In what cases and how is the uterus cleansed after childbirth?
After reading mothers’ stories about cleaning after childbirth in Internet forums, I came to the conclusion: the less you know, the better you sleep.
But then, upon reflection, I realized that the information from the forum was not enough for a sound sleep. Naturally, cleaning after childbirth is an unpleasant ending to the most important moment in a woman’s life, and those who have experienced this condition are sometimes unable to contain their emotions, so their stories may be classified as “not for the faint of heart.” And we will add: not for pregnant women. In order not to be afraid of postpartum cleansing (after all, it does not mean at all that you will need it), you need to get as much information about it as possible, but medical information, and not “from personal experience.”
Technique of the procedure
If a procedure for cleaning the uterus is required after childbirth, it is practically no different from that during an abortion. The operation is performed under local or general anesthesia, so the woman does not experience pain. How to clean the uterus after childbirth? The algorithm is as follows:
- The external genital organs are treated with aseptic solutions; you can use a solution of iodine or ethyl alcohol.
- A speculum is inserted into the vagina to expose the cervix.
- The doctor fixes the neck by the front lip and expands the cervical canal if it has already closed.
- A curette is used to remove blood clots and placental debris from the uterine cavity.
The duration of the procedure is 15-20 minutes.
In rare cases, during the procedure for separating the placenta from the walls of the uterus, bleeding occurs, and only complete removal of the uterus can save a woman’s life.
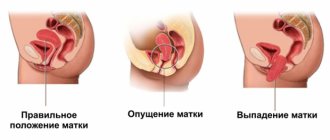
When does it become necessary to cleanse after childbirth?
Each woman gives birth twice (in one visit to the maternity hospital): a baby and the placenta (afterbirth), with which he was kept for all 9 months. Many women do not even notice the birth of the placenta, since at this time they are already busy looking at the baby, who has buried his small nose in the mother’s chest. But this does not always happen, unfortunately. Sometimes the placenta is too tightly “fused” with the uterus and is born “partially” or does not come out at all, then manual separation of the placenta should be performed, which is always carried out after a cesarean section.
Before discharge from the maternity hospital (on days 2-3), the woman undergoes a diagnostic ultrasound to assess the condition of the internal cavity of the uterus. If the doctor finds traces of placenta or blood clots in the uterus, then the woman in labor is prescribed a cleaning.
Indications
Curettage of the uterine cavity is the removal of mucous from the inner wall. Among medical personnel, the procedure is called curettage. Previously, to carry it out, they used a special device, a curette, resembling a spoon.
Why is it done:
- solving gynecological problems that require additional examination;
- elimination of diseases associated with women's health through surgery.
This leads to 2 directions:
- diagnostic;
- therapeutic.
Postpartum curettage is carried out to remove the remains of the child's place from the genital organ. These include a child's place, blood clots. Cleaning is carried out immediately or a couple of days after the end of labor. It allows you to avoid the inflammatory process, the walls of the uterus contract freely.
Sometimes they need curettage to perform an abortion. This procedure is necessary for frozen, abnormally developing fetus. When an ultrasound shows a stalled pregnancy, cleansing should be done immediately.
During the manipulation, mechanical removal of the remaining placenta in the uterus after childbirth occurs. The new mucous membrane soon grows from the germinal layers of the endometrium. Before carrying out the procedure, it is necessary to take into account contraindications. The main ones are an active inflammatory process, diseases of the internal organs, 3 – 4 degrees of vaginal cleanliness.
Is it possible to do curettage for nulliparous women? The diagnostic cleaning procedure is not considered dangerous. It does not interfere with the reproductive functions of the female body. Therefore, curettage is done for the nulliparous woman.
Is it possible to give birth after curettage? Yes. A woman can become pregnant during the procedure. However, the body needs to get stronger and recover. Therefore, you should plan to conceive a child no earlier than 3–6 months after cleansing.
How to cleanse after childbirth?
“Cleaning” in “medical language” means scraping. This procedure may be familiar to women who have had an abortion. Curettage of the uterine mucosa is an operation in which mechanical removal of the functional layer of the endometrium is performed. A new mucous membrane grows from the germinal layers of the endometrium soon after curettage.
Typically, cleaning is carried out under general anesthesia in a gynecological chair. Before the operation, the external genitalia are treated with a 5% alcohol solution of iodine, and the vagina and cervix with 50% ethyl alcohol. Using inserted dilators of various diameters, the cervical canal is expanded and the remaining placental tissue is removed using a special blunt curette or an obstetric curette with teeth. The operation lasts no more than 20 minutes.
Consequences of cleaning the uterus
If the doctor has prescribed cleaning of the uterus, then undergoing the procedure is mandatory, since complications will occur not because of the cleaning, but because of the refusal to undergo it. After the operation, the endometrium (inner mucous membrane of the uterine body) will gradually recover. The uterus will be covered with a new healthy layer of epithelium.
