general characteristics
Magnesia (acceptable names: magnesium sulfate, Epsom salt) – magnesium oxide in the dosage form of a white powder. The drug is used to cleanse the body, get rid of problems with the gastrointestinal tract, and lose weight.
Salt does not contain impurities, additives, or auxiliary substances. The beneficial effect for the body is achieved due to the influence of sulfuric acid and magnesium salt - the two main components of the drug.
Properties of the drug:
- anesthesia;
- cleaning of internal organs;
- reducing the possibility of developing seizures;
- reducing the risk of developing arrhythmia (impaired heart rate);
- mild diuretic effect;
- laxative effect;
- reduction of total body weight by cleansing the body.
The properties of the drug directly depend on the route of entry into the body:
- Oral method. Choleretic and laxative effects are achieved 2-3 hours after administration of the drug. This effect can last for 4-6 hours. In the body, there is an influx of fluid into the intestinal lumen, which provokes loosening of stools, dilution of stool, increased intestinal motility and, accordingly, defecation. The oral route of administration provides irritation to the walls of the duodenum and relieves spasms. A certain part of the drug is excreted from the human body through the kidneys, which has a beneficial effect on their functionality. Magnesium sulfate is used as an antidote for poisoning by mercury, barium, arsenic, and lead. The composition of Epsom salt begins to actively interact with unfavorable components. Provides a laxative effect and rapid removal of pathogenic substances from the body systems.
- Intravenous/intramuscular route. Thanks to this method of administration, the risk of developing seizures, arrhythmia, and hypotension is reduced. The product has calming and vasodilating properties. Exceeding the recommended dosage of the drug is fraught with oppression of internal organs (similar to narcotic effects). When administered intramuscularly, Epsom salt is activated 60 minutes after the composition enters the blood. The time frame of the active phase is about 4 hours. When administered intravenously, the active phase begins instantly and is maintained for 30 minutes.
- Local application. It is often used for compresses and dressings that improve blood flow, provide pain relief and resorption of unfavorable components.
https://youtu.be/jToSk5cdOzE
Use during pregnancy
The drug is used during pregnancy when there is a threat of premature birth. As an anticonvulsant with a hypotensive effect, it is the drug of choice for the treatment and prevention of seizures in eclampsia. Therapy is started if diastolic blood pressure {amp}gt; 130 mmHg Art. Magnesium therapy is carried out for another 24–48 hours after birth.
Animal studies with intravenous administration of magnesium sulfate have not been conducted. It is not known whether magnesium sulfate can cause adverse fetal effects when administered intravenously to pregnant women or affect reproductive capacity. Should be used during pregnancy only if necessary.
When administered parenterally for eclampsia in pregnant women, it quickly passes through the placenta and reaches concentrations in the fetal serum approximately equal to those in the mother. The effects of magnesium sulfate in newborns are similar to those in the mother and may include hypotension, hyporeflexia, and respiratory depression if the woman received magnesium sulfate before delivery.
Therefore, magnesium sulfate is usually not used in the prenatal period (2 hours before birth), except in cases where it is necessary to prevent seizures during eclampsia. Magnesium sulfate can be administered continuously via IV drip at a rate of 1–2 g every hour, provided that plasma magnesium concentrations, blood pressure, respiratory rate and deep tendon reflexes are carefully monitored.
Mechanism of action
The drug is administered orally.
For a qualitative effect on the intestines, it is recommended to choose an oral method of administering the drug into the body (the instructions for use included in each package of the medication determine this regimen as the most effective). As mentioned earlier, after entering the body, the drug irritates the receptors of the duodenum, after which bowel cleansing begins.
By using magnesium, you can eliminate the risk of excessive amounts of the drug entering the blood. Only a small part is absorbed into the blood, the rest is excreted by the kidneys.
Other Benefits of Epsom Salts
In addition to facial and body care, Epsom salt has other uses, always associated with the presence of magnesium sulfate.
Among them we can mention:
- Fertilizer: The magnesium content of Epsom salt is beneficial for fertilizers, plants and soil, and in particular it is used as a fertilizer for tomatoes, peppers and roses.
- Pesticide: Epsom salts are an excellent pesticide. Mix a quart of water with one tablespoon of Epsom salts and spray the mixture on plants or the affected area to repel insects and pests.
- Cleaning: Epsom salts can be used to clean tile and ceramic surfaces and to remove scale.
- Herbicide: A mixture of 4 tablespoons of Epsom salts, a liter of vinegar and two tablespoons of eco-friendly laundry detergent is an excellent weed killer.
