Home / After childbirth / How long does it normally bleed after childbirth?
92303
0
Postpartum bleeding is a normal process, which results in the natural cleansing of the uterine cavity from lochia and retained remnants of placental tissue. The severity of bleeding depends on its nature, total blood loss and duration. How long does blood bleed after childbirth is a question that concerns every young mother.
For many women, bleeding as a result of childbirth is not a cause for alarm and does not pose any threat. Abundant in the first days, it gradually decreases and disappears within a few weeks. Severe bleeding, which occurs with painful contractions and nagging pain, pronounced odor and putrefactive discharge, is not normal and requires urgent medical intervention.
How long does it take to bleed after childbirth?
The question of how long postpartum bleeding lasts arises for almost all young mothers. The duration of this process can be from 2 to 6 weeks or even a little more. The duration depends on several factors: the ability of the uterus to contract, blood clotting, the rate of tissue regeneration, etc. In women who are breastfeeding, recovery occurs faster.
It is important to evaluate not only the duration of bleeding, but also the general nature: it should gradually become less profuse. In the first day after birth, the discharge is strong, then it becomes less and less and eventually turns into a brownish “smudge.” This sequence is the norm.
General information
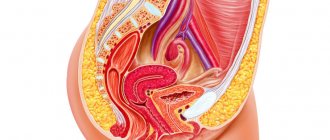
The postpartum period begins from the moment the placenta with membranes leaves the uterus and lasts for 6 weeks. During this time, involutive (reverse) changes occur in the reproductive system and organs that have undergone changes during pregnancy. In other words, the female body gradually returns to its original state.
Immediately after birth, the inner surface of the uterus is an almost continuous wound surface. But due to the contraction of muscle fibers, its size is minimized. The uterus decreases in volume, sinking lower and lower into the pelvic cavity and by the 10th day it is already located behind the symphysis pubis. This is facilitated by breastfeeding, during which the hormone oxytocin is produced.
At the end of 2–3 weeks, the cervical canal also closes. But the mucous membrane - the endometrium - requires a longer recovery. The basal epithelium grows by 10 days after birth, and the complete formation of the functional layer will occur only towards the end of the entire period.
Causes of bleeding after childbirth
Heavy pathological bleeding in the early postpartum period, lasting about 2 hours after the birth of the baby, is caused by the following reasons:
- Insufficient blood clotting. With this complication, it flows out in a stream without the formation of clots and lumps (thrombosis disorder). To prevent the situation, before giving birth it is necessary to donate blood for a general analysis and stop all medications with anticoagulant effects.
- Rapid labor activity. It is accompanied by ruptures of the birth canal: the cervix, vagina, and, in rare cases, the uterus are damaged. Read more about rapid labor →
- Placenta accreta. With this complication, the reverse development of the uterus is difficult, which leads to heavy bleeding.
- Insufficient ability of the uterus to contract. Most often this happens when the walls are greatly stretched (large fetus, twins, polyhydramnios);
- The presence of fibroids and myomas in the uterus. Read more about uterine fibroids→
The causes of postpartum hemorrhage in the period from 2 to 6 are:
- The release of placenta particles remaining in the uterine cavity.
- The release of blood clots, difficult due to spasmodic contraction of the cervix after surgical delivery (caesarean section).
- Slow recovery due to inflammation in the pelvic area (high fever is also noted).
Dangerous symptoms in the delivery room
After giving birth, the woman remains in the delivery room for 2 hours under the supervision of medical staff. During this period, hypotonic bleeding most often occurs. It is characterized by a sudden onset against the background of apparent well-being and a rapid course: in a short period of time, a postpartum woman can lose up to a liter of blood. Such a volume can be critical and lead to rapid decompensation, the development of hemorrhagic shock and death.
Therefore, in order to notice unfavorable signs in time, have time to respond to them and reduce the time for providing assistance, the patient does not shift from a chair to a couch or gurney: medical care will be provided in a gynecological chair if a critical situation develops.
How long does bleeding last after childbirth?
It all depends on individual characteristics. It continues directly in the delivery room, when transferred to the ward, and even during the first day it looks like liquid blood. By the second day, it is no longer blood, but lochia, thicker in consistency, containing a mucous component. Over the next four days, the discharge decreases, first becomes dark brown, and then gradually becomes lighter. Lochia continues to be released for another month.
Signs of bleeding in the early postpartum period are difficult to determine on your own. It is accompanied by weakness, which already worries a woman after childbirth. There may be a feeling of chills, but this is also a nonspecific symptom. After muscle tension during the period of pushing, a postpartum woman may experience a period of muscle tremors, which is difficult to distinguish from a state of severe blood loss.
While the patient lies motionless, blood can accumulate in the uterine cavity, gradually stretching it. When pressing on the uterus, a large amount of blood is released through the abdominal wall, sometimes with large clots. Gradually, normally this amount should decrease. But this does not happen with the development of pathology.
Blood pressure measurement is required. With a significant decrease in it, as well as an increase in signs of tachycardia, a conclusion is drawn about significant blood loss.
Features of postpartum hemorrhage
Symptoms of postpartum hemorrhage can be described in two parameters: the volume and nature of the discharge. There may also be disturbances in heart rhythm, changes in arterial and venous pressure, and deterioration in general well-being.
A blood loss of 0.5% or less of a woman’s body weight is considered physiologically acceptable. If this indicator is higher, then pathological postpartum bleeding is diagnosed. Massive blood loss is its release in a volume of 0.5 to 1% of the mother’s weight. This may lead to a decrease in blood pressure, weakness and dizziness.
