discontinuation of the drug, the condition improves.
Important information: Side effects after taking Escapel and does bleeding rule out pregnancy?
Endometriosis
Blood clots in the urine are one of the symptoms of endometriosis. The disease is characterized by the growth of the endometrium outside the uterine cavity. With this pathology, pain appears in the lower abdomen or back, stool upset, pain during sexual intercourse and during menstruation. Droplets of blood indicate a pathological process in the bladder. The urge to go to the toilet becomes painful and more frequent.
Taking anticoagulants
Side effects may occur after taking medications. Undesirable reactions include blood from the urethra. Anticoagulants such as Warfarin and Heparin cause bladder discharge to turn red in some patients. It is necessary to reduce the dosage of medications or stop taking them so that the condition returns to normal. Clots in the urine may appear after taking aspirin, cyclophosphamide and penicillin.
Infections of the genitourinary system
Infections of the genitourinary system cause pain when urinating and blood. The infection enters through the urethra and begins to multiply in the organs of the genitourinary system. Additionally, burning, pain and itching in the perineum, and frequent urges may occur. Urine has an unpleasant odor and becomes cloudy in color mixed with blood drops. The cause is hypothermia, weakened immunity, and poor hygiene. Infection can occur through sexual contact.
Which doctor should I contact?
When red blood cells stain the urine due to endometriosis, it is necessary to contact a gynecologist. If hematuria in women is caused by urethritis, urolithiasis, cystitis, glomerulonephritis, you will need to consult a urologist. When the urine is bloody due to taking hormonal drugs or anticoagulants, you need to visit a specialist who recommended these medications. The doctor will conduct an examination, cancel the previously prescribed drug or replace it with an analogue.
When blood is excreted in the urine in pregnant women, you should contact an observing gynecologist. But if the hematuria is intense, you need to call an ambulance and limit physical activity until the doctors arrive. An oncologist should be visited if a tumor process is detected in the urogenital tract. Restoring the integrity of the parts of the genitourinary system is carried out by a urologist or gynecologist, depending on the damaged organ. If you have functional hematuria, you should make an appointment with a therapist. Then, taking into account the established underlying cause, treatment is carried out by a specialist.
Treatment methods
It is recommended to spend as much time as possible in a calm state.
After identifying blood in the urine, it is important to conduct a thorough diagnosis and undergo an examination as soon as possible.
Treatment begins with eliminating the cause of hematuria, namely:
- stopping blood flow;
- taking medications;
- bed rest, limitation of physical activity;
- taking vitamin and mineral complexes;
- blood transfusion for medical reasons.
Several types of drugs can be used to carry out drug therapy: antibiotics, painkillers, hemostatics. In addition, medications are prescribed to improve well-being, these can be dietary supplements and vitamins.
The most common names of drugs on the list of prescribed drugs are as follows:
- Monural. This is an antibiotic with a wide spectrum of action, available in tablet form. Can be used to treat not only elderly women, but also children. The main advantage of the drug is its destructive effect on pathogenic microorganisms. But there are also disadvantages: the intestinal microflora suffers.
- No-spa is an antispasmodic agent with an analgesic effect. Prescribed for the treatment of acute cystitis. The main advantage is the rapid achievement of the desired result, but there is also a disadvantage - it has a detrimental effect on the liver.
- Ibuprofen and its analogs. This is a non-steroidal drug that has an analgesic effect and helps eliminate the inflammatory process.
- Vikasol. The drug, which has a hemostatic effect, contains sodium bisulfate and vitamin K. This is the most effective remedy in the fight against hematuria. The main advantage is low toxicity, as well as low cost.
One of the drugs for treatment
Any drugs for treatment, even those sold in a pharmacy without a prescription, can only be prescribed by the attending physician. Self-medication without finding out the cause of the disease is strictly prohibited.
Prevention
The pelvic organs should not be compressed by anything.
One of the most common reasons for the development of hematuria is the addition of a bacterial infection to the urinary tract, and all due to the fact that a person does not follow the rules of personal hygiene.
In order to protect the mucous membranes and prevent germs and other pathogenic microorganisms from penetrating them, it is recommended to adhere to the following recommendations:
- give preference to loose underwear made from natural fabrics;
- visit public toilets and baths carefully because this is the main source of germs;
- Make sure that during the cold season the body is not hypothermic;
- During menstruation, you should change pads as often as possible;
- monitoring personal hygiene, timely change of underwear;
- It is not recommended to engage in excessive physical activity;
- Several times a day you should visit a medical facility and examine the entire body.
