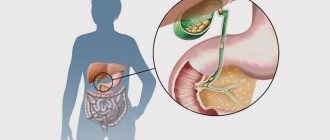
Gallstone disease, in which calculi (stones) form in the cavity of the gallbladder, is a very common disease. Alas, its effective treatment is often only possible through surgery, in which this organ has to be removed. However, the main task of doctors has always been and remains to do everything possible to avoid surgical intervention. Crushing or dissolving stones in this internal organ are techniques that, in some cases, can cure the disease without surgery.
Cholesterol gallstones
Modern medicine has in its arsenal several methods of non-surgical treatment of this pathology.
These include:
- drug therapy;
- shock wave lithotripsy;
- crushing stones using a laser.
Before we look at the existing methods of conservative treatment of this pathology, let's figure out where gallstones come from and what factors influence the development of this disease.
Etiology and symptoms of pathology
The main reasons for the formation of gallstone deposits:
- metabolic disorders;
- pregnancy;
- long-term use of hormonal drugs and various medications;
- age-related changes;
- obesity;
- diabetes;
- long-term feeding through intravenous catheters - the production of bile, necessary for digesting food, is disrupted;
- cirrhosis of the liver;
- internal organ transplantation operations;
- intestinal pathologies with impaired absorption of nutrients;
- anemia;
- eating large amounts of foods containing iron (meat, seafood).
Exacerbation of cholelithiasis makes itself felt by the following symptoms:
- paroxysmal cutting pain in the stomach area, radiating to the right hypochondrium;
- signs of dyspepsia: nausea, heartburn, vomiting, accumulation of gases in the intestines;
- high fever;
- the skin begins to turn yellow due to stagnation of bile.
If left untreated, gallstones provoke a narrowing of the bile ducts, the gallbladder becomes inflamed, and chronic cholecystitis develops. In the future, lesions may affect other organs of the urinary system: bladder, kidneys, liver. In acute attacks of the disease, emergency surgery and removal of stones from the organ are required.
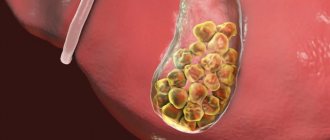
According to their composition, stones are divided into the following types:
- Cholesterol stones that arise from the abuse of fatty carbohydrate foods, when the level of cholesterol in the blood increases due to a sedentary lifestyle, excess weight, diabetes mellitus or hereditary predisposition.
- Pigmented (bilirubin) arise as a result of anemia, with cirrhosis of the liver, when hematopoietic processes are disrupted. They make up 10–20% of all gallstones. Most often they are black.
- Calcareous ones are formed when bile becomes infected with pathogenic bacteria during inflammatory lesions of the mucous tissue of the walls of the gallbladder. They come in brown color.
- Mixed stones are a mixture of cholesterol and calcium formations.
To select a treatment method, diagnostics are carried out and the composition of the stones is determined. Stone formations can be based on cholesterol, lime deposits, enzymes and a mixed composition. Cholesterol deposits can be dissolved using bile-based medications. Grinding of stronger and larger stones is carried out using ultrasound or laser.
Unconventional ways to deal with gallstones
Traditional medicine offers many recipes that allow you to remove stones from the gallbladder naturally. This option does not provide a 100% guarantee of success; it requires a long time, but does not cause any particular harm to the body. However, you should consult your doctor before using any of the recipes.
sunflower root
To prepare, you will need to take 250 g of root and add three liters of water. Bring to a boil, let the mixture simmer for a few minutes, cool and take one glass 4 times a day for 60 days.
Rowan
Red rowan fruits are well suited for fighting stones. It is enough to eat two glasses of berries per day for 45 days. To improve the taste characteristics, it is allowed to mix the berries with honey or sugar, and also eat them with bread.
