Among the many diagnostic methods, detection of leukocyte smear analysis takes a leading position in identifying female gynecological pathologies. This is a completely common procedure, well known to many women who control their intimate health. Certain norms of leukocytes in the body are laid down by nature itself, and as part of various microflora they are present in the vagina of any woman.
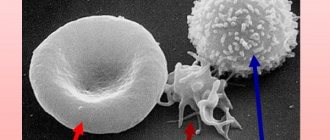
Leukocyte cells perform an important function - being, in fact, a natural protective barrier against the penetration of pathogenic microorganisms into the body. An increase in the level of leukocytes, for example, in the blood or smears indicates the development of pathological processes - this means that the number of cells is rapidly increasing to cope with the “malicious alien”.
It is clear, of course, that it is impossible to determine all pathological conditions with one smear analysis, but in addition to white blood cells, it helps to identify the presence of pathogenic microorganisms, epithelial cells, formed elements and other inclusions in the structural environment of the vagina. The presence of such additional information allows us to suspect the development of certain pathologies and decide in the direction of more in-depth and informative diagnostic methods.
The informative significance of the analysis is due to the possibility of identifying inflammatory and infectious gynecological diseases and determining their clinical severity.
Microscopic examination of a vaginal smear for flora
Regular visits to the gynecologist help a woman maintain the health of the reproductive system and eliminate pathological processes in a timely manner. At the appointment, the doctor interviews the patient, examines her, and takes material for flora analysis. This study shows the qualitative and quantitative composition of microorganisms present in the urethra, vagina, and cervical canal.
During the examination of the patient, the gynecologist takes scrapings in several places with a disposable instrument. When collecting biomaterial, gynecological speculum is used. If it is necessary to examine a child or a virgin, doctors use soft instruments. All manipulations are carried out by the doctor very carefully, so the procedure does not cause discomfort to the patient. The specialist applies the resulting samples to glass slides (there are 3 of them - for material from the vagina, urethra, and cervical canal) and sends them to the laboratory.
Medical slides for smears
Analysis results are usually ready within 1 day. During the research, the laboratory assistant determines the content of erythrocytes, leukocytes, epithelium in the biomaterial, as well as the composition of microorganisms. Among them, both normal and pathogenic forms are identified - gonococci, Trichomonas, Candida.
The reason for carrying out an extraordinary analysis is the woman’s malaise. You will have to do a smear if:
- pain in the lower abdomen;
- itching, burning or swelling in the genital area;
- discharge of unusual color, with an unpleasant odor
It is necessary to take a smear test for those who are planning to conceive a child or suffer from infertility or have changed sex partners. And also after a long course of treatment with antibacterial drugs, taking cytostatics. These drugs affect the number of immune cells in the female body, as well as the ratio of beneficial and pathogenic microflora.
Preparation for the study involves abstaining from sexual intercourse for 1-2 days before the smear. Doctors also do not recommend using vaginal suppositories, creams, or abandoning the douching procedure during this period. 3 hours before visiting the gynecologist, you should refrain from visiting the toilet.
The result of the analysis depends on the day of the monthly cycle on which the biomaterial was collected. Therefore, it is advisable to do a smear immediately after the end of bleeding, approximately on the 4th or 5th day of the new cycle.
How is a smear taken?
The procedure for collecting biomaterial to determine the degree of cleanliness of the vagina.
The material for research is taken using a sterile cotton swab, spatula or special brush from the vagina when the woman is located on the gynecological chair. The procedure is absolutely painless; discomfort is possible only in the case of an active inflammatory process or injury to the mucous lining.
Examination of smears for cervical cytology: interpretation
After collecting the biomaterial, it is applied to a glass slide. Then it is recorded if the glass is planned to be transferred to the laboratory in more than three hours. After the smear is sent to the laboratory, it is stained, dried and microscopically examined. Smear microscopy is performed by a clinical laboratory diagnostics physician.
Table of normal white blood cell count
The leukocyte count depends on the location where the scraping was made. For example, in a sample of biomaterial from the urethra, the normal number of white blood cells ranges from 0 to 10. Their concentration in the vagina can reach 15, and a smear from the cervical canal of a healthy woman should not show more than 30 white blood cells.
The table will help you find out in more detail how many leukocytes and other cells there should be, as well as the main types of representatives of the urogenital flora.
| Index | Vagina | Cervix | Urethra |
| White blood cell count | From 0 to 10-15 | From 0 to 30 | From 0 to 5-10 |
| Epithelium | No more than 10 | No more than 10 | No more than 10 |
| Key cells (vaginal epithelium with bacteria attached to it) | Not identified | Not identified | Not identified |
| Gonococci | Not identified | Not identified | Not identified |
| Trichomonas | Not identified | Not identified | Not identified |
| Other flora | Lactobacilli (Gram-positive Dederline bacilli) in moderate or large quantities | Not identified | Not identified |
| Candida | Not identified | Not identified | Not identified |
| Slime | Moderate or absent | Moderate or absent | Not identified |
Samples taken from a patient in a gynecology office are examined by a laboratory technician. Based on the results of the analysis, the gynecologist makes a diagnosis and, if necessary, prescribes therapy.
Experts distinguish 4 degrees of smear purity. The first is characterized by the absence or presence of several white blood cells in the field of view. A significant number of Dederlein rods are present, and an acidic reaction is detected.
In a smear of an intermediate type (second degree of purity), an acidic reaction of the environment and a predominance of lactic acid bacteria over other microbes are detected. The number of leukocytes can reach 15 (and in pregnant women 20) units. A woman with such a smear has no signs of inflammation.
In dysbiosis (third degree of purity), lactobacilli are absent or present in the biomaterial in insignificant quantities. The analysis shows the accumulation of gram-positive cocci, gram-negative rods, the number of leukocytes and epithelial cells exceeds the norm. The medium has a slightly acidic or alkaline reaction.
The development of vaginitis (with the fourth degree of purity) is judged by the presence of a large number of leukocytes and epithelium. The smear also contains pyogenic microbes; lactobacilli are absent. The reaction of the material under study is alkaline.