You should saturate your body with something useful every day.
Many women who find blood in their urine begin to panic, and rightly so. It is forbidden to make a diagnosis and start treatment on your own; you need to visit a urologist or therapist as soon as possible. The sooner treatment is started and the more correct it is, the more favorable the prognosis.
Diagnostics
To determine the cause of the development of hematuria, it is necessary to conduct an ultrasound of the pelvic cavity, a laboratory test of blood, feces (to identify hidden red blood cells), and urine. Additionally, undergo an MRI or CT scan. The parameters of the stone and its exact location in case of urolithiasis are determined using a survey X-ray examination and subsequent excretory urography. If a tumor process is suspected, a biopsy of the affected organ is performed with further study of a tissue sample.
Diagnostic features
As soon as you suspect such a problem, you should immediately visit a doctor. The specialist will need to verify the fact of hematuria, its nature, and determine the root cause. Based on the pathology or physiology, the manifestations of which are bloody discharge in the urine, methods for a comprehensive examination will be developed.
When collecting complaints, you should clarify how the patient sees the changed shade, the presence of clots, their parameters and shapes. In addition, it is necessary to determine the period of appearance of blood - during the entire process of urination, at its beginning or at the end.
Information about the duration of such changes must be analyzed and other manifestations of the disease (fever, pain, weakness, rash on the skin, changes in body weight) clarified. The specialist examines the patient, palpates the abdomen and kidneys, and taps the lumbar girdle.
When the location of the cause is identified, a three-glass urine sample is prescribed. In addition, a blood test is performed to detect inflammatory processes of various origins.
The main methods of instrumental research include:
If a woman is pregnant, the kidneys are first checked for diseases to prove or disprove this possibility. During this period, the ureteral system functions under increased load, and diseases that were previously hidden appear. If necessary, it would not be superfluous to consult a nephrologist. Subsequently, the woman is under the supervision of a gynecologist and obstetrician.
If blood gets into the urine due to hormonal changes occurring in the body, or taking contraceptive medications, then you can only get by with medical supervision and periodic examinations.
Treatment
Stopping blood is performed with drugs such as Dicynone, sodium etamsylate, aminocaproic acid, calcium chloride. In case of injuries to parts of the genitourinary system, emergency surgical intervention is required. The doctor restores the integrity of the tissues, installs drainages (to prevent the accumulation of blood masses and subsequent inflammation of adjacent tissues). Glomerulonephritis is eliminated with antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs, and hemostatic agents.
Stones in the urogenital tract are removed conservatively or surgically. The type of treatment depends on the characteristics of the stones (size, composition, quantity), the likelihood of their independent removal. The patient’s age and blood pressure are also taken into account. If the calculus is subject to conservative removal, it is removed with the help of Fitolit, Urolesan, and water loading is performed.
The patient needs to drink 2 liters of water over 1 hour, after which she is injected intramuscularly with a diuretic drug - Furosemide or Lasix. After the injection, the woman should increase her physical activity - by walking, jumping, and exercising on a simulator. Physical activity will provoke the movement of the stone and its removal out. In order not to miss the release of a stone, when you have the urge to urinate only into a container.
When stone deposits cannot be removed conservatively, the patient undergoes surgery: contact lithotripsy. The method involves crushing the stone into sand and then washing it out of the urogenital tract. This type of operation does not require a skin incision and is aimed at rapid recovery of the body.
The tumor process is eliminated through chemotherapy, radiation exposure, the use of hormones, and surgery. Cystitis and urethritis are eliminated with the help of antibiotic therapy, uroseptics, antispasmodics, and sometimes diuretics. Additionally, it is necessary to regularly rinse the bladder and urethra with antiseptic solutions. In case of injuries to internal organs, a replacement blood transfusion is performed - transfusion of a volume of blood equal to the amount removed from the body.
In all of these cases, the patient is prescribed a diet. Depending on the factor that caused the staining of urine with red blood cells, nutrition involves increased consumption of vegetables, fruits, meat, and fish. The purpose of the diet is to increase the level of hemoglobin in the blood, restore the body’s activity, and improve the overall well-being of the woman.
How difficult is the treatment ahead?
If the symptom is bacterial, the doctor will prescribe antibiotics.