However, the consequences of cleaning the uterus cannot be completely excluded. In some cases, the following may occur:
- uterine bleeding. This phenomenon occurs rarely after cleaning. It usually affects women who have previously had problems with blood clotting;
- hematometers - retention of liquid blood or blood clots in the genitals. This pathology after cleansing is quite rare and occurs due to severe compression or spasms of the muscles of the cervix or vagina. To avoid hematomas, obstetricians-gynecologists can prescribe Aspirin or No-shpu. These drugs help relieve muscle spasm, ensuring free cleansing of the female genital organ;
- endometritis - inflammation of the inner layer of the uterus. It can occur due to the penetration of bacteria and microbes into the wounded surface of the uterus. To exclude the occurrence of endometritis, it is necessary to take a course of antibiotics.
With proper and delicate cleaning, the risk of negative consequences after the procedure is reduced to zero. Therefore, you should not be afraid of the operation and its consequences. Agree to medical intervention.
How to behave after cleaning?
After cleaning, a woman should be under the supervision of doctors who monitor body temperature, pulse rate, and discharge from the genitals. The external genitalia should be treated with antiseptic solutions 2 times a day.
After the operation, you cannot use vaginal tampons, douche, take a bath, go to the sauna, lift weights, or play sports for 2 weeks. Vaginal sex is also contraindicated due to the fact that the cervix remains open and there is large erosion on the uterine mucosa, which can become favorable conditions for the development of an infection that can be “introduced” by a sexual partner.
Why is cleaning done?
If the natural cleansing process is disrupted, then doctors have to intervene. Curettage of the uterus after childbirth will be required if:
- Lochia has stopped secreting due to cervical spasm, and blood accumulates inside. This leads to an increase in body temperature and pain during examination.
- Particles of the baby's place remain on the walls of the uterus or in its cavity. This usually happens if for some reason its integrity has been violated.
- Blood clots are difficult to pass out.
Remains of the placenta or blood clots can provoke an inflammatory process, and also lead to blood poisoning and tissue necrosis due to the onset of the rotting process. Any particles in the uterus are perceived by the body as foreign, which forces it to spend its precious energy, which is depleted after childbirth, to get rid of them.
Recovery after the birth of a baby is delayed and the risk of infection increases. To avoid all this, manual cleaning of the uterus is carried out.
What complications can there be after cleaning?
Hematometra is precisely a common complication of curettage. It can occur due to strong compression (spasm) of the cervix, which will cause blood to be retained in the uterine cavity. The rapid cessation of bleeding is the main symptom of hematometra. To support the cervix in a relaxed position, No-shpa is prescribed, as mentioned above.
Another complication of cleansing is uterine bleeding, but this is extremely rare (mainly only in women with bleeding disorders). But if microbes penetrate into the uterine cavity after cleaning, endometritis may occur - infections and inflammation of the uterine mucosa.
All complications require specific treatment, which can only be prescribed by the attending gynecologist. “Ideally,” after cleansing, there is heavy bleeding with clots for several hours, but soon they become less abundant. After curettage, scanty spotting, bloody, brown or yellowish discharge should be observed for at least 10 days.
As you can see, cleaning after childbirth is not so scary if you follow simple rules of personal hygiene and doctor’s instructions. Therefore, there is no need to worry! Everything will be okay!
Consequences and complications
Despite the fact that the procedure for vacuum cleaning of the uterus is considered the safest after childbirth, it can provoke the appearance of some complications, since due to the removal of the upper layer of the epithelium, the risk of infections, the development of inflammation, and bleeding increases.
Among the main consequences of the operation are:
- the appearance of bleeding, which can provoke the development of anemia;
- menstrual irregularities;
- inflammatory diseases after infection attaches to the wound surface;
- formation of adhesions and scar tissue;
- fusion of uterine tissues;
- development of isthmic-cervical insufficiency due to damage to the cervix;
- loss of ability to bear a subsequent pregnancy;
- infertility.
The onset of pathology after childbirth can be recognized by the appearance of the following symptoms:
- increase in body temperature to 39.9 degrees;
- the appearance of vaginal discharge that has a yellowish, greenish color and an unpleasant odor;
- the presence of severe bleeding, in which the woman must change the postpartum pad every 2–3 hours;
- absence of any discharge on days 2–3 after surgery;
- the appearance of severe pain in the lower abdomen;
- presence of dizziness, chills.
If these symptoms or complications appear, a woman needs to urgently consult a gynecologist.
