Prolapse of the genital organs is a diagnosis that almost all women fear, and the result that many who do not take care of their health come to. There are many reasons for the development of this condition - from hereditary properties of connective tissue and injuries during childbirth, to obesity and hormonal deficiency.
In the early stages, the symptoms are difficult to notice on your own, but even in the absence of signs of the disease, all women should engage in its prevention. Why does uterine prolapse occur after childbirth, how to detect it and what to do about it?
Read in this article
What is pathology
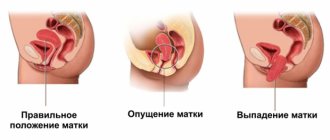
Prolapse of the genital organs is a change in the relative location of the uterus, appendages, vaginal walls, pelvic floor muscles and nearby structures - the bladder, rectum, etc.
Normally, the uterus is held almost in the center of the pelvic cavity with the help of ligaments and a frame. The latter consists of the muscles of the perineum. The ligaments support the uterus both above and in the middle, and also fix it in a certain relationship to the bladder and rectum. That is why, when the position is disturbed, various disorders of urination, defecation, etc. occur.
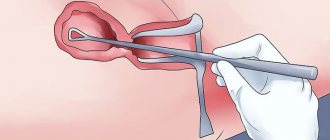
Most often, the uterus descends, “prolapses” through the pelvic cavity, i.e. The level of the cervix gradually becomes lower, followed by the body of the organ itself. As a result, you can even palpate the parts yourself without inserting your fingers into the vagina. At the final stage, the uterus falls out completely and almost constantly outside the genital slit, between the inner surfaces of the thighs, and a “sac” is determined. Its surface is the walls of the vagina, and inside is the uterus, often along with the appendages.
Causes of pathology
There are many reasons for the occurrence and progression of genital prolapse. Most often, the first signs appear in women after 35 - 40 years.
Features of connective tissue in women
Some girls do not suspect that they have genetically inherited a special type of connective tissue, which is more susceptible to sprains and injuries and recovers less well. In most cases, in parallel, they have long fingers and toes, thin wrists, flat feet, frequent problems with the spine (especially with age), scoliosis, they have good stretching, and some other signs.
It is in these women that the ligamentous apparatus is more often subject to excessive stretching under even minor loads, and the progression of prolapse is faster.
Childbirth
Natural childbirth does not always go smoothly and without consequences for the woman, including long-term ones. It happens that the process is complicated by a rupture or even a slight injury to the ligamentous apparatus of the uterus. Immediately after childbirth, this condition may not manifest itself in any way, and subsequently insolvency develops. Then the uterus, under the influence of gravity and in the absence of proper tone of the perineal muscles, gradually descends.
Deep vaginal lacerations are dangerous. Episiotomy, which is often performed during childbirth, on the contrary, prevents excessive stretching of the tissue and, if the parts of the incision are correctly aligned, it prevents prolapse in the future. But it happens that even dissection of the perineal muscles does not save the woman from other ruptures.
Also dangerous is the independent violation of the integrity of the muscles that lift the ani. This complication is rare if childbirth assistance is provided correctly, but it does happen sometimes. Subsequently, the genital fissure may not completely close, incontinence of feces and gases occurs, and formation occurs. These conditions require surgical treatment, as they bring discomfort and many problems to the woman.
In the following cases, prolapse of the cervix after childbirth, body and vaginal prolapse are most likely:
- At the birth of a large baby. Often this is a repeat birth.
- If a woman does not follow the midwife’s recommendations during pushing, this provokes genital ruptures.
- When using obstetric forceps, vacuum extraction of the fetus.
- During prolonged labor.
- If childbirth is complicated by acute hypoxia, bleeding and other situations.
It should be noted that competent actions of medical personnel and strict adherence to all recommendations will help to avoid complications in the future, even with serious ruptures. And then the woman is no longer at risk of uterine prolapse after childbirth.
Caesarean section does not protect against subsequent genital prolapse. But the probability is reduced by an order of magnitude.
Physical work
Types of genital displacement
There are several degrees and types of prolapse of the genital organs in women. If the displacement concerns the vaginal walls to a greater extent, then the following classification is used:
- 1st degree.
In this case, the drooping is noticeable only when straining. In a calm state, the walls of the vagina are not visible from the genital slit. - 2nd degree.
Even without tension, mucous membranes protruding outward can be detected. In this case, the anterior wall of the vagina pulls the bladder along with it due to its anatomical location - a vesicocele is formed. This leads to various urinary disorders. And the posterior wall pulls the rectum along with it, forming a rectocele. - Grade 3
is always combined with uterine prolapse.
If, in addition to prolapse of the vagina, displacement of other parts occurs, then the classification is as follows:
- 1st degree, in which the cervix remains in the vagina even with tension. But at the same time, its lengthening and lowering relative to the positioned axis is noted.
- 2nd degree, when the cervix comes out of the genital slit only with straining. In a calm state, it is located at the level of the entrance to the vagina.
- 3rd degree, in which the cervix and part of the body are identified outside the genital opening, even in normal conditions.
- Grade 4 is characterized by complete loss. In this case, the body of the uterus is completely outside the vagina.
Is it necessary to treat (consequences of changes)
The earlier pathology and changes are detected, the easier it is to combat them, and the more effective any kind of treatment will be. As a rule, in the initial stages, exercises for prolapse of the uterus after childbirth give noticeable results.
What can happen if you ignore the problem? The main consequences of the disease:
- The risk of infectious complications in the cervix, cavity and appendages increases.
- Discomfort and pain during sexual intercourse, and with complete loss, intimate relationships are almost impossible.
- During prolapse, the walls of the vagina are constantly exposed to unusual effects for them, which causes maceration, etc. Ultimately, in advanced forms, this can lead to decubital ulcer cancer.
- Urinary incontinence even with the slightest exertion. And when stagnation prevails, inflammatory diseases of the entire urinary system can recur.
- Constant constipation and even the formation of fecal stones in the rectum, which will lead to hemorrhoids, anal fissures, proctitis, etc.
It becomes clear that genital prolapse should not be left unattended. But only a doctor, after examination and some research, can determine the most effective treatment and preventive measures in a particular situation.
Method of therapy
If uterine prolapse occurs after childbirth, treatment should begin with preventive measures after 6 to 8 weeks. For genital prolapse, conservative therapy, surgery, and also traditional and non-traditional methods can be used.
Conservative methods
These methods are of little use for women of reproductive age. They are more suitable for those who are not sexually active.
There are a large number of gynecological rings of different sizes, shapes, materials, etc.