If an infectious bacterial complication is diagnosed, the patient is prescribed a course of antibiotics, uroseptics, diuretics and other auxiliary agents. During the therapy period, it is important to strictly follow the treatment regimen prescribed by the doctor and in no case stop taking antibacterial drugs after the symptoms disappear. On average, the duration of antibiotic therapy should not be less than 5-7 days, otherwise the untreated disease will go into the chronic stage, which will subsequently cause frequent relapses.
In the presence of neoplasms of malignant etiology, surgical removal is mandatory, followed by chemotherapy and radioirradiation. If the tumor is benign, the doctor conducts additional diagnostic tests and decides on a further treatment regimen.
In case of cervical erosion, in the case of a pronounced process, cauterization is prescribed. If a serious injury to the bladder occurs, first of all, the patient is given hemostatic drugs, then an operation is performed to suture the damaged areas. If a woman has uterine prolapse, treatment is carried out exclusively by surgery. For non-pathological conditions, treatment is not prescribed; the patient is advised to monitor the condition and, if it worsens, seek medical help.
Prevention
To prevent the occurrence of conditions that are accompanied by hematuria, you need to:
- Avoid uncontrolled use of any medications and do not exceed the dosage prescribed by your doctor.
- Dress according to the ambient temperature and avoid hypothermia.
- Avoid damage to the body - at home, during sports training or work.
- Normalize the diet and quality of nutrition.
- Avoid significant physical activity and do not lift heavy objects.
- Carry out hygiene measures carefully and regularly.
- Stop drinking alcohol.
- Improve or change working and living conditions, avoid staying near sources of intoxication.
If you have a hereditary predisposition to the development of any disease, you need to undergo regular diagnosis by a specialist in the appropriate field. Timely examination and, possibly, identification of pathology will allow it to be stopped without consequences for health. It is important to eliminate all diseases in the acute form of their development, preventing them from taking a chronic course.
Bloody urine always indicates health problems. The main reason may be disease or damage to the pelvic organs and abdominal cavity. To avoid the development of negative consequences and maintain reproductive status, a woman needs to visit a doctor and not deviate from his recommendations.
Symptoms
Hematuria may be accompanied by pain during urine output, increased body temperature, burning, aching pain in the lower back and other symptoms.
Most often, in female diseases, painful urination is observed, which accompanies inflammation of the urinary tract. The high incidence of this pathology is due to the anatomy of the female genitourinary system (short and wide urethra, through which infection easily penetrates).
Without pain
Painless discharge of blood during urination can occur against the background of swelling, hypertension or hypotension, increased volume of daily urine, weight loss, bleeding gums, frequent bruising of the skin, swelling of the lumbar area and other symptoms.
Important information: What to do when your tongue bleeds when bitten and how to stop the bleeding
The absence of pain and accompanying symptoms may indicate false hematuria - staining of urine when consuming foods and medications containing red pigments (beets, phenolphthalein compounds, etc.).
The clinical picture of hematuria, laboratory and instrumental studies allow for differentiated diagnosis.
With pain
Painful urination accompanied by hematuria occurs when the lower urinary tract is inflamed or damaged. Pathological processes may be accompanied by an increase in the patient’s body temperature, burning in the urethra, frequent urge to urinate, heaviness in the pelvic area and other symptoms.
Pain can be observed not only during urine output, but also outside the toilet. The appearance of blood after urination in women with pain in the lower back or lower abdomen may indicate injury, cancer, and inflammation of the glomerular system of the kidneys.
Hematuria of traumatic origin
A separate reason for the appearance of blood in the urine in patients of different sexes and ages is traumatic damage to the mucous membranes of the genitourinary system.
Injuries are classified into spontaneous, caused by bruises, falls, blows, and resulting from manipulations when damage to the mucous membranes occurs during surgery, diagnostic procedures, or instrumental examination of the patient. The appearance of bleeding in the latter case is due to the following reasons:
- trauma during catheterization (during or after surgery, manipulation);
- violation of the technique for installing the drainage system after surgery.
When hematuria of any form is detected, corrective measures are taken to eliminate the cause and blood loss. Internal organs must be examined after abdominal surgery for internal bleeding.
Types of hematuria
Urine with blood, or hematuria, is the presence of red blood cells in urine above the physiological norm. Depending on their concentration, 2 types of pathology are distinguished:
- microhematuria - blood cannot be detected by eye, but is detected only in the laboratory;
- macrohematuria - there are a lot of red blood cells in the urine, so the liquid takes on a pinkish tint.