When the rate exceeds 1%, critical blood loss develops. It may be accompanied by hemorrhagic shock and DIC (coagulation disorder). These complications lead to irreversible changes in organs.
Heavy postpartum bleeding develops with decreased or absent uterine tone. The more pronounced the atony, the less amenable to treatment. Drugs that cause myometrial contraction eliminate bleeding only for a while. The condition is accompanied by arterial hypotension, tachycardia, pale skin, and dizziness.
Clinical course of hypotonic and atonic bleeding
First option: Immediately after the birth of the placenta, the uterus loses its ability to contract; it is atonic, does not respond to mechanical, temperature and drug stimuli, the bleeding from the first minutes is profuse, quickly leading the woman in labor to a state of shock.
Second option: The uterus periodically relaxes; under the influence of agents that stimulate muscles and tone, its contractility is temporarily restored; then the uterus becomes flabby again; bleeding is wavy; periods of intensification alternate with almost complete stop; blood is lost in portions of 100-200 ml. The mother's body compensates for such blood loss if obstetric care is provided on time and in sufficient volume. If obstetric care is late or carried out haphazardly, the body's compensatory capabilities are depleted. The uterus stops responding to pathogens, hemostasis becomes impaired, bleeding becomes massive, and hemorrhagic shock develops. The second variant of hypotonic bleeding occurs much more often.
Diagnostic procedures
The diagnostic process begins during pregnancy. In modern obstetric and gynecological practice, assessment of the risk of postpartum hemorrhage is based on data from monitoring changes in the level of hemoglobin, red blood cells, and platelets in the blood at different stages of gestation. Coagulability indicators (coagulogram) are taken into account.
Hypotonia and atony of the uterine muscles are diagnosed in the third stage of labor. These conditions are indicated by flabbiness and weak contractions of the myometrium, an increase in the time of the afterbirth stage.
Diagnosis of bleeding after childbirth includes a thorough examination of the integrity of the released placenta, membranes, and examination of the birth canal to identify possible injuries. If necessary, the woman is given a general anesthetic and the doctor manually examines the uterine cavity to determine if there are ruptures, placenta, blood clots, malformations or tumors that could interfere with myometrial contraction.
For bleeding in the late postpartum period, diagnosis is carried out using ultrasound. On the 2nd or 3rd day after the birth of the child, the condition of the pelvic organs is examined. The procedure allows you to identify the remains of the placenta and membranes in the uterus.
How to distinguish postpartum menstruation from spotting?
In some cases, postpartum discharge returns with renewed vigor after a few weeks. How to distinguish menstruation from bleeding after childbirth? There are several different criteria that can be used to distinguish postpartum bleeding from menstrual bleeding.
When breastfeeding, menstruation does not resume in the immediate postpartum period. This occurs due to the effect on the female body of the hormone prolactin, which is responsible for milk production, but at the same time suppresses the menstrual cycle. Therefore, under the condition of constant breastfeeding, menstruation usually occurs no earlier than four months after birth, and sometimes much longer.
Information If more than half of women stop breastfeeding, their periods may resume within 6-14 weeks. Thus, menstruation cannot begin immediately after the birth of a child, since the body needs time to restore the menstrual cycle.
Postpartum bleeding can also be distinguished from normal menstruation by the color of the blood. The discharge after childbirth in the first days is bright red, gradually becoming lighter and more transparent. By day 4-5 of the cycle, menstrual blood acquires a brownish tint, but not light pink.
Menstruation and bleeding after childbirth vary in severity. If during bleeding a woman who has given birth loses from 500 to 1000 ml of blood, then in 5 days of menstruation the volume of blood loss will not exceed 100 ml.
Pathological bleeding is the loss of large volumes of blood, it will be accompanied by the following symptoms:
- Weakness and dizziness;
- Sweating;
- Cardiopalmus;
- Paleness of the skin;
- Rapid breathing.
Important If you suspect you have these symptoms, tell your doctor immediately.
https://youtu.be/qTklinJC0v8
Normal bleeding after childbirth
Normal bleeding in the postpartum period is caused by the release of remnants of the placenta and membranes from the uterus. This process is divided into several periods, each of which is characterized by certain characteristics: color and intensity of discharge.
The first three days after the birth of a child, bleeding is profuse, the volume is more than during menstruation. The color is bright red. Blood comes out of those vessels that were at the placenta attachment site. This condition develops due to insufficient contractility of the uterus in the first days after childbirth. It is considered normal and does not require medical intervention. Postpartum bleeding after a cesarean section may be longer because the incised uterus contracts less well.
Over the next two weeks, the intensity of discharge decreases noticeably. They turn light pink, brown or yellowish white. The uterus gradually contracts, and by the end of the second week the bleeding completely disappears. This option is considered the norm.
In some cases, bleeding is observed in the late labor period. It can be either normal or pathological, requiring medical intervention. If, in the period from 2 to 6 weeks after the birth of the child, light discharge from the uterus with impurities of blood appears, then there is no need to worry. This symptom may be present constantly or may appear and disappear for several days. This intermittent regimen is typical for women who quickly return to sports training or other physical activity.
Sometimes the bleeding disappears by the end of the second week, and then appears for a few days between 3 and 6 weeks after birth. The discharge is insignificant and painless and is normal.
