What is the cause of infertility in women?
The main causes of infertility in women:
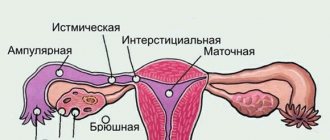
- obstruction of the fallopian tubes, which is the result of adhesions. In this case, they talk about female infertility of tubal origin;
- adhesions in the pelvis, as a result of operations or an inflammatory process. Adhesions may be located between the tube and the ovary, which prevents the egg from entering the tube;
- endocrine (hormonal) disorders, as a consequence of pathology of the ovaries and other endocrine glands (hypothalamus, pituitary gland, thyroid gland, adrenal glands). With various hormonal disorders, hormonal infertility in women is diagnosed;
- congenital and acquired pathology of the uterus: intrauterine septum, bicornuate uterus, scars on the uterus after operations, endometritis, uterine fibroids, adenomyosis, polyposis;
- endometriosis as one of the causes of infertility in women. Foci of endometriosis form adhesions that cause tuboperitoneal infertility.
There are other reasons for female infertility - this is a chromosomal pathology that leads a woman to sterility. What else causes infertility in women? In 5-8% of cases, the presence of an immunological factor (antisperm antibodies) causes immunological infertility in women. The reasons for psychological infertility in women are a woman’s reluctance to have a child due to fear of pregnancy and childbirth, reluctance to have a child from a given man, etc.
Examination of a couple for infertility
Infertility due to the female factor is registered in 45% of cases, due to the male factor - in 40%, the rest of the causes of infertility are due to both male and female pathologies.
If an infertile couple comes to see a reproductologist, a specific diagnostic algorithm is prescribed:
- the man is prescribed a sperm analysis and, in the absence of pathology, no other measures are taken at this stage;
- postcoital test (diagnosis of the immune form of infertility);
- two-stage examination of a woman.
At the first stage, methods are used to exclude three common female diseases: ovulation disorder, tubo-peritoneal factor, infectious and inflammatory processes of the reproductive tract. This diagnostic stage consists of a standard set of minimally invasive techniques.
Primary diagnosis of infertility in women, the stages of which are divided into blocks, includes:
- Study of anamnesis and clinical data.
- Infectious screening: vaginal smears for purity, bacterial culture, PCR examination of a cervix smear for chlamydia, urea and mycoplasma, herpes simplex, CMV, HPV, as well as blood for antibodies to toxoplasma.
- Hormonal screening: on day 2 with short cycles, on days 2-5 (with a 28-32 day cycle), on days 6-9 (with a cycle length of 35 days) donate blood for sex hormones, including FSH, LH, estradiol, free testosterone, prolactin, DEA sulfate, 17-OH-progesterone. To determine the level of progesterone, blood is examined on the 7th day after ovulation proven by ultrasound.
- Ultrasound diagnosis of diseases of the mammary glands, pelvic organs, thyroid gland, adrenal glands.
In the absence of menstruation, blood is donated for hormones any day.
Primary diagnosis and treatment of infertility identified by research in women involves normalization of hormonal balance, removal of pathological formations, and vitamin therapy.
Diagnosis at the second stage is always individual. The set of methods usually includes studies based on identified pathologies during the first stage of infertility diagnosis, and also includes:
- tests that detect genetic abnormalities (karyotypes, determination of HLA compatibility of partners);
- blood tests for hemostasis mutations, thrombophilia, antiphospholipid syndrome;
- instrumental diagnostic methods (MRI of the sella turcica, laparoscopy, hysteroscopy, hysterosalpingography).
48% of infertile women are diagnosed with 1 infertility factor, and 52% have more than two.
If, during the diagnosis of infertility, diseases that cannot be fully cured are identified, for example, ovarian wasting syndrome, severe endometriosis, asthenozoospermia, false aspermia, azoospermia, bilateral adhesions in the tubes, the couple is offered IVF or artificial insemination.
https://youtu.be/30B7c_1pMaY
Types of infertility in women
There is absolute infertility in women, which is associated with irreversible pathological conditions, which means that a woman will never be able to become a mother. For example, a woman may not have ovaries, fallopian tubes, or a uterus. Relative female infertility is temporary, treatable, and if the cause is eliminated, a woman can give birth to a child.
