Pregnancy is a wonderful and unforgettable time in the life of every woman. But this period rarely passes without complications. Toxicosis, bone discrepancy, hypertonicity. Almost all expectant mothers have to deal with these unpleasant phenomena.
Every second pregnant woman knows about increased tone. For some, it may be asymptomatic, while others will feel nagging pain in the lower abdomen and feel tension. In both the first and second cases, the tone cannot be ignored - it can provoke miscarriage, fetal hypoxia and cause other complications.
What kind of tone is this?
The uterus is an internal reproductive organ consisting of three layers:
- Perimetry is the first outer layer.
- Myometrium is a muscular layer.
- The endometrium is the inner layer, which is the mucous membrane.
Like any other muscle, the uterus can be relaxed and tense. Its reduction during childbirth helps the baby to be born, but increased tone in the first and second trimester of pregnancy must be removed, as it can cause a miscarriage.
Hypertonicity can be observed throughout all three trimesters of pregnancy . There may be several reasons for increased uterine tension:
- Active physical activity;
- Stress;
- Poor nutrition;
- Previous abortions;
- Multiple pregnancy.
What is hypertonicity?
The uterus is a hollow organ. Its walls are formed by three layers: the outer layer is the serous membrane, the intermediate layer is the myometrium, and the inner layer is the endometrium. The myometrium consists of smooth muscle fibers that can contract, that is, become toned, under the influence of certain factors.
Pregnancy or gestation causes strong changes in the hormonal balance in a woman’s body, as a result of which the uterus is in a relaxed state - normotonus. This occurs under the influence of “pregnancy hormones” - progesterones. If the muscles of the uterus are tense or contract during this period, then we are talking about hypertonicity. Often this pathology does not manifest itself in any way, and it can only be diagnosed during a gynecological examination.
It is necessary to distinguish between physiological and pathological uterine hypertonicity. In the first case, muscle tension is weak, painless and occurs in response to a change in the woman’s condition: after physical activity, due to fatigue or stress. It passes quickly and, in most cases, does not cause any inconvenience to the pregnant woman.
The pathological tone of the uterus persists for a long period of time and is a threat to the normal course of pregnancy. This condition requires mandatory monitoring by a gynecologist and timely therapy if necessary.
Products for uterine tone
A pregnant woman needs to take care of her nutrition more than ever. Therefore, many foods during this period should be excluded from the diet or their consumption should be limited.
- Coffee, strong tea and drinks containing caffeine . They increase heart rate and blood pressure.
- Sugary carbonated drinks lead to gas formation and bloating, which provokes contraction of the back wall of the uterus.
- Alcohol and tobacco have a detrimental effect, first of all, on the development of the child. They should be completely eliminated from use.
- It is necessary to significantly limit the consumption of dishes made from legumes, cabbage, radishes and other products that increase the formation of gases.
Any foods that can be harmful to health should not be present in the diet of a pregnant woman. It is advisable to replace fatty meat with lean veal, rabbit or chicken. Eat more fresh vegetables and fruits.
What is hypertonicity?
The uterus is a hollow organ. Its walls are formed by three layers: the outer layer is the serous membrane, the intermediate layer is the myometrium, and the inner layer is the endometrium. The myometrium consists of smooth muscle fibers that can contract, that is, become toned, under the influence of certain factors.
Pregnancy or gestation causes strong changes in the hormonal balance in a woman’s body, as a result of which the uterus is in a relaxed state - normotonus. This occurs under the influence of “pregnancy hormones” - progesterones. If the muscles of the uterus are tense or contract during this period, then we are talking about hypertonicity. Often this pathology does not manifest itself in any way, and it can only be diagnosed during a gynecological examination.
It is necessary to distinguish between physiological and pathological uterine hypertonicity. In the first case, muscle tension is weak, painless and occurs in response to a change in the woman’s condition: after physical activity, due to fatigue or stress. It passes quickly and, in most cases, does not cause any inconvenience to the pregnant woman.
