Suppurative diseases (abscesses and phlegmons) are serious complications of many inflammatory processes occurring in the body. Such complications are especially dangerous in the area of the face and head, since it is possible for pus to spread from the lesion to the brain and develop life-threatening complications.
Abscesses and phlegmons in diseases of the ENT organs are in second place in frequency after odontogenic suppurative complications.
An abscess is a purulent inflammatory process of a limited nature. When a virulent infection penetrates deep into the tissues, purulent inflammation occurs with necrosis, the formation of a cavity filled with pus and limited from the surrounding tissues by a capsule. The formation of a capsule is a protective reaction of the body to prevent the spread of suppuration.
Cellulitis is a more serious complication, which is characterized by a diffuse spread of purulent inflammation, unrestricted from surrounding tissues.
Abscesses and phlegmon can form in almost all inflammatory diseases of the ENT organs, as well as as a result of injury. There is no clear classification of suppurative processes in the ENT organs. The most common forms in practice can be listed:
- Abscess diagram
Peritonsillar abscess;
- Periopharyngeal abscess;
- Retropharyngeal abscess;
- Boil of the nose;
- Furuncle of the external auditory canal;
- Retrobulbar abscess;
- Orbital phlegmon;
- Phlegmon of the lacrimal sac;
- Facial phlegmon;
- Cellulitis of the neck.
The development of abscesses and phlegmon occurs most often in the subcutaneous or interstitial tissue, which is rich in blood and lymphatic vessels.
Causes and risk factors
A peritonsillar abscess occurs against the background of an inflammatory process in the oropharynx (often a complication of a sore throat, less often develops against the background of dental and other diseases).
Risk factors for developing peritonsillar abscess include:
- pharynx injuries;
- decreased immunity;
- metabolic disorders;
- smoking.
Tobacco smoking is a risk factor for the development of peritonsillar abscess
Infectious agents in peritonsillar abscess are often staphylococci, group A streptococci (the participation of non-pathogenic and/or opportunistic strains is also possible), somewhat less frequently - Haemophilus influenzae and Escherichia coli, yeast-like fungi of the genus Candida, etc.
Prevention
Unfortunately, quite often patients are admitted to hospitals with already formed advanced forms of suppurative complications. This indicates a late visit to the doctor for treatment of the underlying disease. Need to remember:
- All inflammatory, especially purulent processes in the face, nose and throat are very dangerous.
- You should not delay seeking medical help for sore throats, prolonged runny nose, boils, or injuries to the nose and throat.
- Follow all recommendations strictly, go to the doctor for observation, especially with purulent sore throats.
- Do not self-medicate.
- It is advisable to carry out radical treatment for chronic diseases of the ENT organs (tonsillectomy for chronic tonsillitis, sanitizing operations on the sinuses for chronic sinusitis).
Forms of the disease
The disease can be unilateral (usually) or bilateral.
Depending on the location of the pathological process, peritonsillar abscess is divided as follows:
- posterior (the area between the velopharyngeal arch and the tonsil is affected, there is a high probability of inflammation spreading to the larynx);
- anterior (the most common form, the inflammatory process is localized between the upper pole of the tonsil and the palatoglossal arch, often opens on its own);
- lower (localized at the lower pole of the tonsil);
- external (the rarest form, the inflammatory process is localized outside the tonsil, there is a possibility of pus breaking into the soft tissues of the neck with the subsequent development of serious complications).
Most often, peritonsillar abscess is diagnosed in children, as well as in adolescents and young adults.
Anatomy of a disease
Only timely diagnosis allows one to determine an acceptable treatment method.
The changes that occur in the tissues around the tonsils during a peritonsillar abscess are quite varied. First of all, the first phase of the disease is characterized by tissue swelling, without pronounced clinical manifestations. At this point, the disease is practically not diagnosed.
At the next stage, the inflammatory process of the peritonsil connective tissue joins - paratonsillitis begins. This stage is accompanied by hyperemia, fever and pain.
It is quite possible that the pathological process will be limited to the inflammatory stage, and suppuration will not begin. The use of antibiotic-based medications significantly increases the likelihood of an abscess-free pathology.
Signs of defeat.
