After being diagnosed with hepatitis C, it is important for the patient to learn not only everything about the disease, but also what consequences it can lead to. The HCV virus has a devastating effect on the liver, since it cannot be treated without a trace, completely changing a person’s life. The severity of complications depends on the state of immunity, age and the presence of other pathologies. In approximately 10-15%, complete self-healing is observed, while in 20%, the acute phase almost immediately becomes chronic and smoothly develops into cirrhosis.
How can you get infected?
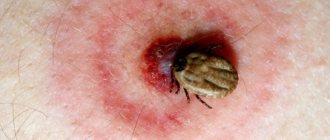
Hepatitis C can be transmitted through blood. To become infected with this disease, it is enough for a small amount of the virus to enter the bloodstream for a person to develop clinical symptoms of the disease after some time. The largest amount of virus is found in the blood, but it is present in semen and saliva. Since the concentration in other biological fluids is negligible, the likelihood of contracting hepatitis is low. An interesting fact is that hepatitis C is contagious even in dried blood, since the activity of the virus in this state remains for about four days. In order not to become infected with this disease, you need to know how hepatitis is transmitted, whether you can become infected with hepatitis through domestic or sexual contact, and where you can become infected with this terrible disease.
Read more about what hepatitis C is and why it is dangerous here.
We also recommend that you read the article: step-by-step instructions on how to cure hepatitis C
The routes of infection with hepatitis C are as follows:
- through accidental contact with the blood of a virus carrier;
- sexually (the least common method);
- during blood transfusion;
- through infected tools.
Preventive actions
The development of viral hepatitis can be prevented by following a number of simple rules. This is especially true for people at risk. These include medical personnel, people who inject drugs, donors (blood, organs). The main preventive measures that must be followed are:
- It is mandatory to have a condom when having sexual intercourse with an unknown partner.
- You should not lend your personal items for use and not take other people’s (toothbrushes, razors, nail scissors).
- Place only specialized cosmetology clinics, use the services of trusted professionals, monitor the quality of processing of working tools.
- Do not use disposable syringes after another person, stop taking injecting drugs.
- When coming into contact with the blood of an infected person, use latex gloves.
The hepatitis C virus is highly mutagenic, so it is impossible to create a vaccine against it. But simple preventive measures will help protect yourself and your loved ones from infection. If contact with infected blood cannot be avoided, emergency measures should be taken. They include urgent PCR tests, as well as taking alpha interferon and Ribaverin for a month. The treatment regimen with antiviral drugs and dosage are determined by the doctor.
Hepatitis C is a serious disease that does not always result in a complete recovery. In most cases, the disease becomes greatly complicated and develops into more severe pathologies. If the fight is not started in time, the patient’s life expectancy will not be more than 15-20 years.
People at risk
For some categories of people, the routes of transmission of hepatitis C and the causes of infection become especially relevant due to the nature of their activities. For example, the virus poses a danger to medical workers, especially operating room nurses and operating room nurses who perform medical procedures every day. If a doctor is pricked with a needle and handled carelessly, he or she can become infected with HCV. Workers of nail salons, tattoo salons and lovers of such establishments can also become infected with hepatitis, since there is a mutual risk of damaging the skin with a tool infected with the virus.
Drug addicts who inject drugs are at risk of contracting the infection. In this group of the population, hygiene rules are not observed, and drug addicts use one syringe for several people, which leads to infection with pathology.
There is also a certain risk of infection among persons held in temporary custody. As you know, prisons have one of the most unfavorable conditions in all respects, since prisoners often use drugs, engage in homosexual relationships, etc.
Risk groups for hepatitis infection
Having found out whether hepatitis is sexually transmitted, it should be noted that this is not the only method of infection. The most common types of the disease are hepatitis B and C. This infection occurs through contact with blood. Infection of children with hepatitis in most cases occurs in utero, transplacentally.
In adults, those at increased risk of infection include:
- drug users;
- practicing promiscuous sex;
- living together with people infected with hepatitis;
- recipients of blood and its components;
- those who have undergone transplantation and other surgical interventions;
- undergoing medically invasive procedures.
It is customary to separately identify a risk group for occupational hepatitis infection, which includes:
- students of medical schools and colleges;
- healthcare workers who collect blood for research and perform blood transfusions.
Where is the virus most often contracted?
As already mentioned, there is a high risk of contracting pathology in those places where the blood of a healthy person can come into contact with the blood of a virus carrier. These places become:
- beauty salons;
- tattoo and piercing salons;
- hairdressers;
- dental and gynecological offices;
- blood poisoning in an accident (in a fight, car accident, etc.);
- blood transfusion points;
- places where antisocial elements gather;
- places of detention.
Statistics
| Transmission path | Risk percentage |
| Unprotected sexual intercourse | 3-5% |
| From mother to newborn | 5% |
| During blood transfusion | 4% |
| In direct contact of the virus with blood | 80% |
Prevention of hepatitis infection
Everyone should know how viral hepatitis is transmitted, which contributes to infection. However, knowledge alone is often not enough to prevent disease.
Prevention of infection with viral hepatitis includes the following aspects:
- Healthy lifestyle.
- Providing the population with high-quality drinking water and clean food.
- Compliance with personal hygiene rules.
- Use of methods for indicating hepatitis markers in blood and tissue donors.
- Compliance with the rules of disinfection and sterilization of medical instruments and equipment.
- Vaccination against hepatitis using recombinant yeast vaccines.
Transmission through blood
Transmission through blood is called parenteral route. This is how most patients become infected. This route most often causes viral infection, since the transmitted viral contents enter directly into the blood. Patients are interested in how much infected blood is needed to become a victim of the disease? This question can be answered unequivocally - the virus is so strong that even a small drop of blood from an infected person is enough for the infection to easily establish itself in the body of a new host.
Sources of infection
Jaundice is transmitted from person to person during subclinical course and in the early phases of the disease. Many people are interested in the question of whether jaundice is contagious after staining the whites of the eyes and skin. Once signs of jaundice appear, the likelihood of infection decreases. At the 3rd week of disease development, HAV is isolated from 5% of infected people.
When jaundice appears, most patients do not shed the virus
The period when hepatitis A can be transmitted lasts about 4 weeks, and sometimes about 6 weeks. It includes the incubation period of jaundice, when the disease does not manifest symptoms, but the patient is already excreting the virus.
Methods of spread of HAV:
- Feces, urine, mucus from the nose and throat. As mentioned earlier, viral hepatitis is transmitted by the fecal-oral route. As a rule, this occurs after contact between a healthy person and a sick person.
- Contact with the patient. People become infected after close contact with an infected person by profession (medical workers). It also increases the likelihood of infection spreading among people who have poor hygiene skills. Infection often occurs in preschools, schools, nursing homes, etc.
- Contaminated food products. It is almost impossible to determine from which product the virus was transmitted due to the long incubation phase. But doctors highlight products that most often provoke the spread of infection. HAV is transmitted to people by consuming poorly or uncooked foods. The risk of infection increases when consuming products after storage (salads, cold appetizers, fruits and berries after drying, especially from regions such as Kazakhstan or Central Asia). Berries grown on site, fresh or frozen. This is especially true for plants near which slugs are found or where they are treated with fertilizers made from human excrement. Seafood that is not subjected to prolonged high-temperature processing is also dangerous.
- Water. This method of transmission of the virus is typical for regions where public infrastructure is insufficiently developed and water supply is poorly organized. The likelihood of infection increases during emergencies (accidents, natural disasters).
- Aerosol. There is a threat of infection through airborne droplets (although some doctors reject this method of transmission). The virus spreads during epidemics of colds in groups with weakened immune systems. HAV is transmitted by coughing and sneezing along with mucus from the nose and throat.
- Sexual. Unprotected sexual contact or anal-oral sex also increases the likelihood of infection.
- Transmissible. Hepatitis A can be transmitted by flies, but there is no evidence for this hypothesis.
- Parenteral. HAV is transmitted during blood transfusion from an infected donor, during intravenous administration of solutions with a non-sterile syringe.
In addition, there is a possibility of vertical infection, when the virus is transmitted from a sick mother to her child. To prevent the development of the disease, a vaccine is administered to the small patient.