The pathological tone of the uterus persists for a long period of time and is a threat to the normal course of pregnancy. This condition requires mandatory monitoring by a gynecologist and timely therapy if necessary.
Exercises for uterine tone
The question of how to relieve the tone of the uterus during pregnancy worries many pregnant women. Before contacting a doctor, you can try to relieve tone with exercises that will be easy to perform even for those who do not like to exercise.
- Exercise No. 1 . Relaxation of muscles (including muscles of the face and neck). Take a comfortable position and try to relax all your muscles, inhale deeply. Try to let go of all anxious thoughts that provoke muscle tension.
- Exercise No. 2 . Cat pose. Get on all fours and lower your head. When raising your head, you need to slowly bend your back, and when lowering it, you need to arch it. Perform the movements slowly. Exercise will help relieve tension in the lower back and eliminate tone.
- Exercise No. 3 . Get on all fours. Let your stomach hang for a while. After performing, take a horizontal position and relax.
Why is increased tone dangerous?
During pregnancy, especially in the first trimester, it is very important that the uterus is in normal tone. If the myometrium is pathologically tense for a long time, this can negatively affect the condition of the expectant mother and fetus.
Most often, increased tone occurs in pregnant women in the early stages. The appearance of any alarming symptoms is a reason to urgently consult a doctor. The most severe complication of hypertonicity is embryo rejection and the risk of spontaneous termination of gestation.
In the first 6-7 weeks of pregnancy, a woman’s body tries to adapt to its new state. Hormonal changes occur very actively, which is fraught with deterioration in health, toxicosis, sudden mood swings and increased fatigue. During this period, it is very important to get more rest and minimize any stress and harmful influences.
In the 1st trimester of pregnancy, the embryo is especially vulnerable. Until the middle of the 2nd month of gestation, it has not yet become entrenched in the wall of the uterus, and the formation of the placenta, which protects the fetus from external influences, continues until 13-15 weeks. Hypertonicity leads to an increase in intrauterine pressure, and, as a result, the expulsion of a non-implanted fertilized egg. That is why the manifestation of myometrial tone in the 1st trimester is very dangerous.
The tone of the uterus in the second trimester also has a detrimental effect on the course of pregnancy. This pathology can lead to fetoplacental insufficiency - a condition in which the fetus does not receive the required amount of oxygen and blood. A constant deficiency of substances necessary for life causes slow development of the fetus.
Fetoplacental insufficiency develops due to the fact that during myometrial spasms, numerous vessels of the placenta are compressed and the blood supply is disrupted. In addition, the placenta cannot contract, which is why, with hypertonicity, its detachment often occurs.
How to quickly relieve uterine tone during pregnancy?
Quick relief of uterine tone during pregnancy is possible with the help of medications:
- Antispasmodics;
- Vitamins and magnesium B6;
- Sedatives;
- Hormonal drugs.
Attention! Taking any medications on your own is strictly prohibited. Be sure to consult your doctor!
The duration of medication depends on the reasons that caused hypertension. When increased tone threatens miscarriage, the patient may need hospitalization.
Causes of pathology
Hypertonicity of the uterus during pregnancy can be caused by a number of different factors:
- 1. Hormonal imbalance. Hypoplasia (underdevelopment) of the placenta, depressed ovarian or adrenal function and other disorders provoke insufficient production of progestogens and excess production of oxytocins or androgens. Hormonal disorders cause pathological contractions of the uterus;
- 2. Anomalies of the reproductive system: bicornuate or saddle-shaped uterus, genital infantilism - underdevelopment of the genital organs;
- 3. Infections, viruses and sexually transmitted diseases;
- 4. Neoplasms in the area of the uterus, appendages or vagina: fibroids, carcinomas, cysts;
- 5. Rh conflict: if the expectant mother’s Rh factor is negative, and the embryo’s is positive, then the woman’s body begins to reject the fetus;
- 6. Constant physical and emotional stress, depression, overwork;
- 7. Diseases not directly related to the genital organs, but negatively affecting the functioning of the entire body: disturbances in the functioning of the cardiovascular, excretory, and central nervous systems;
- 8. Previous instrumental abortions or genital surgeries;
- 9. Use of emergency contraception.
