Hepatitis B is a viral inflammation of the liver caused by the hepatitis B virus. In most cases, the disease has a favorable prognosis. With an adequate response of the patient’s immune system, the pathology occurs in an acute form and is characterized by vivid symptoms. Within a month, the symptoms of the process disappear, then a complete cure occurs.
In 10% of cases, the disease becomes chronic, initially characterized by a mild clinical picture. It is this condition that is most dangerous for humans and requires early diagnosis and selection of a comprehensive treatment regimen. How to treat hepatitis B and what new hepatologists can offer to fully restore the patient’s body is discussed in the article.
Classification of the disease
The first signs of hepatitis B are different for everyone. First you need to identify the classification:
- Lightning fast . It is the most dangerous, since a person can experience cerebral edema and coma within a few hours. Unfortunately, this category is almost always accompanied by a tragic outcome. Death occurs in a short period of time.
- Spicy . This form involves several stages of the disease: first, the first symptoms of hepatitis B are expressed, then the skin becomes yellow. The last stage is liver failure. Acute hepatitis B symptoms: loss of appetite, malaise, fever, nausea, vomiting, development of jaundice.
- Chronic . The chronic form is acquired after 1-6 months since the virus entered the body. This period is called incubation. Symptoms of chronic hepatitis B: fatigue, malaise, yellow eyes, development of hepatocellular carcinoma. At the first symptoms of chronic hepatitis B, you should immediately consult a specialist.
Consequences and complications
The most favorable outcome is for acute hepatitis B. The disease is accompanied by symptoms, is detected in a timely manner, the patient is prescribed medications and is provided with rest. In people with strong immunity, the disease can go away on its own; the body can cope on its own.
In the absence of treatment or low resistance of the body, the pathology becomes chronic, which is difficult to treat . The patient is forced to see a doctor for many years. Often this causes the development of liver cirrhosis or liver failure.
There is also hepatitis B virus carriage. In this case, the body resists, preventing the development of the disease. But the immune system is weak enough to get rid of the virus completely. The prognosis is this: either the body will cope with the pathogen, or the virus will win and the development of one of the forms of hepatitis will follow.
Viral hepatitis requires treatment, and it is better if it is under the supervision of a doctor. Even after recovery for several months, poor test results are possible. If the treatment regimen and diet are not followed, viral hepatitis progresses and complications develop, including oncology and death.
Hepatitis B, what kind of disease is it, symptoms and development of the disease
Hepatitis can be contracted directly by having direct contact with a carrier of the virus. The danger is that signs of hepatitis B appear late . The infected person may not suspect for a long time that he is sick and is in his usual way of life.
However, if you undergo a laboratory examination in a timely manner and the virus is detected, the chance of recovery is one hundred percent .
The virus negatively affects not only the liver, but also other vital organs. The liver contains microcellular levels that contain hepatitis and spread throughout the body.
There are 2 stages of symptoms:
- Pronounced form.
- Asymptomatic. This is due to the fact that there are practically no nerve endings in the liver.
The chronic stage is accompanied by the development of cirrhosis and cancer.
The first signs of hepatitis B in men are slightly different from the signs of hepatitis B in women. This is due to the fact that women have higher immunity and are more susceptible to diseases.
What to do after infection?
The causative agent of hepatitis B is contained in the biological fluids of a carrier of the virus or a sick person. The largest amount is found in the blood, secretions of the salivary glands and seminal fluid. If you suddenly come into contact with an infected person, you must immediately contact a medical facility to prevent infection.
It should be remembered that the virus is transmitted in the following ways:
- Parenteral - during the transfusion of infected blood or its individual components, during manipulations with non-sterile instruments, during the use of one syringe by drug addicts.
- Vertical - from mother to baby during the last trimester of pregnancy, during the passage of the child through the birth canal.
- Sexual – in the presence of macerations and microcracks in the genital area, but subject to high aggressiveness of the virus.
If a person suddenly realizes that he has had contact with a sick person, he should contact a medical facility within the first 12 hours from the moment of the injection or sexual intercourse. In a hospital setting, a specific immunoglobulin will be administered, which will strengthen the body’s defense response, and then vaccination against hepatitis B will be carried out.
The first vaccination against hepatitis B is carried out on the first day of the baby’s life.