Rowan - a folk remedy for the treatment of gallstones
Beet syrup
You will need to take and peel 2 - 3 root vegetables. Chop them and leave to simmer until the liquid becomes syrupy. The resulting solution is cooled and it is ready for use. The recommended dosage is 100 ml three times a day before meals.
Olive oil
The oil is consumed half an hour before meals, starting with half a teaspoon, and then gradually increasing the dose to 100 ml. The course of treatment in this way is 2 – 3 weeks.
Birch leaves
A tablespoon of dried leaves is poured into 200 ml of boiling water and simmered over low heat for 20 minutes. Then the solution is removed, wrapped and left warm for another hour. After this, the resulting medicine is filtered and drunk 250 ml half an hour before meals, twice a day.
Another version of the recipe from birch leaves: pour 2 tablespoons of the raw material with a glass of boiling water and boil until the amount of liquid is reduced by half. The decoction is ready, it is cooled, filtered and taken three times a day before meals. The course of treatment is 90 days.
This method is not recommended for use in the presence of large stones, since removal naturally can cause injury to internal organs.
Other treatments
Gallstones in the gallbladder can be treated in the following ways:
- diet therapy and health procedures;
- medicinal dissolution of gallstones without surgery;
- crushing of stones (lithotripsy);
- surgical removal of the affected bile organ with all existing stone formations (cholecystectomy).
Treatment with drugs
As noted above, with the help of bile-based drugs (Ursosan, Ursofalk, Henochol) only cholesterol stones up to 2 cm in size can be dissolved. At the same time, it is necessary to influence the cause of stone formation in the biliary organs, aimed at restoring the activity of the gallbladder and stimulating the production of bile . For this purpose, the drugs Allohol, Holosas and Lyobil are prescribed.
Contraindications to treatment with medications:
- pathologies of the digestive system (gastritis, tumors of various etiologies, motility disorders, intestinal obstruction, etc.);
- inflammatory processes in the kidneys (pyelonephritis);
- use of hormonal oral contraceptives;
- excessive body weight;
- pregnancy and lactation.
Disadvantages of this method:
- the likelihood of a recurrence of the disease after stopping medication;
- long course of treatment (from 6 months to several years);
- disturbance of intestinal microflora;
- high cost of medicines.
Drug dissolution of stones
The dissolution of stones is carried out with drugs such as Ursosan and Henofalk, which allow treatment quite quickly. The presented medications can and should be used because they reduce cholesterol levels in bile and also ensure an increase in the content of so-called bile acids in it. Such a litholytic effect is necessary in the following cases:
- the stone is characterized by its cholesterol nature. It should be understood that the composition can be identified through duodenal intubation (examination of the duodenum) or oral cholecystography;
- the stones are small in size (from five to 15 mm) and fill no more than 50% of the gallbladder;
- the contractility of the gallbladder is assessed as normal, and the patency of the bile ducts is good;
- the patient is allowed to take acids continuously over a long period of time.
It will be very important to simultaneously stop using other medicinal compounds that provoke the formation of stones. For example, we are talking about estrogens included in the list of components of contraceptives or antacids used for ulcerative lesions to reduce acidity
You can and should also give up cholestyramine, at least because it is designed to bind and remove cholesterol.
Dosages and duration of use should be determined by a specialist solely on an individual basis. The recovery course will last from six to 24 months (at least). Its implementation is advisable exclusively under ultrasound control. It should be understood that the effectiveness of therapy will depend on the dosage of the medication and the size of the stones. It ranges from 40 to 80%
At the same time, it is very important to lead a correct lifestyle, and also remember to follow certain preventive measures to prevent the formation of new stones, the removal of which may later prove to be truly difficult
Experts draw attention to the fact that the presented method is characterized by a high frequency of relapses after the end of the rehabilitation course (no more than 70%). This is explained by the fact that after stopping the use of drugs, cholesterol levels in bile increase again
That is why, as a preventive measure, it is possible and necessary to continue to use the so-called low (maintenance) dosages of the presented drugs.
