A herniated disc can occur for various reasons. This disease brings a lot of discomfort to a person: he stops living life to the fullest, because everything is overshadowed by pain that is increasing every day, which literally shackles him.
Spinal hernia symptoms in women
A hernia can occur with equal frequency in both men and women. The structure of the spine in both sexes is similar in almost everything - women have slight differences due to the fact that their body is prepared for bearing a child and the process of childbirth. But often girls ask the question: what are the symptoms of a spinal hernia in women? In this article we will try to figure this out and find out how to recognize the disease, what to do if it occurs, and what to do to avoid its occurrence in the first place.
general description
With a hernia of the lumbar spine, a person experiences pain only in the lower zone of the spinal column. This is a distinctive feature of the disease. Along with pain, stiffness and even paralysis may appear.
A rupture of the spine as a result of heavy load can lead to the appearance of a lumbar hernia. When damaged, the nucleus pulposus protrudes, resembling a jelly in consistency. The deformed part compresses the nerve root, thereby causing sudden discomfort. As a result, it becomes difficult for the patient to get up. Painful symptoms can become too painful. If severe pain occurs in the lumbar region, it is recommended to immediately contact a medical center to determine the cause of its occurrence.
First aid for intervertebral hernia
The formation of intervertebral hernias occurs very quickly, and the person feels severe pain. At the moment when a hernia forms, the patient feels a crunch or click in the back, and after this severe pain immediately appears.
The pain is especially intense in the first few days after the formation of a hernia. Thus, a person can spend a sleepless night suffering from severe pain. Around the fourth day, the pain becomes slightly less pronounced. A herniated disc during the acute period of the disease should be treated in a hospital. If you have such symptoms, before contacting a doctor, it is necessary to provide assistance to the person suffering from pain. The patient must be placed on a hard, flat surface. He can be fitted with a corset to secure his lower back. Such a corset or belt can be made from a piece of fabric or sheet. You can also apply heat to the place where the pain is localized - mustard plasters, a heating pad.
Symptoms of a lumbar hernia
The main symptoms of a lumbar disc herniation include pain. But it can vary in place of occurrence and degree of intensity. These factors depend on the direction in which the bulging of the nucleus pulposus occurred. Such convexities can be posterior or lateral. The appearance of a number of symptoms depends on the size of the intervertebral hernia:
- difficult (stiff) back movements in the lumbar region;
- sharp pain in the lower body;
- the possibility of only limited movements (problems with bending and turning the body, as well as raising the legs);
- numbness and tingling sensations in the buttocks and lower extremities;
- involuntary bending of the legs;
- weakness in the legs;
- increased sensitivity of the skin in the area of deformation, even burning;
- painful attacks and dizziness;
- disruptions in the functionality of the bladder and intestines;
- muscle atrophy in the legs.
Causes of hernia in the spine
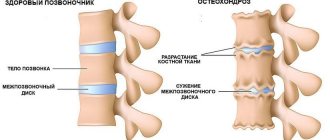
The spinal column is divided into 5 parts: cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral and coccygeal sections. A hernia can occur in any region, but most often it occurs in the cervical and lumbosacral regions, less often in the thoracic region.
There are a total of 5 sections in the spine, in each of which an intervertebral hernia can occur.
There are several reasons for a hernia:
- Excessive physical activity . If a person regularly strains his back very much, then the appearance of a hernia is almost inevitable. This situation can arise during intense sports activities or when regularly carrying heavy objects (for example, when working as a loader). Under such loads, fabric fibers can begin to wear out, and therefore their integrity is destroyed.
- Lack of physical activity . If a person does not exercise at all, then a hernia in his spine can also occur. Bone tissue cannot feed itself, and its enrichment occurs through the process of diffusion - exchange. The tissue “exchanges” nutrients with the intervertebral discs and blood. If a person moves enough, then this process proceeds normally, otherwise “starvation” of tissue occurs, leading to degenerative processes.
- Age. With age, all processes in the body slow down, and tissues become weaker and more susceptible to destruction. In addition, people in adulthood do not exercise too often, and their body suffers from a lack of nutrients. Therefore, the majority of registered cases occur in people aged 45+.
- Bad habits . If a person regularly abuses cigarettes and alcohol, the fruits of this can affect their health in the near future. And this affects the entire body - in a smoking person, blood circulation is slowed down, a lack of oxygen is created, and the spinal column does not receive vital substances.
People who do not strive to get rid of bad habits are more susceptible to various diseases, and spinal hernia is no exception.
- Sedentary work . A load of 150-200 kg (depending on body weight) is placed on the spine of a person in a sitting position. Although the structure of the spine is quite strong, it requires regular changes in the load distribution, that is, warm-up.
- Excess weight . This creates a very large load on the spinal column, which cannot constantly withstand it. This leads to injuries, scoliosis, osteochondrosis and the hernia itself.
In women during pregnancy, a hernia may be more likely to occur because her body is weakened
Prices for back belts
Having dealt with the reasons, we can move on to the symptoms of spinal hernia in women.
Painful symptoms
The main symptom of a lumbar hernia is pain. It accompanies the disease at all stages. The sensations may vary in location and strength. They occur independently or are combined with other signs of a hernia of the lumbar spine.
At the initial stage of development of the syndrome, a person suffers from mild pain in the back arising from a damaged intervertebral disc. In some cases, pain may not appear immediately at the onset of deformity. Along with it, the patient may experience weakness in the legs, numbness and mild but unpleasant tingling sensations.
At the first stage of the occurrence of a lumbar hernia, rapid treatment of the disease is possible. But with further development of the syndrome, the symptoms will increase. In subsequent stages, attacks can be aching, sudden and sharp. They occur even during coughing or sneezing. The patient may develop radicular syndrome.
As a result of damage to the intervertebral disc, its cartilage ring begins to deform. But this process is quite long. It is caused by a malnutrition of the disk and a decrease in its wear resistance. The first symptom of the pathology is severe and sudden pain that hinders movement. As a result, a person cannot even get up on his own.
Treatment methods
After a detailed examination, the patient is prescribed complex therapy, which completely depends on the type of vertebral hernia and the degree of neglect of the disease. If the problem was identified at an early stage, patients are recommended conservative treatment, including:
- Taking medications. First of all, these are painkillers designed to improve the patient’s condition, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (provided there are no chronic gastrointestinal diseases), muscle relaxants to relieve muscle spasms and chondroprotectors that promote the restoration of cartilage tissue. Medications to stimulate blood circulation in the problem area, multivitamin complexes and drugs that protect the gastric mucosa may also be prescribed. In cases where conventional painkillers are not enough to relieve an attack, X-ray-controlled blockade can be used - injection of glucocorticoids, local anesthetics and vitamin B12 directly into the lesion. The procedure is carried out under local anesthesia and X-ray control, and is much more effective than intramuscular injections in restoring blood circulation, removing swelling and relieving pain.