- Tree removal: To eradicate an old and diseased tree, simply drill into the trunk with a drill, put a handful of Epsom salts inside, and then wait a couple of weeks. Salt will speed up the decomposition process and cutting down the tree will be much easier.
Indications/contraindications for use
Indications
- cerebral edema;
- chronic diseases of the nervous system;
- non-inflammatory brain diseases, such as encephalopathy;
- risk of premature birth;
- magnesium deficiency in the blood;
- violation of heart rate and rhythm;
- constant psycho-emotional stress, excessive excitability and activity;
- inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract;
- excessive sweating;
- bronchial asthma;
- entry into the body of unfavorable components of heavy metals that can cause poisoning;
- warts;
- damage to internal organs.
Contraindications
- decrease in blood pressure (20% below the permissible value);
- disruption of the supply of impulses from the atria to the ventricles;
- violation of contractions of the heart muscle;
- pathologies of the respiratory center;
- renal failure;
- rectal bleeding;
- appendicitis;
- period before childbirth;
- dehydration of the body;
- intestinal obstruction, problems with the functioning of the stool.
Interaction
Use with cardiac glycosides increases the risk of AV block; with muscle relaxants, neuromuscular blockade increases. When used together with vasodilators, the hypotensive effect is enhanced. The likelihood of depression of the respiratory center and central nervous system increases when used with barbiturates and narcotic analgesics.
Calcium salts reduce the effect of the drug. A precipitate is formed with clindamycin phosphate, polymyxin B, hydrocortisone, procaine hydrochloride, salicylates, Ca2 preparations, ethanol, strontium salts, arsenic acid, barium.
Taking nephrotoxic drugs, such as amphotericin B, cisplatin, cyclosporine, gentamicin, increases the need for magnesium. Loop and thiazide diuretics, with long-term use, can reduce the magnesium-storing ability of the kidneys, which leads to hypomagnesemia (monitoring of magnesium levels in the blood is necessary).
Potassium-sparing diuretics, when used long-term, increase tubular reabsorption of magnesium in the kidneys, which can cause hypermagnesemia, especially in patients with renal failure. Calcium salts (for intravenous administration) neutralize the effects of magnesium sulfate administered parenterally. However, calcium gluconate or calcium chloride is used to eliminate the toxic effects of hypermagnesemia.
Concomitant use of calcium-containing drugs for oral administration and magnesium-containing drugs may lead to increased serum concentrations of calcium or magnesium in sensitive patients, mainly in patients with renal failure. The depressant effect on the central nervous system when administered parenterally increases when combined with drugs that depress the central nervous system.
The development of hypomagnesemia has been reported in patients concomitantly taking digitalis glycosides, which can lead to digitalis intoxication (serum magnesium levels should be monitored). With simultaneous oral use, magnesium preparations can reduce the absorption and concentration of digitalis glycosides in the blood (extreme caution is required, especially in cases where intravenous calcium salts are also used;
Possible cardiac conduction disturbances and heart block. Muscle relaxants enhance neuromuscular blockade. Reduces the absorption of etidronic acid and tetracyclines (forms non-absorbable complexes with oral tetracyclines). Excessive intake of alcohol or glucose increases renal excretion of magnesium.
Magnesia, used for intestinal obstruction, enhances the effect of certain medications, for example:
- “Ciprofloxacin.”
- “Streptomycin.”
- "Tobramycin".
- “Nifedipine.”
- Anticoagulants.
- Glycosides.
- Muscle relaxants.
The drug is not recommended for use in combination with the following liniments: Hydrocortisone and Clindamycin. In addition, magnesia cannot be combined with tartaric acid, calcium, procaine hydrochloride, and strontium.
When used together, the drug enhances the activity of other drugs that suppress the central nervous system (hypnotics and alcohol). When used with barbiturates, it depresses the respiratory center. Nifedipine and aminoglycosides strengthen the neuromuscular blockade caused by magnesium salts.
When using magnesium sulfate with other vasodilators, the hypotensive effect is enhanced. The product forms a sediment when combined with calcium supplements and alcohol in high dosages.
The use of similar magnesium products should be under the supervision of a physician. Products that have a similar composition are produced in different versions and may have different prices.
Among similar drugs are the following:
- Diasporal Forte;
- Pentaxifylline;
- Diabazol.
Like any other medicine, magnesium sulfate is not a panacea, but a drug that not only cleanses the intestines, but under certain circumstances can save someone's life.
