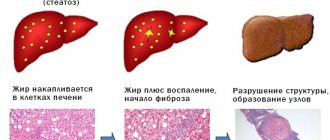
Fatty hepatosis (steatosis of the liver, steatohepatosis, fatty liver, fatty degeneration, fatty infiltration of the liver) is a chronic liver disease characterized by histopathological changes in liver tissue in the form of accumulation of fat, mainly triglycerides, in hepatocytes, which in some cases turns into inflammation of the liver (steatohepatitis) and the development of fibrosis (steatofibrosis).
In addition, fatty hepatosis can also provoke such a symptom as pathological enlargement of the liver - hepatomegaly. Currently, fatty hepatosis of alcoholic and non-alcoholic origin is distinguished.
The leading role in the development of fatty hepatosis due to alcohol consumption is played by the toxic product of ethanol metabolism - acetaldehyde, which reduces the activity of enzymes that transport fatty acids into the mitochondria, which leads to impaired fat metabolism and the subsequent accumulation of triglycerides in liver cells.
The main etiological factors of non-alcoholic hepatosis are combinations of various metabolic risk factors (abdominal obesity, hyperglycemia, hypercholesterolemia, arterial hypertension, type 2 diabetes), viral hepatitis, taking certain medications, rapid weight loss/fasting.
Let's look at the question: why is it so important to follow a diet when treating fatty hepatosis?
How to identify the disease
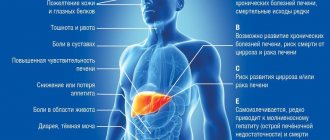
Liver hepatosis is a silent disease. Often, until the process becomes advanced, a person develops cirrhosis of the liver, nothing is noticeable. However, this is only an appearance. If you listen carefully to your own body, you can notice something that was not observed before. The first symptoms of fatty liver disease include:
- Soreness in the right side.
- Enlarged liver size, noticeable on palpation.
- Digestive disorders: vomiting, diarrhea, nausea or constipation.
- Deterioration of skin and hair condition.
- Predisposition to colds, poor immunity and allergic reactions.
- Reproductive dysfunction, inability to conceive.
- Women experience irregularities in the menstrual cycle, heavy or irregular bleeding.
- Impaired blood clotting.
Typically, anxiety symptoms do not appear suddenly, but increase over time. First, patients complain of pain and discomfort, then symptoms of intoxication of the body appear, because the affected organ ceases to perform its function.
If treatment is not carried out at the initial stage, symptoms characteristic of different stages of liver failure begin to appear.
If fatty liver disease is not treated, symptoms of liver cirrhosis and liver failure appear:
- behavior change; jaundice;
- monotony of speech;
- weakness;
- aversion to food;
- ascites;
- lack of coordination.
It is important to diagnose fatty liver hepatosis at an early stage - symptoms and treatment are determined and prescribed only by a doctor. Then there is a higher probability of completely restoring its functions.
The patient can reduce the healing time if he follows all the instructions. Unfortunately, the symptoms of fatty liver disease do not appear at an early stage.
People at risk should be screened periodically to identify diffuse changes and initiate treatment.
Symptoms of the disease
The disease is characterized by 3 main degrees of severity, in which different symptoms dominate.
Each person is individual, some may show signs. It is possible that a latent form occurs and symptoms do not appear, but the disease will be noticeable on medical monitors.
First degree of disease
Fats accumulate, but hepatocytes are still active. Only in-depth laboratory tests will determine the pathology. There are no external signs.
Mild pain is possible, but only if the liver lining begins to stretch.
Second degree of hepatosis
Parenchyma cells become overgrown with fat, serious problems occur in the liver, and obvious symptoms appear:
- Characteristic coating on the tongue;
- Feeling of nausea, possible vomiting;
- Bitter taste in the mouth;
- Digestive disorders such as diarrhea or constipation;
- Flatulence;
- Periodic pain in the right hypochondrium, especially after eating non-dietary food;
- Enlarged and painful liver when palpated;
- Constant weakness, malaise;
- Yellowness of the skin may appear.