Vertical infection
In some cases, it is possible to observe how hepatitis infection occurs through the vertical route - this is the route of transmission of HCV from mother to child. Infection of the fetus does not occur in the prenatal period, but most often during childbirth, when hepatitis C is transmitted through the blood. Most often, a high concentration of the pathogen in the child’s mother provokes one hundred percent receipt of the virus. Complicates the course of HIV disease, problems with the placenta, and birth injuries.
Children born to mothers diagnosed with hepatitis C have antibodies to this type of virus in their blood. Usually, by the end of the first year of life, such antibodies disappear if no complications of the disease are observed. In this case, no special treatment is required. The RNA of the virus is found in every twentieth child born from a sick mother.
Brief description of the disease
Hepatitis C is an acute infectious disease that primarily affects the liver or other vital organs. Its causative agent is the HCV virus, which is prone to constant mutation, so it is impossible to create a vaccine against it. The main distribution routes are:
- Domestic. You can become infected from a loved one or acquaintance, through his personal hygiene items, or by letting him use his own. This is especially true for toothbrushes, razors, nail scissors and tweezers.
- Sexual. The causative agent of the virus is found in almost all human biological fluids. Therefore, casual sex without a condom can result in infection.
- From mother to child. The virus can be transmitted to the fetus by a woman during pregnancy or during childbirth.
- Transfusions. Donated blood is still a risk factor, although it is tested before the procedure.
Most often, the pathology is diagnosed in middle-aged people. For the first six months, the disease may not show itself in any way, after which symptoms such as yellowing of the skin, increased body temperature, change in the color of urine, constant fatigue and weakness, pain in the right hypochondrium, lightening of the stool, aching joints, nausea and complete loss appear. appetite. When the first signs appear, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Sexual transmission
Sexual transmission of hepatitis C may not occur if sexual partners use condoms. The risk of becoming infected in this way is one of the lowest, but it still exists. Doctors believe that infection occurs when the integrity of the skin of sexual partners is violated. In addition, a partner can be infected by menstrual blood if there was sexual intercourse during this period. Speaking about the route of infection with hepatitis C, it is worth understanding that one of the partners does not always know about his carriage, so he can unwittingly infect another person.
Danger to pregnant women and children
The consequences of hepatitis C in women during pregnancy can be the most unpredictable. There is always a risk of intrauterine infection, fetal hypoxia, and spontaneous abortion. The infection seriously weakens the woman's body, and the liver cannot fully perform its function. This invariably affects the condition of the mother and fetus.
Therefore, during pregnancy planning, a man and a woman are recommended to be tested for hepatitis C and HIV and undergo a comprehensive examination. Often the infection is in an inactive form, but this does not mean that it does not need to be treated.
Attention! The disease has a negative impact on pregnancy, so regular monitoring of the viral load is required.
Is it possible to become infected at home?
People with the disease worry whether hepatitis C is transmitted through household means and how one can become infected with hepatitis from a sick relative. Note that most of the virus is contained in the blood, and other biological fluids have an insignificant amount of it, which does not lead to infection. Therefore, methods of transmitting hepatitis C through household means are practically not considered. However, patients can infect their loved ones if they cut themselves with a razor, kitchen knife, etc., and then the blood can get on the damaged skin of a healthy person. In order not to put their loved ones at risk, when sick or carrier, the patient must use exclusively individual personal hygiene items - a toothbrush, comb, razor, towel. You also need to have your own dishes - cup, plate, cutlery. This is the only way to protect others from HCV infection.
Hepatitis B
Is it possible to become infected with hepatitis B and how does the infection enter the human body? Infection most often occurs in two ways - from an already infected person to a healthy person, as well as through household objects on which the biological fluid of the infected person is present (sweat, sperm, blood, etc.).
Infection through the blood occurs when using unsterile medical instruments; for this reason, this disease is often diagnosed in drug addicts. You can also become infected in a medical facility, for example, through transfusion of blood and its components or during dental treatment if poorly sterilized dental devices and instruments are used.
What kind of hepatitis is transmitted through bed? Hepatitis B can be contracted during unprotected intimate contact, because the virus is present in both vaginal discharge and semen.
The infection can also be transmitted through personal hygiene items, the use of which can damage the skin - razors, manicure tools, combs, etc.
Infection is also possible during childbirth; this is the so-called vertical transmission route. When passing through the birth canal, the child will most likely become infected with the virus from the sick mother. Therefore, if a woman is diagnosed with this pathology, the newborn is given an injection against hepatitis B.
Is hepatitis B transmitted through kissing? It is possible to become infected with hepatitis B through kissing, since the infection is also contained in saliva. However, the likelihood of infection in this way is low, especially if there is no damage to the mucous membrane (wounds, cracks, scratches).
Many people are interested in the question of whether hepatitis B is transmitted by airborne droplets. It is impossible to become infected with this disease through handshakes, sneezing, or sharing utensils.
Incubation period
From the moment you become infected with hepatitis C until the clinical symptoms of the disease appear, the incubation period lasts. This means that the virus is in the human body, but he most likely does not even know about it. This period for HCV is quite long - from two weeks to six months. During this entire time, the virus reaches the liver cells, actively multiplies there, after which manifestations of the disease begin. Note that very often the incubation period goes directly into the chronic stage, bypassing acute hepatitis.
Types of hepatitis and methods of infection
Depending on the morphological and pathogenetic properties, doctors distinguish the following types of hepatitis:
1. By nature of origin:
- viral: A, B, C, D, E, F.
- toxic: alcoholic hepatitis, drug hepatitis;
- radiation hepatitis (develops during radiation therapy);
- autoimmune.
2. According to the clinical course:
- acute hepatitis
– characterized by a sharp deterioration in health, increasing signs of intoxication, changes in blood counts; - chronic
- does not manifest itself for a long time, over time there is an enlargement of the liver, dull pain appears in the right hypochondrium.
How is hepatitis A transmitted?
Viral hepatitis A, popularly known as Botkin's disease, jaundice, is an acute infectious disease that damages the liver. Hepatitis A infection occurs most often through food and contaminated water. The source of infection is a sick person.
According to experts, you can become infected with viral hepatitis A:
- when eating unwashed fruits and vegetables;
- while using contaminated utensils;
- during transfusion of infected blood.
In children, the disease often occurs in a latent form, so transmission of the infection often occurs through contact with a sick child. The first symptoms appear after a while. Against the background of general intoxication, pronounced yellowing of the skin is observed, which indicates damage to the patient’s liver.
How is hepatitis B transmitted?
The disease develops as a result of the entry of a type B virus into the human body. Viral hepatitis B itself is transmitted through contact of an infected person with a healthy person.
This can happen in the following ways:
- through wounds, animal and insect bites;
- with the saliva of an infected person (during a kiss);
- as a result of contact with contaminated blood or damaged mucous membranes and skin (shared shaving utensils, toothbrushes, handkerchiefs, towels);
- through the placenta from mother to child, during childbirth and during breastfeeding;
- unprotected sexual intercourse with a carrier of the hepatitis virus;
- as a result of parenteral medical interventions: transfusion of blood components, injections.
How is hepatitis C transmitted?
When talking about how hepatitis C is transmitted from humans, doctors put the parenteral route of infection first. Infection with the virus occurs through contact with the blood of a person infected with the virus.
This can happen in the following ways:
- transfusion of infected blood;
- giving injections to a patient with hepatitis;
- use of untreated instruments for cosmetic procedures: manicure, haircut, piercing.
How is hepatitis D transmitted?
Viral hepatitis D is accompanied by severe liver damage. This virus is a kind of superinfection, which was originally caused by hepatitis B. In the absence of virus B form, the delta virus is not able to multiply in liver cells. Transmission of the virus from a sick person to a healthy person occurs through blood. In general, hepatitis D is similar to hepatitis B, but is more severe and is fraught with frequent complications - dystrophy and necrosis of the liver tissue.
How is hepatitis E transmitted?
Having learned about the presence of this form of the disease in a loved one, relative or acquaintance, people often wonder whether hepatitis E is transmitted to others. This viral infection is characterized by a fecal-oral route of transmission. This means that the virus can be transmitted from a sick person to a healthy person by shaking hands or contact with a carrier of the virus. A patient with hepatitis E is a source of the disease only at the initial stage of the pathological process.
The virus is distributed mainly in countries with hot climates and poor quality tap water. The incubation period is 14–50 days. Characteristic manifestations of the disease are:
- asthenia;
- dyspeptic disorders;
- jaundice.
How is hepatitis F transmitted?