There are also degrees of infertility: 1st degree infertility in women (or primary infertility in women) and 2nd degree infertility in women (or secondary infertility in women). Primary infertility in women is said to occur if a woman has not had a pregnancy at all. Secondary infertility in women is a condition when there are currently problems with conception, but there was a pregnancy before.
Secondary infertility in women occurs in 40% of cases. The most common causes of secondary infertility in women are abortions, adhesions and gynecological diseases. Therefore, secondary infertility in women is considered as a complication of gynecological diseases and surgical interventions. Secondary infertility in women is often associated with tubal or peritoneal factors.
Where to start: screening for infertility for women and men
Infertility can be associated with various disorders of the reproductive function of both men and women. Before conducting instrumental or ultrasound diagnostics of the internal genital organs, the doctor examines the medical history of each spouse. It is important to evaluate both lifestyle, which can affect the possibility of conception, and past illnesses or surgery.
There is also such a factor as incompatibility of partners. In order to determine whether this is the cause of infertility, the couple takes a post-coital test, as well as blood to determine the Rh factor.
Many people ask when women should be tested for infertility. Experts are unanimous in this opinion and note that after a year of regular sexual activity without contraceptives and no conception occurring, it is worth considering conducting a study. Although, according to the reviews of the women themselves, you should not be guided so much by this particular time of 12 months.
Initially, the woman undergoes tests, including a smear on the flora, which can reveal the presence of inflammatory processes, viruses or infections. Representatives of the fair sex are also prescribed an ultrasound of the pelvic organs. Ultrasound can reveal pathologies in the development or location of the internal genital organs, especially the uterus and its appendages. If all these tests do not reveal any problems in the woman’s health, then the sexual partner is diagnosed.
For men, it is worth starting with a spermogram analysis. According to women's reviews, men are reluctant to agree to the procedure, but with the help of this analysis it is possible to determine whether there are viable sperm and in what quantity they are.
Female infertility: symptoms
Symptoms of infertility in girls attract attention during puberty: congenital pathology of the genital organs, late onset of menstruation, a long menstrual cycle, scanty and irregular periods. Symptoms of infertility in girls can be suspected by the lag in physical (low weight) and sexual development.
The first signs of infertility in women are menstrual irregularities. These are scanty or heavy, irregular and excessively painful periods.
Signs of infertility in women include the appearance of acne and oily skin - this indicates an excess of male hormones. Signs of female infertility appear in changes in the hairline. Excessive hair growth on the chin and chest may indicate an excess of male sex hormones. Insufficient pubic and armpit hair growth will occur as estrogen levels decrease. Signs of female infertility include milk production in non-breastfeeding women. Increased levels of the hormone prolactin suppresses ovulation, resulting in infertility.
Since infertility in women is caused by various pathological conditions, certain symptoms will dominate the clinical picture. Thus, polycystic ovary syndrome is the absence of menstruation and ovulation, obesity, hypertrichosis. With endometriosis, a woman complains of painful periods. Symptoms of the underlying disease, which causes infertility in women, facilitate differential diagnosis and establishment of a final diagnosis.
Postcoital test
Where to take tests for infertility in men and women, as well as which ones, is determined by the doctor. Diagnostics can be done in a private clinic or public medical institution if the necessary modern equipment is available.
Quite common in Russia, but considered ineffective in European countries, is the postcoital test. The method can identify the causes of infertility in both men and women. Its essence lies in examining mucus under a microscope, which is collected several hours after sexual intercourse. The test can determine whether a woman has enough mucus after intercourse, its quality, and whether there are live sperm in it. If the sperm count is insufficient or most of them are immobilized, this may indicate poor sperm quality.
Recently, there are many methods and invasive techniques that are used instead of the postcoital test as an analysis for infertility in women and men.