There are special ones for urinary incontinence or rectocele, etc. The essence of their action is that they are placed in the vagina and create a mechanical obstacle to prolapse.
It is advisable to choose such products with a doctor. Only he can determine the required size and recommend the type of ring.
The disadvantage of these products is that they, like any foreign body, cause constant inflammation in the vagina with discharge, even if all recommendations for use are followed.
Surgery
There are many options for surgical interventions used for prolapse.
It all depends on age, the degree of prolapse and changes in the cervix and body of the uterus, the number of births in history and some other aspects. The main ones are the following:
- Standard colporrhaphy is suturing the vaginal walls. Often, surgery to shorten the cervix is also performed.
- Hysteropexy is an operation whose purpose is to fix the uterus in the pelvis, for example, to stitch it to the anterior abdominal wall. This operation is used least often due to the ambiguity of treatment results. More suitable for those who are planning pregnancy and childbirth in the future.
- The most popular are various modifications of TVT operations. Their essence is that in addition to suturing the vaginal walls, allografts are installed - “mesh”, which prevent the prolapse of the anterior and posterior walls of the vagina. Problems with urination and defecation are also eliminated.
- There are also techniques for stitching the front and back walls tightly. But sex life is impossible.
Traditional methods
Treatment with traditional medicine will definitely not help to cure completely, but they can relieve pain, reduce the likelihood of inflammatory phenomena and increase local immunity, and they can stop the progression. Popular recipes in cases where the uterus prolapses after childbirth:
- It is necessary to prepare a decoction of oak bark and douching. The course is at least 15 - 20 days. To do this, take 100 g of oak bark and pour 2 - 2.5 liters of water, then simmer over low heat for about an hour. You can store the solution in the refrigerator.
- It is useful to take lemon balm internally. To do this, you need to prepare a solution: 2 - 3 tbsp. l. herbs pour 500 ml of hot water and leave for 12 hours. You should take 100 - 150 ml 2 - 3 times a day.
- Everyone knows the beneficial properties of elecampane. He can help here too. To do this, grate about 2 tbsp of dry root. l. and fill with alcohol or vodka. Let it brew for about a week, and then take 2 - 3 tbsp. l. Once a day in courses of 20-30 days.
Is it possible to somehow prevent the prolapse of the uterine wall after childbirth? Of course, but you should start not when all the signs of the disease are obvious, but throughout your entire life. Strengthening the pelvic floor muscles is useful not only for the prevention of prolapse, but also thanks to the exercises, the sensations for the woman and partner during intimate relationships improve.
- You should monitor your weight and physical fitness. Regular exercise, for example, yoga or dancing, is already a good prevention of this kind of disease. It is also important that the abdominal muscles are in good condition, since intra-abdominal pressure largely depends on this.
- It is better to follow all the recommendations of doctors after childbirth, carefully monitor the condition of the stitches (if any). It is useful to attend courses during pregnancy to prepare for the birth of a baby, where they will teach you how to breathe correctly and behave during different periods. This will help prevent injury as much as possible.
- You should not engage in heavy physical labor, even if the girl is healthy. In the post-war years, every second woman had signs of complete or partial prolapsus, as they had to do all the men's work.
- Kegel exercises are one of the most effective exercises for strengthening the pelvic floor muscles. Today there are many modifications of them - with loads, “elevator” and others. They are not difficult to perform, and the results are not long in coming.
Genital organ prolapse is a common pathology. There is both a genetic feature of the structure of the connective tissue for this disease, and provoking moments for the development and progression of the disease are located everywhere.
Often you have to deal with prolapse as a long-term consequence after childbirth. Timely and proper prevention of pathology, compliance with all doctor’s recommendations will help avoid the disease if possible.
It is not uncommon for labor to cause minor disturbances in a woman’s body. Most often, cervical prolapse occurs after childbirth. How to recover after the birth of a child? Usually the cervix recovers within the first month after birth. However, you should carefully monitor yourself so as not to miss the prolapse of the uterine walls or the descent of the pelvic bones.
Prolapse of the cervix after childbirth: the essence of the problem
Childbirth is a big test for the female body. Despite the fact that a woman’s body miraculously copes with a huge load during childbirth, you need to be very careful about yourself after this event. One of the most pressing threats is the prolapse of the cervix after childbirth and the development of muscle weakening to a critical level. As a result of ignoring the issue, you can lead your body to uterine prolapse, and even to the possibility of losing the uterus in principle.
Prolapse of the cervix after childbirth: how to recover?
What needs to be done before, during and after childbirth to prevent the process of displacement of the normal position of the uterus.
If a woman has already encountered the problem of cervical prolapse and/or is giving birth to a second child, then she needs to carefully prepare for pregnancy. Strengthening exercises, Kegel techniques, cycling or running will prepare the body for childbirth and give the muscles the necessary training.
During pregnancy, you need to carefully monitor the condition of the cervix and its location. Scheduled ultrasounds and consultations with a doctor will help with this. Sometimes, women with the problem of uterine prolapse are placed in preservation in order to protect the fetus and the health of the mother in labor.
If during pregnancy a problem with the cervix begins to develop, then the woman lies in bed for almost the entire period. This causes less harm to the mother’s body and helps keep the baby healthy. The consequences of such a pregnancy are always complex. Recovery takes a long time.
After childbirth, rehabilitation should not be ignored. Even if the woman in labor has not had any problems with the uterus before, and the birth was easy, the muscles should be protected. Muscle training will allow you to quickly get back into shape and make it easier to endure the already difficult period of the first year for your baby.
It is possible to stop cervical prolapse after childbirth, the main thing is to pay yourself a little attention.
Prolapse of the cervix after childbirth: how to recover at home?
Fortunately, modern medicine offers women in labor a lot of variations on the theme of restoring the elasticity and strength of the ligaments that hold the uterus.
To begin with, a simple Kegel method will help you recover from cervical prolapse. It does not require any additional equipment, mats, flat surfaces and other nonsense, the absence of which often stops the desire to play sports. Just three exercises will help in a sitting position, restore elasticity to the muscles, and restore the natural position of the uterus.
It is also worth using classical gymnastics when the cervix prolapses after childbirth. One of the best exercises is walking up the stairs. If you are familiar with sports, then a month after giving birth, you can go jogging. Running with high knees is especially good.
Oriental dancing has an excellent effect on strengthening the pelvic muscles and the condition of the cervix. Skeptics can say whatever they want, but at the heart of this dance style is the wise training of the female body to give birth to a large number of children.