Third degree of disease
The organ is so destroyed that hepatosis turns into a more severe, irreversible form - cirrhosis. All signs of the previous degree increase, severe intoxication develops - the organ stops removing toxic substances and toxins. The disease is progressing.
Causes of fatty hepatosis
The main causes of fatty hepatosis include:
- obesity;
- metabolic diseases;
- physical inactivity;
- binge eating;
- alcohol abuse;
- vegetarianism with impaired carbohydrate metabolism;
- diets for weight loss;
- long-term use of certain medications:
- cordarone, diltiazem, expired tetracycline, tamoxifen;
- deficiency of alpha-antitrypsin in the body;
- antiviral treatment for HIV;
- overdose of vitamin A;
- diseases of the internal secretion organs;
- systematic abuse of alcoholic beverages;
- exposure to radiation;
- diseases of the digestive system.
What does liver in fat mean?
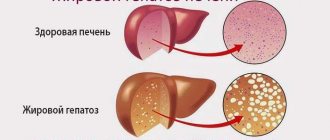
As a result of the development of the pathological condition, the liver becomes overgrown with fat, and small-droplet or large-droplet accumulation of lipid deposits is observed in certain areas of the liver parenchyma.
In advanced cases, fat accumulation can reach a large size, which leads to complete filling of the liver parenchymal tissue with lipids.
When examining liver tissue affected by a pathological process under a microscope, the doctor observes a large number of hepatocytes containing large fatty droplets or a large number of small lipid accumulations.
The accumulation of lipids leads to the fact that the liver becomes unable to fully perform its physiological functions.
Steatosis becomes a serious disorder when it provokes the occurrence of hepatomegaly and one of the forms of hepatitis - steatohepatitis. At this stage of progression, fatty liver disease provokes its increase and the development of inflammatory processes.
In the process of fat accumulation, a pathological process develops, consisting in the degeneration of liver tissue. As a result of this degeneration, specialized cells of the liver parenchyma - hepatocytes - are replaced by fat cells.
The development of fatty hepatosis in the absence of timely adequate therapy can lead to irreversible cirrhotic changes. In particularly advanced cases, pathology can provoke the appearance of liver failure and subsequent death.
The progression of steatosis increases the likelihood of liver cirrhosis, cardiovascular disorders, endocrine and metabolic pathologies. In addition, the presence of fatty liver can provoke the occurrence of allergic reactions, varicose veins and some others.
In order to avoid the negative consequences of the development of pathology in the body, you should know the causes of its occurrence and methods of treating the disease.
Degrees of fatty liver disease and symptoms
As fat accumulates, fatty liver disease is divided into three degrees of development.
- The first degree is characterized by a slight accumulation of simple fat cells. If these accumulations are noted in the number of several foci and a large distance is diagnosed between them, then this form is diffuse fatty hepatosis.
- When the volume of fat in the liver increases, and areas of connective tissue appear in the structure of the organ, the second degree of hepatosis is diagnosed.
- The most severe third degree of the disease is observed when areas of liver cells overgrowing with connective tissue and large deposits of fat are clearly visible.
Is it possible to stop fat deposition in the liver?
Fatty liver hepatosis requires conservative treatment. It involves a complete restructuring of lifestyle, eating habits, and selection of drugs for complex drug treatment. In the early stages of hepatosis, the pathological process can be stopped with diet alone. In advanced cases, medication support and inpatient treatment will be required. More often the disease is treated on an outpatient basis. Basic rules for effective treatment of fatty hepatosis:
- correction of body weight to a normal level;
- rejection of bad habits;
- complete exclusion of alcoholic beverages;
- diet;
- transition to fractional nutrition mode;
- regular and long-term use of medications prescribed by a doctor;
- refusal to use hepatotoxic drugs;
- increased physical activity;
- treatment of metabolic disorders and pathologies identified during diagnosis.