How to determine infertility in women. Diagnosis of infertility in women
Diagnosis of female infertility begins with a survey and collection of information about the woman’s gynecological health. To diagnose female infertility, the nature of menstrual function is important: the time of arrival of the first menstruation, the regularity, duration and pain of menstruation, the presence of discharge from the mammary glands. In diagnosing female infertility, the presence and number of pregnancies, if any, and how they proceeded are important. The history of infectious and gynecological diseases in the woman and the hereditary factor in the mother are determined.
How to check for infertility in women? The most common functional tests for infertility in women are:
- analysis of basal temperature, which allows you to assess ovarian function and the presence of ovulation;
- determination of the cervical index, which reflects the saturation of the body with estrogen;
- postcoital test to study the activity of sperm in the contents of the cervix, as well as to determine antisperm bodies.
Testing for infertility in women necessarily involves examining the levels of hormones in the blood and urine. When checking for infertility in women, the following hormonal studies are informative: DHEA-S and 17-ketosteroids in the urine, prolactin, testosterone, thyroid hormones, cortisol, follicle-stimulating progesterone, luteinizing hormones, estradiol in the blood plasma. In case of infertility, screening for sexually transmitted infections is of particular importance.
Lab tests
An infertility test for women is a set of laboratory tests and diagnostic procedures aimed at identifying the cause of infertility. When you first contact a doctor, a medical history is collected and the patient is thoroughly examined. At this stage of the examination, the specialist assesses the condition of the woman’s reproductive organs for erosion and inflammatory processes. Further activities are related to instrumental and laboratory methods.
- Blood analysis. The study of clinical and biochemical blood parameters is necessary to determine the general state of health. The amount of total protein, bilirubin, ALT, AST, creatinine, urea and glucose is determined in the patient’s blood. Blood is also tested for infections and viruses: syphilis, hepatitis, HIV. To exclude an endocrine cause of infertility, tests are performed to determine the level of hormones: prolactin, AMH, FSH, LH, progesterone, TSH, 17-OPA, testosterone and others. Hormone testing should be carried out on the 2-5th day from the start of menstruation. Separately, blood is donated to determine the group and Rh factor.
- A general urine test is prescribed to determine the functional functioning of the kidneys.
- Tests for sexually transmitted infections. Very often it is not possible to get pregnant due to the presence of infections in the woman’s body. Infectious damage to the mucous membrane of the cervix and uterine cavity creates unfavorable conditions for the development of pregnancy. To identify them and subsequently treat or exclude this problem, several tests are prescribed. Most often, such tests reveal diseases that are initially asymptomatic: gonorrhea, herpes virus, chlamydia, trichomoniasis, ureaplasmosis. In addition to the blood test, smears are taken from the vagina and cervical canal.
- Postcoital analysis - determination of the number of sperm and their motility in the cervical mucus of the cervix. This important research shows the ability of sperm to interact with the egg. For fertilization to occur, conditions are necessary for sperm to penetrate through the cervical mucus. It is best to carry out the test during the periovulatory period of the cycle; before the examination, the presence of sexually transmitted infections should be excluded. We recommend the Kurzrock-Miller test.
After laboratory tests, the woman is prescribed instrumental studies.
Treatment of female infertility
The decision on the treatment of female infertility is made after assessing the results of examinations and establishing the causes of infertility.
In cases of endocrine infertility in women, correction of hormonal disorders is carried out, so the basis of drug treatment is hormonal therapy. Hormonal treatment is selected for the woman, and the treatment process is monitored by the dynamics of hormone levels in the blood. For tubo-peritoneal infertility, treatment is aimed at restoring the patency of the fallopian tubes. The operation is performed using laparoscopy.
In case of endometriosis, pathological foci are removed using laparoscopic coagulation. The result of laparoscopy is confirmed by a course of drug correction of hormonal levels. Immunological infertility in women is overcome by artificial insemination with the husband's sperm, bypassing the immune barrier of the cervical canal.