In addition, when the cervix prolapses after childbirth, you can use special simulators. They help quickly restore muscle tone and allow you to “feel” the muscles that you actually need to train.
It is imperative that during prolapse, you should carefully monitor your diet, although for a woman in labor this is a resolved issue. Vitamins and microelements must be supplied in double doses so that there is enough for both you and the child you will feed.
The main thing that will help you notice uterine prolapse after childbirth is diagnosing your own condition. If you continue to feel heaviness in the lower abdomen, experience nagging pain in the vagina, and pain in the lower back, then you should undergo an examination and find out about the current state of your body.
In a full-term pregnancy, the weight of the uterus at birth reaches 1 kg. Immediately after the end of the third stage of labor - after the birth of the placenta, the uterus significantly decreases in size due to a sharp reduction in its muscles and atrophy of muscle fibers.
The woman herself may not know about the expansion of the uterine cavity for a very long time, because the uterus is an organ that is located in the pelvic cavity and it is almost impossible to palpate it. As a rule, most often the uterine cavity expands during pregnancy, but we will talk about this a little later, but for now let’s look at other causes of this pathology. However, it is worth knowing that with age this organ changes its size, and this must be taken into account during the study.
The uterine cavity is dilated - reasons
The most common cause of dilation of the uterine cavity is fibroids. The fibroid itself is a benign tumor that very rarely turns into cancer. Fibroids can grow in several places, such as outside the uterus, inside the uterus, or in the wall of the uterus. At the same time, it is worth knowing that fibroids grow very quickly, which means that the uterine cavity will grow just as quickly.
The second reason is uterine cancer. Cancerous tumors, as a rule, grow in women during menopause, so at the first symptoms - bleeding from the vagina and pain during intercourse - you should immediately consult a doctor.
An ovarian cyst is also a common cause of an increase in the size of the uterine cavity. This also includes ectopic pregnancy and a disease such as adenomyosis.
The uterine cavity is dilated during pregnancy
During pregnancy, the uterine cavity begins to expand from the very first day the fertilized egg enters the uterus itself. In this case, all increases should not be more or less than the norm. If the uterus grows too rapidly during pregnancy, then a condition such as polyhydramnios can be suspected, and if the size of the uterus does not correspond to pregnancy and is less than normal, then the woman most likely has oligohydramnios.
The uterine cavity can be greatly dilated during pregnancy with twins or triplets. Ultrasound helps determine this. This is the only way to understand whether a pregnant woman has any pathologies during pregnancy.
The uterine cavity is dilated after childbirth
After childbirth, the uterine cavity remains dilated for some time. In order for it to return to its previous size, at least 6 months must pass. If there are no blood clots or placenta remains in the uterus, which can be determined using an ultrasound, then the uterine cavity itself will shrink without difficulty. But if after childbirth some tissue remains in the uterus, then an inflammatory process may begin, which will have to be treated with antibiotics and curettage of the cavity in order to remove foreign tissue.
Contraction of the uterus after childbirth
Over the next 6-8 weeks, the size of the uterus decreases, its weight decreases and returns to its prenatal size - 60-70 grams. By the end of the first week of the postpartum period, the uterus weighs 500-600 g, by the 10th day after birth the weight of the uterus is 300-400 g, by the end of the third week the weight of the uterus decreases to 200 g.
The process of involution (reverse development) of the uterus is individual for each woman and depends on factors such as the degree of distension of the uterus during pregnancy with polyhydramnios, multiple pregnancies, and large fetal weight during pregnancy. Correct involution of the uterus is facilitated by timely emptying of the bladder and intestines. But the best way for good contraction and restoration of the uterus is breastfeeding the newborn from the first hours after birth, since when the nipples are stimulated, the hormone oxytocin is released, which causes contraction of the myometrium.
Restoration of the uterus is accompanied by the formation and release of lochia.
Why doesn't the uterus contract after childbirth?
There are many reasons why the uterus may temporarily stop contracting. The most common of them are:
- Two or more fruits;
- Features of a woman’s body;
- fetal weight and size are larger than average;
- Complications during pregnancy or the postpartum period.
When there is an inflection in the uterus or it is not fully developed, then there may be no contractions at all.
A similar situation can arise with polyhydramnios, injuries of the birth canal or uterine appendages. What to do?
As soon as the baby is born, ice must be applied to the woman's stomach. This will help stop the bleeding and provoke the uterus to contract. Over the next few days, mom will be under medical supervision. And she will be able to go home only after the gynecologist is convinced that the uterus is contracting quite normally.
If problems are noticed with this, the doctor should prescribe medications that will help contract the muscles of the uterus. But the best way to make the uterus contract is breastfeeding. Movement and lying on your stomach are also helpful.
Don't forget about personal hygiene. You need to go to the toilet as often as possible so that your bladder is not full. This will also affect how the uterus contracts. And another very important point is that the uterus will contract better in those women who did physical activity from time to time during pregnancy. Therefore, during pregnancy you should at least think about walking in the fresh air.
Dimensions of the uterus after childbirth
The degree of contraction of the uterus can be judged by the level of its fundus. The height of the uterine fundus after childbirth decreases by 1-2 cm per day.
Immediately after birth, the size of the uterus corresponds to 20 weeks of pregnancy: the fundus can be felt 1-2 transverse fingers (about 4 cm) below the navel.
After a few hours, the tone of the pelvic floor and vaginal muscles is restored and the uterus moves upward. Therefore, by the end of the first day after birth, the fundus of the uterus is at the level of the navel.
On the 2nd day, the fundus of the uterus is 12-15 cm above the pubic junction; on the 6th day – 9-10 cm above the pubic joint; on the 10th day - 5-6 cm above or at the level of the pubic joint. One and a half to two months (6-8 weeks) after birth, the size of the uterus corresponds to normal.
Subinvolution is manifested by a decrease in the rate of decrease in the height of the uterine fundus above the womb, and more abundant and bright lochia. A woman does not feel the usual postpartum cramping pain in the lower abdomen, even during breastfeeding.
Atony and hypotension of the uterus after childbirth
Unfortunately, not all women in labor have a contraction of their uterus after childbirth. This condition is called uterine atony (in other words, it is a direct consequence of the fatigue of its muscles), as a result of which it does not contract and uterine bleeding occurs. Atony most often occurs in multiparous women, also during the birth of a large fetus, with polyhydramnios or multiple pregnancies.
More on the topic
The uterus does not contract after childbirth
How the uterus recovers after childbirth
In what cases and how is the uterus cleansed after childbirth?
Why does uterine prolapse occur after childbirth and what could be the consequences?