Article design: Mila Friedan
Colon cleansing with magnesium sulfate
Preparatory stage at home
Intestinal cleansing with magnesium begins with preparation.
In order to qualitatively cleanse the body of various impurities, impurities, and toxins, certain preparation is necessary. It is recommended to start the preparatory stage 10-14 days before the start of cleaning. Basic Rules:
- Quitting bad habits such as uncontrolled drinking of alcoholic beverages or smoking.
- Switch to a healthy, proper diet. It is necessary to give up harmful fast carbohydrates, increase the amount of protein and fiber in the diet. You should adhere to the drinking regime (about 2 liters of water per day, depending on the needs of the body). You should eat food in small portions at regular intervals.
- Strong physical activity. It is recommended to reduce (or increase) the overall activity rate to the acceptable minimum.
- If cleaning is carried out at home, you should consult a doctor regarding your current health status and possible consequences. It is recommended to discuss all the details of the future cleansing course. If the patient's condition worsens, you should stop the course and seek help from a doctor.
Recommendations for cleansing
Colon cleansing at home can be dangerous:
When cleansing the intestines with magnesium, do not forget about the need to maintain the body's water balance.
- dehydration;
- inhibition of favorable microflora;
- development of unfavorable pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract;
- violation of water-salt balance;
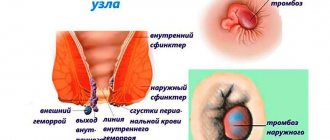
- burning in the anus, the occurrence of blood discharge along with feces.
To avoid unfavorable symptoms, you must:
- consult with your doctor regarding the general cleaning process;
- strictly follow medical instructions and do not self-medicate;
- carry out the preparatory stage before cleansing;
- lubricate the anus with vegetable oil after each bowel movement;
- maintain water-salt balance in the body;
- take appropriate medications (prescribed by the treating doctor) to maintain favorable microflora and general strengthening of the body;
- undergo a recovery course after cleansing the intestines.
How to use for one-day cleansing?
In one day you can perform a colon cleansing procedure with magnesium.
To properly cleanse the intestines in 1 day, you need to choose a free day for the procedures (the required amount of time is 10 hours). Prepare magnesium sulfate (25 grams), water (2 liters), lemon juice. Mix magnesium sulfate, lemon juice and 1 cup of liquid, leave to infuse overnight. The resulting solution should be drunk at 6 am (experts say that at this time intestinal activity reaches its highest levels). To reduce the unpleasant aftertaste, it is recommended to drink lemon juice diluted with liquid after the solution. After one-time use, you need to take 1 glass of lemon water every 20 minutes.
After 2-4 hours the need to defecate will arise. The time frame depends on the individual metabolism of the patient. After each bowel movement, you need to take another 1 glass of lemon liquid. If the instructions are followed correctly, the last bowel movement (the fourth in a row) will consist of a clear liquid. After this, it is recommended to consume a sufficient amount of fiber dishes. Consume raw or cooked vegetables and fruits.
Mineral water + sodium sulfate
Thanks to this combination of ingredients, unfavorable waste and toxins are removed from the body. In addition, there is a decrease in total body weight ranging from 1 to 2 kilograms. The time frame for the cleansing procedure is 1 day.
- Drink plenty of medicinal mineral fluid. Give preference to liquids without gas or with a low concentration.
- Do not consume food products.
- Drink a solution of 20 grams of magnesium sulfate and 200 grams of warm water in the morning on an empty stomach.
Cleanse before fasting
It is good to cleanse the intestines before fasting with magnesium.
The time frame for preparing for fasting should not exceed 3 days. For the first 2 days, it is necessary to reduce the total number of calories consumed in food products . On the last day before fasting you need to consume:
- a large amount of liquid;
- 45 grams of magnesium sulfate.
Epsom salt enemas
Such enemas are recommended for chronic stool disorders. Recipe:
- Dissolve 1 tablespoon of the drug in half a glass of water. The liquid should be at room temperature.
- Inject the resulting solution into the rectum.
Epsom salt - what is it?
Epsom salt is a mixture based on epsomite heptahydrate or magnesium sulfate . Epsom salt is used for a wide variety of purposes: related to both general human health and cosmetic care.
It can be purchased from traditional medicine specialists, in pharmacies or online, in the form of crystalline salts or tablets for dissolution in water.
Moreover, Epsom salt is often used to care for house plants. Its beneficial properties are determined mainly by the presence of magnesium sulfate.
