What is intestinal colic
Acute spasmodic pain in the abdomen is usually observed in a young child (sometimes a teenager), but intestinal colic is also common in adult men and women. In adults, acute pain in the intestines warns of a malfunction of the digestive organs. The cause of the attack can be various pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract, as well as stress and age-related changes.
The term “intestinal colic” in adults refers to several symptoms of acute abdominal pain that are common to many diseases. Acute pain can be paroxysmal in nature or appear as spasmodic pain of increasing intensity.
How to relieve intestinal spasms in a child
The occurrence of an attack in an infant is determined by the failure of digestive functionality. This phenomenon occurs in 50% of babies in the first months and usually goes away by six months. You need to take the baby in your arms and hold it like a “soldier”, pressing it to you.
Frequent attacks indicate the presence of some serious disorders, so if the mother notices spasms in the child, she should urgently consult a doctor.
Symptoms of seizures in a newborn:
- anxiety;
- poor sleep and appetite;
- constant regurgitation and rumbling in the tummy;
- flatulence;
- tone of the anterior wall (noticeable even with light palpation).
In addition, the baby, to alleviate his condition, intuitively pulls his legs towards his stomach. The duration of the spasm ranges from 30 minutes to three hours, and relief occurs mainly after defecation or release of gases. When attacks are infrequent, and the baby is generally calm, takes food well and, according to his age, accumulates weight, then there is no need to worry. Although a visit to the clinic has never harmed anyone.
In this video, a young mother relieves intestinal colic in her baby.
Factors that provoke intestinal colic
Intestinal colic is often combined with the concept of “acute abdomen”; such pain may indicate functional intestinal disorders or deep organic lesions.
The following factors can contribute to the appearance of intestinal colic:
- diseases of the digestive system (gallbladder, liver, pancreas, gastritis, ulcers). Such pathologies are accompanied by indigestion if, after eating, some time later, semi-digested food penetrates the small intestine, causing it to spasm.
- unbalanced and irregular nutrition, overeating, snacking.
- consumption of stale food, cold dishes or foods during the preparation of which fermentation occurs (yeast dough products, kvass, pickled apples, sauerkraut).
- food and drug poisoning.
- intestinal infections caused by the penetration of pathogenic microbes into the body (dysentery bacilli, salmonella). These microorganisms produce toxins when they get into food, and when consumed, food toxicosis occurs - toxic infection. Such intestinal infections include salmonellosis, dysentery, and cholera.
- nervous tension, stress. The appearance of such a symptom is acceptable due to nervousness, often in a particularly impressionable person.
- intoxication with salts of heavy metals (lead is the most dangerous). Chemical production workers who are exposed to toxic substances for a long time are at risk. Once in the body, lead salts provoke the so-called “lead” colic.
- helminth infection. Parasites that live in the intestines constantly affect its walls and mucous membranes, irritating the nerve endings.
- influenza or ARVI. Viral infections affect not only the respiratory system, but also the digestive system, settling in the lymph nodes of the peritoneum, provoking their inflammation. These nodes are located in the mesentery of the small intestine and cause spasmodic pain, irritating it. Colic can be combined with indigestion (diarrhea) and manifestations of infection in the respiratory tract (runny nose, redness and sore throat, cough). Pain in the abdominal muscles can be quite severe and worsen with movement.
- intestinal obstruction, malfunction, stretching of intestinal loops, mechanical obstruction (adhesions, tumor), accumulation of feces. Discomfort may occur due to heavy lifting and heavy physical activity.
There are many factors that can cause intestinal colic, so only a specialist can determine the causes of this symptom and prescribe precise treatment that can eliminate pain and alleviate the patient’s condition.
Prevention
You can only prevent colic that is caused by eating low-quality foods - just don’t eat spoiled foods. Colic of other origins, accompanying illnesses or everyday disasters, is almost impossible to stop.
With chronic intestinal diseases, it is only possible to undergo anti-relapse treatment on time and eat right.
The main thing is not to panic when intestinal colic appears. You need to calmly find out the cause and behave according to the diagnosis. Cooperation with a doctor and reasonable behavior are the key to good health.
Symptoms of intestinal colic
The most severe signs of intestinal colic are attacks of unbearable acute pain, which is accompanied by spasmodic pain. The most severe pain is recorded in the navel area (umbilical pain), in case of stomach diseases it can radiate to the epigastric region, upward, in other cases the pain will radiate downwards. The pain can quickly increase and radiate to the testicles (in men) and to the genitals (in women).
