Cervicitis is an inflammatory process in the cervix. It is most often located in the vaginal segment in the area of the cervical canal. Cervicitis is also called endocervicitis, meaning inflammation in the inner lining of the cervical canal. The disease requires mandatory treatment, since it is dangerous for the pathology to spread to the upper parts of the reproductive system, in particular the uterus. This is especially true for infectious cervicitis, which occurs in many women.
Now let's look at this in more detail.
General information
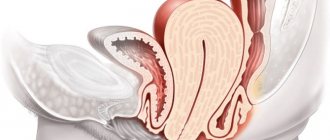
Cervicitis is a disease in which a woman develops inflammatory infectious processes in the cervix. To more accurately determine the essence of this disease, it is necessary to know about the structure of the genital organs of a woman’s uterus. The cervix continues the body of the uterus, located between the vagina and the uterine cavity. The cervical canal runs down the center of the cervix and connects the vagina and uterine cavity. The cervical canal contains a mucus plug, which prevents microorganisms from the external environment from penetrating into the internal reproductive organs.
Causes of the disease
Inflammation in the internal or external part of the uterine cervix begins after the infection penetrates the mucous membrane. At the same time, the thick protective mucus begins to liquefy, and inflammation forms.
Pathogenic microflora (chlamydia, gonococci, trichomonas, treponemas and other pathogens) can penetrate the cervix during sexual intercourse. Through blood and lymph from other organs, penetration of conditionally pathogenic microorganisms (Escherichia coli, staphylococci, streptococci and fungi) can occur.
The causes of cervicitis include various diseases in which general and local immunity is reduced:
- Urogenital infections that are transmitted through sexual contact.
- Diseases of an autoimmune and rheumatic nature.
- Hormonal disorders.
- Allergic reaction to contraceptives (spermicides and latex).
- Abortion and uterine curettage.
- Ruptures of the uterine cervix during childbirth (it is very important that all ruptures are properly sutured).
- Promiscuity and early sexual life.
- Failure to maintain personal hygiene (incorrect use of tampons and failure to remove the IUD in time).
- After severe infections, immunodeficiency due to HIV.
- Douching with solutions that cause dryness of the vaginal mucosa and lead to disruption of the microflora.
- Systematic and uncontrolled use of antibiotics.
- The presence of neoplasms in a woman.
Cervicitis itself rarely occurs. More often it is combined with other diseases in the female genital area: pseudo-erosion, colpitis, bartholinitis and others.
Types of cervicitis
First of all, experts divide cervicitis into infectious and non-infectious forms of the disease. However, infectious cervicitis caused by diseases that are sexually transmitted is more often diagnosed. In turn, the causes of the non-infectious form of the disease are often injuries, the presence of neoplasms, chemical or radiation exposure. According to the localization of the disease, it is customary to distinguish between endocervicitis (in this case we are talking about inflammation of the mucous membrane of the cervical canal) and exocervicitis (the vaginal part of the cervix is affected).
The course of the disease can be either acute or chronic . If timely treatment of the disease is not undertaken, chronic cervicitis develops. Assessment of the type of causative agent of the disease allows us to distinguish specific and nonspecific cervicitis.
Types
Scientists who have been studying cervical diseases for many years have classified cervicitis. Each type has its own symptoms, but accurate diagnosis will still require laboratory and hardware examination.
Spicy
In the acute form of cervical pathology, inflammation affects the endocervical glands, but squamous epithelium may also be involved in this process. At the initial stage, purulent discharge appears.
As the disease progresses, pain occurs, the temperature rises, and hot flashes occur.
Chronic
If the cervix is affected by different types of pathogenic bacteria, fungi, viruses, then the woman will begin a strong inflammatory process. The chronic form of the disease can be a consequence of poor hygiene and frequent changes of partners.
You can suspect a problem based on the characteristic symptoms:
- purulent and mucous discharge;
- painful sensations (dull);
- itching and burning during urination;
- bloody discharge appears after sexual intercourse;
- swelling of the mucous membranes.
Purulent
The disease is transmitted during sexual contact (causative agents - gonococci, trachoma). On the cervix, the subepithelial and cylindrical layers of the epithelium are affected. In parallel, patients are almost always diagnosed with urethritis.
Viral
Inflammation of the cervix begins after unprotected sexual intercourse. In patients, not only internal but also external tissues can be affected. You can suspect a problem based on the following symptoms:
- discharge (purulent, mucous);
- severe itching;
- painful sensations in the lower part of the peritoneum.
Causes of cervicitis
The main cause of cervicitis are diseases that are sexually transmitted . With the development of a certain sexually transmitted disease, thick mucus gradually liquefies, resulting in inflammation of the mucous membrane. After this, the infection begins to spread to the base of the cervix. Due to such changes, microbes gradually enter the uterus, appendages, and later spread to the bladder, kidneys and other organs. As a result, pathological phenomena develop in the woman’s pelvic cavity, including peritonitis .