There are 3 types of microscopic hematuria. If the source of bleeding is the urethra, initial (initial) is diagnosed, if the urethra is the final (terminal), and if the kidneys, complete (total) microhematuria is diagnosed.
It is necessary to distinguish true hematuria from false hematuria (pseudohematuria), in which the coloring of urine is associated with an increase in the level of hemoglobin oxidation products.
False hematuria is sometimes referred to as urine that is reddish in color due to certain foods (such as beets).
The classification of hematuria is carried out taking into account the factors that led to its development and the amount of blood in the urine.
| Types of hematuria | Characteristics |
| Classification by factors of occurrence | |
| Postrenal | The symptom appeared as a result of kidney pathologies or injuries. |
| Extrarenal | The symptom appeared as a result of other pathological conditions. |
| Classification by the amount of blood in the urine | |
| Macroscopic | The amount of blood is enough for the urine to be colored red. In addition to blood, it may contain other impurities and pus. |
| Microscopic | The amount of blood is minimal, so it has virtually no effect on the color of urine. Abnormal changes can only be detected by special tests. |
Therapeutic measures
Given the variety of causes of blood in the urine, it is important to conduct a differential diagnosis and examine the patient. To reliably determine hematuria, you should take a urine test. To do this, collect the first morning portion of urine, about 150 ml.
You should perform genital hygiene with plain water the night before the test is taken. This way you can evaluate not only the presence of blood, but also the microflora of the genital organs and a large number of red blood cells.
Despite the visible change in urine color, blood in a patient’s urine can only be detected in a laboratory setting. Food products (beets, pomegranate, tomato juice) can change the color of urine.
A doctor may prescribe a 24-hour urine test for red blood cells, where urine is collected in one container for 24 hours. Collection begins with the second void of the morning and ends with the first void of urine the next morning. For convenience, it is better to take a glass jar into which you need to pour 150 ml of the total portion of the next urine.
Urine examination allows you to determine many indicators of the functioning of the genitourinary system, including blood impurities. A urine test in men can reveal traces of prostate secretions. Other diagnostic methods are:
- detailed, general blood test (hemoglobin, bilirubin, creatinine, urea);
- Ultrasound of renal structures, pelvic organs;
- excretory urography with contrast agent;
- prostate juice analysis;
- radiography of the kidneys;
- tissue biopsy of renal structures (if necessary);
- MRI and CT examination (to determine the location of stones, tumors).
Based on the diagnostic data, a medical consultation can be assembled to prescribe the optimal treatment regimen. Additionally, consultations with a urologist, surgeon, nephrologist, hematologist, and cardiologist are required.
If the causes are established, treatment begins immediately. It is always worth remembering that you should never make a diagnosis solely visually. Thus, the color of urine may change if menstrual blood enters the urine. Various food dyes, such as beets, can change their color, creating a false impression of the presence of disease.
Only an analysis carried out in a laboratory under a microscope can give a completely reliable result, because even taking certain types of medications can significantly distort the actual picture of the patient’s condition.
Since the appearance of red blood cells is not considered an independent disease, but is only one of the symptoms of the development of other diseases, it is possible to rid the patient of blood in the urine only by curing the underlying disease. To do this, you will have to undergo tests such as ultrasound, biopsy, blood and urine tests.
Typically, hemostatic drugs such as Dicinone, Aminocaproic acid, and Vikasol are used in the treatment of hematuria. In this case, in case of blood loss of more than 500 ml, infusion therapy is prescribed.
If, during a subsequent examination, the patient is found to have stones in the ureter or urethra, treatment is accompanied by the use of antispasmodics or thermal procedures that facilitate the natural process of stone passage.
In the same case, when hematuria occurs due to kidney injuries, emergency surgical intervention is required. If the disease has entered a chronic stage, B vitamins and iron supplements are mandatory.
In children, it is treated taking into account hereditary factors, and it is worth knowing that the appearance of blood cells in the urine of young children is usually associated with the presence of congenital defects in the latter. In order to exclude this, a special genetic study is carried out.
Treatment of pathology
If urine with blood in women is caused by inflammation of the genitourinary system, then antibacterial therapy is prescribed, which is aimed at destroying pathogenic microflora. Pain and other symptoms are relieved with antispasmodic drugs, diuretics, and auxiliary therapy. If tests show traces of cancer cells, therapy depends on the stage of the disease; most often, surgical removal of the tumor is carried out with the parallel use of chemotherapy and radiation. For urolithiasis, laser crushing of salt inclusions is indicated, then the tissues of the ureter and bladder will stop inflaming and bleeding will not bother you.