Prevention is easier than cure
Prevention of bleeding in the postpartum period consists of proper management of pregnancy and childbirth. The anamnestic and clinical data of a particular pregnant woman is assessed and a risk group for the development of bleeding is established. Such women in labor need special attention. Already during childbirth, they are prescribed oxytocin, but not with the aim of enhancing labor, but to reduce the risk of massive blood loss. Preventive measures include examination of the child's place, a thorough inspection of the birth canal and suturing of existing ruptures.
https://youtu.be/qykzCJzwP5g
Pathological bleeding after childbirth
A deviation from the norm that requires the help of a doctor is late bleeding with the following features:
- duration more than 6 weeks;
- scanty discharge with ichor is replaced by scarlet blood;
- the woman’s general condition becomes worse;
- bleeding is accompanied by pain in the lower abdomen;
- signs of intoxication appear (fever, dizziness, nausea, etc.);
- The discharge becomes brown or yellow-green in color and has an unpleasant odor.
If there is an intense flow of blood, especially if it is scarlet, you should immediately call an ambulance. Pain, fever, change in color of discharge indicate the development of complications: endometriosis, infectious diseases, etc. Such conditions require the earliest possible diagnosis and treatment.
Reasons to see a doctor
The recovery process after childbirth does not always go well. Reasons to contact a specialist:
- lack of discharge (usually this indicates a spasm of the uterine pharynx due to large particles of the placenta that blocked the cervix);
- the duration of heavy scarlet discharge, the appearance of temperature, chills and high pulse (these signs may indicate endometritis - an inflammatory process of the uterine mucosa);
- brown discharge on the third day after birth, terrible headaches, sleep disturbances, rapid heartbeat, fever (if, in addition to these signs, the gynecologist notices an increase in the size of the uterus, this indicates complications of endometritis);
- disappearance of discharge and increase in temperature to thirty-nine degrees with a generally satisfactory condition (all these are symptoms of metroendometritis);
- discharge accompanied by an unpleasant odor (a sure sign of infection).
Only a specialist can correctly determine the condition, which is why it is so important to see a doctor for the first few months after the birth of the child.
Treatment methods
Acute postpartum hemorrhage requires first of all establishing its cause, as well as prompt cessation. Treatment uses an integrated approach and often drug therapy must be combined with invasive methods.
To stimulate uterine contractions, a catheter is inserted into the urethra to empty the bladder, and ice is applied to the lower abdomen. Sometimes gentle external massage of the uterus is performed. If all these procedures do not bring results, then uterotonic drugs, for example, Methylergometrine and Oxytocin, are administered intravenously, and injections with prostaglandins are given into the cervix.
Replenishing the volume of circulating blood and eliminating the consequences of its loss is carried out using infusion-transfusion therapy. Plasma replacement drugs and blood components (primarily red blood cells) are injected into a vein.
If examination with the help of mirrors reveals ruptures in the birth canal and perineum, then a local anesthetic is applied and the doctor stitches up the damage. Manual examination and manual cleansing of the uterus is indicated for violations of the integrity of the placenta and hypotonic processes in the myometrium. The procedure takes place under general anesthesia.
If a uterine rupture is detected during a manual examination, then emergency laparotomy, suturing or complete removal of the uterus is necessary. Surgical intervention is also required for placenta accreta and in cases where the bleeding is massive and cannot be stopped. Such procedures are carried out with simultaneous resuscitation actions: blood loss is compensated, hemodynamics and blood pressure are stabilized.
What are the causes of late uterine bleeding
Late bleeding refers to those that manifest themselves two hours after birth. They are caused by parts of the placenta or other biological tissue remaining in the uterus. It is possible that parts of the placenta adhere to the walls of the uterus. Sometimes, under such conditions, infection and inflammation develop, and the overall tone decreases.
We must not forget about the mistake of doctors - uncoordinated actions can lead to bleeding. Bleeding is caused by disturbances in the functioning of the inner layer of the uterus, which is caused by previous abortions, cesarean sections and other surgical interventions.
Late bleeding is common after caesarean section
Preventive actions
Prevention of postpartum hemorrhage helps reduce its duration and intensity, and also avoid complications.
It involves implementing the following recommendations:
- go to the toilet regularly: a full bladder and intestines put pressure on the uterus and prevent it from contracting;
- take all possible measures to prevent infection of the uterine cavity: observe the rules of intimate hygiene, do not swim in open water, refrain from sexual intercourse and taking baths;
- do not engage in sports or other intense physical activity for one and a half months;
- develop the habit of sleeping lying on your stomach, so the uterus contracts and cleanses faster;
- breastfeed the baby;
- avoid overheating: do not visit baths, saunas, or be outside on a hot day.
Bleeding after the birth of a child is a normal physiological process that still needs to be controlled. It is important to pay attention to the duration, intensity and nature of the discharge. If you suspect complications, you should see a doctor as soon as possible, and if intense scarlet bleeding appears, call an ambulance.
Author: Olga Khanova, doctor, especially for Mama66.ru
https://youtu.be/jQLVHclTI-M
Bleeding one month after birth
Normally, one month after birth, bleeding decreases, turning into a more transparent form (ichor). But in some cases, the discharge resumes with renewed vigor, and this happens suddenly and is accompanied by large blood loss .
Information What does sudden resumption of bleeding after childbirth mean? Most often this happens due to incomplete exit of the placenta from the uterine cavity. After the placenta is born, the doctor carefully examines it for integrity. If a lobule or part of a lobule is missing, this means that it remains attached to the internal cavity of the uterus and will eventually cause an inflammatory process, and then bleeding.
However, it is not always possible to determine the integrity of the placenta using a visual examination, because it may also have additional lobules. In most modern maternity hospitals, the condition of the uterus after childbirth is diagnosed using ultrasound - the device will show the presence of placental remnants or clots in the uterine cavity. In this case, manual cleaning of the uterus is necessary. This is an unpleasant procedure, but it is much preferable to inflammation and infection, which can lead to quite serious consequences.