If the main reason for the development of cervicitis in a woman is considered to be sexually transmitted diseases , then doctors also identify a number of factors that contribute to the development of this disease. The risk of developing cervicitis increases significantly if a woman has been infected with the herpes or human papillomavirus . Cervicitis can overtake a girl at a time when she is just beginning to have an active sexual life. Also, cervicitis of the cervix can manifest itself as a consequence of mechanical or chemical irritation (we are talking about contraceptives or hygiene products). In some cases, the inflammatory process occurs as a result of an allergic reaction of the body to latex or other components of contraceptives or personal hygiene products.
A factor that provokes the disease is also weakened immunity due to other somatic diseases. In addition, cervicitis can develop as a result of injuries caused during abortion or childbirth (in this case, it is important to qualitatively suture all ruptures of the perineum and cervix caused during the birth process), with prolapse of the genital organs in women. The disease also often affects women who have entered menopause.
All the reasons described above contribute to the active reproduction of microorganisms classified as opportunistic ( staphylococci , streptococci , enterococci , E. coli ). In a woman’s normal health, such microorganisms are present in the vaginal microflora.
Drugs for the treatment of cervicitis
Modern medicine knows many methods that can be used to treat cervicitis. First of all, provoking factors (hormonal imbalance, weak immunity) and necessarily associated pathologies are eliminated.
Treatment of the disease involves prescribing antibacterial and antiviral drugs to the sick woman, depending on the identified pathogen and the form of the disease. If the cause of cervicitis is chlamydia, taking antibacterial drugs belonging to the tetracycline group ( tetracycline, doxycycline ) is indicated.
Macrolide drugs ( erythromycin, josamycin ) and drugs from the quinoline group ( tarivid ) can be used. In case of candidiasis, systemic therapy with antifungal agents ( fluconazole, natamycin ) is mandatory.
When the main symptoms of the disease subside, women are prescribed local treatment: treatment of the vagina and cervix with a 1-2% solution of chlorophyllipt , a 3% solution of dimexide or a solution of silver nitrate .
Treatment of viral cervicitis
Treating cervicitis of a viral nature is problematic. Thus, for genital herpes, long-term course treatment with antiviral drugs ( acyclovir, Valtrex ), vitamin therapy, specific antiherpetic immunoglobulin, immunostimulating agents, and local use of ointments ( gossypol, megasin, bonafton ) are prescribed.
To eliminate papillomavirus lesions, interferons and cytostatics are prescribed, and, if necessary, condylomas are removed. If the inflammation is atrophic in nature, then female hormones are used to restore the vaginal and uterine epithelium, the balance of microflora and cervical tissue.
For cervicitis of viral etiology, in order to avoid re-infection, not only the woman, but also her sexual partner should undergo treatment according to the regimen. Even if a man shows no signs of illness, this does not mean that he is not infected. Chlamydia, gonorrhea and trichomoniasis in men can be asymptomatic.
In any case, the woman is prescribed local therapy. These can be candles, the type of which depends on the pathogen. For example, for fungal infections, micogal, clotrimazole, and dafnedzhin . If cervicitis is caused by bacteria, hexicon, pimafucin, and terzhinan .
By the way, the drugs terzhinan, neopentran forte - L, tantum rose not only have an anti-inflammatory effect, but also reduce pain.
Treatment of chronic cervicitis
If there is chronic inflammation (cervicitis, endocervicitis), which has caused depletion of the mucous membrane of the cervix, hormonal drugs are used in local form ( ovestin, estriol ).
Drug therapy for chronic cervicitis does not always give positive results, so they resort to surgical methods such as laser therapy, diathermocoagulation, and cryotherapy.
In parallel with this, the pathologies associated with the disease are treated (functional disorders, colpitis, ectropion, salpingoophoritis) and the normal microflora is restored.
In order for the doctor to monitor the entire treatment process, the woman is periodically prescribed colposcopy, smears are taken for laboratory examination, and the cervix is examined.
Symptoms of cervicitis
Most often, the symptoms of cervicitis in women practically do not appear, or only blurred signs of the disease appear. There may be periodic appearance of small vaginal discharge, which is predominantly mucous in nature. If a woman develops gonorrheal cervicitis , the discharge will become yellow; if the disease is accompanied by trichomoniasis , the discharge will be foamy. With thrush, vaginal discharge takes on a cheesy consistency. As a rule, discharge with cervicitis is more intense in the first days after your period ends.
