Itching of the vulva or vagina can occur in any woman at different periods of life, at any age. Most often, redness and itching in the vagina are combined with the appearance of wounds from scratching, and this is already a provoking factor for possible infection by pathogenic pathogens, leading to inflammation with the formation of ulcers. A healthy woman who observes intimate hygiene should not have any unpleasant sensations, and in the case where burning and itching appears, in no case should you engage in self-diagnosis and self-medication, you should urgently undergo examination by a gynecologist. Because treatment with folk remedies without establishing the true cause that caused the discomfort is unacceptable, stupid and reckless. Only a doctor, based on test results, will make a diagnosis and prescribe appropriate treatment.
Itching in the vaginal area is not a disease, but only a symptom of a dozen different pathological conditions of the female body, indicating that some kind of malfunction has occurred in the body, the development of some disease. Only by finding out which of them arose in this case can you take action. Without a clear diagnosis based on test results, you should not use douching or use medications in suppositories, ointments, creams (see how to do douching and the potential harm from it).
This will change the clinical picture and the results of subsequent tests will be false, which may lead to inadequate treatment and worsening of the condition. If a woman experiences itching, white, cheesy discharge, an increase in the amount of discharge, or discharge with a fishy odor that lasts more than 3 days, she should definitely consult a doctor. The causes of discomfort can be different - a sexually transmitted disease, an allergic reaction, or the body’s reaction to constant long-term stress.
How to prepare for a visit to the gynecologist?
- You should not use any medications in the form of suppositories or sprays 1-2 days before the visit
- You should abstain from sexual intercourse for 1-2 days
- You should not use antibacterial products for intimate hygiene 1-2 days before visiting a doctor, especially if you douche.
- On the eve of visiting a doctor, in the evening it is necessary to toilet the external genitalia with regular, preferably baby soap and warm water.
- It is better not to urinate 2-3 hours before the visit.
The doctor will perform an examination, take a smear from the cervical canal for flora, as well as bacterial culture for anaerobes, aerobes, fungi with determination of sensitivity to antimicrobial agents, and send for PCR diagnostics, RIF and ELISA for sexually transmitted infections. In addition, it is advisable to take a stool test for worm eggs and for intestinal dysbiosis. This must be done to establish an accurate diagnosis. Only on the basis of complaints of vaginal itching, the causes of which are different, the doctor cannot make a diagnosis without additional research.
Treatment
If the cause of discomfort is not external irritants and improper hygiene, treatment of vaginal itching should only take place after an accurate diagnosis and according to doctor’s prescriptions. In each specific case, treatment is selected individually.
- Fungal infections can be cured through the use of antimycotic drugs, and in some cases, antibiotics. Usually Nystatin, Levorin, Clotrimazole, Ginesol are prescribed. At the same time, suppositories can be prescribed to restore the microflora of the mucous membrane: Vagilak, Ecofemin, Bifidumbacterin.
- For allergies, antihistamines are prescribed. Tablets that perfectly relieve itching and help cope with increased sensitivity to sensitizing agents: Telfast, Erius, Suprastin, Tavegil injection solution, Enterosgel paste, Hydrocortisone and Menthol ointment.
- If the itching is caused by parasites found in the stool, the woman is prescribed medications aimed at eliminating adult worms and eggs. These medications are: Vermox, Nemozol, Mebendazole, Pyrantel.
- Laktozhinal, Lactobacterin, Lactonorm, Femilex, and a fermented milk diet help restore the vaginal microflora.
- Sexually transmitted diseases require long-term and complex therapy with the mandatory intake or administration of antibiotics intramuscularly. Metronidazole, Erythromycin, Doxycycline, Chlorhexidine, Trichopolum, Betadine are often prescribed. How to treat (course of therapy) can only be determined by the attending physician; self-medication in this case is contraindicated.
If it itches inside the vagina due to diseases of the internal organs, treatment is carried out by a specialist after diagnosis using instrumental examination.
Additionally, during therapy you need to take vitamins and immunomodulators. The doctor must also prescribe the correct course.
After studying the tests and research results, the doctor will tell you what to do to achieve a complete cure. When the infectious nature of the disease is identified, etiotropic therapy is used. Suppositories relieve itching in the vagina, tablets have a general therapeutic effect.
Antipruritic and antiallergic drugs can reduce pain and burning in the vagina when an allergy is detected. Sedatives in combination with anti-inflammatory drugs can quickly relieve the manifestations of dermatitis. In some cases, the doctor prescribes hormonal therapy and physiotherapy.
Psychotherapy methods and sedatives are prescribed if mental disorders are detected. In addition to medicinal products, medicinal herbs that have a calming and anti-inflammatory effect help well. They can be used in the form of infusions and baths, but the effectiveness of douching is hotly debated among doctors.
If vaginal redness is caused by decreased hormone production, age-related atrophy or other diseases, the specialist will prescribe a specific treatment regimen.
Itching and discomfort in the intimate area should not go unnoticed. If they do not go away within a short time after removing the irritant, and are accompanied by dermatitis and discharge, you should definitely consult a doctor. Only timely diagnosis and treatment can eliminate the disease without consequences.