Instrumental studies
These tests are carried out using specialized equipment and can confirm the suspected diagnosis.
- 1. Ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs. The method allows you to visually determine the cause of infertility, which may be neoplasms of the reproductive organs. Using ultrasound you can find out:
- cervical condition;
- size and condition of the uterus;
- condition of the ovaries;
- structure and condition of the endometrium;
- condition of the fallopian tubes.
During the examination, you can identify polyps and cysts that interfere with getting pregnant. In addition to neoplasms, ultrasound helps diagnose hydrosalpinx - the presence of fluid in the fallopian tubes. Elimination of these pathologies is a step towards treating infertility. It is better to conduct the study in phase I of the cycle.
- 2. Sonohysterography (Echo-HSG) is a method of ultrasound checking the condition of the endometrium and patency of the fallopian tubes using saline solution. It is carried out on days 6-14 of the cycle (can be carried out on any day, but in the second phase of the cycle the presence of an already existing pregnancy cannot be ruled out).
- 3. Hysterosalpingography (HSG) – an image of the pelvis and using contrast, displaying the uterus from the inside, as well as capturing the fallopian tubes. Provides information about the condition of the endometrium, tubes and their patency. It often makes it possible to judge the presence of adhesions in the pelvis. Can be done on any day except the days of menstruation (it is better not to plan pregnancy for this cycle).
- 4. Laparoscopy is the most accurate and fastest method of studying the condition of the pelvic organs and the causes of infertility. Allows you to visually examine the pelvic organs, check the patency of the tubes, and dissect adhesions. It is performed under anesthesia and does not require a long hospital stay. Before consenting to surgery, we recommend consulting a fertility specialist, especially in cases where childbearing is planned in the future. It is carried out in the first phase of the menstrual cycle.
- 5. Hysteroscopy with endometrial biopsy: visual examination of the uterine cavity and taking a sample of the uterine mucosa (endometrium) for histological examination to identify pathology. Allows you to most reliably identify changes in the uterine cavity and cervical canal and conduct targeted histological diagnostics. Before the procedure, you must abstain from sexual intercourse and vaginal medications. It is carried out in the first phase of the menstrual cycle, after the end of menstruation and before the 10th day.
The full list of tests for IVF can be found here.
Tests for infertility in women in our clinic are carried out as quickly as possible and are accompanied by the necessary consultations with specialists. Once the cause is identified, based on the test results obtained, a diagnosis is made and treatment is prescribed.
| Name of service | Price |
| Initial consultation with a gynecologist-reproductologist | 3,000 rubles |
| Initial consultation with a gynecologist-reproductologist with ultrasound | 3,900 rubles |
| Repeated consultation with a gynecologist-reproductologist | 1,300 rubles |
| Repeated consultation with a gynecologist-reproductologist with ultrasound | 2,200 rubles |
| Initial consultation with an obstetrician-gynecologist | 2,400 rubles |
| Repeated consultation with an obstetrician-gynecologist | 1,900 rubles |
| Ultrasound of the pelvic organs | 1,500 rubles |
| Abdominal ultrasound | 2,100 rubles |
| Ultrasound of the prostate and bladder | 1,600 rubles |
| Ultrasound of the kidneys and bladder | 1,800 rubles |
| Ultrasound of the kidneys, prostate and bladder | 2,000 rubles |
| Ultrasound of the thyroid gland | 1,600 rubles |
| Ultrasound of the mammary glands | 1,800 rubles |
| Ultrasound of lymph nodes | 1,250 rubles |
| Colposcopy | 1,400 rubles |
| Office hysteroscopy | 17,500 rubles |
| Diagnostic hysteroscopy (without the cost of histological examination) | 19,500 rubles |
| Operative hysteroscopy (without the cost of anesthesia and histological examination) | 24,500 rubles |
Prevention of female infertility
It would be appropriate to talk about the prevention of male and female infertility, since male infertility is observed in 50% of cases of infertile marriages.
