IMPORTANT!
Sergey Bubnovsky:
There is an effective remedy for sexually transmitted diseases... Read more >>
An enlarged ovary may not always indicate the development of the disease. It would be correct to say that such changes in the reproductive system inform a woman about some malfunctions in the body. Medical practice says that the ultrasound procedure allows you to see an enlarged ovary at an early stage.
If you do not pay attention to the anomalies that have arisen in time and the enlargement of the pelvic organs, then the gynecologist will not need special equipment to establish an accurate diagnosis.
It is very important not to miss the first signs of a female illness in order to start treatment on time. You should be attentive to your body’s signals and not consider frequent ailments and other symptoms to be commonplace.
Symptoms of the disease
Some symptoms may tell a woman that she has an enlarged left ovary or an enlarged right one. Such signals are:
- frequent malaise and fatigue;
- opening of bleeding in;
- aching pain in the area of the female appendages;
- pain in the back;
- pain during intimacy;
- heavy discharge every day.
The acute form of the disease may be accompanied by a sharp increase in temperature (up to 39 °C). Such alarming symptoms require immediate intervention by a qualified specialist. The acute form of the disease is treated only in a medical hospital under the supervision of doctors.
Symptoms
Although enlarged ovaries are not always accompanied by any symptoms, women with this condition may experience:
- Changes in bowel function
- Increased frequency of urination
- Irregular menstrual cycle
- Pain or pressure in the pelvic area
- Swelling in the pelvic area
- Persistent abdominal discomfort such as bloating or nausea
- Thinning hair on the head
- The appearance of excess hair on various parts of the body
- Unexplained fatigue
- Weight gain or loss
Sometimes the ovaries may become so enlarged that the woman or doctor can feel them in the pelvic area, although this is quite rare.
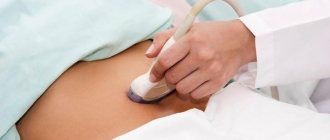
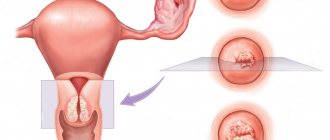
If you are experiencing symptoms that may indicate enlarged ovaries or another related problem, your doctor may recommend an ultrasound. Ultrasound uses sound waves to create images of the pelvic organs. The doctor may do an ultrasound through the abdomen (transabdominal ultrasound) or insert a probe into the vagina (transvaginal ultrasound).
Causes of the phenomenon
After a routine ultrasound, almost every woman hears a diagnosis - enlargement. What could be the reason for the development of this pathology? Probably every woman is concerned about the causes of this pathology. Enlarged ovaries can be the result of certain disturbances in the body's functioning or a consequence of illness.
Why the ovary is enlarged - the reasons are:
- long-term use of hormonal drugs;
- period of breastfeeding - prolactin is significantly increased;
- stressful and depressive states, psycho-emotional tension;
- sudden weight loss;
- period of adolescence;
- different degrees of obesity;
- disturbances in the functioning of the endocrine system.
To establish why enlarged ovaries in women, the reasons are determined with the help of a specially designed examination by a specialist. Sometimes certain types of microorganisms are to blame for changes in the size of the ovaries. This reason why the ovary could become enlarged can be discussed if the disease is infectious in nature.
Enlarged ovaries can be due to thrush, gonorrhea, under the influence of staphylococci, enterococci and other pathogens. If the cause is one of the diseases mentioned, then you first need to address the root cause.
The first bell and serious sign that a gynecological disease is beginning to occur is an enlarged ovary. Quite often the disease takes a chronic form. This happens because many women do not notice symptoms or the clinical signs are not very noticeable. But we must remember that treatment must be carried out without fail.
Why do women have enlarged ovaries: reasons
During a routine ultrasound, every representative of the fairer sex can hear the diagnosis - the right ovary is enlarged. What provoked this pathology? The ovaries enlarge if disturbances occur in the body or a disease occurs. Each woman is interested in what reasons can cause pathology.