The last stage of the inflammatory process, in the loose connective tissue of the paramygdaloid space, is the development of an abscess. It is accompanied by suppuration, softening and melting of tissues, and vein thrombosis.
Based on the above described pathological changes in the pharyngeal cavity, the following stages of disease development are distinguished:
- edematous;
- infiltration;
- the appearance of an abscess.
The location of the onset of the disease depends on the individual physiological characteristics of the body, previous pathological suppurations, and the pathogenic pathogen.
How is an abscess treated?
Classification of purulent cavity depending on location:
| Name | Localization location |
| anterosuperior | between the anterosuperior surface of the palatine arch and the tonsil; |
| back | between the tonsil and the posterior arch; |
| lower | behind the lower anterior arch, outside the lower pole of the tonsil; |
| external or lateral | between the lateral edge of the tonsil and the wall of the pharynx; |
The pus has a thick consistency, an unpleasant odor, and denser masses are found in it. The tonsil itself is relatively rarely subjected to significant suppuration.
Drug therapy does not always give a positive result.
Symptoms of paratonsillar abscess
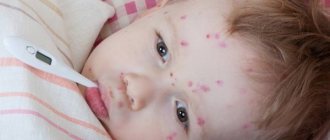
Symptoms of a paratonsillar abscess, as a rule, appear 3–5 days after an infectious disease, primarily a sore throat.
Typically, patients complain of severe sore throat, which is usually localized on one side and can radiate to the teeth or ear. One of the characteristic signs of the disease is trismus of the masticatory muscles, i.e. restriction of movements in the temporomandibular joint - difficulty or inability to open the mouth wide. In addition, patients may feel the presence of a foreign object in the throat, which leads to difficulty swallowing and eating. The lymph nodes under the jaw become enlarged, causing head movements to become painful. These symptoms in patients with peritonsillar abscess are accompanied by general weakness, headaches, and increased body temperature to febrile levels (39-40 °C). As the pathological process progresses, breathing becomes difficult, shortness of breath occurs, bad breath appears, and the voice often changes (becomes nasal). The patient's tonsils on the affected side are hyperemic and swollen.
With peritonsillar abscess, patients complain of a sore throat on one side, radiating to the ear and teeth
In the case of self-opening of the abscess, a spontaneous improvement in general well-being occurs; general and local symptoms usually disappear within 5-6 days. However, the disease is prone to recurrence.
Causes
When the temperature rises
The main cause of the development of an abscess is bacteria - streptococci, staphylococci and other harmful microorganisms. Factors such as weak immunity, other oral diseases and hypothermia can affect their activation and development. Abscess of the tonsils is the most striking symptom of diseases such as chronic tonsillitis and tonsillitis.
On video of tonsil abscess:
But they can be of different types:
- Angina. This pathological process is accompanied by inflammation of the upper tonsils. Occurs as a result of damage by viruses and bacterial activity. Temperatures can reach up to 40 degrees. Sore throat can be of two types: lacunar and follicular. The first type can be recognized by the presence of white or yellow plaque on the tonsils. It is concentrated in the gaps. Abscesses that have formed in these openings can leave their boundaries and merge with each other. Sometimes during diagnosis, doctors discover that the tonsils are completely covered with purulent plaque. It is very easy to remove, but without the necessary treatment it will form again. But follicular tonsillitis is characterized by redness and hyperemia of the tonsils, followed by the formation of small ulcers. They may be yellow or white. But this article will help you understand what bacterial tonsillitis in children looks like and how it is treated.
This is what a purulent sore throat looks like.
- Chronic tonsillitis. If an exacerbation stage is observed, then the abscess formed against the background of the disease will occur with an increase in temperature. Its readings will be 338.5-39.5 degrees. In this case, redness and enlargement of the tonsils, pain when swallowing and small pustules are observed. (This article will help you understand whether it is possible to warm your throat if you have tonsillitis) In the photo - chronic tonsillitis:
Chronic tonsillitis
If there is no temperature
An abscess on the tonsils without fever can occur against the background of a sore throat, which is called ulcerative-necrotic. This pathological process is characterized by almost all the symptoms of a common sore throat, but without an increase in temperature.