Many people have never heard of this form of the disease and do not know how hepatitis F is transmitted. It refers to two different types of post-transfusion virus. In their properties, they differ from hepatitis B and C. One of the identified type F viruses was present in donor blood samples and was resistant to fat solvents. As a result of these studies, specialists were able to establish how viral hepatitis F is transmitted. The main mechanism of transmission is blood transfusion, the transfusion of infected blood.
Symptoms
For a long time, no symptoms appear with hepatitis, after which the body signals that the liver is not functioning properly. Unfortunately, these manifestations already occur at the stage of serious violations. At the initial stage, hepatitis is characterized by fatigue, depression, and decreased performance. Nausea and problems digesting food occur. At the stage of liver damage, patients experience classic symptoms - jaundice of the skin and sclera, ascites may develop, and some patients lose weight. Pressure indicators change, temperature rises. A carrier of hepatitis suffers from intoxication of the body, which occurs due to disturbances in the functioning of the liver.
Treatment of hepatitis A
Treatment of hepatitis A with medications
There is no specific drug treatment for hepatitis A. Therapy is aimed at eliminating symptoms, removing intoxication and quickly restoring normal liver function.
| Group of drugs | Mechanism of therapeutic action | Representatives | How to use |
| Vitamins | Reduce vascular permeability, reduce swelling of liver tissue, increase the body's resistance to the virus | Askorutin, Askorutin, Undevit, Aevit | 1 tablet 3 times a day |
| Hepatoprotectors | Accelerate the recovery and division of damaged liver cells. Supply structural elements necessary for the construction of cell membranes of hepatocytes | Essentiale, Karsil, Hepatofalk | 1-2 capsules 3 times a day |
| Enterosorbents | To remove toxins from the intestines and eliminate bloating | Smecta, Polyphepan | 2 hours after each meal |
| Enzyme preparations For moderate and severe forms | Promote the breakdown of proteins, fats and carbohydrates and speedy absorption of food in the intestines | Creon, Mezim-Forte, Pancreatin, Festal, Enzistal, Panzinorm | With each meal, 1-2 tablets |
| Glucocorticoids For a sharp deterioration of the condition | They have an anti-inflammatory anti-allergic effect, reduce the attack of immune cells (lymphocytes and leukocytes) on damaged liver cells | Prednisolone, Methylprednisolone | 60 mg/day orally or 120 mg/day intramuscularly for 3 days |
| Immunomodulators | Improves immune function. Stimulates the production of antibodies to fight hepatitis A virus | Timalin, Timogen | Administered intramuscularly at 5-20 mg per day for 3-10 days. |
| T-activin | 1 ml of 0.01% solution is administered subcutaneously for 5-14 days | ||
| Detoxification solutions | Binds toxins circulating in the blood and promotes their rapid elimination in the urine | Hemodez, Geopolyglyukin | Intravenously drip 300-500 ml per day |
| Choleretic agents | Eliminate stagnation of bile in the liver, help cleanse it and improve digestion | Sorbitol Magnesium sulfate | Dilute 1 tsp of the drug in a glass of warm boiled water and drink at night |
Currently, doctors are trying to avoid unnecessary drugs, prescribing only the minimum necessary to eliminate symptoms.
Is hospitalization required for hepatitis A treatment?
For hepatitis A, hospitalization in the infectious diseases department is required in the following cases:
- for complicated forms of hepatitis A
- with the co-occurrence of Botkin's disease and other hepatitis
- with alcoholic liver damage
- in elderly patients and children under 1 year of age
- in weakened patients with severe concomitant diseases
Diet for hepatitis A
Diet 5 is recommended for the treatment of hepatitis A. In the fight against infection, therapeutic nutrition plays an important role. It reduces the load on the liver and protects its cells. It is recommended to eat small meals 4-6 times a day. Recommended products for hepatitis A:
- fermented milk products : low-fat cottage cheese, kefir, yogurt, low-fat sour cream for dressing
- lean meat : beef, chicken, rabbit
- meat products: steamed dumplings, meatballs, meatballs, sausages and boiled beef sausages
- lean fish : pike perch, pike, carp, hake, pollock
- vegetables : potatoes, zucchini, cauliflower, cucumbers, beets, carrots, cabbage, tomatoes
- side dishes : cereals (except legumes and pearl barley), pasta
- soups with added cereals
- bread , crackers
- eggs : white omelette, 1 soft-boiled egg per day
- desserts : mousses, jelly, jelly, marshmallows, marmalade, marshmallows, hard biscuits, honey, homemade jam, dried fruits
- fats: butter 5-10 g, vegetable oils up to 30-40 g
- drinks : black tea, herbal tea, compotes, juices, uzvar, rosehip decoction, coffee with milk, alkaline mineral water, 5% glucose solution.
- Rehydration drugs to restore electrolyte balance are recommended: Regidron, Humana Electrolyte, Gidrovit Forte.
Exclude from the diet:
- fried smoked dishes
- canned fish, meat, vegetables
- fatty meats : pork, goose, duck
- fatty fish : sturgeon, gobies, spicy herring, caviar
- fats : lard, lard, margarine
- pastries from butter and puff pastry, fresh bread
- fatty dairy products : whole milk, cream, full-fat cottage cheese, salted cheese
- soups with concentrated meat and fish broth, sour cabbage soup
- vegetables : radish, radish, sauerkraut, sorrel, onion, parsley, pickled vegetables, mushrooms
- desserts : ice cream, chocolate, products with cream, sweets, steamed
- drinks : strong coffee, cocoa, carbonated drinks, alcohol
The diet must be followed during illness and for 3-6 months after recovery. Limiting fats and simple carbohydrates helps prevent fatty liver degeneration. Easy-to-digest meals and split meals contribute to better bile flow and normalization of digestion. It is very important to adhere to the drinking regime. To remove toxins, you need to drink at least 2 liters of clean water without gas.
Can Hepatitis A be treated at home?
If the disease is mild, hepatitis can be treated at home. This requires several conditions:
- the patient has been examined, taken tests, and will regularly visit the doctor
- the disease occurs in a mild, uncomplicated form
- It is possible to isolate the patient in a separate room
- diet and bed rest
By the time jaundice appears, the patient becomes virtually harmless to others. He can eat at the same table with his family, use a shared toilet and bathroom. Restrictions . It is not advisable to involve the patient in cooking. All family members must strictly observe personal hygiene rules and wash their hands thoroughly after using the toilet. Mode. Pre-icteric period - bed rest is required. The patient experiences severe weakness and excess energy expenditure can lead to additional stress on the liver. And in a horizontal position, the diseased organ receives more blood, which promotes a speedy recovery. Jaundice period - semi-bed rest is allowed. Once the symptoms of the disease have subsided, you can gradually increase your activity. This helps restore physical and emotional well-being.
What tests should I take to check for hepatitis C?
To find out if a person has viral hepatitis, it is necessary to do a series of tests, since external signs of the disease appear late, and the sick person may not be aware of his status as an HCV-positive patient. First of all, a blood test is done to check for antibodies to the pathogen. Then transaminase levels are checked, which are consistently elevated in hepatitis. To determine the RNA of the virus in the blood, a polymerase chain reaction analysis is performed, which gives an unambiguous answer whether a person has the virus or not. Additional studies include ultrasound diagnostics of the liver, as well as a biopsy, because having contracted the disease, patients suffer primarily from necrotic changes in the liver cells.
The test results are sent to the doctor, where he interprets and plans a treatment regimen.
Prevention of hepatitis A
Prevention of hepatitis A includes several areas.
- Disinfection in the area of hepatitis A Disinfection is carried out in the apartment of the sick person. Medical personnel teach family members how to handle objects that the sick person has come into contact with.
- Bed linen and clothes are boiled in a 2% soap solution (20g of any washing powder per liter of water) for 15 minutes, and then washed as usual.
- After eating, the dishes are boiled for 15 minutes in a 2% soda solution.
- Carpets are cleaned with a brush soaked in a 1% chloramine solution.
- Floors and other surfaces are washed with hot 2% soap or soda solution. The door handles of the toilet and flush cistern are treated in the same way.
- Vaccination against hepatitis A Vaccination is aimed at reducing susceptibility to the virus.
- Human immunoglobulin is normal. The drug is administered intravenously to people living in the same apartment as the sick person. The drug contains ready-made donor antibodies against hepatitis A and other infections. Its use reduces the risk of getting sick several times.