Let's look at the most common reasons:
- if a woman has been continuously taking hormonal medications for a long time;
- breastfeeding when prolactin levels are elevated;
- stress, depression, psycho-emotional tension;
- sudden loss of body weight;
- adolescence;
- obesity of different feet;
- if there are disturbances in the endocrine system.
Diseases that can cause ovarian enlargement
According to medical practice, it is the right ovary that most often enlarges. It is difficult to explain exactly why this happens; there are guesses that it is close to appendicitis. After all, infections can pass from the ovary to appendicitis and vice versa.
Let's look at what diseases can cause ovarian enlargement in women:
- Inflammatory processes. Quite often the cause in women is inflammatory processes occurring in the pelvic organs. As a rule, the infection does not manifest itself clearly, then it develops into a chronic form, becomes inflamed and enlarges the ovary. The increase occurs due to the appearance of adhesions and infiltration, and not due to the fact that the ovary itself is growing. If diagnosis and treatment are delayed, the ovary and uterus cannot be palpated separately; one large organ can be felt.
- Cervical erosion. Also, one of the reasons may be cervical erosion. It can injure a small part of the organ, to which pathogenic flora attaches and an inflammatory process begins, which can reach the ovary and cause an enlargement of the right and left organs.
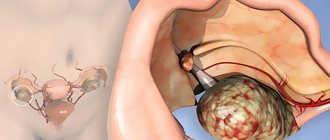
- Cystic formation. Enlargement can occur due to those cysts, of which there are many and their size is more than 3 centimeters. A slight enlargement of the ovary can be determined using an ultrasound; it is very difficult to do this by simple examination and palpation.
- Oncology. Each woman needs to remember one thing: if there is cancer in the pelvis, then the ovaries also suffer. It can be determined by feeling only in the later stages. Metastases that began in other organs may also be the cause.
- Ovulation phase. Pathology may appear during ovulation, but this period is short-lived; if you feel that the condition is not improving, you need to visit a doctor.
How to treat
It all depends on what caused the enlargement of the ovaries. When the doctor determines the true cause, he selects the appropriate therapy. Most often, gynecologists restore a woman’s health in the following ways:
- return of hormonal levels to normal;
- improvement or restoration of metabolism;
- restoration of the menstrual cycle;
- restoration of reproductive function.
For treatment to be effective, the patient will be advised to lead a healthy lifestyle. In addition, you should stick to a diet: low-calorie and healthy foods will help improve metabolism and reduce excess weight. But you need to take into account an important point: you cannot bring the body to stress, the transition to dietary nutrition should be slow. It is recommended to talk with your doctor about choosing a diet.
If necessary, your doctor may prescribe hormonal medications to balance female and male hormones.
If treatment with diets and medications is useless, the primary cause of the disease has been identified and eliminated, and the ovaries are still enlarged, then the doctor may suggest contacting a surgeon. Using laparoscopy, the surgeon will restore the ovarian tissue, after which the organ will return to normal.
The answers given above were why the ovaries enlarge. There may actually be many reasons. A competent gynecologist, after a thorough examination, based on the results of tests and ultrasound, can refer you to other specialists for advice. Until the cause is determined, ovarian shrinkage is unlikely. Exceptions may include stress and lifestyle changes. In case of serious pathologies, the doctor will explain what to do and how to treat. In addition, it is recommended to do a control ultrasound every year or more often (at the insistence of the attending physician).
https://youtu.be/v808UoEauJc
Often, an ultrasound examination reveals an enlarged ovary in women. The reasons for such changes are both pathological and physiological. Only after identifying the factor that provoked the change in the size of the organ will it be possible to take measures aimed at eliminating the problem.
Diagnosis of pathology
As a rule, for correct diagnosis, a specialist prescribes an ultrasound at the beginning and middle of the cycle. It is generally accepted that the ovary is enlarged when a woman has more than 12 follicles, which are of different sizes.
