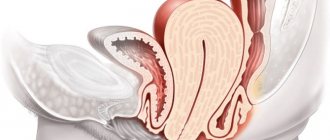
The uterus is a reproductive organ that has an endometrial thickness of 0.5 cm to 1.4 cm at different stages of the cycle. One of the pathologies affecting the female organ is uterine hyperplasia.
This diagnosis is not yet oncology, but some forms can degenerate into malignant tumors. Therefore, timely diagnosis and high-quality treatment are a guarantee of preserving women’s health.
What is endometrial hyperplasia
Hyperplasia of the endometrium of the uterus is a malfunction in the functioning of the mucous ball of the organ, which occurs as a result of hormonal imbalance in the body and is characterized by pathological growth of the inner lining - hypertrophy.
Normally, a woman's endometrial thickness changes throughout the menstrual cycle. At first, its layer is thin, but gradually, under the influence of sex hormones, it begins to thicken, preparing for the implantation of a fertilized egg.
If it is not fertilized or does not reach the uterine cavity, the mucous ball sloughs off and leaves the body during menstruation. It is important to know that there are two types of endometrium - basal and functional.
The first is always present in the uterus, and the second is susceptible to menstrual changes, being rejected during menstruation and growing again from the basal ball after its end.
If hormonal surges occur in the female body, the uterine mucosa is the first to react to changes in the concentration of sex hormones. Moderate hyperplasia of endometrial tissue develops, which gradually increases in size and volume.
Not all areas of the inner membrane are equally sensitive to the effects of hormones, so only a part of the cells can succumb to pathological growth - local damage.
When the endometrium grows diffusely, the entire surface succumbs to hyperplasia more or less evenly. In the photo you can see how thick the endometrium is during hypertrophy in comparison with the physiological state of the uterine mucosa.
The uterine cavity is small, only 3-4 cm in length and 2-3 cm in width, so the mucous ball cannot hypertrophy for too long.
As a result, detachment of the pathologically hyperplastic endometrium occurs, which leads to severe uterine bleeding. After separation of the endometrium, a large area of the uterus looks like a continuous bleeding wound.
To stop this process, you will need the help of a specialist who will prescribe medications or perform curettage.
It is important that the disease will recur cyclically until the cause of endometrial hyperplasia is eliminated. This means that the functional ball will be layered over and over again, and then released with great blood loss.
Prevention and complications
To prevent the development of pathology, several rules of prevention should be followed. Preventive measures, according to doctors, include:
- use of barrier contraceptives instead of intrauterine and oral ones;
- regular sex life;
- maintaining normal body weight;
- prevention of unwanted pregnancy;
- regular scheduled visit to the gynecologist once every 6 months.
Complications of endometrial hyperplasia:
- transition of the atypical form to endometrial cancer;
- relapse of the disease (the most common complication);
- infertility during reproductive age;
- chronic anemia.
The hormonal levels in the female body are very easily disrupted even due to strong emotions, and therefore no woman is immune from the occurrence of such a problem as endometrial hyperplasia. This disorder is completely reversible, and the earlier it is detected, the faster it can be dealt with. For this reason, even minor disruptions in the cycle or discharge in the middle should be a reason for an immediate visit to the gynecologist.
How to treat hyperplasia
The choice of tactics for treating endometrial hyperplasia depends on many factors - the woman’s age (reproductive or menopausal), the severity of the disease, the presence of cysts or polyps, and the patient’s wishes.
Previously, the disease was treated radically by removing the problem organ, that is, the uterus.
Modern techniques make it possible to treat hyperplasia without loss of reproductive function, and in mild forms, even without surgical intervention, by prescribing medications.
Typically, the pathology manifests itself in the form of heavy, prolonged periods. Therefore, at the first stage of therapy, the main thing is to stop the bleeding. To do this, curettage of the uterine cavity is performed.
Drug treatment
Treatment can be either medication or surgery followed by drug therapy. In this case, the tactics and principles of treatment are selected taking into account many factors: the type of hyperplasia, the age of the patient and her state of health.