Also, a patient with cervicitis experiences periodic discomfort in the lower abdomen. However, with concomitant diseases that are sexually transmitted, the sensations may be more intense. At the same time, depending on the disease, the pain can be either dull or severe, cutting. A woman suffering from cervicitis may experience discomfort or pain immediately after sexual intercourse. Sometimes after sexual intercourse a small amount of blood or pinkish discharge is released. Another symptom is the urge to urinate, which later turns out to be false. A woman may be bothered by itching and irritation of the genitals, and a burning sensation during urination.
However, all these symptoms do not appear in all cases of cervicitis. Therefore, it is understandable that cervicitis is detected in a patient by chance, during a routine examination or during research for other diseases.
If the infection spreads and affects other organs, the symptoms become pronounced: the patient has a fever, headaches, nausea, fainting and very severe abdominal pain. In this case, you should immediately seek help from a doctor.
The first signs of cervicitis
In acute cervicitis, signs of the disease are immediately noticeable. The woman develops copious mucopurulent discharge and pain in the lower abdomen. During a gynecological examination, swelling and hyperemia of the cervical canal, protrusion of the mucous membrane, and disruption of its structure (hemorrhage) are clearly visible. Discomfort and excessive discharge forces a woman to consult a doctor.
Chronic cervicitis occurs in an erased form and is often discovered by chance during a routine examination.
Diagnostics
It is initially possible to diagnose cervicitis during a gynecological examination of the cervix in a speculum. This examination demonstrates redness and swelling. During touching, bleeding is possible, and sometimes the gynecologist notes the presence of purulent discharge, erosions, and pinpoint hemorrhages. If it is not possible to accurately establish the diagnosis during the examination, a colcoscopy is performed. In which an image of the surface of the cervix, enlarged several times, is available. Such a study helps to detect the slightest defects in the mucous membrane.
In addition to the studies described, a patient with suspected cervicitis must undergo a study of discharge to identify the nature of the bacterial flora. A smear and culture are also taken to determine the type of pathogen and sensitivity to antibiotics. To exclude oncological pathology, an oncocytology smear is taken.
As additional studies, it is also practiced to conduct a general analysis of urine and blood, tests and studies to exclude a number of sexually transmitted diseases, and an HIV test. An ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs can determine whether complications occur.
Compliance with preventive measures
To avoid inflammation of the cervix, a number of preventive measures should be followed.
- mandatory personal hygiene.
- Douching should not be done unless there is compelling evidence for it.
- When having sex, barrier contraception methods should be used.
With regular visits to the gynecologist, most gynecological diseases can be successfully avoided. Whatever the causes of the disease, timely treatment of cervical inflammation produces excellent results. At the slightest sign of illness, it is advisable to visit a doctor who, if necessary, will perform an examination and prescribe adequate treatment.
Prevention of cervicitis
To prevent the manifestations of cervicitis, a woman must undergo regular examinations with a gynecologist, which makes it possible to identify cervicitis and other diseases at the earliest stages. It is important to prevent abortions and adhere to a monogamous type of relationship, having sex with only one permanent partner. To prevent contracting sexually transmitted diseases, a condom should be used if there is a possibility that your partner is the source of the infection.
It is equally important to ensure effective and timely treatment of sexually transmitted diseases , as well as other ailments of the genitourinary system. A woman should not allow the manifestation of prolapse of the genital organs, promptly seeking medical help in case of such symptoms. Particular attention should be paid to strengthening the immune system by periodically taking vitamins, practicing sports and hardening, which strengthens the body. The correct approach to personal hygiene is also an effective method of prevention. Doctors recommend that women not use hygiene products with fragrances, as they can contain components that irritate the mucous membrane.
During menopause, women are in some cases recommended to take medications containing hormones to prevent genitourinary diseases.
Treatment
When cervical inflammation is diagnosed, treatment should be comprehensive. First of all, it is necessary to eliminate the causative factor - microbial infection, and then restore the accompanying disorders in the immune, hormonal and metabolic spheres. Conservative methods are successfully used for this, but sometimes you have to resort to more radical methods.
Conservative
In most cases, cervicitis responds well to conservative correction. And the leading role in therapy is played by medications, which allow them to influence all aspects of the mechanism of disease development. Patients are prescribed the following groups of drugs:
- Antibiotics (macrolides, fluoroquinolones, penicillins, tetracyclines).
- Antifungals (fluconazole, nystatin).
- Antiviral (acyclovir, ganciclovir, interferon).
- Antiprotozoal (metronidazole).
Local forms of medicines are widely used - ointments, gels, vaginal suppositories. This allows you to get a local effect without unwanted side effects. This is especially true for women in a position where they try to use the safest drugs possible and in the minimum permissible concentration.
After acute inflammation subsides, antiseptics are used - Dimexide, chlorophyllipt, Miramistin - in the form of applications, irrigations, douchings. For atrophic cervicitis, local treatment includes the use of estrogens (Ovestin). In parallel, correction is carried out with other medications: immunomodulators, probiotics, vitamins. For viral condylomas, it is possible to use cytostatics.