- The hepatitis A vaccine is a mixture of neutralized, purified viruses. In response to the vaccine, the body produces specific antibodies. Therefore, if infection occurs, the disease does not develop - antibodies quickly neutralize the viruses.
The vaccine is not included in the list of mandatory vaccinations due to its expensive cost. Its administration is recommended for people at risk :
- Travelers departing to countries with poor hygiene levels
- For military personnel who spend a long time in the field
- People in refugee camps and other places where hygiene is impossible due to lack of running water and sewerage
- medical staff
- food industry workers
- wash your hands thoroughly after using the toilet
- Quarantine in groups and children's groups for a period of 35 days from the moment of isolation of the last sick person
Hepatitis A is considered a relatively benign disease, but requires serious attention and treatment. Otherwise, its effects may be felt for months and years.
Treatment
Treatment of the pathology for a long time was carried out with the standard prescription of ribavirin and interferons in various interpretations, but such therapy gave many side effects, and its effectiveness was not high. Now treatment
HCV is based on the use of progressive drugs - Sofosbuvir, Daclatasvir and Ledipasvir. These drugs have the highest effectiveness against the virus, and treatment with them can be shortened to three months. These drugs can be used to treat hepatitis complicated by HIV, compensated and decompensated cirrhosis of the liver.
Risk of infection after contact with a sick person
Many people are interested in the question of whether it is possible to communicate with a person if he is contagious. Doctors say that this is acceptable, the main thing is to follow the rules of hygiene. To avoid infection with hepatitis A, it is recommended to isolate children from the patient.
The vaccine will stop the development of the virus if it is administered no later than 2 weeks after contact with the patient
A person will not get jaundice if he has previously suffered from the disease and has antibodies in his body. In this case, even if the virus penetrates the blood, immunoglobulins will destroy it. If there are no antibodies to HAV, and the microorganism is already in the bloodstream, then jaundice cannot be avoided.
After suspected infection, it is recommended to vaccinate no later than 2 weeks. This way the patient will protect himself from infection or from developing the disease when infected with HAV.
It is impossible to become re-infected with hepatitis type A.
How the hepatitis C virus is not transmitted
How is the virus not transmitted? People who are forced to live or work with a person who has symptoms of the disease always think about this. In order to socialize such a patient as much as possible, you need to understand that the virus is not transmitted in the following way:
- when breastfeeding (provided that the nipples and oral mucosa of the child are intact);
- from a person when shaking hands, hugging;
- during coughing and sneezing;
- hepatitis C is not transmitted at home through shared food and drinks;
- for insect and animal bites;
- with blood transfusions, if they are tested for the presence of the virus.
Hepatitis C
Is hepatitis C contagious or not? This type of virus is the most dangerous and can be compared in severity to HIV infection. If we compare hepatitis C and HIV, the hepatitis virus is more contagious and infection occurs much more often.
The routes of infection with hepatitis C are similar to hepatitis B. The source of the virus is an already infected person. Hepatitis C is transmitted primarily parenterally (through blood). Infection occurs when using personal hygiene items shared with a sick person—toothbrush, razor, manicure tools. The virus can also enter the body through poorly processed medical instruments - during surgical procedures, transfusion of infected blood, visiting the dentist (such cases are quite rare, but possible).
Hepatitis C is transmitted sexually. The pathogenic virus is present in semen and vaginal secretions, therefore, during unprotected intimate contact with existing microdamages to the skin and mucous membranes, infection with hepatitis C can occur. In particular, this applies to people who are promiscuous. Hepatitis C is very rarely transmitted through kissing. The likelihood of contracting an infection in this way, in comparison with parenteral or sexual methods, is negligible.
Is hepatitis C transmitted during childbirth? Yes, the vertical route of infection is also not excluded.
A child can become infected while passing through the birth canal. The risk in this situation is no more than 5%. There is still debate among experts about breastfeeding a child by an infected mother.
According to the majority of doctors around the world, this fact is not an absolute contraindication to natural feeding of the baby. In the event that pregnancy and childbirth provoke an exacerbation of the pathological process, temporary (!) weaning of the child from the breast is indicated. In addition, a nursing mother must monitor the condition of her nipples and prevent cracks from occurring, otherwise the risk of infection increases many times over.
Is hepatitis C transmitted by airborne droplets? Household contact with a sick person cannot lead to infection with this type of hepatitis. You cannot become infected through saliva (during a kiss), hugs, food, or drinks. If there is a fact of domestic infection, then this is necessarily due to the penetration of blood particles of an infected person into the body of a healthy person (in case of scratches, cuts, abrasions and other injuries).
What to do if there is an infected person in the family?
When a person suffering from this disease appears in a family, it is necessary to understand that hepatitis C is not dangerous for others, it will not be transmitted if all conditions are met, and the patient can lead the same full life as healthy relatives, only with some restrictions. For such a patient, it is necessary to organize special dietary meals and give vitamins in the required quantities. Do not be afraid of contracting the virus - if you follow all the rules, the risk of infection is reduced to a minimum. Also, you should not protect yourself from a sick person, so as not to provoke depression - it is this that can significantly aggravate the course of the disease.
In addition, today, drugs for hepatitis C have already appeared in the world with an effectiveness close to 100%. The modern pharmaceutical industry has created drugs that have virtually no side effects. Many patients receive the first results in the form of relief of symptoms and a decrease in viral load within a week of use. In the market of companies transporting Indian medicine for hepatitis C, “GalaxyRus (Galaxy Super Specialty)” has proven itself to be excellent. This company has been successfully helping people recover from illness for more than 2 years. You can watch reviews and videos of satisfied patients here. They account for more than 4,000 people who have recovered thanks to the drugs they purchased. Don’t put your health on hold, go to www.galaxyrus.com or call 8-800-3500-695, +. Call and your loved one will regain health!
Diagnosis of viral hepatitis
Specific tests for viral hepatitis help diagnose the disease in the absence of obvious clinical manifestations.
Among the main laboratory diagnostic methods, doctors call:
- general blood test, biochemistry (decrease in leukocyte level, increase in ESR, decrease in albumin and bilirubin);
- Antibody tests (PCR): anti-HAV IgM (found in hepatitis A);
- analysis for HBsAg antigens, HB-coreAg antibodies (detection of hepatitis B);
- analysis for IgM antibodies and RNA virus using PCR (diagnosis of hepatitis C);
- analysis for IgM, IgG antibodies (determination of hepatitis D, F, E).
Treatment of the disease
The widespread prevalence of hepatitis C forces specialists to closely study HCV. There are various antiviral medications that help block the proliferation of pathogens and reduce the rate of disease progression. The standard treatment regimen is Ribavirin and Interferon-alpha.
The consequences of treating hepatitis C with these medications can be expressed by varying degrees of severity of organ dysfunction. They concern damage to the cardiovascular, nervous, urinary and digestive systems. The duration of antiviral therapy is 24-48 weeks, which depends on the genotype of the pathogen.
It is worth mentioning a new drug that is used for hepatitis C, namely Sovaldi. It is an original medicine and is produced in the United States. Its mechanism of action is to block the enzyme responsible for the synthesis of viral RNA. The effectiveness of combination therapy with Daclatasvir is 100%. The only limitation to the widespread use of the drug is its high cost. The price of one tablet is about $1,000, and the full course of treatment can reach hundreds of thousands of dollars.
Taking this into account, many countries, for example, India, began to produce generics, that is, medicines that are analogues of the original. These manufacturers have a license to manufacture antiviral agents issued by an American company. The price of these medications is more affordable, which allows many virus carriers to complete the full therapeutic course without large financial costs.
Not all countries have received permission to produce generics, but they are still producing them. In this regard, they are not responsible for the quality of the drugs, and the technological process does not always meet WHO requirements.
What is hepatitis and why is it dangerous?
Hepatitis is an inflammatory process that develops in the liver tissue for various reasons. Most often it is viral. There are seven types of the disease in total, which can occur in acute or chronic form.
In acute cases, the patient does not always have jaundice or it is mild. Therefore, most people are not aware of their problem. Gradually the disease becomes chronic.
It is asymptomatic and can destroy the liver over many years.
Quite often, patients find out about their disease by chance during a routine examination.
The danger of the disease is as follows:
- The liver has the ability to restore its tissues. But with chronic infection, this ability decreases.