Complications and consequences
Massive blood loss after childbirth is fraught with the occurrence of disseminated intravascular coagulation syndrome, renal failure and death. Suffering massive blood loss can lead to postpartum necrosis of the pituitary gland and the development of Sheehan syndrome.
Sozinova Anna Vladimirovna, obstetrician-gynecologist
5, total, today
( 58 votes, average: 4.17 out of 5)
Multifollicular ovaries - what are they?
Ovarian dysfunction: why it occurs, how it manifests itself, pregnancy planning
Related Posts
Pathological discharge after childbirth and the reasons for its appearance
If lochia began to decrease, but then its volume increased sharply, this is a cause for concern. This symptom may indicate the opening of uterine bleeding. If a standard pad becomes saturated with blood within 40-60 minutes, we are talking about internal bleeding.
If the discharge acquires a putrid odor or becomes yellowish-green, this may indicate the development of an inflammatory process in the internal genital organs. The reasons for its occurrence may be a bend in the uterine tube and the accumulation of lochia there. An inflammatory process that has developed in the uterus can cause endometritis. This phenomenon is accompanied by severe pain localized in the lower abdomen. Additionally, there is an increase in body temperature and the appearance of purulent discharge. To combat the pathology, the doctor will prescribe a course of antibacterial drugs and curettage of the uterus.
The following symptoms may indicate the presence of pathologies:
- the woman experiences an increase in body temperature;
- mucus and clots appear in the discharge;
- there is a general deterioration in health;
- there is weakness;
- there is pain in the lower abdomen.
The cause of incessant bleeding in the first hours after childbirth can be ruptures of the cervix, if they were poorly sutured or went unnoticed. In this case, local hemorrhage is observed in the tissues of the vagina and perineum. After a careful examination, the doctor will open the hematoma and re-suture the tears. The consequence of uterine bleeding may be the development of anemia. This name was given to a lack of hemoglobin and, as a result, a disruption in the supply of oxygen to the body’s tissues. If a woman in this condition breastfeeds a child, it cannot develop in him either. The list of other reasons leading to the occurrence of spotting a month after childbirth can include:
- Parts of the placenta and membranes remained in the uterus. This significantly slows down the healing process and can cause severe bleeding that develops suddenly. Its characteristic feature is the absence of pain.
- There is atony or hypotension of the uterus. Pathology is associated with its excessive stretching, flabbiness or weakening. If weak contractile activity is observed, blood flows out of the vagina either in a continuous stream or in separate portions. The condition is life-threatening for the woman and requires urgent medical attention.
- Excessive physical activity after childbirth. A similar phenomenon occurs as a result of too early sexual intercourse.
- Small menstruation. This is the name given to the gradual return of a woman’s reproductive system to menstrual function. In certain groups of women in labor, on days 21-28, bleeding begins to reappear.
Bleeding in the ward
The postpartum period can be complicated by bleeding a few days after birth. There are symptoms that should alert a woman. The first sign is a decrease in the number of lochia. They become scarcer or stop altogether. You should definitely inform your doctor about this.
Previously, postpartum bleeding develops when the cervix is blocked by clots that do not allow the lochia to flow normally. They stagnate in the uterine cavity and lead to its subinvolution. This symptom is clearly visible on ultrasound.
Diagnosis is mandatory for all women in the postpartum period to exclude this pathology. On ultrasound, signs of subinvolution are:
- expansion of the uterine cavity more than 1 cm;
- discrepancy between the size of the organ and the postpartum period;
- presence of homogeneous contents in the cavity.
After a long absence of discharge, sudden bleeding may begin. Therefore, treatment of subinvolution is carried out immediately after diagnosis. To do this, it is necessary to eliminate from the uterine cavity the remains that prevent it from contracting. By the third day, the cervix begins to form, so the procedure cannot be performed only with your hands; a surgical instrument is required.
A curette is used to remove remnants of membranes and clots.
It is carefully used for scraping. After the procedure, a solution of oxytocin or methylergometrine is administered intravenously to improve contractility.
Be sure to compensate for blood loss with special saline solutions.
The duration of discharge in this case should correspond to that during normal childbirth.
Causes
The main causes of bleeding in this condition are:
- Rapid childbirth, which became the culprit of severe damage to the woman’s birth canal. In this condition, a woman in labor may experience severe ruptures of organs. At the same time, copious bleeding can be observed for several days after rapid labor.
- Pathologies of the attachment of the placenta to the uterus, which subsequently provoke severe bleeding.
- Poor blood clotting in a woman in labor can provoke excessive bleeding. In such a condition, doctors should urgently administer hemostatic drugs to the woman. Otherwise, death from blood loss cannot be ruled out (which is why it is dangerous to give birth outside a hospital setting without medical supervision).
- Presence of changes in the uterus.
- Poor contractility of the uterus, which can be caused by very strong stretching of its walls.
- Rupture of the uterus, which was provoked by difficult childbirth (usually occurs with a large fetus).
- Accumulation in the uterus of amniotic mucous tissue that has not yet come out.
- The appearance of blood that cannot completely leave the organ due to reflexive contraction of the uterus. This condition is often observed during cesarean section.
- The presence of a focus of acute inflammation, which led to a slowdown in the recovery process.
Is discharge with an unpleasant odor a deviation?
Discharge with an unpleasant odor should not go unnoticed. Let's take a closer look at what discharge should be normal. In the first 3-4 days, the secretion is released most actively and has a characteristic smell of blood. By the 10th day, its quantity decreases and acquires a slightly sour smell.