The basis of drug therapy in the treatment of endometrial hyperplasia is hormone therapy using combined oral contraceptives, gestagens or GnRH agonists. Conservative treatment is aimed at regulating hormonal levels by reducing estrogen levels, as well as stopping the proliferation of the uterine mucosa and reducing foci of hyperplasia.
Combined oral contraceptives
Treatment with COCs is often prescribed to adolescent girls or young nulliparous women with heavy, irregular menstruation due to glandular or glandular cystic hyperplasia. In some cases, in order to avoid curettage, COCs are also prescribed for hormonal hemostasis, so as not to resort to emergency curettage. The course of therapy is long, lasting at least 6 months. The drugs are taken according to a contraceptive regimen.
Synthetic analogues of progesterone
Treatment with gestagens is prescribed to women of any age with any form of this disease. Long-term treatment is often carried out over 3–6 months. While taking gestagens, intermenstrual bleeding may occur.
Duphaston
One of the most well-known effective gestagenic drugs used in conservative treatment. Prescribed for long-term use for at least 3 months, 2 tablets 3 times a day from 16 to 25 days of the menstrual cycle. In case of bleeding for 3-4 days, the dose is doubled, then the standard regimen is continued.
Norkolut during the period of illness
The drug is not an active gestagen, but has a pronounced antiestrogenic character. For glandular cystic hyperplasia, 1 tablet per day is prescribed from the 16th to the 25th day of the menstrual cycle for 3–6 months. To stop bleeding caused by hormone therapy, take 1-2 tablets per day for 6-12 days.
Mirena
The Mirena intrauterine device is used as an effective contraceptive, as well as a means of hormonal therapy as a local progestogen. The positive aspects of treatment with Mirena include a long-term (5 years) and effective method of protection against unwanted pregnancy and the local therapeutic effect of hormones on the endometrium of the uterus.
The negative aspects of using the product include the possibility of intermenstrual bleeding in the first few months after installation of the IUD, as well as painful menstruation.
Gonadotropin releasing hormone agonists
AGnRH is a modern and most effective class of drugs used in the treatment of endometrial hyperplasia. The advantage of treatment with drugs of this class is the high percentage of positive treatment results, the possibility of flexible dosing, as well as switching to a convenient regimen of taking the drug - only once a month.
The active ingredients of the drugs block the production of sex hormones, resulting in endometrial atrophy and inhibition of cell and tissue proliferation. With the help of GnRH agonists, in most cases, infertility and hysterectomy can be avoided.
Symptoms
Treatment of endometrial hyperplasia after the appearance of clear symptoms (bleeding) consists of curettage, and in case of significant blood loss and ineffectiveness of therapy, removal of the uterus.
Often, signs of endometrial hyperplasia are difficult to determine because there are no characteristic symptoms, but some manifestations may indicate pathological thickening of the inner layer of the uterus:
- Disruptions in the menstrual cycle are the most common manifestation of pathology. Menstruation occurs at different intervals and is often delayed. The structure of the discharge is heterogeneous; blood clots and exfoliated particles of the endometrium are present in large quantities.
- Amenorrhea is the absence of menstruation for several cycles. For a long time, the mucous ball grows in the uterine cavity, when its thickness reaches 2-3 cm, it is rejected and comes out. This process is usually accompanied by large blood loss, which can threaten the patient's life.
- Pathological vaginal discharge - appears a few days before or after menstruation, looks like ichor. The symptom is characteristic of hyperplasia with the appearance of polyps in the uterus.
- Pain during menstruation - thickening of the endometrium leads to painful detachment from the walls of the uterus. It is important that such a sign indicates hyperplasia only in the case when menstruation was previously asymptomatic, and then pain appeared. If a girl always experienced discomfort during this period, then this is considered a variant of the physiological norm.
- A stable cycle in the presence of heavy discharge for a long time - more than a week.