- Damaged cells are replaced by connective tissue, and fibrosis develops.
- Gradually, scars appear throughout the liver, cirrhosis and failure of organ function are formed.
- Increases the risk of developing liver cancer.
Lack of treatment leads to the death of the patient. In some cases, even prescribed therapy does not bring results. A photo of a liver affected by the disease shows the danger of this condition. Therefore, it is necessary to know how hepatitis is transmitted in order to avoid infection.
Consequences of pathology
Symptoms of hepatitis often appear already at the stage of the disease when it becomes chronic. Diagnostics shows serious changes in the liver due to the infectious agent. Treatment does not always bring the desired effect. If complex therapy is not carried out, then the chances of developing unpleasant consequences increase.
Complications of hepatitis C:
- hepatosis,
- cirrhosis of the liver,
- liver failure,
- carcinoma.
Without treatment for chronic hepatitis C, the chance of developing cirrhosis is 20% over 15 years. About 5% of infected patients without proper therapy develop a complication in the form of liver cancer.
The dynamics of the disease depend on the genotype of the HCV virus. Forms 1b and 3a are developing especially rapidly.
At the first stage of pathological complications, necrotization (death) of the liver tissue occurs due to inflammatory processes. The structure of the organ changes, its functionality decreases. Different types of hepatosis develop. With steatosis (fatty hepatosis), functional tissue is replaced by adipose tissue. Fibrosis is characterized by the proliferation of epithelial tissue in place of dead liver cells.
The progression of HCV infection in a chronic course without therapy leads to more severe complications. Fibrosis progresses to liver cirrhosis. This pathology can no longer be treated. After all, irreversible changes have occurred in the entire structure of the gland.
Manifestations of cirrhosis:
- Proliferation of connective and adipose tissue in place of the parenchyma (main functional fibers) of the liver.
- Deformation of the hepatic arteries and gastric veins. Under the influence of an enlarged gland, they change their structure and size.
- Impaired blood supply due to narrowing of the lumen of the arteries, thrombosis.
- Ascites. Due to disruptions in metabolic processes and problems with blood flow, fluid accumulates in the abdominal cavity.
Cirrhosis causes internal bleeding, intoxication of the body, and liver encephalopathy. These changes are dangerous to human life.
Particularly severe complications are malignant tumors caused by chronic hepatitis C without treatment. At this stage, hepatocellular carcinoma (in 5% of patients) and cellular lymphoma (1% of patients) develop.
Liver cancer grows very quickly and metastasizes to other organs located near the liver (lungs, stomach). Cancer pathology can be cured with timely therapeutic methods. Doctors use surgery to remove the tumor and radiation therapy. In advanced cases, an organ transplant is required.
Complications of the development of the HCV virus may include disturbances in the functioning of other body systems:
- decreased kidney function (glomeruloneuritis),
- inflammation of blood vessels (vasculitis),
- pathologies of the digestive system,
- endocrine diseases.
The consequences of hepatitis C in men and women in the form of severe stages of pathology with a fatal outcome do not develop if treatment is started on time. It is important to adhere to the course of therapy and your doctor’s lifestyle recommendations to ensure a positive prognosis.
Hepatitis D and differences from other forms
Another name is delta hepatitis. This is an infectious lesion of the liver tissue, coinfection or superinfection of viral form B, which negatively affects the course and prognosis of the disease.
The cause of development is an RNA virus, which belongs to the Deltavirus family. Unlike other hepatitis pathogens, D cannot independently produce proteins for reproduction, and uses substances that are produced by the foreign agent B.
Pathogen D is immune to environmental factors. It is not affected by freezing and thawing, heating, acid, or alkaline solutions. The route of transmission is parenteral, a prerequisite for the disease is the active hepatitis B virus. The pathogen D is introduced into its genome, enhancing the ability to replicate.
The disease comes in several varieties:
- Coinfection is when viruses D and B are transmitted at the same time.
- Superinfection is the joining of virus D to B.
Pathogen D aggravates the clinical picture of hepatitis B. The incubation period is no more than five days (coinfection), and with superinfection it is about 3-7 weeks. The pre-icteric period is characterized by a rapid course.
The combination of viruses in the body can be diagnosed using laboratory methods - in the acute period, IgM antibodies are observed, during the subsequent period, exclusively IgG is determined. The only reliable method of diagnosis is PCR analysis to detect RNA viruses.
Errors in analyzes
There are two main types of tests for detecting HCV. These are ELISA (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay) and PCR (polymerase chain reaction). In the first case, antibodies to HCV are detected in the blood, in the second - pathogen RNA.
PCR is the most accurate test, and obtaining a questionable result is usually associated with one of the following factors:
- errors made directly during blood sampling;
- non-compliance with the temperature regime for storing and transporting blood;
- errors during the formulation of the reaction.
With appropriate qualifications of laboratory technicians who manipulate blood sampling and perform research, the likelihood of a false PCR result is low. In any case, after testing for qualitative detection of the virus, quantitative determination and genotyping are carried out. Thus, the risk of diagnostic error is reduced to zero.
A false positive result from an ELISA test depends not only on the qualifications of medical laboratory workers. Antibodies are compounds with a protein structure, their structure is strictly specific (depending on the antigen), and their production is “controlled” by the immune system. Therefore, some immunoglobulins may be erroneously “recognized” by test systems as antibodies to HCV.
If a false positive test for hepatitis C is suspected, the reasons may be:
- pregnancy (regardless of gestational age);
- severe systemic infections (for example, tuberculosis), accompanied by massive production of immunoglobulins;
- autoimmune diseases;
- oncology;
- HIV.
That is why a positive ELISA result must be confirmed by a qualitative and quantitative PCR test. However, a negative ELISA in the presence of symptoms and laboratory signs indicating liver damage requires PCR.
How are hepatitis A and E infected?
When a type A virus enters the body, it quickly penetrates the liver cells, contributing to the development of the inflammatory process in the organ. But the problem does not cause serious damage and usually does not become chronic.
The infection can be transmitted from sick people like this:
- fecal-oral route through dirty hands,
- as a result of drinking contaminated water from open reservoirs,
- when eating poorly washed vegetables and fruits.
The first variant of infection is possible if a person does not follow the rules of personal hygiene. You can also catch the hepatitis E virus in the same way. People living in regions with contaminated water especially suffer from the problem.
How is hepatitis C transmitted?
Hepatitis C is the most insidious type of virus, which is also called the “gentle killer”, since it can live in the human body for several years and not manifest itself in any way, but significantly harm internal organs and slowly destroy the entire body. Patients or carriers of the hepatitis C virus cannot be distinguished from healthy people. The disease has a sluggish course and does not cause any suspicion in a person. Hepatitis C infection most often occurs in the following ways:
- Hematogenous or parenteral route (through blood) - blood transfusion or sharing a syringe needle by several people.
- Contact. You can become infected with hepatitis C in beauty salons, through piercings, tattoos, through nail scissors and other instruments that have not undergone the necessary sterilization and contain infected blood of a sick person on their surface.
- Medical manipulations. During surgery, the administration of medications, and dental procedures, there is also a risk of contracting this disease.
- Infection through sexual contact. It occurs quite rarely and only in 3% of cases during unprotected sexual intercourse. Hepatitis C is transmitted sexually only in cases of unprotected sexual intercourse. Transmission of the virus through oral sex is little known to medicine.
- Intrauterine infection of the fetus. This route of infection is also quite rare, occurring in less than 5% of cases. But the risk of infection of the child during childbirth is quite high. There is no exact information about whether the disease can be transmitted to a child through breastfeeding, but if a mother in labor suffers from hepatitis C, breastfeeding is recommended to be discontinued.
In any of the above cases, hepatitis C is transmitted only through blood.
Probability of transmission to child during pregnancy
Couples who have maintained their relationship despite the illness of one of their partners know almost everything about chronic hepatitis C: how it is transmitted and how to reduce the likelihood of infection. But often spouses think about children. If during unprotected sex the risk of infection is insignificant, then future parents worry: is it possible to give birth to a healthy child.
It is worth considering whether there will be transmission of the virus from an ill man at conception. And also find out whether it is possible for a woman with hepatitis C to give birth to a healthy baby.
From father at conception
First of all, a couple where the man is sick is concerned about whether hepatitis C is transmitted from father to child during conception. There is no risk here. Despite the viral concentration in the seminal fluid, sperm are not infected with hepatitis C and infection does not occur when fused with an egg. If the father is sick, then his disease will not be passed on to the baby.