- Therapeutic gymnastics. Daily performance of special exercises is extremely important both to combat the disease in its early stages and during rehabilitation after surgical removal of a spinal hernia. An exercise plan is developed by the attending physician individually for each patient, and when performing exercises independently at home, it is extremely important to strictly adhere to it and be careful, avoiding excessive stress, sudden movements and heavy lifting. At the first signs of a spinal hernia, yoga classes have a good effect, but in this case it is recommended to perform the exercises not on the bed, but on a hard surface.
- Physiotherapy. It includes manual therapy to release pinched nerve endings by moving and stretching the vertebrae, massage, reflexology, UHF, electrophoresis and phonophoresis.
In addition, hirudotherapy (the use of leeches to stimulate blood flow and resorption of the prolapsed fragment under the influence of active substances contained in their saliva), cryotherapy (improving blood circulation in the problem area under the influence of liquid nitrogen) and acupuncture (irritation nerve endings by influencing active points).
If the diagnosis of a spinal hernia was made in the later stages of the disease, and traditional treatment methods did not bring the desired effect, the patient may be recommended to undergo surgery. The main indications for surgical removal of a hernia are severe pain that cannot be treated with conventional medications, complications in the form of neurological disorders, as well as urinary incontinence and impotence in men.
There are several options for surgical removal of a vertebral hernia:
- Discectomy. The nucleus pulposus, which has left the annulus fibrosus, is removed through a small incision. In especially severe cases, the entire disc must be removed, and a titanium implant takes its place. But such a procedure is performed quite rarely due to the high risk of infection and the difficult recovery period.
- Endoscopic surgery. A minimally invasive method of removing a spinal hernia, which involves inserting a camera and instrument through a small puncture and practically does not lead to muscle damage.
- Laser surgery. It is used in patients under 40 years of age and only if the spinal disc has not been destroyed. It involves inserting a needle with a light guide through a puncture and “evaporating” the damaged areas using a laser.
However, it should be understood that surgery to remove a herniated disc is an extreme measure that doctors try not to resort to as long as the patient’s health is relatively safe.
Radicular syndrome
When a posterolateral or posterior hernia of the lumbar spine forms, compression of the spinal cord nerves occurs. In this case, the person suffers from acute pain. Its cause is irritation of the nerve roots as a result of their exit from the spinal canal.
Due to irritation, the damaged roots begin to become inflamed, and discomfort spreads throughout the nerve. This leads to the fact that a person begins to hurt not only the lower back, but also the part of the body for which the damaged nerve is responsible.
Also, a hernia of the lumbar spine can affect internal organs. The most common such complications include problems with urination (incontinence or frequent urges), bowel movements (diarrhea or constipation), potency in men and gynecology in women.
Symptoms in the cervical region
The pathology, located in the neck area, reveals itself even in the early stages. Due to the large accumulation of nerve bundles in this place, it manifests itself in the form of severe pain, stiffness of the shoulder area or sudden numbness. Most often, a vertebral hernia is localized between the 6th and 7th segments. Its size is much smaller than in other areas, but its location is closer to the spinal nerve, which makes it more dangerous.
The main signs of pathology in this department are:
- piercing pain from shoulders to hands;
- weakness of the neck muscle corset;
- numbness and tingling in the fingers when trying to squeeze your hands;
- headaches and migraines;
- pain in the hand, which appears as a result of pinching of the cervical nerve;
- loss of orientation;
- dark spots or spots before the eyes;
- tinnitus or sudden increase in blood pressure.
Symptoms have their own variations, so the occurrence of problems in each individual case is considered in conjunction with the individual characteristics inherent in the body. The intensity and degree of pain depends on the cause of the bulging disc. In cases of trauma, the signs are pronounced and do not go unnoticed. If a hernia is suspected, the doctor must prescribe comprehensive treatment.
As the hernia increases in size, it puts pressure on the spinal nerve, which is what causes acute pain.
Sciatica
Often, with a herniated spine, prolapse occurs in the lumbar and sacral regions. As a result, the sciatic nerve, which is considered one of the largest, is pinched. It is he who supplies the lower limbs with nerve fibers. This pathology is called “sciatica”.
When a sciatica hernia occurs, the patient experiences severe pain in the leg. These unpleasant sensations spread to the entire limb, since the branches of the sciatic nerve run along the entire length. They have a pulling and sharp nature of pain, sometimes reminiscent of electric shocks. The intensity depends on the severity of the compression of the nerve at the site of its protrusion. If a nerve is severely or completely compressed, the patient may develop the following complications:
- paralysis of the lower legs;
- loss of plantar and Achilles response;
- severe numbness of the skin;
- severe weakness in the knees when bending;
- autonomic dysfunction.
Diagnosis of intervertebral hernia
To establish a diagnosis, doctors initially use the simplest methods: they use special tests to identify symptoms of the disease, and check tendon reflexes . Such a test allows you to determine how damaged the spinal column is. However, without the use of hardware diagnostics, it is quite difficult to determine the presence of an intervertebral hernia in a patient.
The most widely used method for diagnosing this spinal pathology is MRI ( magnetic resonance imaging ). Computed tomography is also used to obtain transverse images of the spinal canal. The radiography method in this case is designed to exclude the presence of fractures, tumors or infectious diseases. Based on the examination results, the doctor prescribes the optimal therapy.
The most thorough examination should be carried out by those patients who complain of back pain that appears under the following circumstances and meet the following characteristics:
- the person has recently had a noticeable back injury;
- the patient has a constantly elevated body temperature;
- the occurrence of pain is not associated with movement;
- painful sensations resemble electric shocks;
- pain that appears in the back radiates to the legs, stomach, and genitals;
- back pain sharply manifests itself after eating, during sexual intercourse, while the patient is in the toilet;
- if you have constant back pain, problems with the menstrual cycle appear;
- in a lying position the pain is more intense, when walking it subsides a little;
- the pain is of an increasing nature, every day it intensifies;
- the patient feels weakness in the legs, and when walking this feeling becomes more pronounced.
Schmorl's hernia
One type of spinal column deformity is called Schmorl's hernia. This pathology is not always accompanied by painful attacks, since it is characterized by protrusion of the nucleus pulposus into the vertebral body. Severe pain can only occur if the height of the affected disc is significantly reduced. Such prolapse appears after physical exertion, with injuries to the body after a serious fall or against the background of osteoporosis.
With Schmorl's hernia, standard pathological symptoms are rarely observed. Most people only find out they have a hernia through x-rays taken because of other health problems. Until this moment, it may not manifest itself in any way and may not affect a person’s life and ability to work.
