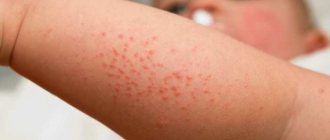
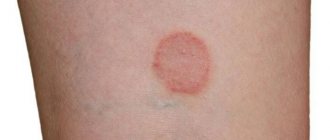
The symptom of itching a certain part of the body is called pruritus in medicine. It, like pain, is an attempt by the body to convey to a person’s consciousness that there is a problem in him that requires an urgent solution. To some extent, itching can be called a protective reaction, since such mechanical stimulation of the pathological focus helps to shake off parasites, poisonous plants or stinging insects.
Often itching is caused by individual intolerance to some substance that gets either on the skin or inside the body - through the mouth or by injection. It can occur due to thermal, mechanical or electrical stimulation of skin receptors. The symptom also indicates an excess of substances in the blood other than histamine, which appears during allergies. Some of these diseases can be life-threatening.
Types of itching
According to the classification of the mechanism of origin, there are several types of itching:
- Pruritoceptive. Occurs on skin prone to dryness, inflammation, or damaged surface.
- Psychogenic. Occurs against a background of depression, depressed state, and constant nervous tension.
- Neuropathic. Accompanies nervous system disorders.
- Neurogenic. It is a symptom of pathologies that do not affect the central nervous system.
Itching is divided into 2 types, based on the location of the rash:
- Local (universal). Severe itching occurs in a certain place.
- General (widespread). Itching spreads throughout the body. Often, itching is not accompanied by redness, rash or other visible manifestations.
Both universal and common types of itching can be permanent or temporary and range from mild to intense.
If itching is accompanied by the appearance of rashes, then their location on the body is a characteristic sign indicating the type of disease.
Systemic diseases
Systemic diseases are diseases of internal organs that may be accompanied by itchy skin. To accurately diagnose a particular disease, listen to other symptoms and consult a doctor.
| Why the body itches for no apparent reason is a disease | Nature of itching | Other symptoms |
| Allergy | Most often accompanied by the skin diseases listed above. The patient suffers from severe itching throughout the day. | Skin rash, digestive disorders. |
| Cancer | Body itching may occur after swimming. Most often, itching is localized in the lower extremities. Itching is the first symptom of cancer, after which others appear. | Skin rashes, spots, swelling of the limbs and face. |
| Cholestasis | Itching and skin rashes indicate problems with the gallbladder. The skin may turn yellow. The skin reaction occurs due to the accumulation of bile in the bile ducts. | Jaundice, nausea, weakness, pain in the right hypochondrium. |
| Diabetes | Due to excessive accumulation of sugar in the blood, peeling and itching of the skin, dryness and deterioration of its condition appear. Scratching can lead to infection with infectious and viral diseases. | Thirst, frequent urination, blurred vision, weight loss. |
| Anemia | The itching is not permanent; most often it is localized to a specific area of the body. Skin burning may occur. | Weakness, headache, appetite disorder, exercise intolerance. |
| Multiple sclerosis | In cases of nervous system disorders, the skin may experience itching and burning. Other unpleasant sensations also occur: tingling, numbness, and decreased sensitivity. | Photosensitivity, impaired color perception, hand tremors, changes in gait, instability, frequent urination or retention, sexual dysfunction. |
| Thyroid diseases | There is dryness, flaking and itching of the skin. The skin of the hands and face is most often affected. You can soften the symptoms with moisturizing creams and oils. | Rapid heartbeat, anxiety, irritability, weight loss or gain, sweating, depression. |
| Liver diseases | Any of the liver diseases affects the external condition of the skin. When there are parasites or toxins in the liver, itching is observed, localized mainly on the hands and face. | Jaundice, pain in the right hypochondrium, burning skin. |
| Kidney diseases | Most often, itching occurs in the genital area, this indicates an inflammatory process. With kidney failure, skin diseases may develop, which are accompanied by itching and rashes on the skin. | Swelling, pain in the kidney area, blood in the urine, urination problems. |
Why the body itches for no apparent reason - the answer may lie in diseases of the internal organs.
Most often, this is not the only symptom and the disease can be diagnosed by other symptoms. But it is best to immediately consult a doctor who will conduct an examination and make the correct diagnosis.
Read the popular article on the site: Menopause in women: symptoms, age-related characteristics, treatment with effective methods.
Localization of the rash
Localization may indicate the type of disease:
- Rashes in the facial area are clear signs indicating diseases such as allergic dermatitis, demodicosis, eczema, lupus erythematosus, toxicerma, psoriasis.
- If the rash covers the hands, this is a sign characteristic of: dermatitis, allergies, secondary syphilis, lichen, mycosis, scabies.
- A rash that affects the lower extremities is a clear accompanying sign of the following diseases: contact dermatitis, infective endocarditis, scabies, viral infections, mycosis.
- The appearance of rashes on the torso and groin area is considered one of the symptoms: scarlet fever, measles, rubella, herpes zoster, chickenpox.
Bottom line
To summarize all of the above, I would like to say the following: there are a lot of reasons for the appearance of itching, regardless of its location.
In most cases, we are talking about an allergic reaction, which can be caused by a number of factors, ranging from individual intolerance to insect bites.
In addition to allergies, itching of the body and head can be a symptom of the development of a certain disease within the body.
Therefore, in order to know how to get rid of itching of the body and head, you first need to understand what caused its manifestation. And only by knowing the true cause can you choose the right treatment.
Sun rash
Itchy skin rashes appear as a result of prolonged exposure to open sun. Moreover, it is especially pronounced in areas exposed to the greatest sun exposure. This is a characteristic sign of photodermatitis, or allergy, to sunlight .
The disease is quite common: according to statistics, 3 out of 10 people suffer from photodermatitis. A severe form of the disease is accompanied by the appearance of swelling and watery blisters.
How to get rid of night itching?
If a person’s whole body itches, but the cause has not yet been determined, following a number of simple recommendations can help.
- Itchy skin can be a reflection of dry skin, so the patient needs to regularly take baths with non-hot water for 2-3 days, using special moisturizers widely sold in pharmacies and hardware stores.
- Dry indoor air can cause itching. To eliminate this, you need to place a container with liquid in the room where a person sleeps, or buy a special air humidifier.
An air humidifier will maintain a comfortable level of humidity in the apartment
- If itching appears on certain types of clothing, they must be removed from the wardrobe, noting for themselves what fabric they were made from. The same applies to shower and bath detergents.
- To make your skin itchy less, you need to stop scratching it. If you still want to scratch the skin, you can use wet bandages, which significantly reduce the itching.
If these methods do not help, then it is necessary to look for the cause of this condition and use drug therapy.
Only a doctor should prescribe medications, as otherwise it may intensify the itching and develop side effects of the medications.
Skin pathologies
Types of diseases:
- Scabies is caused by a microorganism called the scabies mite. This disease is contagious, its symptoms are unbearable itching and distinctive rashes in the form of papules and vesicles. The nature of the rash is scattered or confluent. Localization in the areas of the hands, armpits, and genitals. In the advanced stage, rashes occur on the buttocks, elbows, navel, and folds under the breasts in women. The defining feature of this disease is the appearance on the skin in the affected areas of light gray stripes, 2-3 cm in length. These are the so-called scabies burrows, which are made by the female mite in the upper layer of the skin. They rise slightly above the skin and are discontinuous. The cause of the rash is the body's allergy to the waste product of mites.
- Contact dermatitis occurs when the skin comes into contact with substances that cause an irritant effect. Contact dermatitis is characterized by the appearance of pimples and blisters, which are located in places of contact with the irritant. In rare cases, the rash spreads to closed areas of the body.
- Pyoderma is an infectious disease that is caused by a combination of bacteria (staphylococcus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa). The impetus for the development of this disease is weak immunity, nervous tension, poor ecology, and increased sweating. The main places where the rash is localized are the sweat glands in the armpits, hair follicles on the face, in the groin area and labia in women. The pyoderma rash looks like pus-filled blisters. When they burst, they turn into crusts. The whole process is accompanied by itching and peeling.
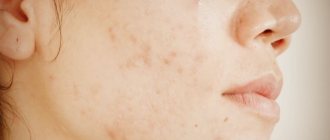
- The body itches in different places (the reasons for this symptom can be different, including this is typical for eczema) - a chronic disease of the upper layer of the skin, the visible symptom of which is a polymorphic rash in the form of small blisters and plaques. As the disease progresses, the plaques become covered with microcracks, the blisters burst, releasing a cloudy gray-green purulent fluid. The main locations of the rash are: hands, feet, face, neck, ears. The rash is accompanied by severe itching. The disease develops against the background of chronic fatigue and nervous stress.