An abscess on the tonsils without fever may indicate the development of chronic tonsillitis or purulent tonsillitis. The formation of the acute phase occurs with inflammation of the palatine tonsils.
Purulent tonsillitis affects the body 2-3 times a year, and the immune system is not able to provide adequate protection, which leads to chronicity. In this case, pus on the tonsils can occur for the slightest reason.
But what the holes in the tonsils look like in the photo will help you understand the content of this article.
It will also be interesting to see what a child’s loose tonsils look like in the photo.
But what stomatitis on the tonsils looks like and how this disease can be cured is described in this article: https://prolor.ru/g/detskoe-zdorove-g/stomatit-na-mindalinax.html
But how tonsils are treated with cryotherapy and how effective it is is described in this article.
Diagnosis of peritonsillar abscess
Diagnosis of paratonsillar abscess is based on data obtained from collecting complaints and anamnesis, as well as pharyngoscopy and laboratory tests. When examining the pharynx, hyperemia, protrusion and infiltration are observed above the tonsil or in other areas of the palatine arches. The posterior arch of the tonsil is shifted to the midline, and the mobility of the soft palate is usually limited. Pharyngoscopy (especially in children) can be difficult due to trismus of the masticatory muscles.
A bacteriological culture of the pathological discharge is prescribed to determine the sensitivity of the infectious agent to antibiotics.
In a general blood test, patients with peritonsillar abscess show leukocytosis (about 10–15 × 109/l) with a shift in the leukocyte formula to the left, and a significant increase in the erythrocyte sedimentation rate.
A general blood test for peritonsillar abscess shows leukocytosis and an increase in ESR
Ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging can be used to confirm the diagnosis.
Differential diagnosis is carried out with tonsillitis, diphtheria, scarlet fever, erysipelas of the pharynx, and malignant neoplasms.
Diagnostics
A presumptive diagnosis can be determined during the initial examination.
Diagnosing pathology is usually not difficult for an otolaryngologist. Thanks to the pronounced clinical picture of the disease, the specialist makes a preliminary diagnosis already at the stage of the initial examination.
A completely objective diagnostic instruction consists of the following activities:
- General inspection. At the first examination, the doctor will pay attention to the external signs of the disease. The patient comes to the appointment with a characteristic tilt of the head, and gives the impression of a person exhausted by constant pain. He has a fever, painful lymph nodes, and an unpleasant odor coming from his mouth. The patient complains of pain when swallowing and difficulty opening his mouth. The otolaryngologist should pay attention to what preceded the onset of painful symptoms. Very often, suppuration of the paramygdaloid retina forms after treatment of angina.
- Pharyngoscopy (video in this article) . This method makes it possible to visualize the abscess area in the most informative way. The specialist draws attention to the pathological asymmetry of the pharynx - the uvula moves to the healthy side due to painful protrusion of the tonsil. If a more rare, bilateral lesion occurs, then the tonsils seem to clamp the tongue. On the surface of the peri-almond tissue, zones with a yellow tint will be visible - these are the places of future breakthrough of pus. Swelling will appear on the palatine arches and part of the soft palate.
- Lab tests . To determine the pathological pathogen and sensitivity to drugs, a smear and bacterial culture are made from the pharynx, nose and pharynx. A general blood test will show leukocytosis with neutrophilia and elevated ESR values.
For a more detailed differential diagnosis and to exclude the spread of infection to other tissues, ultrasound, CT, and x-ray are prescribed. With an odontogenic abscess, an x-ray can detect a granuloma or an unerupted wisdom tooth.
The disease is differentiated from the following pathologies:
- inflammation of the hypertrophied tonsil;
- paratonsillitis due to diphtheria;
- scarlet fever;
- tumor neoplasms;
- carotid artery aneurysm;
- phlegmon of the neck.
Based on the above methods, peritonsillar abscess can be diagnosed according to the indications of an infectious disease specialist, surgeon and dentist.
Treatment of peritonsillar abscess
Depending on the severity of the disease, treatment is carried out on an outpatient basis or in an otorhinolaryngological hospital.
In the initial stages, treatment of peritonsillar abscess is usually conservative. Antibacterial drugs of the cephalosporin or macrolide group are prescribed.
