What is PCR for STIs
PCR (polymerase chain reaction) for STIs is an analysis that allows you to identify the 12 most common sexually transmitted infectious diseases.
Indications for prescribing PCR for STDs
Indications for prescribing PCR for STIs:
- rashes in the genital area;
- pain during urination;
- itching or burning;
- copious discharge with a pungent and unpleasant odor;
- erosions on the mucous membrane or in the genital area;
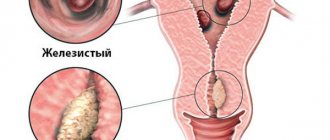
- modification (proliferation of the epithelium) of the mucous membrane in the cervical area;
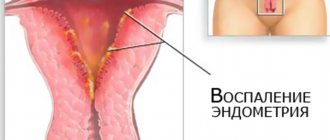
- inflammation of the genitourinary system;
- change in the color of seminal fluid in men;
- enlarged lymph nodes in the groin area;
- menstrual irregularities;
- cases of miscarriages, pathologies during pregnancy, difficulties with conception;
- the presence of a cyst on the ovaries;
- the presence of adhesions in the pelvic area;
- pain in the lower abdomen;
- the presence of prostatitis in men.
It should be noted that, regardless of symptoms, everyone should be examined in the following cases:
- unprotected sexual intercourse with two or more partners within 6 months;
- pregnancy planning.
Advantages and disadvantages of the method
Advantages of the method:
- High percentage of reliability. Even if a single pathogen cell was found in the biomaterial, diagnostics will reveal it.
- Efficiency of obtaining results.
- Universality of the study. PCR for STIs can be performed when taking any material: a smear from the vagina or urethra, blood, semen.
- Specificity of the procedure. During the analysis, a specific DNA fragment is found that belongs to a specific virus.
- Availability. Almost all laboratories conduct such examinations.
- One sample is enough to determine the presence or absence of an STI.
There are also disadvantages to the procedure that must be taken into account before taking the test:
- Possibility of a false result. Its percentage is very low, but still possible.
- The ability of microorganisms to mutate the structure of DNA. In this case, it will be difficult to identify the disease. This is rare, but it is worth taking this factor into account during the examination.
- Some pathogens are difficult to identify. For example, chlamydia or trichomoniasis. In order for the result to be accurate, you have to resort to stimulation. Such infections are called hidden.
What diseases can be detected using PCR?
Using the PCR technique, almost all viruses and infections can be detected. A comprehensive analysis involves submitting a standard list called in medicine the “STI-12” group.
Composition of the STI-12 complex
STI-12 can be used for a whole range of infections, which includes:
- Ureaplasmosis. It is usually asymptomatic, but can cause miscarriage and therefore requires immediate treatment when planning a pregnancy.
- Mycoplasmosis. The most common symptoms: pain in the groin (intensified by sexual intercourse), burning sensation when urinating, discharge. Men are carriers.
- Chlamydia. Chlamydia is dangerous because it affects the urethra, intestines and cervix. In the absence of proper therapy, they lead to infertility in women.
- Trichomonas. The most common symptoms include: redness and swelling of the genitals, profuse discharge with a strong unpleasant odor, small sores on the genitals. In men, infection is generally asymptomatic, but a burning sensation may occur when urinating. Along with this infection, doctors can identify another disease in women, such as trichomonas colpitis. If left untreated, the uterus, ovaries and bladder are affected.
- Candidiasis (thrush). The most common symptoms: itching and copious curdled discharge.
- HPV (human papillomavirus) 16 and HPV 18. There are asymptomatic (dysplasia) and clinically pronounced variants of the disease (condylomas, papillomas and warts). Most of them are safe. But it is necessary to constantly see a gynecologist. The most dangerous complication is oncology.
- Cytomegalovirus. Most often it is asymptomatic. But it can manifest itself in the form of a common ARVI.
- Genital herpes type 1 and type 2. A small reddish spot appears on the labia, which causes a burning sensation and itching. Then the bubble inflates and the pain increases. After 3–5 days, the blister bursts and fluid leaks out. Crusts form at the site of the wound. On the tenth day, all symptoms completely disappear.
- Gonorrhea. The causative agent of which is Neisseria. Symptoms: severe pain in the lower abdomen, burning and discomfort when urinating, yellowish-white discharge with a strong unpleasant odor.
- Gardnerellosis (bacterial vaginosis). The symptoms are similar to thrush.
- Syphilis and neurosyphilis (symptoms similar to meningitis).
- HIV AIDS).
Preventive measures
To prevent infection, you must follow basic prevention tips. This list of rules may include:
- the use of barrier protection during sexual intercourse with an unfamiliar partner;
- getting vaccinated if necessary;
- careful adherence to intimate hygiene;
- timely examination by a urologist and gynecologist every six months;
- use of special antiseptics if possible infection is suspected (must be used in the first few hours after the act);
- timely detection and treatment of infectious diseases.