- Impossibility of pregnancy because ovulation does not occur in every cycle. Even if the egg is fertilized, it will have nowhere to attach due to changes in the endometrium.
Symptoms of endometrial hyperplasia can easily be confused with signs of other pathologies, so you should not self-medicate. With the first manifestations, you need to consult a doctor and undergo an examination.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis is made based on various methods, the results of which are specific to the corresponding age period.
Among the diagnostic methods, the main ones are:
Ultrasound examination using a transvaginal probe
According to various sources, its information content ranges from 78 to 99%. The thickness of the endometrium during hyperplasia in the secretory phase exceeds 15 ± 0.4 mm (up to 20.1 ± 0.4 mm); in the postmenopausal period, a thickness of more than 5 mm indicates a hyperplastic process. Exceeding the value of 20.1 ± 0.4 mm already raises suspicion of the possibility of adenocarcinoma. Other M-echo signs of hyperplasia are the heterogeneous structure of the uterine mucosa, inclusions similar to small cysts, or other ECHO-positive formations of varying sizes.
Separate diagnostic curettage of the mucous membrane of the cervix and uterine cavity
The study is most informative on the eve of menstruation. Further histological examination of the obtained material allows us to more accurately determine the nature of the morphological changes occurring. Cytological examination reveals the presence of cellular atypia. Indications for repeated curettage are recurrent bleeding in the postmenopausal period and monitoring the effectiveness of the course of hormonal treatment.
Read more about the procedure in our previous article.
Hysteroscopy
Being a fairly informative technique (informativeness ranges from 63 to 97.3%), the study significantly increases the diagnostic value of separate curettage. It is advisable to carry it out on days 5-7 of the menstrual cycle. Hysteroscopy for endometrial hyperplasia makes it possible to differentiate the morphological forms of transformation of the uterine mucosa. Hysteroscopic signs are:
- with simple hyperplasia - the thickness of the endometrium is more than 15 mm, its uneven surface with the presence of multiple folds of pale pink or, less often, bright red color, pronounced vascular pattern, uniform arrangement of the excretory ducts of the glands;
- with cystic - folded bright red surface, increased thickness, unevenness of the vascular network, in the projection of superficial vessels - a large number of cysts.
Classification of the disease
Based on the nature of the lesion and the type of cells that predominate in pathological tissues, several types of endometrial hyperplasia are distinguished:
- Atypical is a dangerous form of the disease characterized by the presence of abnormal cells. They can succumb to cancerous transformation at any time. Atypical hyperplasia is usually treated by removal of the uterus and adnexa.
- Focal - not the entire mucous ball is susceptible to pathological growth, but only its individual sections, so small lesions appear.
- Glandular-cystic - endometrial glands increase in size, cysts form over its entire surface.
- Glandular - the glandular tissue of the inner ball of the uterus grows, significantly increasing the thickness of the entire endometrium.
- Complex is the second name for an atypical type of pathology, or adenomatosis. The structure of endometrial cells is disrupted, and the proliferation of glandular epithelium predominates.
- Simple endometrial hyperplasia is characterized by a uniform increase in all cells of the mucous membrane and the absence of structural changes.
Classification of hyperplasia
According to histological origin, hyperplastic processes are divided into:
- directly glandular and glandular-cystic hyperplasia (changes occur only in the functional layer of the endometrium): focal and diffuse;
- polyps: glandular (only the functional layer is involved in the pathological process), glandular-fibrous (pathology in the superficial and deep layers), fibrous (proliferation of only the deep layer). Polyps of the deep layer have a “leg”, which includes connective and muscle tissue. Polyps grow from the fundus of the uterus, as well as from tubal nodes.
The term "polyp" was introduced in the mid-18th century.
And the first mention of polyps can be found in the works of Hippocrates, where polyps were identified as one of the causes of infertility. Endometrial hyperplasia is also divided into typical and atypical (adenomatosis). With adenomatosis, the distinctive features of atypia are recorded in endometrial cells.