Bend of the uterus after childbirth
In the case when the uterus contracts after childbirth, but very slowly, the mother in labor is diagnosed with hypotension. This is a condition in which the contractility and tone of the uterus are sharply reduced.
Both of these conditions of the uterus after childbirth are equally dangerous for the health of the mother in labor, as they can provoke massive bleeding or cause a number of other complications.
Causes of uterine contraction disorders
Violation of contractile function of the uterus and causes of postpartum hemorrhage:
| Causes | Factors |
| Overdistension of the uterus | polyhydramnios multiple births large fetus |
| “Depletion” of myometrial contractility | rapid labor prolonged labor high parity (>5 births) |
| Infection | chorioamnionitis fever during childbirth chronic viral-bacterial infection |
| Anatomical/functional features of the uterus | uterine malformations uterine fibroids placenta previa operated uterus |
| Retention of parts of the placenta | placenta defect; uterine hypotension; partial tight attachment of the placenta; partial rotation of the placenta. |
| Retention of blood clots in the uterine cavity | hypotension of the uterus hematometer |
Retention of lochia in the uterus (lochiometra)
At the beginning of the postpartum period, there may be an accumulation of secretions in the uterine cavity due to poor contraction of the uterus, bending of the uterus overstretched during pregnancy into an unphysiological position, or blockage of the cervix with a blood clot. This is usually accompanied by pain of various types in the lower abdomen.
In the future, due to the reduced tone of the uterus, the retention of lochia in its cavity and the formation of lochiometra are also possible.
To understand why the discharge has stopped, after an examination, the doctor may refer the patient for an ultrasound. In the absence of contents and blood clots in the uterine cavity, cessation of discharge is normal, although it is possible that it will resume later.
Cervix after childbirth
Restoration of the cervix occurs somewhat more slowly. Immediately after childbirth, the cervical canal allows the hand to enter the uterine cavity. 10-12 hours after birth, the internal os begins to shrink, decreasing to 5-6 cm in diameter. By the 10th day, the internal os is almost closed. The formation of the external os occurs more slowly, so the final formation of the cervix occurs by the end of the 3rd week of the postpartum period.
In nulliparous women, the external uterine pharynx has a point shape, in women who have given birth, it has the shape of a transverse slit (slit-like).
During the birth of your baby, your body experiences stress. A woman in labor does not return to normal immediately; it takes a lot of time. In this case, sexual function suffers the most.
The entire course of events that a woman goes through can be divided into prenatal (before childbirth), natal (birth) and postnatal (postpartum). Let's figure out what the cervix, uterus and the entire reproductive system as a whole look like after childbirth.
Divided into three stages:
- Contractions. They begin when contractions are observed every 15-20 minutes. After the discharge of amniotic fluid and the complete opening of the cervix, the second stage begins.
- Expulsion of the fetus. During this period, attempts are observed - contractions of the muscles of the anterior abdominal wall. Everything is aimed at the birth of the baby. After birth, the baby is placed on the stomach. There is physical contact with the mother.
- Posledovoy. The afterbirth is the placenta, or “baby place.” After the second stage, the obstetrician again suggests pushing and freeing yourself from the “baby place” - the placenta. It is carefully inspected for integrity. Not a single piece should remain inside in order to avoid complications. Blood clots should be released and normal muscle contraction should occur.
What happens to the cervix and uterus after childbirth?
Genital prolapse, as a rule, extends over time and does not happen at once. Initial changes cannot be recognized externally; this requires a gynecological examination. The difficulty of diagnosis lies in the fact that a woman, being already sick, does not feel anything. Sometimes they have pain in the lower abdomen, discomfort, but such symptoms are not given much importance and people do not go to the doctor.
The first degree of uterine prolapse is established only after examination in a gynecological chair. The doctor observes a picture in which the cervix reaches approximately the middle of the vaginal canal. This diagnosis is still considered quite favorable, since the problem can be eliminated without surgery, using special Kegel exercises, gynecological massage, pessaries, bandages, etc. can be prescribed.
Unfortunately, it is not uncommon for women to see a doctor only in this condition. Conservative treatment will be completely ineffective and will be used rather in the form of symptomatic therapy. A woman can only be cured through surgery.
The hollow organ consists of a body, which in the prenatal state is about 5 cm, and a cervix - 2.5 cm in size. When a child is born, the tissues stretch and grow along with the fetus.
Restoration (involution) of female organs after childbirth is a natural process. If the delivery was natural, the uterus recovers and shrinks within 2 months.
The postpartum period is:
- early – 2 hours after the birth of the placenta;
- late – up to 8 weeks after delivery.
Scarring on the uterus after childbirth is normal. Severe damage is located in the area where the placenta is attached. This zone contains the most thrombosed vessels.
Blood clots in the uterus after childbirth and the remains of the placenta will leave the body within three days. These secretions are called lochia.
Epithelization (regeneration of endometrial tissue) occurs 10–12 days after birth. And the scar at the placenta insertion site heals by the end of the first month.
The uterus after childbirth is a sterile organ. Over the course of 3–4 days, processes such as phagocytosis and proteolysis take place in the hollow organ. During them, bacteria located in the uterine cavity are dissolved with the help of phagocytes and proteolytic enzymes.
The first days after the birth of a child, the hollow organ is too mobile due to sprains and insufficient tone of the ligamentous apparatus. This is noticeable when the bladder or rectum is full. The tone is acquired in a month.
Contractions of the uterine cavity feel like contractions. In the first days after delivery, they do not have an aching character.
The release of the hormone oxytocin during breastfeeding causes muscle spasms. During muscle tissue contraction, blood and lymph vessels are compressed, and some dry out and become obliterated.
The tissue cells that appeared during pregnancy die and are resorbed, while the rest decrease in volume. This helps restore the uterus after childbirth.
Change in organ mass:
- after childbirth – 1 kg;
- after 7 days – 500 – 525 grams;
- after 14 days – 325 – 330 grams;
- at the end of the postpartum period – 50 – 65 grams.
To speed up contractions, immediately in the delivery room, after the birth of the placenta, ice or a cold heating pad is placed on the stomach.
Postpartum uterine parameters:
- the length of the organ is 15–20 cm;
- its transverse size is 12–13 cm;
The bottom of the hollow organ drops sharply after the birth process, not reaching the navel by 2.5 cm, and the body tightly touches the abdominal wall. The uterus has a dense structure and often shifts to the right.
Due to contractions, it drops by 1 cm every day. At the end of the first week, the bottom reaches the distance between the navel and the pubic area. Already on the 10th day the uterus is below the pubis.
