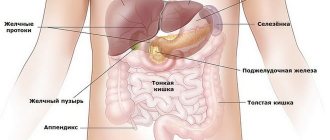
The liver is the most important organ of our body, which performs several hundred different functions. The modern human lifestyle is associated with dirty air, a lot of stress, and the presence of chemical additives in food. The reasons also lie in the regime and diet.
Overeating, long intervals between meals, snacks dry and on the go - all this negatively affects the health of the entire digestive system, in particular the liver. That is why timely liver treatment is the key to future health.
It is important to pay attention to the first signs of organ dysfunction. Heaviness in the abdomen, weakness, nausea, loss of appetite, bitterness in the mouth - all this may indicate developing disturbances in the functioning of the filtering organ. As the pathological process progresses, the area of the right hypochondrium aches, and the liver increases in size.
A seemingly harmless inflammation can quickly develop into dangerous pathologies that pose a threat to human life. Many people put off visiting a doctor until later, thereby aggravating the situation even more. Timely diagnosis allows early detection of pathologies in the organ, for example, compactions, structural changes or neoplasms.
Dysfunctions in this organ can affect the functioning of the entire body, leading to depression, bad breath, fatigue, headaches, skin diseases, excess weight, and poor digestion. Unique is the fact that the liver has the property of self-healing.
It will take one to two years for complete regeneration of hepatocytes. When you give the organ nutrients, healthy foods and herbs that improve liver function, it tends to recover. But how else can you help the organ? Is it possible to cure the liver completely?
Causes of the inflammatory process
Liver inflammation develops under the influence of various factors that trigger pathological changes. It is believed that the main reason lies in excessive consumption of alcoholic beverages. Ethyl alcohol destroys liver cells, and adipose tissue takes their place. Other causes of inflammation in a child or adult:
- Hepatotropic viruses. I distinguish several types of pathology, which differ in the method of infection and course.
- Medicines. Taking certain medications causes the development of an inflammatory process in the liver. The peculiarity of this type of disease is that after stopping the medication, the progression of the pathology stops.
- Impaired flow of bile. If stagnation occurs in the intrahepatic bile ducts, this causes inflammation of the liver tissue.
Antibiotics are a special group of drugs
Antibiotics are a special group of drugs that are used to treat infectious diseases of a bacterial nature.
They directly destroy bacteria or prevent them from reproducing. There are a great variety of drugs from this group, the effects of antibiotics are different, which gives the doctor the opportunity to choose the most optimal drug for each patient. The use of antibiotics is justified only in the case of a confirmed bacterial infection, because these drugs do not act on viruses. Therefore, only a doctor should make a decision on prescribing a drug, choose a specific medicine, its route of administration, dose, frequency of administration and duration of treatment. Also, it is the doctor who must monitor the patient’s condition during treatment, because the effect of antibiotics on the liver and kidneys can sometimes be very serious and require medical attention. Particularly dangerous from the point of view of the development of complications is the combination of antibacterial agents and analgesics in doses exceeding the permissible ones.
Types of pathology
Steatosis disease
This is a protective function of the liver; it blocks toxins in fatty lumps.
Fatty hepatosis is formed as a result of the liver’s reaction to toxic effects or inflammation develops under the influence of certain diseases. Steanosis is the accumulation of fatty deposits in liver cells. The symptoms of the pathology are not pronounced; during diagnosis, increased echogenicity of the parenchyma is revealed. Most often it occurs due to the following factors:
- metabolism is impaired;
- poor nutrition;
- chronic gastrointestinal pathologies;
- myxedema.
Types of hepatitis
The group of inflammatory liver diseases is classified depending on the etiology. Provoking factors include viral infections, alcohol, and medications. An inflamed liver occurs under the influence of such hepatitis:
- A - viral pathology, characterized by an acute course, transmitted through infected food and water.
- B - the virus is transmitted parenterally and naturally (sexually and domestically). Stable in the environment, that is, the pathogen persists in a blood stain for several weeks.
- C - infection occurs through the blood, in most cases as a result of medical procedures.
- D - transmitted by blood and its derivatives, diagnosed only in the presence of hepatitis B.
- E - the mechanism of infection is fecal-oral, common in poor sanitary conditions.
- F - transmitted sexually, through blood and personal hygiene items.