To prevent infection, a woman can use the drug Pharmatex in the form of suppositories or cream; this product is also a contraceptive. Hexicon candles have proven themselves well; they contain chlorhexidine. Immediately after contact, you should wash the genitals well with soap and then treat with Miramistin.
Types of tests for STDs
When conducting laboratory tests, an accurate diagnosis is established and therapy is prescribed, aimed specifically at eliminating the identified pathogens.
The most effective methods are:
- blood analysis;
- Analysis of urine;
- scraping from the urethra and cervical canal;
- sperm examination;
- analysis of prostate secretions.
Blood analysis
A blood test for STIs is performed using direct and indirect immunofluorescence methods. The material is stained with special antibodies in combination with dyes.
For example, the reliability of such a study is achieved by identifying:
- syphilis - 100%;
- mycoplasmosis – up to 70%;
- chlamydia – 98%.
The following studies can be highlighted:
- blood test for TORCH infections: toxoplasmosis, rubella and cytomegalovirus;
- RW – Wasserman reaction (used to detect syphilis);
- HIV infections, hepatitis B and C.
Analysis of urine
Using a general urine test, an inflammatory process in the genitourinary system, as well as the presence of infection, is diagnosed.
Mostly men donate urine for PCR. The only and main disadvantage of this examination method is that it is possible to establish only the fact of the presence of bacteria, but it is impossible to determine their quantity.
Scraping from the urethra and cervical canal
This diagnosis is the most effective for identifying STIs. The technique is completely safe and painless. A smear allows you to detect both the presence of harmful microorganisms and their quantity.
The collection is carried out in the following way: the doctor scrapes the material from the urethra and cervical canal (women only) using special instruments.
Sperm and prostate secretion
The diagnostic method is intended to detect in biomaterial:
- specific DNA fragments of the main pathogens that can be sexually transmitted;
- urogenital infections of the genitourinary system in men (these include: gonorrhea, chlamydia, trichomoniasis, mycoplasmosis, ureaplasmosis).
The main advantage of diagnostics is to establish not only the presence of pathogens, but also to determine their exact quantity.
The patient collects the seminal fluid into a container himself. The doctor collects prostate secretions after massaging the prostate gland.
The first signs of STIs in women
Clinicians identify seven main signs of sexually transmitted diseases, upon detection of which you should immediately contact a gynecologist:
- painful menstruation (previously uncharacteristic);
- discharge from the genitals, which has a specific odor and thick consistency;
- itching and burning in the intimate area;
- enlargement of regional lymph nodes;
- pain inside the vagina and lower abdomen;
- frequent urination, accompanied by pain.
Along with the listed symptoms of sexually transmitted diseases, women may experience redness in the genital area, in some cases – rashes, erosions and blisters.
https://youtu.be/qAGIbC42nLw
Preparing for the test
To obtain a reliable PCR result for STIs, you need to thoroughly prepare for it.
When it comes to blood tests, you should follow simple rules:
- It is not recommended to eat food 8–12 hours before collection.
- You should give up bad habits 24 hours before the test.
- You cannot take antibiotics two days in advance, otherwise the picture of the examination result will be blurred. You should also stop taking other medications 4 weeks before diagnosis.
To take a urine test, you must follow the following recommendations:
- abstain from sexual intercourse 1 day before the examination;
- 4 weeks before the examination you should stop taking antibiotics;
- You need to collect the biomaterial yourself in a container in the morning on an empty stomach.
When preparing to take a smear from the urethra and cervical canal, the following recommendations should be followed:
- 7 days before collecting the material, you must stop taking suppositories, douches and sprays;
- exclude sexual intercourse 2–3 days before the examination;
- in the evening before the procedure, carry out hygiene procedures, preferably without soap;
- It is recommended not to urinate 2–3 hours before the procedure;
- In women, a smear should be taken 3 days after menstruation or 3 days before it begins.
Before taking a semen test in men, you must:
- the day before, perform genital hygiene;
- stop taking antibiotics 4 weeks before the test;
- refrain from sexual intercourse 3 days before collecting material.
From the video you will learn about PCR diagnostic methods, as well as how to prepare for the examination. Filmed by the Moscow KVD.
Microflora smear
A smear is taken when diagnosing the presence of STIs in men and women and is a mandatory procedure. Almost all infectious pathologies that damage the female genitourinary organs are located in the vagina. To test for STIs in women, the necessary biomaterial is collected from the urethra and nasopharyngeal tract.
Decoding the results
There are only 2 options for deciphering the result:
- A negative answer indicates that no harmful microorganisms were found in the material taken for research.
- A positive PCR result indicates the presence of traces of infection in the sample. With a high probability, such a response confirms the presence of pathogens at the moment.
We cannot exclude situations where the PCR test is positive, but no active infection has been detected. This is a “healthy carrier”, without pronounced clinical symptoms. It does not require special therapy, but it is necessary to undergo scheduled periodic examinations as prescribed by a doctor.
Photo gallery
PCR for hidden infections
PCR for papillomavirus
PCR for genital infections
Sperm analysis for PCR for STDs