When gross hematuria in women is caused by damage to internal organs, treatment is aimed at rapid healing of damaged tissue and prevention of inflammatory complications. If you follow all the doctor’s instructions, the disease can be completely cured, which means that you should seek medical help in a timely manner, do not self-medicate and do not change the treatment regimen at your own discretion.
Return to contents
Treatment of diseases
Each condition that causes blood when urinating is treated differently. The following options to correct the situation are possible:
- For cystitis, antibiotics (ceftriaxone, norfloxacin) are prescribed to suppress bacteria. To reduce inflammation, paracetamol and nimesil are used. To improve the outflow of urine, antispasmodics (drotaverine) or diuretics are used.
- For urethritis, the principle is no different from the treatment of cystitis. It is possible to use antiseptic solutions to wash the urethra.
- For vaginitis: antiseptics and antibacterial drugs are used.
- Cervical erosion can be simply observed if the process is not pronounced. When the process is severe, the erosion is cauterized and cryodestruction is performed.
- Urolithiasis is treated by crushing stones and removing them surgically.
- In the case of a tumor, it is necessary to determine its location, nature, and size. The tumor is surgically removed. If required, chemotherapy is carried out with the required medications.
In case of injury to the genitourinary system, substances that stop bleeding are used. For significant wounds, suturing of the damage is possible. A bruise in the area where the kidneys are located requires an ultrasound.
Hematuria cannot be ignored. When the smallest drop of blood appears, in women or men, it is imperative to consult a doctor.
If blood appears not for the first time, you should think about your lifestyle. Be sure to monitor the condition of the genitourinary system and treat inflammatory diseases in a timely manner. Self-medication is prohibited.
Video : Hematuria
Hematuria (blood in urine)
Hematuria syndrome in men
The appearance of blood cells in urine in men in the absence of painful sensations may be a consequence of excessive physical exertion. All other cases of detection of red blood cells in male urine are accompanied by pain of varying intensity. Pain and hematuria characterize the following conditions:
- prostate cancer;
- urolithiasis or stones in the urethral canal;
- bladder injuries of various nature.
Prostate adenoma and bacterial advanced prostatitis can contribute to the release of blood into the urine, so it is important to carry out an immediate examination.
What treatment is indicated?
The doctor includes antispasmodic drugs in the treatment course.
Micro- and macrohematuria in women is treated under the supervision of a doctor. In case of inflammatory complication, the following must be prescribed:
- course of antibacterial therapy;
- uroseptics;
- immunostimulants;
- antispasmodics;
- diuretics.
In case of urolithiasis, stone removal followed by restorative therapy is indicated. If the integrity of the organs of the genitourinary system is violated, a scheme is prescribed that will help to quickly heal the damaged organ and restore its functioning. If an oncological disease is detected, the malignant neoplasm is removed, followed by chemotherapy and radioirradiation. The problem can be treated using traditional medicine, but only in consultation with the doctor. Any self-medication and use of folk remedies at your own discretion will negatively affect your health and lead to serious consequences.
prourinu.ru
Diagnostic methods
The primary stage of diagnosis begins in the doctor’s office, who will examine the patient, and if suspicions are confirmed, a referral is given for a series of tests. Laboratory diagnosis includes a general analysis of urine and blood, in which, with an inflammatory complication, an increase in the levels of leukocytes, red blood cells and cylinders will be observed. When a bacterial complication occurs, for example, when pyelonephritis develops, the number of pathogenic microorganisms in the urine will significantly exceed the norm.
To find out the condition of a woman’s internal organs, an ultrasound is indicated.
To examine the condition of the internal organs of the urinary system, it is recommended to undergo:
- Ultrasound diagnostics;
- urography;
- MRI or CT examination.
To assess the condition of the tissues of the bladder and urethra, cystoscopy is prescribed, the results of which can be observed on the monitor in real time. However, this method is contraindicated in case of complicated inflammation, therefore, taking into account the picture of the disorder and the general condition, the doctor selects the optimal diagnostic method.
Return to contents
Traditional medicine recipes
There are folk remedies for treating hematuria. Usually these are various diuretic preparations, tinctures aimed at suppressing inflammation in the organs of the urinary system.