Effect of cirrhosis
The liver is connected with the vital processes of our body.
The pathology is characterized by a chronic course, during the development of which normal liver cells are replaced by connective tissue, which leads to organ dysfunction. Very often the disease is caused by secondary diseases such as pneumonia. If the provoking factor is not eliminated and appropriate therapy is not carried out, cirrhosis will lead to death. Inflammation of the liver is formed due to the following effects:
- intoxication of the body;
- circulatory disorders;
- syphilis;
- brucellosis;
- malaria;
- tuberculosis;
- hepatitis of various etiologies.
Temperature in liver cirrhosis
When the liver is damaged by hepatitis C, the subferal body temperature remains at 37 – 37.5 degrees.
Fluctuations in indicators depend on the form and stage of development of the disease. The increase can be short, but critical, and can last for several months. Elevated temperature often appears with any type of liver cirrhosis; it can be more pronounced or less pronounced:
- Viral cirrhosis – the temperature rises sharply, can reach 40 degrees. The patient suffers from severe chills and fever. In the results of blood tests you can see that the concentration of bilirubin is critical.
- Secondary biliary damage - a sharp increase in temperature, troubling chills. The skin and sclera of the eyes turn yellow, itchy skin appears. Upon palpation, you can feel that the liver and spleen are enlarged in size. In a blood test, you can see that the level of leukocytes and bilirubin is increased.
- Compensated cirrhosis. There are practically no symptoms; many people confuse them with a simple malaise. The liver performs its functions, there are no complications.
An increase in body temperature above normal may indicate a pathological process in the body.
In addition to cirrhosis, other diseases can develop, which include the following:
- blood diseases;
- malignant tumor;
- portal vein thrombosis.
Each of these diseases requires careful examination and prompt treatment.
Symptoms of the disease
Acute inflammation of the organ is expressed by jaundice and cutting pain in the right hypochondrium. During the acute period, there is constant nausea and periodic vomiting, and apathy and loss of strength are observed. Sometimes a flu-like type of inflammation may be present, then the patient has a fever, a sore throat and a runny nose. Other symptoms of liver inflammation also appear:
- High bilirubin. The substance is toxic to the body, its increased concentration is manifested by the coloring of the skin, tongue, and eyeballs yellow.
- Stagnation of bile. Bile is not excreted and enters the blood and skin cells. Signs of gallbladder inflammation: itching all over the body;
- bitterness in the mouth;
- belching.
Splenomegaly develops, that is, an increase in the size of the spleen, pain in the lymph nodes, joint pain, vascular lesions of the lungs and skin. This condition is called inflammatory liver syndrome.
Complications and diagnosis
Recognizing the disease is possible, although not easy, if you are attentive to the signals.
If the liver is inflamed, this condition can lead to the development of complications:
- varicose veins of the stomach and esophagus;
- internal bleeding;
- peritonitis;
- accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity;
- encephalopathy;
- death.
To make a correct diagnosis, you need to contact a specialist who will prescribe appropriate diagnostic measures. The disease is diagnosed equally in men and women of different age categories. Procedures for diagnosing pathology:
- blood test for liver function tests;
- MRI;
- Ultrasound;
- organ fibroscanning;
- biopsy;
- fibromax.
What is hyperthermia
Literally translated, this term means “excessive heat.” Body temperature can increase for two reasons: either heat from outside has disrupted thermal exchange, or it is the body’s protective reaction to the actions of pathogenic factors.
There are several stages of increasing body temperature:
- Low-grade period, 370-380. The infection has already penetrated, the protective mechanism in the cells has activated, and the temperature begins to rise. At this stage, it is not recommended to knock it down.
- Febrile stage, 380-390. A signal that the disease is progressing. In some pathologies, this temperature can persist for quite a long time. As a rule, an antipyretic drug helps bring it down, but not for long. Even if there are no other symptoms, this is a good reason to see a doctor immediately.
- Pyretic temperature is 41 degrees. With such high values, the patient will not be able to cope with the disease on his own. Usually, specialists are already involved in treatment at this stage and the person is in the hospital.
- Hyperpyretic fever is life-threatening, its temperature range is above 410. It is extremely rare in medical practice.