The fishy smell of discharge after childbirth should alert a woman. The problem develops due to exacerbation of thrush, when personal hygiene rules are not observed.
The putrid odor of lochia is characteristic of:
- endometritis;
- vaginitis;
- colpitis;
- postpartum peritonitis.
Prevention
In order to minimize all chances of postpartum hemorrhage, it is necessary to carry out timely prevention and take a number of measures. They are all very simple and obvious. For example, pregnancy should be planned, preparing for it, that is, examination, identification and treatment of all chronic diseases. It is also important to register with the antenatal clinic in a timely manner, preferably before 12 weeks.
In addition to the above measures, the following should also be observed:
- Visit your gynecologist regularly. Throughout your pregnancy, it is important to come for examination once a month in the first trimester, once every 2-3 weeks in the second trimester, and once every 7-10 days in the third trimester.
- Eliminate muscle tension in the uterus in a timely manner. This is done with the help of medications, namely tocolytics.
- Timely establish and eliminate gestosis. As a rule, such complications during pregnancy include edema, high blood pressure, and kidney problems.
- Follow a diet. It is important for a pregnant woman to adhere to a proper diet, excluding all harmful foods.
- Perform physical therapy. For pregnant women, it is important to exercise lightly every day - up to 30 minutes a day. This could be walking, breathing exercises and stretching.
- The obstetrician must carry out rational management of labor. Assessment of indications for natural or surgical delivery, adequate use of uterotonics, proper examination of the discharged placenta and other necessary medical measures.
These simple preventive actions will help you avoid severe complications after childbirth. Good luck to you!
What does yellow discharge indicate?
When the discharge ends, the secretion becomes yellow or light in color. It should not have any smell.
Yellow discharge is a sign of successful healing of the uterine epithelium.
The following signs indicate progressive diseases:
- discharge with an odor;
- sensation of itching and burning in the perineum;
- hyperthermia;
- abdominal pain.
The sticky, jelly-like consistency of yellow secretion is also a reason to contact a gynecologist. The sign is characteristic of a developing infection and endometritis.
It is difficult to answer exactly how much yellow discharge occurs after childbirth. Typically this period lasts up to 2 weeks, after which the secretion becomes light in color.
Why does it occur
Obstetric hemorrhages are usually divided into those that begin with the onset of labor, in the afterbirth and early postpartum periods. Bleeding in the first stage of labor and in the second can be caused by premature abruption of a normally located placenta. In the third period there are many more reasons.
After the birth of the fetus, during the normal course of labor, the placenta separates and the placenta is released. At this time, an open placental area appears, which contains up to two hundred spiral arteries. The terminal sections of these vessels do not have a muscular membrane; blood loss is prevented only by uterine contractions and activation of the hemostatic system. The following happens:
- After expulsion of the fetus, the uterus decreases significantly in size.
- A powerful contraction and shortening of muscle fibers occurs, which draw in the spiral arteries, compressing them with the force of myometrial contractions.
- At the same time, compression, twisting and bending of the veins occurs, and intensive formation of blood clots occurs.
In the area of the placental site (the place of the former attachment of the placenta) in healthy women, blood clotting processes are accelerated ten times compared to the time of thrombus formation in the vascular bed. During the normal course of the postpartum period, the first thing that occurs is a contraction of the uterus, which triggers a thrombosis mechanism, which requires a decrease in the lumen of blood vessels and a decrease in blood pressure.
It takes about two hours for the final formation of a blood clot, which explains the observation time due to the risk of the described complication. Therefore, the causes of bleeding during childbirth can be:
- conditions that impair the contractility of the myometrium;
- pathology of the blood coagulation system;
- birth canal injuries;
- premature placental abruption, disruption of the processes of its separation and excretion.
Bleeding can begin after the birth of the fetus with a decrease in myometrial tone, abnormalities in the location of the placenta, disruption of its attachment and incomplete separation from the walls in the third stage of labor. The likelihood of pathology occurring is higher with the development of the following complications:
- anomalies of labor;
- inappropriate use of uterotonics;
- rough handling of the third period.
The risk group includes women with previous gynecological diseases, genital surgeries, abortions, and infantilism. In the afterbirth period, due to pathologies of the placenta, the force of myometrial contractions may be impaired, and the operation of manual separation of the placenta disrupts the process of thrombus formation in the placental site.
Additional provoking factors are disruption of the integrity of the birth canal. In the first hours after birth, bleeding can be caused by low levels of fibrinogen in the blood, atony and hypotension of the uterus, retention of parts of the placental tissue and membranes.
Recovery in the postpartum period
Breastfeeding an infant
Every woman in the postpartum period should know that breastfeeding is an excellent prevention of all kinds of complications. After all, when a baby is applied to the breast, there is an immediate release of the hormone oxytocin, which also causes contractions of the uterus. After feeding, a woman may observe a visible increase in discharge, which is associated precisely with contraction of the muscles of the uterus and should not cause concern.
To speed up uterine contractions, you should empty your bladder in a timely manner. During the postpartum period, it is advisable to do this every three hours, even if the woman does not have a pronounced feeling of bladder fullness, and to avoid constipation.
For 1-2 months after giving birth, discharge cannot be absorbed with tampons, precisely because they do not remove lochia, but simply absorb them. This can lead to the proliferation of pathogenic bacteria and microorganisms. It is recommended to use pads or diapers instead of tampons. Choose unscented products, as you need to control not only the color and number of lochia, but also their smell.