Thus, when treating this disease with traditional medicine, barberry bark or root is used. To do this, pour a glass of boiling water over them, then boil the mixture for 20 minutes. The resulting infusion is drunk 3 tbsp. 2-3 times a day.
In addition, you can pour 20 g of blackberry roots with 0.5 liters of red wine. Next, keep it on low heat for 10-15 minutes. Use is similar to the first recipe.
The third way to cure hematuria without the use of medications is to use bearberry leaf powder. It is mixed in equal proportions with powdered sugar. The resulting solution is taken every 4 hours, 1 tbsp.
At the same time, it is always worth remembering that any self-medication without medical supervision can only worsen the situation, therefore, if you are planning to take even the most harmless medicine, be sure to consult your doctor. It is quite possible that he will not recommend you to use this or that type of medicinal infusion.
What to do with hematuria
Single blood spots in the urine in 80% of cases do not indicate illness. It is recommended to make an appointment with a urologist if the symptomatic picture includes the following signs:
- pain when urinating;
- chronic fatigue;
- change in taste;
- frequent constipation;
- pain in the lumbar area;
- elevated temperature;
- white flakes in urine;
- headache;
- pain when touching the groin area.
Timely diagnosis and treatment of diseases prevent dangerous complications. Women with chronic pathologies of the urogenital system should undergo a routine examination by a urologist at least once every six months.
What to do if there is blood in the urine? The appearance of gross hematuria, which is noticeable due to the atypical color of urine, causes concern in many patients.
First of all, you should consult a urologist or nephrologist, undergo the necessary tests and accurately determine the diagnosis, since multiple diseases can be suspected. If hematuria is detected during routine testing, you should do the same - contact a specialized specialist.
During the period of bearing a child
During pregnancy, blood in the urine can be detected at any stage, which will naturally cause concern both for the woman herself and for the obstetrician-gynecologist. Even taking into account that in most cases this symptom is not associated with serious disorders, an examination of the expectant mother is still necessary. Often in pregnant women, hematuria is idiopathic, that is, it appears “on its own.” Its causes include hormonal changes, fetal pressure on the kidneys and urinary tract.
In addition, this symptom is observed when the small veins surrounding the renal calyces rupture as a result of intra-abdominal pressure in late pregnancy. Idiopathic hematuria during pregnancy most often disappears without a trace after childbirth, and this means that the diagnosis was made correctly. Much less often after childbirth, relapses of hematuria are observed, but they are usually associated with diseases of the urinary organs.
Even if there is a small amount of blood in the urine during pregnancy, you should undergo a full examination
In children, hematuria can be physiological in nature and occur at an early age. Clinicians call this condition benign hematuria, which can be a consequence of long-term drug treatment, for example, antibiotic therapy.
If there are traces of scarlet color on the diaper, diapers or underwear of a newborn, and the child screams, then this is a consequence of injuries to the bladder and ureters. It is important to call emergency services immediately.
In children aged 8-9 years, hematuria is usually serious and, as in adults, is a symptom of various diseases:
- infectious diseases of the genitourinary system;
- prolonged inflammation;
- bladder reflux;
- traumatic kidney injury;
- oxalate deposits, stones in the renal structures;
- thinning of the walls of the renal vessels;
- oncological diseases.
Perhaps there is a previously undetected pathology of the urinary system, the symptoms of which increased in the latent phase and sharply manifested as hematuria syndrome with pain and pulling sensations in the groin area.
What to do
If there is bleeding from the bladder, treatment must be started. After diagnosis, a urologist or nephrologist treats the disease that caused the unwanted symptom. If a few drops of blood come out, the patient should be observed. The doctor prescribes medication and diet. In the absence of infectious diseases, ruptures of internal organs and malignant formations, you can get rid of blood clots during urination using traditional methods. In severe cases, surgery is performed.
Drug therapy
To stop bleeding from the urethra, you need to start taking medications. Depending on the disease, the doctor may prescribe:
- Infectious pathologies of the genitourinary system. In case of frequent urination with blood, antibacterial therapy is carried out - Monural, Nolitsin, Nitroxoline or Palin. Drugs with a diuretic effect are also prescribed - Furadonin, Cyston. During pregnancy, anticholinergic and painkillers are used. Canephron is taken when breastfeeding.
- Urolithiasis disease. In the presence of small blood clots, antibacterial agents, vitamins and diuretics are prescribed. If the patient has renal colic, antibiotics are excluded.