If you take therapy seriously and follow all of the above rules, fat deposition in the liver can be reversed.
Lifestyle change
The patient must tell the doctor what medications he is taking on a regular and periodic basis. All excess funds will be cancelled. Drugs with hepatotoxic properties will be replaced with less harmful medications.
It is important to give up bad habits - smoking, drinking any types and doses of alcohol. If a person is employed in hazardous conditions (forced to inhale toxic fumes, work in dusty conditions), the place of work will have to be changed.
Physical activity is very important to normalize metabolic processes. Exercise eliminates insulin resistance and facilitates energy consumption by cells. The type of sport should be selected with a doctor, taking into account concomitant pathologies and the degree of physical fitness of the patient.
Diet therapy
The diet for fatty liver hepatosis should provide the body with energy and reduce the load on the gland. The goal of dietary nutrition is to rebuild metabolism in order to enhance the breakdown of fat deposits. Compliance with a special diet will also be required to correct the patient’s weight.
If you have fatty hepatosis, you cannot lose weight suddenly. The optimal weight per week is 600-700 g. With rapid weight loss, the risk of fibrous liver damage and the formation of gallstones increases.
The patient's diet should limit the intake of cholesterol and refractory fats. It is advisable to saturate the menu with lipotropic substances, complex carbohydrates, and fiber. To correct weight, moderately reduce the total caloric content of the diet and increase the daily amount of protein. The patient switches to a regimen of fractional and separate meals (up to 6 meals per day). It is important to combine products correctly. Proteins are consumed with vegetables, complex carbohydrates - as an independent product.
During the diet you should avoid:
- fried and fatty foods;
- industrial products (sausages, canned food, confectionery);
- natural sources of simple carbohydrates (honey, jam, sugar);
- baked goods and homemade baked goods, fresh white bread;
- fatty meat (pork, beef, lamb);
- fatty varieties of river and sea fish (herring, catfish, carp);
- rich broths;
- snacks with added sauces;
- fatty dairy products (homemade dairy and fermented milk products);
- high-calorie cereals (rice, wheat derivatives).
The diet limits the number of eggs (up to 2 per week), butter (15 g per day). The menu is based on vegetables and cereals as sources of fiber and complex carbohydrates. It is preferable to boil food, steam it, or bake it in the oven. Salads should be seasoned exclusively with cold-pressed vegetable oils. Use butter (5 g per serving) to season ready-made dishes. It is allowed to eat pasta made from durum wheat in its pure form 2 times a week.
To enrich your diet with proteins, you should prepare dishes from poultry meat (turkey, chicken); you can also eat rabbit meat. If tolerated well, legumes can be consumed. Fish and seafood are eaten in unlimited quantities, provided they are properly prepared (boiled, baked). A large number of low-fat fermented milk products are shown as protein sources. Low-fat cottage cheese is very useful for metabolism in liver cells.
One of the folk recipes recognized by medicine is the use of rosehip infusion for liver diseases. To prepare the drink, pour 2 tablespoons of fruit with boiling water and keep in a water bath for 15 minutes. After cooling, strain, drink half a glass 4 times a day.
In complex therapy of fatty hepatosis, the diet is followed until complete recovery. It is recommended to adhere to the rules of a healthy diet even after eliminating the pathology.
Diagnostics
Upon examination and palpation by a doctor, the liver was not enlarged, without any features. Only when a large amount of fat accumulates can the liver become enlarged with soft, rounded edges and painful to the touch. In the early stages of fatty hepatosis, pronounced symptoms are usually not detected. In patients with diabetes mellitus due to hepatosis.
The list of necessary measures to make an accurate diagnosis includes:
- Ultrasound of the liver. Traditionally, an ultrasound examination of the liver helps to detect its enlargement, and this almost always indicates problems with the organ.