Removal of gallstone deposits by crushing them
Main indications for the use of lithotripsy:
- the presence of calcium elements in the stones;
- duration of the disease: the older the stones, the more difficult it is to dissolve them;
- contraindications to the use of drugs;
- large size stones.
The essence of the method allows you to crush stone formations with a shock wave into smaller fractions, which are removed from the bladder with bile fluid into the duodenum and leave the body along with feces.
Disadvantages of this method of therapy:
- the likelihood of failure of larger fragmented fragments in the gallbladder;
- the possibility of particles getting stuck in the bile ducts;
- possible injury to the ducts by the sharp edges of calcium particles upon exiting.
Such complications may be due to the fact that the gallstone formation has divided into relatively large parts that exceed the size of the ducts. For this purpose, drug dissolution of particles or several shock wave lithotripsy procedures are used in combination. There are 2 main methods: ultrasonic and laser crushing of gallstones.
Types of lithotripsy of gallstones
In clinical practice, several techniques are used to remove stones. Shock wave and laser lithotripsy are widely used. Each method has its own advantages and disadvantages, which are taken into account when selecting treatment.
Shock wave
The technique refers to procedures prescribed in the presence of contraindications to surgical intervention. The size and number of identified stones are preliminarily determined. There should be no more than 3 of them, and the size of each should not be more than 2 cm. Ultrasound scanning, radiography or computed tomography are used as diagnostics. One of the additional conditions for the procedure is that the patient’s weight does not exceed 150 kg.
Currently, there are several types of shock wave lithotripsy, these include:
- Piezoelectric lithotripsy is based on the propagation of waves from a piezoelectric plate, which is made of a special ceramic material. As a result, the stone is crushed to 1 cm in diameter. There is no high-frequency noise produced during the procedure. The cost of the procedure is explained by the need to frequently replace the plates.
- Electrohydraulic therapy is based on the use of impulses simultaneously with water. It must first be pumped into a special bag capable of transmitting impulses to the patient. Due to the high force of the wave, stones up to 3 cm in size are quickly crushed.
- Electromagnetic lithotripsy is based on the formation of pulses emanating from an electromagnetic coil. Using a biconcave lens, a beam of waves is created that is directed towards the crushing area. The procedure can also be expensive due to the need to replace equipment components once a year.
In particular, strong vibration leads to damage to capillaries and small vessels, which leads to the formation of hematomas and inflammation of the bladder walls.
Laser
This type of lithotripsy is classified as an invasive technique. It is performed during ERCP (Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography). Together with the conductor, a light guide is inserted into the common bile duct; a radiation source will subsequently come from it. In order to achieve maximum effect, it is necessary to connect the light guide to the stone.
Due to the supply of energy, it is destroyed into many parts. Removal of broken remains is carried out using special forceps. To clean the cavity, it is washed with saline solution. These procedures reduce the risk of complications and relapses due to the preservation of small stones.
The advantages of the technique include:
- the possibility of dissolving large stones;
- use against the background of developed obstructive jaundice;
- performed without anesthesia with percutaneous transhepatic puncture.
The disadvantages of laser lithotripsy include an increased risk of bleeding or wall burns, as well as possible wall perforation.
Ultrasonic crushing
The separation of gallstone deposits with an ultrasonic device is based on the impact of a wave on them. Ultrasonic crushing of them into fragments measuring 4-8 mm is considered ideal, then they can freely exit the gallbladder. To get the desired result, as a rule, 5-7 sessions are required.
Indications for the use of ultrasonic stone grinding:
- the number of formations in the bubble is no more than 4 pieces;
- formations consist of cholesterol deposits, without calcareous substances;
- the size of each stone is no more than 3 cm in diameter;
- The functionality of the gallbladder is not damaged, bile leaves it unhindered.