In a healthy woman, a smear normally corresponds to the first or second degree of purity.
What is found in a smear
To correctly understand the results of a smear analysis for the degree of purity, you need to understand what elements may be found in it:
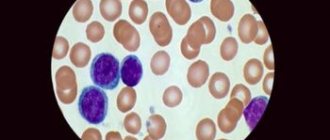
- Leukocytes. Normally, the vagina should contain up to 10 leukocytes per field of view. These cells are needed to protect against pathogenic microorganisms. An increase in the number of these cells indicates an active inflammatory process.
- Squamous epithelial cells in a smear. In a healthy state, a smear should contain from 5 to 10 epithelial cells. An increase in the content of epithelial cells indicates an inflammatory process, and a decrease is possible due to hormonal imbalance. In addition, the number of epithelial cells in a smear may vary depending on the phase of the menstrual cycle.
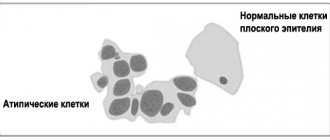
- Atypical epithelial cells. Their presence allows one to suspect an oncological process.
- Mucus in a smear on the flora should be in moderate quantities. An increased mass of mucus indicates either inflammation or non-compliance with the rules of personal hygiene and preparation for the study.
- Red blood cells. Single red blood cells may be found in the smear depending on the phase of the cycle. If their number is higher than normal, then this indicates inflammation, erosion or injury to the vaginal mucosa.
- Rod flora. A large number of Doderlein bacilli, or lactobacilli, is a necessary condition for the health of the female reproductive system.
- Coccal flora. Microorganisms that have a spherical shape. They can be opportunistic (staphylococci, streptococci) and pathogenic (gonococcus is a pathogen that causes gonorrhea).
- Fungi of the genus Candida. A conditional pathogen that, under certain conditions (deterioration of the functioning of the immune system), provokes candidiasis. Candidiasis often occurs with intensive antibiotic therapy.
- Gardnerellas are small sticks. A conditional pathogen, an increase in the number of which causes bacterial vaginosis.
- The key cells in the flora smear are epithelial cells, “glued together” either by Gardnerella or other microorganisms. Their appearance most often indicates bacterial vaginosis.
- Trichomonas. Pathogenic microorganisms that provoke specific inflammation - trichomoniasis.
Ultrasound of the cervix: methods and procedures during pregnancy
Also in the form of the results of the analysis for the degree of cleanliness of the vagina, you can find such a term as “detritus”. Detritus in a smear is exfoliated dead epithelial cells in a smear, an increase in the number of which confirms an active inflammatory process, most often vaginitis.
Does the indicator change with age?
The number of leukocytes in smears should not differ greatly by age. In little girls, young and older women, normal levels may vary only slightly.
The result of the analysis directly depends on the hormonal background. Therefore, often girls of puberty have an increased content of white blood cells in the smear. An increase in the number of protective cells above normal occurs if the genitals of a child or girl become infected with pathogens. This happens when the rules of personal hygiene are violated, using someone else’s towel, washcloth, or underwear.
Leukocytes in a stained smear
An abnormal phenomenon often accompanies a period of decline in reproductive function. Changes in hormonal balance cause dryness of the vaginal mucosa and injury to the walls of the organ due to itching. This also causes an increased number of white blood cells found in the smear.
After 50 years, many women's bodies produce more white blood cells than before. The analysis shows an excess of white blood cells by 1-2 units. Norms of leukocytes in blood and urine in women.
A significant excess of the norm of leukocytes in a smear in an elderly woman signals the presence of a problem. Additional examination and treatment is required.
In some women, over a long period, tests may show a higher number of protective bodies than normal. At the same time, other tests do not reveal any signs of pathological processes in women. Polymerase chain reaction and enzyme immunoassay of blood show normal values. This condition does not require drug therapy. But regular visits to the gynecologist and analysis of vaginal microflora are mandatory.
Enterobacter cloacae: norm and pathology
Many bacteria belong to the opportunistic flora. They can be located in almost all parts of the body, most often in the gastrointestinal tract. One of the representatives of such microorganisms is Enterobacter cloacae. These bacteria live together with a person constantly, and do not harm his condition in any way. Under the influence of unfavorable factors, they begin to multiply intensively, as a result of which they become pathogenic. Enterobacteriaceae are ubiquitous; they can live both in a free state (in rivers, wastewater, on the surface of plants) and inside the body of humans and animals. Enterobacter cloacae are saprophytes that live on the mucous membrane of the small and large intestines, in the distal parts of the digestive tract.
What are enterobacteria?
Enterobacteriaceae are gram-negative bacilli that are unable to form spores. They are facultative anaerobes, meaning they can survive without oxygen. Enterobacteriaceae are resistant to most disinfectants, as well as to many antibacterial drugs. These microorganisms are divided into many genera, some of which cause serious diseases. Enterobacter cloacae does not belong to the pathogenic flora, therefore, in the normal state of the body, they do not pose any harm. These bacteria become pathogenic when the body is severely weakened, so they are often called opportunistic infections. You can only become infected from a person or animal, through the fecal-oral or nutritional route (by eating infected meat, milk, eggs). In a hospital setting, enterobacteriaceae are also transmitted through the hands of medical personnel. This type of microorganism often causes nosocomial infections.
Enterobacter cloacae: symptoms of infection
Enterobacteriaceae most often cause disorders of the digestive tract, but can also parasitize other parts. Due to the fact that the genitourinary organs in women are in close proximity to the intestines, inflammatory processes caused by the microflora of the latter are often observed there. With severe weakness of the immune system, enterobacteria can multiply intensively in other parts of the body, for example in the pharynx. Thanks to this, they enter the respiratory tract and become one of the causative agents of nosocomial pneumonia, a serious condition that is difficult to treat. When enterobacteria enter the bloodstream, septicemia occurs - a disease as a result of which they parasitize all organs and systems. The most common symptoms of infection are abdominal pain, stool disorders, nausea, itching and burning in the genital area (more often in women), and increased body temperature to low-grade levels. In newborns and seriously ill patients, enterobacteria can cause meningitis, pyelonephritis, and septicemia.