Some expectant mothers are at higher risk of developing hypertension than others. The risk group includes women who:
- 1. History of one or more surgical abortions;
- 2. Weak immunity;
- 3. The body is often exposed to harmful factors: radio emissions, toxic substances, etc.;
- 4. There are bad habits: smoking, alcohol abuse, drug addiction;
- 5. Weak nervous and immune system;
- 6. The functioning of the genital organs is impaired;
- 7. Multiple pregnancy.
Pregnant women with a high risk of hypertonicity should be attentive to their well-being and undergo regular examinations by a gynecologist.
Other methods of relieving uterine tone
A warm, relaxing bath or shower will help relieve uterine tone during pregnancy at home. It is best to take a bath before bed. Water relieves tension and fatigue. After water procedures, you can take soothing tea. Mint, motherwort, valerian and lemon balm are herbs that will help relieve stress and relax.
To add flavor, it is recommended to add a spoonful of honey. You can experiment with the components, but provided that they are not contraindicated for pregnant women and will not cause an allergic reaction.
The positive effects of aromatherapy cannot be underestimated. The smell of myrrh, lotus, jasmine, vanilla and other oils will calm, relax and help cope with tension.
Causes of pathology
Hypertonicity of the uterus during pregnancy can be caused by a number of different factors:
- 1. Hormonal imbalance. Hypoplasia (underdevelopment) of the placenta, depressed ovarian or adrenal function and other disorders provoke insufficient production of progestogens and excess production of oxytocins or androgens. Hormonal disorders cause pathological contractions of the uterus;
- 2. Anomalies of the reproductive system: bicornuate or saddle-shaped uterus, genital infantilism - underdevelopment of the genital organs;
- 3. Infections, viruses and sexually transmitted diseases;
- 4. Neoplasms in the area of the uterus, appendages or vagina: fibroids, carcinomas, cysts;
- 5. Rh conflict: if the expectant mother’s Rh factor is negative, and the embryo’s is positive, then the woman’s body begins to reject the fetus;
- 6. Constant physical and emotional stress, depression, overwork;
- 7. Diseases not directly related to the genital organs, but negatively affecting the functioning of the entire body: disturbances in the functioning of the cardiovascular, excretory, and central nervous systems;
- 8. Previous instrumental abortions or genital surgeries;
- 9. Use of emergency contraception.
Some expectant mothers are at higher risk of developing hypertension than others. The risk group includes women who:
- 1. History of one or more surgical abortions;
- 2. Weak immunity;
- 3. The body is often exposed to harmful factors: radio emissions, toxic substances, etc.;
- 4. There are bad habits: smoking, alcohol abuse, drug addiction;
- 5. Weak nervous and immune system;
- 6. The functioning of the genital organs is impaired;
- 7. Multiple pregnancy.
Pregnant women with a high risk of hypertonicity should be attentive to their well-being and undergo regular examinations by a gynecologist.
Prevention
A good way to prevent tone is to constantly wear a prenatal bandage, which takes the load off the uterus, causing the muscles to strain less. You can avoid uterine tone if you follow the following rules throughout pregnancy:
- Eat right, more fresh vegetables and fruits.
- Don't forget about vitamins and folic acid.
- Medical care and bed rest should not be neglected;
- Get rid of negative emotions. Of course, it’s easier said than done, because stress is a constant companion in our lives. But the expectant mother should remember that during pregnancy her main priority should be the child.
- Take a walk in the fresh air, avoid active physical activity.
- Get tested on time and undergo an ultrasound.
- Wear comfortable clothes and low-heeled shoes.
Important! To avoid hypertension, it is important to regularly visit a gynecologist who will monitor the course of pregnancy. All changes occurring in the body must be reported to the gynecologist.