- Psoriasis is a chronic dermatological disease that is accompanied by the appearance of lumpy, scaly skin rashes called “plaques.” The localization of the rash depends on the type of psoriasis, mainly affecting the scalp, elbows, knees, feet, hands, and less often in the folds of the skin.
Causes of localized skin itching
Localized body itching is mainly recorded with skin diseases. It is accompanied by a rash. If the lesion is infectious, your health worsens and your body temperature rises.
Among the skin diseases that occur with itchy skin are:
Contact dermatitis occurs when the skin comes into contact with allergens and irritants. The primary manifestation of the disease is itchy skin. In acute cases, it is red, swollen, with nodules, erosions, and blisters. Peeling often occurs, after which pigmentation remains. In men, such dermatitis can develop when wearing synthetic underwear, causing irritation in the scrotum area.
- Atopic dermatitis (neurodermatitis) is a chronic allergic skin lesion with a recurrent course. The first signs of the disease appear in childhood. Redness, dryness, peeling of the cheeks, diaper rash in the folds of the skin and on the buttocks are detected. Scales appear on the scalp and stick together. On damaged areas of the body, a rash appears in the form of nodules that cause itching. Concomitant eye inflammation and ARVI are also recorded in children. For treatment, Bepanten ointment and Epidel cream are prescribed. For severe exacerbations, hormonal ointments are used.
Psoriasis is characterized by the formation of red spots that rise above the skin level and merge with each other, forming plaques. Any part of the body can be affected, but more often rashes appear on the head, knees, elbows, back, and nails are also affected. Characterized by excessive dryness and severe itching of the skin.
- Photodermatosis (sun allergy) manifests itself as small red spots that cause burning, itching, discomfort, and worsen the appearance of the skin. More often, rashes appear on the limbs, shoulders, and neck. With photodermatosis, peeling, pustules, and pigmentation of damaged areas may be observed.
- Lichen planus is a chronic skin disease. First, small nodules with a shiny pink or purple surface appear on the body. Subsequently they merge. Patients are bothered by itching. Pigmentation remains at the site of the rash: the skin becomes darker in color than healthy areas.
- Ringworm is caused by fungi and manifests itself as damage to the skin, scalp, and nails. The disease is accompanied by the appearance of round spots with clear boundaries, which are covered with nodules and blisters along the periphery. Children get sick more often. Itching and flaking of the skin occurs throughout the body. When the skin on the head is affected, focal baldness is observed (the disease leads to hair breaking off at a level of several millimeters from the skin).
- Eczema is a non-contagious inflammation of the skin, which has an acute or chronic course, manifested by a rash in the form of blisters, erosions, crusts and scales, burning, itching. Seasonal exacerbations are typical in the autumn-winter period.
- Urticaria is a term that unites a group of diseases that have a common symptom - a rash in the form of blisters, which resembles a nettle burn. The rashes are symmetrical, accompanied by itching, and can migrate throughout the body and merge. During treatment, the skin is restored, there is no hyperpigmentation or scars.
- Diseases of the nervous system . In multiple sclerosis, itching occurs in areas that correspond to the affected segment of the spinal cord. It has a paroxysmal character - it begins suddenly, lasts from several seconds to several minutes. If the itching is severe, the patient may wake up at night. With thrombosis of cerebral vessels, hemorrhages in the brain tissue, itching also occurs. It is disturbing from the side opposite to the brain damage and is accompanied by motor disturbances and changes in sensitivity. Other pathologies of the nervous system include postherpetic neuralgia. Its development is associated with damage to nerve endings by the herpes virus. It manifests itself as pain, but may also be accompanied by neurological itching. It always has a local character, occurring in places where innervation is disrupted.
Itching in certain areas of the body can be a result of insect bites, poor hygiene, or wearing uncomfortable clothing.
Ringworm
Ringworm is a contagious dermatological skin disease caused by viral or fungal infections. Dermatologists distinguish a large number of varieties of lichen.
The most common forms of this disease:
- The ringworm appearance is accompanied by the appearance of well-defined spots covered with white flakes and severe itching. In advanced forms of the disease, the appearance of purulent vesicles and yellow plaque is observed. As the infection progresses, the scalp is damaged, causing breakage of the hair shaft and, as a result, hair loss.
- Lichen planus is characterized by the distribution of characteristic bright pink spots on the skin with a shiny, rarely flaking surface. In this case, rashes appear all over the body and are very itchy. If the disease is not treated at an early stage, the spots become connected to each other. In its advanced form, the rash affects the genitals and mucous membranes.
- Pityriasis rosea appears as large red-pink spots. The course of the disease is accompanied by itching distributed throughout the body.
- Shingles is accompanied by characteristic rashes in the form of small watery blisters, united in large groups. As a rule, the rash appears in the intercostal spaces. The disease is characterized by severe itching, which spreads throughout the body, intensifying in the evening.
- Pityriasis versicolor causes flat, round, pink spots to appear. The disease is not accompanied by itching or other discomfort. Gradually, there are more spots, they merge together and form large lesions.
- Ringworm is accompanied by swelling and redness of the affected areas of the skin. After some time, small watery blisters appear on the skin, which are very itchy. In an advanced form, the bubbles burst, forming yellow crusts that become covered with cracks. Bubbles appear all over the body.
Where does the itching sensation come from?
The imperative desire to scratch an area of skin occurs when blood with a high concentration of dissolved substances flows to the pain receptors (nociceptors), spread out in the form of a network under a layer of epithelial cells:
- histamine and/or histidine. These substances are formed in excess by immune cells when certain – specific to each organism – foreign proteins enter the body;
- bile acids produced in the liver. They enter the skin cells and cannot leave them when a condition such as cholestasis develops - when bile cannot completely enter the duodenum and is forced to stagnate in the cells of the liver and biliary tract;
- serotonin is a substance formed from an amino acid, which, when released, leads to a significant contraction of smooth muscles located in blood vessels and internal organs. This is a neurotransmitter, that is, a chemical compound that allows communication between nerve endings (the signal passes from nerve to nerve not like electricity, but rather like a bubble with a chemical substance, depending on the structure of which the activity of a neuron can be inhibited or activated). Its structure is very similar to the psychoactive hallucinogen LSD;
- cytokines – molecules that enable “communication” between immune cells;
- endorphins – natural pain-relieving molecules;
- nitrogenous wastes that accumulate in the blood during kidney disease;
- some other bioactive substances: thyroid hormone calcitonin, pancreatic enzymes (trypsin, kallikrein), VIP neuropeptides and substance P.
Since each person’s body has its own characteristics, no direct connection has been identified between the concentration of the above substances and the severity of the need to perform mechanical stimulation. Thus, severe itching in one individual may accompany the initial stage of renal failure, while in another it will not appear even with the terminal stage of uremia.
Only the skin and those mucous membranes, the layer of epithelial cells in which is in contact with the external environment and is located near the skin: gums, tongue, genitals, are “subject to itching”. The signal from the pain receptors located underneath them travels along type C and A-delta nerve fibers, reaches the spinal cord and, together with its structures, is delivered to the brain, to its sensitive zone.
Itching can be of a different nature: from a mild “tickling” to severe, painful. Its nature dictates to a person how to “process” its localization:
- scratch: this is more typical for skin pathologies such as neurodermatitis or eczema;
- rub gently: inherent in lichen planus;
- cool (typical for acute urticaria).
However, a diagnosis cannot be made based on these characteristics alone. In determining the cause of itchy body skin, the following are important:
- its localization;
- the condition of the skin at the site of such sensations;
- conditions for the appearance and relief of itching;
- additional symptoms.
Let’s consider the combination of these factors to make it easier to get examined and choose exactly the specialist who can quickly alleviate your condition.
Mycoses
A fungal infection is also accompanied by the appearance of itchy rashes, which spread depending on the type of infection.
For example:
- Rubrophytia - is characterized by the formation of extensive red spots throughout the body with clearly defined boundaries, on the surface of which inflamed blisters filled with liquid and flour-like peeling appear.
- Trichophytosis is accompanied by the appearance of round-shaped spots, bright red in color, surrounded by inflamed ridges. The skin on the affected area peels off and becomes covered with small nodules. The infection affects the scalp, face, hands, and rarely the skin of the body.
- Seborrheic dermatitis characterized by severe peeling of the affected areas of the skin, which are covered with hemorrhagic crusts. The disease is accompanied by intense itching. In advanced form, suppuration is observed in the foci of infection. The main places where fungal infection is localized are: eyebrows, scalp, mustache, facial skin, skin folds behind the ears, and the area of the ear canal in the ears.