On palpation, the patient feels severe pain, but there is no tension in the abdominal muscles. The pain can last for hours and even days; it is never short-lived. The cramping pain may subside slightly, but other signs may appear that accompany the deterioration of the patient's condition (constipation, gas retention, abdominal pain). In the acute form of gastritis, colic can be supplemented by dyspeptic symptoms - belching, vomiting, nausea, bloating.
Diarrhea with mucus may appear during bowel movements. The patient experiences weakness, aversion to food, and general health deteriorates.
Acute intestinal obstruction may begin to develop from intestinal colic. Intense, excruciating, cramping pain is felt throughout the entire abdominal area, and vomiting occurs. Further, gas and stool retention is possible, abdominal bloating is observed, and a sharp drop in pressure is possible.
Doctors distinguish several forms of intestinal colic, the symptoms of each will be supplemented by other signs. Depending on the pathology that caused intestinal colic, additional symptoms and, accordingly, treatment will differ.
| Disease | Additional symptoms | Primary care | Treatment |
| Gastritis, cholecystitis | Belching, nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, pain - tingling in the epigastric region | Refusal of food, taking painkillers - “Spazmalgon”, “No-shpa” | Treatment by a gastroenterologist to avoid attacks |
| Intestinal obstruction | Constant increase in attacks, rapid deterioration in general condition, loss of strength, decreased blood pressure, lack of stool, bloating, vomiting | A cool heating pad is placed on the pain area | Immediate surgery required |
| Infectious diseases | Severe diarrhea, rising temperature, diarrhea, rising temperature and blood pressure, signs of intoxication, general weakness | Taking Smecta, Regidron, a cold heating pad on the pain area, drinking plenty of fluids | Treatment in the infectious diseases department is required. The patient's condition may be life-threatening |
| Lead poisoning | Gray complexion, gum ulcers, gray plaque on the gums, teeth, dizziness | The patient's condition may be life-threatening; emergency medical attention is needed | |
| Appendicitis | The attacks intensify, the pain covers the right side | Cold heating pad on the pain area | Surgical intervention |
| Poisoning | Pale skin, watery diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, dry skin, rare urination | Drink plenty of fluids, take activated carbon, gastric lavage | Treatment under the supervision of a doctor at home |
| For helminthiasis | Itching, burning in the anus, during sleep - teeth grinding, allergic rash, sudden weight loss | Warm bath, use of “No-Shpa”, “Spazmalgon”, “Becarbon” | After pain relief - treatment of helminthiasis |
Causes
Normal contractions of the intestine serve to push food through. The muscles of all parts except the rectum work alternately. The spasm occurs as a result of severe irritation of the walls. This can come from:
- food poisoning;
- parasite activity;
- heavy metal poisoning;
- infection with viruses, bacteria;
- diseases that change the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract (dysbacteriosis, Crohn's disease, ulcers, irritable bowel syndrome, gastritis);
- prolonged stress;
- poorly digested foods that reach the intestines as a result of overeating;
- food allergies;
- intestinal underdevelopment (in newborns);
- high intra-abdominal pressure, hormonal changes (during pregnancy);
- insufficient physical activity;
- microflora disorders due to consumption of expired products, bacteria entering the body.
Particularly severe pain occurs during colic with intestinal obstruction. Urgent medical attention is needed; the problem can only be solved by surgery.
The cause of obstruction is blockage of the intestinal lumen. It can be formed by a foreign body, a tumor, or a collection of parasites. Perhaps a lot of gallstones or fecal stones have accumulated in one place. If operations were performed, the formation of adhesions could also cause obstruction.
Symptoms of various localizations of colic
The symptoms of colic are distinguished according to the location of the pain. It often happens that pain initially appears in another part of the peritoneum, and if left untreated, it spreads to the intestines.
With rectal (rectal) colic, a painful false urge to defecate occurs.
With appendicular colic, the pain is located on the right side and radiates to the iliac region. Usually appears in the first hours of the formation of acute appendicitis and is characterized by severe pain of an increasing nature.
With renal colic, intense periodic paroxysmal pain is felt, which radiates to the groin, tailbone, genitals, lower back, while nausea and a rare complete absence of urination are observed. The pain worsens with movement. Blood pressure drops, temperature rises significantly to +39. At the peak of the pain syndrome, loss of consciousness, convulsions and fainting may occur. Renal colic can be caused by: acute or chronic inflammation (pyelonephritis), urolithiasis, tuberculosis and kidney tumors.
With hepatic colic, pain appears in the right hypochondrium, can radiate to the shoulder, to the shoulder blade, bitterness is felt in the mouth, nausea occurs and vomiting with bile is possible. Hepatic colic is caused by cholelithiasis or acute cholecystitis.