Causes
To understand what causes contribute to the development of intervertebral disc herniation, you need to know the anatomical features of the structure. Intervertebral discs do not have blood vessels, so they receive oxygen diffusely from the spinal muscles. For this reason, cartilage tissue, which is in the same ligament with the capillary network, begins to collapse in the absence of nutrition. Fasting in this case is caused by prolonged exposure to an uncomfortable position or lack of physical activity.
Cell regeneration in any part of the musculoskeletal system occurs slowly, so the disease can progress for years.
According to statistics, the development of the disease begins no earlier than a person reaches twenty years of age. This is due to the fact that children and adolescents lead an active lifestyle, preventing oxygen diffusion from being disrupted. During adolescence, there is still a nutrient reserve in the cartilage tissues, which is depleted along with changes in the carrier’s lifestyle.
Based on the above, we can conclude that the factors due to which a vertebral hernia develops are:
- Venous stagnation caused by a sedentary lifestyle;
- Lack of the necessary vitamin and mineral complex in the body;
- Poor choice of mattress and pillow: on a hard mattress, the spine, instead of relaxing, is tense all night;
- Genetic predisposition;
- Severe spinal injuries;
- Frequent drinking and smoking.
You may also be interested in: symptoms and treatment of thoracic disc herniation.
Hernia development in men
Males more often suffer from lumbar disc herniation. The symptoms of the pathology are more pronounced in them than in women. If treatment is not started on time, then pain shock is accompanied by a number of other unpleasant consequences:
- limited body movements;
- dysfunction of the hip joints;
- deterioration of posture due to weakened back muscles;
- frequent urination due to inflammation of the nerves.
Also, with a similar syndrome, problems with potency may develop. The age of the patient does not matter at all, since both young men and pensioners are equally susceptible to the disease.
Manifestations of thoracic lesions
The appearance of pathology in the central part of the spine becomes noticeable, even in the early stages. The main reasons for the formation of a hernia in this area in men and women are infectious processes. The symptoms are similar to those of trauma or oncology, so there may be an erroneous preliminary diagnosis. Patients with intervertebral hernia often consult a doctor with the following complaints:
- feeling of weakness and numbness in the back in general;
- periodic dull pain in the chest, aggravated by stress on the spine, coughing or prolonged stay in one position;
- partial loss of back mobility, it is difficult for the patient to bend over, lift bags, and keep the spine straight;
- problems with the intestines and excretory system (constipation, poor or painful urination, diarrhea);
- compression in the chest area, heart pain;
- severe weakness of the muscular corset of the back.
As pressure increases in the spine, spinal dysfunction gradually develops, which leads to paralysis of the legs. Constant pain in the thoracic region is felt by people who work all day at the computer in an uncomfortable position, as well as by seamstresses, surgeons, welders and others. Often the problem is not an independent disease in this area, but is also accompanied by kyphosis and scoliosis.
Signs of a thoracic intervertebral hernia cannot be ignored, as it quickly develops on its own. If you do not see a doctor in time, it can cause paralysis of the lower limbs. Treatment is selected depending on the prerequisites for the appearance, as well as the location of localization.
Methods for detecting the presence of a herniated disc
To identify the disease and determine its type, you should contact a specialist. The first signs of a hernia of the lumbar spine are pain in the back during an uncomfortable body position or after exertion. During the examination, the neurologist must take into account the presence of these symptoms and their intensity.
Pain with this pathology varies in intensity. Along with it, numbness, muscle weakness and the “goose bumps” effect may appear. As the bulge grows, it begins to compress the spinal canal, which can ultimately lead to consequences such as paralysis of the lower extremities.
To diagnose a hernia, the doctor performs an external examination. Since the nucleus pulposus protrudes in a specific area of the spinal column, a curvature will be visible in this place. In addition, the patient has a curvature of posture, stooping and hunching. External signs of a hernia and decreased sensitivity will help make a presumptive diagnosis, but additional examination is required to clarify it.
Prevention of intervertebral hernia
In this case, all preventive measures that are used to prevent osteochondrosis . Thus, it is important to pay special attention to the condition of the muscle corset, which is responsible for the functioning of the spine.
The load on the intervertebral discs increases significantly during the process of flexion and extension of the spinal column, that is, when bending. Therefore, when bending, you need to tighten your stomach, tighten your buttock muscles and round your back. It is important to form the correct gait: your back should be straight when walking, your neck should not be pulled forward. Your back should be kept straight and in a sitting position, with your feet touching the floor. When sitting, it is optimal to place your legs on a special stand, so that your hips are below your knees.
Proper sleep is important : the bed should be flat and moderately hard. The best option is a high-quality orthopedic mattress.
It is important to prevent the appearance of excess weight , which is a strong additional load on the spine. A healthy diet not only guarantees protection against obesity, but also contributes to the proper functioning of metabolic processes in the spine. The diet should contain a lot of protein, as well as a sufficient amount of calcium, which strengthens bones. Potassium ensures optimal water-salt metabolism, vitamin C helps strengthen tendons and ligaments.
Considering the structure of the central nucleus, which consists only of protein substances, the presence of a sufficient amount of amino acids in the body is very important. Moisture quickly accumulates and is lost in the protein substance, so protein synthesis will be provided by amino acids contained in food of animal origin.
Preservatives have a negative effect on the condition of the spine. Spicy foods, salt, sugar, and smoked foods also have a detrimental effect on the skeletal system.
As a preventive measure, quitting smoking is important, because nicotine constricts blood vessels, and the intervertebral discs do not have adequate nutrition.
The most useful sport for the prevention of intervertebral hernia is swimming; yoga and Pilates are also suitable.
Diagnostic symptoms
The main sign is the center of the pain. When the sciatic nerve is pinched, the most painful sensations are observed in the buttocks. In this case, the pain travels along the back of the thigh, lower leg and foot. It can be easily determined by palpation along the path of the nerve fiber.
Also, when the sciatic nerve is pinched, other symptoms occur:
- Painful sensations when the nerve is stretched.
- Bekhterev's symptom, i.e. severe pain in the leg and lower back with simultaneous bending of the leg at the hip and extension at the knee.
- Neri's symptom, i.e. shooting pain in the leg and lower back when pressing the chin to the chest from a lying position.
- Dejerine's symptom, i.e. painful sensations in the sacral area and in the direction of the nerve fiber during attacks of coughing or sneezing.
With large or prolonged nuclear protrusion, the patient may develop neural atrophy or degeneration of the tissues controlled by these fibers. Subsequent diagnostic symptoms are considered to be vegetative disorders:
- dry skin;
- change in color of skin and nails;
- thickening of the epidermis layer on the feet;
- swelling of the legs;
- decreased or increased sensitivity in the legs.