Typical endometrial hyperplasia and polyps are background processes. Atypical hyperplasia is a precancerous disease. In 40-50% of cases, atypical hyperplasia degenerates into cancer.
Causes of pathology
The most common cause of endometrial hyperplasia is a failure in the production of hormones, as a result of which the level of progesterone decreases and the concentration of estrogen in a woman’s blood increases.
The disease can also occur due to immune dysfunction when antibodies attack endometrial cells, which leads to accelerated growth.
Damage to the basal layer of the endometrium, for example, after carelessly performed abortions, leads to the disease. Receptors that respond to the saturation of the body with progesterone are damaged, and even with normal hormone levels, the growth of the mucous ball does not stop.
The genetic factor plays a large role in endometrial hyperplasia of the uterus. If close relatives have been diagnosed with the disease, the risk of its occurrence increases.
It is important to know! If the causes of endometrial hyperplasia are not eliminated, the treatment will not bring results and the disease will soon appear again.
Treatment
There are many different opinions about initial treatment, but they all boil down to the fact that therapy should begin immediately after diagnosis, without waiting for clinical manifestations and complications.
Knowing what causes the retrovirus to die, the doctor can choose the right treatment regimen and prescribe antiviral drugs. Usually two antiretroviral drugs are selected, which are taken under laboratory control of blood serum.
Most often prescribed:
- drugs belonging to the group of reverse transcriptase nucleosides;
- agents from the protease group;
- drugs related to non-nucleoside transcriptase inhibitors.
Therapy of secondary pathologies plays a huge role in the treatment of retroviral infection. For this purpose, the doctor prescribes a full examination, during which they determine what ailments the patient suffers from. After identifying chronic diseases, therapy is selected aimed at getting rid of the disease or achieving stable remission.
As additional treatment, vitamin therapy, physical therapy, immunotherapy, and nutrition correction are mandatory.
After treatment, the patient will have to be observed by a doctor for the rest of his life, lead a healthy lifestyle, and follow strict recommendations. Otherwise, the retrovirus may reactivate.
Why is endometrial hyperplasia dangerous?
If you ignore the symptoms of the disease, the growth of the endometrium in the uterus can lead to a number of complications:
- development of the oncological process;
- large blood loss during endometrial rejection;
- inability to carry a pregnancy to term;
- chronic anemia.
To avoid unpleasant consequences, it is important to start correct treatment on time.
Pathologies during menopause
During menopause, the normal thickness of the uterus should not exceed 5 mm. If its thickness increases by 2 mm, it is necessary to undergo regular examinations. In cases where deviations from the norm are more than 3 mm, the woman requires full-fledged therapy, since endometrial hyperplasia develops.
Endometrial pathology in menopausal women quite often develops in the form of uterine dysplasia. In its normal state, the basal layer consists of rounded cells containing one nucleus. As it matures and moves to the surface layer, the core decreases. When there is a disorder (dysplasia), a large number of atypical cells are formed, gradually replacing healthy cells with diseased ones. Dysplasia comes in three forms:
- light;
- moderate;
- heavy.
Related article: symptoms and signs of cervical dysplasia
Prevention
Twice a year, a girl of reproductive age should visit a doctor and undergo a gynecological examination. This will help identify changes at an early stage of development and prevent hyperplasia.
It is also important to treat inflammatory diseases of the pelvic organs in a timely manner and prevent them from becoming chronic.
It has been proven that taking hormonal contraception reduces the risk of pathology, since the drugs stabilize the condition of the patient’s reproductive system.
Traumatization of the walls of the uterus leads to hyperplasia, so it is necessary to avoid interventions in the organ cavity - abortion, caesarean section if physiological childbirth is possible, curettage for no apparent reason.
Symptoms of the disease
The most common and common symptom indicating an ongoing disease is open uterine bleeding. Additionally, as endometrial hyperplasia progresses, the following signs are observed:
- Amenorrhea is a delay in menstrual flow for more than a month. The condition is replaced by intense discharge of blood clots from the genital organ.