As the pathological process progresses, conservative methods are insufficient. In this case, the most effective treatment method is surgical opening of the peritonsillar abscess. Surgery is usually performed under local anesthesia (the anesthetic is applied by lubrication or spraying), general anesthesia is used in children or in anxious patients. Surgery can be performed using the following methods:
- puncture of the peritonsillar abscess with removal of purulent infiltrate;
- opening the abscess with a scalpel followed by drainage;
- abscessonsillectomy - removal and opening of a paratonsillar abscess by removing the affected tonsil.
At the initial stages of peritonsillar abscess, the patient is prescribed antibiotic therapy
When opening a peritonsillar abscess, an incision is made in the area of greatest bulge. If such a landmark is absent, the incision is usually made in the area where frequent spontaneous opening of the paratonsillar abscess is noted - at the intersection of the line that runs along the lower edge of the soft palate on the healthy side through the base of the uvula, and the vertical line that goes up from the lower end of the anterior arch affected side. Next, Hartmann forceps are inserted through the incision for better drainage of the abscess cavity.
With a peritonsillar abscess of external localization, opening it can be difficult; spontaneous opening of such an abscess usually does not occur, therefore, in this case, abscessonsillectomy is indicated. In addition, indications for abscessonsillectomy may be a history of recurrent peritonsillar abscess, lack of improvement in the patient’s condition after opening the abscess and removing the purulent contents, or the development of complications.
Recurrences of peritonsillar abscess occur in approximately 10–15% of patients, and 90% of relapses occur within a year.
In addition to surgical treatment of peritonsillar abscess, the patient is prescribed antibacterial drugs, analgesics, antipyretics and decongestants.
The main treatment is supplemented by gargling with antiseptic solutions and decoctions of medicinal herbs. In some cases, for peritonsillar abscess, physiotherapy, primarily UHF therapy, can be used.
After discharge from the hospital, patients with peritonsillar abscess are advised to undergo clinical observation.
Treatment of tonsil abscess
Drug treatment of tonsil abscess should be carried out as prescribed by the attending physician. Any deviation from the treatment regimen can lead to complications and the formation of new abscesses.
The basis of treatment is antibacterial drugs, which are selected based on the results of bacteriological examination. But, since the tests take quite a long time to prepare, broad-spectrum antibiotics are initially prescribed - Ampicillin, Amoxicillin, Sumamed, Augmentin, Flemoclav or Suprax. The duration of taking the drugs is from 7 to 10 days.
Attention! You cannot stop treating tonsil abscess at the first improvement - the course of drug treatment must be completed to the end.
It is imperative to gargle to clear the tonsils of accumulated mucus and bacteria, as well as to prevent infection of other tissues.
The most effective rinsing solutions:
- Furacilin.
- Stopangin.
- Eludril.
- Chlorophyllipt.
- OKI.
- Miramistin.
It is recommended to combine antiseptic rinse solutions with infusions of chamomile, eucalyptus, sage or calendula. This combination allows for faster relief of the inflammatory process.
Treatment includes symptomatic drugs:
- Antipyretic and anti-inflammatory - Nise, Nimesulide, Next, Nurofen, Ibuklin.
- Antihistamines - Suprastin, Cetirizine, Diazolin, Zyrtec.
- For poor sleep - tincture of valerian or motherwort, Novopassit, Valium.
If drug treatment for inflammation of the tonsil does not produce results or there is a possibility of pus breaking into deep tissues, surgical opening of the abscess is prescribed. During the operation, the abscess is opened with a scalpel and the cavity is washed with an antiseptic solution and drainage is installed. After the operation, it is necessary to continue the treatment prescribed by the otolaryngologist. In the most advanced cases, complete removal of the tonsils may be required.
Possible complications
The most severe and common complications are mediastinitis and phlegmon of the neck. They develop as a result of perforation (perforation, hole formation) of the lateral wall of the pharynx and involvement of the parapharyngeal space in the pathological process.
From there, the purulent contents quickly spread into the mediastinum or into the cranial cavity, which leads to the development of life-threatening complications:
- encephalitis;
- meningitis;
- meningoencephalitis;
- brain abscess.