You should definitely monitor your own condition and monitor the appearance of hepatitis symptoms during the first 4 months after such an incident. Usually this period is enough for liver inflammation to make itself felt. In case the person was still infected. He will develop weakness, headache, pain in muscles and joints, and hyperthermia. Later, yellowness of the skin and sclera, skin rash, itching, soreness and heaviness in the right hypochondrium will appear.
Particular symptoms in women, men and children
The first and accompanying signs of hepatitis B in women and men are identical.
- Women may experience uterine bleeding , as well as a prolonged period of the menstrual cycle. These symptoms of hepatitis B in women occur due to changes in female hormones.
- Symptoms of hepatitis B are more pronounced in men. There are cases when the stage reaches alcoholic cirrhosis of the liver. Also, the first sign of hepatitis B in men is breast enlargement .
- The signs of hepatitis B in children are the same as in adults. But given that children have developing bodies and weak immunity, the first signs of hepatitis B in children can easily be confused with other diseases.
Features of HCV
The disease is caused by an RNA virus of the flavivirus family. The pathogen is not stable in the external environment, but has a high degree of mutation. To date, 11 genotypes with different subtypes have been registered. Essentially, the virus is constantly genetically mutating within one organism, creating new quasi-types. This is precisely where its main danger lies.
Due to the high level of heterogeneity of the pathogen genome, the immune system does not have time to recognize and attack it. The acute form occurs in no more than 20% of patients, but even in this case it is not easy to diagnose the disease without testing, since the symptoms are similar to influenza or ARVI.
Self-healing rarely occurs, so the pathology takes a chronic course with vague symptoms.
Main signs and symptoms of hepatitis B
Many patients do not observe external manifestations of the disease. It can be detected with the help of specialist intervention by conducting a laboratory blood test.
However, as the disease progresses, an exacerbation of hepatitis B occurs, the symptoms are as follows:
- My head is spinning;
- Often feeling nauseous;
- A person gets tired quickly at the slightest exertion;
- General weakness, dry cough, pain in the nasopharynx and head;
- Fever;
- A yellow tint appears on the skin;
- Loss of appetite;
- Feeling of heaviness in the right hypochondrium;
- Chills.
When hepatitis B progresses and becomes chronic, people begin to suffer from kidney failure, which results in intoxication of the body.
During this stage, it is necessary to undergo complex treatment in a timely manner, otherwise damage to the central nervous system is inevitable.
Remission stage
After the jaundice phase, the patient’s well-being gradually improves. Weakness, attacks of nausea, belching and changes in skin color disappear. Appetite appears again.
The recovery stage begins at different times for each patient. Sometimes a month passes before remission begins, in some cases - six months. This depends on the activity of the patient’s immune system, the speed of liver recovery and the correct treatment. If the infectious disease doctor's orders are strictly followed, the remission stage occurs quickly.
If at this moment the regimen or prescribed diet is violated, an exacerbation of hepatitis B may occur. The patient again begins to complain of increasing weakness, loss of appetite and the appearance of jaundice. A relapse occurs.
If the latent stage does not last long and the symptoms of the disease appear quickly and clearly, complete recovery occurs in 95% of patients.
Causes for hepatitis B, symptoms and treatment
People with weak immune systems are most often exposed to the virus, especially if the person drinks alcohol, tobacco, or is under the influence of chemicals or toxic substances. In them, symptoms of hepatitis B infection appear within one to two weeks, and the disease itself progresses intensively.
If a person shows signs of hepatitis B infection, he cannot be socially isolated, because this will have consequences: he may withdraw into himself, “fold his hands,” fall into deep depression and deny treatment.
If signs of hepatitis B are detected, there is nothing to fear from those around you, since the disease is not transmitted by airborne droplets. Persons in contact with the patient must adhere to basic precautions.
Let's summarize: which virus is more dangerous?
The difference between hepatitis B and C is significant, but any type of infection can cause irreversible changes in the liver tissues. In terms of spread, HBV is considered the most dangerous; in all other respects, HCV is the leader.
Why hepatitis C is the most dangerous:
- no vaccination;
- in 80% the process becomes chronic;
- difficult to detect in the early stages, as it is asymptomatic;
- directly destroys hepatocytes;
- complications are diagnosed more often;
- there is no post-infectious immunity, you can become infected again;
- difficult to treat.