Diagnosis of diseases caused by enterobacteria
It is possible to understand that a patient has an enterobacter infection using a number of diagnostic criteria. Firstly, such patients are most often severely weakened, take antibiotics for a long time or are hospitalized in a hospital for a long time. Taking into account these factors, as well as characteristic symptoms, special research methods are carried out. When isolating Enterobacter cloacae in feces, it is necessary to take into account that the intestine is the habitat of these microorganisms, so their small number does not indicate infection. The norm is 10*5; pathological conditions caused by enterobacteria are observed as this indicator increases. Increased levels of Enterobacter cloacae in the urine most often occur with cystitis, vaginitis, and vulvitis.
Treatment of enterobacter infections
Due to the fact that enterobacteriaceae cause disease only in weakened patients, it is first of all necessary to increase immunity, avoid unfavorable factors, and treat the underlying pathology. In addition, increased levels of Enterobacter cloacae may occur with long-term use of antibiotics. In this case, it is necessary to discontinue therapy. If this is not possible, it is recommended to use drugs that protect against intestinal dysbiosis. These include preparations containing lacto- and bifidobacteria. Also, do not forget about symptomatic therapy.
fb.ru
How long should you be during pregnancy?
A smear for leukocytes and microflora is given to women during pregnancy registration. The analysis is done at 30 weeks of gestation and shortly before the expected day of birth. Doctors monitor the results of the study in expectant mothers especially carefully.
The increased load on a woman’s body leads to a decrease in immune defense, as a result of which the quantitative composition of the microflora in women changes. Bacteria, viruses and pathogenic fungi quickly become active in such conditions.
A high level of leukocytes in pregnant women is often detected during infectious processes.
The most common reasons for exceeding the norm of leukocytes in expectant mothers are candidiasis (thrush), colpitis (vaginosis). Often the disorder occurs with genital infections:
- gonorrhea;
- syphilis;
- ureaplasmosis;
- genital herpes.
A high level of leukocytes is observed in women during the first 5 days after the birth of the baby. Afterwards, the white cell count should return to normal. If this does not happen, the protective cells significantly exceed the standard value - this is a reason to suspect a postpartum complication. It may be the development of infection inside the uterus, kidneys, or other urinary organs.
When are deviations from the norm possible?
During pregnancy, changes in the smear may be observed, however, the degree of vaginal cleanliness usually does not change if proper hygiene and doctor’s recommendations are observed.
Deviations of study parameters from normal values are possible in the following situations:
- Specific or nonspecific inflammation. The smear contains a lot of epithelium, leukocytes, the balance of the flora is most often disturbed: there are few lactobacilli, the flora is mixed or coccal, pathogens are detected. Inflammatory processes in which there is an imbalance of flora include vaginitis, vulvovaginitis, cervicitis, adnexitis, endometritis.
- Hormonal imbalance. Hormonal imbalance in the female body can also cause changes in the smear. The epithelium in the flora smear becomes smaller due to a lack of hormones. In a hyperfunctional state of the ovaries, mixed flora is recorded in the smear.
- Puberty and menopause. During these periods, a mixed, polymorphic flora is often found; during menopause it can be sparse. During menopause, there are fewer epithelial cells due to hormonal changes.
- Pregnancy. During the normal course of pregnancy, Doderlein rods become much more numerous - abundant flora in this case is necessary to protect against the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms. In addition, the number of epithelial cells in the smear increases. Tests are taken from pregnant women upon registration, as well as at 30 and 38 weeks of pregnancy.
Why are white cell levels elevated?
The reasons for detecting an abnormal white blood cell count are most often inflammatory processes:
- cervicitis (the process occurs inside the cervical canal);
- salpingo-oophoritis (ovaries and tubes);
- endometritis (the lining of the uterus suffers);
- vaginitis (intravaginal pathology);
- urethritis (inflammation affects the urinary tract).
Infections transmitted through sexual contact also cause an increase in white blood cells. These include:
- genital herpes;
- cytomegalovirus;
- Trichomonas;
- treponema pallidum;
- tuberculosis bacillus (Koch);
- mycoplasma, ureaplasma;
- gonococcus;
- chlamydia;
- fungi of the genus Candida, actinomycetes.
Exceeding the norm is detected during oncological processes in the organs of the reproductive system, dysbiosis of the vagina, intestines. Also, high white blood cells in the smear appear during exacerbation of the allergic process, endocrine pathologies, weakening of local and general immune defenses, stress, and physical fatigue. The disorder is detected in women after a miscarriage.
Enterococcus faecalis what is it: symptoms and treatment
All representatives of microflora are divided into pathogenic and conditionally pathogenic. The first type of substances are viruses and bacteria, whose entry into the body leads to the development of serious diseases. Opportunistic microorganisms live in the body of each of us, but do not pose a danger until they begin to actively reproduce. One of these representatives is the bacteria enterococcus faecalis.
general description
Enterococcus (enterococcus) is a family of bacteria belonging to aerobic and anaerobic microorganisms. That is, these are strains that have increased viability - they are not afraid of the acidic environment of the mucous membrane of the genitourinary organs, as well as oxygen. Enterococci are one of the most common strains: they number more than 15 species, but these are only those that have been studied. Among these microbes there are quite safe ones that have found application in the pharmaceutical and food industries. But there are those that provoke the occurrence of serious diseases. For a long time, enterococci belonged to the family of class D streptococci (streptococcus), but based on a different DNA structure they were separated into a separate class.
IMPORTANT! As medical statistics show, the enterococcal family “loves” women more, but even in the body of the stronger sex they can cause serious diseases, especially in the urethra and other parts of the urinary system.
Enterococci are representatives of opportunistic microflora present in the intestines of both adults and children, from where they spread throughout the body. If the patient is healthy, then the sticks help the gastrointestinal tract function properly, being responsible for the digestive processes. Their number is limited, since the vital processes of these cells are controlled by the body’s defenses: the immune system simply does not allow them to increase their colonies, protecting a person from the development of diseases.