- Glomerulonephritis. If there is blood in the urine, antibiotic therapy is indicated - Ampicillin, Penicillin or Erythromycin. Drugs are prescribed to increase immunity, relieve inflammation, reduce swelling and reduce blood pressure.
- Injuries. If there are bloody drops and a minor bruise, it is necessary to take hemostatic drugs, antibiotics, painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs.
- Endometriosis. The disease is treated with hormone therapy and painkillers. If there is bleeding from the bladder, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, electrical stimulation of nerve endings to relieve pain, and hemostatic agents are used.
- Oncology. With neoplasms, blood may bleed into the urine. Chemotherapy and radiation therapy are carried out. After the tumor shrinks, surgery is prescribed.
Important information: How to identify internal bleeding in the abdominal cavity in women and what to do (first aid) to stop
If blood is released after taking hormonal drugs or anticoagulants, you must stop taking them.
Diet and traditional methods
If drops of blood appear, you need to follow a diet. It is recommended to drink plenty of fluids, avoid alcoholic beverages, drugs, coffee and smoking. It is advisable to exclude sour, salty, fatty and fried foods. It is necessary to replace semi-finished and canned foods with foods rich in proteins and healthy fats. There are traditional methods that will help alleviate the course of certain diseases:
- Cystitis. A warm heating pad applied to the stomach helps. It is allowed to take warm baths without the use of sea salt and other cosmetics. The water should be warm, but not hot. It is useful to add decoctions of chamomile and other herbs to the bath. It is recommended to eat more berries, fruits and vegetables, including cranberries.
- Urolithiasis disease. An effective method is to drink water with honey on an empty stomach 15 minutes before breakfast. For 1 glass of water take 1 tsp. natural honey. Drink half a glass before each meal. If urate stones are present, dissolve 1 tsp in a glass of water. soda Drink 30 minutes before meals. Drinking alkaline water and freshly squeezed beet juice helps.
- Urethritis. It is recommended to drink decoctions of raspberries, lingonberry leaves, nettles, chamomile, and linden. The affected areas can be washed with a decoction of oak bark and chamomile. Herbs are taken in equal proportions and poured into 3 glasses of water. Take 1 glass per day in 3 doses.
- Glomerulonephritis. In case of illness, diet number 7 is prescribed. The consumption of protein foods, fatty meats and fish, and spices is limited. A decoction is used to treat the disease. Take corn silks and cherry tails and add 2 cups of water. You need to take half a glass up to 4 times a day. Make an infusion of black elderberry flowers. Pour water over the flowers and leave for 40 minutes. Take 1 glass per day.
- Endometriosis. Blood during urination can be eliminated by taking herbal infusions. In equal quantities you need to take hogweed and red brush. Pour 2 glasses of water and leave for 40 minutes. Take half a glass twice a day. Infusions containing elderberry, raspberry leaves, nettle, and celandine are effective.
Traditional methods in the presence of blood in the urine should be combined with drug therapy. With an integrated approach, the condition quickly improves and negative symptoms disappear.
Operation
Surgery is required for urolithiasis. Abdominal surgery, laparoscopy or extracorporeal lithotripsy are performed. Endometriosis must be treated with medications, but if there is no result, laparoscopy is performed. If instead of urine there is a lot of bloody discharge due to a rupture of the pelvic organs after an injury, it is necessary to carry out suturing and drainage.
Traces of blood in the urine appear with neoplasms. Treatment is removal of the tumor and corrective therapy. At an early stage, radiation therapy followed by surgery helps. In severe cases, the bladder is removed and an artificial organ is formed.
Hematuria after sexual intercourse
If blood in the urine appears in a woman exclusively after sexual intercourse, most likely the cause is postcoital cystitis. The disease has no age restrictions, so it can occur both after the first sexual intercourse in life and at a later age.
Postcoital cystitis occurs due to sperm or “female” discharge entering the urethra, which in turn becomes inflamed and bleeds after sex.
In order to diagnose blood in the urine after sexual intercourse and start treatment in a timely manner, a woman needs to visit a gynecologist or urologist and undergo the necessary tests. After the final diagnosis, the specialist will prescribe treatment.
Treatment tactics
Based on the data from diagnostic studies, treatment tactics are drawn up. Considering that hematuria is a symptom of a disease, complex treatment is begun aimed at relieving symptoms and eliminating the root cause. Among such events, the following are particularly noteworthy:
- stopping bleeding;
- prescription of certain medications;
- bed rest.