In the prevention of male and female infertility, the leading place is occupied by the prevention and timely treatment of inflammatory diseases of the genitourinary system, as the main cause of infertility. This is especially true for sexually transmitted diseases.
Compliance with the basic rules of hygiene and sexual hygiene is of particular importance. It is the presence of promiscuous sex life, frequent changes of partners and sexual intercourse without the use of protection that lead to the occurrence of diseases of the genital area.
Prevention of female infertility consists in the prevention of gynecological diseases, therefore, sexual activity during menstruation, unauthorized use of contraceptives, and douching with chemicals are unacceptable. Do not forget about the consequences of abortion, as the main cause of infertility.
The topic of “infertility in women” is often raised on the forum. As you yourself understand, information is often shared by persons who do not have a medical education. When visiting the “female infertility” forum, you cannot self-medicate and “try on yourself” the suggested recipes. To become more fully familiar with the topic that interests you, you can read an essay on the topic “female infertility” written by a specialist.
Female infertility is such a pressing problem for some couples that they undertake any treatment options: from medical, for example, treatment of female infertility in Israel, to making requests and prayers to higher powers.
It is known that there are “places of power” on earth, after visiting which a person improves his health. The power of these places is often associated with extraordinary natural phenomena. And temples and monasteries give the power of “prayed” places. Such a place is the Murom Convent, which is visited by women diagnosed with infertility and dreaming of becoming a mother. It is believed that pilgrims who fall before the relics of Saints Peter and Fevronia in this monastery receive healing from infertility.
Giving birth and raising a child is the main purpose of a woman. When it is not possible to get pregnant for a long time, thoughts arise about her or the man’s infertility. In this case, it is important to understand the situation.
Diagnosis of male and female infertility
Methods for diagnosing infertility
Diagnosis of infertility is the initial and one of the most important stages of preparation for IVF. The future possibility of making the only correct diagnosis that stands in the way of a woman to motherhood depends on the set of examinations and tests prescribed by the doctor. Our Clinic uses modern and effective methods for diagnosing infertility, which allow the patient to obtain a complete clinical picture of his reproductive health with minimal investment of time and money.
Diagnosis of infertility in the clinic consists of:
— Gynecological examination (involves examining a woman in a gynecological chair and taking a smear).
— Ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs (during the entire period of infertility treatment, not to mention the subsequent onset of pregnancy, a woman may often need to undergo an ultrasound examination. This is necessary both to examine the pelvic organs for the presence of pathologies, to check the reaction of the reproductive system to the therapy, and, for example, during puncture of follicles as part of one of the stages of IVF).
— Hormonal examination (a wide range of peripheral blood tests for hormones are performed, including the express method). Diagnosis of infertility is not the only reason why it is necessary to conduct a hormonal examination of a patient. Firstly, if infertility is not confirmed, information about hormonal levels will be needed for subsequent treatment of identified abnormalities. Secondly, if the patient needs an in vitro fertilization procedure, which involves hormonal stimulation of superovulation, the doctor will need to know the state of the patient’s endocrine system in advance.
— Examination for the presence of a chronic infection (tests for sexually transmitted infections (blood tests using ELISA and PCR methods, smears using the PCR method). This examination must be completed in order to exclude the presence of an infectious disease in partners, and also so that in the event of subsequent pregnancy treatment to protect the unborn child from negative consequences.
— Endoscopic methods for diagnosing infertility (hysteroscopy, laparoscopy). Today, these methods of diagnosing infertility are the safest for the patient and effective for the doctor, who receives all the necessary information without resorting to major surgery. The purpose of laparoscopy and hysteroscopy is to identify abnormalities in the anatomy of the female genital organs that prevent pregnancy and/or pregnancy. Some of these anatomical changes can be eliminated, which increases the chances of a spontaneous (natural) pregnancy. When irreversible changes are detected, laparoscopy allows one to avoid obviously ineffective measures aimed at restoring natural fertility. With hysteroscopy , in most cases, it is possible to carry out therapeutic surgical measures to restore or improve the functional potential of the uterine cavity and cervical canal. In addition to the treatment of infertility, hysteroscopy is the only accurate diagnostic method in the treatment of intrauterine pathology.