The cervix recovers more slowly: 12 hours after birth, its diameter will be 5–6 cm. By the middle of the second week, the internal os closes, and the external one is formed at the end of the second month after birth.
The pharynx is not restored to its original appearance, since the tissue fibers are too stretched. Based on this sign, a gynecologist can determine whether a woman has given birth or not.
Initially, the pharynx has a round hole. After childbirth, a transverse gap remains on it. The shape of the cervix changes: if previously it looked like a cone, now it looks like a cylinder. Gradually all organs return to normal.
The speed of recovery depends on the following factors:
- hormonal background;
- woman's age;
- child parameters;
- number of previous pregnancies;
- type of labor activity;
- polyhydramnios;
- inflammation of the genital organs.
Nature has thought out the female body down to the smallest detail. Restoration of the hollow organ occurs according to the standard dimensions of 1–2 cm daily. But if minor deviations from the norm begin to be noticed, you can resort to accelerating the reduction process.
Restoring the uterus after childbirth involves the following steps:
- If the uterine fundus is soft, then the uterus will contract more slowly. An effective method is to massage the surface of the abdominal wall from the outside.
- To shrink the organ after childbirth, a cold heating pad or ice is applied to the abdomen. Medications that stimulate spasms may be used.
- Maintain genital hygiene. The penetration of infections and various complications affect the ability to contract.
- Active walking.
- The bladder and rectum should not be allowed to fill.
- Lactation. Breastfeeding releases oxytocin, which causes uterine contractions. Breastfeeding mothers restore the uterus faster.
- Postpartum exercises that stimulate contraction of the uterine muscles.
Restoration of the uterus must take place under the strict supervision of a physician. Any deviation from the norm is a pathology and requires surgical intervention.
Blood in the uterus after childbirth is formed due to wounds on the surface. The discharge is called lochia. The secretion for 3-4 days is red. At this time, lochia has a sweetish smell of blood.
They consist of 20% fluid from the uterine glands, and the rest is unchanged blood. Restoration of the uterine mucous tissue begins immediately after delivery.
Further, the lochia becomes paler, similar to ichor. After day 20, the discharge becomes light in color and has a liquid consistency. Normally, lochia comes out within 6 weeks. After this they stop.
If the discharge continues longer than the specified period or has an unpleasant odor, be sure to consult a doctor.
This may happen for the following reasons:
- bending of the cervix;
- weak contractions in the uterus;
- blockage of the pharynx with blood clots.
This condition is dangerous, as it may indicate an inflammatory process. If lochia ends in the fifth week or lasts longer than the ninth, you need to consult a gynecologist.
Process flow without deviations:
- Vessels burst in the cavity, as a result of which the bloody discharge has a bright red color for 2–3 days.
- During the first 7 days, the remains of the placenta and atrophied endometrium come out - discharge with clots.
- After 7 days, liquid lochia has a pinkish tint.
- Mucus gradually comes out - the result of the activity of the fetus inside the womb. They stop within a week.
- After a month and a half, the lochia disappears and spotting appears.
All women are interested in what the uterus looks like after childbirth. Its cavity decreases from 40 to 20 cm, and is restored by 1–2 cm daily. In order for contractions to be normal, it is necessary to periodically be examined by a gynecologist. There are many techniques for restoring the uterus.
Nettle has a good effect on uterine contractions. Three tablespoons of the plant are infused in 0.5 liters. boiling water Let it brew and cool. Drink 1/2 glass 3 times a day.
You can buy water pepper tincture at the pharmacy. It also promotes uterine contractions.
Flowers and grass of the white claret are used in a decoction and help restore the hollow organ. The decoction does not cause an increase in blood pressure. You can drink it for hypertension.
The shepherd's purse plant helps with bleeding. You can use 3-4 tbsp of tea per day. spoons of herbs per 400 ml of boiling water.
Red geranium also helps with profuse bloody lochia. Drink iced tea from 2 teaspoons of dry plant to 2 cups of boiling water. The liquid should sit overnight. Drink in small portions throughout the day.
May birch leaves help speed up postpartum cleansing. Three tablespoons of leaves are brewed in 600 ml of boiling water. Add a pinch of soda and drink 200 ml 3 times every day. The product is effective from the 12th day after the birth process.
Feeding your baby releases oxytocin, which influences uterine contractions.
From the first day you can do light physical exercises - postpartum rehabilitation exercises. Charging should be carried out in a well-ventilated area at an optimal temperature of 18 to 20 degrees.
Postnatal period
- Early. First 2 hours. The first thing that happens at this moment is an examination by an obstetrician-gynecologist to determine the presence of injuries. The medical staff monitors the condition of the uterus: whether spasms are occurring well, what the nature of the discharge is, what condition it is in. At this time, the risk of bleeding is very high. That is why at this time the woman is under the close supervision of an obstetrician or doctor. They take her temperature and measure her blood pressure. If no complications arise, they are transferred to the gynecological department.
- Late. The patient lies down for 8-12 hours, since the process she underwent is energy-consuming. It takes time to restore strength and energy. After resting, the young mother is asked to first sit on the edge of the bed. They monitor her reaction. She is then advised to stand up, then walk. During this time, the uterine cavity decreases in size. There is a redistribution of blood pressure. Fainting and dizziness are possible. What's happening? which lasts up to 8 weeks. A young mother has lochia.
In 42 days, the lochia should change its color. Initially, the discharge is red (it turns out that 80% is blood and 20% is uterine gland fluid). After this, they change and acquire a brown tint, and look like ichor. Then their color turns yellow. Until the twentieth day, the discharge should be light in color. Normally they end after two months.
If you have stitches in the pubic area, it is imperative to adhere to good hygiene. from caesarean section. Watch how the scar heals. . After every trip to the toilet, wash yourself.
If lochia does not stop, this is a reason to consult a specialist.
Reasons for long discharge:
- Curvature of the genitals.
- Coagulation disorders (hemophilia).
- Inflammation of scars.
- Infections.
- Mild spasms.
To identify this or that pathology, the patient needs to contact an obstetrician-gynecologist. The examination is carried out on a gynecological chair, smears are collected, a general blood test, a general urine test, and an ultrasound examination is prescribed.
Condition of the uterus in the postpartum period
- early – the first 2 hours after birth of the placenta;
- late – about 2 months after birth.
Involution or restoration of the uterus is a natural process that occurs in the mother’s body after childbirth. Scarring on the uterus is normal. Excessive bleeding occurs at the placenta insertion site because there are many thrombosed vessels in this area.