The body itches in different places. The reasons may lie in seborrheic dermatitis, which is localized in different places.
- Cutaneous candidiasis At a later stage, the affected area becomes bright red, and pronounced areas of erosion appear in place of the bubbles. The spots have clear boundaries, which are covered by the dead stratum corneum of the skin.
Local itching and peeling of the skin
- Itching and flaking of the skin are inherent in a disease such as psoriasis. This is a chronic inflammation, the causes of which are not fully known. The skin becomes covered with spots with whitish scales. Characteristic rashes occur on the elbows, knees, and at the edge of the scalp. When scratching the plaques, a pink film is discovered on the surface, peeling off which can provoke the symptom of blood dew. Today, ointments based on solidol (Magnipsor, Cytopsor, Antipsor) are widely used against psoriasis, diet, sanatorium treatment (climate change has a beneficial effect in most cases), phototherapy and other methods are prescribed;
- Itchy skin is characteristic of scabies, which is caused by the scabies mite. With this disorder, itching occurs between the fingers, on the wrists, on the surface of the abdomen and groin area. Unpleasant sensations increase at night, spreading to new areas. The disease is contagious, it is very important to disinfect the premises. To eliminate symptoms, sulfur-based ointments, benzyl benzonate, Spregal spray, Permethrin (ointment, spray, lotion) and other medications are used. Traditional medicine suggests fighting the disease with the help of turpentine, celandine juice, bay leaf and other mixtures of herbs and products of animal origin;
- Neurodermatitis is one of the most common reasons why the skin is dry and itchy. The affected areas of the skin quickly become rough and rough, and small bumps also appear. After a few days, the symptoms begin to subside and the skin gradually recovers. Neurodermatitis can recur many times when stress occurs. Sedatives (tincture of valerian, motherwort) and antihistamines (Loratadine, Chlorpheniramyl) are prescribed, ointments and lotions are used to relieve itching, the patient is referred to physiotherapy;
- Contact dermatitis is characterized by a pronounced desire to scratch, redness, and blistering. Therapy involves avoiding contact with the irritant, using anti-allergy medications (Zodak, Suprastin), applying corticosteroid-based ointments (Lorinden, Elokom, Beloderm);
- Hives appear when the skin comes into contact with a specific allergen and manifests itself in the skin itching and redness. As a rule, symptoms do not last long - about a day;
- Fungal infections on the hairy parts of the body cause a strong desire to scratch. In addition, hair may fall out, suppuration, redness, and peeling may occur. Treatment in this case is aimed at eliminating the pathogen;
- Lice cause itchy sensations. For pediculosis, special shampoos, lotions and sprays are used that destroy parasites. They may contain the following substances: phenothrin, malathion, dimethicone;
- Skin irritation is also common in atopic dermatitis, angioedema, sexually transmitted diseases, intestinal diseases, insect bites and other painful conditions.
Allergic rash
In 80% of cases, allergies cause rashes to appear on different parts of the body.
The type and location of the rash depends on the type of allergy:
- Hives are accompanied by the appearance of small, smooth blisters that are pale pink in color. The disease is accompanied by itching sensations. The rash affects any part of the body.
- Atopic dermatitis is accompanied by the appearance of red spots that vary in size. When scratching, weeping wounds appear, which subsequently become covered with crusts. The main areas where the rashes are located: temples, cheeks, elbows and kneecaps.
- The body itches in different places (the cause may be neurodermatitis ) and small red pimples appear that spread throughout the body. In an advanced form of neurodermatitis, pimples turn into nodules that merge. This forms large lesions, the skin of which acquires a bright crimson color. The skin in the affected areas peels off greatly, becomes covered with cracks, and the whole body begins to itch in different places.
Periodic itching all over the body: types and associated symptoms
To date, the mechanisms of itching have not been fully studied. Until relatively recently, official medicine equated this sensation with pain, but modern doctors are confident that itching is not a type of pain syndrome. The fact is that pain occurs in any part of the human body, and only the skin, corneas and mucous membranes of the eyes can itch. However, both pain and itching still have a common characteristic: both of these sensations arise due to the adverse effects of internal or external factors on the peripheral nervous system.
Based on the results of research on what factors can act as a “trigger” for the occurrence of itching, official medicine has identified 4 types of this sensation:
- Neuropathic itching - occurs due to damage to areas of the brain responsible for skin sensitivity
- Neurogenic itching - appears as a result of disruption of physiological processes in the body, but is not associated with malfunctions in the functionality of the nervous system
- Pruritoceptive itching is one of the symptoms of skin diseases, inflammation of the dermis or allergies.
- Psychogenic itching is a psychosomatic disorder that occurs as a result of severe stress, increased anxiety and some phobias.
Neuropathic and psychogenic itching in most cases is itching all over the body for no apparent reason. The unpleasant sensation is not accompanied by any external manifestations, and the skin looks clean and healthy. But with neurogenic and especially pruritoceptive itching, there are often other symptoms of the disease: redness of the skin, the appearance of rashes or swelling, coarsening and peeling of the upper layers of the epidermis.
Rash like mosquito bites
The appearance of rashes on the skin, similar in shape and appearance to mosquito bites, is a symptom that accompanies allergies.
Factors that provoke an allergic reaction include:
- food products containing allergens;
- chemical substances;
- poor quality cosmetics;
- antibiotics;
- mold fungi;
- plants (poplar, pollen);
- animals.
Kinds
There are not many of them, according to the topic at hand, it is worth identifying the following varieties:
- Senile. Occurs in people aged 70 years.
- Reflex. With increased emotionality.
In addition to these, there is also aquagenic and high-altitude itching, since they are not classified as nocturnal, it makes no sense to specify them, especially since the etiology is clear based on their name.
Varieties of symptoms based on the reasons for its formation:
- Psychogenic. The itch is caused by a disorder;
- Neuropathological. The central nervous system or PNS is affected;
- Systemic. Problems with the gastrointestinal tract, kidneys, liver, thyroid gland;
- Dermatological. Damage to the skin due to insect bites, hives or scabies.
This phenomenon has a mixed etiology, so it is quite difficult to find out the true source of this problem.
Rash due to intestinal infection
The allergy is accompanied by the appearance of small, swollen blisters and severe itching. The rash disappears immediately after the allergen is removed. Harmful bacteria and microorganisms can cause a rash to appear on the body not only from the outside, but also by attacking internal organs. The intestines are a favorable environment for the proliferation of pathogenic infections.
By infecting this organ, bacteria contribute to the weakening of the immune system, which is reflected on the skin in the form of characteristic rashes. Externally, the rash in the form of small red spots and dots, which can appear on any part of the body during intestinal infections, resembles the rashes associated with scarlet fever and measles.
Diagnostics
To eliminate itching, it is necessary to establish the exact cause of its occurrence. If you experience any discomfort, you should visit a dermatologist. But in most cases, just examining it is not enough. If a pathology is suspected, he will refer you to specialized specialists: endocrinologist, therapist, allergist, immunologist, gastroenterologist and other colleagues.
First, the doctor finds out the general condition of the patient:
- chair;
- fatigue;
- dream;
- vomit;
- weight change;
- headache;
- visual impairment;
- Body temperature;
- pressure.
For a detailed examination, different methods and methods are used:
- blood, urine and stool tests;
- genital swab;
- ultrasonography;
- coagulogram;
- Magnetic resonance imaging;
- CT scan;
- electrocardiogram.
Before going to see a doctor, you should not take antihistamines or carry out procedures to eliminate itching, so that the doctor can correctly diagnose and tell you what to do to eliminate it.
Causes of infectious nature
One of the most common causes of a skin surface rash is infection with an infectious disease:
- Scarlet fever is accompanied by the appearance of a rash in the form of numerous, small blisters of bright red color that cover the legs, arms, and torso. The skin acquires a rough texture to the touch and remains that way for a week after there is no trace of the rash left.
- Measles is characterized by a rash of pale pink, smooth spots. The localization of the rash is the lateral areas of the neck, folds of skin behind the ears. Then, the rash spreads to the area under the hair on the scalp and cheeks. Within 24 hours, the rash covers the entire neck, arms, and chest. The spots take on the appearance of papules that merge with each other.
- Rubella rash appears as a small pink rash on the face, which quickly covers the arms, chest, and back. Flat pale pink spots gradually lighten and merge with each other. The rash disappears on its own within 4-5 days.
- The body itches in different places (the causes of this symptom are very diverse) - one option is chicken pox, which is characterized by the formation of round red spots that rise above the surface of the skin, turning into pimples after a few hours. As well as vesicles and pustules, which can leave behind scars. After the watery bubbles fall off, a crust forms.