With pancreatic colic, pain first appears in the left hypochondrium, and then becomes encircling, spreads throughout the body, accompanied by an autonomic reaction in the form of nausea, vomiting, and possible diarrhea. It appears in pancreatic pathologies. This condition can be caused by pancreatic tumors or acute pancreatitis.
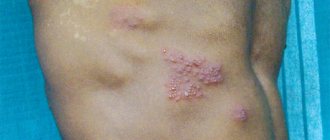
Lead colic. Clinical manifestations of lead poisoning are characterized by sharp cramping pain, pain in the abdomen, muscle tension in the abdominal wall, high temperature (up to 39°C), bleeding (hemorrhagic syndrome) from the gums, and the presence of gray plaque between the gums and teeth.
If you suspect these types of colic, you should urgently call an ambulance. Primary aid is as follows: loosen the patient’s clothes, put a cool heating pad on the stomach, call an ambulance.
If the cause of colic is known, then take the drug prescribed by the doctor; in other cases, no medications should be given to the patient until the doctor arrives.
Video on the topic:
How to relieve symptoms at home
Colic can be caused by various reasons, so it is not recommended to apply a heating pad to the stomach or give an enema before the doctor arrives. This can blur the clinical picture and complicate the patient's condition. Especially when there is a suspicion of intestinal obstruction or appendicitis, and there is no way to distinguish it from other pathologies.
If the doctor determines that the patient has simple intestinal colic, the following actions are allowed:
- take sedatives if the attack is caused by stress;
- take 2 tablets of “No-shpa”, washed down with mint decoction, or a sachet of “Smecta”, having previously dissolved it in 100 ml of water.
- Apply a heating pad with warm water to the groin area. This helps relax muscles and relieve spasms.
- after this, do an enema with a decoction of lemon balm or mint. As a rule, after the intestines are freed from feces and gases, the pain subsides.
Chamomile decoction or immortelle decoction will help relieve intestinal colic.
You can take several tablets of Bellalgin, Besalol, Becarbona, or administer rectal suppositories with belladonna extract.
After such procedures, the patient must refuse to eat for half an hour; he is allowed to drink warm unsweetened tea with crackers. In the following days, you should refrain from eating foods that cause excessive gas formation.
Activated carbon to the rescue
Activated carbon is classified as a sorbent. It removes harmful substances from the body:
- medications;
- microbes;
- poisons;
- food allergens;
- alkaloids.
The medication acts in the body for 24 hours. It is not absorbed into the walls of the stomach. Removes unnecessary substances naturally.
Release form. Tablets with a rough black surface. Available in paper packaging of 10 pieces. Several standards are sorted into a cardboard box and instructions are attached.
Contraindications. The drug should not be used by patients with ulcerative and intestinal pathologies in the acute stage.
Pregnancy and lactation period. The medicine is allowed for use by pregnant and nursing mothers. The components are not absorbed into the body and blood.
Instructions for use. Application depends on the severity of the disease. Start taking 2 tablets 3 times a day. In case of severe poisoning, the dose is determined based on the patient’s weight. The recommended dosage is 1 tablet per 10 kilograms. Activated carbon is diluted in half a glass of water or taken dry with water. Interaction with other medications Activated carbon affects the effect of any medications. Its main task is to remove foreign substances from the body.
Diagnosis of intestinal colic
To make a correct diagnosis, you need to undergo a full examination. First, the doctor finds out the history of the disease, listens to the patient’s complaints about the location and nature of the pain and additional symptoms.
The doctor examines the patient and palpates the abdomen. A pathological cause of colic is indicated by tension in the abdominal wall muscles and soreness.
To make an accurate diagnosis, the patient should undergo the following examinations:
- stool occult blood test;
- Analysis of urine;
- biochemical and general blood test;
- coprogram;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs. This will make it possible to determine the pathology causing intestinal colic;
- colonoscopy;
- CT. The study is done if there is a suspicion of a tumor or trauma to the intestines and internal organs.
- sigmoidoscopy. Using an endoscope, a visual examination of part of the sigmoid and rectum is performed.
Main signs of pathology
The main symptoms of intestinal spasm include:
| Sign of pathology | Characteristic |
| Pain | Occurs in the navel area, may be recurring, intense or mild, increasing over time or constant |
| Stool disorder | Both constipation and diarrhea may occur. This symptom is characteristic of both irritable bowel syndrome and dysbiosis, therefore it is necessary to conduct tests to clarify the diagnosis |
| Flatulence | This symptom, together with bloating, indicates the presence of irritable bowel syndrome if it recurs over several months. |
| Nausea, vomiting | Signs indicate problems in the digestive system; together with spasms, they can be perceived as symptoms characteristic of one disease, or as various phenomena that arise from pathologies accompanying each other |
| Feeling of heaviness, insufficiently emptied intestines | This feeling that appears after defecation in combination with cramps may indicate irritable bowel syndrome. But if other phenomena also occur - bleeding during defecation, pain in the rectum - one can suspect the presence of more serious pathologies - polyps, neoplasms, internal hemorrhoids |
If your health condition worsens due to intestinal spasm, the following symptoms will develop:
- headache;
- the appearance of chills;
- increased sweating.