— Microbiological studies (cultures on the flora of sperm, discharge from the urethra and cervical canal with determination of sensitivity to antibiotics; smear for the degree of purity from the vagina).
— Cytological and histological studies (endometrial biopsy; colposcopy; cytological examination of cervical smears).
— Immunological examination (examination for the presence of antisperm and antiphospholipid antibodies; anti-hCG). This specific examination is prescribed when the doctor suspects possible immunological incompatibility of partners.
— Examination of men (detailed spermogram, examination by an andrologist, ultrasound, hormonal and infectious examination, MAR test of sperm, sperm test). Diagnosis of a man's infertility should be carried out in parallel with examinations of his wife, since a long absence of pregnancy can be associated with both female and male factors of infertility equally.
— Other examinations (clinical blood test and general urine test, determination of blood group and Rh factor, anti-Rh antibodies, coagulogram, biochemical markers, tumor markers and much more).
Tags: hysteroscopydiagnostics and treatment of infertilityeco
Female infertility
Types of disease
The following forms of infertility are distinguished:
- Primary, in which the woman has never been pregnant.
- Secondary – the woman was pregnant.
- Relative - there are diseases that need to be eliminated for conception to occur.
- Absolute – the disease that causes infertility is incurable.
Infertility is divided into types depending on the organ that is affected:
The last type is especially important, since its development is provoked by the thoughts of a woman who really wants a child, or, conversely, is afraid of getting pregnant. This leads to disruptions in the body that prevent the fertilized egg from implanting.
Symptoms and causes
How to determine infertility? The first signs of the disease appear in adolescence. First of all, the problem is indicated by menstruation, which began late, an interrupted or prolonged cycle, pain during menstruation, scanty discharge. Another reason is congenital abnormalities of the uterus and fallopian tubes, as well as weight loss as a result of diets, etc.
The provoking factor is inflammation of the reproductive organs, sexually transmitted infections, the presence of only one ovary, hormonal imbalances, tubal obstruction and chromosomal disorders.
Regular ovulation is an important component of women's health. In 25% of women, disruption of this process causes infertility. Regular menstruation does not mean that ovulation is occurring and it is complete. You can check for ovulation at home by measuring your basal temperature daily. It tends to increase and persist for a couple of days after the follicle ruptures. A few days before menstruation, it decreases, but this happens unless the woman becomes pregnant.
Procedures for diagnosing infertility
- general examination of the patient to identify conditions that negatively affect the function of childbearing,
- examination by a gynecologist,
- detection of infections: syphilis, AIDS, hepatitis B and C, etc.
- bacteriological and clinical tests identifying sexually transmitted infectious agents,
- study of hormone levels in the blood (AMH, LH, FSH, Prolactin, Estradiol, T-3, T-4, Cortisol, STH, TSH, Progesterone),
- Ultrasound to assess the condition of the tubes, uterus and ovaries. It is carried out using transvaginal and, if necessary, transabdominal sensors,
- endometrial biopsy followed by histological and immunohistochemical examination of the obtained material,
- hysteroscopy to detect and eliminate intrauterine pathology,
- laparoscopy – diagnosis of the genital organs through the abdominal cavity
- sonohysterography - ultrasound examination of the patency of the fallopian tubes and uterine cavity with fluid administration
Important! Do not conduct any further research on the woman, except for collecting anamnesis, general and gynecological examination, determining hormone levels, in the absence of results of examination of the partner and his spermogram. This is due to the fact that achieving pregnancy in severe forms of spermatogenesis disorders is carried out only with the help of IVF methods and their modifications. In these cases, a detailed study of the woman’s reproductive system is not advisable.