To select the correct treatment, it is necessary to make the correct diagnosis, since the first signs of lumbar intervertebral hernia are similar to a number of other pathologies. To exclude other diseases, the doctor must prescribe the following diagnostic procedures to the patient:
- ECG;
- MRI;
- ultrasonography;
- X-ray;
- urine and blood analysis.
Symptoms of spinal hernia in women
A hernia in the spine is a disease that can equally occur in both women and men. The symptoms are the same for both sexes, with the exception of only some points related to the location of the hernia. First, let's talk about common symptoms.
- Backache . It can occur in any part of the spine, depending on the location of the hernia. If it is in the neck, then pain will arise in it, in the shoulders, in the upper limbs and collarbones. A hernia in the neck can also cause headaches. A hernia that occurs in the chest will be characterized by pain in and between the shoulder blades, in the chest (may resemble pain in the heart or lungs), as well as in the upper extremities. Pain can be felt both in the back and in the front - in the chest. If the hernia is in the lower back or sacrum, then the pain is localized in the waist, pelvis and lower limb. This symptom can be confused with pain due to diseases of the internal organs, mainly with pain in the kidneys. Pain in the intestines may occur.
- Stiffness. It accompanies pain and occurs in the part where the hernia is localized. Turning and bending cause severe pain, which is difficult to suppress with analgesic drugs. A person has to be fixed in one position, which is fraught with the emergence of new diseases, for example, scoliosis.
- Feeling of "pins and needles". It is most often found in the upper extremities, fingers and hands, and also in the lower extremities - in the buttock, thigh, knee and foot.
- Numbness . It occurs due to strong pressure on the nerve endings. At first, this feeling can be very weak and almost unnoticeable, but over time, in the absence of treatment, it intensifies.
Often, with a hernia, numbness occurs - a clear symptom of this disease and a sign that it is already “advanced”
- Noise in ears . This symptom may appear with a hernia in the cervical spine. The patient develops a headache, thinking and reaction often become sluggish, and dizziness and noise may occur. This occurs due to disruption of nutrient supply and normal blood circulation.
- Decreased performance . A woman begins to experience too much fatigue more and more often, even after a long rest. Concentration levels decrease. She is tormented by incessant pain, which constantly distracts her. This symptom can occur with a hernia in any part.
If a woman’s spine is affected by a hernia, then one of its symptoms is fatigue and an almost complete lack of concentration
- Pain in the pelvic organs. Most often, such pain occurs with a hernia in the lumbosacral region, as well as in the coccyx. The patient may experience pain in the lower abdomen - they are similar to pain during menstruation. In this case, urination is usually difficult, and pain in the genitals may occur.
Hernia during pregnancy
Distinctive symptoms in women most often occur with a hernia in the coccyx. If for men it does not perform many functions, then for women it is vital, especially when carrying a child and the birth process.
You can read more about pain in the coccyx in women in this article. In it we talk about what can cause pain, as well as how you can get rid of it.
The tailbone is necessary for women because it helps to bear the baby, and during the birth process it seems to move, opening up a larger area for the baby to be born. Although the coccyx is a solid dense bone, it can still be damaged, which is very dangerous for a woman.
Often the occurrence of a hernia in the lower back occurs during pregnancy. The weight of the fetus in the uterus is quite large, especially in the last weeks of pregnancy. Although the spine is a strong enough system to withstand heavy loads, it can still suffer from very high pressure.
A pregnant woman should be especially careful about the health of her spine
At this time, a woman needs to be doubly careful, because any improper movement of the tissues in the spine can destroy. During pregnancy, the amount of nutrients in the female body decreases as it “shares” them with a new person. The first “blow” falls on the amount of calcium in the body, the lack of which leads to injuries to the spine and other bones. Therefore, a woman will have to constantly monitor her diet and make sure that it is saturated with necessary substances.
Bandages for pregnant women
The truth about treatment: analysis of the effectiveness of all tactics
Of course, it will not be possible to get rid of the disease through special gymnastic exercises for the neck. Exercise, even the best, is not able to “retract” the fallen pulpous element back or destroy it without a trace, or “patch” the gap in the fibrous ring. This can only be accomplished during surgical treatment.
However, exercise therapy has been proven to improve well-being and, importantly, prevent the development of atrophy of the muscles of the cervical and cervicothoracic complex and upper extremities. Let us immediately emphasize that the productivity of LH action is significantly reduced in the penultimate and final stages of the hernia. Still, unique physical training makes the greatest contribution to the restoration of musculoskeletal potential after surgical repair of a hernia. In general, the effect of physical therapy both during conservative therapy and at the time of postoperative rehabilitation is due to:
- stimulation of blood circulation;
- activation of metabolic processes;
- increasing the production of nutrients necessary to maintain the functions of the spinal structure;
- strengthening and increasing endurance of the neck muscles;
- correct, gentle development of motor and support functions of the neck;
- increasing the distance between the vertebrae, which helps prevent or reduce radicular/vascular compression.
But in order to really benefit from gymnastics, you need to get a training program from a specialist that is specially designed just for you, taking into account all the characteristics of the clinical picture on MRI. Plus, indicators of age and body weight, level of physical fitness, and associated health problems are taken into account.
It is advisable to take the first course in a physical therapy room under the supervision of a professional instructor in order to thoroughly understand and hone the technique of each individual exercise. When performing training, it is important to follow 5 rules:
- Regularity of exercise therapy.
- Gradual increase in load.
- Smooth and accurate movements of the cervical spine.
- Complete abolition of physical exercise if the slightest pain or changes in sensitivity appear in any part of the body.
- Based on point No. 5, urgently contact a treating specialist so that he can conduct a high-quality examination and make adjustments to the therapeutic exercise plan.
Taking and applying any physical activity on your own from the Internet, at random, or on the advice of other patients is highly not recommended! In the acute phase, exercise therapy is contraindicated! If you neglect these rules, the likelihood of achieving disastrous results is too high. The consequences of an illiterate approach are exacerbation of the symptoms of a spinal hernia, increased frequency of relapses, progression of disc displacement, even greater reduction of the spinal lumen, pinching and death of nerve endings, damage to the spinal cord/brain, compression and narrowing of the cervical arteries, separation of the hernial sequestrum. As a result, the deadline for the operation will not move away, but will noticeably get closer.
Pathogenetic therapy
The next block included in drug therapy is pathogenetic treatment. It involves completely stopping the process that causes the hernia: medications are prescribed to dilate blood vessels, restore hormonal levels, and relieve swelling.
This group includes: muscle relaxants, hormones (glucocorticosteroids). Drug treatment of intervertebral hernia using these drugs is carried out within a short period of time. Glucocorticosteroids include "Milgamma" - it improves blood circulation and contains essential vitamins.
The most popular muscle relaxant is Baclofen. It relieves muscle tension well, thereby reducing pain.