In addition, you need to pass the following tests:
- for testosterone;
- thyrotropin;
- luteinizing;
- insulin;
- follicle-stimulating hormone;
- cortisol;
- thyroxine.
Before making a correct diagnosis, it is necessary to exclude pathologies such as:
- increased cortisol levels;
- decreased thyroid function;
- excess of the hormone prolactin;
- increased amount of testosterone.
About pathology
The standard dimensions of the ovary for a woman of childbearing age are (according to ultrasound): length up to 3.5 centimeters, width up to 2.5 centimeters, thickness up to 15 millimeters.
During an internal examination, the gynecologist should not palpate the ovary.
An enlarged ovary is considered to be an excess of more than 10% of the normal size or an ovary detected during vaginal examination.
This can be typical for both the left and right organs; the reasons for the increase are also the same.
Enlargement is possible at any age. In 40% of women, after undergoing an examination by a gynecologist and performing an ultrasound examination, it is discovered that one ovary is larger than the other.
Treatment of enlarged ovaries in women: methods
Treatment of enlarged ovaries must be mandatory, since delaying this process can lead to serious consequences.
The goal of therapy is:
- stabilize hormonal levels;
- resume regular cycle;
- restore and improve the reproductive functions of the body;
- protect yourself from serious disturbances in the metabolic process.
If a woman has such a pathology on ultrasound, treatment is carried out in stages:
- You need to adhere to a strict diet. Many doctors are confident that you can bring your hormonal levels back to normal simply by losing extra pounds. It is very important that weight loss be gradual and gradual, otherwise it can only cause harm. You need to adjust your diet, enrich it with healthy and fortified foods.
- Hormonal therapy. This treatment helps create the right balance between hormones.
- Surgical intervention. Used as a last resort if medications do not help. Quite a large number of women do not notice the development of pathology, and lead its development to a serious condition. In such a situation, an operation is urgently needed. One of the safest methods of ovarian surgery is laparoscopy. There is a great possibility of rapid recovery of the organ. The operation is safe and harmless.
Traditional treatment of pathology in women
Each woman must clearly understand that she will not be able to cure the disease on her own. If the disease is allowed to progress to a severe state, the consequences may be irreversible. For example, if an increase is a sign of amenorrhea, then with the help of infusions and herbal decoctions you can restore hormonal levels. Amenorrhea should only be treated under close medical supervision.
If your ovaries are enlarged and this is a sign of polycystic ovaries, you need to pay attention to yoga. This is the most gentle method for improving the functioning of the pelvic organs. Remember that yoga is only an additional therapy; the main treatment is prescribed by a specialist.
Effective folk methods are considered to be:
- use of medicinal tampons;
- the use of healing compresses;
- taking infusions, decoctions, herbal teas, as well as herbal remedies.
Representatives of the fair sex should remember preventive measures and know the reasons why the ovary is enlarged, which can become a catalyst. You need to visit a gynecologist or endocrinologist every six months, monitor your weight, eat right, exercise, listen to your body, it will always tell you if something is wrong.
A serious symptom indicating the presence of gynecological diseases is an enlarged ovary in women, the causes of which may vary, but it will definitely bring discomfort to the woman. Moreover, it can occur both in women of childbearing age and those who are in menopause.
According to doctors, the right ovary is most often enlarged.
Why is this happening? The answer to this question lies in the fact that the appendix is on the right side. Inflammatory processes in it can also provoke an enlargement of the ovary.
What are the other reasons that cause this phenomenon? They may be as follows:
- Inflammatory diseases of the female reproductive system. This can be inflammation of the uterus, tubes, including inflammation of the ovary itself, which is called oophoritis. Sometimes these diseases are practically asymptomatic. Their cause can be hypothermia, as well as STDs.
- Erosion. Such a pathology of the cervix, even a small one, can cause an enlargement of this organ. Any violation of the integrity of the epithelium can lead to inflammatory processes and enlargement of the ovaries.