Along with fecal enterococcus, the human intestines also contain a beneficial anaerobe - enterococcus faecium (enterococcus faecium). It also belonged to the streptococcal family, but unlike fecal faecium, even with a weakened immune system, it cannot cause serious inflammation.
The danger of enterococcus fecalis is that it can multiply not only in the organs of the digestive system, but also in other components of the human body. This leads to the formation of dangerous ailments, and if left untreated, to serious complications. Enterococcus fecalis is transformed from an opportunistic microorganism into a pathogenic one if the patient’s immunity is weakened by internal or external factors. A classic urological analysis - bacterial culture for the microflora of the urethra - can detect the presence of fecal enterococcus in men. If its indicators exceed the permissible norm (10 to the fifth power), therapy should be started immediately.
Specific characteristics of cocci
Enterococci of the faecalis class are highly resistant to antibiotics. As soon as a patient begins to take antibiotics intended to fight a serious infection, the potent components begin to kill the “beneficial” microflora. Since enterococci have increased sensitivity to such medications, the rods begin to actively multiply, taking the place of dead substances.
Also, these sticks are resistant to temperature changes and can withstand even critical temperatures. This makes them related to microorganisms of the enterobacteriaceae family - a group of bacteria that includes such dangerous representatives as Escherichia coli, plague coli, salmonella and others.
All rods can live both in environmental conditions and in the human body, and under certain conditions they provoke the appearance of serious diseases. They can be transmitted from person to person or animal, where they live as parasites.
Manifestations of diseases caused by cocci
Inflammations caused by cocci affect not only parts of the digestive system, but also the urinary organs. Moreover, for a very long time they practically do not manifest themselves at all, affecting more and more of its components: the urethra, prostate gland, bladder, testes. Symptoms become more pronounced only when the immune system is severely weakened.
What is it - manifestations of the inflammatory process provoked by enterococcus faecalis? This:
- acute pain in the urethra and groin area;
- painful bowel movements;
- increased urge to go to the restroom;
- erectile dysfunction and difficulty ejaculating;
- change in urine color;
- presence of white or green discharge;
- decreased potency and libido.
There is also a burning sensation when urinating, a general deterioration in health: weakness, fever, psycho-emotional health disorders. With a sluggish course of the pathology, enterococcus faecalis is usually discovered in a smear in men by chance - during a routine examination or taking a smear to diagnose other diseases. With a slight increase in titers, serious medical medications are not required; procedures aimed at strengthening the defenses are sufficient.
The presence of enterococcus faecalis in women is also determined by taking a smear from the vagina or using urine culture. For representatives of the fairer sex, enterococcus sp is more dangerous, as it contributes to the transition of genitourinary diseases to a chronic form.
But for a baby carried by a gram-positive mother, these substances are completely harmless: they do not in any way affect the development and formation of the fetus. Therefore, the elimination of genitourinary diseases is usually carried out after childbirth.
Reasons for the increase in colonies of microorganisms
The main reason causing an increase in the number of enterococcus spp in tests is the transmission of infectious diseases. Also included in the list of factors contributing to increased levels are:
- avitaminosis;
- unbalanced diet;
- autoimmune diseases;
- endocrine pathologies;
- decreased local immunity.
An increase in the concentration of enterococcus spp (in men) or sp (in women) often occurs after instrumental examinations of the urethra, which damage its mucosa or as a result of violations of personal hygiene rules.
Treatment and prevention
Therapy always begins with diagnosing the patient and establishing the correct diagnosis. The examination consists of a number of diagnostic procedures, since the symptoms provoked by this strain are similar to many other infectious diseases.
The list of diagnostics includes:
- bacterial culture of the urethral flora from the urethra;
- culture with collection of prostate secretions;
- bacteriuria of fresh urine.
Also, some clinics offer patients a spermogram to assess the composition of sperm and sperm activity. This will exclude or confirm the presence of prostatitis, which is also a consequence of a bacterial infection.
It will take quite a long time to be treated for this disease, since the anaerobe is very sensitive to most antibiotics. Only a qualified specialist with experience in dealing with such diseases can prescribe effective therapy.
IMPORTANT! If the treatment is chosen incorrectly, the disease may become chronic, that is, it will appear again and again. The only treatment option in this case will be to transfer the pathology into a form of stable remission.
The infection can be cured in the following ways:
- Antibiotics. In addition to prescribing tetracyclines, the most effective means against these substances, the use of a special group of medications – bacteriophages – will be required. These pharmaceutical products are selected individually based on the strain of bacteria detected.
- Topical medications: suppositories, gels, ointments, antiseptic solutions, whose task is to restore the healthy microflora of internal organs. Such medications help regenerate damaged mucous membranes, improve blood supply to the pelvic organs, and reduce the risk of complications.
- Immunomodulatory drugs: vitamins and minerals that help strengthen the body's defenses.
As an addition to drug treatment, the patient is prescribed physiotherapeutic procedures, physical therapy, massage, and dietary nutrition.
#
annahelp.ru
If the number of leukocytes is reduced
A decrease in the number of leukocytes or their complete absence in the smear is not considered a deviation from the norm. If a woman does not use an intrauterine device to protect against an unplanned pregnancy, adheres to good hygiene and is not sexually active, white blood cells will not be detected during the analysis. However, there are other factors that lead to a general decrease in the number of leukocytes. A decrease in the level of these cells in the vaginal flora may indicate the presence of:
- diseases of a viral nature;
- general exhaustion of the body;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- pathologies of the endocrine system.
About the diagnostic method
The collection of biomaterial for research is carried out by a doctor in a special gynecological chair using sterile instruments. After inserting the gynecological speculum, biomaterial is taken from the posterior wall of the vagina (V) for examination using a cytobrush, from the surface of the cervix (C) with an Eyre spatula, and from the urethra (U) with a Volkmann spoon.