Blood clots leave the uterus within 3 days in the form of lochia (profuse bleeding from the vagina). Endometrial tissue is restored within 14 days after birth, by which time the discharge should become less intense. The scar at the placenta insertion site heals by the end of the first trimester.
https://youtu.be/b4LvRbJwJ6I
In the first days after childbirth, the uterus is too mobile due to stretching of the ligamentous apparatus and insufficient tone. This manifestation is especially noticeable when the bladder or rectum is full. The condition returns to normal by the end of the first month of recovery, the tone is restored.
After delivery, the uterus actively contracts and returns to its original state. During an examination in the maternity hospital, the doctor daily probes the position of the uterine fundus. After childbirth, the bottom is located in the area above the navel. After 2-4 days it descends to the level of the navel. Returns to the fold within 10 days.
| Period | Height above the pubis, cm | Weight of reproductive organ, g |
| 2 hours after the birth of the placenta | 15 – 16 | 1000 |
| 2-3 day | 12 – 14 | 750 |
| 1 Week | 8 – 10 | 500 |
| 3 week | 6 – 8 | 250 |
| 6-8 week | 5 – 6 | 50 – 70 |
Based on this information, the doctor examines the picture of recovery. This table is applicable only for women who have undergone natural childbirth. The recovery process after a cesarean section is different.
Fact! In women who breastfeed, the uterus shrinks faster and often becomes smaller than it was before childbirth.
The contraction of the uterus is provided by the hormone oxytocin. Against this background, the woman feels a nagging or aching pain that manifests itself in the lower abdomen. During breastfeeding, the intensity of the pain syndrome increases because hormone production increases during lactation. There is no need to worry about this; feeding helps speed up the regeneration process.
The woman is discharged from the maternity hospital on the third day. Before this, an ultrasound examination is mandatory. A manual examination is also carried out to assess the condition of the organ after childbirth. Normally, ultrasound shows blood clots in the upper part of the uterus. The weight of the organ is about 750 g, length and width are about 140 mm.
The cervix of the reproductive organ takes much longer to recover and no longer takes its original shape. Immediately after birth, the dilation remains at 12 cm, and by the end of 3 months the section takes on a cylindrical shape. The expansion goes away gradually, the woman may feel a slight pulling pain in the perineal area. The cervical canal looks slit-like, as can be seen in the photo. Such changes are not noticeable during sexual intercourse; only a gynecologist can see them.
The process of restoration of the uterus after the second, third or subsequent births is accompanied by peculiarities. Most often, the uterus contracts with greater intensity, which is why the woman experiences intense pain in the postpartum period. At this time, the woman has severe pain in the lower abdomen, and the mammary glands noticeably increase in size. The patient’s well-being improves by taking painkillers.
Attention! The process of restoration of the uterus after a cesarean section also differs from that characteristic of natural childbirth.
In some cases, against the background of weak labor or rapid labor, uterine contractions in the postpartum period are regarded as weak. In this case, doctors recommend taking special medications. Oxytocin helps ensure the restoration of the natural tone of the uterus after childbirth.
During the third or fourth birth, the cervical canal remains more stretched than after the first. The size of the uterus itself also changes, its weight increases by 50-70 g from the original. Recovery does not always follow a certain pattern, without complications, therefore the risk of their occurrence cannot be excluded. A mandatory gynecological examination, carried out after 2-3 months, will help reduce the risk of progression of pathologies.
- performing a gentle massage in the direction from the navel to the bottom;
- natural feeding;
- rest and sleep - lying on your stomach;
- applying a cool heating pad to the stomach (excluding hypothermia);
- maximum physical activity;
- performing light gymnastic exercises (with the doctor’s permission);
- use of medicines and traditional medicine.
The hollow organ consists of a body, which in the prenatal state is about 5 cm, and a cervix - 2.5 cm in size. When a child is born, the tissues stretch and grow along with the fetus.
Restoration (involution) of female organs after childbirth is a natural process. If the delivery was natural, the uterus recovers and shrinks within 2 months.
The postpartum period is:
- early – 2 hours after the birth of the placenta;
- late – up to 8 weeks after delivery.
Scarring on the uterus after childbirth is normal. Severe damage is located in the area where the placenta is attached. This zone contains the most thrombosed vessels.
Blood clots in the uterus after childbirth and the remains of the placenta will leave the body within three days. These secretions are called lochia.
Epithelization (regeneration of endometrial tissue) occurs 10–12 days after birth. And the scar at the placenta insertion site heals by the end of the first month.
The uterus after childbirth is a sterile organ. Over the course of 3–4 days, processes such as phagocytosis and proteolysis take place in the hollow organ. During them, bacteria located in the uterine cavity are dissolved with the help of phagocytes and proteolytic enzymes.
The first days after the birth of a child, the hollow organ is too mobile due to sprains and insufficient tone of the ligamentous apparatus. This is noticeable when the bladder or rectum is full. The tone is acquired in a month.
The speed of recovery depends on the following factors:
- hormonal background;
- woman's age;
- child parameters;
- number of previous pregnancies;
- type of labor activity;
- polyhydramnios;
- inflammation of the genital organs.
We suggest you read: How long does it take for blood to bleed? How much do you bleed after childbirth? How long does bleeding last after childbirth?
Nature has thought out the female body down to the smallest detail. Restoration of the hollow organ occurs according to the standard dimensions of 1–2 cm daily. But if minor deviations from the norm begin to be noticed, you can resort to accelerating the reduction process.
Restoring the uterus after childbirth involves the following steps:
- If the uterine fundus is soft, then the uterus will contract more slowly. An effective method is to massage the surface of the abdominal wall from the outside.
- To shrink the organ after childbirth, a cold heating pad or ice is applied to the abdomen. Medications that stimulate spasms may be used.
- Maintain genital hygiene. The penetration of infections and various complications affect the ability to contract.
- Active walking.
- The bladder and rectum should not be allowed to fill.
- Lactation. Breastfeeding releases oxytocin, which causes uterine contractions. Breastfeeding mothers restore the uterus faster.
- Postpartum exercises that stimulate contraction of the uterine muscles.
Restoration of the uterus must take place under the strict supervision of a physician. Any deviation from the norm is a pathology and requires surgical intervention.
Blood in the uterus after childbirth is formed due to wounds on the surface. The discharge is called lochia. The secretion for 3-4 days is red. At this time, lochia has a sweetish smell of blood.
They consist of 20% fluid from the uterine glands, and the rest is unchanged blood. Restoration of the uterine mucous tissue begins immediately after delivery.