- Vaginal discharge of a spotting nature, colored brown or brownish.
- Painful sensations during long-lasting menstruation, in rare cases accompanied by intense bleeding.
- Disturbed menstrual cycle and shifting of dates.
Uterine endometrial hyperplasia in most cases occurs in parallel with metabolic syndrome. The syndrome itself, in addition to intense bleeding, includes:
- weight gain;
- increasing the amount of insulin in the blood;
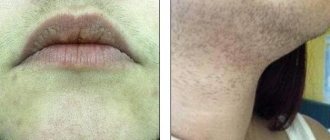
- a hormonal imbalance that provokes a complex of symptoms containing masculine characteristics - the female body is covered with vegetation in areas where there was no hair before, the timbre of the voice decreases.
In addition to the symptoms described above, a woman with endometrial hyperplasia encounters the following symptoms:
- diagnosing recurrent infertility;
- it is not possible to carry a child to term normally;
- development of chronic inflammatory lesions in the reproductive organs;
- mastopathy or uterine myomatosis.
Among the rarely observed accompanying signs of the hyperplasia process are:
- Discharge of blood clots during sexual intercourse or during hygiene procedures.
- If there are polyps on the tissues of the reproductive organs, cramping-type pain in the lower abdomen is regularly possible.
Recipes
Since ancient times, nettle decoctions have helped to overcome many ailments. These included endometrial hyperplasia. To carry out therapy using this herb, you will need to prepare a tincture from the plant. To do this, take 200 g of nettle and pour in 500 ml of vodka or alcohol. Infuse the mixture for two weeks, and then drink a teaspoon every day in the mornings and evenings. This treatment helps restore the immune system and improve the condition of the uterus.
The next effective folk therapy method is cucumber decoction. To prepare it, cucumber lashes are dried, and then 50 g of the component are boiled in 0.5 liters of water. Boil the product for no more than 5 minutes, then leave for 60 minutes, drink 100 ml three times a day.
To get rid of endometrial hyperplasia, they also drink peony decoctions. To do this, dilute the plant extract with water in a ratio of 1:2. The initial dosage is 2 ml. Take the decoction three times a day. It helps normalize hormonal levels and prevents further development of the disease.
Also, supporters of alternative medicine advise drinking plantain infusion 4 times a day. The herb leaves are finely chopped and then brewed in a glass of boiling water. Infuse the decoction for 2 hours. Before use, strain through cheesecloth.
Traditional healers also recommend using herbal remedies to combat hyperplasia. For example, every day they advise drinking 0.5 cups of a mixture containing serpentine roots, shepherd's purse grass, calamus and cinquefoil roots, knotweed grass and nettle leaves. Mix all ingredients in the following proportion: 1:1:2:2:2:2. The collection is thoroughly crushed, and then take 2 tablespoons of the mixture and pour 0.5 liters of boiling water. Boil the broth for 5 minutes, then pour it into a thermos and leave for 1.5 hours. Take the product 100 ml at a time. The full course of therapy lasts 1 month, then take a break for 10 days, and then repeat the procedure.
Proven recipes from alternative medicine can quickly get rid of the disease if they are combined with drug treatment and surgery. It should be remembered that it is worth fighting to the last to preserve the uterus, since its removal provokes a number of negative consequences in the body. There are cases when, due to hormonal imbalance, women with a removed uterus began to experience panic attacks and lost their jobs.
Therefore, it is important to promptly treat endometrial hyperplasia. Its transformation into a malignant tumor occurs in 55% of cases. The likelihood of developing cancer depends on the patient's age and her history of previous illnesses.
Treatment with tampons
Tampons for the treatment of the disease are used either ready-made, purchased at a pharmacy, or made independently. The medicine is Beautiful Life tampons; they contain herbal ingredients. They have anti-inflammatory and antispasmodic effects. They are effective in the early stages, when endometrial hyperplasia is without complications, and are used to prevent relapses.