Diagnosis of infertility is very important; it provides specialists with extensive information about the state of the body of both partners. Based on the information received, the doctor draws up a well-thought-out program, which will include only effective treatment methods that are suitable for each specific case. The specialist’s recommendations depend on the data obtained during the examination - how to effectively and quickly achieve the desired result with less moral and material costs. Nowadays, patients can choose a variety of medical institutions where infertility diagnosis and treatment is carried out. Moscow and other large cities in Russia can boast of having quite a large number of centers where these problems are dealt with. We recommend contacting Professor Zdanovsky’s clinic, which has been successfully treating infertile couples for decades. Experience, constant improvement of qualifications and scientific knowledge of our doctors allow us to achieve success even with the most difficult cases of infertility. Our motto: We will do everything in our power for you.
Male infertility
If the examination does not reveal any pathology in a woman, we are talking about male infertility. Many men believe that an erection indicates the absence of health problems. But they are wrong.
Diagnosis of infertility in men begins with a spermogram: a study is carried out by an andrologist who performs a sperm analysis. If there are no sperm in the ejaculate, a spermatogenesis disorder is diagnosed. Such infertility is considered secretory. Another option is that sperm are produced, but they do not penetrate the vas deferens. In this case, it is obstructive infertility. Bilateral genitography helps to check for obstruction of the ducts.
Agglutination (gluing of sperm with antibodies) may be detected on the spermogram, which indicates an autoimmune disease in men. In this case, the sperm are devoid of motility and cannot fertilize the female egg.
The diagnostic component in determining the causes of infertility is of great importance, so men must follow the rules established when donating sperm. It is recommended to abstain from sexual activity for several days before the examination. During this period, you should not take medications, alcohol, or coffee. It is better to avoid going to the bathhouse, sauna, or solarium.
Male infertility is a pathological disorder in the reproductive system. The inability of a sexually mature man to conceive a child does not in any way affect his sex life or the presence of an erection.
The first sign of this problem is the absence of children in a couple who have been sexually active for a long period (up to 1 year) without contraception.
If a woman has a high ability to fertilize, confirmed by examination results, and pregnancy has not occurred during this time, a diagnosis of male infertility is made.
There are several methods for determining male fertility. This pathology can be recognized at home. Just first you need to get acquainted with the reasons for this condition.
Causes of infertility in men
The following factors contribute to the development of male infertility:
- infectious diseases of the reproductive system;
- abnormal structure of the pelvic organs;
- anatomical features of the external genitalia;
- inflammatory processes and complications after serious illnesses;
- varicocele – varicose veins of the spermatic cord;
- hydrocele - a congenital pathology in which fluid inside the scrotum puts pressure on the testicle, disrupting the blood circulation in it and reducing sperm production;
- cryptorchidism is an abnormal deviation in the development of the reproductive system, when the testicles do not descend into the scrotum, but remain in the abdominal cavity of the man;
- hormonal disbalance;
- autoimmune mechanism;
- genetic and hereditary diseases;
- erectile dysfunction (impotence);
- premature ejaculation;
- ailments in which soft tissues of the whole body are damaged (tuberculosis, diabetes mellitus, liver cirrhosis, thyroid pathologies, mumps, and the like);
There are also additional causes of male infertility that are indirectly related to the development of such pathology. These include:
- bad habits such as smoking, alcohol and drug abuse;
- unbalanced diet;
- frequent stress;
- injuries to the external genitalia;
- lack of vitamins in the body;
- prolonged exposure to toxicological fumes or direct contact with hazardous toxic substances;
- infantilism – a man’s reluctance to have children;
- sexual illiteracy.
It happens that a man has completely no indications for the development of infertility, but his partner never becomes pregnant. Then doctors can make a disappointing diagnosis - infertility of unclear history. Dealing with this problem is difficult, but possible.
Types of male infertility
Male infertility is divided into 2 types:
- relative – the possibility of fertilization with one’s own sperm remains possible, only this process requires additional conditions;
- absolute – a man’s sperm is sterile, it does not produce sperm for conception.
According to physiological characteristics, fertility in men can take different forms. Let's look at them in more detail.