Treatment rules
In the treatment of hernial protrusions, predominantly conservative methods are used. Only an integrated approach is practiced with the simultaneous use of medications, physiotherapy, massage sessions, and exercise therapy. In the acute or subacute period, wearing semi-rigid elastic corsets that stabilize the lumbar structures is indicated. During the remission stage, warming belts-bandages made of sheep and camel wool are used.
If the hernia is large enough, the body will report this with unbearable pain.
Medicines
Drug treatment of lumbar hernia is aimed at improving the patient’s well-being, reducing its size, and preventing relapses. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in the form of injections, tablets, and gels help relieve pain. These are Diclofenac, Meloxicam, Ibuprofen, Nimesulide, Ketorolac. If they are ineffective, blockades with glucocorticosteroids (Triamcinolone, Diprospan, Dexamethasone) and anesthetics (Lidocaine, Novocaine) are used.
Treatment regimens also include drugs to improve blood circulation - Pentoxifylline, Xanthinol nicotinate. The use of chondroprotectors (Teraflex, Structum, Artra) helps prevent the enlargement of the hernial protrusion.
Exercise therapy
Daily physical therapy exercises help reduce the size of the hernia by strengthening the muscular corset of the lower back, improving posture, and properly redistributing loads on all parts of the spine. Patients are recommended to do shallow bends, side turns, lunges, and simulate riding a bicycle in a lying or sitting position. All movements should be smooth, with low amplitude.
Physiotherapy
Electrophoresis and ultraphonophoresis are most in demand in the treatment of hernial protrusions. During exacerbations, procedures are performed with glucocorticosteroids, analgesics, and anesthetics. During the period of remission, B vitamins, chondroprotectors, and solutions of calcium salts are used.
Applications with paraffin, ozokerite, therapeutic mud, laser therapy, UHF therapy, magnetic therapy, and ultraviolet irradiation are also used.
UHF therapy.
Massage
To improve trophism, eliminate muscle spasms, and restore innervation, patients are recommended 15-20 massage sessions. During the procedure, kneading, rubbing, and vibration are performed. The massage therapist treats only tense muscles, without affecting damaged vertebral discs. In addition to classical massage, vacuum (cupping), acupressure (acupuncture), and segmental massage are used in the treatment of lumbar hernias.
Acupuncture
Acupuncture sessions can also be performed in the subacute period to relieve pain and eliminate stiffness. Thin, short steel or silver needles are installed at biologically active points. They are located along the spinal column, on the arms, legs, and shoulders. After the needles are installed, impulses are sent to the central nervous system, and in response, the process of producing substances with an analgesic and decongestant effect is launched. The production of endorphins also increases, improving the patient’s psycho-emotional state.
Hirudotherapy
After placing 3-7 leeches on the lower back, these annelids bite through the skin, injecting saliva into the blood. It contains more than 100 different biologically active substances that have analgesic, blood thinning, and anti-inflammatory effects. After saturation, the leeches fall off and are immediately disposed of. In total, about 10 sessions are prescribed with a break of 2-3 days.
Spa treatment
In sanatoriums, mud, mineral waters, radon and hydrogen sulfide baths are used to treat lumbar hernias. Physiotherapeutic and massage procedures, physical education and gymnastics classes are mandatory. Even a short stay in a sanatorium has a general healing effect due to walks on the sea coast or in forests.
You need to be careful with hot baths.
Patient nutritional features
Nutritionists recommend that patients with lumbar hernia completely exclude foods high in fat and simple carbohydrates from their diet. These are semi-finished products, smoked meats, mayonnaise, sausages and confectionery products. Instead, you need to eat fresh vegetables and fruits, low-fat cheeses and cottage cheese. Every day you need to drink at least 2.5 liters of liquid - water, chamomile tea, rosehip infusion, sweet and sour compotes, jelly, juices, fruit drinks.
Folk non-traditional methods
The use of compresses, oil and alcohol rubbing, homemade ointments cannot reduce the size of the hernia or eliminate compression of the nerve roots and blood vessels. Therefore, the use of folk remedies is advisable only after the main conservative or surgical treatment.
Surgical intervention
If a hernia is detected at the initial stages of its formation, the strength of the still slightly damaged disc is increased by intradiscal electrothermal therapy or puncture laser vaporization.
Small hernias up to 0.6 mm are removed using endoscopic microdiscectomy. Large protrusions are excised during discectomy or microdiscectomy. To stabilize the spine, a B-Twin implant is installed in the lumbar region.
Prevention
Treatment of a vertebral hernia, the symptoms of which have reached their peak, is an unpleasant and lengthy process that requires maximum rest. Therefore, it is worth following simple rules that will delay the onset of the disease or prevent it altogether:
- Standing in place for a long time creates a load on the tibia joints, at which point a forced change of position occurs. The body weight is transferred to one leg, while the curvature of the spine changes and blood flow is disrupted. Such factors become ideal conditions for lordosis and scoliosis. It is almost impossible to get rid of this habit, however, if you bend your toes at the moment of such a stance, the center of gravity is leveled.
- In men, knowledge of what an intervertebral hernia is appears after strong physical exertion, for example, after lifting heavy objects. Doctors recommend that before lifting anything, bend your knees and squat. After this, the severity will be evenly distributed along the spinal column.
- Doctors categorically do not recommend taking water procedures before leaving the house: the protective film is washed off. This means that the vessels are open to any drafts and their cold is a matter of time. If going outside is unavoidable, then a cream applied to the lumbar and neck area can save the situation.
- You should perform morning or evening exercises. It allows you to maintain a balance between activity and relaxation of muscle tissue in the spine area and keep the body in good shape.
- In order not to wonder how to get rid of the disease, it is worth preventing its occurrence. Proper nutrition and plenty of clean drinking water will help with this.
- Be sure to read: exercises for hernias
Disease of the musculoskeletal system is an unaffordable “luxury” in the modern world. In order not to miss the onset of the disease, you must carefully monitor your health and follow the recommendations of your doctor, whose visit is mandatory once a year.
| Please rate the article |
I RECOMMEND ON
How to treat?
Based on the examination results, the doctor selects a comprehensive treatment for the patient for intervertebral hernia of the sacral spine. Treatment of the disease is a comprehensive approach consisting of drug treatment, physiotherapeutic procedures and therapeutic exercises. Sometimes alternative treatment methods are prescribed: folk remedies, hirudotherapy, wearing corsets, breathing exercises.
Drug therapy
One of the main goals of disease therapy is to relieve pain, eliminate other symptoms and improve metabolic processes in tissues. For this purpose, drug therapy is prescribed, including:
- painkillers: Diclofenac, Analgin, Ketanov;
- NSAIDs: Aspirin, Ibuprofen;
- chondroprotectors: Teraflex, Adgelon;
- angioprotectors: Detralex, Vasoket;
- muscle relaxants: Mydocalm, Tizanidine;
- anticonvulsants: Phenytoin, Carbamazepine.