But we should not forget about how chronic viral hepatitis is transmitted. When a man’s sperm contains a high concentration of the virus, the expectant mother may become ill during conception. If such a risk exists, it is recommended to resort to in vitro fertilization.
From the mother during pregnancy
Concerns about whether hepatitis C is transmitted from mother to child during pregnancy always arises when a woman is sick.
There is no risk to the fetus during intrauterine development. The virus does not penetrate the hematoplacental barrier, which means it is not transmitted to the fetus from the mother’s body.
During childbirth
When clarifying whether the virus is transmitted from mother to child, doctors note that at the moment it passes through the birth canal, the newborn is deprived of placental protection. By contacting the blood and mucous secretions of a sick mother, an infant can become infected with hepatitis C. The probability of infection is about 5%.
Characteristics of the virus and development of the disease
The causative agent of hepatitis C is an RNA virus that persists in the blood and infects liver cells. Its reproduction in the body is accompanied by inflammation of hepatocytes and their gradual death. After the pathogen enters the bloodstream, a long incubation period follows - from 2 weeks to 2 months or more. After this, the first clinical signs begin to appear, which you should definitely pay attention to:
- chronic fatigue, decreased performance and concentration, disturbances in sleep and wakefulness;
- a feeling of heaviness in the right hypochondrium, sharp or dull pain that intensifies after physical activity or eating heavy food;
- nausea and vomiting, stool disorders;
- in severe cases - yellow coloring of the skin and mucous membranes, lightening of the stool and darkening of the urine.
REFERENCE. The unofficial name for hepatitis C is “the gentle killer.” He received it for a long asymptomatic course, during which liver tissue is destroyed slowly and imperceptibly. The first symptoms appear already at the stage when the processes have affected a significant part of the organ.
To understand why hepatitis C is dangerous for others and how to protect yourself when communicating with an infected person, you need to know what routes of transmission of the virus exist. The causative agent of this disease is in the blood, so the only way of infection is direct contact with contaminated liquid. This may occur in the following situations:
- during a blood transfusion or during a hemodialysis procedure;
- when sharing injection syringes without first sterilizing them, this is the most common method of infection among drug addicts;
- when visiting nail salons and tattoo parlors, there is virtually no risk if you choose the establishment responsibly;
- The virus is rarely transmitted through sexual contact, only in the presence of damage to the mucous membranes of the genital organs.
When diagnosing hepatitis C, several genotypes of the virus are distinguished. The most dangerous of them is type 1b. It is difficult to treat with specific antiviral drugs, progresses quickly and often leads to the development of complications.
Danger of the disease to others and precautions
In theory, hepatitis C can be transmitted even if a small amount of infected blood comes into contact with damaged skin or mucous membranes. Such situations can arise in the family or at home, so there is a risk of infection. However, in practice it is often found that the disease persists for many years in only one family member. Everyone who has been in contact with the patient’s blood or lived in the same area with him needs to be examined, but the results in most cases are negative.
Autoimmune hepatitis
Autoimmune hepatitis is understood as a progressive and chronic inflammatory process in the liver, which occurs with signs of extensive damage to the organ, the presence of autoantibodies to the gland’s own cells. In the structure of hepatitis, autoimmune forms account for about 10-15% of cases.
Women are diagnosed with the disease 8 times more often than men. The course of the pathological process is characterized by a rapid nature, in which serious complications develop relatively early - portal hypertension, cirrhosis, hepatic cell failure.
The etiology of the disease is not fully understood. The basis of genesis is a lack of immunoregulation. Depending on the antibodies produced, the following types of autoimmune hepatitis are distinguished:
| Type of disease | Description |
| First type | Most often found in patients 10-20 years old and after 50 years of age. The prognosis is favorable, since in 90% of cases immunosuppressive drugs help, which allows achieving stable and long-term remission. If there is no therapy for 3 years, cirrhosis of the liver develops. |
| Second type | Type 2 is characterized by high biochemical activity and manifests itself in childhood. The response to immunosuppressive treatment is insufficient; when medications are discontinued, a relapse of the disease is quickly detected. According to statistics, with this type, cirrhosis develops several times more often. |
| Third type | In type 3, the presence of rheumatoid factor and antimitochondrial antibodies is determined. |
Manifestations in children and adults
The disease manifests itself suddenly, the clinical manifestations are practically no different from the signs of acute viral diseases. At first, patients complain of severe weakness, loss of appetite, and intense jaundice.
After 1-1.5 months, symptoms appear:
- Pain in right side.
- Skin itching.
- Nausea, vomiting.
Against the background of pathology, the liver and spleen enlarge. The autoimmune process in 50% of cases occurs along with other diseases - myocarditis, type 1 diabetes mellitus, vitiligo, Sjögren's syndrome.
Diagnostics
The criteria for the disease are biochemical, serological and histological markers detected. An autoimmune form of pathology is said to exist if the following criteria are present:
- If the patient has not taken hepatotoxic medications, there is no alcohol dependence.
- When there are no markers of viral pathogens in the blood.
- The concentration of γ-globulins and IgG is higher than normal.
- AST and ALT are above normal.
- Antibody titers (SMA, ANA and LKM-1) for an adult from 1:80; for a child from 1:20.
A biopsy is required. Using manipulation, a chronic disease with signs of pronounced activity is diagnosed. Histology shows stepwise or bridge-like necrotic transformations and lymphoid infiltration.
Hepatitis A or Botkin's disease
The viral form of hepatitis A is an acute infectious lesion of the liver, characterized by a benign course, leading to necrosis of liver cells. Botkin's disease rarely transforms into a chronic course.
Causes
The mechanism of transmission of the virus is fecal-oral. An infected adult or child sheds many viral particles into the environment through feces. They get into water, food, and household items.
When pathogens enter the oral cavity of a healthy person susceptible to infection, hepatitis develops.
Infection occurs when swimming in dirty pools or bodies of water. When consuming contaminated foods or poorly purified water. When living together with a sick person, infection occurs when touching household objects - door handles, towels, toys, etc.
Clinical manifestations
The incubation period is 14-28 days. The entire clinical picture can be divided into three periods - pre-icteric, icteric and recovery stage.
In the pre-icteric period, symptoms are scanty, the patient is concerned about signs of intoxication and an increase in body temperature. An increase in temperature is not observed in everyone - in approximately 50% of patients.
The duration of the icteric period is 14-28 days, it is manifested by the following symptoms of hepatitis:
- On days 5-10 the skin turns yellow.
- Change in color of urine - becomes darker in color.
- Discoloration of feces.
- Pain in the right hypochondrium.
- Enlarged spleen.
- Dyspeptic disorders.
- Joint and muscle pain.
- Itching of the skin.
The recovery period lasts from 7 to 150 days. Symptoms gradually weaken and then disappear completely.
Features of therapy
Acute hepatitis A is not a dangerous disease, since it rarely leads to serious complications and does not require specific treatment. In case of severe symptoms, symptomatic therapy is carried out, including drugs from the following groups:
- Vitamin complexes (Aevit).
- Hepatoprotectors (Karsil).
- Enterosorbents (Smecta).
- Enzyme agents (Creon).
- Immunomodulators (Thymogen).
- Choleretic medications (Allohol).
Against the background of a sharp deterioration in health, hormonal therapy is carried out, Prednisolone and Methylprednisolone are prescribed.
Features of a dangerous disease
To understand why hepatitis C is dangerous, it is necessary to define it. Hepatitis C refers to inflammation of the gland caused by a virus. There are 7 different hepatitis viruses: A, B, C, D, E, F, G. The most common viruses are A, B, C. The HCV viral disease consists of 6 types (genotypes), which consist of 30 subtypes.
The peculiarity of Hepatitis C disease lies in its ability to constantly change, which makes it impossible to develop an effective vaccine against the disease. When an infection enters the bloodstream, viruses are distributed throughout all parts of the body. Liver cells provide ideal conditions for infection to multiply, as a result of which they begin to decompose.
An inflammatory infection is the body's attempt to fight disease. Without treatment, HCV disease becomes chronic. When shrinkage of the gland occurs with loss of its functions, this characterizes the development of cirrhosis as a consequence of the Hepatitis C virus, hepatocellular carcinoma, an irreversible process as a result of malignant degeneration of hepatocytes (liver parenchyma cells). The only way to save life is a gland transplant, its transplantation from a donor to a recipient.