- Tomographic research. MRI allows you to evaluate the structure of the liver. If fat is deposited in an organ, this will be visible on an MRI.
- Blood chemistry. ALT and AST indicators are assessed. When they increase, we are talking about liver disease.
- Biopsy. It doesn't happen that often. Allows you to find out whether fat is present in the structure of the organ.
Why is NAFLD dangerous?
Fatty hepatosis, especially at the very beginning, can be practically asymptomatic, and the existing symptoms are not specific and, thus, make diagnosis difficult. However, you should not relax - diagnosing fatty hepatosis is important for any suspicion of the presence of this disease. Because this disease, developing gradually, practically without manifesting itself clearly, nevertheless increases the risk of cardiovascular death several times - in other words, it increases the risk of developing strokes and heart attacks.4 In addition, advanced fatty hepatosis can ultimately lead to ultimately, to the development of cirrhosis and liver failure. The likelihood of this event is low, however, if it occurs, the consequences can be fatal. The fact is that cirrhosis usually requires organ transplantation, which can be further complicated in the presence of cardio-metabolic disorders and diseases that often accompany fatty hepatosis.3
Stages of development of NAFLD
- 1
Stage of fatty hepatosis (steatosis)
The initial stage of the disease, often asymptomatic
- 2
Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis
Hepatosis with accompanying inflammation of liver cells
- 3
Fibrosis with further transition to cirrhosis
At this stage, liver tissue begins to be replaced by connective tissue, which leads to disruption of the structure and, ultimately, disruption of the organ.3
Treatment
The main treatment for fatty hepatosis is aimed at eliminating the factors that caused the disease, improving the regenerative abilities of the liver, improving metabolism, and detoxification. With fatty hepatosis, you need not only to take medications, but also to adjust your lifestyle and diet.
Medications are used in combination - an effective membrane-stabilizing agent and antioxidants are needed.
Drug therapy for fatty hepatosis includes taking medications to improve the function of the liver and its cells:
- essential phospholipids (essliver, essentiale forte, berlition),
- group of sulfamino acids (taurine or methionine),
- herbal hepatoprotector preparations (karsil, LIV-52, artichoke extract),
- taking antioxidant vitamins – tocopherol or retinol,
- taking selenium supplements,
- Group B drugs intramuscularly or in tablets.
Herbal medicine has proven itself well - the drugs Cholagol, Hepabene, extracts of turmeric, milk thistle, and curly sorrel are used.
Groups of drugs for the treatment of disease
A patient diagnosed with fatty hepatosis must be prescribed an individual course of medications, taking into account the patient’s condition. Also, the selection of medications is influenced by the reasons that caused the formation of a fatty layer in the organ, identified as a result of diagnostic measures. Only the first stage of the disease can be treated without the use of medications; more severe stages require medication.
We suggest you read: Why does my husband drink beer every day?
Here are the main groups of drugs that doctors use to treat fatty hepatosis.
- Medicines that help restore metabolic processes in the liver, and as a result in the whole body. These include drugs of the lipotropic group - folic and lipic acid, B vitamins.
- Drugs of the hepoprotective group, whose main property is to restore damaged organ cells and protect the remaining healthy ones so that the liver can continue to function normally. Typically these include the following types of drugs: Hepa-Merz, Karsil, Heptaral, Esencealie Forte, Ursohol.
- Medicines aimed at normalizing lipid metabolism in the liver. These include the statin and fibrate groups. They prevent the formation of new fat cells, both around the organ and in place of normal liver cells. These medications are taken only as part of complex therapy in compliance with the precise dosage prescribed by the attending physician.
- Antidiabetic drugs of the thiazolindiones group. Diabetes mellitus is a standard disease directly related to liver dysfunction, so drugs from this group are often included in complex therapy, since testing for high sugar does not always show an excessive amount. The main property of these drugs is to increase sensitivity to insulin in liver tissue. Only they have a number of side effects, so you cannot take them on your own initiative, but only under the supervision of a doctor. These drugs include: Rosiglitazoline, Pioglitazoline.