- Roseola is accompanied by the appearance of small pale pink spots and blisters. The spots have different shapes and unclear boundaries. They never merge with each other, despite being located close to each other. The rashes do not itch or peel.
How to determine the cause of itching?
If itching of the skin occurs at night, a person should always seek professional medical help at a medical facility. Diagnosis of such a condition should include several stages.
- Clinical examination of the patient. The attending physician should not only carefully examine the surface of the skin to identify any elements of the rash, but also pay attention to possible clinical manifestations and diseases of the internal organs. For example, thyroid dysfunction can be manifested by increased sweating, emaciation of the patient, and exophthalmos. Already at this stage, the doctor can draw up a plan for further examination.
- Conducting laboratory diagnostic methods. As a rule, such an approach includes conducting a biochemical blood test to determine the following parameters: glucose (possibility of detecting diabetes mellitus) and bilirubin (diagnosing jaundice).
- Special allergy tests. If an allergic component of itching is suspected, they must be carried out to identify the causative allergen.
Carrying out skin allergy tests
- Tests for the presence of parasites. If the patient has itching in the anus or other signs of a parasitic infection..
- The use of instrumental diagnostic methods (ultrasound, CT and MRI). May be indicated if there is suspicion of damage to internal organs, for example, jaundice caused by cholelithiasis, etc.
The use of an integrated approach to diagnosis makes it possible to establish the cause of the development of itching and begin to eliminate it.
Insects
The bites of some types of insects can leave specific marks on the human body.
They are not only noticeable visually, but can also be accompanied by severe itching:
- A mosquito bite blister is itchy and swollen. As a rule, mosquito bites are localized on open areas of the body. They go away on their own within a few days if you do not disturb the blister by scratching.
- The midge bite site turns red, burns and itches. A characteristic sign of a midge bite is severe swelling and the appearance of small blisters at the site of the bite.
- The bite marks of wasps, bees, bumblebees and hornets are distinguished by whitened skin in the center of the bite, severe swelling and redness around it. It is also accompanied by severe pain and burning.
- Bed bug bites appear as small red spots all over the body that become swollen and itchy after 24 hours.
- The rash from linen lice bites is identical to bed bug bites.
- Flea bites become covered with small red swellings that itch very much. A distinctive feature is the location of the bites, mainly on the ankles, knees, stomach, calves, and armpits.
Effective Home Remedies
Folk remedies for the treatment of irritated and inflamed skin combine the effectiveness of their action and the absence of side symptoms that may occur when taking medications for itchy body skin.
Cold bath, shower and compress
Until now, scientists have not established the exact mechanism that leads to itching, but cold water can be effectively used to relieve it. Therefore, you just need to take a cold bath or shower. You can also direct a stream of cold water to areas of the body that itch.
To quickly cure itching , while taking a bath, you can add some vegetable oils to the water, which soften the skin, relieve irritation and relieve and remove itching. These oils include the following:
- Navel - has relaxing and anti-inflammatory properties;
- Frankincense - can relieve skin inflammation;
- Calendula tincture - helps in relieving itching and moisturizing the skin.
In turn, some oils irritate the skin, so their use should be avoided: bay, cloves, cinnamon, lemon, oregano, thyme and marigold.
You can get rid of itching by applying a cold compress. To do this, moisten a towel with cold water and place it on the place where the itching is most pronounced. This compress moisturizes inflamed skin and removes dead cells from it.
In addition to cold water, you can use ice cubes or some frozen product, which should be wrapped in a towel and placed on the affected area of the skin for no more than 10-20 minutes. Hot compresses and water can only increase inflammation and redness of the skin.
Baking soda and oatmeal
A solution of sodium bicarbonate or baking soda is a good home remedy for any type of itching, but is most effective if the condition is caused by bee and other insect stings. It is necessary to dissolve a spoonful of baking soda in a bowl of cold water and immerse the affected area for 30 minutes. Usually the symptoms can be eliminated immediately.
Oats are a plant that contains many antioxidants that soften the skin and relieve irritation. It is most effective to use fresh oats that have not previously been subjected to any processing and prepare oatmeal from it using a regular coffee grinder. Then you should pour a bath of cold or slightly warm water and dissolve two tablespoons of prepared oatmeal in it. Taking such a bath for half an hour daily can effectively combat itching.
Itching without rash. Causes
Not in all cases, itchy skin is accompanied by the appearance of a rash. However, this does not make the discomfort any less.
In addition, itchy skin without rashes is a symptom of many diseases:
- Seasonal itching . At different times of the year, different factors can cause itchy skin. In winter, itchy skin occurs due to hypothermia of the skin or from dry indoor air from heating devices. In spring, the lack of vitamins and minerals in the body affects. In summer, itchy skin is caused by a lack of vitamin E, photodermatosis and sunburn. In autumn, lack of light affects.
- Senile itching is a mild itching sensation that appears on different parts of the body. It occurs in older people. The discomfort is explained by age-related changes in the structure of the skin. Localization of this type of itching is the back and chest. However, the itching may spread throughout the body. Senile itching also occurs in people who have quickly lost a large amount of excess weight. In this case, the folds of remaining excess skin on the abdomen, arms and legs become covered with stretch marks (striae), which can be very itchy. No rashes are observed during this process either.
- Psychoneurosis is accompanied by itching that spreads over the surface of the skin of the entire body. The main reasons are severe stress, overwork, and depression.
- The body itches in different places (the causes of itching are often serious diseases) - one of the causes of diabetes . Unpleasant itching sensations are associated with increased blood glucose levels. Localization of itching in diabetes mellitus is the perineum, joints of the limbs.
- Anemia is often accompanied by itching in the pelvic area, genitals, and heart area.
- The presence of helminth parasites in the body. Itching is localized in the anus at an advanced stage throughout the body. This is due to the proliferation of parasites inside a person and their penetration into the abdominal organs.
- Menopause is accompanied by itching, which is localized in the chest and neck.
- The body itches in different places (the reasons may be hidden in external factors) due to synthetic underwear . This factor causes severe itching of the skin in the back, chest, lower and upper extremities. Synthetic fabric does not breathe, does not absorb sweat and moisture, and therefore the skin becomes dry, which causes itching.
- A low-quality laundry detergent can cause itchy skin, especially if the powder contains components to which you may be allergic.
- Itching after a shower can be caused by a number of factors:
- hard water, due to its high content of chlorine and other impurities, tightens and dries out the skin, which subsequently itches;
- Low-quality shower and bath products dry out the skin or cause an allergic reaction.
It is not recommended to ignore itchy skin . If the body itches in different places, the cause may be a serious illness. To get rid of a discomforting symptom, it is necessary to identify its root cause. Only a doctor can do this.
If there is local itching, you should seek help from a general practitioner or, in general, a dermatologist. After the initial diagnosis, if necessary, the patient will be referred to a specialized specialist.
Author of the article: Anna Mars
Article design: Oleg Lozinsky
Causes of generalized itching
Among the internal diseases that cause itching, there are several.
Lesions of the liver, biliary tract
The most common symptom of itching is cholestasis, a condition in which the production or flow of bile is impaired. Cholestasis of various origins is characterized by common symptoms:
- liver enlargement;
- pain in the right hypochondrium;
- stool discoloration;
- yellowness of the skin;
- digestive disorders;
- darkening of urine;
- skin itching.
The itching intensifies in the evening, upon contact with warm water. This leads to excessive excitability and provokes insomnia. Other pathologies that are accompanied by body itching are:
- hepatitis;
- cirrhosis;
- pancreas cancer;
- obstruction of the bile duct.
Kidney diseases
Itching is accompanied by pathologies:
- glomerulonephritis;
- pyelonephritis;
- urolithiasis disease.
Also, the cause may be a kidney tumor, malignant formations in the body of any location (cancer produces proteins that disrupt the filtration process).
Thyroid diseases
Diffuse toxic goiter (thyrotoxicosis) is accompanied by excessive secretion of thyroid hormones and increased metabolism. This in turn increases blood supply to the skin, causing fever and itching. With severe deficiency of thyroid hormones and the development of myxedema, patients also complain of body itching. The skin is dry, pale, with a yellow tint, and cold to the touch.
Diabetes
The disease manifests itself as intense itching throughout the body. At the same time, not only the skin itches, but also the mucous membranes, including in the genital area. The appearance of itching is caused by an increase in blood sugar levels and impaired kidney function due to the disease. Constant itching over time can provoke neurodermatitis of a neurogenic-allergic nature. The skin with diabetes is very dry, thin, and prone to microcracks (especially if the patient itches). In this case, the skin can become infected, which causes ulcers and abscesses that are difficult to treat.