Treatment of the disease
Diet for an inflamed liver
The diet is designed in such a way as to reduce the load on the diseased organ and improve the functionality of the bile ducts. If the liver is inflamed, then to alleviate the patient’s condition, you can eat boiled or steamed dishes. The diet should be fractional, the last meal should be taken 4 hours before bedtime. A diet for liver inflammation excludes the consumption of the following foods:
- fresh bakery;
- dishes with spices;
- fried food;
- mushrooms;
- marinades;
- coffee and alcohol;
- rich broths.
Drugs
Therapy for hepatomegaly is individual and complex.
Treatment of liver inflammation includes medication. Medicines are prescribed by the doctor after the diagnostic results. If the liver is inflamed due to infection with hepatotropic viruses, then it is necessary to take special antiviral medications, which are selected depending on the pathogen. The drug "Alfarona" has proven itself well. The medicine will help relieve inflammation and is active against hepatitis viruses. The following drugs are also prescribed in complex therapy:
- "Viferon";
- "Heptor";
- "Pegasis";
- "Rabavin";
- "Trivorin";
- "Essentiale".
Folk remedies
You can treat an inflamed liver at home only on the recommendation of a doctor. Several effective recipes to relieve symptoms:
- Squeeze juice from 1 beet and radish. Mix the ingredients and drink 50 ml every day until symptoms disappear.
- Squeeze the sauerkraut to obtain half a glass of juice. Take after meals in the morning and evening for 6 weeks.
- Pumpkin pulp in the amount of 500 grams should be eaten for breakfast and washed down with 1 glass of fresh pumpkin juice.
General recommendations
It is possible to reduce the temperature in cirrhosis without the use of medications. However, they are all aimed at eliminating the symptom itself, and not the cause of its occurrence. Manifestations of the disease cannot be ignored, as they may indicate the development of side diseases and infectious complications. If, during examination by a hepatologist, no obvious disturbances in the functioning of the organs of the hepatobiliary system were detected, physiotherapeutic procedures will help eliminate low-grade and febrile fever.
Special indoor microclimate
If the thermometer approaches 38-38.5°C, you need to take care of creating a suitable microclimate in the house. Reducing the room temperature to 18-19°C will increase the body’s heat exchange with the environment, due to which the fever will pass. During the winter season, it is recommended to ventilate the room at least 4-5 times a day. The patient should dress lightly, since clothing that is too warm only retains heat in the body, causing the temperature to rise.
In the summer, air conditioners and fans are used to reduce the temperature in the house. If you don't have the appropriate technology, simply keep your curtains and blinds closed. Perhaps such measures will seem ineffective to some, but more than 35% of the heat enters the house through the windows.
Cool bath
In extreme heat, it is recommended to take cool baths. Water is a good heat conductor, through which you can reduce body temperature by 2-3°C. To prevent serious stress on the cardiovascular system, several important nuances must be taken into account during the procedure:
- fill the bath with cold water (temperature no more than 20°C);
- Before plunging into the water, wash your feet;
- while bathing, massage the skin with a washcloth (increased blood microcirculation will ensure rapid heat exchange with the environment);
- If you feel better, complete the procedure.
Cold compress
A cold compress is one of the simplest and safest methods for eliminating low-grade fever. To restore normal temperature, it is recommended to apply wet compresses to the wrists, groin area, forehead and calf muscles. Cold compresses have antipyretic and analgesic effects. To cope with fever due to cirrhosis of the liver, you need to do the following:
- wrap a fairly large piece of cotton wool in gauze;
- moisten the prepared material in cold water;
- apply a compress to the forehead, shin, interscapular area;
- As the compress heats up, wet it in cold water.
It is impossible to apply compresses to the heart area, as this can lead to spasm of the arteries and disruption of normal blood circulation. To enhance the antipyretic effect of the compress, you can apply it to areas with large vessels - subclavian, inguinal, axillary, etc. Contraindications to the use of cold compresses are infectious and skin diseases.
Sources
- https://bolitpechen.ru/simptomatika/temperatura-pri-zabolevanii-pecheni-479
- https://alcogolizm.com/pechen/temperatura-pri-cirroze-pecheni.html
- https://gemor.su/soputstvoyushie/cirroz/byvaet-li-temperatura-pri-cirroze-pecheni
- https://zhkt.ru/pechen/cirroz/povyshenie-temperatury.html
- https://propechenku.ru/tsirroz/temperatura.html