- Cyst. Most often women of childbearing age encounter it. Cysts form regularly, but their size does not exceed 3 cm. If the cyst is larger, then it can cause the organ to enlarge.
- Polycystic. A condition in which numerous cysts form. The reason is a hormone imbalance.
- Oncological diseases of the pelvic organs. A symptom such as enlarged ovaries can also indicate a serious illness. That is why you should be very careful about your women's health.
- Ovulation. A slight enlargement of the ovary in women, caused by the release of an egg, can be observed on certain days of the cycle. However, this is normal and should not be a cause for concern.
This condition may be asymptomatic. It depends on the reason that caused it. However, most often the increase is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- nagging pain in the right or left side;
- temperature increase;
- weakness;
- headache.
Physiological reasons
If the ovaries are enlarged, treatment is not always required. Sometimes the organ becomes enlarged due to physiological reasons, which can be either temporary or permanent. It is important to differentiate physiological enlargement from pathological enlargement.
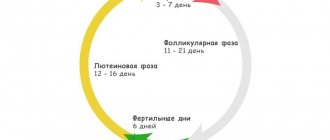
Ovulation
The release of a mature egg from the ovary occurs in the middle of the cycle in women in their reproductive period. A follicle matures inside the ovary, which becomes dominant over time. The maturation and development of the egg inside the follicle leads to a temporary enlargement of the ovary.
Hormonal drugs
In gynecological practice, specialists often have to prescribe hormonal drugs to treat various endocrine disorders. The effect of these hormonal drugs on the body and the female reproductive system can lead to ovarian enlargement, which is sometimes bilateral.
Puberty
An enlarged ovary can be detected in teenage girls. As a rule, this phenomenon is noted during the formation of menstrual function. To exclude pathology, it is necessary to perform ultrasound diagnostics and take a blood test for the content of sex hormones. In some cases, conservative therapy may be required.
Reproductive period
Typically, enlargement of the appendages is detected in representatives of the reproductive cycle. This is also due to the fact that women of childbearing age undergo regular preventive examinations to identify various pathologies.
Normally, a change in the size of the ovary is observed in the middle of the cycle and is associated with ovulation. Experts note that the right ovary is usually larger in volume than the left, which is confirmed during ultrasound diagnostics.
Depression, stress
The general level of psycho-emotional state affects not only a woman’s well-being. With chronic stress, hormonal function is distorted, which can lead to an enlargement of the paired organ and disruption of its functioning.
Climax
Menopausal changes are a natural stage, which are manifested by a decrease in hormonal activity of the ovaries. As a rule, this process begins at 45 years of age. Early or late onset of menopause may indicate the presence of pathologies, for example, of an endocrine nature.
Menopause is a long period that lasts for many years. The peculiarities of the duration of the menopausal period allow the body to adapt to a decrease in the production of sex hormones, which reduces the risk of developing various unpleasant symptoms.
In the first months, a temporary enlargement of the appendage is possible due to hormonal dysfunction, which should be differentiated from inflammatory processes and benign formations.
What to do?
If you have any symptoms - pain, atypical discharge from the genitals - you should definitely see a doctor. In this case, this is also necessary.
In order to accurately determine the cause of this condition, the woman will be referred for an ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs. This method is very informative and will give an accurate answer to the question of why exactly this phenomenon occurred. In addition, a vaginal smear will be required to exclude the presence of sexually transmitted diseases.
After identifying the cause, the doctor prescribes treatment, which will be aimed at curing the disease that caused such a symptom. As a rule, such treatment takes place on an outpatient basis, and only in rare cases is the patient hospitalized.
Often, as a complement to drug treatment, doctors prescribe physiotherapeutic procedures that have a beneficial effect on the condition of the entire reproductive system. Such treatment is strictly prohibited only for oncology.