Gynecological diseases
Burning and itching in the vagina are symptoms of almost any infectious process in the genital area. Diseases caused by opportunistic microorganisms - their presence in the vaginal microflora normally does not cause discomfort, but when provoking factors occur, they multiply, which leads to inflammation, these include:
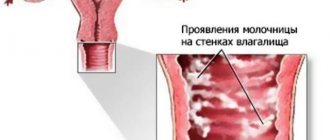
Candidiasis of the vaginal mucosa
This inflammation is caused by the yeast fungus Candida (Candida albicans or Monilia), it is also called thrush, yeast colpitis. In addition to severe itching and burning, it is characterized by thick, abundant, curdled, white discharge (Thrush in women - symptoms, signs).
Bacterial vaginitis, colpitis, vulvovaginitis
When opportunistic bacteria actively grow in the vaginal microflora, most often gardnerella, in addition to unpleasant itching, may cause discharge with a fishy odor. Vaginitis, colpitis caused by E. coli or coccus infections - these infections often occur as mixed infections, that is, candidiasis, gardnerellosis, and other infections develop. Before menstruation, discomfort usually intensifies.
Allergy to sperm
Sometimes married women who have only a single partner experience vaginal itching after unprotected intercourse due to an allergic reaction to the husband's sperm. This happens quite rarely and is manifested by burning, redness, itching of the external genitalia after sexual intercourse. An allergy to sperm, as well as incompatibility of the microflora of husband and wife, can be a serious problem for a married couple, as it causes discomfort in the woman, suspicion of infidelity, and sexually transmitted diseases in each other. However, the irritating component can be the sperm protein itself, as well as possible food products and medications that the beloved man takes. To clarify this cause of itching, you should take special allergy tests for your husband’s sperm.
Vaginal itching: mechanism of occurrence
Itching in the vagina is caused by inflamed, irritated walls. Such irritation is caused by biological microorganisms or chemicals. The brain's reaction to inflammation of the vaginal mucosa is weak pain impulses, which the body interprets as a feeling of itching.
Sometimes the mechanism for the occurrence of such sensations is the formation of central impulses in the brain due to psychological abnormalities. Naturally, in this case, even anesthetics will not help - corrective psychotherapy is needed.
Sexual infections
There are also a lot of hidden sexually transmitted infections, which may not show any symptoms for a long time, but when the immune system is weakened, with an exacerbation of concomitant chronic diseases or previous viral infections, they manifest themselves as minor discomfort, burning, itching. This is possible even if questionable sexual contact took place a long time ago, and unpleasant symptoms arose much later. These STIs include:
- Sexually transmitted diseases - The Russian Ministry of Health identifies 5 main sexually transmitted diseases, many of which are common in some southern resort countries: gonorrhea, syphilis, lymphogranuloma venereum, chancroid, donovanosis.
- Chlamydia in women, which very often has a chronically recurrent nature.
- Trichomoniasis, which is also characterized by an unpleasant fishy odor and greenish or yellow-green foamy discharge.
- Ureaplasmosis, mycoplasmosis, similar discomfort is also a characteristic feature for them.
- Genital herpes, in which, in addition to severe itching around the vagina, painful rashes caused by the herpes virus cause concern.
- Genital warts or genital condylomas are a viral disease that occurs in the genital area in the form of skin outgrowths, condylomas, the causative agent of which is the human papilloma virus (see condylomas in women).
- As a complication of STDs, cervicitis, enometritis, and urethritis can occur. Cervicitis is an inflammation of the mucous membrane of the cervix, either due to an STI or occurring after an injury. Endometritis is an inflammation of the uterus; in these diseases, unpleasant sensations in the external genitalia occur due to the release of exudate, which has an irritating effect on the walls of the vagina. Urethritis is an inflammation of the mucous membrane of the urethra, and in addition to itching, burning and pain occur when urinating.
Diseases in older women
The following list of gynecological pathologies is associated with other diseases that may occur in women of reproductive age, but are most often recorded in women over 45 years of age, during menopause:
Kraurosis of the vulva
This is a progressive chronic atrophic process on the mucous membrane and skin of the vulva, associated with age-related changes. This disease is accompanied by dryness, itching at the entrance to the vagina, sclerotic changes in the clitoris, small and large labia, stenosis of the vagina (see kraurosis of the vulva).
Atrophy of the vaginal mucosa
Dryness of the vagina, labia and tingling, burning sensation can occur with atrophic processes that appear with age in women. In menopausal women, the glands already secrete much less lubricant, the vaginal mucosa becomes more sensitive, discomfort, pain and itching appear during and after sex. Most often, mucosal atrophy in women begins during menopause, when the vaginal tissue becomes thinner. (How to get rid of hot flashes during menopause, Signs of menopause in women). It can also occur against the background of autoimmune diseases (see Sjögren's syndrome).
Urogenital fistulas
They can occur after a cesarean section, after childbirth and other gynecological or urological operations. If urogenital fistulas form, this leads to inflammation of the vagina from exposure to urine during urination.