Overdose/side effects
The maximum dose of the drug administered once per day is 30 grams. For intramuscular administration - 200 milliliters.
Dosage for children:
- up to 12 years: up to 10 grams;
- 12-15 years: 10 grams;
- from 15 years: from 10 to 30 grams.
Possible side effects:
- disturbance of heart contractions;
- decreased blood pressure;
- excessive uncontrollable sweating;
- dysfunction of the central nervous system;
- general weakness of the body, decreased performance;
- decrease in general body temperature;
- nausea, vomiting;
- diarrhea, flatulence, constipation;
- dehydration;
- pain occurring in various parts of the body.
https://youtu.be/g7nN7wM1aYs
How to properly use magnesium for constipation in the elderly, children and pregnant women
1 Children under 3 years old should not take this type of laxative; for children over three years of age, the advisability of taking it is assessed by the local pediatrician. Without his consent, parents are not recommended to act independently, so as not to harm the child’s health.
2 During the period of bearing a baby, it is advisable for a pregnant woman to treat constipation by choosing an analogue of a mild saline laxative or turning to recipes for herbal decoctions with a laxative effect. In injection form, the drug is prescribed to normalize blood pressure, stimulate the removal of excess fluid if there is a tendency to edema, and prevent the threat of premature birth. It is better for pregnant women to avoid taking magnesium sulfate solution orally.
3 For nursing mothers, magnesium should be excluded from laxative options, since it passes into breast milk and can cause diarrhea in a breastfed baby.
4 Older patients who often suffer from constipation can take advantage of magnesium to clear the intestinal lumen of accumulated feces. This laxative is good for “loose bowel syndrome.” However, it is worth considering that the presence of inflammatory foci in the gastrointestinal tract is a contraindication to taking magnesium solution.
5 Hypotonic patients should refrain from using magnesium, as it lowers blood pressure levels.
Preliminary preparation
Before using the solution you need to prepare. Initially, you need to adjust your diet. And also avoid excessively salty, fatty and sweet foods. Canned and fried foods should also not be consumed.
If fatty foods were eaten before using magnesium, the solution will not work. Bread and pastries are all empty carbohydrates that clog the intestines.
You must adhere to the diet for at least three days before taking the medicine. At the same time, it is necessary to move more, as well as take walks and do morning exercises. Increasing your activity will help improve intestinal motility.
In addition, you should measure your weight before taking the suspension, and carefully monitor your health. If there is an abnormal change, you must consult a doctor.
Causes of the disease
Intestinal obstruction can occur due to lifestyle and eating habits. Constipation appears after regularly restraining the urge to have a bowel movement, which over time suppresses the reflex functioning of the intestines:
- prolonged bed rest;
- busy work schedule;
- frequent moves.
Frequent use of laxatives due to unreasonable expectations of bowel movements, as well as a diet poor in fiber products are factors that contribute to the appearance of chronic difficulties with bowel movements.
Constipation can be the result of a serious illness, which in most situations requires surgery, for example, for coprostasis. Depending on the degree of stenosis of the intestinal lumen, obstruction can be complete or partial.
Neurological disorders may contribute to chronic defecation problems. In addition, most medications can cause suppression of intestinal motility and cause constipation as a side reaction.
Advantages and disadvantages of the procedure
When magnesium is used to cleanse the intestines, doctors and patients note the positive aspects of the procedure. The advantages of the method are accessibility and cost-effectiveness. The benefits of cleaning include:
- choleretic effect, improving the functioning of the liver and gall bladder;
- possibility of a long course of treatment;
- no effect on internal organs, no effect on the peristalsis of the stomach and intestines;
- lack of addiction to the drug;
- effective bowel cleansing in a short time;
- minimal irritation of mucous membranes;
- effective detoxification of the body.
The disadvantages of the procedure appear in the case of a prolonged cleansing process and violation of the dosage of magnesium sulfate. The disadvantages of the technique are:
- dehydration of the body;
- violation of water-salt balance;
- loss of microelements (calcium, sodium);
- leaching of beneficial microflora;
- weakened peristalsis (lazy bowel syndrome);
- lowering blood pressure.
Among the negative aspects of the process of cleansing the intestines with magnesium is the appearance of general weakness of the body. The disadvantages of the procedure include:
- discomfort while taking magnesium;
- the need to change nutrition during preparation;
- spasms of smooth muscles causing pain;
- burning in the anus;
- the appearance of blood during bowel movements;
- dizziness;
- the occurrence of edema;
- discomfort in the abdomen.