You should not self-medicate in such situations. All kinds of douching and compresses can only do harm. After all, the most important thing is to find out the reason for this phenomenon. Naturally, all medications and treatment methods are prescribed by a doctor.
Ovaries during menopause
In women during menopause, the size of the ovaries should normally decrease.
This happens because the production of hormones sharply decreases. The hormone-producing tissue of these organs is replaced by connective tissue. Normally, the size of the ovaries in menopause is 4.5 cm3 by the end of the first year, 2.5 cm3 after five years, and 1.5 cm3 after ten years.
There is no such thing as a functional cyst for menopausal women, so any formation in the ovaries is regarded as a tumor. Due to the high risk of malignant neoplasms in women experiencing menopause, experts recommend regular ultrasound examinations. Moreover, it is best to use a transvaginal sensor, which provides a clearer picture of the condition of the female organs.
At this age, they may not manifest themselves for a long time, and an enlarged ovary will be the only symptom. It is for this reason that gynecologists recommend that women in menopause undergo such an examination at least once a year. This will to some extent protect them from cancer.
In any case, an increase in these female organs is a dangerous symptom. Therefore, you should not delay visiting a doctor and getting diagnosed. After all, any disease, even the most severe, can be treated if it is detected at an early stage.
Health to you, dear women!
After a routine ultrasound, a woman may be diagnosed with enlarged ovaries. What caused the pathology? The ovaries become enlarged due to various disorders and diseases. Multifollicular ovaries are quite often observed; in this case, a large number of follicles are formed. They are sacs containing a mature egg. How dangerous is ovarian enlargement?
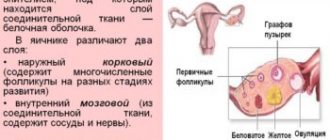
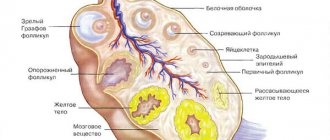
What are follicles?
Every woman’s body has many unique features, one of which is the functioning of the reproductive system.
Even in the womb, girls develop approximately 500 thousand follicles (a structural component of the ovaries), and only 40 thousand remain by the time she reaches puberty.
But not every one of them matures and releases an egg at the time of ovulation. During a woman’s life, only thousands of follicles fully mature, while the rest fade away in development.
This process is very complex from a biological point of view and is influenced by many factors. It begins in the first phase of menstruation and is controlled by a number of hormones.
An average of 19 follicles mature at the same time, but only one remains, called the dominant one. During ovulation, he will release an egg.
The main function of the follicles of both ovaries is to protect the immature eggs inside from various harmful influences.
It is located under a reliable layer of epithelium and a double layer of connective tissue. Fertilization and the entire pregnancy period depend on the follicles and their abilities. They also participate in the production of hormones - estrogens.
How long can it ripen?
In some cases, two follicles may mature and develop in each ovary. But they both have to be dominant and ovulate at the same time, which rarely happens. This is considered normal, as the chance of early conception increases, and the birth of twins is possible.
Women's diseases and ovarian enlargement
Inflammation of internal organs
Inflammatory process of the pelvic organs becomes a common cause of an enlarged ovary. The infection may not manifest itself for a long time, then the disease becomes chronic and the ovaries enlarge significantly. Attention! In this case, the organ enlarges not because the ovary is growing, but because a large amount of infiltration and adhesions appears. If measures are not taken in a timely manner, the gynecologist cannot palpate the uterus and ovary separately. Everything can be felt as one organ.
Cervical erosion
Pathology can injure a small part of the cervix, as a result of which painful microflora joins and inflammation develops, which negatively affects the functioning of the ovaries. Subsequently, the gynecologist observes an enlargement of the right or left ovary.
Ovarian cyst
Female reproductive organs in the presence of cysts can be enlarged by more than 3 cm. You can only find out about the slight enlargement that occurs with a cyst by ultrasound.
Cancer
The ovaries enlarge significantly if a woman has a malignant tumor. Take this into account! A gynecologist can feel an increase in cancer only at the last stage of cancer. Sometimes the cause of changes in the ovary are metastases of other internal organs.