At home, use cotton-gauze swabs soaked in celandine infusion. (pour 250 ml of boiling water over 30 g of raw materials, leave for half an hour, strain). The infusion has an anti-inflammatory effect, but frequent use can cause burns to the mucous membrane. Exposure time is no more than 10-15 minutes.
The possibility of using tampons in treatment, the duration and frequency of their use should be determined by the gynecologist.
Causes of the disease
The main factor that triggers the process of disease activation is associated with hormonal imbalances.
A woman's body faces a lot of changes, especially during the childbearing period. First, the endometrium grows, preparing the body for conception; if fertilization does not occur, the dead tissue comes out in the form of menstruation.
Hyperplasia is characterized by an increase in epithelial cells, muscle tissue and intercellular substances of the mucous membrane. This is caused by a hormone imbalance: more estrogen is released than progesterone.
There are a number of other reasons:
- diabetes;
- bad heredity;
- disturbances in metabolic processes;
- malfunction of the thyroid gland;
- overweight;
- abortions;
- problems with the adrenal glands;
- myoma;
- age;
- infertility;
- irregular menstrual cycle;
- polycystic ovary syndrome;
- inflammatory processes in the reproductive organs;
- use of hormonal drugs.
Based on research, 73% of women experience hyperplasia of the endometrial mucosa during menopause. The disease during the decline of childbearing function is characterized by abundant bleeding and the development of oncological tumors.
When the ovaries stop functioning, a sharp change in hormonal levels occurs. The endometrium of the uterus becomes sensitive and more susceptible to the influence of estrogen.
Video from Dr. Malysheva:
Folk remedies
Often, upon learning of their diagnosis, women resort to unconventional methods of therapy. To understand how to treat endometrial hyperplasia with folk remedies, you should in any case first consult with your doctor. Although such treatment methods are always gentle, they should not be used recklessly or completely relied on.
How to treat endometrial hyperplasia with folk remedies? Doctors recommend combining drug treatment with this gentle type of therapy. This enhances the effect.
If you correctly combine hormonal therapy, herbal medicine and surgery, you can get rid of the disease quite easily. If a woman, having found information on how to treat endometrial hyperplasia with folk remedies, relies entirely on them, then there will be no effect.
The main goal of therapy is to block excessive hormone production, since these conditions provoke the division of cancer cells. Alternative medicine methods are aimed at solving precisely this problem.
Survival prognosis
The prognosis for recovery from endometrial hyperplasia is based on the form of the disease and the stage of progression. A positive result indicates the possibility of successfully treating the diagnosed type of lesion. At the same time, the chance of degeneration into malignancy is minimal. After treatment, with a positive prognosis, the woman’s reproductive function stabilizes, the menstrual cycle and the ability to engage in sexual intercourse are restored. A good outcome is likely for the following types: simple, glandular, glandular-cystic and cystic, including the formation of polyps.
A worsening prognosis is observed in the older age category of patients. In youth, the disease can be cured more often. Failure of endocrine and metabolic processes, increased body weight, diabetes and hypertension reduce the recovery rate. If hyperplasia is detected after menopause, the prognosis is negative depending on the person’s health status, but regarding life expectancy it is good. In the period after menopause, the disease often takes on a malignant type and acts as a precancerous condition.
The complex or atypical hyperplasia form reflects a negative outcome in the health indicators and life expectancy of the patient. These types of pathogenic course are called precancerous conditions, when there is a high probability of accelerated degeneration of the affected cells into dangerous cancer. When atypia is highly resistant to conservative treatment, surgical methods come into play - curettage and removal of the uterus. In such situations, the prognosis is a positive outcome in the woman’s health.
The result is influenced by the presence of chronic diseases. Hypertensive pathology worsens the outcome of therapy for endometrial hyperplasia. The likelihood of secondary formation of lesions increases. The situation is observed when endocrine metabolic processes are disrupted - susceptibility to glucose decreases, the amount of cholesterol in the blood increases, and diabetes mellitus develops.