Why is increased tone dangerous?
During pregnancy, especially in the first trimester, it is very important that the uterus is in normal tone. If the myometrium is pathologically tense for a long time, this can negatively affect the condition of the expectant mother and fetus.
Most often, increased tone occurs in pregnant women in the early stages. The appearance of any alarming symptoms is a reason to urgently consult a doctor. The most severe complication of hypertonicity is embryo rejection and the risk of spontaneous termination of gestation.
In the first 6-7 weeks of pregnancy, a woman’s body tries to adapt to its new state. Hormonal changes occur very actively, which is fraught with deterioration in health, toxicosis, sudden mood swings and increased fatigue. During this period, it is very important to get more rest and minimize any stress and harmful influences.
In the 1st trimester of pregnancy, the embryo is especially vulnerable. Until the middle of the 2nd month of gestation, it has not yet become entrenched in the wall of the uterus, and the formation of the placenta, which protects the fetus from external influences, continues until 13-15 weeks. Hypertonicity leads to an increase in intrauterine pressure, and, as a result, the expulsion of a non-implanted fertilized egg. That is why the manifestation of myometrial tone in the 1st trimester is very dangerous.
The tone of the uterus in the second trimester also has a detrimental effect on the course of pregnancy. This pathology can lead to fetoplacental insufficiency - a condition in which the fetus does not receive the required amount of oxygen and blood. A constant deficiency of substances necessary for life causes slow development of the fetus.
Fetoplacental insufficiency develops due to the fact that during myometrial spasms, numerous vessels of the placenta are compressed and the blood supply is disrupted. In addition, the placenta cannot contract, which is why, with hypertonicity, its detachment often occurs.
Consequences for the fetus
In the second trimester, the placenta is already actively functioning and the baby is fed through the umbilical cord. With hypertonicity, sharp contractions of the uterus occur, while the placenta remains at rest.
Such an imbalance can provoke the development of various pathologies, which (without timely consultation with a doctor) trigger labor and lead to premature birth .
It is worth noting that the Russian Federation has adopted a law on saving premature babies who are born more than 22 weeks and weighing more than 500 grams. Not all perinatal centers are equipped with modern resuscitation equipment and have experienced neonatologists among their staff. It is not recommended to self-medicate; you must trust your doctors and follow all the rules.
Pathologies that can cause premature birth include:
- Placental abruption. During the period of active uterine contractions, the placenta is able to detach from the uterus, which can result in premature birth and disruption of blood supply in the placenta-fetus system.
- hypoxia caused by impaired blood supply to the placenta.
- Heavy uterine bleeding caused by contractions of the uterine walls and endometrial detachment.
- Delay in fetal development. The contracting uterus puts pressure on the fetus and causes intrauterine hypoxia. Lack of oxygen affects the brain activity of the unborn child.
- Intrauterine fetal death. Occurs as a result of prolonged hypoxia and impaired blood supply to the placenta.
Symptoms of uterine hypertonicity in the 2nd trimester
In the second trimester, the fetus has already acquired human shape and some vital organs have formed. Starting from the 20th week of pregnancy, the baby begins to move and feel influences from the outside world. Hypertonicity of the uterus in the second trimester is a serious threat of premature birth or miscarriage. It is necessary to know the signs of this condition in order to contact your doctor in time for medical help.
Uterine hypertonicity is manifested by the following symptoms :
- Aching, nagging pain in the lower abdomen. Pain occurs as a result of uterine contractions, which stimulate the onset of labor. Pain with hypertonicity of the uterus is almost identical to pain with menstrual bleeding, since during menstruation the uterus is also in good shape and actively contracts, trying to get rid of the outdated layer of the endometrium.
- Spotting bloody discharge from the vagina. When the walls of the uterus contract, some parts of the endometrium can be torn off and leave the body in the form of bloody discharge. Bleeding in the second trimester is an extremely dangerous symptom that requires immediate hospitalization in the gynecological department to maintain pregnancy.