Benign or malignant tumors of the uterus, cervix or vagina
These are polyps, fibroids, fibroids, Gartner's cyst, oncological pathologies of the uterus, cervix, vagina or ovaries (signs of cervical cancer).
Diseases not related to gynecology
Intoxication, which occurs with almost any infectious disease, can affect all organs and systems of the body, including the vaginal mucosa, as well as:
- Any allergic disease, allergic skin rash, dermatitis in the genital area can cause itching around the vagina.
- Genital itching may be a symptom of diabetes (see signs of diabetes in women).
If, after visiting a gynecologist, no pathological inflammatory processes are detected in an older woman, there is no intestinal dysbiosis (treatment), diabetes mellitus should be excluded, for this it is enough to take a sugar test (blood glucose is normal).
Stress, overwork
One of the reasons may be nervous fatigue, depression, stress, or any prolonged emotional overload in particularly sensitive, anxious women. Mental disorders, serious diseases of the nervous system, such as peripheral or central neuropathy, and any other brain lesions can also provoke itching.
Diseases of the liver, kidneys, thyroid gland
Thyroid dysfunction, liver disease (cirrhosis, hepatitis), kidney or blood disease (leukemia), anemia, can affect the entire body, including causing discomfort in the perineum.
Helminthiasis or pubic lice
Sometimes helminthiasis causes unpleasant itching both in the anus and in the vestibule of the vagina, so a test for worm eggs should also be taken during a comprehensive examination (Itching in the anus - causes, signs of worms in humans, pinworms in adults). Pubic lice may also contribute to this symptom.
Digestive diseases
Diseases of the digestive system, intestinal dysbiosis, external and internal hemorrhoids, anal fissures, proctitis can cause pain, burning and mild itching near the vagina, since the anus and vulva are nearby (Signs of hemorrhoids in women).
Cystitis
Cystitis, which is a common disease in women, often combined with sexually transmitted infections, candidiasis and often with pyelonephritis, can also cause skin itching of the labia and vagina (Cystitis in women - symptoms, treatment).
Blood diseases
In the human body, everything is interconnected, that any disease can affect seemingly unrelated organs; a failure in one system causes disruptions in the functioning of the entire organism. Especially if it is an oncological disease, for example, leukemia, lymphagranulomatosis, as well as cancer of the female genital organs, it may even be in its early stage, which does not yet manifest itself symptomatically, but is already having an impact, causing discomfort in the perineum (Signs of blood cancer).
Vaginal itching during pregnancy
The occurrence of itchy sensations in the groin in pregnant women is due to similar reasons as in women who are not expecting a child. In some cases, we have to talk about stress, increased sensitivity to certain things and hormonal imbalances during pregnancy.
Vaginal itching during pregnancy may not be pathogenic in nature. Stretch marks and hormone fluctuations provoke scabies, including in the genital area. It is enough to observe precautions and hygiene. If you have allergies, limit intake of appropriate products and contact with cosmetics and chemicals.
The climatic factor (hot/cold weather) also affects the condition of the pregnant woman. Often the cause of genital itching is neurotic disorders against the background of expected changes. Support from relatives is needed - care and concern.
The most common cause of vaginal itching is considered to be candidiasis, which is much more common in pregnant women. Loyal therapy prescribed by a doctor is necessary to prevent complications, infection of the fetus and possible consequences. Self-treatment, especially with pharmaceutical medications, is contraindicated.
Causes of thrush in pregnant women. Recommendations for combating the disease. Effective traditional medicine against vaginal candidiasis.
Other reasons
Listed below are external triggers that contribute to the appearance of itching. If, after eliminating them for 3 days, symptoms of discomfort persist, you should definitely visit a gynecologist:
- With uncomfortable, tight, synthetic, rough, poor-quality underwear, a greenhouse effect is created or permanent injury to the perineum occurs.
- Due to exposure to too low or high temperatures, that is, hypothermia or overheating.
- External irritants can be various aggressive chemicals, additives, fragrances found in deodorants, soaps, shower gels, pads, toilet paper, tampons, pads, clothing dyes, washing powders. There can be an allergic reaction to any aggressive substance.
- A woman may also have an inadequate reaction to vaginal contraceptive pills (see non-hormonal contraceptive pills), creams, and suppositories.
- Individual intolerance occurs in some women to the lubrication of condoms, to the lubricants or spermicides with which they are treated, as well as to the latex itself from which they are made, this is the cause of itching in the vagina after sex.
- Powerful stress and prolonged nervous tension provoke any malfunction in the body.
- Violation of the rules of intimate hygiene - a woman should wash her external genitalia without soap at least once a day (preferably in the morning and evening), as well as before and after sexual intercourse.
- Poor nutrition. Addiction to diets (vitamin deficiencies and lack of microelements weaken the immune system, impair the regenerative properties of the skin and mucous membranes, which leads to microcracks), as well as the consumption of semi-finished products and fast food, which are rich in dyes, preservatives, stabilizers, leads to allergic reactions. And also a passion for sweet, spicy, pickled foods can provoke itching.