Important! An extremely serious complication is the melting of the blood vessels of the pharynx with purulent contents, resulting in massive bleeding in the patient.
Treatment
The goal of therapy is to open the abscess and relieve inflammation from the tissues. This can be done in two ways: surgically or through conservative treatment. As a rule, regardless of the choice of treatment method, the patient is offered inpatient treatment.
Medication
In order to achieve opening of the abscess without the intervention of a surgeon, heating the neck is used. At the same time, broad-spectrum antibiotics are used or, if there is a result of a throat smear, corresponding to the identified sensitivity spectrum.
Constant rinsing of the larynx is also necessary. The following can be used as rinses:
- salt solutions;
- furatsilin;
- decoction of oak or chamomile.
The larynx can also be irrigated with Miramistin.
If necessary, medications are prescribed for symptomatic treatment: against pain, fever, insomnia.
Surgical
If conservative treatment is ineffective, the issue of surgical treatment is decided. If the abscess can be easily removed, this is done under local anesthesia. But if the purulent formation is in a place inaccessible to low-traumatic intervention, the doctor may recommend removing the tonsils completely.
The same method can be recommended if resection of the abscess was previously carried out repeatedly, but then a relapse followed.
Opening a tonsil abscess:
What is an abscess and how does it develop with sore throat?
During inflammation of the palatine tonsils, the pathological process can spread beyond the affected tissue. Around the tonsils there is fiber, which is quite loose. Inflammation, moving into this space, leads to the formation of a cavity filled with pus. This is how an abscess develops with a sore throat.
As a rule, suppuration occurs at the upper pole of the tonsil with tonsillitis. In this part, the fiber has a loose structure, there are deeper crypts, therefore, if the outflow of pus worsens, the penetration of inflammation into the surrounding tissues is quite likely.
In the throat, ulcers are found in the retropharyngeal, lateral and paratonsil spaces. Of these, paratonsillar abscess is characteristic of tonsillitis.
Abscesses can also occur around other tonsils (tubal, lingual, nasopharyngeal). The reasons for the appearance of such ulcers include chronic diseases of the ENT organs and the oral cavity. The rarest form is purulent inflammation around the lingual tonsil.
Complications and consequences
Complications of phlegmonous sore throat are very dangerous, as they affect not only the throat and nearby tissues, but also internal organs. The infection can spread along with blood and lymph fluid throughout the body. Particularly dangerous is infection with streptococcus, which causes rheumatic diseases - osteomyelitis, endocarditis, polyarthritis, systemic scleroderma.
Other consequences of peritonsillar abscess:
- Sinusitis.
- Nephritis.
- Thrombophlebitis.
- Laryngeal stenosis.
- Necrosis.
- Erysipelas.
- Infectious-toxic shock.
- Lymphadenitis.
When bacterial pathogens penetrate arterial vessels, there is a risk of developing cavernous sinus thrombosis and purulent meningitis. When pathogenic microflora enters the systemic bloodstream, sepsis can develop, which is life-threatening for the patient.
Kinds
An abscess is classified into at least two categories:
- tonsillar;
- paratonsillar.
The difference between these two types is that the peritonsillar abscess is symmetrical, affecting both tonsils.
Based on the immediate localization of the formation, they are distinguished:
- upper - upon examination it is clear that the tonsils move forward from the lacunae;
- external - the tonsils are clearly visible during visual inspection and almost cover the throat;
- internal - the formation of pus occurs inside the tissues of the tonsils;
- lower - the tonsils rise upward.
The photo shows a throat with tonsil abscess
What to do and how to treat
You cannot treat an abscess with a sore throat on your own. The obligatory action of the patient is to contact a specialist and hospitalization.
Treatment of patients with peritonsillar abscess is carried out only in a hospital setting. Therapy can be conservative, with surgery or combined. Tactics are selected individually depending on the stage of the process, the general condition of the patient, the presence of concomitant pathology, and the patient’s immune status.
The most appropriate is the use of conservative therapy in conjunction with surgery. The principles of drug treatment include:
- bed rest, liquid food, plenty of warm drinks;
- antibacterial agents;
- infusion therapy;
- analgesics;
- anti-inflammatory drugs - NSAIDs, glucocorticoids;
- local antiseptics.