- By the end of the second trimester, when the abdomen acquires an impressive size, with hypertonicity of the uterus, you can notice a change in its shape. The abdomen pulls in a little , becomes hard and tense.
- Girdle pain in the sacrum and pelvis area , which occurs as a result of pinching of nerve endings.
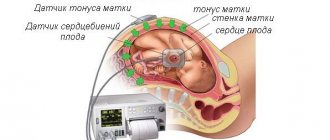
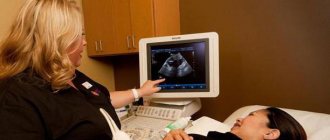
You can determine uterine contractions at an appointment with a gynecologist using a simple palpation of the abdomen or ultrasound diagnostics. On the ultrasound picture, the shape of the uterus will be changed. If hypertonicity is suspected, the doctor prescribes calming and sedative medications that help relieve muscle tone.
Causes
Today in medical practice there are many factors that are the causes of the development of hypertension during pregnancy. They are divided into 2 groups: physiological and psychological. However, despite such a strict gradation, the cause of pathology in most cases is a complex negative impact on the body of both groups. Next we will consider them in more detail.
Physiological factors
Physiological factors causing increased uterine tone:
- hormonal disruptions: the specific hormone progesterone is responsible for the process of fetal development on the inner surface of the uterus; hormonal disruptions during pregnancy can cause a lack of synthesis of this substance, which can directly affect the development of pathologies of uterine tissue;
- Rh factor conflict: due to a discrepancy in the Rh factors of the mother and the unborn child, the female body reacts to the developing fetus as a foreign body. Because of this, increased excitability of the uterus occurs with the aim of rejecting a foreign body;
- infectious and inflammatory processes: this is one of the most common causes of hypertension. Due to untreated or new infections and inflammatory processes, the uterus is released from the resting state, as a result of which pathological contraction of the myometrial walls may occur;
- late toxicosis: severe vomiting caused by toxicosis leads to a sharp contraction of many muscles in the abdominal area, the walls of the uterus are no exception;
- stretching of the uterus: the cause of this process is polyhydramnios, multiple pregnancies, or too large a fetus;
- medications: among the many medications on the market, there are those that can negatively affect the reproductive system, as well as muscle contractility, which during pregnancy can cause an increase in myometrial tone;
- disruption of the gastrointestinal tract: active restructuring of a woman’s entire body during fetal development leads to changes in the digestive system. As a result of this, increased gas formation is observed, as well as impaired intestinal motility, which can cause hypertension;
- abortion: often those women who have undergone artificial termination of pregnancy are prone to increased tone, especially if such a procedure has been carried out more than once. This is explained by the fact that abortion leads to intrauterine synechiae (adhesions), which causes not only hypertonicity, but also complicates the process as a whole;
- age: quite often, hypertonicity occurs in pregnant women over 35 years of age.
Find out more about the factors that cause increased uterine tone: Rh factor conflict, diarrhea, sore throat, abortion and colpitis.
Psychological factors
Prolonged psycho-emotional arousal is one of the main conditions for the development of many diseases, and pathologies of the reproductive system are no exception. Despite the fact that most people turn a blind eye to this factor, it is one of the main causes of health problems during pregnancy. It is especially acute for those expectant mothers who have a physiological predisposition to hypertonicity, in which case the psychological factor becomes an aggravating cause.
Did you know? By the end of pregnancy, the volume of the uterine cavity increases approximately 500 times, after which it safely decreases to its original size.
This is explained by the fact that prolonged depression or constant stress leads to increased blood pressure, excessive excitability of the nervous system, and with this, to voluntary contraction of muscle tissue of organs, including the reproductive system. In addition, in this condition, there is a disturbance in gas exchange in the womb, as a result of which the fetus may suffer from a lack of oxygen. That is why pregnant women should never be nervous or put themselves into a depressive state, as this can cause hypertension even in an absolutely healthy woman.
Depression during pregnancy