The level of leukocytes is determined by microscopy. In the laboratory, a Gram-stained and fixed (killed cells) smear is examined under a microscope to count the number of opportunistic bacteria and white blood cells. In addition, the presence of atypical cells characteristic of cancer pathology is visually determined.
The turnaround time for the analysis depends on the workload of the laboratory, but on average does not exceed 1 day, excluding the day of collection of the biomaterial.
How to prepare?
Preparation for taking biomaterial for research includes the following rules:
- restriction of sexual life for 2-3 days;
- for 2 days, the use of vaginal medications, as well as douching, is excluded;
- 2-3 hours of abstaining from urination;
- At least 2 days must pass from the end of menstruation. The preferred time for research is before the start of menstruation;
- Hygiene procedures are carried out in the evening and exclude the use of soap and gel.
If an increased level of leukocytes is detected in the smear, you should consult a doctor:
- Gynecologist.
- Dermatovenerologist.
- Infectious disease specialist.
The doctor chooses the treatment method based on laboratory tests. To establish an accurate diagnosis, additional diagnostics are prescribed.
The following types of diagnostic procedures are most often prescribed:
- sowing on flora;
- flora smear;
- ELISA (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay);
- test for antibodies in the blood;
- biopsy;
- PCR (polymerase chain reaction);
- CBC (complete blood count);
- OAM (general urinalysis);
- Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity.
Despite the high information content of microflora analysis, it does not allow diagnosing:
- Pregnancy. To diagnose it, it is necessary to take a blood test for hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin) and perform an ultrasound of the pelvic organs.
- Viral infections (HIV, papillomavirus, herpes, chlamydia, ureaplasmosis, mycoplasmosis). An HIV test is performed using venous blood ELISA; other infections are performed using a urogenital smear using the PCR method.
- Cancerous and precancerous conditions of the studied tissues. Assessment of the presence of atypical or cancer cells is carried out through a cytological examination (oncocytology or PAP (PAP) test), as well as examination using a colposcope.
If a woman has an increase in the number of leukocytes in a smear, it is necessary to establish the cause that provoked this phenomenon. Typically, an increase in the number of white blood cells is accompanied by an increase in opportunistic microflora, which allows one to immediately suspect a particular disease. However, in practice, only leukocytes can increase, and specific pathogens are absent.
In this situation, the gynecologist will direct the woman to take a smear test again, choosing the most successful day of the menstrual cycle and recommending that she properly prepare for the test. If an increase in the number of white blood cells is observed in a repeat smear, an extended examination is carried out. Can be done:
- PCR for sexually transmitted infections. The method allows you to identify hidden diseases that may not manifest themselves clinically, but can lead to infertility.
- Colposcopy. The study is an examination of the cervix under multiple magnification. The method allows you to detect leukoplakia, dysplasia or cancer at the initial stage.
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs. Various tumor formations can provoke an increase in the number of leukocytes, which can be diagnosed using ultrasound.
Based on the data obtained, the doctor can refer the patient to related specialists. So, if a woman is overweight, has thyroid disease or diabetes, she will need to consult an endocrinologist. If diseases of the urinary system are detected, they are referred to a nephrologist.
Therapy directly depends on the cause that provoked the increase in the number of leukocytes. Most often, their growth occurs as a result of inflammation. In this situation, local or general treatment can be carried out. The first category includes medicinal douching. The course is short. Its duration usually does not exceed 4-5 days.
High content after childbirth
Leukocytes instantly react to the slightest deviations or changes in the functioning of the body. Therefore, their levels often increase for physiological reasons. This also includes the postpartum period.
During childbirth, a woman loses a lot of blood.
To prevent complications, immune white cells are prepared in advance for such a situation and accumulate in large numbers in the uterine area.
This is associated with an increase in the number of their indicators in a smear after childbirth.
Their number increases during the onset of labor and during the recovery period. The indicators return to normal 4-5 days after birth.
If the elevated level of immune cells lasts more than 5 days and has serious deviations from the norm, this indicates the development of complications after childbirth and inflammation in the uterine cavity, kidneys or urinary system.
In such cases, you should immediately consult a doctor.
How to take a smear from the cervix
There are 4 types of cervical smears:
- flora research;
- sterility examination;
- testing for latent infections using polymerase chain reaction;
- Pap test for cytology.
A flora smear from the cervix reveals not only pathogenic bacteria, but also pathogenic epithelial cells.
The procedure is carried out using a Cusco mirror. This mirror is not in the usual sense of the word. It is more like transparent forceps that push apart the walls of the vagina, allowing access to the cervix. Then a scraping is made with a spatula or cytobrush, by which the condition of the epithelial cells is assessed.
Microflora tests during pregnancy
Pregnant women undergo flora tests somewhat more often than “ordinary” women. This can be explained by a simple fear of infection or inflammation, because carrying a fetus significantly reduces the immunity of the expectant mother, which means it can lead to the development of diseases or inflammation that is not specific to the pre-pregnancy state.
The collection of the mucous membrane is carried out in exactly the same way, with the exception of the collection from the cervical canal - it is carried out more carefully so as not to provoke a miscarriage in the pregnant woman.
Why carry out such analyzes?
Surprisingly, even if a woman previously did not have any adverse symptoms, sexually transmitted infectious diseases are often detected with the onset of pregnancy. Here they highlight:
- gonorrhea;
- syphilis;
- ureaplasmosis;
- microplasmosis;
- genital herpes and other diseases.
Timely detection of present infections will allow treatment to begin on time, and, therefore, protect the child from possible infection and the development of various pathologies. During pregnancy, women produce progesterone, which can significantly affect the production of white blood cells. That is why during pregnancy up to 20 units are allowed. Its excess indicates the onset of inflammation, which often leads to miscarriage in the early stages and premature birth in the third trimester.
Unfavorable test results indicate the presence of an inflammatory or infectious disease, and this may not always be associated with the genitals. For example, in pregnant women, elevated white blood cells can help detect malaria, typhus and other similar diseases. To clarify the diagnosis, doctors prescribe additional examinations for women - DNA diagnostics, bacteriological culture and other additional studies.