An ENT doctor may also prescribe antihistamines and antifungal drugs as part of complex treatment. After symptoms subside, physiotherapy methods are used.
Antibiotics are selected based on the clinical and epidemiological picture of the disease. Preference is given to broad-spectrum drugs with proven effectiveness - protected penicillins, macrolides, cephalosporins, including:
- Sumamed;
- Augmentin;
- Ospamox;
- Emsef;
- Klacid.
In the acute period, these drugs are administered only by injection. The therapeutic course is 5 - 10 days. If there is no desired effect within 3 days, the doctor may prescribe another drug.
Many drugs are prescribed for symptomatic therapy due to severe pain and intoxication. Anti-inflammatory drugs, analgesics, improve the patient’s condition and promote recovery.
Antiseptics for local treatment by rinsing and washing have a local therapeutic effect on the affected tissue. In this case, solutions of Furacilin, Miramistin, Bioparox are used.
Is it possible to cope with an abscess on your own?
In principle, if the abscess is less than 1 cm in diameter and does not cause much concern, you can try to deal with it yourself. Warming compresses for 30 minutes 4 times a day help.
Under no circumstances should you try to “squeeze out” an abscess. By pressing on the cavity with pus, you create increased tension in it, which contributes to the spread of infection. You cannot pierce an abscess with a needle. The sharp tip of the needle can damage healthy tissue or blood vessels underneath the pus. Malicious microbes will not fail to take advantage of this opportunity and rush to develop new “territories”.
If you have something resembling an abscess on your skin, it is better not to delay a visit to the surgeon. Especially if:
- the abscess is very large or there are several of them;
- you feel unwell, your body temperature has risen to 38°C or more;
- an ulcer appeared on the skin;
- a red line appears from the abscess on the skin - this indicates that the infection has spread to the lymphatic vessel and lymphangitis has developed.
Symptoms of the disease
A feature of the disease is that the symptoms of an abscess are usually localized on the side of the lesion that caused them. If treatment is not started, the inflammation may spread to the second side. In the presence of a peritonsillar abscess, symptoms are caused by the formation of pus in the tissues:
- the person's health deteriorates,
- there is a sharp increase in temperature, although with reduced immunity it may remain unchanged,
- a tugging pain appears in the throat, which covers the jaw, ear,
- when swallowing, the pain is so severe that the person refuses to drink or eat,
- irritation of the salivary glands leads to increased salivation,
- A putrid odor appears from the mouth.
In addition, due to spasm of the masticatory muscles, a person cannot fully open his mouth. To avoid pain, he tries to move his jaw less. Therefore, his speech becomes slurred and a nasal sound appears. The progress of the process is indicated by enlarged lymph nodes; when turning the head, pain occurs in the neck. When trying to swallow liquid, a person may choke.
A feature of the disease is that the symptoms of an abscess are usually localized on the side of the lesion that caused them
This condition is accompanied by psychological problems caused by constant pain, the inability to sleep properly, and lack of adequate nutrition. To reduce drooling, a person tries to take a position that is not always comfortable for him: on his side, sitting with his head bowed. The doctor selects treatment taking into account the characteristics of the disease and the general condition of the patient.
You can identify a peritonsillar abscess localized in the upper part of the throat yourself. Upon examination, a spherical formation is clearly visible. Its edematous surface looks swollen and bulges upward. The mucous membrane around it becomes bright red, and purulent contents can be seen through it. When pressing with your finger, you can feel a pulsation.
The abscess may open spontaneously on the 4th day. Thanks to this, the condition improves: the pain subsides, the temperature drops. In other cases, the abscess is opened surgically. After this, rinsing with antiseptics is recommended.
Features of treatment
Once the doctor has made the diagnosis, further treatment is usually carried out in a hospital. It is almost impossible to stop purulent processes using home methods. First, the surgeon opens the abscess. First, the site of inflammation is anesthetized with a local anesthetic (lidocaine, dicaine). Then, with a scalpel, the doctor makes an incision along the protruding part of the abscess. Using pharyngeal forceps, the cavity is expanded, then it is thoroughly cleaned. The operation is completed by treating the wound with an antiseptic. To ensure the drainage of pus, a drainage is inserted into the cavity. Then conservative treatment is prescribed, including taking medications and rinsing.