Pathological causes
Not in all cases, the enlargement of the female reproductive glands is physiological. This can be a manifestation of various diseases from appendicitis to malignant tumors.
Inflammatory diseases
Inflammation of the ovary is called oophoritis, and inflammation of the appendages is called adnexitis . Diseases can be caused by both nonspecific (streptococcus, E. coli) and specific (chlamydia, trichomonas) microorganisms. Inflammation is accompanied by an increase in general and rectal temperature, chills, pain in the lower abdomen, and deterioration in health.
Enlargement of the appendages is due to the fact that during inflammation, blood flow to the organ increases and vascular permeability increases. Swelling of the organ develops, which is manifested by an increase in its size. The consequence of the disease can be the formation of adhesions in the pelvis, which are very difficult to treat.
Polycystic
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) occurs in approximately 20% of women . Polycystic disease manifests itself:
- an increase in the size of the ovaries;
- menstrual cycle disorders (shortening or lengthening);
- chronic anovulation (in almost all cycles the egg does not mature);
- infertility due to anovulation;
- manifestations of androgen excess.
An increase in the size of the gonads occurs due to the formation of cystic cavities.
Reference. With PCOS, the content of male sex hormones (androgens) in a woman’s body is increased.
Endocrine diseases
Most often, the ovaries are affected by pathology of the thyroid gland. Insufficient or excessive production of thyroid hormones can lead to an increase in the size of the ovary. Other endocrine disorders also lead to hormonal imbalance in a woman’s body and affect the size of the gonads.
Neoplasms
New growths may appear in the female reproductive glands. They are both benign and malignant. These can be various cystic formations, nodes, tumors. The size of the ovaries with a neoplasm may be slightly increased or gigantic.
The neoplasm can appear at any age, including in children. There are congenital tumors (teratomas) that increase in size as the patient ages.
Cervical erosions
Erosions, as a rule, appear in mature women, often after termination of pregnancy (abortion) or after childbirth.
They are localized on the mucous membrane of the cervix.
They represent defects of the mucous membrane, i.e. are open wounds.
When microorganisms come into contact with erosion, local inflammation develops. Under certain circumstances (decreased immunity), inflammation can spread to the ovaries. The increase in size due to inflammatory diseases was described earlier.
Appendicitis
In rare cases, the appendix may be located in an atypical location, more precisely, in the pelvis. When an inflammatory process develops in the appendix, it increases in size due to swelling. An inflamed appendix can push the ovary upward, so during the examination the gynecologist can feel it. With acute appendicitis, the lower abdomen hurts and the body temperature rises.
Ovarian pregnancy
Pregnancies developing in the ovary are extremely rare (less than 1% of all ectopic pregnancies).
Reference. Normally, the egg meets the sperm and fertilization occurs in the lumen of the fallopian tube. Then the fertilized egg enters the uterine cavity, where it attaches to the wall - pregnancy develops.
Ovarian pregnancy develops if fertilization for some reason occurs directly in the gland itself. The causes of this pathology may be:
- adhesions in the pelvis after inflammatory diseases, operations, injuries;
- congenital anomalies of the uterus and fallopian tubes;
- endometriosis;
- underdevelopment of the ovary;
- endocrine disorders.
Pregnancy outside the uterus, like intrauterine pregnancy, can be suspected by a delay in menstruation and a positive pregnancy test result. However, unlike a normal pregnancy, an ectopic pregnancy is life-threatening for a woman.
Diagnosis of enlarged ovaries
To confirm the diagnosis, the gynecologist prescribes an ultrasound in the middle and beginning of the menstrual cycle. An ovary is considered to be enlarged when a woman has more than 12 follicles of varying sizes.
Additionally, a woman must be tested for:
- Testosterone.
- Luteinizing hormone.
- Follicle stimulating hormone.