Disadvantages of ultrasonic stone extraction:
- there is no guarantee of the formation of new stones due to persistent gallbladder pathologies;
- only 15% of patients with cholelithiasis meet the above conditions;
- the sharp edges of the fragments can injure the mucous membranes of the gallbladder, duodenal intestine upon exit, and also get stuck in the bile ducts, which will require surgery;
- Vibration can damage the walls of the gallbladder, causing inflammation and the formation of scar tissue in the peritoneum.
Contraindications to ultrasonic crushing:
- dysfunction in the gallbladder;
- gastrointestinal diseases (gastritis, pancreatitis, ulcers, duodenitis, etc.);
- the presence of an electronic cardiac pacemaker;
- poor blood clotting;
- bearing a child.
Video
Lithotripsy and laser for gallstone disease.
Gallstone disease is a disease characterized by the formation of stones in the cavity of the bladder or its ducts. The formation of stones is associated with the deposition of bile pigments, cholesterol fragments, protein and calcium ions, as well as products caused by impaired metabolic processes of fatty acids.
Laser crushing of stones
Gallstones can be crushed using laser beams. To do this, the anterior part of the peritoneum is pierced, and the device is inserted into the bile organ. The laser beam acts directly on the accumulation of stones, crushing them into small fractions. The procedure lasts no more than 20 minutes. Indications for the use of laser surgery are the same as for ultrasonic crushing.
Crushing gallstones with a laser has the following possible side effects:
- burn of the mucous membrane of the gallbladder when exposed to a laser beam, which can provoke the formation of ulcerative foci of the mucous epithelium;
- painful sensations when particles leave the bladder;
- damage to the walls of the bladder and intestines due to the movement of crushed particles with sharp edges;
- getting stuck of larger particles in narrow bile ducts;
- the likelihood of re-formation of stones.
Contraindications for laser lithotripsy:
- the patient's weight is more than 120 kg;
- elderly age of the patient (over 60 years);
- concomitant pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract and cardiovascular system.
To avoid cases of destruction of the biliary tract and injury to the mucous membranes, the simultaneous use of ursodeoxycholic acid preparations to dissolve small fragments is recommended.
Chemical (drug) contact lithotripsy
Chemical contact lithotripsy is considered one of the most gentle methods, which consists of injecting directly into the gallbladder a special substance that can dissolve stones. Before starting the procedure, a test is carried out to determine the patient’s tolerance to this medication. The medicine is administered through a laparoscopic incision in the abdominal cavity. After the stones are dissolved, the gallbladder cavity is washed with a special solution to remove the smallest particles from the organ. Chemical contact lithotripsy is indicated for extremely narrow bile ducts when the use of other non-invasive techniques is contraindicated. The operation is performed under general anesthesia.
The advantage of the technique is that all stones can be removed in one session, the disadvantages are that intolerance to the chemical substance occurs in approximately 15-20% of patients.
You may be interested in: Laser tonsil removal, tonsillectomy
Contraindications to chemical contact lithotripsy
One of the main contraindications is pathological blood diseases; in addition, the doctor pays attention to the age, weight and general condition of the patient.
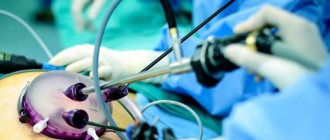
Surgical intervention
With this method, several punctures are made in the abdominal cavity under general anesthesia. First, carbon dioxide is injected into the peritoneum. An endoscope is then inserted into one puncture to obtain an image that helps locate the deposits. A metal tube is inserted into another hole, through which stones are pulled out from the organ.
Contraindications for surgery:
- overweight;
- large stone sizes;
- the body's predisposition to form adhesions;
- purulent inflammation of the gallbladder;
- cardiovascular pathologies.
Removal of the gallbladder (cholecystectomy)
In cases where the presence of particularly large stone formations is diagnosed, with corresponding contraindications for other treatment methods and in particularly emergency situations, a surgical operation is performed to remove the affected gallbladder.