A woman should be attentive to her health, including the condition of her genital organs, especially if she plans to conceive a child. Infections and bacteria often become provocateurs for the development of cancer, so at the first unpleasant symptoms you should immediately consult a doctor.
How to prepare for the test and when it is needed
The doctor takes a smear from the patient on the gynecological chair (regardless of whether she is pregnant or not) using a special brush or a sterile Volkmann spoon. It doesn't hurt at all and is very fast.
It is technically possible to achieve a good, even perfect smear if you sanitize the vagina with chlorhexidine or miramistin, for example. But what's the point?
To get a reliable smear result, 48 hours before taking it you cannot:
- douche;
- have sex;
- use any vaginal hygiene products, intimate deodorants, or medications unless they have been prescribed by a doctor;
- do an ultrasound using a vaginal probe;
- undergo colposcopy.
- Before visiting a gynecologist or laboratory, 3 hours before visiting a gynecologist, you should not urinate.
You need to take smears outside of menstrual bleeding.
Even if there is just a “spot” on the last day of your period, it is better to postpone the study, since the result will probably be bad - a large number of leukocytes will be detected. There are no prohibitions regarding drinking alcohol.
Is it possible to take a smear while taking antibiotics or immediately after treatment?
It is not advisable to do this within 10 days after using topical drugs (vaginal) and one month after taking antibacterial agents orally.
Microscopic examination is prescribed:
- as planned when visiting a gynecologist;
- upon admission to the gynecological hospital;
- before IVF;
- during pregnancy (especially if smears are often bad);
- if there are complaints: unusual discharge, itching, pelvic pain, etc.
Back to contents
Full transcript of flora smear results
How to understand the results?
A breakdown of the smear norms for flora in women is given in tables that list more than 10 types of bacteria that are found in the secretion discharged from the vagina:
- Doderlein's rods have another name - lactobacilli. They are the main component of the intravaginal flora and are responsible for regulating its acidity. They destroy most of the live sperm that enter the vagina. Normally, a smear for the flora of Doderlein bacilli should contain 107 - 109 CFU/ml.
- Bifidobacteria - protect the walls of the vagina and cervix from the penetration of pathogenic microbes. They do not form spores and suppress decay processes. Normally, bifidobacteria in a smear should be 103 – 107 CFU/ml.
- Propionibacteria - produce propionic and acetic acid, die when using antibiotics and at very high body temperatures. They have strong immunomodulatory properties. Normally, vaginal secretions should contain no more than 104 CFU/ml.
- Clostridia are bacteria that are mainly found in the vagina and gastrointestinal tract. In large quantities they cause intoxication and local damage to the mucous membranes of the genital tract. High levels of these bacteria cause the development of tissue necrosis. Normally, clostridia in a smear for flora in women should not exceed 104 CFU/ml.
- Mobiluncus - a large number of these microorganisms causes the appearance of bacterial vaginosis in the vagina. If the level of mobiluncus is not corrected for a long time, this can lead to a chronic inflammatory process in the pelvis. Normally, these bacteria should contain up to 104 CFU/ml.
- Peptostreptococci - help maintain an acidic environment in the vagina. In large quantities they cause fermentation and rotting processes. There should be 103 - 104 CFU/ml in the smear.
- Corynebacteria are the causative agents of diphtheria. It is important that these microorganisms do not reproduce uncontrolledly, so normally their number should not exceed 105 CFU/ml.
- Staphylococci - exceeding the levels of these bacteria causes severe inflammatory processes that affect not only the vagina, but also the cervix, the uterus itself, and rise up the urethra to the bladder. Their normal amount varies from 103 – 104 CFU/ml.
- Streptococci – when immunity decreases, colonies of bacteria begin to multiply uncontrollably. The consequence of this is purulent lesions of the mucous membranes and severe intoxication of the body. Streptococci are able to penetrate the placenta to the fetus. Normally, they should be contained in the vagina no more than 105 CFU/ml.
- Enterobacteriaceae are mainly present in the intestines, but in an amount of 103 - 104 CFU/ml they should also be present in the intravaginal secretion. An increased number of enterobacteria causes urethritis, cystitis, and colpitis.
- Bacteroides – a large number of bacteria leads to inflammation. A reduced number of them, on the contrary, leads to dysbacteriosis. The norm should vary between 103 – 104 CFU/ml.
- Leukocytes - perform a protective function, are not microorganisms. In a smear for flora, the norm of leukocytes in women is up to 30 cells in the field of view of the researcher.
- Prevotella - an increased number of these bacteria causes inflammation, but they are extremely difficult to treat with penicillin, since bacteria of this genus are highly resistant to it. Normally, prevotella are up to 104 CFU/ml.
- Porphyromonas - uncontrolled proliferation of bacteria contributes to the appearance of a putrid odor. Recent studies in the USA have determined the relationship between the occurrence of malignant neoplasms and the increased content of porphyromonas in the secretion. The normal value of bacterial colonies is up to 103 CFU/ml.
- Veillonella - promote the production of propionic and acetic acid. Certain types of these bacteria cause acute inflammatory diseases of the female genital tract. Normal values are up to 103 CFU/ml.
- Fusobacteria - with a persistent decrease in immunity causes purulent tissue lesions, although at a rate of up to 103 CFU/ml they are present in the secretion secreted by the cervix and vaginal walls.
- Mycoplasmas are bacteria that are responsible for the development of severe infections in the organs of the reproductive system. They can penetrate the placenta and cause pathologies in the structure of the fetus. Normally, the smear should contain up to 103 CFU/ml.
- Ureaplasma - causes ureaplasmosis - a disease that occurs when the bacterial balance in the vagina is disturbed. The stronger this imbalance, the faster ureaplasma multiplies. Their normal amount should not exceed 103 CFU/ml.
- Candida are fungi that cause thrush. Should not exceed 104 CFU/ml. If the balance is disturbed, the patient develops signs of candidiasis.