Medicines are the basis of modern therapy for cervicitis. Your doctor will tell you which medications to use.
Operational
Sometimes conservative methods are not enough. This situation often occurs with chronic cervicitis. Therefore, the question of how to treat inflammation of the cervix in such cases will be answered by gynecologists involved in minimally invasive manipulations. For patients who do not have acute infections, the following interventions are indicated:
- Diathermocoagulation.
- Laser therapy.
- Cryosurgical methods.
They are minimally traumatic, therefore they allow you to avoid cicatricial changes in the cervix, and also make it possible to correct concomitant conditions (ectropion, erosion). After the operation, a fairly rapid restoration of the normal mucous membrane occurs.
To avoid the development of cervicitis, a woman should follow simple rules of personal and intimate hygiene, lead a healthy lifestyle, promptly treat other gynecological diseases, and rationally plan pregnancy. And if you still have to face a similar problem, then you need to consult a doctor as soon as possible. The specialist will tell you what the cause of the disease is, determine the symptoms and treatment necessary to eliminate the pathology. And a woman should only follow all the recommendations.
Complications of cervicitis
For a long time, the disease may not have a negative impact on the general condition of the woman. However, if cervicitis becomes chronic, then as the disease progresses, the integrity and differentiation of the epithelium of the cervical canal, as well as the vaginal part of the cervix, is disrupted. Against the background of such disorders, cervical erosion , eventually turning into dysplasia. If the inflammatory process in the cervical canal continues for a long time, then the properties of the cervical mucus change. The result of such pathological changes can be infertility . Endocervicitis can cause obstruction of the cervical canal. In the absence of adequate treatment, further spread of the infection is possible, which leads to adnexitis and endometritis . In addition, the spread of infection during cervicitis can cause pyelonephritis and peritonitis . If cervicitis is combined with an oncogenic human papillomavirus, the risk of developing cancer in the cervix increases significantly.
Women with chronic cervicitis often experience constant pain in the pelvic area. In addition, the disease can lead to ectopic pregnancy , miscarriages and other complications during pregnancy and childbirth.
Pregnancy and cervicitis
Inflammation, and especially the infectious process, negatively affects the course of pregnancy. From the cervical canal, the pathogen can enter the uterus and lead to infection of the fetus.
The presence of cervicitis increases the risk of premature birth or complications after childbirth for the mother.
Treatment of cervicitis during pregnancy must be carried out, but the choice of drugs is more limited. It is important for expectant mothers to kill pathogenic microbes, and anti-inflammatory treatment can be continued after childbirth.
In the early stages of pregnancy, inflammation of the cervix leads to placental insufficiency and negatively affects the development of the child. In some cases, this causes fetal death and miscarriage. All gynecologists advise you to take your pregnancy responsibly and plan ahead. This will give you the opportunity to undergo a full examination and eliminate existing problems before conception.
List of sources
- Podzolkova N.M. Human papillomavirus and herpetic infections in obstetrics and gynecology: educational manual / N.M. Podzolkova, L.G. Sozaeva, V.B. Osadchev. M., 2002;
- Sokolovsky E.V. and others // Sexually transmitted infections. - M.: Medpress-inform. - 2006;
- Krasnopolsky V.I. and others // Pathology of the vagina and cervix. - M.: Medicine. - 1997;
- Sverdlova E. S. Diseases of the cervix: diagnostic algorithms and treatment technologies. - Irkutsk, 2010;
- Kozlova V.I., Puchner A.F. Viral, chlamydial and mycoplasma diseases of the genitals. M.: Filin; 1997.
Features of the cervix leading to inflammation
Anatomically, the cervix is the lower part of the uterus protruding into the vagina. The cervix reliably separates the sterile cavity of the uterus and the vagina, populated by various microflora - conditionally pathogenic and pathogenic, penetrating from the outside. The cervix is folded. The external and internal pharynx are anatomical narrowings that protect against infection. The external pharynx is visible in the mirrors. This is where the cervix becomes inflamed. The cervical canal itself is closed by a protective mucous plug. Mucus is produced by special glandular cells lining it from the inside and performs a barrier function.
Pathogenic microorganisms most often enter from the vagina. Normally, 98% of all vaginal flora are lactobacilli. There are also conditionally pathogenic microflora. Lactobacilli create a special protective film that traps infectious agents. In addition, lactobacilli take part in the formation of lactic acid, which creates acidic contents in the vaginal cavity (pH 3.8 - 4.5). This is also one of the protective functions.
If for some reason a failure occurs in the protective mechanisms, infectious agents multiply and penetrate the cervix - inflammation develops.