Secretory infertility. In medicine, this form of the disease is considered the most common. It is characterized by dysfunction of sperm production in the male reproductive system. As a result of pathogenic processes, the number of sperm changes, their motility and gene pool are disrupted.
The main causes of secretory infertility are varicocele and hydrocele. In both cases, blood circulation in the testes slows down, which leads to a decrease in sperm activity and even their death.
Mumps contracted in adolescence, cryptorchidism, an unfavorable environmental situation, and banal hot baths can cause secretory infertility in men.
Obstructive infertility. This form of the disease is characterized by the inability of sperm to move along the vas deferens. This can be either a congenital pathology or an acquired one. Only two factors contribute to the development of obstructive infertility - physical and chemical.
Cysts, postoperative scars and tumors are physical factors of sperm obstruction. If such problems occur only on one side of the canal, obstructive infertility is considered unilateral, and if it affects the entire duct, it is considered bilateral. In the latter case, the release of sperm during orgasm in men is practically absent.
Excretory toxic infertility. With this form of the disease, the removal of seminal fluid from the canals is considered impossible. The precursors are dangerous diseases: prostatitis and epididymitis (inflammation of the epididymis). The mucous membrane of the vas deferens becomes sensitive, it sticks together and blocks the release of sperm during orgasm.
Autoimmune infertility. The most mysterious form of the disease, in which the male body produces antibodies to its own seminal fluid. This can happen due to severe physical trauma to the genital organs and serious genetic changes in the cytological structures of the body.
Secondary infertility. The man already has one child, but he can’t conceive a second one.
The following forms of male fertility are common:
- retrograde ejaculation - removal of sperm into the bladder instead of the urethra;
- immune conflict, absolute incompatibility - absence of pathologies in both partners, but the desired pregnancy does not occur due to a conflict of immune systems;
- combined – an accumulation of different factors leading to infertility (infection, toxicity and hormonal levels).
Diagnosis of male infertility
There are several ways to determine infertility in men. First, it is necessary to exclude any pathological changes in the partner that may cause the impossibility of fertilization.
If everything is fine with the other half, the algorithm for examining a man looks like this:
- collecting information and familiarizing the doctor with the patient’s complaints;
- general examination and palpation of the scrotum;
- determining the frequency of sexual intercourse, erection and the nature of ejaculation;
- laboratory diagnostics, which includes infectious screening (if indicated), biochemical analysis of sperm, hormonal studies, ultrasound of the thyroid and genitourinary system, radiography.
- In the most severe cases, a testicular biopsy may be necessary.
Treatment of male infertility
The first and most important rule in the treatment of male infertility is the correction of the disease that provokes fertility. After eliminating the cause of the disease, treatment begins.
You can get rid of male infertility using one of 3 methods: conservative, surgical and alternative. It all depends on the severity of the disease and its form.
- Strengthening therapy. You can improve the generative function of the testicles with a powerful vitamin boost in the form of Tocopherol and a group of multivitamins.
- Treatment of neuroses. Infertile men are very vulnerable; they are prone to prolonged depression, excessive irritability and severe fatigue. Phosphorus-rich drugs and, of course, consultation with a neurologist will help you cope with the situation.
- Therapy of secretory infertility. It consists of taking androgens to stimulate the secretion of gonadotropins, sperm motility, and increase their quantity and quality.
- Treatment of excretory infertility. Relieving the source of the problem with the genitourinary system leads to the restoration of the reproductive function of the male body. In parallel with drug therapy for prostatitis, urethritis or another similar disease, biological stimulation of metabolic processes in the body begins, which have a positive effect on a man’s spermatogenesis.
- Surgical treatment. This type of therapy is indicated for obstructive aspermia. The reasons for surgical intervention are quite serious: varicocele, cryptorchidism, vasostomy, resection of the prostate gland.
Another method of fertilization is modern reproductive technologies, namely IVF.
Diagnosed male infertility is not a death sentence. A thorough examination and adequate treatment will give the first results within a month. The main thing is not to delay your visit to the doctor, and then you have every chance to experience the joy of fatherhood.