In case of severe blood loss, blood transfusions and infusion therapy may be prescribed to replenish the electrolyte balance. An important aspect in treatment is the elimination of the underlying disease - surgical or conservative methods.
Treatment of hematuria is prescribed not only on the basis of diagnostic data, but also based on the age and medical history of the patient at the moment.
Surgical methods are used for injuries, urolithiasis, and neoplasms in the prostate gland. Conservative treatment is used for inflammation of the kidneys and other organs of the urinary system, infectious diseases of various origins.
If, against the background of treatment and hematuria, renal function sharply decreases and the development of chronic renal failure is observed, then replacement therapy may be indicated in the future: hemodialysis (sometimes emergency hemodialysis is prescribed), peritoneal dialysis, nephrotransplantation.
Prevention of hematuria
Prevention of the described disease consists of preventing the development of the main diseases that accompany it. Thus, treatment of the same pyelonephritis allows you to normalize the composition and color of urine, and therapy of various tumors and injuries of the urinary tract removes blood clots from urine.
Also, persons predisposed to this disease need to carefully monitor physical activity, especially in old age. This avoids injury to internal organs, which could cause blood to appear in the urine. Therefore, if you are engaged in heavy training associated with intense physical activity, it may make sense for you to reduce its intensity, at least for a while.
In addition, for prevention purposes, it is recommended to drink about 8 glasses of water daily, increasing the dose of fluid taken during hot weather. You also need to quit smoking and drinking alcohol. The fact is that these bad habits can cause such a serious disease as cancer, a symptom of which may be the appearance of blood in the urine.
By following these recommendations, you can not only get rid of unpleasant sensations when urinating, but also prevent various very serious diseases.
In old age
The presence of red blood cells in the urine of elderly people usually accompanies chronic nephrotic diseases, including pyelonephritis and glomerulonephritis.
If blood is detected, it can indicate the development of dysplastic changes in the tissues of the genitourinary system, the deposition of calcifications and urolithiasis, adenoma and prostatitis, and infectious kidney damage. Gross hematuria in men over 45-50 years of age indicates the development of prostate cancer.
Hematuria in older people of the fairer sex is most often the result of the development of inflammatory and infectious processes of a secondary nature. The causes of such pathologies in older women are:
- oncological formations of the genitourinary system - uterus, ovaries, kidneys, ureters, bladder, etc.;
- anatomical narrowing (stenosis) of the urethra and other urinary tract;
- urolithiasis when the urinary tract is blocked by stones or the mucous membranes are damaged when moving.
In old age, the likelihood of developing serious diseases of the genitourinary system increases significantly. This is especially due to hormonal changes in the body. Therefore, it is necessary to be regularly examined and tested so as not to miss the occurrence of pathologies.
Of course, these recommendations also apply to younger women, especially those whose urine tests reveal blood impurities, as well as protein, which indicates the presence of an inflammatory process. In such cases, it is imperative to find out the cause of the deviation from the norm and prescribe adequate treatment.
Associated symptoms
Hematuria is only sometimes asymptomatic; usually blood in the kidneys and urine has many accompanying symptoms - this is how the body tries to report serious dysfunctions of the genitourinary system. Associated signs of the disease are:
- pain (dull pain, sharp pain when urinating, constant or episodic, radiating);
- dizziness;
- pain during sexual intercourse (during intercourse or after);
- intensity of bleeding (drops or flowing, especially when the integrity of the mucous membranes is violated);
- signs of intoxication (vomiting, nausea);
- headache;
- paleness of the skin, dull complexion;
- excessive sweating.
If the hematuria is intense, then the patient will certainly show symptoms of iron deficiency anemia and blood loss. Simultaneously with the hematuric symptom, stones (with urolithiasis) and kidney prolapse are often detected. All patients experience severe muscle weakness and severe thirst. Other symptoms may include:
- yellowing of the skin, sclera (gallbladder insufficiency and hemolysis);
- excretion of cylindrical bodies in the urine (with inflammation of the parenchymal layer of the kidneys);
- violation of the outflow of urine (prolonged inability to empty the bladder).
Blood in the bladder requires mandatory diagnostics, the task of which is to accurately differentiate one disease from another. Timely treatment of advanced hematuria can save not only the health, but also the life of the patient.