Hepatitis B how it is transmitted symptoms treatment
This virus is transmitted through biological materials : blood, saliva, urine, semen.
The virus is predominantly transmitted sexually: the probability of infection during sexual contact is 40%.
At the time of birth, it can be transmitted from mother to baby, the likelihood of such infection is 2-10%.
There are often cases when a person shows the first signs of hepatitis B due to the fault of doctors who use non-sterile syringes, surgical instruments, and other medical equipment. To avoid such a situation, you must ask doctors to properly clean the instruments in your presence.
You should not fold your arms if symptoms of hepatitis B were detected, and the analysis showed a “positive” result. There are many drugs and generics that keep the virus under control and prevent it from becoming a threat to life .
If hepatitis is not in a chronic form, it can be completely eradicated, but you should follow a clear system built by your doctor.
Having identified the aggressiveness and activity of the virus and assessed the condition of the liver, the doctor prescribes drug treatment, the period of which ranges from 2 to 10 months.
In 90% of cases , the disease can be eradicated , but periodic examination is recommended.
Treatment of the chronic form
The question of whether hepatitis B can be treated or not has received a clear answer. Yes, hepatitis can be cured and quite successfully. If we compare the prognosis for patients with liver damage by a B-type virus, they are much more comforting than for patients who encountered a C-type pathogen or combined infection.
The treatment regimen is selected only after receiving diagnostic results
Doctors have identified a number of criteria by which the effectiveness of the therapy is assessed:
- normalization of transaminase levels in the blood;
- absence of viral cell DNA, which is confirmed by real-time PCR;
- disappearance of HBeAg;
- stopping the progression of deterioration of the histological picture of the liver.
A decrease in transaminase levels to normal levels is a biochemical response to the treatment. A decrease in the amount of pathogen DNA and the disappearance of HBeAg indicates a virological response. Normalization of liver condition indicators at the level of hepatocytes – histological response. The combination of all responses is called a complete response to therapy.
Important! A persistent positive result of the treatment is the normalization of all of the above indicators and maintaining them at this level for 6-12 months from the end of therapy.
At this stage, two drugs are most often used for antiviral therapy: Interferon and Lamivudine.
Interferon
The group of interferons is characterized not only by its antiviral effect. These drugs are able to fight tumor cells and strengthen the body's immune system. Scientists have found that interferon alpha suppresses the reproduction process of the hepatitis B virus, which contributes to the development of remission of the disease. However, the drug is not prescribed to all patients, since there are certain restrictions regarding selection criteria for treatment.
A good virological response to the use of interferon is observed in treated people with persistently or periodically elevated serum ALT levels and the presence of HBeAg. If the ALT level is normal, response to treatment will be recorded in less than 10% of patients.
The effectiveness of therapy in pediatric patients is similar to that in adults. Clinical data have proven that the use of interferon alpha against the background of a chronic form of the disease, in which HBeAg is absent, is accompanied by a positive response to treatment, but is fraught with relapses of the disease within 5 years from the date of completion of treatment. Permanent cure is achieved in only a quarter of patients.
Interferon is not recommended for use in patients with liver cirrhosis, since when taking such drugs, the level of ALT in the blood serum increases sharply, which confirms the occurrence of a cytolytic crisis. The result may be the development of liver failure.
The antiviral drug is prescribed as injections under the skin, the course of treatment is 3-4 months
Adverse reactions to interferon therapy:
- weakness;
- decreased appetite;
- pain in joints and muscles;
- depression;
- decrease in the level of leukocytes in the blood;
- anxiety;
- hair loss.
Lamivudine
This drug stops the process of reproduction of the hepatitis virus by integrating the active substance into the growing DNA chains. Recommended for use in patients who have HBeAg-positive hepatitis. A persistent virological and histological response is observed in half of the patients. Children, as a rule, are not prescribed Lamivudine.
The drug is also recommended for those patients who do not have HBeAg. In such a case, the effectiveness of therapy over 5 months is 63%. Lamivudine is excellent for those patients who are resistant to interferon alpha. Also, a number of studies have proven that the medication can be used against the background of liver cirrhosis. Among the undesirable effects of taking the drug, a slight increase in the level of transaminases in the blood can be noted, but this is far from critical. Otherwise, the drug is tolerated quite well.