Psychogenic itching
Itching can appear against a background of constant stress, overwork, and depression. Such conditions are accompanied by an increase in the level of the hormones dopamine and serotonin in the blood, which causes itching throughout the body. Other psychogenic causes include parasitophobia (fear of insects). It can be intrusive and provoke generalized itching, which worsens the condition of patients because they are constantly itching.
Periarteritis nodosa
This damage to small vessels (arteries), which leads to impaired peripheral circulation, can provoke heart attacks and irreversible tissue death (necrosis). Symptoms depend on the location of the damaged vessels.
Avitaminosis
Vitamin deficiency is a lack of vitamins A, group B, and ascorbic acid, which worsens the condition of the skin and causes excessive dryness and itching. Zinc deficiency also has a negative effect.
Drug allergies
An allergy is the body’s reaction to certain drugs and their individual components. Its symptoms appear immediately (faster than an hour). These are basically red blisters that are very itchy and merge into one large spot. With significant skin damage, the general condition is disrupted, which requires the abolition of allergen drugs and symptomatic therapy.
Blood disease
Polycythemia is accompanied by a significant increase in the number of red blood cells. Symptoms depend on the stage of the disease, the level of blood cell growth, and the increase in blood viscosity. Mainly concerned about:
- headache;
- visual impairment;
- noise in ears;
- dizziness;
- increased blood pressure.
In 30-70% of cases, skin itching occurs, which intensifies after contact with water. Sometimes this is the only symptom of the disease for a long time.
With iron deficiency and the development of anemia, note:
- pale skin;
- mucous membranes;
- cardiopalmus;
- hair loss;
- brittle nails;
- taste changes;
- skin itching, which quickly disappears if treatment is started.
The skin itches in 30% of patients with lymphogranulomatosis. The itching is mainly localized on the legs, tends to spread to the torso, and over time to the whole body. The skin itches more intensely at night, the itching is accompanied by a burning sensation.
Lymphoma is a malignant tumor arising from lymphocytes (white blood cells). Sometimes severe itching of the skin occurs, which occurs several years before the first symptoms of lymphoma develop.
HIV infection
In 90% of cases, the skin itches due to excessive dryness, secondary to various infections due to low immunity.
Parasite infestation
Infection with lice, which provokes pediculosis, is accompanied by itching of the scalp at the bite sites and the appearance of gray spots. Children get sick more often. Pediculosis can only be transmitted from a sick person through direct contact, through the use of shared combs, bed linen, and household items.
When infected with a subcutaneous mite, demodicosis develops. It provokes the appearance of acne, which is accompanied by itching. The mite is located in the sebaceous glands, hair follicles, causing hair loss, eyelashes, and a sallow-gray complexion. To prevent skin defects, it is necessary to promptly treat with drugs containing metronidazole.
One of the common infectious diseases with severe itching is scabies. Characteristic scabies, blisters, and blood crusts appear on the body. The patient actively begins to itch, facilitating the spread of parasites to healthy skin. It is important to carry out treatment as quickly as possible. Local medications are mainly used in the form of ointments (for example, sulfur ointment is used).
Worm infestation can also be accompanied by allergic rashes with itching, disturbances in the functioning of the digestive system, and general malaise due to intoxication. Infection with worms requires treatment with antihelminthic drugs, taking into account the type of parasites.
Senile itch
Senile itching is more common among men. It can be quite intense, accompanied by burning, tingling, and pain. The discomfort intensifies in the evening. Senile itching is never accompanied by purulent inflammation of the skin, lasts several months, and can disappear and reappear. Before treatment, pathologies that provoke itching should be excluded (diseases of the kidneys, liver, endocrine organs, dermatitis, allergies, infectious pathologies, mental disorders, malignant diseases, etc.).
Skin itching has a different nature, occurs as a result of exposure to irritating substances, parasites, fungi, viruses, and sometimes indicates serious disorders in the body, so consultation with a doctor is required.
Internal factors
Internal causes can cause itching. The symptom accompanies the following diseases and pathologies:
- Allergies are triggered by exposure not only to external allergens that come into contact with the skin, but also internal ones that enter the human body with food, inhaled air or medications taken. Symptoms vary: indigestion, runny nose, dry cough, lacrimation, swelling (including angioedema) and skin manifestations.
- Parasitic infestations: helminthiasis, giardiasis, ascariasis. Parasites feed on the tissues of the human body and secrete waste products and toxic substances that have an irritating effect. There are also numerous microorganisms that live in the dermis.
- Kidney diseases. These paired organs perform metabolic, excretory and other functions, and if their functioning is disrupted, substances that have a toxic effect on various tissues, including the skin, are retained in the body.
- Liver diseases. The organ is responsible for removing toxins, and when they leave the body untimely or remain in it, they gradually penetrate various organs and tissues, reach the dermis and have an irritating effect.
- Cholestasis is a violation of the synthesis or outflow of bile, accompanied by yellowness of the skin, itching, bitter taste in the mouth, darkening of urine, lightening of stool, constipation.
- Endocrine disorders: diabetes mellitus, thyrotoxicosis. The endocrine system performs a number of important functions, including the regulation of metabolic processes and hormonal levels. When the level of individual hormones and other substances changes, the skin suffers.
- Psychogenic scratching is caused by stress, anxiety, nervous strain and overwork suffered during the day. Irritated and excited nerve fibers provoke severe itching that occurs suddenly and for no apparent reason, especially at night.
- Blood diseases: iron deficiency anemia, polycythemia, leukemia, erythremia. Blood penetrates the dermis and directly affects its functioning and condition.
- The body may itch due to some malignant neoplasms. Tumors change the composition of the blood, release toxic compounds, and sometimes affect metabolic processes, reactions occurring in the body and the synthesis of certain substances.
- Pregnancy. During gestation, global changes occur in the body: hormonal levels, metabolism and blood composition change, the skin stretches, and a lack of certain substances occurs. Pregnant women often have an itchy growing belly.
Dry skin and itching
Dry skin is characterized by the following symptoms: peeling, tightness, invisible pores, redness, lack of elasticity. When you press your fingers on the surface of the skin, the marks do not disappear for a long time. When the skin dries out, microcracks appear in the upper layer of the skin. They contain bacteria and toxic substances that cause irritation and itching.
Causes of dry skin and itching:
- weak functioning of the sebaceous glands;
- dry air;
- prolonged exposure to the sun;
- improper skin care, abuse of alkaline detergents;
- dehydration of the body;
- hormonal disorders in diabetes mellitus, hypothyroidism;
- frequent nervous disorders;
- lack of vitamins A and E;
- taking certain medications;
- skin diseases (keratosis, allergies, psoriasis);
- bad habits;
- exhausting diets;
- aging.
Dry skin can be general or localized. Depending on the cause of the appearance and location, drug treatment is selected.
Skin diseases
If a situation arises where there seem to be no visible causes, but the body continues to itch, then check out the list of skin diseases. Most often, they are the main cause of itching of varying intensity and localization.
Dermatitis
This concept means a specific reaction of the body to internal or external factors. The reason may be:
- severe stress;
- frostbite;
- burn;
- food intolerance;
- hereditary predisposition;
- nervous disorders;
- unsatisfactory living conditions;
- poor hygiene.
Dermatitis is characterized by itching, hyperemia of the skin, rashes and peeling.
Eczema
An inflammatory skin disease that is not contagious to others, manifested by a rash, burning sensation, redness and itching. At the site of scratching, the blisters burst, and long-term non-healing erosions form in their place. Subsequently they become covered with crusts. The favorite places for the rash to localize are the face and hands.
The disease quickly becomes chronic, with a tendency to frequent relapses. In most cases, eczema is accompanied by diseases of the upper respiratory tract and metabolic disorders.
Dermatophytosis
Sometimes, for no apparent reason, the body itches due to fungi that multiply in the soil and live on the skin of humans and animals. Pathogenic microorganisms penetrate the epidermis, destroy proteins and absorb decay products. Most often, fungi settle on the scalp, eyebrows and eyelashes, but are also found on smooth skin and nail plates.
Lichen
A contagious skin disease caused by viruses or fungi. The typical route of transmission is from a sick person or animal. Among those infected, the majority are people with weakened immune systems. There are different types of lichen:
- encircling;
- pink;
- weeping;
- shearer
The scalp is most often affected; the affected area is marked by severe itching, flaking, and bright red skin color.
Pediculosis or lice infestation
People's susceptibility to lice is very high; unsanitary living conditions play a dominant role in lice infection.