- Cortisol.
- Insulin.
- Thyroxine.
- Thyrotropin.
When making a diagnosis, the following serious hormonal pathologies must be excluded:
- Kushink's syndrome (with high amounts of cortisol).
- Hyperprolactinemia (excess prolactin).
- Androgenital syndrome (increased amount of testosterone).
- (reduced thyroid function).
Methods for treating enlarged ovaries in women
Purpose of the course of therapy
:
- Normalize hormonal levels.
- Restore the menstrual cycle.
- Improve or restore reproductive function.
- Protect against serious metabolic disorders.
If a woman still has an enlarged ovary on ultrasound, treatment is carried out in several stages:
- Follow a low-calorie diet
. Many gynecologists believe that it is possible to normalize hormone levels if you get rid of excess weight in a timely manner. It is important that weight loss be gradual, so that the body does not experience stress. Nutrition should be healthy and balanced. - A course of hormone treatment
makes it possible to adjust the levels of male and female hormones. - Surgery
is only necessary if medications are ineffective. A lot of women do not pay attention to the pathology of the ovaries in a timely manner and bring them to a serious condition. In this case, urgent surgery is necessary. One of the modern treatment methods is laparoscopy. With its help, a thick layer of the capsule in the ovary is removed, which caused its enlargement. During the operation, not one large incision is made, but several invisible ones, after which a thin needle and laparoscope are inserted. After filling the abdominal cavity with gas, the doctor can clearly see the condition of the internal organs. Laparoscopy makes it possible to quickly restore the ovaries.
Traditional methods of treating enlarged ovaries
A woman must understand that it is impossible to get rid of the pathology on her own at home. Quite often, when the process is neglected, everything can end in serious complications. For example, if enlarged ovaries are one of the symptoms of amenorrhea, you will not be able to restore hormone levels with the help of decoctions and infusions. Amenorrhea can only be treated under medical supervision.
If enlarged ovaries are a symptom, you need to turn your attention to yoga. This is a safe way to improve the condition of the pelvic organs. Important! Yoga is an additional treatment method; the main course of therapy is prescribed by a doctor.
Effective folk methods of treatment for ovarian enlargement are the following:
- Use of vaginal tampons.
- Use of compresses.
- Taking herbal tinctures and tablets.
Thus, if an ultrasound shows enlarged ovaries, urgent measures must be taken to prevent serious pathological processes. For preventive purposes, it is necessary to be observed by an endocrinologist or gynecologist, and also to closely monitor your weight, eat well, exercise, and promptly pay attention to various symptoms. Remember that the ovaries are reproductive organs; they are responsible for fertilization.
Ovulation time
During the period of maturation and release of the egg, the size of the ovary may be higher than normal. It is no coincidence that one of the indications for performing a gynecological ultrasound is determining the timing of ovulation. In most cases, transvaginal and transabdominal examination of the uterus and appendages is used. Less commonly, a rectal examination is performed.
The physiological process (increase in ovarian size) during the period of ovulation should not cause alarm.
If after menstruation the size of an important organ has not returned to optimal values, then additional examination will be needed to determine the causes of the deviation.
If a tumor process, cystic formation or inflammation is detected, treatment is required: antibacterial, anti-inflammatory compounds, physiotherapy, surgery.
If negative symptoms appear that indicate problems with the female genital area, you need to visit a gynecologist.
Ovarian cysts are treated in a variety of ways, from medication to surgery. Cyst on the ovary - treatment or surgery? We'll tell you in detail.
Is it possible to detect an ovarian cyst on your own? About this in this topic.
Perhaps pain, uncharacteristic discharge, discomfort in the abdominal area, deterioration in health indicate an enlarged ovary, the development of a pathological process.
It is necessary to find out the cause of negative symptoms, conduct diagnostics and complex therapy. It is important to stabilize your weight at an optimal level: extra pounds are a sign of problems with metabolism, against the background of which many “women’s” diseases often develop.