Other drugs
Famciclovir - clinical studies have proven that this medication has an antiviral effect, but is inferior in terms of activity to Lamivudine. Moreover, the medicine should be taken three times a day, so it is unlikely that it will be the drug of choice.
Adefovir dipivoxil - the drug cannot be used in high doses, as it becomes toxic to the kidneys. Able to reduce the amount of viral DNA in the patient’s body. Thymosin is a well-tolerated drug that stimulates the activity of T-cell immunity. In some cases, it is combined with other medications.
In the presence of severe intoxication, specialists prescribe detoxification therapy. It involves the introduction into a vein of a number of solutions (sodium chloride, rheosorbilact, hemodez, rheopolyglucin, glucose). At the same time, hormonal agents are administered. Start with high doses, gradually reducing them.
Vemlidy is a new drug recommended for use in the treatment of hepatitis B. It is a European product that is prescribed to patients over 12 years of age and weighing more than 35 kg. The medicine is not yet available in our country.
Features of treatment in pregnant women
Many pregnant women are concerned about hepatitis B treatment because it may affect their baby. In fact, if you follow all the doctors’ recommendations, there will be no consequences of therapy for the fetus. As a treatment, doctors recommend taking only nucleotide and nucleoside drugs. At the same time, taking Interferons during pregnancy is strictly prohibited.
A newborn child should receive immunoprophylaxis immediately after birth. According to generally accepted practice, he needs to be administered specific immunoglobulin against hepatitis B in the first twelve hours of life. Subsequent administration should be carried out when the child is one and a half and six months old.
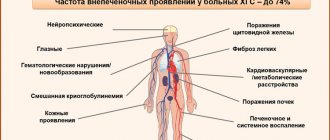
Complications of viral hepatitis B
With sluggish chronic hepatitis, there is a risk of developing cirrhosis and liver fibrosis.
The most dangerous consequence is the development of an acute form of liver failure.
Against the background of massive death of liver cells, the functionality of the organ deteriorates, and a hemorrhagic syndrome is formed, which is characterized by a toxic effect on the central nervous system.
The development of hepatic encephalopathy has the following stages:
| Prekoma I | A sharp deterioration in health, severity of jaundice, increase in dyspeptic disorders, hemorrhagic signs. There is a specific odor from the mouth, problems with emotional stability are revealed. At this same stage, fine motor skills become upset, the liver hurts greatly, and the body temperature rises. |
| Prekoma II | Functional disorders of the central nervous system progress. The main symptoms include complete disorientation in time and space, alternating euphoria and aggressiveness. At this stage, the liver decreases in size, and slight tremors of the legs and arms are observed. Subsequently, the clinical picture worsens and hepatic coma develops. |
| Terminal stage | Accompanied by depression of consciousness, and subsequent complete loss. Initially, the reflexes are preserved, the patient is able to react, for example, to a loud sound or palpation, but after that they are leveled out. Death occurs due to acute heart failure. |
In severe cases, when the patient simultaneously has a history of two types of hepatitis B, D, hepatic coma can develop at an early stage, and death occurs in 90% of cases.
Routes of infection
So, what is the difference between hepatitis B and hepatitis C? First, let's look at the ways the infection spreads and the characteristics of the pathogens.
Hepatitis B
In all cases, type B infection occurs through biological media. We will describe them in order of reducing the risk of getting hepatitis:
- blood, which contains the maximum concentration of pathogens, which is why the risk of infection is greatest. Most often affected are medical workers (surgical, dental departments, hemodialysis units), transfusion station workers, patients requiring frequent blood transfusions, as well as injection drug addicts;
- sperm. With all types of intimacy there is a high risk of infection;
- vaginal discharge;
- saliva;
- tears;
- sweat;
- feces.
Let's talk separately about the vertical route of infection.
Infection of the fetus in the prenatal period is not observed, however, with frequent exacerbations of the disease, the concentration of viruses in the mother’s blood increases, which is fraught with their penetration to the fetus.
More often, infection occurs during labor, when the baby passes through the paths of the injured mucosa. If the integrity of his skin is compromised, blood contact occurs and, accordingly, infection occurs.
It is especially dangerous to live with a person with hepatitis in the same area and share hygiene items (razors, toothbrushes).