You can get lice from people without a fixed place of residence (homeless people), as well as in places where hygiene is practically not observed and there is overcrowding. Most often, pediculosis is like an epidemic; the disease quickly spreads in such close communities as schools, preschool institutions, children's camps, and military barracks.
The bites of lice that live in the scalp or groin cause severe itching, but most importantly, they transmit typhus. Basic preventive measures include maintaining hygiene, using only your own comb, and sleeping on clean linen.
Psoriasis
It is a type of lichen planus and is caused by the body's immune cells. It appears in the form of red dry spots covered with a whitish coating on top.
With psoriasis, the bends of the elbows, head, and lower back are affected; rashes may appear on other parts of the body and the mucous membranes of the genitals. The disease can be triggered by hereditary predisposition, human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), certain infections and medications.
Scabies
The causative agent of the disease is the scabies mite. When they penetrate into the upper layer of the skin, the parasites “gnaw” passages there, thereby causing unbearable itching, which intensifies in the evening and at night. The favorite places for ticks to settle are the hands and stomach, where a specific paired rash appears.
The contagiousness of the disease is high, as in the case of head lice, people most often get sick in groups. Parasites are transmitted through surrounding objects, clothing and bed. The source of infection is a sick person, the incubation period is up to 30 days.
Hives
Refers to allergic diseases, often occurs together with Quincke's edema. Develops from insect bites, food intolerance, hypothermia, and gastrointestinal disorders. contact with household chemicals or detergents.
The hallmark of hives is an itchy red rash ranging in size from tiny elements to blisters. Strong scratching, sometimes to the point of bleeding, can aggravate the disease. There is a chronic form that develops with impaired intestinal, liver or kidney function.
Xerosis
Due to infections or severe itching, abnormal dryness of the skin surface may develop, manifested by skin engorgement, hyperemia, and peeling. The development of xerosis can be provoked by:
- cirrhosis of the liver;
- hepatitis;
- renal failure;
- skin diseases (psoriasis, dermatitis, seborrhea, eczema);
- malignant tumors.
When this symptom appears, it is very important to conduct a thorough examination of the internal organs so as not to miss the onset of serious diseases.
Traditional medicine in the treatment of itching
At home, you can prepare tinctures, teas, compresses, and herbal baths to treat itching. The most effective remedy is celandine. Reduces itching sensations with lemon balm tea, string baths and calendula.
Recipe for tincture of celandine (chain, calendula, burdock leaves, marjoram, nettle):
- chopped herb - 1 tbsp. l.;
- water – 1 glass.
Boil water, pour in the herb, let it brew for 30 minutes. Wipe the affected areas of the skin with the tincture 3-4 times a day. A decoction of plants in large proportions can be added to the bath when bathing. The tincture can be prepared not only with water, but also with vodka in the same ratio.
Peppermint alcohol tincture recipe:
- dry crushed leaves - 1 tbsp;
- vodka – 100ml.
The mint is poured with vodka and left in a dark place for 2 weeks. The mixture is filtered. Wipe the affected areas 3 times a day.
Oatmeal compress recipe:
- oatmeal – 1 cup;
- water – 1 glass.
Oatmeal is cooked in water; it is not salted or sugared. Let it cool down. Apply a thick layer to the sore spot for 30 minutes once a day. Ordinary soda helps with itching. It is added to the bath while bathing or a weak solution is made to wipe areas that are very itchy.
Aloe juice helps relieve discomfort. The leaf of this plant is cut in half and rubbed on the affected areas 2-3 times a day. Apple cider vinegar is a good remedy for skin rashes. It is applied to a cotton swab and wiped over problem areas several times a day.
It is recommended to take action if itchy sensations occur on the body, since without rashes and redness on the skin, malignant neoplasms often make themselves felt. Most often, the body itches with lymphoma, rarely with skin cancer. The use of opium and other medications increases the unpleasant symptoms.
Author: kikavcka1
Article design: Vladimir the Great
What disease can be a symptom of itchy skin?
When internal organs malfunction and various skin diseases occur, unpleasant phenomena such as itching, redness, peeling and much more can develop.
However, itching of the skin without rashes is also common. So, what pathologies can be indicated by itchy skin on the arms, legs and other parts of the body?
Presence of parasites
No person is immune from infection by various parasitic life forms. Parasites that cause itchy skin are lice, bedbugs, and scabies.
In such cases, severe itching of the skin is observed. A characteristic sign of parasites is wave-like attacks of itching, which intensify as the disease progresses.
It is very difficult to independently diagnose and find out the nature of a disease such as itchy skin. Symptoms are the first thing a person pays attention to.
They force him to make certain decisions to eliminate the problem. Skin itching without external manifestations is a special type of neuropsychiatric disease, since there are no rashes, redness, or lesions on the body.
It is impossible to determine it yourself. However, a qualified doctor, by examining the patient’s body, examining the blood tests obtained and the history of the disease, can clearly determine the presence or absence of a disease such as itchy skin.
Photos of painful areas and prior medical reports of past similar problems are additional indicators of the likelihood of itchy skin.
The most obvious symptoms of this disease include: scabies, pain when touching the affected area, spasms of blood vessels, swelling of body tissues, rashes, acne and dry skin.
However, the above signs of itching must be confirmed by a doctor’s opinion, since they are also characteristic of other dermatological, mental and endocrine diseases.
How to remove body itching at home
Treatment at home is aimed at eliminating the symptoms, but you need to work with your doctor to combat the cause of the strong desire to scratch the skin. As temporary help you can use:
- Burdock roots. You need already dried roots to then obtain the powder using a coffee grinder. Pour 2 tbsp into a saucepan. l. powder, pour 1 liter of water. Cook for half an hour. When it cools down, you can make gauze compresses by applying to the irritated area. The effect should occur within half an hour.
- Alcohol tincture of elecampane. You can prepare it at home, for which you take 1 tbsp. l. finely chopped roots, pour them into a suitable dark glass bottle, add 50 ml of alcohol. The tincture is prepared for 10 days, after which you need to make an aqueous solution with the tincture and wipe the itchy skin. According to people's reviews, the effect occurs immediately.
- Needles. You will need young buds and pine needles in the amount of one glass. Pour a liter of boiling water over them and simmer over low heat for 20 minutes. Wash with the cooled broth, wipe the skin, make compresses and lotions. The result is felt quickly.
Mechanism of itching
Itching is a protective reflex that allows you to cleanse the skin and neutralize irritants that have mechanical, chemical and other effects. The symptom is determined by the innervation of the skin and develops due to irritation of receptors or nerve endings. Receptors respond to stimuli and transmit signals to the brain along nerve fibers.
Itching is caused by various reasons and is accompanied by other manifestations: tingling, peeling, keratinization of the skin, rashes. There are also general symptoms that are not related to dermatological ones and depend on the specific disorders that provoked the problem.
Preparations for body skin itching
Treatment for body skin itching is selected based on the causes that contribute to it.
Skin itching can be treated with drugs of 3 groups:
- Antihistamines.
- Hormonal agents.
- 3Antibiotics.
Antihistamines are the most extensive group of drugs. Within a couple of hours after taking it, you can notice the first results - swelling and itching subside and become less noticeable.
There are 3 groups of antihistamines.
1st generation antihistamines
This includes drugs that have a sedative effect and eliminate allergic reactions. They have a rapid-response effect, so you need to take them several times a day.
After taking this group of drugs, severe drowsiness may occur, so the drugs are contraindicated for people working in conditions of increased traumatic risk. These include Diazolin, Suprastin, Tavegil.
2nd generation antihistamines
These drugs do not have an immediate effect, but their effect may last more than a day. They do not have a pronounced sedative effect, so after taking them you can work normally. 2nd generation antihistamines are Claritin, Zyrtec, Claridol, Cetrin.
3rd generation antihistamines
This group has practically no sedative effect; drowsiness after taking them is very rare. This includes drugs such as Telfast, Erius.
Hormonal drugs are a more powerful tool in the fight against allergies and itching. They affect the cells that are responsible for the allergic reaction. The big disadvantage of hormonal drugs is that they have many side effects.
In this regard, their prescription is appropriate only in extremely difficult situations or after ineffective treatment with antihistamines. This group includes Dexamethosone, Prednisolone. Take them strictly as prescribed by the doctor.
Hormonal drugs are a more powerful tool in the fight against allergies and itching
Antibiotics are used to treat itching if infection is present. They are prescribed only after certain tests. In most cases, treatment is with broad-spectrum antibiotics. These include Cephalosporins and Penicillin.
Rash accompanied by itching
Rashes that are accompanied by severe itching can appear on the skin for various reasons. They signal some kind of disease or arise as a result of an irritating factor.
Causes:
- allergy;
- skin diseases;
- insect bites;
- infectious diseases;
- mental disorders;
- sunburn.