Prognosis and prevention
To prevent the development of inflammation, you must follow the following recommendations:
- exclude sexual relations with strangers, and use barrier contraception to protect against infections;
- observe the rules of intimate hygiene and use specialized products or baby soap for this, avoid douching without medical prescription;
- It is mandatory to undergo preventive examinations with a gynecologist, at least 2 times a day and follow all his recommendations;
- promptly treat all diseases, especially inflammations and infections of a specific nature, and after treatment, be sure to restore the vaginal microflora and take rehabilitation measures;
- avoid hypothermia at any age and maintain immunity at the proper level, and for this, take vitamins and immunostimulants;
- avoid hormonal imbalances, use contraception in order not to resort to abortion, which contributes to hormonal imbalance and trauma. Hormone replacement therapy should not be ignored during menopause;
- When the vaginal walls prolapse, special exercises should be performed to compensate for this condition.
If preventive measures did not help, and the woman still fell ill, there is no need to be afraid of pathology. At the initial stages of the acute stage, it is easily treatable with antibacterial and auxiliary agents.
When the first symptoms appear, there is no need to delay a visit to the doctor, since inflammation can quickly become chronic. If it is asymptomatic, microorganisms can become resistant to the action of medications, then it is much more difficult to cope with them.
The consequences if left untreated can be quite serious, since inflammation can turn into erosion, and this is a predisposing factor for the development of oncology. In particular, patients who have been diagnosed with human papillomavirus types 16 and 18 should be wary of such an outcome. Without proper treatment against the background of reduced immunity, the inflammatory process can provoke the development of an ascending infection, especially when infected with specific pathogens. And this can ultimately cause infertility and the appearance of adhesions in the pelvic organs. To prevent this, you should regularly visit a gynecologist for preventive purposes.
Traditional medicines
How to treat cervical inflammation? Many women ask this question. Of course, traditional medicine offers some recipes.
- You can prepare the composition for internal use. To do this, mix one part each of yarrow grass, alder cones and eucalyptus leaves, two parts each of birch buds, tansy flowers, sage grass and juniper berries. Pour two tablespoons of the mixture into a glass of boiling water, boil for five minutes, then leave. You need to drink 70 ml 3-4 times a day. Therapy lasts 1-3 months.
- For douching, decoctions from plants such as chamomile, sage, calendula, and St. John's wort are suitable. These herbs have mild anti-inflammatory properties.
The use of any home remedies is possible only with the permission of the treating gynecologist.
Preventive actions
We have already considered all the questions about why cervical inflammation develops and what it is. Treatment of this pathology is a long process and sometimes fraught with difficulties. It's always easier to protect yourself by following simple guidelines.
- You should not refuse preventive examinations by a gynecologist. They need to be taken twice a year, even in the absence of any worrying symptoms.
- In the absence of a regular sexual partner, it is extremely important to use condoms, because only this will help protect against sexually transmitted infections.
- If an infectious disease still exists, then it is important to complete the course of therapy on time and to the end.
- If you are not planning a child, then it is important to choose suitable contraception.
- Preventive intake of vitamin complexes, proper nutrition, physical activity, stabbing the body - all this will help strengthen the immune system and reduce the risk of developing nonspecific inflammation.
- It is important to regularly do special exercises that strengthen the pelvic muscles - this will help prevent prolapse of the genital organs.
- During menopause, you should not refuse hormonal therapy. Of course, only the attending physician can draw up a diagram.
By following such simple rules, you can significantly reduce the risk of developing such an unpleasant and dangerous pathology as cervical inflammation.
Disease prevention and relapse prevention
To reduce the risk of developing inflammation, you need to visit a gynecologist every six months, get tested and follow a healthy lifestyle.
Inflammation can be prevented by following these rules:
- limit the number of sexual partners;
- regularly use condoms to prevent sexually transmitted diseases;
- stop using scented tampons, which may reduce the risk of an allergic reaction;
- Avoid getting an IUD unless you have more than two or three sexual partners and are aware of their sexual history.
If you notice one of the signs of inflammation (pain in the pelvic area, bleeding, vaginal discharge), do not delay taking tests and visiting a gynecologist.
Research shows that women who become sexually active later in life and who are involved in monogamous relationships are less likely to develop inflammation.
Inflammation of the mucous membrane of the cervix does not just go away. To achieve the desired results, it is necessary to undergo treatment for a long time. It is advisable to combine treatment with medications with folk remedies. With the help of complex therapy, improvement of symptoms can be achieved faster.
Chronic cervicitis – what is it?