Further, the lochia becomes paler, similar to ichor. After day 20, the discharge becomes light in color and has a liquid consistency. Normally, lochia comes out within 6 weeks. After this they stop.
If the discharge continues longer than the specified period or has an unpleasant odor, be sure to consult a doctor.
This may happen for the following reasons:
- bending of the cervix;
- weak contractions in the uterus;
- blockage of the pharynx with blood clots.
This condition is dangerous, as it may indicate an inflammatory process. If lochia ends in the fifth week or lasts longer than the ninth, you need to consult a gynecologist.
Process flow without deviations:
- Vessels burst in the cavity, as a result of which the bloody discharge has a bright red color for 2–3 days.
- During the first 7 days, the remains of the placenta and atrophied endometrium come out - discharge with clots.
- After 7 days, liquid lochia has a pinkish tint.
- Mucus gradually comes out - the result of the activity of the fetus inside the womb. They stop within a week.
- After a month and a half, the lochia disappears and spotting appears.
During the examination, the fundus of the uterus is detected at the level of the navel. Every day it drops within 1.5-2 cm. By the 6th day, the bottom is 4-5 cm above the womb.
If uterine contractions lag behind normal by 24 hours or more, this is a pathology and requires medical intervention.
In this case, a manual examination of the organ cavity is performed to remove remnants of membranes and blood clots. Additionally, uterotonic drugs are prescribed, such as oxytocin, methylergobrevin.
On the 3rd day after childbirth, the woman undergoes an ultrasound of the pelvic organs, which may show expansion of the cavity due to:
- accumulation of blood clots in it;
- remnants of membranes or placenta;
- early closure of the uterine os.
What changes are happening
After childbirth, significant changes occurred in reproductive function. But what does the uterus look like after childbirth? Let's look at what the organs look like before and after.
Before
In a nulliparous woman, it has an inverted pear-shaped shape. If you don't have children, it is about 5-6 cm long and 2-3 cm wide.
During
After the baby is conceived, the cavity will gradually stretch. By the end of pregnancy, its length will be 35-38 cm, width 24-26 cm. It increases not only in volume, but also in weight. In a woman giving birth, it weighs about 1 kilogram. If a girl has polyhydramnios, her weight may be higher. At this time it is at the level of the diaphragm.
After
In the postnatal period, involution—renewal—is observed. The muscle tissue begins to shrink. During breastfeeding due to muscle spasm.
The size of the uterus then decreases. Dimensions: length decreases from 15 to 25 cm, width from 12 to 15 cm. Weight decreases gradually. Immediately after the baby is born, she weighs around one kilogram. Within seven days it is reduced to 500 grams. After 14 days – 300-350 gr. By the end it weighs about 100 grams.
For better spasms, ice is placed on the lower abdomen immediately after childbirth.
Initially, the fetus is at the level of the diaphragm. After birth, due to compression, the uterus drops one centimeter every day. In normal condition, it should be at the level of the pubis.
The cervix recovers more slowly after childbirth. The pharynx gradually closes. The inner one closes first, this will happen by the third week. The outer one will form only after the second month. The muscles do not return to their original form because they are greatly stretched. It is by this sign that gynecologists can identify the woman giving birth.
The pharynx of a nulliparous woman has a round shape, and due to the birth of a child, it is transverse and has the shape of a cylinder.
What happens to the uterus after childbirth? After delivery, the system regenerates. While you are at home, you must monitor your well-being.
- Behind the temperature. Even a slight increase may indicate complications and disorders.
- If you had a cesarean section, you need to monitor the scar. If suppurative processes occur or the appearance of the scar itself is alarming, consult a specialist.
- If the lochia does not stop after two to three weeks, it becomes red and has an unpleasant odor. Contact your doctor immediately.
Ultrasound before discharge from the maternity hospital
An ultrasound examination of the internal genital organs is performed for every woman who has given birth 3-4 days after birth, before discharge from the hospital. During the procedure, the doctor checks the condition of the uterus, ovaries and cervix through the anterior abdominal wall. Ultrasound through the vagina in the first days after childbirth is not used due to the large size of the uterus. Using a transvaginal sensor, it is difficult to thoroughly examine all parts of this organ.
After childbirth, the uterus gradually returns to its pre-pregnancy state. This process is called involution. An ultrasound diagnostic doctor determines the condition of the woman’s internal genital organs and gives permission for discharge from the postpartum department. It is important to consider the following indicators:
- Do the dimensions of the birth canal correspond to the norms?
- Are blood clots present and in what volume?
- How the placental site heals.
- Is the structure of the inner surface of the uterus homogeneous?
- What is the condition of the uterine veins?
- If there was a caesarean section, the doctor checks the condition of the suture.
Normal indicators of the uterus after childbirth
If the birth took place without complications, then the involution of the birth canal occurs at a normal pace.
An ultrasound scan 3-4 days after birth reveals small amounts of blood clots in the upper parts of the uterus. After 7-8 days they descend closer to the exit from the organ cavity. Immediately after birth, the uterus is shaped like a ball, after 3 days it becomes an oval, after 7 days it takes on a pear shape. The tone of the pelvic floor muscles is restored. They gradually shift the uterus to its previous location. Immediately after birth, the fundus of the uterus is located 4 cm below the navel, a week later - in the middle of the distance between the pubic bone and the navel.
The weight of the uterus is also determined by ultrasound. Immediately after giving birth, she weighs 900-1000 grams. A week later - 500-600 gr. After 2 weeks it’s already 350 gr. By the end of the postpartum period, after 5-7 weeks, it returns to its previous volume - 60-70 grams.
What problems does ultrasound reveal?
Using an ultrasound examination, the doctor can diagnose postpartum complications in a timely manner:
- Bleeding. Ultrasound examination reveals the presence of a large volume of liquid blood and clots in the uterine cavity. The causes of postpartum hemorrhage are problems with blood clotting, difficult labor, and a bleeding placental site.
- Endometritis. The inflammatory process is defined as the heterogeneous structure of the mucous membrane of the inner surface of the uterus. The cause of endometritis is a complicated course of childbirth, delayed discharge in the uterine cavity, and chronic foci of inflammation in the body. Read more about endometritis in our article (…)
- Subinvolution of the uterus. This diagnosis is made in the case of a slow decrease in size of the organ. The discrepancy between the size of the uterus and postpartum norms occurs due to a violation of its contractility.
Ultrasound after childbirth helps to timely determine the rate of uterine involution, and as a consequence of postpartum complications. If the contractions are weak, the doctor will prescribe medications that will make it contract more actively.