Vacuum aspiration of the uterine cavity from clots after childbirth
During childbirth, different situations happen. And in some cases, surgery cannot be avoided. When there is a bad contraction and does not come out, or the afterbirth does not come out well, blood clots remain, vacuum cleaning is used after childbirth. This procedure cannot be avoided, because sometimes a woman’s life depends on it.
With the modern level of medicine, this procedure is more gentle. It can also be used for diagnosis and treatment.
There is an opinion that vacuum aspiration of the uterine cavity is used only to terminate pregnancy, but this is far from the case. It is used for heavy bleeding, removal of clots, biopsy analysis, after a miscarriage, fetal death, to remove remnants of the placenta and fluid accumulations.
But today we will not consider all the situations in which this intervention is prescribed. Many young mothers are interested in why, after visiting the ultrasound room, the obstetrician-gynecologist prescribes curettage after childbirth. It would seem, what does the birth of a child have in common with this unpleasant procedure? But not everything is as good as we would like. Let's dwell on this issue.
The main reasons for prescribing aspiration after an ultrasound examination are retention of blood clots, remnants of the placenta (if it does not contract well enough). But they don’t prescribe it right away. First, you need to undergo a course of treatment with contracting drugs (injections or droppers). And when this does not help, then only aspiration is performed.
The fact is that if a foreign body is present in the uterine cavity after childbirth, this will lead to inflammation and suppuration. And if you do not intervene in time, blood poisoning will begin, and as a result, death will occur. Therefore, if you were not examined by a specialist upon discharge, contact a gynecologist yourself.
Complications and consequences after uterine curettage
As with any other operation, complications are possible. Complications can be early or late. Early complications include:
- bleeding due to damage to a vessel located in the wall of the uterus; in this case, heavy bleeding may be from the genital tract, or may manifest itself in the form of hemometra - accumulation of blood in the uterine cavity due to the closure of the exit from the cavity; To prevent hemorrhage, antispasmodics are prescribed - medications that relieve spasms of smooth muscles;
- perforation (violation of the integrity) of the uterine wall with a sharp instrument - a small puncture can heal on its own, but a large one is sutured; As a rule, there are no unpleasant consequences.
These consequences are eliminated on the operating table or with repeated surgery within the first 24 hours. Modern clinics have every opportunity to cope with such consequences.
Hormonal disorders and disruption of the menstrual cycle can be a consequence of too deep curettage of the walls, when not only the upper functional (regenerating) layer of the endometrium is removed, but also the lower, basal layer, which cannot be restored. This complication is difficult to treat and most often causes infertility.
Childbirth is a complex and step-by-step process. Sometimes it happens that the birth of a child is only a small part of what the expectant mother has to endure.
Quite often, the gynecologist prescribes uterine cleaning
after childbirth. Patients get scared and wonder why this is necessary. However, everything is not so simple here. This procedure is carried out if the placenta has separated in pieces or has not come out of the uterine cavity at all.
For some women, it is enough to stimulate muscle contractions with oxytocin or other hormones to release the afterbirth. For the rest, there is nothing more reasonable than to carry out vacuum or manual scraping
.
Complications
Curettage after childbirth can bring a number of complications that cannot be predicted.
- It is normal to have a lot of bleeding in the first few days after this procedure. But if there is too little or no discharge, this indicates that not all clots have been removed. Don’t delay, contact a specialist as soon as you notice something wrong.
- Injury to the cervix or its walls. This may lead to subsequent pregnancies ending in spontaneous abortion. The fact is that the cervix will not be able to perform its function during pregnancy. The situation can be corrected by stitching or installing a pessary.
- Obstruction of the tubes or adhesions will lead to difficulties with conception.
- Hormonal imbalance.
- Infection and subsequent inflammation.
- Sepsis.
Is cleaning required?
After the baby is born, the placenta comes out after some time. The doctor must examine it for integrity. If the baby's place is completely separated and the midwife is sure that there are no residues left in the uterus, then a heating pad with ice is placed on the woman's stomach to speed up the process of uterine contractions.
Over the course of several days, mothers are also given injections of Oxytocin to better contract the uterus and return it to its original prenatal state. Every day during the examination, the doctor feels the mother's abdomen and inquires about the pain of the uterus and the speed of its contraction.
Approximately 5 days after birth, an ultrasound is performed; if the results show that the process of contraction and cleansing is proceeding normally, then curettage of the uterus is not required.
Recovery after surgery
It is necessary to temporarily avoid hot baths, visiting baths and saunas, and excessive physical activity (weight lifting, sports training).
not recommended - vaginal intercourse can provoke the development of repeated uterine bleeding or introduce infection into the woman’s genitals.
To prevent stagnation of contents in the uterus, any antispasmodic drug can be prescribed in , but when taking No-shpa, and when using Papaverine, and any analogue of these drugs, breastfeeding is prohibited due to the undesirable toxic effect of this group of medications on the child’s body.