Allergies can occur to mold, pollen, animal dander, as well as certain foods or chemicals (medicines). A skin rash appears after bites from bees, ants, mosquitoes, and bedbugs.
Types of rashes:
- a blister filled with liquid – herpes, eczema, chicken pox;
- blisters with suppuration - acne, follicles, boils;
- erythema (raised area of bright red color) – allergies to food products, medications;
- blisters (urticaria) – urticaria, insect bites;
- nodules – eczema, psoriasis, lichen ruber, papillomas, warts;
- purpura (skin hemorrhages) – hemophilia, leukemia, scurvy;
- spots (redness or discoloration) – dermatitis, vitiligo, typhoid fever.
Diseases accompanied by rash and itching, symptoms:
- scabies - caused by the scabies mite, blisters, papules, vesicles, whitish lines with a bulge appear on the skin, most often observed on the arms and legs;
- eczema - bright red spots without clear boundaries, papules, erosive formations with serous fluid, spreads throughout the skin;
- chicken pox - caused by the herpes virus, at the beginning of the disease the body temperature is low, convex, red pimples appear on the face, chest, arms, inside of which nodules with clear liquid form;
- measles - a reddish rash in the throat, white spots on the inside of the cheeks, temperature up to 39 degrees, after 3 days - rashes on the face, body, arms, thighs, pimples merge with each other and peel off;
- scarlet fever - the disease is caused by streptococci, a pinpoint rash appears in the upper part of the body, red spots merge, there is a bright blush on the cheeks, the nasolabial triangle is pale, T rises to 39 ° C;
- herpes zoster - rashes in the form of pinkish blisters surrounding the body;
- rubella - roundish redness 2-10mm appears first on the face and neck, then spreads throughout the body, after 72 hours disappears without visible traces, the itching is not severe.
Itching of the body skin without rashes and redness can also occur in children. But often before the age of 6 months, a rash on the cheeks often appears. It is usually associated with the body's reaction to food and is a sign of the body's adaptation to new conditions. Rashes on the skin of infants occur in the case of prickly heat. Small blisters with a reddish liquid appear on the body.
What to do if your whole body itches
Considering that there is only one itching, but there are many causes, its treatment must be approached differently. What to do if your whole body itches? You can use ointments and creams that can relieve discomfort, but if the causes lie in liver disease or endocrine system disorders, then self-medication with local remedies can only aggravate the problem and complicate further treatment. Indeed, in this case, itching on the skin is just the tip of the iceberg, under which lies a serious illness, possibly fraught with tragic consequences.
Diagnostics
Determining the root cause will require diagnosing the itchy areas. First contact a dermatologist to prescribe tests and a detailed examination. If the dermatologist finds it difficult to name the cause, consultation with a therapist, endocrinologist, allergist, gastroenterologist and other specialists will be required. Principles of treating itchy skin:
- eliminating the cause;
- local treatment;
- systemic treatment.
Depending on the reasons that caused the unpleasant symptoms, treatment for itching of the body skin is prescribed. For allergic scratching, antihistamines are prescribed: Zyrtec, Loratidine, Erius, Zyrtec, Suprastin, Tavegil. Additionally, it is recommended to take sedatives: Novo-Passit, valerian, mint tea, motherwort tincture, since the constant desire to itch disrupts sleep and makes the patient irritable. Complex manifestations are treated only under the supervision of a doctor.
However, this will take some time, and you want to relieve the itching as quickly as possible. Therefore, there are general recommendations:
- The diet should not contain salty, hot, spicy foods. It is undesirable to drink strong tea, coffee, and alcohol.
- If an elderly person has body itching (senile, worse in the evening and at night), then iodine preparations will alleviate the condition.
- Take warm baths with sea salt.
- Wipe the skin with calendula tincture in alcohol, lubricate with menthol-based antihistamine ointments.
Folk remedies
Along with drug therapy, folk remedies for body itching are used:
- A quick effect is achieved by taking baths with decoctions of plants: nettle, chamomile, mint, celandine, pine needles.
- Pruritoceptive (insect bites) are removed with coconut oil baths. To do this, dissolve 50 g of oil in a water bath and pour into warm water. The procedure time is 15 minutes.
- Lemon juice works great for itching, but it should not be applied to areas with damaged skin.
- Vaseline will help quickly relieve itching, as it will additionally moisturize and soften.
- To soothe irritations, you should use basil. It contains vitamins A, C, P, which are very important for skin health. You need to wipe the irritated areas with a clean fresh leaf or prepare a decoction of basil and make lotions.
- Apple cider vinegar and celandine are used as applications (do not use celandine for chemical or sunburn).
What causes itching?
The physiology of the origin of itching is quite complex. It can be triggered by multiple factors.
Dry skin is one of the causes of itching
The most common factors are:
- Infections that can affect the upper layers of the epidermis (impetigo, folliculitis).
- Allergic manifestations of the body to certain medications, plants, substances of chemical origin, insect bites, etc.
- Itching, accompanied by a skin rash, is one of the main signs of childhood infectious diseases (measles, chickenpox).
- Infections caused by parasites (lice, pinworms, mites).
- Dry skin.
- Pathologies of the liver or kidneys.
- Endocrine diseases (hypothyroidism, diabetes).
- Blood diseases (anemia).
- Nervous disorders.
These are the main, but not all, causes of itching. It is also worth highlighting intense senile itching, which can affect mature people without any reason.
Itching during pregnancy
In 1/3 of pregnant women, itchy skin sensations occur in the second half of the 2nd trimester. The desire to itch does not require special treatment. You can only drink more fluids and follow a hypoallergenic diet. Hypersensitivity goes away immediately after childbirth.
Causes of itching during pregnancy:
- due to stretching of the skin;
- liver pathologies, cholecystitis, pancreatitis, hepatitis;
- allergies to food, cosmetics, clothing;
- an increase in the number of estrogens in the body;
- scabies, eczema;
- bacterial vaginosis of the genital organs.
During pregnancy, a woman needs to take care of body hygiene and wear clothes made from natural fabrics. You should not comb the affected areas of the body with your hands; the skin may be injured, bacteria may enter the wounds and cause an inflammatory process.
What is itchy skin
Human skin is penetrated by billions of nerve endings, which are very sensitive to all sorts of irritants: vibration, touch, chemical or thermal effects. A crawling insect, an insect bite, the touch of a feather, a cobweb, or a hair can cause a desire to itch, burning, tingling at the site of irritation: you want to quickly remove this unpleasant sensation by scratching the itchy skin.
Generalized itching - unbearable discomfort in the superficial layers of the dermis - can cause some diseases of the internal organs, allergic reactions due to dermatitis. Among the symptoms of dermatological diseases, skin itching dominates, but scratching syndrome of the anogenital zone, conjunctiva, trachea, pharynx, nose, and oral mucosa often occurs. There is a distinction between itching of the whole body without rash and with rash.
Body itching without rash
Itching all over the body without rashes can occur due to the following diseases:
- Kidney: chronic failure.
- Liver, gallbladder, pancreas: cancer of the head of the pancreas, biliary cirrhosis, hepatitis, bile stagnation, obstruction of a large bile duct, increased bile salts in the blood, sclerosing cholangitis, obstruction of the duodenal papilla by a neoplasm or stone.
- Neuroendocrine: hypo- and hyperthyroidism, hyperparathyroidism, carcinoid syndrome, diabetes mellitus, symmetrical erythrocyanosis.
- Hematological (blood diseases): leukemia, paraproteinemia, mastocytosis, lymphogranulomatosis, iron deficiency anemia, polycythemia vera, lymphomas, multiple myeloma, Waldenström's macroglobulinemia.
- Neurological: brain tumor, multiple sclerosis, brain abscess, cerebral infarction.
- Paraneoplastic syndrome: visceral carcinoma, Sjogren's disease.
- Rheumatological: dermatomyositis.
- Mental: depressive states and psychoses.
- Infectious and parasitic: parasitosis, HIV.
- Other conditions: age-related changes (senile), pregnancy, alcoholism and hangover.
Rash and itching on the body
When multiple changes occur on the mucous membrane and skin that differ in color, texture, and appearance from normal skin, they indicate a rash. The rash can affect the arms, legs, face, stomach, and chest. These may be primary symptoms - pustules, redness, spots, goosebumps, blisters, pimples, blisters. As the disease progresses, the rash is replaced by secondary elements:
- Loss of natural skin color (discoloration, darkening).
- Erosions and ulcers are the result of opening an abscess with a violation of the integrity of the skin with the capture of subcutaneous fatty tissue.
- Peeling - scales of dead epidermis.