The causative agent of the disease is highly resistant. It can withstand treatment with alcohol and boiling for an hour, but dies when autoclaving. The virus is not afraid of two-hour chlorination, exposure to formalin and freezing.
Hepatitis C
The routes of transmission are similar to hepatitis B, but the risk of getting sick is slightly lower. This is predisposed by the lower stability of the pathogen in the external environment. In addition, to infect “C”, a double concentration of viruses is required.
Slow progression of the pathology leads to the development of cirrhosis. Often it is at this stage that the disease is diagnosed, which worsens the life prognosis. Hepatitis C is especially dangerous due to its asymptomatic course, which predisposes to latent virus carriage.
It is quite difficult to select effective drugs to combat HCV, since the pathogen has the ability to mutate and change its structure. One patient may have several types of pathogenic agents that easily evade the immune system.
The most common route of transmission is through blood. Today, thanks to disposable medical kits and careful testing of donated blood, the incidence of infection in medical institutions has significantly decreased. At the same time, tattoos and piercings became more popular, which increased the number of infections in beauty salons.
Infection is not possible by shaking hands, coughing, kissing, or eating food from shared utensils.
As for the sexual method of infection, it is not so typical for “C” and is observed only in 5% of cases. Note that in 10-30% of people the cause of infection remains unknown.
Diet
In the process of treating the liver with both folk remedies and medications for the hepatitis B viral infection, it is necessary to follow a diet and certain diets that do not burden the diseased organ with unnecessary work.
It is necessary to remove from the diet all foods prepared by frying, smoking or pickling . Judicious use of spices and salt must be observed. Opt out:
- Boiled or smoked sausages.
- Eggs, it doesn’t matter: boiled or fried.
- Fatty foods.
- Sweets, candies, cakes and other confectionery products.
- All flour products, from bread to puff pastry products.
- Anything that contains alcohol.
To improve overall health, immunity and restore normal liver functions, it is recommended:
- There are fresh fruits.
- Lean meat and broth.
- Boiled vegetable dishes.
- Dairy products and cereals with milk.
- Juices, fruit drinks and fruit compotes.
- Crackers.
- Greenery.
- Use honey in cooking and drinking.
- From sweet jams and preserves.
Diet: small portions, 5-6 times a day.
Prevention
Prevention of many diseases is possible through vaccination. Unfortunately, a vaccine has not yet been developed for viral hepatitis C. Prevention of HBV is possible through vaccinations, which are given in infancy. The vaccination schedule is as follows:
- The first vaccination is within the first day after birth.
- The second one 30 days later.
- The third at the age of 6 months.
- The effect lasts for 12 months.
This vaccination provides lasting immunity for many years. Some sources say at least 20.
Other measures to prevent infection with both types of the virus include maintaining a healthy lifestyle and seeking medical and dental care from officially established institutions.
Diagnostics
Serological blood tests are of great importance in diagnosis, which determine markers, virus activity and the phase of the disease. Patients are tested for the presence of HbsAg, HBc antibodies. A positive result indicates HBV or immunity.
If the test is negative, an HCV antibody test is prescribed. If in this case the answer is positive, a diagnosis of viral hepatitis C is made. The next step in diagnosing HCV is genotyping the virus. Further etiotropic treatment depends on this.
Biochemical methods help to establish the concentration of transaminases, alkaline phosphatase, and bilirubin. The histological characteristics of the lesions are provided by a puncture biopsy. With chronic HCV, the following symptoms appear:
- fatty degeneration;
- stepwise necrosis;
- lymphoid infiltration;
- damage to the ductal system.
It is important to know! “Frosted glassy hepatocytes” (a marker of HbsAg) and “sandy nuclei” (a characteristic sign of HbcAg) in the study of liver tissue are what distinguishes hepatitis B from hepatitis C. The main differences are in treatment methods.
The comprehensive treatment program for viral hepatitis includes two directions: etiotropic and pathogenetic. The first is aimed at suppressing viral replication and preventing the chronicization of pathology, the second is aimed at eliminating liver dysfunction. Despite common methods of drug and non-drug therapy, antiviral treatment regimens may differ.
Features of hepatitis C treatment
All patients with chronic hepatitis C are potential candidates for antiviral drugs. Indications:
- high risk of disease progression to cirrhosis;
- necrotic inflammation;
- fibrosis;
- elevated ALT levels.