After the source of acute pain - the abscess - has been eliminated, you need to undergo treatment. The patient is advised to rest, eat a gentle diet, and drink plenty of fluids. Antibiotics must be prescribed. Their choice is determined by the characteristics of the disease and the pathogen that caused the exacerbation. At the same time, it is important to prevent the development of fungus, so antifungal drugs (for example, intraconazole) are prescribed for prevention.
Painkillers will help relieve pain. They are prescribed intramuscularly (analgin, paracetamol). Antihistamines help prevent allergies. If the patient’s condition is determined to be severe or moderate, hemodez is administered intramuscularly to remove toxins. Gargling with antiseptic drugs (miramistin, furatsilin and others) is mandatory.
Complications
Further development of purulent processes without adequate treatment allows the infection to spread to other organs. Various complications may occur - parapharyngeal abscess, phlegmon. The cause of their occurrence is a breakthrough of the abscess, damage to the mucous membrane during its opening.
A parapharyngeal abscess is usually limited to the back of the throat. If treatment is started in a timely manner, it goes away quickly. Its danger lies in the possibility of sepsis, phlegmon of the neck, swelling of the mucous membrane leads to compression of the throat. Due to its deep location, the phlegmon of the neck cannot break through on its own. Therefore, surgical intervention is required. Antibiotic therapy is then prescribed.
Another consequence of untreated paratonsillitis is mediastinitis. It is caused by the spread of infection to the middle parts of the chest. The particular danger of the disease is associated with a high probability of damage to the heart and lungs.
Prevention
Faced with such an unpleasant and dangerous disease, people often wonder: could it have been prevented? You can protect yourself from peritonsillar abscess by constantly taking care of your health. This includes sports and hardening. You need to spend more time in the air, and don’t neglect sunbathing.
A prerequisite for the prevention of peritonsillar abscess is the cessation of alcohol and smoking.
An important component of prevention is the systematic treatment of chronic diseases of the nose and throat - rhinitis, sinusitis, tonsillitis. If an exacerbation occurs and antibiotics are prescribed, then it is necessary to complete the entire course, observing the dosage and frequency of administration. Often, at the first signs of improvement, patients refuse antibiotics, believing that this way they protect the body from negative effects. This is a fundamentally erroneous opinion. The remaining microbes adapt to the drugs, cause constant inflammation, and lead to the development of chronic diseases.
A prerequisite is the cessation of alcohol and smoking. It is recommended to exclude other factors that irritate the organs of the nasopharynx - polluted air, inhalation of chemicals, hypothermia. Timely elimination of sources of infection will also help avoid the disease and its complications.
Classification
Timely diagnosis and identification of the type of peritonsillar abscess allows you to correctly select medications and quickly cure the pathology. Initially, paratonsillitis is classified according to the cause of its occurrence - fungal, bacterial, traumatic.
Peritonsillar abscess is divided into several types according to the location of the inflammation:
- Anterosuperior (front) is the most common. It affects the tissues located above the tonsils.
- Posterior - the pathological process develops behind the posterior arch, accompanied by swelling of the larynx. In rare cases, the lesion covers the arch itself.
- Lower - usually caused by the penetration of bacteria through the circulatory system. An abscess forms closer to the root of the tongue, covering the lower part of the tonsils.
- Lateral (external) - paratonsillitis develops in the area of the lateral edge of the palatine tonsil. The lesion usually develops only on one side, so left-sided and right-sided abscesses are distinguished.
Based on external changes, there are three stages of peritonsillar abscess:
- Edema – has no obvious signs. This stage is characterized by swelling and loosening of the tissues located near the tonsils.
- Infiltration – pronounced symptoms of an abscess appear. It is characterized by severe swelling, hyperemia, and painful sensations.
- Abscess - manifestations of this stage occur 5-7 days from the onset of the disease, if appropriate treatment of the previous stages has not been carried out. Due to extensive swelling, the pharynx area is deformed.
Classification of the disease makes it possible to predict the further development of the pathology and select treatment methods that can cure phlegmonous sore throat without negative consequences.