- Another drug that is often prescribed for serious liver damage is Metformin. Its main function is to interfere with the production of glucose by the liver. This is how the body restores fat and sugar metabolism. This makes it easier for the patient to lose excess weight.
- Complex therapy also includes taking medications based on milk thistle. This plant contains the substance silymarin; this component has a positive effect on affected liver cells. Protecting them from exposure to toxic substances. Other drugs in this group relieve inflammation of the liver, helping to restore its normal size. Also, the symptoms of the disease become less obvious. Such medications include: Silimar, Gepabene, Legalon, Karsil.
If the disease is in a particularly advanced stage, when inflammatory processes begin accompanied by the presence of infection, the doctor prescribes antibiotics and anabolic steroids.
It is worth considering several drugs belonging to different groups of medications that help restore liver function.
- The drug Hepa-Merz helps protect healthy liver cells. This medicine is produced in various packages, and the cost of the drug depends on this, ranging from 1,500 to 3,000 rubles.
This medicine is taken orally after meals, 1-2 sachets, previously dissolved in boiled water, three times a day. The dosage depends on the doctor's orders. The medicine has side effects such as diarrhea or nausea, and people with cardiovascular problems may experience numbness in the limbs. An allergic reaction to the components of the medication is also possible.
- Drugs aimed at blocking the enzyme in the liver that is responsible for the production of cholesterol, thereby lowering its level in the blood. One of these drugs is Pravachol. The release form of this medication is with a dosage of 10 and 20 mg and the cost starts from 1800 to 200 rubles.
The drug has a number of contraindications and side effects, so consultation with a doctor and the risk-benefit ratio for the patient is required. Taking this medicine on your own is strictly prohibited.
- The milk thistle-based medicine Silymar is available in tablets and is sold at a very affordable price, ranging from 120 to 180 rubles per pack. Side effects include laxative properties or allergies to certain components.
The course of treatment with the drug takes up to a month, repeated treatment can be carried out only after 2 months, much depends on the stage of development of hepatosis. Dosage of the drug: 2 tablets 3 times a day, half an hour before meals.
How to treat fatty liver hepatosis with medications? Antioxidants are used in medicine to treat this pathology. They help stabilize the cell membranes of the organ. Antioxidant agents are divided into several groups:
- essential phospholipids;
- sulfamino acids,
- preparations based on plant extracts.
Essential phospholipids are often used in the treatment of fatty liver. The substances included in the formula of these medications are natural components of the membranes of liver cells (hepatocytes). The task of essential phospholipids is to normalize metabolic processes in liver tissue and protect hepatocytes from harmful effects. Essential phospholipids:
- increase the ability to recover and protect the outer shells of hepatocytes from negative influences;
- stimulate the work of complex enzymes (enzymes) located in the membrane of the organ;
- improve the metabolism of fats and fat-like substances (lipids);
- promote better maturation of RNA, improve the processes of plastic and energy metabolism of protein molecules;
- increase glycogen content in the gland;
- accelerate the processes of breakdown and neutralization of toxic substances;
- convert low-density lipoproteins into simple forms that are easily metabolized;
- reduce the body's energy costs;
- reduce the number of fat cells that make up the functional tissues of the liver;
- prevent the development of cirrhosis and liver fibrosis;
- improve the quality of bile (liver secretion).
We suggest you familiarize yourself with Alcohol and the gallbladder do not get along together due to the toxicity of alcohol
Treatment of fatty liver with medications is also carried out using sulfamino acids, which:
- increase the number of complex lipid molecules containing phosphoric acid and fatty acids;
- have antioxidant properties;
- help cleanse the liver of excess fat;
- restore normal carbohydrate production;
- help improve blood supply to the organ, facilitating greater penetration of useful substances into hepatocytes;
- accelerate the outflow of bile, dilute the formed clots of bile secretion.