If high-quality treatment is carried out using highly effective medications, therapy will slow down the progression of the harmful process and lead to good remission. Infection with the Hepatitis C virus occurs through direct contact through blood or tissue containing the infection. The most common routes of infection are:
- intravenous injection of narcotic substances;
- blood transfusion;
- contact with infected blood;
- transmission routes through dried blood, for example, on razor blades, dressing materials;
- sexual contact with an infected person.
The ability to infect others is acquired at the time of infection and lasts as long as the Hepatitis C virus is present in the blood. After introduction into the body, the virus multiplies quickly, the liver tissue degenerates into connective tissue, and the functions of the gland are limited.
What causes infection during sex?
No more than 10% of cases of hepatitis infection occur as a result of sexual contact. This is much less than in the case of the immunodeficiency virus.
Saliva, vaginal secretions, and seminal fluid contain a small amount of the pathogen. Therefore, during sex, hepatitis C becomes infected in very rare cases.
Such a development of events is possible under the influence of the following factors:
- If the genital tract or oral cavity is damaged and bleeding.
- If an inflammatory process develops in the genitals.
- Sex without barrier contraception during menstruation.
- The presence of pathological processes in the urinary tract, infection with the human immunodeficiency virus.
- Lack of sexual culture.
- Anal sex without a condom.
- Aggressive sexual acts accompanied by injuries.
Considering these factors, we can conclude that sexual intercourse without condoms is undesirable. It is important to have your blood tested once a year to identify markers of hepatitis C.
Symptoms of the disease
Viral hepatitis is often called the “gentle killer.” But why? The fact is that diseases of type B and C very often are completely asymptomatic . This means that despite all the destructive processes occurring in his body, the patient feels healthy (in some cases there is mild aggression and a bad mood, which many patients do not associate with illness). This greatly complicates the diagnosis of the disease in question.
However, in some cases, at the acute stage of the disease, the following signs of a serious illness can be observed :
- Jaundice discoloration of the patient’s skin and eyeballs;
- Painful sensations in the right side, a feeling of heaviness and squeezing;
- Light shade of fecal matter and sharply darkened color of urine (shade of dark beer);
- Attacks of nausea, vomiting, a feeling of disgust for food, a sharp decrease in appetite;
- General malaise, as in the case of influenza;
- Slight increase in temperature (up to 37-38 degrees);
- Depression, apathy and sleep disorders (from complete insomnia to daytime sleepiness).
If these symptoms occur, you must make an appointment with a hepatologist. The doctor will first prescribe examinations to identify signs of liver inflammation , namely:
- Blood chemistry . With a viral infection, blood biochemistry changes;
- Ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs. With HCV, liver volume increases;
- Blood test for hepatovirus markers . Markers are antibodies to a pathogen antigen - special protein compounds that appear as a consequence of the immune response to infection. Their appearance indicates that the person is most likely sick;
- Analysis to identify the genotype of the virus . It is carried out after a confirmed diagnosis. Necessary for selecting an appropriate course of treatment.
It is important to note that in some cases, symptoms and even test results may be erroneous. Therefore, additional diagnostics may be needed to confirm the diagnosis.
What are hepatitis?
Hepatitis is an inflammatory pathology of the liver. Depending on the course, acute and chronic varieties of the disease are distinguished. The acute form is distinguished by pronounced clinical manifestations and has 2 outcome options - complete cure or chronicization of the pathological process.
In most cases, the cause of development is: viral agents, excessive consumption of alcoholic beverages, uncontrolled use for a long time of drugs that have a hepatotoxic effect.
When a diagnosis of “chronic hepatitis” is made, it is assumed that the “experience” of inflammation is more than 6 months. According to the morphological picture, dystrophic transformations are observed in the liver tissues, which do not affect the lobular structures.
Primary chronic forms occur in the absence of symptoms or with minor manifestations. Often the problem is discovered by chance - during a preventive medical examination or during an examination due to other complaints of the patient.
Pathogenesis of the development of acute and chronic forms of the disease
The acute form is a consequence of direct damage to the liver by hepatotoxic substances or the activity of a viral infection, an autoimmune disorder in the body - the immune system produces antibodies that attack its own liver.
Regardless of the cause, an acute inflammatory reaction is observed in parenchymal tissues, hepatocytes are damaged and destroyed, the liver swells, and the functionality of the internal organ deteriorates.
Since the gland tissues are not equipped with pain receptors, pain syndrome develops in exceptional cases against the background of severe hepatomegaly - a significant increase in the right and/or left lobe of the liver.
The cause of the chronic form appears to be the lack of conservative therapy or an incorrect therapeutic strategy of the acute variety. Often anicteric hepatitis is not diagnosed in time, which causes the pathological process to become chronic.
With chronic hepatitis, foci of dystrophy form, liver tissue degenerates, the functioning of the organ is disrupted, and the risks of developing cirrhosis increase.
Classification of hepatitis
In medical practice, several classifications of diseases are used. So, depending on the symptoms and course, acute and chronic varieties are distinguished.
Classification by etiological factors:
- Alcoholic.
- Medication.
- Viral.
- Autoimmune.
- Secondary hepatitis (develops due to concomitant diseases).
- Cryptogenic (idiopathic) hepatitis means that the cause of the disease has not been established.
There is a separate group of specific hepatitis. For example, there is opisthorchiasis (liver damage by opisthorchiasis), echinococcal (against the background of liver echinococcosis).
Classification depending on clinical manifestations - anicteric form, icteric and subclinical. Autoimmune types of hepatitis differ by type; they are caused by antibody targets - type 1, 2, 3.
Diseases caused by intoxication
Toxic hepatitis is a pathological condition of the liver caused by exposure to toxic substances (alcohol, drugs, toxic substances). The disease is characterized by an acute or chronic course, jaundice (yellowness of the sclera, skin, mucous membranes), pain in the right hypochondrium, as well as changes in blood tests (increased ALT, AST, bilirubin).
Note! The acute form of toxic hepatitis manifests itself after receiving a high dosage of toxin (poison). Clinical manifestations develop within a few days. With this type of disease, the patient requires urgent care and hospitalization.
The chronic form of the disease is characterized by the gradual death of liver cells over 3-4 months or many years. In this case, symptoms of the disease may appear when there are already lesions in the liver.
Toxins and development factors
Liver toxins are divided into 2 types:
- hepatotropic (directly affects liver cells, killing them);
- having no effect on liver cells (drugs and substances that cause deterioration of blood flow).
Also, toxins that can cause hepatitis are divided into groups depending on their chemical properties and scope of application (Table 2).
Table 2 – Types of toxins by chemical composition
| Group | Substances |
| Industrial |
|
| Natural | Weeds, mushrooms (white toadstool). |
| Alcohol-containing substances | Alcohol, vodka, cognac. |
| Medicines |
|
Toxic substances can penetrate the skin, lungs, and digestive tract. After this, the toxins pass into the bloodstream and then into the liver. Poisons lead to the destruction of liver cells, replacing them with connective and fatty cell structures. This provokes liver failure, hepatic coma or encephalopathy. Failure of the liver leads to the death of the patient.
Factors in the development of the disease:
- work in hazardous industries: agriculture, metallurgy, oil and ore mining, food production.
- the presence of diseases that require taking medications that are toxic to the liver (oncology, tuberculosis);
- living in an area contaminated with pesticides, heavy metals, and oil discharges;
- liver disease in the previous generation;
- alcoholism;
- diabetes;
- low or overweight.
The following groups of patients are more susceptible to the disease:
- children;
- patients with chronic diseases;
- alcohol and drug addicts;
- patients with viral hepatitis, liver dysfunction.
Clinical manifestations
Toxic hepatitis of any origin has general and specific clinical signs. Typical manifestations for all toxic liver pathologies:
- manifestations of jaundice (yellowness of the skin, sclera and mucous membranes);
- enlarged liver (the lower edge of the liver protrudes from under the costal arch);
- pain in the right hypochondrium;
- itching;
- liver failure: encephalopathy (drowsiness, weakness), hepatic coma, ascites, swelling, hemorrhagic diathesis.
Specific symptoms depend on the type of toxin:
- When affected by benzene, aplastic anemia, brain damage, and cataracts are observed.