It should be noted that leukocytes in a smear for flora in women show an increase in any type of pathogenic bacteria. The abbreviation CFU is Colony Forming Unit.
What diseases can the test detect?
A smear on the flora is quite simple to do, and, at the same time, it can be used to determine the presence of a whole range of diseases:
- Colpitis
- Vaginitis
- Thrush
- Cervicitis
- Endocervicitis
- STDs (particularly chlamydia and gonorrhea)
- Urethritis (in some cases)
A smear examination will not only show which bacteria caused the development of the inflammatory process, but will also determine what medications the patient should be treated with. Prescribing treatment at random, without knowing the results of a microflora study, can aggravate the course of the disease, since certain types of bacteria do not respond to treatment with penicillin drugs.
Degrees of vaginal cleanliness
In accordance with the results of a smear test for flora, the gynecologist determines the degree of cleanliness of the patient’s vagina:
- I degree – the vaginal environment is defined as acidic. The state of the microflora is considered good, leukocytes do not exceed the value of 10. Pathogenic microorganisms are minimal. Most often, this degree of purity is found in girls and girls who are not sexually active.
- II degree – the vaginal environment is defined as slightly acidic. This state of microflora is typical for a healthy woman who is sexually active and carefully monitors intimate hygiene and protection from STDs.
- III degree – the vaginal environment is defined as neutral. There are more than 10 leukocytes, there is a moderate number of pathogenic microorganisms. When such microflora is detected, the doctor usually diagnoses colpitis and prescribes treatment depending on the predominant type of harmful microorganisms.
- IV degree – the vaginal environment is defined as alkaline. This means that a woman’s resistance to infections is extremely low, and vaginal secretions contain many pathogenic microorganisms. The inflammatory process is pronounced and requires treatment not only with oral medications, but also with suppositories, baths and medicinal tampons.
Urine examination
To determine the content of Enterobacter cloacae in urine, a urine culture test is prescribed. This study is indicated in the following cases:
- during pregnancy;
- if bacteria or fungi are detected in a general urine test;
- for diabetes mellitus;
- with signs of inflammation in the excretory organs;
- for chronic cystitis, urethritis and pyelonephritis.
7 days before the test, you need to exclude spicy, salty and fatty foods, as well as alcoholic beverages from your diet. 2 weeks before the test, you must stop taking antibiotics.
Before collecting urine, you should thoroughly wash your external genitalia without using antibacterial soap. Urine is collected in the morning in a pharmaceutical container and delivered to the laboratory within 2 hours.
Then the urine is cultured on nutrient media. After this, the number of bacteria in 1 ml of urine is determined.
Interpretation of analyzes
As soon as a woman has received tests to determine the microflora of the genital organs, she is faced with a huge number of designations, symbols and numbers. Only a specialist can disassemble them, but with a detailed examination you can do it yourself.
So, first, determine the indicators for the smear sampling site being studied. The letters are highlighted here:
- V – vagina;
- C – cervical canal of the cervix;
- U – urethra.
The designations identify the first letter of the place name in Latin.
Next, you should pay attention to the main indicators:
- L - leukocytes - are present in a healthy state and during the development of pathology. Their purpose is to protect the woman’s genitals from the penetration of bacteria. In normal condition, there should be no more than 10 in the vagina, no more than 30 in the cervix and no more than 5 in the urethra. When the indicators increase, an assumption is made about the presence of an inflammatory process.
- Ep - epithelium - mucosal cells that must be present in a healthy and sick state. The absence of epithelium indicates hormonal imbalances in women. Epithelium indicators for all mucosal sampling sites should not exceed the limit of 5-10 units. If it increases, it indicates the presence of inflammation.
- Mucus is necessarily present in small quantities in the vagina and cervical canal of the cervix. An increase or presence at the sampling site in the urethra indicates the presence of inflammation.
- General indicators of microflora - Dederlein bacilli must be present in large quantities in the vagina. These rods are the main defenders of a woman’s microflora, which have another name – lactobacilli.
When indicators increase, the laboratory records their excess - the usual “+” signs are placed next to each indicator. Their definition appears to be:
- «+“- a small amount indicates an excess, but without the development of inflammation;
- «++"- a moderate increase indicates the onset of the inflammatory process;
- «+++“—increased amount—inflammation develops and progresses;
- «++++“- a copious amount can signal the presence of a serious disease of the genital organs, up to advanced stages or an oncological nature.
This is a simplified form of deciphering the results. The received documents contain many more indicators.
Normal values of urethral smears
When taking a smear from the urethra, the normal smear is as follows:
| Number of epithelial cells | Leukocytes | Red blood cells | Candida | Slime | Flora composition |
| to 10 | up to 5 | up to 2 | No | No | in small quantities Staphylococcus aureus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Neisseria |
- Normally, 95% of the urethral microflora should be lactobacilli. If opportunistic microflora dominates, this indicates a weakened immune system or diseases of the pelvic organs.
- A large amount of squamous epithelium indicates previous inflammatory diseases (cystitis, kidney disease).
- Red blood cells indicate severe swelling caused by the inflammatory process, as well as damage to the urethra.
- White blood cells are higher than normal during inflammation caused by hypothermia, decreased immunity, or infection.
- Yeast, in particular candida, is a consequence of the transfer of infection from the vagina when the disease reaches a serious form. Normally, there should be no yeast in the urethra. As well as mucus, the appearance of which in the urethra indicates infection.
To find out the causative agent of the infection, a bacterial culture is taken from the patient - a laboratory test that allows you to find a competent antibiotic to which there is good sensitivity.
Degree of vaginal cleanliness
The result of a flora study characterizes the degree of purity of the vagina, which is expressed in four states.
The first degree is a moderate rate of leukocytes in the smear, moderate levels of epithelium and mucus secretion. This degree is characterized by the absence of pathogenic and conditionally pathogenic bioenvironment, the presence of a sufficient number of lactobacilli. In practice, this condition of the vaginal environment is very rare.
The second degree is characterized by the presence of yeasts and cocci. This indicates a decrease in local immunity and the risk of developing inflammatory processes. This state of the vaginal environment is most common among subjects.