It is extremely important to maintain good personal hygiene. You should especially carefully monitor the hygiene of the genital organs one to two weeks after childbirth, when the discharge is still bloody. During this time, it is forbidden to take a bath, limiting yourself to showering only. The stream of water from the shower should not be very strong and should be directed from front to back - and only from the outside. To safely clean the external genitalia and vaginal mucosa, it is recommended to use special products - for example, washing gels for intimate hygiene Ginocomfort. These products were developed by specialists from the pharmaceutical company VERTEX, are characterized by a safe composition, including natural active ingredients, and also have all the necessary certificates, certificates and other necessary documents.
Sexual rest continues up to 42 days, and intimate relationships are resumed only after a control ultrasound of the pelvic organs, examination by an obstetrician-gynecologist and an adequate selection of a contraceptive method.
Exercising after childbirth
Sources:
- EARLY DIAGNOSIS AND PREVENTION OF SUBINVOLUTION OF THE POSTPARTUM UTERUS. Naumkin N.N., Ivanyan A.N., Smirnova T.I. // Bulletin of new medical technologies. – 2008. – No. 2. – pp. 46-48.
- CYTOLOGY OF UTERINE LOCIA IN ENDOMETRITIS AFTER BIRTH. Kupert M.A., Kupert A.F., Solodun P.V. // Acta Biomedica Scientifica. – 2004. – No. 2. – pp. 172-175.
- Cystic fibrosis: modern achievements and current problems. Kapranov N.I. and others // M., 2005.
- The importance of cytological examination of lochia in assessing the condition of the uterus in the postpartum period. Z.K. Fursova. A.P. Nikonov, N.A. Lutfulaeva, E.A. Kuchuchurova // Obstetrics and gynecology. - 1991. - No. 1. pp. 45-49.
- Postoperative purulent-septic complications in obstetrics (prediction, prevention, early diagnosis and therapy). Kryukovsky S.B. // Dis. Dr. honey. Sciences. – M., -2002. – P. 266.
- https://www.aafp.org/afp/2017/0401/p442.html
- https://www.pubfacts.com/detail/19674353/Early-postpartum-discharge-and-breastfeeding-an-observation…
- https://parenting.firstcry.com/articles/lochia-normal-bleeding-and-discharge-after-pregnancy/
Late postpartum discharge
Bleeding may also occur a month after birth. Later, lochia can be triggered by various factors. In a normal situation, uterine contractions continue for a certain period after childbirth. They intensify when a woman puts a baby in her breast. This helps the uterus to cleanse itself of blood particles and clots located in it. If a woman does not breastfeed, the hormone prolactin, which stimulates uterine contractions, is not produced. This causes slow cleansing of the organ. If there are no blood clots in the discharge and the lochia does not have an unpleasant odor, there is no reason to worry. Gradually the discharge will stop.
There are a number of other reasons that prolong the period of cleansing the uterus after childbirth. The list includes:
- Blood clotting disorder. If the problem is known in advance, it must be reported to the doctor at the stage of pregnancy planning. A woman should be prepared for the fact that natural bleeding will last much longer.
- Big fruit. This causes the uterus to stretch more during pregnancy. A similar phenomenon is observed if there are several fruits. Strong stretching increases the time it takes for the organ to return to its previous size.
- The birth was performed by caesarean section. As a result, a suture is formed on the uterus. It prevents it from contracting properly. As a result, the recovery process slows down. A similar phenomenon is observed if injuries and ruptures were sustained during childbirth, and severe bleeding occurred, which required surgical intervention and suturing.
- The uterus contains polyps, fibroids and fibroids, which prevent its normal contraction. All this leads to an increase in the duration of discharge.
Typically, a woman does not have menstruation for 2 months after giving birth. However, the rule only applies to patients who are breastfeeding. In this case, prolactin is released, which inhibits the production of estrogen, which is responsible for follicle maturation and restoration of the menstrual cycle. In women who, for one reason or another, did not put their baby to the breast, menstruation can resume within 1-1.5 months after birth. Such phenomena are considered a positive sign. The appearance of menstruation indicates the rapid restoration of the uterus and hormonal levels. During menstruation, the discharge becomes abundant and has a bright color. A woman in the postpartum period needs to make sure that it is really her period. We must remember that there is a risk of uterine bleeding, which requires emergency care.
conclusions
How many days after childbirth will blood bleed is a question that all women who have just given birth ask. But there is no definite answer to this, since everything in this matter depends on the physiological characteristics of the postpartum woman. But in any case, no matter how much blood flows after childbirth, it is important that it does not have a rotten smell, and that you do not feel pain. If your postpartum recovery process proceeds without complications, then a month and a half after the birth of the baby, any unpleasant discharge from the birth canal will stop and will no longer cause you discomfort.
How long is blood discharge after childbirth normal and when should you sound the alarm?
Normal postpartum discharge
The first few days after birth, the discharge will be as heavy as possible. Approximately 400 ml of blood should be released daily. Most often it is not homogeneous, but with mucus or clots. There is no need to be afraid, this is a completely natural process. That's how it should be. These days the discharge is bright red.
After 3 days the color will gradually change to brown. The closer to the end of the postpartum period (8 weeks), the less discharge there will be. Gradually they will look like menstruation, then they will become light and turn into regular mucus.
When to sound the alarm
If a woman notices in the maternity hospital that the discharge has become more intense or less frequent, thicker or, conversely, more watery, she must immediately tell the doctor about it.
Also, postpartum discharge should be monitored after discharge from the hospital. Despite the fact that each woman’s recovery process after childbirth is individual, there are general points that should be a reason to contact a gynecologist.
What should every young mother be wary of?