Endometrial hyperplasia is a disease characterized by several varieties that differ in their specific course, origin, treatment methods and prognosis for recovery. Constant gynecological examination, timely treatment of genital pathologies and adherence to a healthy lifestyle help maintain women's health at a high level.
Preventive actions
Prevention of uterine pathology includes the following recommendations:
- gynecological examination every six months;
- treat genital inflammations in a timely manner;
- use COCs;
- treat irregularities in the menstrual cycle in a timely manner;
- early diagnosis and fight against genital, psychosomatic and endocrine abnormalities, including diseases of the hepatobiliary structure;
- maintaining a normal body weight level;
- reduce the likelihood of abortion, plan pregnancy;
- rejection of bad habits;
- prevention of stagnation of fluid and lymph in the pelvic areas;
- active life;
- proper nutrition;
- performing physical exercises.
Types of endometrial thickening
There are four types of endometrial thickening:
- Simple - the number and size of glandular cells increase, but their structure remains unchanged.
- Complex (grade 1 hyperplasia) - focal accumulations of glandular cells appear, having a heterogeneous shape.
- Moderate – stands out as a separate stage of the disease, representing a transition from a simple phase to a complex one.
- With atypia – atypical cells are formed, which is possible with simple and complex types.
The division into types allows us to make predictions regarding the development of oncology. The risk of uterine cancer with a simple form is only 1%, with a complex type – 3%, with a simple type with atypia – 8%, with a complex type with atypical cells – in 30% of cases.
Gravidarny
Gravid endometrium is indicated by certain signs on ultrasound. The changes are extensive, as they are recorded throughout the entire uterine cavity.
The main reasons for changes in the structure of the endometrium are changes in the hormonal background. This condition is typical only during pregnancy.
The appearance of gravid endometrium during pregnancy is normal. The danger lies in the formation of such mucous membrane outside of pregnancy. The fertilized egg does not attach well to such endometrium, which means there will be problems with conception. Treatment is needed.
Drug hormonal therapy is prescribed. The course of treatment and medications are selected individually.
Gravid endometrium on ultrasound
Diet as part of treatment
Uterine hyperplasia, its symptoms and treatment depend on adherence to a certain diet. During this period, support for the immune system, normalization of metabolism (hormones), and normal functioning of the digestive system are necessary.
Principles of nutrition for endometrial hyperplasia:
- Meals should be frequent, in small portions. Dinner 3 hours before bedtime.
- The diet requires vegetables and fruits high in ascorbic acid, which helps reduce endometrial growth.
- taking herbal products that affect the level of hormones in the blood. Foods high in cellulose increase the amount of estrogen. Celery, peas, pumpkin seeds, sunflower seeds, on the contrary, reduce the release of the hormone into the blood.
- To reduce the load on the liver and gall bladder, it is advisable to steam, stew and boil dishes.
- Eating enough varieties of fish rich in polyunsaturated fatty acids can improve uterine contractions and reduce bleeding.
- Avoid eating red meat, the fatty acids of which cause disturbances in hormonal metabolism.
Therapy
The disease is treated using complex therapy methods. How endometrial hyperplasia is treated will be described below. There are several stages of treatment. Each of them contains several different techniques. They are selected depending on the type of hyperplasia. Typically therapy consists of four stages.
Before treating endometrial hyperplasia, stop the bleeding. Then treatment with hormonal agents is carried out. Next, the cycle is normalized. The patient has been observed for 5 years, with follow-up examinations every 6 months.
In extreme cases, the uterus is removed. But such surgical intervention has an extremely negative impact on the woman’s condition, as artificial menopause and hormonal imbalance begin.
Modern classification
According to the classification, hyperplasia can be simple or complex, atypical or without atypia.
With simple hyperplasia, the number of glandular and stromal structures increases. There is an increase in the size of the endometrium and changes in its structures. Part of the gland expands in a cystic manner. The vessels are distributed evenly. There is no atypia observed in the nuclei. In 3% of cases, this type of disease develops into a malignant tumor.