Patients are prescribed:
- interferons (IFN): “Reaferon”, “Roferon A” (IFN-α2a); “Intron A”, “Realdiron” (IFN-α2b), “PegIntron”, “Pegasys” (long-acting drugs);
- cytokines;
- antiviral drugs (“Amantidine”, “Ribavirin”);
- immunosuppressants: “Prednisolone”, “Azathiaprine”;
- combined means.
Currently, preference is given to drugs with a direct antiviral effect: Sofosbuvir, Daclatasvir, Simeprevir. The drugs make it possible to refuse long-term treatment with interferons. However, it should be taken into account that a course of treatment with these drugs will cost the patient several thousand dollars, so they are not available to everyone.
Features of treatment of viral hepatitis B
For chronic viral hepatitis B patients, the following types of drugs are recommended:
- IFN-α2a, IFN-α2b;
- "PegIntron";
- immunostimulants (“Interleukin-2”, “Cycloferon”);
- HBV vaccine;
- antiviral agents: Famciclovir, Lamivudine, Vidarabine;
- thymus preparations: “Imunofan”, “Myelopid”.
It is important to know! Only an infectious disease specialist prescribes medications and treatment regimens!
How is hepatitis B different from hepatitis C?
Let us briefly outline the main differences between the diseases.
| Difference | IN | WITH |
| Pathogen | DNA-containing species of hepadnaviruses | RNA (flaviviruses) |
| External environment | More stable | Less viable |
| In organism | Has no subspecies | Able to mutate, allowing it to escape from attack by the immune system |
| Chance of getting sick | High | Small, since a higher concentration of pathogenic agents is required for infection |
| Effect on the liver | Indirect, through an autoimmune process | Direct effect on hepatocytes |
| Recovery | In 90% of cases | No more than 25%, the rest are chronic |
| Vaccination | Exists | Not yet developed due to the large number of subtypes of the virus |
| Post-infectious immunity | Formed after illness and protects against re-infection | Develops against one type of pathogen. The risk of infection with a virus of another subspecies remains |
| Course of the pathology | Rapid with pronounced symptoms | Asymptomatic |
Unconventional methods
Every year, many treatment options for hepatitis B appear, which, according to their manufacturers, can help quickly and more effectively get rid of this problem. These include:
- healing solutions of alkaline secret composition;
- tinctures and decoctions;
- energy waters (polyactive drops, bio-water);
- coal with milk;
- seaweed, corn silk, lemon, etc.
The above treatments for hepatitis B are not approved by the Ministry of Health and the World Health Organization. This is due to the fact that these methods have not passed any official tests or appropriate certification. The effectiveness of these funds is currently either unproven or refuted by the initiative of certain clinics.
You need to be very careful and careful when choosing drugs for the treatment of hepatitis B. There are some counterfeits and fraudulent schemes on the market. In any case, you should definitely consult with your doctor before you start taking alternative remedies.
Some traditional methods can help eliminate certain uncomfortable symptoms for the patient associated with the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract or liver. But there is no way to cure or get rid of hepatitis B. Despite the fact that work is underway to create new drugs, scientists have not yet been able to create a universal drug that can completely cure a person from this disease, in a short time and without side effects.
Features and routes of transmission of the virus
Chronic hepatitis B is caused by a virus that has a number of symptoms:
- found only in humans;
- has high resistance to adverse environmental factors;
- its place of reproduction is the liver.
Main transfer routes:
- parenteral (through blood);
- sexual;
- from mother to child during pregnancy or childbirth.
Children under 5 years of age and people with weakened immune systems are most susceptible to the virus.
A feature of chronic hepatitis B is the presence of an immune tolerance phase. There are no symptoms of the disease, and tests show no changes.
Herbs and infusions
It must be remembered that treatment of the liver at home with folk remedies for the hepatitis B virus must be agreed with the attending physician and be sure that there is no allergy to the herbs used.
- Calamus root decoction. Add a tablespoon to 200 ml of boiling water and leave for half an hour. Drink 50 ml four times a day, before eating.
- Liver collection. It contains many plants necessary to maintain the functioning of the liver organ. For 500 ml of boiling water, 2 tablespoons of this collection. Leave for 3 hours. Take 50 ml 4 times a day, before meals.