Vitamin and mineral complexes are also prescribed. All medications and their dosage are selected only by the attending physician.
Operations
Surgical intervention for intervertebral hernia of the sacrum is prescribed in approximately 10% of cases, since spinal surgery is very dangerous and the person may remain disabled. Surgical intervention is permitted only when the hernia is large, conservative treatment does not produce results, or leg atrophy has begun. To treat a hernia, the affected nucleus can be replaced with an implant, or the hernia can be removed using a laser.
Physiotherapy
After the pain syndrome has been eliminated, the doctor moves on to the second stage of treatment - eliminating the immediate problem and restoring the functions of the spine. For this purpose, the following physiotherapeutic procedures are prescribed:
- electrophoresis;
- magnetic therapy;
- phonophoresis;
- paraffin treatment;
- application of galvanic current;
- EHF and others.
Each of the physiotherapeutic procedures has its own contraindications, and therefore can only be prescribed by a doctor.
Exercises
Physical therapy is one of the main components of the treatment of sacral hernia. First of all, the exercise therapy complex is aimed at stretching the spine, which, in combination with stretching, strengthening muscles and ligaments, allows you to gradually get rid of the hernia. But therapeutic exercises are impossible if the following conditions are present:
- acute inflammation;
- thrombosis;
- cerebral circulatory disorders;
- severe pathologies of the cardiovascular system;
- tumor with metastases in the spine;
- elevated body temperature.
Exercises for hernias of the sacral spine are selected individually by the doctor and performed under his supervision. Dikul’s gymnastics brings good results, which allows not only to relieve muscle tension and strengthen muscles, but also to eliminate headaches and improve blood flow. There are several effective and simple exercises for intervertebral hernia:
- Lying on your back, you need to pull your toes first away from you (5 seconds) and then toward you (5 seconds).
- Starting position: lying on your back, arms along your body, legs straight. Without lifting your feet from the floor, you need to slightly raise your body and stay in this position for 7-10 seconds, then slowly return to the IP. Take a break for 10 seconds, repeat the exercise 10 more times.
- IP: lying on your back, arms along your body, palms down, legs bent at the knees. The heel of your left foot should be crossed over your right knee. As you exhale, you need to pull your right leg as close as possible to your chest and, as you inhale, return it to the IP. Do 10 times on each leg.
- IP: lying down, arms along the body, legs bent at the knees. Without lifting the shoulder blades from the floor, the knees of both legs lower to the floor on the left side. The same is repeated on the right side.
Gymnastics for the sacral spine for hernias helps very well, but only if it is performed correctly and regularly. To achieve a positive effect, it is recommended to combine exercise therapy with massage and swimming.
How does a hernia form?
It takes quite a long time for the nucleus pulposus to be outside the intervertebral disc. The formation of a lumbar hernia occurs in several stages.
| Stage of lumbar hernia formation | Characteristics |
| Disc protrusion | Due to a decrease in the elasticity of the fibrous ring, a slight displacement of the nucleus pulposus occurs within its limits |
| Incomplete prolapse of a disc area | The fibrous ring becomes loose and fibrous, so in one of the areas its integrity is disrupted and the nucleus pulposus rushes there |
| Complete disc prolapse | The nucleus pulposus emerges from the annulus fibrosus, compressing the vertebrae and spinal roots |
| Disc sequestration | The prolapsed nucleus pulposus hangs like a drop outside the intervertebral space, causing a disorder of the blood supply to the spinal cord |
How dangerous is the pathology?
In the absence of treatment for intervertebral hernias, the consequences are quite severe:
- Lumbodynia is dull or aching pain in the lower back. More often present in the morning or prolonged interruption of the body in one position.
- Lumbago – this syndrome is called “low back pain”. It is characterized by acute pain, stiffness of movement, and severe muscle tension. Appears with a sharp turn of the body or lifting heavy objects.
- Lumboischialgia is severe neurological pain. In addition to pain, there is a decrease in sensitivity and numbness of the limbs.
Such complications are not a consequence of the disease, but only its symptoms and manifestations of complications. When there is no treatment for a vertebral hernia, it is carried out incorrectly, or the patient contacts doctors too late, the consequences of the disease can be irreversible. Paresis or paralysis of the limbs is considered dangerous, which causes disability, complete or partial decrease in performance. In men, the disease often leads to decreased potency, problems with bowel movements and urination.
How to treat a vertebral hernia in order to prevent its complications is one of the main questions of interest to many patients. Doctors in the field of neurology assure that the only way to eliminate complications is to seek their help in a timely manner and not self-medicate.
conclusions
Please note: the disease should never be left to chance - it will not go away on its own. Self-medication is also not worth it. Only a qualified doctor will prescribe medications and help stop attacks.
Today, the disease can be overcome with medications, a certain type of sports activity, massage and surgery. When the situation is advanced, they resort to the last method.
Prevention is constant exercise, including: swimming, yoga, fitness; weight loss to normal; refusal of high-heeled shoes; an adequate daily routine with sufficient time for rest.
A herniated disc always manifests itself as pain. Discomfort is felt most in the place where the pathology is localized. Often pain radiates to other organs, which can confuse inexperienced specialists and the patient himself. All of the above symptoms may not manifest themselves in full.
Symptoms of an intervertebral hernia in the thoracic spine are varied and can be disguised as other, very diverse diseases.
We invite you to read: Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine with pain radicular syndrome
Unfortunately, patients with thoracic osteochondrosis are “diagnostic orphans”: no one wants to deal with “unexplained” abdominal pain in the absence of a stomach ulcer or pain in the heart region with a normal electrocardiogram. But if doctors have not been able to find the cause of your chest pain for several months, find a qualified neurologist.
Muscle relaxants
In the complex of therapeutic therapy, the following muscle relaxants are prescribed for hernia:
- "Mydocalm";
- "Baklosan";
- "Tizanil."
“ Mydocalm ” for hernia helps relieve pathological muscle tone and spasm. The drug helps speed up the patient's recovery process. Also, “Mydocalm” for hernia helps relieve pain, enhancing the effect of analgesics and anti-inflammatory drugs.
The use of the drug is contraindicated in autoimmune neuromuscular pathologies. Usually, Mydocalm is well tolerated, but in some cases it can still provoke allergic reactions and cause hypotension. An analogue of a muscle relaxant is Tolperisone.
“ Baklosan ” is a muscle relaxant, the main active therapeutic element of which is baclofen. Unlike Mydocalm, it has an impressive list of contraindications, among which are mental disorders, epilepsy, Parkinson's disease, stomach ulcers, and lactase intolerance. Also, a muscle relaxant of this group has many side effects, so it is prescribed less often. Its direct analogue is Baclofen.