Fatty liver hepatosis is also treated with medications based on plant extracts. These drugs:
- reduce the harmful effects of free radicals (oxidants);
- inhibit the oxidative processes of fatty acids;
- protect liver cells from damage by decay products;
- accelerate the maturation of proteins of the cellular framework of organ tissues and phospholipids in already affected liver cells;
- stabilize cell membranes of hepatocytes;
- increase the rate of recovery of organ parenchyma cells;
- prevent the penetration of decay products and toxins into the liver parenchyma.
A hepatologist prescribes the use of medicinal herbal preparations after conducting a detailed examination of the organ and making an accurate diagnosis.
To prevent steatosis, it is necessary to maintain a proper diet and limit the consumption of alcoholic beverages.
If these conditions are not met, it is recommended to prevent fatty liver transformation with hepatoprotectors. The name of these drugs indicates their ability to protect the liver from the influence of harmful factors and restore its functionality.
Hepatoprotectors can reduce the load on the entire hepatobiliary tract: liver, gallbladder and bile ducts when harmful substances and ethanol regularly enter the body. With the help of these drugs, the liver is able to quickly process and remove harmful decay products and poisons.
Hepatoprotectors also have a significant antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and antifibrotic effect.
The doctor selects hepatoprotectors for the prevention of steatosis after a detailed examination and diagnosis. Drugs are selected based on their content of the following components:
- Glycyrrhizic acid. It is the main active ingredient of licorice root. Able to protect the liver and relieve inflammation. The acid has antifibrotic, antioxidant and protective effects. The product is prohibited for use by pregnant women, patients with an allergy to licorice root, and children under 12 years of age.
- Phospholipids. They are the main component of hepatocyte membranes. If they are deficient, regeneration of damaged tissue becomes impossible. Medicines based on phospholipids accelerate the recovery of liver cells. To achieve lasting results, the drugs should be taken for a sufficiently long time. Phospholipids are contraindicated in case of individual intolerance to the components, as well as in young children.
- Ursodeoxycholic acid. Prevents the formation of stones and other concretions in the bile ducts, is able to destroy small clots, and reduces the number of low-density lipoproteins. Preparations based on ursodeoxycholic acid are prohibited for use if renal or liver failure or large cholesterol formations are detected.
- Ademetionine. Improves the removal of harmful breakdown products from the liver. Preparations based on this active substance are used as part of complex treatment of alcohol dependence. Ademetionine is a good antidepressant. Not prescribed to women during the first and second trimesters of pregnancy, as well as during breastfeeding.
- Ornithine. The drug is prescribed to reduce the concentration of ammonia in toxic hepatitis and steatosis. Contraindicated in case of kidney dysfunction, during pregnancy and breastfeeding.
- Extract from milk thistle. It has a good antioxidant effect and effectively protects liver tissue. Preparations based on it promote rapid restoration of hepatocytes and increase appetite. Not prescribed for allergic reactions to the components of the medication.
- Fumigata (wild rue) extract. It protects the liver well from the effects of toxins, normalizes its size, and eliminates spasms of the bile ducts. Preparations based on it are contraindicated in children under 18 years of age and in patients with inflammation of the liver and bile duct.
- Thioctic acid. Prescribed for chronic hepatitis, hepatosis, cirrhosis and liver poisoning. Not prescribed for children under 7 years of age and patients with allergic reactions to the components of the drug.
Diet
A person who is forced to struggle with fatty hepatosis needs to completely reconsider his lifestyle and diet, in which it is necessary to exclude the consumption of animal fats. At the same time, the diet should include foods that help dissolve fats deposited in the liver.