- A mixture of bee honey and pollen in equal proportions. Take a tablespoon once a day.
- Radish juice for every half liter is mixed with 200 grams of honey. Take 50 ml before each meal.
- To cleanse the liver of toxins, flax, rose hips, chamomile, and peppermint are used.
- Oats or spotted milk thistle are used as protection and to enhance resistance to the disease.
- Mix hot honey with apple juice. Drink in the evening, before bed.
- Mix a teaspoon of mint, yarrow and dill seeds and add water. Bring the mixture to a boil. Cool, strain and let sit for 8 hours. Drink the resulting infusion throughout the day.
- Mumiyo. Take mixed with milk and a couple of spoons of honey in the morning, an hour before meals.
- Lemon juice with soda. Diluted citric acid or squeezed lemon juice is mixed with a teaspoon of soda. Waiting for the reaction to finish. The resulting result is consumed once every three days, in the morning, before meals.
Anicteric period
The duration of the anicteric stage is from 8 hours to 2 weeks. Sometimes there are no symptoms of hepatitis B in women: symptoms of the acute icteric stage immediately appear.
The first signs of HBV in women may appear 1 - 1.5 months after infection. The course of the anicteric period is generally characterized by:
- moderate intoxication;
- moderate dyspeptic syndrome;
- moderate arthralgia in large joints at night
- skin rashes and mild itching.
That is, all manifestations are not clearly expressed and develop gradually. In the anicteric stage, the onset of the disease in a woman resembles the development of influenza and is manifested by symptoms of intoxication:
- weakness;
- constant drowsiness;
- unmotivated fatigue;
- feeling tired even after a long sleep and long rest;
- reduced mood level up to the development of depression;
- aches throughout the body and pain in the joints;
- fever (from low-grade fever to high fever - up to 40c);
- indigestion (constant repeated diarrhea or constipation, sudden loss of appetite, constant nausea and vomiting);
- poor sleep;
- rash;
- possible.
The first symptoms of hepatitis B in women include abdominal pain (an enlarged liver is detected by palpation). They have a dull, aching character and are constant or periodically sharply intensify. But pain in the epigastrium, along sections of the intestine due to a disorder of the digestive processes, can also be a concern.
Risk group
Risk factors for hepatitis B infection
Now, at the state level, a list of people who are at risk of contracting this disease has been approved, so they need to be given a vaccine against hepatitis B:
- students of schools and institutes;
- drug addicts;
- patients who regularly require intravenous administration of drugs;
- people who need regular hemodialysis;
- children who go to kindergartens;
- workers of medical institutions;
- people who are promiscuous.
Probability of recovery
Despite the high degree of aggressiveness of the hepatitis B virus, doctors say that with proper therapy, recovery occurs in 90% of cases. This is also due to the fact that HBV is detected in the first stages of the disease, due to its vivid symptoms.
With HCV it is somewhat more complicated. Until recently, hepatologists believed that only 25% of patients could overcome the disease. For others, it becomes chronic and cannot be completely cured. After the discovery of the drugs Sofosbuvir, Daclatasvir and their generics in 2019, 80% of those sick had a chance of recovery.
General information about the disease
Viral hepatitis B is an infectious disease with predominant damage to hepatocytes and a decrease in the functional activity of the liver. Its causative agent is the HBV virus (HBV) from the hepadnovirus family.
The pathogen is transmitted only from person to person, and the source of infection can be either a patient with hepatitis B receiving treatment or a virus carrier with an innaparent (asymptomatic) form of the disease. HBV is found in blood, semen, vaginal secretions and other body fluids. The contagiousness of the infection is very high: even with a single contact with a small amount of viral particles, infection can occur.
Among the main routes of transmission are:
- sexual;
- parenteral, including injection;
- domestic;
- transplacental.
Note! The prevalence of hepatitis B in adults and children remains very high: in some areas (Central Africa, Southeast Asia, Latin America), up to 10% of the total population is infected with the virus.
The development of effective treatment methods and timely treatment of hepatitis B is one of the health priorities. Early diagnosis and the beginning of a comprehensive detoxification, antiviral and hepatoprotective effect on the body can significantly reduce the number of possible complications and achieve complete recovery.