" Tizanil " refers to muscle relaxants that contain tizanidine. The drug has good bioavailability and is quickly absorbed into the blood. In case of serious problems with the liver, it is not used. It should also be noted that it is completely incompatible with fluvoxamine. A well-known substitute for a muscle relaxant is Sirdalud.
Prevention and treatment
Prevention of the disease largely consists of maintaining a healthy lifestyle and playing sports that do not involve excessive stress on the spine. The best option is light gymnastics and swimming. Optimizing your diet plays an equally important role. Often, pathologies of the human skeleton arise against the background of a deficiency of vitamins and minerals in the body.
Treatment for cervical disc herniation usually involves:
- drug therapy (aimed at eliminating inflammation and pain);
- physiotherapy;
- manual therapy;
- Exercise therapy and therapeutic exercises;
The complex of therapy for each patient is compiled individually based on his clinical picture and the presence of a disease progression factor. If after 4-6 months no positive result is observed, then, according to the decision of the attending neurologist, the patient may be referred for surgical treatment (most often this involves removing the damaged part of the disc).
Types and stages of intervertebral hernias in the neck
We told you that discs can be pre-herniated and truly herniated. At the stage of protrusion in the cervical region, the cartilaginous layer is considered small up to 0.2 cm and corresponds to stage 1 of the pathology. Protrusions exceeding 0.2 cm are classified as medium and large sizes (2, 3, 4 degrees). So, let's give a more precise description of each stage.
- Stage 1 – the integrity of the disc is preserved, the size of the bulge is up to 2 mm inclusive.
- Stage 2 – moderate severity, the integrity of the fibrous ring is compromised, the protrusion is increased from 2 mm to 4 mm.
- Stage 3 – severe, the ring is torn, the disc displacement is strong, equal to 4-6 mm.
- Stage 4 (extrusion or sequestration) – a critically severe degree of deformation, which can end in sequestration at any time. The size of the hernia at this stage {amp}gt; 6 mm, can reach up to 8 mm or more.
Sequestration is the most dangerous form of the disease, when a sagging cartilage fragment is completely torn off from the disc with a piece of dead cartilage entering the spinal space. Such pathogenesis can, in a short period of time, cause serious irreversible damage to the nerve, including its death, which leads to paralysis.
In general, all disc prolapses at the level of the neck, which are greater than 4-6 mm in volume, are considered clinically extremely unfavorable, since they seriously impair cerebral circulation, depress and disrupt the unity of the two main parts of the central nervous system - the brain and spinal cord.
The species diversity of such disc lesions in the cervical region is similar to lumbar and thoracic hernial protrusions. The pathological focus is classified according to its location (direction) relative to the spinal canal and vertebral bodies. According to this criterion, the following types of hernias are distinguished:
- lateral, or lateral – located strictly on the sides of the vertebral bodies;
- anterior, or ventral - grow anteriorly, that is, oriented in the opposite direction from the spinal canal (less dangerous view);
- posterior, or median – the protruding component faces clearly towards the center of the spinal canal (the most dangerous form);
- posterolateral, or paramedian - the deformed element is tilted several degrees away from the median axis leading directly into the spinal canal.
The share of lateral and posterolateral localizations is approximately 85%, median and ventral – 15%. Unfortunately, the relatively favorable location of the neck hernia - anterior - is the least common (5%) among patients.
Stages of the disease
Classification of intervertebral hernia according to degrees of progression:
- First. Lumbar protrusion. The intervertebral discs are displaced minimally, by a maximum of 2 mm. The nucleus pulposus does not extend beyond the edge of the spinal column.
- Second. The displacement occurs by no more than 1.5 cm. The core is located at the level of the spinal body.
- Third. It's called extrusion. The nucleus pulposus shifts to the outer edge, extending beyond the spine.
- Fourth. The nucleus pulposus begins to hang down, resembling a drop in appearance. Sometimes the fibrous ring ruptures, allowing its contents to leak out.
Leading signs of the disease
The cervical region is the narrowest part of the spinal system, in which the largest arteriovascular highway passes. The department includes the largest arteries - the left, right vertebral and basilar, each of which forms up to 6 groups of vascular branches.
In the back of the neck there is also an important cervical nerve bundle (node), which consists of the hypoglossal, lesser occipital, greater auditory, transverse, and supraclavicular nerves.
Thus, even slight deformations of the disc, displacement of the vertebrae in an overly narrow area, densely penetrated by nerves and blood vessels, can cause a real catastrophe:
- clamping of arteries and nerve roots, constant severe pain;
- blocking the circulation of blood and cerebrospinal fluid between the spinal cord and brain with severe cerebro-vertebral signs;
- neurotic nature of auditory and visual disturbances, frequent loss of consciousness, coordination disorders;
- serious dysfunctions of the gastrointestinal tract (nausea, vomiting, fecal incontinence), urinary system (uncontrolled urination) and genital organs (impotence, frigidity, infertility);
- muscle weakness of the arms, including complete or partial paralysis;
- depression of respiratory functions due to severe damage to the spinal substance and nerve nodes, up to the cessation of breathing;
- insufficient blood supply to the brain, which can lead to cerebral ischemia and stroke.
Pathological transformations in the intervertebral discs affect the elasticity and elasticity of bone tissue. The thoracic spine is made up of 12 vertebrae separated by discs. Fragments of the upper spinal column are more often affected by the painful process. If the inflammatory process is not stopped in time, the consequences can be serious, ending in surgery and sometimes disability.
The thoracic spine is rarely captured by a developing intervertebral hernia. Serious consequences can be prevented if symptoms are identified in time and treatment is started. Diseases are inherent:
- pain in the chest area;
- feeling of goosebumps, numbness, tingling in the arms, on the back, in the upper part of the stomach;
- weakening of the muscles in the arms;
- complete or fragmented paralysis localized at the site of the lesion;
- the disease affects the legs, pelvic organs - impaired urination, defecation, male sexual impotence.
- complete immobility of the body, except for the head, when the upper vertebrae of the thoracic region are affected;
- Nausea and vomiting are less common.
The increasing severity of symptoms of intervertebral herniation is due to the degree of compression of the disc roots. When a hernia reaches a large volume and compresses the nerve processes of the spinal column, the painful sensations vary.
| Boundaries of the thoracic vertebrae | Associated symptoms |
| Upper | Localization of pain between the shoulder blades, upper back. Pain in the heart muscle is possible, imitation of angina is observed. The effect of crawling goosebumps, numbness of the hands, tingling. |
| Average | Intercostal neurological symptoms - girdle pain, aggravated by the cough reflex, sneezing, sudden movements, deep sighs. There are no neurological symptoms. |
| Lower | Pain creeping from the shoulder blades down the back, chest, in the stomach area (imitation of kidney infection or stomach ulcer. Breathing rhythm is disrupted, shortness of breath. |
Symptomatic therapy
With symptomatic therapy, the main signs of the disease that cause discomfort to the patient are eliminated: pain, limited movement, as well as side symptoms from the use of certain medications.