An undetected disease that lasts for a long time and has not been treated is called chronic. The symptoms are smoothed out so much that it allows the woman to lead a normal life and not experience discomfort or pain. Promotes this condition:
- low immunity, when the body is not able to cope with the infection on its own because it does not have the necessary resources (poor nutrition, smoking, drinking alcohol);
- concomitant diseases (lack of sex hormones, thyroid dysfunction);
- constant change of sexual partners, which contributes to an increase in the number of sexually transmitted infections;
- allergic diseases that reduce the body's protective potential;
- viral diseases;
- mechanical damage to the cervix;
- the presence of gynecological diseases and inflammation of the pelvic organs.
With inadequate sexual life (lack of orgasm), chronic cervicitis may develop due to blood stagnation, even in the absence of pathogenic specific microflora.
Important! Without going to a medical facility, without taking measures to eliminate the disease, a woman exposes herself to the risk of malignant neoplasms that develop as a result of the constant presence of infection and pathological changes in tissue.
During pregnancy
Women planning a pregnancy need to cure all inflammatory processes, especially if it concerns the genital area, since inflammation of the cervical canal is dangerous not only for the expectant mother, but also for the fetus.
During pregnancy, hormonal levels change dramatically, which contributes to changes in the composition of the vaginal microflora and leads to the proliferation of conditionally pathogenic microorganisms. But most often, inflammation in pregnant women is caused by nonspecific infections. The pathology is dangerous for a pregnant woman, and this is why:
- in the early stages, inflammation can affect not only the cervix, but also spread to the deeper parts of the reproductive system, thereby infecting the chorion or the embryo itself;
- It happens that the infection breaks the protective barrier and provokes a sluggish inflammatory process, as a result of which the abnormal development of the placenta begins, leading subsequently to its failure. When the fetus becomes infected, it leads to abnormalities in its development;
- spontaneous abortion or frozen pregnancy, cervical insufficiency;
- in late gestation, placentitis or polyhydramnios may develop;
- if the disease is not treated for a long time, the fetus may have delays in growth and development, and the nervous and cardiovascular systems may also be affected; in some cases, children, not yet born, develop intrauterine pneumonia;
- prematurity and premature birth.
During pregnancy
Cervicitis is very dangerous for expectant mothers and their offspring, since the pathology has a destructive effect on the mucus plug, which protects the uterus from external infections.
The likelihood of developing pathology and its chronicity in pregnant women is much higher, since their body’s immunity in any case decreases during this period. This feature is provided by nature to prevent premature rejection of the fetus, but the other side of the coin is precisely the higher risk of developing various gynecological ailments. Cervicitis in pregnant women can provoke the development of the following complications:
- spontaneous abortion;
- premature birth.
For the fetus, this pathology is dangerous due to infection, which can lead to disturbances in development, deformities, death of the embryo and death of the newborn in the first days of his life. Cervicitis is most dangerous for the fetus in the first months of pregnancy, when its organs and systems are formed. In the early stages, this pathology quite often causes miscarriages. When the disease appears in the second half of gestation, the child may develop hydrocephalus, problems with the kidneys and other organs.
Since cervicitis can cause a large number of serious complications for the mother and child, in the process of planning pregnancy it is very important to first cure the pathology and strengthen your immunity.
Causes
Most often, the development of the disease is provoked by infections that have entered the body. With nonspecific cervicitis, a pathological proliferation of conditionally pathogenic microflora occurs: streptococci, staphylococci, mycoplasmas and other organisms. If a specific inflammatory process occurs on the cervix, its causative agents are sexually transmitted diseases. Every 4th patient with trichomoniasis or gonorrhea has signs of cervicitis.
There are a number of factors that provoke the occurrence of pathology:
- concomitant inflammatory diseases of the genitourinary system. Since the cervix, vagina and urethra are located close to each other, inflammation in them cannot develop in isolation. Usually, with inflammation of the cervix, at the same time the inflammatory process provokes colpitis, cystitis and other ailments in the vagina or urethra. Cervicitis is often found in patients suffering from endometritis or inflammation of the appendages;
- trauma to the cervix. These may be cracks or tears caused during childbirth, diagnostic curettage or abortion. Through damaged areas of the mucous membrane and canal of the cervix, the pathogenic flora quickly enters the deeper layers and inflames them;
- excessive douching with highly concentrated solutions of iodine, potassium permanganate, etc., which are used for medicinal purposes. Such procedures can burn the neck, to the wound surface of which inflammation will then join;
- pseudo-erosion or ectropion are frequent companions of cervicitis;
- drooping cervix and vagina. When the genitals are displaced, this provokes a disruption in the nutrition of their tissues, which provokes a decrease in local immunity;
- promiscuity in sexual relations leads not only to the development of sexually transmitted diseases, but also disrupts the normal composition of the vaginal microflora, which leads to the development of inflammation;
- use of contraceptives not according to instructions. The spermicides that they contain contain aggressive chemical components that mechanically injure the mucous membrane of the cervix;
- biotic imbalance of the vagina. Due to a change in the volume of lactic acid bacteria and due to a shift in the acidity of its environment, the amount of pathogenic microflora increases, which provokes the development of bacterial cervicitis;
- hormonal imbalance, causing dysfunction of the reproductive system. Since the normal state of the mucosa largely depends on the level of hormones, changes in hormonal levels can contribute to the development of pathological changes at the local level in the tissues of the vagina and cervix. Atrophic inflammation of the cervix in old age provokes a drop in estrogen levels, as a result of which the mucous membrane becomes thinner, is more quickly susceptible to trauma and pathogenic microflora enters microcracks;
- extragenital ailment, which is a consequence of diabetes mellitus, hormonal and endocrine pathologies.