You need to eat food 5 times a day, in small portions, in order to reduce the load on the liver.
| Authorized Products | Prohibited Products |
|
|
Medicines
In the initial stage of the disease, with a mild course of the disease, a combination therapy is prescribed, consisting of antioxidant protection, stabilization of hepatocyte cell membranes, immunomodulation, providing anti-inflammatory protection and aimed at preventing and relieving bile duct dysfunction.
The leading place among drugs that help improve the functional state of the organ is occupied by Ademetionine. The drug is considered complex, as it includes two natural substances - adenosine, which is part of some enzymes, and methionine, which is an amino acid necessary for human health.
"Ursosan", Ursofalk" - bile acid. The drug has a high acid-neutralizing and analgesic effect, regulates the action of the immune system, has the property of regulating cell proliferation (proliferation) and apoptosis (programmed cell death), affects the biochemistry of bile and indicators of steatosis.
“Taurine” is an amino acid that accelerates the removal of toxins from the body in the form of “Dibikor” and “Heptral” tablets, “Taufona” in capsules. They have membrane-stabilizing and antioxidant properties, help increase hepatic blood flow, improve the activity of hepatocytes and the excretion of bile, dissolve bile acids and reduce total cholesterol levels.
Tablets "Karsil" contain plant extracts; it is a natural drug that has antitoxic and hepaprotective effects (improving metabolic processes).
The action of essential phospholipids - the drug "Essentiale" is aimed at increasing the liver's resistance to the action of pathological processes and at its gentle cleansing and restoration.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with what will happen to underage drinking alcohol
The doctor may prescribe Heptral or Essentiale in the form of injections.
The complex drug treatment includes an excellent membrane-stabilizing natural preparation based on field artichoke leaf - “Hofitol”. Hofitol tablets have a choleretic and protective effect. Provide liver resistance to pathogenic microbes and normalize metabolic processes.
If thickening of bile is noted, a natural medicinal preparation, “Holosas,” is prescribed to improve its outflow. Its action removes the feeling of discomfort in the form of heaviness and bloating in the side, is prescribed to relieve alcohol intoxication, and has a strengthening effect.
The use of stanines and fibrates is due to a decrease in blood lipids (cholesterol).
Increased glucose levels (insulin resistance) play an important role in the genesis of fatty hepatosis. The use of insulin sensitizers - Metroformin and Rosiglitazone - improves glucose absorption, activates liver enzymes, helps reduce obesity, and normalizes the effects of hypertension.
Vitamins PP and B2 play an important role in the neutralization of various toxic substances.
The drug treatment plan for fatty liver hepatosis, the dosage of drugs and the duration of the course, should be drawn up by a therapist or gastroenterologist. You should not independently select medications from various sources. Many drugs are fraught with many pitfalls and, if used incorrectly, can cause more harm than good. Entrust your health to specialists.
The use of drug therapy will be untenable if you do not adjust your diet and lifestyle.
As preventive medications to restore liver function, it is possible to independently use medications based on herbal components. Such, for example, as Esencealie Forte-N, or preparations with milk thistle extract.
But you should carefully read the instructions and do not exceed the prescribed dose. In addition, after completing the course, you should give the body a rest and drink restorative herbal decoctions.
We must not forget about strict adherence to the diet prescribed by the doctor. The diet of permitted foods includes low-fat and mainly steamed foods. Not to mention the fact that it is mandatory to give up all alcoholic and carbonated drinks.
It is difficult to adhere to strict restrictions during liver treatment. Therefore, it is better not to lead to serious disruptions in the functioning of the organ and regularly carry out preventive restorative procedures to cleanse the liver of accumulated toxins.
A healthy liver is the key to the effective functioning of the entire body as a whole. After all, this organ takes on all the hard work; it fights poisons and toxins that enter our body. And if you do not take care of the liver, diseases may develop that will require long-term treatment. Remember, if you do not take care of yourself, then an incorrect lifestyle will lead a person to a hospital bed, and in severe cases to the operating table. Take care of yourself!