They take medications together with NSAIDs to protect the stomach: Almagel, Gastal, Phosphalugel.
The second group of symptomatic drugs are the latest generation antidepressants. They are necessary to relieve irritation factors, insomnia, depression and apathy that can occur with prolonged pain.
Diagnosis of hernia at home
Self-diagnosis of an intervertebral hernia can be conditional, since an intervertebral hernia requires a comprehensive examination. The reason for determining the disease is most often pain syndrome (constant pain or temporary, systematic pain).
If you suspect an intervertebral hernia, you can perform a number of tests, after which in any case you should consult a doctor:
- most often, if there is a hernia, the patient does not sit on a chair straight, but takes the most comfortable position (even if this means bending slightly);
- When moving, the pain intensifies, when resting it subsides;
- pain spreads to the limbs;
- When turning or bending, the pain intensifies, especially when returning to the starting position.
Important! Self-diagnosis of an intervertebral hernia can only be a suspicion of the nature of the disease. For a clearer picture of the disease, you should consult a doctor.
Pain in the spine itself, not associated with temporary fatigue, occurring systematically and complicating movement can cause not only the development of an intervertebral hernia, but also other destructive processes.
In addition, if a hernia is present, it must be treated in order to prevent serious problems with the motor ability of the spine and the entire musculoskeletal system.
Video: “How to treat intervertebral hernia?”
The truth about treatment: analysis of the effectiveness of all tactics
In the acute period, doctors prescribe medications for pain, inflammation and swelling for local and internal use to relieve painful manifestations of the disease. The basis of such drug therapy is NSAIDs:
- Indomethacin;
- Ibuprofen;
- Meloxicam;
- Diclofenac.
In addition to non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for pain, specialists prescribe medications from a series of analgesics:
- Analgin;
- Spasmalgon;
- Ketorol.
If the clinical picture is aggravated by muscle hypertonicity, muscle relaxants are recommended to relax the spasmodic muscle structures. Among the most used muscle relaxants are Mydocalm and Siralud.
With constant debilitating pain, which NSAIDs and analgesics cannot cope with, a transition to treatment with strong hormonal or anesthetic drugs is carried out. These include glucocorticosteroids, lidocaine and novocaine. Using powerful hormone-containing and anesthetic agents, only as prescribed by a doctor in specialized conditions, the patient is given a course of spinal blockades. In the very near future, a person with such a critically unsafe diagnosis needs to undergo surgery.
All of the listed drugs act purely symptomatically: there will be no effect in terms of reducing the hernia component. In fact, they only temporarily relieve pain by blocking the transmission of nerve-pain impulses in the problem area. They also have a moderate anti-inflammatory effect. All intervertebral deformations and degenerations still do not disappear.
Note that limiting yourself only to drug therapy, even if it helps to get rid of pain, is the height of recklessness. With this approach, a hernia of the cervical spine will soon remind itself, and next time in a more vivid manifestation. But the worst thing is that, living only on painkillers, intervertebral pathogenesis will actively progress, increasing the risk of disability more and more every day.
Achieving stable remission through a drug regimen in complex combination with other conservative methods, as observations show, is not always achievable. If the initially prescribed complex treatment for 3 months, maximum 6 months, does not lead to tangible and lasting improvements, the patient is recommended to undergo surgery.
It is impossible not to say a few words about popular chondroprotectors, the action of which is aimed at improving metabolism and activating nutrition in osteochondral structures. Remember, their benefits have been clinically confirmed exclusively for osteochondrosis that has not developed into a cervical hernia. It is acceptable to use such drugs for small protusions as a preventive measure for further degeneration of the cervical intervertebral disc. But!
Impact of massage
The leading function of massage is to create a trophic effect. This means that massage techniques make it possible to increase blood circulation in the area of interest, ensure better lymph outflow and the supply of necessary metabolites and oxygen to tissue cells. Another goal of massage is to prevent atrophic phenomena in muscle structures and reduce intradiscal compression. However, we note that in no way can special techniques for massaging the cervical-collar area eliminate the hernia and reduce its volume.
This type of treatment is recommended strictly according to indications, since it is not equally useful for all types of hernias. It is prescribed especially with caution for medium and large protrusions, nerve pinching in the projections of the neck. Such manipulations in a neglected, complicated clinic can give a completely opposite effect, since it is easy to turn a large hernial mass in an unfavorable direction using this method of influence. Therefore, before prescribing a massage, the doctor must weigh the pros and cons.
At the beginning of the development of a hernia, massage can serve as an excellent measure to prevent the progression of degenerative-dystrophic pathogenesis in a still slightly changed disc. But we emphasize that massage techniques, if the doctor gives the go-ahead for them, should be carried out by a good massage therapist from the neurology department.
Diagnostics
Since the symptoms and treatment of the disease can be very different, to determine the presence of a pathological process it is necessary to conduct a preliminary diagnosis. At the appointment, the doctor interviews the patient, collects anamnesis and prescribes additional hardware tests, in particular such as:
- radiography;
- ultrasonography;
- CT scan;
- myelography;
- laboratory research.
Based on the research, it is possible to select the most effective means for performing therapy. The course of medical therapy is selected exclusively by the doctor.
Spinal syndrome
Increased pain in the second stage is accompanied by constant spasms of the back muscles . This leads to even greater discomfort for the patient. He cannot move freely, straighten his back, or stretch. The gait of such a person becomes uncertain, he constantly leans in the direction opposite to the patient, and stoops.
Due to impaired coordination of movements, a person’s quality of life deteriorates. He cannot perform the tasks assigned at work well, and active rest becomes unrealistic due to constant pain.
What to do if a hernia worsens
It is forbidden to exercise or attempt to do so that your back is straight. This will only lead to a worsening of the patient's condition. During the period of exacerbation, you should not engage in any sports . It is necessary to adhere to bed rest so that the patient feels comfortable and can find a comfortable position. You cannot make sudden movements or bend in different directions. When the disease worsens, the patient is forced to seek help from a doctor.
The doctor will prescribe effective treatment to relieve pain and inflammation. It happens that a specialist may prescribe warming up the sore spot, but this is done extremely rarely. You need to drink at least two liters of clean water per day.
Eat small and healthy meals, eat more fresh vegetables and fruits. Remove fried, smoked, salty, fatty foods from your diet. Do not drink alcoholic beverages and tobacco products, because bad habits will not only make the patient worse, but also harm their health.
When an intervertebral hernia worsens, you need to remain calm and try to rest more. Sleep at least eight hours a day. It is imperative to purchase an orthopedic mattress and pillow.