Rules to Follow
- You can't take a bath. Obstetricians and gynecologists strongly advise against taking a bath. In this case, there is a high risk of uterine bleeding and infections of the genitourinary system. It is only possible to take a shower with medium-temperature water.
- Moderate loads. Heavy loads can cause large blood losses and deteriorate health. The seams may come apart. It is possible to play sports after time has passed. Exercise should be moderate. You can easily do Pilates or stretching. It is unacceptable to lift weights or engage in strenuous sports. The heaviest weight you can lift is the weight of a baby.
- Visiting public reservoirs and swimming pools is prohibited. Reservoirs are a repository for various infections. There is a high risk of infection.
- It is not advisable to sunbathe in the sun. Very high risk of deterioration of tone. Possible development of cancer cells.
- The onset of early sexual activity is prohibited. Physiologically, there was no recovery. After discharge from the hospital for a period of two months, sexual intercourse risks bleeding and poor scarring. When the penis is inserted, your reproductive function suffers. In addition, the risk of getting sexually transmitted diseases is much higher.
Complications
Very often complications and pathologies can occur. The most common of them are:
- Subinvolution (poor muscle contraction). The reasons for this may be: remnants of the placenta, ruptures, poorly placed sutures, residual clots. In this case, the patient is injected. The gynecologist prescribes antibiotics as needed. In rare cases, vacuum cleaning is carried out.
- Endometritis (inflammation of the endometrium). The reasons may be: impaired venous outflow, early abortions, irresponsible examination by a gynecologist. In severe cases of the disease, hospital treatment is prescribed. . Mandatory prescription of antibiotics. Self-treatment can harm your health
- Bleeding. The norm is the cessation of lochia within 7-10 days. The reasons may be: intense physical activity, decreased blood pressure, early restoration of sexual activity, red discharge from the uterus.
If you suddenly experience bleeding, call an ambulance immediately.
In order to avoid pathologies for you.
If you observe a poor condition or constant ailments, you should contact a gynecologist. Timely treatment will help avoid problems.
The uterus undergoes numerous changes after childbirth. Let's consider what exactly these changes are, what is considered normal, and what may be a pathology.
Immediately after the birth of a child, the uterus weighs about 1 kilogram. Its bottom is approximately at the level of the navel. That is, a woman in the first days of her motherhood looks like she has not yet given birth. During the postpartum period, which lasts up to 40 days, the uterus contracts after childbirth, and as a result it acquires its previous, “non-pregnant” size” and a weight of about 50 grams.
The cervix also undergoes changes. Immediately after the birth of the child, it is open by 10-12 cm, but gradually by the 10th day it closes completely, by about 21 days the external pharynx closes and takes on a slit-like shape (a distinctive gynecological feature of all women who have given birth). This is what the uterus looks like after childbirth from the point of view of a gynecologist.
What a woman feels and notes normally
Severe pain goes away immediately after childbirth. But in the coming days, uterine spasms may still be felt as a result of its contractions. This is especially noticeable in women who are injected with Oxytocin to improve uterine contractility.
In the first 3-7 days, fairly heavy uterine bleeding is observed. But every day the discharge becomes less and less, it becomes lighter and turns into “daub.” Normally, the discharge completely disappears no later than the end of the postpartum period. The name of these secretions is lochia. But before they have time to end, some women become concerned about the bleeding that has started again, but this is no longer lochia, but normal menstruation. For women who are not breastfeeding, as well as for some who are breastfeeding, their periods come as early as 6-8 weeks after the baby is born.
Possible pathologies
1. Increased uterine bleeding after childbirth. This can happen for 2 reasons: either there are pieces of the placenta left in the uterus, or the uterus contracts poorly. The first pathology can be diagnosed using ultrasound. Surgical treatment is curettage of the uterine cavity. The second pathology should also not be ignored, since large blood loss and endometritis are possible - inflammation of the endometrium of the uterus. Treatment consists of taking drugs that contract the uterus, and, if necessary, hemostatic agents and antibiotics. This pathology is called uterine subinvolution. This is a typical complication after gestosis, multiple pregnancy, or polyhydramnios.
2. Cervical erosion may occur after childbirth, but treatment is not required in all cases. A small ectopia, with normal smear and colposcopy results, only needs observation. While ectropion of the cervix is its inversion, it necessarily requires surgical treatment.
3. And another unpleasant pathology is uterine prolapse after childbirth. The cause is pelvic floor trauma resulting from difficult and/or multiple births. Symptoms appear depending on how advanced the process is. With slight ptosis, the woman feels well. She is recommended to perform special exercises to strengthen the pelvic floor muscles. With significant prolapse of the uterus, women complain of pain in the lower abdomen and urinary incontinence. For second and third degrees of uterine prolapse, only surgical treatment is effective.
To identify possible pathologies in time or make sure you are in good health, visit your doctor 6-8 weeks after giving birth. Even if you have no complaints.
How the cervix changes during pregnancy
With the onset of pregnancy, the cervix changes from the first weeks. This is necessary for the proper development of the fetus and its unhindered presence in the uterus until the due date.
Changes in the first days after conception: are there any?
Immediately after fertilization of the egg has occurred, the cervix becomes soft and changes its position. This helps the uterus move forward, causing the cervix to descend. Changes begin within a few days after conception: the color of the organ changes and its tissues become wider.
What does the cervix look like at the beginning of pregnancy in the first trimester?
When examining a pregnant woman in the first trimester, the doctor notes changes in the cervix:
- bluish or purple color;
- the cervical canal is tightly closed;
- the structure is dense;
- length at least 3cm.
With the onset of pregnancy, the lumen of the cervix becomes tightly clogged with mucus produced by the endocervical canal. This is necessary to protect the fetus from infection and maintain normal microflora in the uterine cavity. This is exactly the “mucus plug” that comes off in most women shortly before the onset of labor.
The changes are associated with the active proliferation of blood vessels in the organ, which is necessary for the protection and full development of the fetus. Under the influence of changing hormonal levels, the muscle layer grows, reaching what is necessary for bearing a child without pathologies.
What it looks like before giving birth: what should be normal
At the end of pregnancy, during the examination, the doctor pays attention to three indicators of the cervix:
- its length;
- location in the pelvis;
- degree of softness.
Normally, immediately before birth, it should be soft, which indicates readiness for labor. The doctor notes the beginning of dilation, the degree of which differs depending on the number of births: in nulliparous women, the cervical canal may allow a finger to pass through, and in repeated pregnancies - two. A woman often feels the beginning of softening and opening, she has “training contractions”, during which this process occurs.