One of the fundamental factors in the development of the disease is immunity. In a woman with high protective functions of the body, it copes with unwanted changes on its own and responds well to treatment. If a representative of the fair sex with a weakened immune system encounters provoking factors, in most cases she cannot avoid inflammation.
Only by establishing the exact causes of the disease can adequate and effective treatment be prescribed.
How to treat at home
In no case should you self-medicate, but with the permission of a doctor, in addition to the main therapy, you can use folk remedies for inflammation, the components for which can be bought at a pharmacy or prepared at home.
A few simple recipes:
- chamomile decoction. The plant has anti-inflammatory properties. To prepare the decoction, you need to pour boiling water over dried chamomile flowers, leave for about an hour until warm, and then moisten a tampon in the decoction and place it in the vagina overnight. If the tampon is installed for a few minutes, but the procedure must be done three times a day;
- sage decoction. Relieves inflammation and is suitable for allergy sufferers. The sage herb should be steamed with boiling water or boiled in a water bath for about 10 minutes. The prepared broth should cool, then it should be diluted with boiled water in a ratio of 1:1 and douched with it three times a day;
- Using the same methods, you can prepare and use a decoction of calendula, that is, moisten a tampon in it and place it in the vagina or douche with it;
- Oak bark has high anti-inflammatory properties. You need to douche with a warm solution from its decoction for 7-10 days. A single dose is 5 ml.
There are many other recipes, but it should be remembered that any treatment with folk remedies must be agreed upon with the attending physician.
Differences between exocervicitis and endocervicitis
Cervical exocervicitis, as mentioned earlier, is an inflammation of the vaginal segment of the cervix. It is characterized by the following signs:
- Ulceration of the mucous membrane.
- Visually noticeable hyperemia of the external pharynx of the cervical canal.
- Detection of microabscesses.
- Swelling of the mucous lining.
- Copious discharge.
- Leukocyte infiltration of the cervix in the form of multiple periglandular infiltrates.
Endocervicitis of the cervix is manifested by symptoms of inflammation of the cervical canal. More often it develops as a result of invasive procedures and diseases of nearby organs of the reproductive system. The pathology is characterized by rapid progression and a high probability of chronicity and a blurred clinical picture. There is not as much discharge as with exocervicitis, and the intensity of the pain syndrome can vary.
What is endometrial hyperplasia during menopause and how to treat it
During the examination, the gynecologist may note swelling of the mucous membrane of the cervical canal, its hyperemia, a large number of small ulcers, and pathological discharge in the cervix. Cervical endocervicitis is dangerous due to its complications. Often, an erased clinic plays a negative role: despite apparent well-being, the disease spreads and manifests itself in a more severe form.
Diagnosis of cervix inflammation
Many women do not suspect that a disease such as cervicitis can be practically asymptomatic. Pathology is often diagnosed during a preventive medical examination or when visiting a gynecologist for other reasons. The diagnosis can be made by a doctor after examining the cervical canal in speculums, colposcopy and analyzing some laboratory tests.
Studying smears under a microscope is an important diagnostic method.
Colposcopy is necessary to detail pathological changes in the tissues of the cervix (proliferation of the glandular epithelium of the cervix), to identify hyperemia and swelling, erosion, ectopia, and to specify the extent of the process - focal or diffuse.
The following laboratory diagnostic techniques are used:
- smear microscopy;
- culture of bacterial flora and its sensitivity to antibiotic substances;
- polymerase chain reaction to identify a specific pathogen;
- enzyme immunoassay to determine the infectious agent and antibodies to it in the blood;
- a general blood test to determine the severity of the inflammatory reaction.
In acute pathology, a smear reveals a large number of leukocytes, intensive proliferation of the columnar epithelium of the cervix (the cells have a hypertrophied nucleus), and dystrophic changes in the squamous epithelium. The chronic form is also characterized by proliferation of the columnar epithelium of the cervix, but there are signs of cytolysis. Bacteriological diagnostics, PCR, ELISA are important for identifying a specific pathogen and selecting methods for therapeutic correction of the condition.