The glandular cells acquire an unusual, rounded shape. Polymorphism often appears in the cell nuclei, and vacuoles expand. In such cases, there is a 20% chance that the cells will later become cancerous.
Complex hyperplasia manifests itself in the fact that the glands in the endometrium are located too closely or in separate foci. An abnormal structure of the gland is observed, an imbalance occurs in the growth of stroma and glands. There is no atypia observed in the nuclei. Cancer develops with a 10% chance.
Complex atypical endometrial hyperplasia is recognized as the most dangerous form for patients. In 57% of cases it develops into uterine cancer. With it, the proliferation of the epithelium is significantly pronounced, and atypia is established in cells and tissues. A variety of shapes and sizes appears in the glands.
The epithelium contains large cells whose nuclei are elongated and polymorphic.
A moderate form of hyperplasia is also distinguished separately. This is a transitional phase from a simple to a complex variety. It has few individual characteristics and is not always identified as a separate stage.
Scraping
Before treating simple endometrial hyperplasia, you need to understand that traditional methods of therapy can lead to complications. Pregnancy after curettage is possible. Moreover, it may well occur in a month if the patient did not use hormonal drugs. If she followed all the specialist’s instructions while being treated with hormones, then she can become pregnant 2 months after completing the course.
In which cases pregnancy after the procedure is possible and in which it is not is determined only by the attending physician. The thing is that a specialist examines endometrial scrapings under a microscope.
Most often, it is not recommended to get pregnant immediately after the first cycle. There is no guarantee that the internal uterine membranes have already been renewed and can allow the fetus to develop normally before the end of term. Gynecologists advise waiting about 3-6 months before stopping using contraception.
Symptoms of the disease
In the vast majority of cases, liver hyperplasia occurs without any symptoms, so this disease is not diagnosed immediately. Most often it is discovered during examinations by a gastroenterologist or during various operations.
Clinical manifestations of the disease are not only nonspecific, but also occur in less than half of patients. The most common symptom is pain in the right hypochondrium.
It is constantly present, but is weakly expressed and may be severe. Most people don't pay attention to it.
- One of its most characteristic signs of the disease is a star-shaped scar that appears in the central part of the formation. However, it does not occur in all patients. In addition, such a scar can be a sign of some other diseases.
- Sometimes the disease may be accompanied by nausea or decreased appetite.
- If the tumors are large, they can be detected by palpation through the abdominal wall. The size of the formation and the presence of certain symptoms are not related to each other. The location of the tumor in relation to other organs is of great importance, as it can put pressure on them and interfere with normal functioning.
- Complications of this disease in the form of obstructive jaundice, malignancy or bleeding are very rare.
Classification
Experts distinguish 2 types of liver hyperplasia:
- classical;
- non-classical.
The first option occurs in 80% of cases. It is characterized by the presence of 3 main signs, which include:
- the appearance of tortuous vessels with thick walls;
- enlarged bile ducts;
- abnormal lobule structure.
In the non-classical course there is always an enlargement of the bile ducts. This type can be divided into 3 subtypes:
- adenomatous hyperplastic;
- telangiectatic;
- nodular hyperplasia of the liver with cellular atypia.
Causes
Having discovered endometrial hyperplasia on ultrasound, the first step is to identify the cause of its appearance. In fact, the disease always develops against the background of hormonal imbalances, when the estrogen content increases. It is this that leads to tissue proliferation.
Among the reasons leading to increased secretion of the hormone are the following factors:
- The presence of excess fatty tissue promotes the production of a certain amount of estrogens. Progesterone levels, on the contrary, become lower.
- Symptoms of the disease appear during the perimenopausal period. Then the female body undergoes hormonal changes.
- Often, taking a number of medications aimed at treating a malignant breast tumor leads to the development of this disease.
- Polycystic ovaries are also a prerequisite for the development of the disease.
- The predisposition to endometrial hyperplasia is inherited.