Quickly stop discharge. If lochia stops occurring earlier than 5 weeks after birth, this is a serious cause for concern. Every woman should know that the functional layer of the endometrium is completely restored no earlier than 40 days after delivery. If the discharge stops very soon after the baby is born, this does not indicate the body’s good ability to recover. Most likely this is due to complications. They are often infectious in nature. However, it could also be cervical spasm. It traps lochia in its cavity, preventing it from coming out. This situation requires an immediate solution, as it leads to serious consequences.
Red color of discharge. 5 days after birth, lochia takes on its color. It can be individual for each woman. But if the discharge remains bright red, as in the first days after childbirth, you urgently need to tell your doctor about it. This may indicate problems such as hematopoiesis or blood clotting problems.
Change in color of lochia. If at first the discharge changed its color from red to brown, and after some time, it turned back to red, this also indicates problems. In most cases, this is due to intrauterine bleeding, which urgently needs to be eliminated. Seeing a doctor in a timely manner will help avoid serious consequences. A repeated change in the color of the blood after childbirth may indicate the existence of a polyp or rupture of soft tissue in the birth canal.
Odor appears
If after some time the discharge begins to have an odor (no matter what), this means that an infection has entered the uterine cavity. It can cause endometritis
By consulting a doctor in time and diagnosing the disease, a young mother can avoid such an unpleasant procedure as curettage. It is carried out when other methods of treatment (taking drugs that suppress the development of microorganisms and forcibly increasing uterine contractions) have been ineffective.
Sources
- https://nashirody.ru/skolko-idet-krov-posle-rodov.html
- https://ginekolog-i-ya.ru/krovotechenie-posle-rodov.html
- https://birth-info.ru/222/afterbirth-Skolko-krov-idet-posle-rodov/
- https://zhenskoe-mnenie.ru/themes/maternity/normalny-li-obilnye-krovianye-vydeleniia-posle-rodov-pochemu-tak-dolgo-ne-zakanchivaiutsia-skolko-idet-krov-posle-rodov/
Treatment of early bleeding
Treatment for hypertensive bleeding is complex and should have two principles. The first is to immediately begin the fight against bleeding with all available means, and these means are applied sequentially one after another. The second group of manipulations are all actions aimed at replenishing the volume of circulating blood. If suddenly the urine was not removed in the third stage of labor, which should be done, then the urine must be removed immediately with a catheter. Next, the midwife performs an external massage of the uterus through the anterior abdominal wall. The fundus of the uterus is covered and circular massaging movements are performed - in no case should force be used. Movements must be very measured because the use of force can only squeeze out the thromboplastic substances that have formed blood clots in the vessels and the bleeding may increase. Therefore, with very careful, pressing movements, the uterus is massaged until the uterus contracts and the bleeding stops. After this, it is imperative to put cold on the woman’s stomach, but this event helps to somewhat reduce blood loss due to spasm of blood vessels on the placental site (cold is applied for 20-30 minutes through a diaper). And of course, at the same time, contracting agents are administered: this is either Oxytocin (1 ml intravenously, and then you can repeat it or add a second ml by dropper) or Orgametril. If there is no desired effect, the next drug will be Dinoprostone (Prepidil) - 0.25 milligrams of this substance are injected intramuscularly or into the cervix. If, after a massage and the introduction of contractile agents, the uterus does not contract or, having contracted, relaxes again, then the next action will be manual entry into the uterine cavity: here a manual examination of the uterine cavity is performed in order to remove blood clots that are attached to the wall and prevent the uterus from contracting and examine whether there is any injury in the uterus. If you are performing a uterine massage, you need to remember that this operation is done very gently - the inner hand is clenched into a fist and most often placed in the area of the uterine fundus (in no case should it be placed on the placental area - it is easy to distinguish them, the placental area is velvety, and the muscles of the uterus are very dense and slightly rough), and with the outer hand the uterus is massaged on the fist. This operation is done very delicately so as not to damage the uterine muscle. Simultaneously with the uterine massage, contractile agents are reintroduced. If manual entry into the uterine cavity does not help, the next method is the so-called clamps according to Baksheev - these are 6 clamps that are applied to the cervix on each side, three clamps (the clamps are left for 3-4 hours, but no more, so as if the terminals remain on the soft tissue of the cervix for a longer period of time, necrosis may occur). Installation of these clamps helps to compress the uterine artery and stop bleeding almost instantly. If all these conservative methods do not help and blood loss reaches 700 milliliters and continues, then the woman is provided with urgent surgical assistance, that is, a laparotomy operation is necessary. The doctor ligates the uterine and ovarian vessels and this often helps stop the bleeding, but it must be said that this is not always effective. In this case, the following operation is performed - ligation of the iliac artery on both sides. This dressing is performed by an experienced surgeon and in this case the operation is quite effective.
If vascular ligation suddenly does not help, then the next method will be supravaginal amputation of the uterus or even hysterectomy if there is a phenomenon of coagulopathy.