Treatment and diagnosis of parakeratosis
Treatment of chronic cervicitis
The treatment regimen for chronic cervicitis depends on the type of infection, the age of the patient, the state of the immune system, and the presence of concomitant diseases.
In case of viral infection, treatment costs are disproportionately higher, since the use of stimulants, immunoglobulins, and vitamins is necessary. In addition, it is necessary to strictly monitor the quality and diet.
The woman's age also plays a role. During menopause, additional hormonal therapy and calcium supplements may be required to balance the body's condition. Treatment of cervicitis during pregnancy is complicated by the fact that many drugs are contraindicated and it is necessary to use homeopathic suppositories or tablets with bactericidal properties.
To boost your immunity, you can drink plant-based dietary supplements. As an option, Entocid is a dietary supplement that tidies up the intestines.
Important! The main part of immune cells is located in the human intestine, so the normalization of its work affects the general condition of the body.
All types of chronic and acute cervicitis can be treated with broad-spectrum antibiotics, for example, Azimed (active ingredient azithromycin). In addition, anti-inflammatory medications are prescribed, which can be replaced with decoctions of herbs that have similar properties: St. John's wort, sage, yarrow, oregano, echinacea.
Women during menopause can be advised to use herbal decoctions that normalize hormonal levels, thereby promoting recovery: boron uterus, red brush, flaxseed, sage, hop cones, licorice root, sesame seed. It is recommended to include apricots in the diet, which are rich in substances similar in action to estrogen. Dried fruits have the same qualities as fresh ones.
Recently, the drug for treating animals, ASD fraction 2, has become widespread. This drug, according to reviews, has a powerful healing effect, even in advanced forms of cancer. The downside of ASD is that its smell is extremely unpleasant and most people simply refuse to use it for treatment; moreover, the “aroma” does not dissipate from the room for a long time, which creates problems for others.
Methods for treating inflammation
There is no standard therapy for cervicitis. Each time the treatment regimen changes. It depends on the cause of the inflammation, the patient's general health, medical history, severity of symptoms, and degree of inflammation.
During the treatment period, the patient is prohibited from having sexual intercourse until drug treatment is completed. Typically, recovery requires from 7 days to 2 months of treatment.
Surgical treatments are resorted to when an accumulation of pus forms. Depending on certain conditions, the operation can be performed using laparoscopy or laparotomy.
If abscesses have formed on the uterus itself or on the ovaries, the doctor may recommend a hysterectomy (removal of the uterus) or oophorectomy (removal of the ovaries).
In addition, if conservative treatment methods are unsuccessful, cryosurgery, electrocautery, and laser therapy are recommended.
Drugs for the treatment of inflammation
Timely and correct treatment of inflammatory diseases of the cervix prevents the development of serious complications. General drug treatment includes the use of antibiotics, painkillers and antifungals, vaginal suppositories, antiviral agents, antiviral drugs.
If a bacterial or viral infection causes serious complications, the administration of intravenous antimicrobial agents is necessary. Antibiotics may be inserted directly into the vagina.
The following drugs are also used in the treatment of cervicitis:
- Antifungal agents - Diflucan, Mycoflucan;
- Medicines that restore microflora - Acylact, Gynoflor, Bifidumbacterin;
- Immunocorrective agents - Immunal, Immunomax.
Viral inflammation is treated with antiviral drugs such as Acyclovir and its analogues.
As a rule, the duration of the course of therapy is 5 days. Chronic inflammation is treated with hormonal suppositories, ointments and creams.
The most common medicine is Ovestin. Positive reviews about it indicate the high effectiveness and safety of the product.
Vaginal suppositories
The advantage of candles is that they quickly begin to act. Within half an hour after administration of the suppository, the drug is completely absorbed into the blood and begins its anti-inflammatory effect. Types of candles:
- anti-inflammatory;
- painkillers;
- antifungal;
- immunostimulating.
The advantages of suppositories include ease of use, no negative effect on the liver and gastrointestinal tract, and a low likelihood of allergic reactions.
For inflammation, Ketoconazole, Livarol, Pimafucin, Terzhinan, Polygynax, Betin and others are prescribed.
Antibacterial therapy
To treat inflammation, you must take antibiotics (intravenously or orally).
Therapy should be prescribed immediately. If the patient is on intravenous antibiotics, then after clinical improvement it is necessary to transfer him to oral administration of drugs.
The following antibacterial medications are prescribed for inflammation:
- Cefoxitin;
- Cefotetan;
- Doxycycline;
- Clindamycin;
- Ampicillin-sulbactam;
- Gentamicin;
- Ceftriaxorn;
- Azithromycin;
- Cefixime.
After 72 hours, it is necessary to reconsider the symptoms of inflammation, retake tests and prescribe other medications. Treatment with antibiotics is carried out on an outpatient or inpatient basis.