The third degree is characterized by an increase in the number of leukocytes, which indicates the occurrence of pathological processes. The composition of the microflora in this case is represented by yeast fungi, cocci and a small amount of lactobacilli. The woman needs active treatment.
The fourth degree is characterized by a large number of leukocytes along with a pathological bioenvironment and the absence of lactobacilli. This is an extremely dangerous condition that requires immediate treatment.
Proper preparation for a smear test
Like most diagnostic tests in medicine, a flora smear requires preparation. When going to the gynecologist, a woman should remember that the test result will be reliable only if the following recommendations are followed:
- maintain sexual rest for at least 2 days before donating the biomaterial;
- stop using lubricants, vaginal suppositories, creams on the eve of the study;
- do not wash your face using gels or other intimate hygiene products;
- refrain from taking a test after a course of antibiotics (at least 10 days);
- do not urinate less than 2 hours before visiting a gynecologist;
- Do not get tested during menstruation.
Intimacy, any topical agents, antibiotics distort data about the real state of the microbial biocenosis of the genitourinary system in a woman.
During urination, diagnostically significant objects of study are washed away: cellular elements, microorganisms, which also changes the overall picture. Menstruation makes it more difficult to obtain material for diagnosis - it will be “contaminated” with a large number of red blood cells.
Indications for taking a smear
A smear in women involves taking biomaterial not only from the vaginal mucosa. Samples for analysis are also taken from the urethra and cervix.
After the start of sexual activity, every woman should undergo this diagnostic procedure regularly: at least once a year. In addition to preventive examinations, a smear should also be taken during pregnancy. If there are no alarming symptoms, the expectant mother will have to undergo this procedure twice: at the very beginning of pregnancy when registering and in the third trimester, after 30 weeks.
However, a good reason to undergo a smear test is if any woman, either pregnant or not, has the following symptoms:
- change in color and consistency of discharge;
- the appearance of discomfort when urinating;
- itching in the groin area;
- unpleasant odor of discharge;
- burning sensation in the vagina;
- abdominal pain at rest or during intimacy.
In addition, it should be remembered that prolonged treatment with antibiotics can negatively affect the vaginal microflora: cause the death of beneficial bacteria, which will be replaced by opportunistic inhabitants. Against this background, candidiasis and bacterial vaginosis often develop and can be diagnosed using a smear on the flora. That is why it is advisable to take such an analysis after completing a course of antibiotic therapy.
Tags: analysis, pregnancy
- Green discharge in women - causes and treatment, medications
- Pain when urinating in women - causes...
- Causes of frequent urge to urinate in women and men
- Hormonal imbalance in women - causes, symptoms and...
- Thrush in women - causes, first signs, photos,...
- Vitamins - importance for the body, norm and violations...
Interpretation of the results of gynecological smear tests. Norm
| Index | From the vagina | Their urethra | From the cervix |
| Lactobacilli | Dederlein sticks | No | No |
| Number of rod flora | from + to ++++ | from + to ++++ | from + to ++++ |
| Candida | up to 104 CFU/ml | absent | absent |
| Flat epithelium | 5-10 | 5-10 | 5-10 |
| Leukocytes | 0-10 | 0-5 | 0-30 |
| Red blood cells | 0-2 | 0-2 | 0-2 |
| Slime | moderate amount | absent | moderate amount |
| Gonococcus Gn | absent | absent | absent |
| Trichomonas Trich | absent | absent | absent |
| Key cells | none | none | none |
Symptoms of increase
Signs indicating an increase in the level of leukocytes and the development of an inflammatory process in the urinary system:
- painful urination;
- the appearance of a false urge to urinate;
- discharge of an unusual nature;
- pungent odor of genital discharge;
- burning and itching sensation inside the genitals;
- failure of the menstrual cycle;
- problems with conception;
- discomfort during sexual intercourse.
The manifestation of such symptoms is a reason to take a smear on the flora and check the condition.
The inflammatory process can occur without pronounced symptoms. It is important to listen to the slightest deviations.
Find out what the norm of ESR in the blood of women should be! Study the table of indicators for ladies of different ages.
You will learn about the causes of high bilirubin in the blood in women, and what diseases can be discussed with elevated levels in this text.
What to do if a woman's platelet count is below normal? We will tell you about the functions of these cells and the features of treating abnormalities here.
The cause of elevated leukocytes in a smear in women
An infection or inflammatory process in the genitourinary organs is always accompanied by an increase in leukocytes in a woman’s smear. The reason for the increase in their level may be hidden in various diseases:
- inflammation - appendages (adnexitis), uterine mucosa (endometritis), urethra (urethritis), cervical canal (cervicitis), vagina (colpitis);
- benign and malignant tumor formations of the genitourinary area;
- STDs – syphilis, trichomoniasis, gonorrhea, chlamydia or others;
- dysbacteriosis – vagina or intestines;
- systemic diseases;
- hormonal imbalance.
Deviations from the norm in the analysis of leukocytes can be associated with frequent stress, chronic fatigue, long-term use of antibiotics and other medications.
Sometimes active sexual life leads to a moderate increase in white blood cells in a smear - up to 25 cells.
Microflora smear: what every woman needs to know?
The procedure for collecting a biological sample is painless. The doctor inserts a speculum with a central fixation, which allows you to expand the vagina to examine the surface of the cervix. The material is taken from the wall of the genital organs with a special brush or cotton swab.
Before going to the “women’s doctor”, you must follow certain rules that increase the reliability and information content of the analysis:
- do not enter into intimate relationships for 2-3 days;
- Douching is prohibited;
- It is not recommended to take a bath on the eve of a doctor’s visit;
- when carrying out hygienic intimate procedures, use special non-drying soap;
- During menstruation, visiting a gynecologist is not recommended; it is best to take this test immediately after it stops;
- Do not empty your bladder for at least 2-3 hours.
If a woman is taking any medications, she should inform her doctor. Therapy with certain drugs (for example, antibiotics) may distort the results of the study.