- Crusts are the dried surface of weeping erosion, ulcers, and opened blisters.
- Scratching – superficial or deep abrasions.
- Lichenification – thickening, strengthening of the skin pattern.
It is not worth making a diagnosis on your own, guided by visible signs and information you have read. In case of any suspicious manifestations, you should consult a doctor to identify the underlying internal pathology that caused the scratching. A rash and a strong desire to scratch on the body are accompanied by diseases such as:
- chicken pox;
- postherpetic neuralgia;
- rubella;
- measles;
- scarlet fever;
- herpes;
- meningococcal sepsis;
- hives;
- acne;
- fungal infections;
- psoriasis;
- scabies due to infection by microscopic parasites.
- Itching on hands and redness
- What can cause itchy palms in children and adults - skin and infectious diseases, medications for treatment
- Scabies on the hands - routes of infection, manifestations on the skin, diagnosis and treatment methods
Why does my skin itch?
Itchy skin is a common symptom among patients of all ages. Unpleasant symptoms can appear in both children and older people. The causes of the pathology can be very diverse. Later in the article we will find out the most common of them. Conventionally, all the causes of discomfort on the skin can be divided into exogenous and endogenous factors. So, let's look at them in more detail. The following reasons are considered exogenous:
This is the name for the feeling in which the skin is irritated and you want to scratch it. May be accompanied by tingling and burning.
Itching is not a separate ailment. This is just a symptom, one of a complex characteristic of some disease.
Regardless of what pathology it is caused by, it occurs due to irritation of the nerve endings existing in the upper and middle layers of the epidermis.
Why do people itch? Itching, what is it like? Effective methods of treatment and prevention. Answers to these and other questions in a short video review. Treatment is necessary - itchy skin can lead to thinning of the skin, as well as various damage to the epidermis. A more dangerous situation is the addition of an infection. Therefore, in order to avoid more serious problems, you should promptly respond to your own body’s “alarm signals” and seek qualified medical help.
Treatment methods
If burning, tingling and redness of the skin occurs, you should pay special attention to personal hygiene. If you have itchy skin all over your body, it is recommended to wipe the epidermis daily with a vinegar solution. If there is localized itching (in the anus or perineum), these areas should be thoroughly washed twice a day (morning and evening).
Drug treatment
Ointments are used to eliminate unpleasant symptoms. It is worth remembering that these medications are temporary and will not help get rid of skin irritation forever.
The most effective medications for external use:
- Sinaflan. The ointment is applied to the affected area no more than four times a day. With prolonged use of the product, pigmentation disorders, dryness, hair loss, etc. may appear on the skin. Before using the ointment, read the instructions.
- Levomekol. An effective ointment for itchy skin, has an anti-inflammatory effect. Contraindications: hypersensitivity, presence of trophic ulcers or severe burns. Side effects when using the drug are extremely rare.
- Fenistil gel. The product is applied to the affected areas several times a day. Sometimes the gel can cause dry skin. If more serious side effects occur, you should immediately stop using the product.
Before applying medicinal ointments to the skin, be sure to read the instructions for use.
In most cases, skin irritation occurs due to elevated histamine levels. To eliminate the symptoms of itching, doctors recommend using antihistamines.
Pills:
- Suprastin. The dosage of the drug is prescribed individually (depending on the age and weight of the patient). Side effects are rare and disappear quickly. The drug should not be used in children under three years of age, during pregnancy, lactation and with lactose intolerance.
- Erius. Common side effects when using tablets: dry mouth, weakness, headache, anaphylactic shock. The drug is contraindicated in nursing and pregnant women. It should also not be used for renal failure.
- Claritin. The drug acts on the cause of itching of the skin of the body. You can completely get rid of irritation in just one week. Dosage – no more than one tablet (10 mg) per day.
- Tavegil. Take the tablets before meals with water. Children from 6 to 12 years old are recommended to take 1/2 tablet per day. Dosage for adults and children over 12 years of age – 1 mg twice a day (morning and evening).
Ointments based on glucocorticosteroids:
- Triderm. This product has an anti-inflammatory effect and quickly eliminates redness and irritation of the skin. Treatment lasts no more than one month. Side effects when using the cream are rare. Steroid ointment has a number of contraindications; read the instructions before using it.
- Fluorocort. The medicinal ointment should not be used by pregnant and lactating women and small children. Also, this remedy is not recommended for use against fungus, syphilis and skin tuberculosis. The cream must be applied to the affected area 2-3 times a day. If your whole body itches after using the medicine, you should consult a doctor.
- Lorinden. With long-term use of steroid ointment, some side effects may appear: dryness and short-term redness of the skin, impaired pigmentation of the epidermis. The product is applied in a thin layer to the skin no more than three times a day. The course of treatment is 2 weeks.
It is strictly forbidden to use the above medications without a doctor’s recommendation. Self-medication can worsen your health and lead to various complications.
Traditional medicine
What to do if your body itches, but you don’t have the opportunity to visit a dermatologist? You can eliminate burning and redness using traditional medicine. It is worth remembering that home remedies only provide temporary relief from itching.
Let's look at the recipes:
- First aid for inflammation is a cream with chamomile extract or glycerin. The cream must be applied 4 times a day.
- If the itching appears as a result of an insect bite, wipe the affected area of the body with alcohol.
- Soda lotion. Mix a teaspoon of baking soda with water. If desired, you can add chamomile tincture or baby cream to the paste. Apply the resulting product to the skin, and after a while, rinse it with water.
- Mix tea tree oil and menthol in equal proportions. This product will pleasantly cool the skin and eliminate redness and irritation. Treat itchy body skin until all symptoms completely disappear. Repeat the procedure several times a day.
- Add chamomile tincture, baking soda and salt to your bath. The duration of the procedure is 15 minutes.
- Pumpkin seeds. In order to alleviate unpleasant symptoms, it is recommended to eat 2-3 tablespoons of seeds in the morning (on an empty stomach). You can also add them to various dishes (sauces, salads, drinks).
- After showering, apply a small amount of olive oil to your body.
Treatment with folk remedies
Of course, the treatment of this disease largely depends on the reasons that caused it. For example, if the itchy skin was caused by cholecystitis, it is important to begin treatment for this disease after a complete and thorough diagnosis.
Otherwise, the scabies will not stop, and additional symptoms will only intensify. If the itching is caused by dry skin or nervous tension, to get rid of it, it is enough to choose the right skin care, take a medicinal bath or a sedative herbal preparation.
Traditional medicine contains many valuable and time-tested ways to quickly get rid of this unpleasant symptom. Such recipes will be effective and will help if you are worried, but they are not able to eradicate the main cause of this symptom.
Relaxing baths
This method is especially suitable when the body itches everywhere and it is difficult to act on it locally. It is important that the water is not too hot - this can dry out already irritated skin. Immersion in water itself will significantly relieve annoying itching and calm the nervous system.
Special herbal supplements can enhance the relaxing effect, relieve tension and soothe inflamed areas of the body. For this purpose, add 200 ml of a strong decoction of chamomile or string to hot water. This will help soften the skin and get rid of scabies for 12 hours.
It is recommended to take such baths before evening to ensure restful sleep. You can also use a decoction of chamomile or string to wipe itchy areas after leaving the bath. Also useful for apathy.
Propolis
This substance is used to treat many dermatological diseases, burns, wounds and itchy rashes. Propolis promotes rapid regeneration of wounds, has an antibacterial effect, relieves pain and itching. The most commonly used is propolis ointment. It is applied in a thin layer to the affected areas and left to absorb.
The desired effect will appear within 10 minutes. After this, you need to remove the remaining ointment with a cotton pad. This remedy can be used whenever itching occurs on any part of the body. However, you need to remember: if you are plagued by frequent attacks of causeless itching, you need to seek medical help. It is also used to treat chickenpox.
Disease prevention
Some useful preventative measures:
- it is necessary to regularly visit the clinic and undergo examinations, especially if any symptoms are observed that indicate the occurrence of various diseases;
- maintaining a properly balanced sleep and rest schedule, as well as proper alternation of work and rest;
- It is important to avoid situations that can provoke stress;
- maintaining a proper diet;
- timely treatment of diseases, if any.
When a person constantly itches his body in different places (it is almost impossible to determine the cause on his own), he should consult a doctor. But even doctors cannot always determine the cause of itching based on the patient’s complaints and external examination of the body.
You need to realize that if a person follows the rules of hygiene, then his body will not itch just like that. Therefore, you should not waste time, hoping that the itching will go away on its own. It’s better to get tested right away and find out what’s causing it and get rid of it. You need to fight not the consequence of the problem, but its “root”.