- With toxic copper poisoning, gastralgia (stomach pain), nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, bleeding, and decreased urine volume develop.
- Arsenic damage causes dysfunction of the kidneys and nerve bundles.
- In phosphorus poisoning, the patient experiences low blood glucose levels and bleeding.
- Poisonous mushrooms can cause hallucinations due to brain damage.
- Insecticide poisoning provokes myocarditis, nephritis, brain damage, and a decrease in blood granulocytes.
Viral pathologies
Viral pathologies of the liver develop with the penetration of viruses that are tropic to the liver tissue. Each type of disease has its own transmission routes and development mechanism. Viral hepatitis is divided into 2 main groups, differing in the method of infection (Table 1).
Table 1 – Types of viral liver pathologies
| Path of spread of the virus | Kinds |
| Parenteral | B, C, D, G, F |
| Fecal-oral | A, E, F |
Forms A, E
Hepatitis A is a disease caused by the type A virus and is transmitted by the fecal-oral route. This type of liver pathology does not have a chronic form. The disease is always acute, and after recovery the patient develops stable lifelong immunity. Doctors call the disease “the disease of dirty hands”, as it is transmitted through contaminated water, unwashed vegetables, fruits, contaminated household items, as well as through insufficient heat treatment of food.
The HAV virus enters the digestive tract through the mouth, then enters the blood and then to the liver tissue. In the cells of the liver tissue, the microorganism is embedded inside the cell, creating new viral particles. After this process is completed, viruses enter the bloodstream (secondary viremia). As a response, the body forms a large number of antibodies against microorganisms, killing viral particles. After recovery, immunity is formed.
Hepatitis A occurs everywhere, but is most common in Asia and Africa. At-risk groups:
- children;
- representatives of antisocial groups;
- people traveling to countries where hepatitis A is endemic.
The risk of infection increases with:
- failure to comply with personal hygiene rules;
- drinking unboiled water from springs, water pipes, wells;
- refusal to vaccinate against hepatitis A on the eve of travel to endemic areas.
Hepatitis E has similar clinical manifestations, mechanism of infection, pathogenesis, and risk factors. A distinctive feature of this type of disease is the severity of the disease during the 3rd trimester of pregnancy.
Important! Hepatitis E in pregnant women can lead to complete liver dysfunction and death (50%).
With HEV, the development of hepatic encephalopathy, coma, and hemorrhagic syndrome is possible. The occurrence of severe bleeding leads to fetal death in utero, premature birth, and miscarriages. Up to 50% of children born alive die within a month of birth.
Types B, C, D, G
Such hepatitis are parenteral forms, that is, they are transmitted through the blood. The diseases are common in Asia, Africa, the USA (Canada), and North America. Ways to spread infection:
- cosmetic and tattoo parlors;
- use of non-sterile medical equipment, instruments, syringes, drip systems;
- frequent blood transfusions, dialysis;
- sexual intercourse (unprotected sexual intercourse);
- vertical mode of transmission (from mother to child during passage through the birth canal).
Risk groups for parenteral hepatitis include:
- drug users;
- medical workers (obstetricians-gynecologists, surgeons, operating room nurses, blood transfusion station employees, hepatologists, infectious disease specialists);
- homosexuals;
- people with promiscuous sex;
- newborn children;
- patients traveling to endemic areas for hepatitis;
- people who have constant contact with the patient (relatives).
Hepatitis B is caused by a virus containing a DNA molecule. Other types of viruses have only one strand (RNA). HBV is the most persistent virus outside the body. When a viral particle enters a patient’s body, it is integrated into the genome of the liver cell. Using the genetic material of hepatocytes, the virus generates new viral particles. They, leaving the cells, penetrate back into the blood, increasing their number. The pathogenesis of other viruses proceeds similarly.
Note! Hepatitis D cannot independently penetrate and multiply in the cells of the liver tissue, since it does not have specific receptors on the surface. To reproduce, a viral particle must have another virus present.
Usually the assistant is HBV. If a patient has viruses B and D, the disease is very severe with the development of liver failure in a short time, and also leads to death.
Hepatitis C is a “gentle killer”, since for many years a person may not feel any symptoms, but during this time the microorganism has already significantly damaged the patient’s liver tissue. Also, when conducting a blood test in a patient at the initial stage of the disease, no viruses are detected (blind period 1-1.5 months). HCV can occur in an acute form, but more often becomes chronic.
Interesting! Hepatitis G is a coinfection of hepatitis B, C, D, and HIV. There is evidence that the presence of HGV prolongs the life of HIV-infected patients.
It prevents the effects of the human immunodeficiency virus on the body's cells. HGV does not worsen the course of other viral hepatitis.
The risk of infection is increased by promiscuity, failure to comply with safety precautions when working with blood products, and lack of routine vaccination of children and adults. The danger of parenteral hepatitis is the gradual development of liver failure, cirrhosis, and liver cancer.
To prevent the spread of hepatitis B today there is a vaccine that was developed more than 20 years ago. Vaccination was included in the national calendar. It is given free of charge to all children from birth and adults who have not been vaccinated previously. There is no vaccine for other parenteral hepatitis.
Hepatitis F
Hepatitis F differs from other liver diseases in that the disease spreads through both the fecal-oral route of infection and sexual, parenteral, and vertical. Symptoms of the disease include dyspepsia, jaundice, and enlarged liver. HFV often becomes chronic.
Risk groups for this disease include antisocial sections of the population, children, drug addicts, homosexuals, people with constant changes of partner, medical workers, and HIV patients. To prevent the disease, nonspecific preventive measures are used: hygiene, preventive examinations of patients at risk.
Does a baby get infected while breastfeeding?
There is no evidence that the pathogen can enter the child’s blood through mother’s milk. Although virus particles were found in milk, their quantity was insignificant. Therefore, women in whose bodies an infectious process develops are allowed to feed their children, but with caution.
If the surface of the nipples has been damaged, then breastfeeding cannot be given, as blood will get to the baby. Feeding should be stopped until the mammary glands are completely restored.
If the feeding process is accompanied by painful sensations, this may indicate the presence of microcracks in the nipples, so you cannot continue feeding. To reduce the risk of infection to the newborn, you should use special nipple covers.
Is chronic hepatitis transmitted?
In the absence of adequate antiviral therapy, the acute form of hepatitis C becomes chronic. It is characterized by fibrosis, cirrhosis and liver cancer. In this case, viral particles are present in the body in an inactive, inactive or active form, which determines the rate of progression of liver dysfunction and other complications.
Whether chronic hepatitis is contagious or not depends on the activity of the virus. If it is present in low concentrations or is inactive, the risk of transmission is minimal. A high viral load indicates a serious threat to others. In any case, precautions must be taken when coming into contact with an infected person.
Forecast
With timely treatment, it is possible to avoid many of the consequences of hepatitis C. Modern methods make it possible to defeat both acute and chronic disease. In the first case, it is important to maintain bed rest, diet, and avoid physical and emotional stress.
Sometimes hospitalization and the use of medications to support liver function may be required. Acute hepatitis C is cured in 20–30 patients out of 100. For the remaining 70–85% of those infected, the prognosis is less favorable; hepatitis becomes chronic.
If the disease is chronic, the chances of recovery are 50–90%. Antiviral drugs are used for treatment - interferons and ribavirin. The dosage and duration of therapy are selected individually depending on age, medical history and genotype of the virus. For type 1, the treatment period is usually 48 weeks, for types 2 and 3 - 24 weeks. The first genotype of the hepatitis C virus is more difficult to treat; 50% of patients recover. With the second and third, up to 90 patients out of 100 overcome the disease.
In the absence of treatment, chronic hepatitis C is not always complicated. If the concentration of viral particles in the blood is low and the structure of the liver is not changed, a person can live for many years. However, with high activity of the virus and a diseased liver, the patient faces cirrhosis and cancer. The prognosis is worsened by alcohol consumption, poor diet, excess weight, old age or childhood. Liver cirrhosis cannot be completely cured. In the final stages of the disease, life can only be prolonged through organ transplantation.
The consequences of infection are detrimental not only to the health of the sick person. It is important to understand how dangerous viral hepatitis C is for others. By negligence, you can transmit the disease to your child, wife or other family members. Therefore, hepatitis C should not be left to chance. You need to undergo a full examination and then discuss an effective treatment regimen with a hepatologist. Do not be ill!