With cholecystectomy, all problems associated with the formation of stones in the body are solved. However, if this organ is removed, the patient will be forced to take replacement medications and follow a special diet for the rest of his life.
Laparoscopy and cholecystectomy
The operation is performed using general anesthesia. Metal conductors are used to remove connections from the organ. To do this, incisions are made in the abdomen. The intervention is carried out under the control of special devices. The stones are not crushed, but are removed whole, which eliminates the risk of damage to the walls of the gallbladder. The operation lasts about an hour. After this, the patient is admitted to the hospital for a week.
The method is not recommended for use if there are certain contraindications:
- obesity;
- the presence of large formations;
- the presence of adhesions that appeared after the intervention;
- the presence of a focus of inflammation in the organ;
- diagnosing pathologies of the cardiovascular and respiratory systems.
As for cholecystectomy, it is an operation during which the organ is removed along with the existing connections. Intervention using this method is indicated in the presence of large stones. Cholecystectomy is also prescribed to patients who often experience relapses, accompanied by severe pain, significant fever and other complications.
Prevention of gallstone pathology
To prevent the re-formation of stone deposits in the gallbladder, the following recommendations must be followed:
- exclude foods high in carbohydrates from the diet;
- limit consumption of fatty, salty and spicy foods;
- give up alcohol and carbonated drinks;
- add protein foods, cereals, fruits, vegetables to the menu;
- make meals separate and fractional (small portions 5-6 times a day);
- to avoid stomach irritation, do not eat too hot or cold food;
- practice long walks in the fresh air (at least an hour);
- engage in moderate exercise (swimming, yoga, Pilates, aqua aerobics, dancing);
- for prevention, you can take drugs to thin the bile;
- timely treatment of concomitant diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and biliary organs;
- Regularly undergo preventive examinations and measure your blood cholesterol levels.
Following these simple rules will allow patients to avoid repeated relapses of the disease and surgery to remove the gallbladder.
Possible complications
A possible complication may be acute calculous cholecystitis
No doctor can give a 100% guarantee of recovery from this disease. As practice shows, over the next 5-8 years the patient experiences re-formation of foreign bodies in the affected organ. The cost of re-treatment may vary.
Moving along the ducts and duodenum, stones can cause mechanical damage, possibly causing hepatic colic and acute calculous cholecystitis.
The most severe complications of gallstone disease are pancreatitis and obstructive jaundice.
The entire list of complications manifests itself within 30-40 days after the crushing session.
Mechanism of stone formation
There are 2 mechanisms of stone formation: hepatic-metabolic and bladder-inflammatory. In the first case, we are talking about the production of a special type of bile, which significantly increases the risk of forming cholesterol or mixed stones. The reason for this is often inflammation, which, in turn, leads to a change in the pH of the secretion produced to the acidic side.
Bilirubin crystals precipitate in combination with calcium, forming the center of the calculus with the subsequent layering of other elements on it.
All these processes can be triggered by a number of the following reasons:
- age-related disorders,
- problems with the thyroid gland,
- predominance of animal fats in food,
- diabetes,
- liver damage of toxic or infectious origin,
- intestinal diseases,
- metabolic disease
With cholecystitis, bile becomes viscous, its stagnation and poor discharge from the organ are observed due to changes in the physicochemical properties of the secretion. This is exactly what the vesical-inflammatory mechanism of gallstone formation . Calcium salts, cholesterol and bile elements are deposited in the bladder, triggering the formation of stones.
Concretions are divided into different types depending on the component that became the basis for the formation of the clot.
The disease does not occur in a short period of time, but develops over a fairly long period of time (several years). First, sand particles are formed, which later gradually become larger. On average, stones can reach 3-5 mm per year.
Stones up to 3 mm can still pass through the bile ducts, and larger formations remain in the gallbladder, continuing to increase in size and blocking the passage from the organ. All this causes severe inflammation.