The second group of measures is the fight directly against acute anemia: this is replenishing the volume of circulating blood, restoring hypovolemia and directly restoring perfusion and microcirculation in tissues. This is achieved by administering colloidal and crystalloid solutions, plasma preparations, canned blood and fibrinogen. An indicator of the effectiveness of treatment is this condition of the woman. Firstly, the pressure must normalize and stabilize (it must not be lower than 100 mmHg), and the pulse must not be higher than 90 beats per minute. The woman’s skin should turn pink and not be cold, as happens during the first stage of hemorrhagic shock, when the hands and feet are very cold. Then a blood test is performed - the hematocrit should be in the range of 0.35 - 0.4. Trauma to the birth canal can also cause bleeding in the postpartum period. Such injuries are indicated by the presence of a well-contracted uterus and unstoppable bleeding. In this case, you need to examine the birth canal and treat accordingly. Congenital bleeding disorder (congenital coagulopathy) is extremely rare - approximately one to two cases per 10 thousand births, and diseases such as Werlhof's disease, von Willebrand's disease, thrombocytopenic purpura can also cause such coagulopathic bleeding, but they are somewhat more common. But of course, acquired coagulopathy is one that arose during pregnancy. Acquired coagulopathy is associated with premature abruption of a normally located placenta, the presence of gestosis or amniotic fluid embolism. The principles of treatment also include stopping bleeding and replacement therapy with blood products. Now we will talk about late postpartum hemorrhage. Late postpartum hemorrhage is bleeding that occurs one day after birth, but no later than 6 weeks after birth.
Discharge on the 37th day after birth
After the first days, heavy bleeding subsides and is replaced by lighter or brownish discharge mixed with blood clots and mucus, reminiscent of normal menstruation. It is difficult to predict how long the period of such lochia will last. This process is individual in each specific case and depends on the body’s inherent rate of healing and tissue regeneration. In practice, there are cases of complete cessation of postpartum discharge at least a week, maximum 2 months, or 8 weeks after birth.
It is also impossible to say how long the recovery process takes during repeated births, based on the experience of previous ones. Typically these values vary with each subsequent birth. A sign that everything is going well is that bleeding after childbirth gradually decreases in volume, becomes similar to spotting after menstruation, the nature of the discharge is mucous and becomes light in color, with blood clots appearing more and more rarely. The smell is not pungent or putrid.
How to treat
Treatment is prescribed mixed, that is, it is impossible to solve the problem with medications alone; drug therapy is combined with invasive therapy. Even in the maternity hospital, doctors first empty the bladder so that the uterus can contract on its own; for this, a catheter is placed, ice is placed on the lower abdomen, and an external massage is performed. Not all of these activities always help achieve the desired effect.
Sometimes a woman needs a blood transfusion; she may be given donor plasma or red blood cells. If the integrity of the placenta has been compromised, then a procedure for manual cleaning and suturing of wounds formed during childbirth is needed.
In cases where the uterus is severely ruptured, it may be removed so that the woman’s life is not in the balance. During the operation, blood or donor material is transfused and blood pressure is monitored.
Duration of discharge
Each female body is very individual, and the time frame for its recovery after the birth of a child is also different for everyone. Therefore, there cannot be a clear answer to the question of how long discharge lasts after childbirth. However, there are limits that are considered the norm, and everything that goes beyond them is a deviation. These are exactly what every young mother should focus on.
- Norm
The norm for postpartum discharge established in gynecology is from 6 to 8 weeks.
- Permissible deviations
Range from 5 to 9 weeks. But such a duration of discharge after childbirth should not reassure: despite the fact that doctors consider this a minor deviation from the norm, it is necessary to pay attention to their nature (quantity, color, thickness, smell, composition). These descriptions will tell you exactly whether everything is okay with the body or whether it is better to seek medical help.
- Dangerous deviations
Lochia that lasts less than 5 weeks or longer than 9 should be alerted. It is imperative to detect when the postpartum discharge ends. It's equally bad when it happens too early or too late. The indicated periods indicate serious disorders in the body of a young woman that require immediate laboratory testing and treatment. The sooner you consult a doctor, the less dangerous the consequences of such prolonged or, conversely, short-term discharge will be.
You need to know this! Many young mothers are happy when their postpartum discharge ends within a month. It seems to them that they “got off with little blood” and can return to the usual rhythm of life. According to statistics, in 98% of such cases, after some time, everything ends in hospitalization, because the body was not able to cleanse itself completely, and the remnants of postpartum activity caused an inflammatory process.
Deviations from the norm can be acceptable and dangerous. But in any case, they can have serious consequences for the health of the young mother in the future. Therefore, every woman should monitor how long the discharge lasts after childbirth, comparing its duration with the norm established in gynecology. If in doubt, it is better to consult a doctor in a timely manner for advice. Much depends not only on how many days they last, but also on other, qualitative characteristics.
After discharge home
Bleeding in the late postpartum period occurs after discharge home. Its symptoms are similar to the processes occurring during uterine subinvolution. The secretion of lochia suddenly stops, and after a while a cramp-like pain in the abdomen appears. Blood clots come out of the genital tract, causing blood retention in the uterus. After this, heavy bleeding most often begins.
If such symptoms appear, you should immediately seek medical help. Treatment is no longer carried out in the maternity hospital, but in a gynecological hospital. The correct tactic is to scrape the uterine cavity. Oxytocin drips must be prescribed.
It is very important to maintain lactation. The release of a natural hormone during the act of feeding will improve uterine contractility
While in the hospital, milk is expressed.
To continue therapy at home, oxytocin tablets are prescribed.
The development of bleeding in the late postpartum period - a month or 2 months after birth - is an alarming symptom that may be a sign of a placental polyp. This is a neoplasm that occurs in place of the remaining placental villi. They are covered with fibrin clots and connective tissue and initially look like a flat formation. Bleeding is the main symptom of this pathology. Its consequences can be severe anemia, endometritis, sepsis and infertility in the long term.
The diagnosis is made on the basis of ultrasound of the pelvic organs. Further tactics include hysteroscopy, during which you can finally verify the presence of a pathological formation and remove it. In some cases, they are limited to separate diagnostic curettage followed by histological examination of the obtained material.