If the spasm is provoked by acute intestinal obstruction or thrombosis formed in the mesenteric vessels, the development of symptoms occurs rapidly. The pain may spread to all parts of the abdomen, and noticeable tension in the anterior wall of the peritoneum.
How to treat intestinal colic
Drug treatment will depend on the cause of intestinal colic.
When these are diseases such as stenosis (narrowing) of the urinary tract, pyelonephritis, cholecystitis, urolithiasis or cholelithiasis, hepatitis, tumors, then the diseases themselves must first be treated directly.
When colic is caused by a severe intestinal infection, the patient needs to be hospitalized and treated in an infectious diseases hospital. If acute intestinal obstruction or appendicitis is diagnosed, surgical intervention is performed. When the cause of colic is a parasitic infection, treatment for helminthiasis is carried out.
To get rid of pain, antispasmodics are used: “Drotaverine”, “Notensil”, “Becarbon”. They may prescribe injections of Papaverine, Atropine, and Diphenhydramine as first aid.
After pain relief, the patient is under the supervision of a doctor, since for further therapy it is important to know how the patient will feel after colic. If the cause of colic is due to dietary errors, then after defecation and release of gases, the colic stops and the patient feels relief.
Toxic infection or intestinal infection requires serious treatment. A course of antibiotics is prescribed: Levomycetin, Gentamicin and intestinal antiseptics: Furozalidone, Biseptol. In particularly difficult situations, saline solutions, glucose, blood plasma, and vitamins are used as intravenous infusions.
Intestinal colic, caused by influenza and acute respiratory infections, is treated with antispasmodics, vitamins and activated charcoal.
For vascular colic, which is caused by insufficient blood flow to the abdominal organs, medications are taken that improve the patency of the arteries.
Treatment of intestinal colic with folk remedies
If colic is caused by parasitic infections, the following traditional medicines are suggested:
- pumpkin seeds. To 2 tbsp. Add 300 ml of boiling water to spoons of pumpkin seeds (crushed), add 2 teaspoons of sugar and drink the infusion for 5 days.
- tansy flowers. 1 tbsp. Pour boiling water (1 glass) over a spoonful of tansy, leave to infuse and drink throughout the day. Course - 2-3 days.
- lavender oil. It relieves pain and spasms, calms the nervous system. Place 5 drops of oil in a small amount of water and drink.
- decoction of white wormwood. Pour 100 g of raw material with cold water and leave for 2 days. Then simmer over low heat for about an hour. The finished broth is filtered and 400 g of honey is added to it. Place it on the fire again and cook until the mixture thickens. Drink 1 tbsp decoction. spoon 4 times a day.
- ginger tea. Drink to relieve colic. For tea, take half a teaspoon of ginger root per 1 glass of hot water. Drink 2-3 cups a day.
- fresh cabbage juice. It relieves colic well. Drink cabbage juice after meals, diluting it with water.
- an infusion of cinquefoil root, nettle leaves, alder cones, thyme, St. John's wort, and lemon balm helps with intestinal colic if it is accompanied by diarrhea. All components are taken in equal quantities, 1 tbsp. Pour a spoonful of the mixture into a glass of boiling water and leave. Take half a glass three times a day before meals - morning, afternoon and evening.
Treatment
Treatment should be carried out by a gastroenterologist after a thorough examination. According to the standards of medical care, the tactics are as follows:
- medicinal pain relief;
- nutrition correction;
- lifestyle modification - optimization of physical activity, change in professional stress, normalization of emotional state.
We recommend reading:
Causes of seething and rumbling along the intestines, methods of elimination
Medicines
WHO recommends using only level 1 analgesics – non-opioid – to relieve intestinal colic. The standard drug in this series is paracetamol , recognized as the most effective and safe.
To enhance the analgesic effect, additional drugs are used:
- anticonvulsants – Finlepsin, valproic acid derivatives in the lowest possible doses;
- tricyclic antidepressants - Amitriptyline, Anafranil, Doxepin, Melipramine and the like.
The use of antispasmodics is mandatory, the most effective of which is hyoscine butyl bromide or Buscopan. The substance is an antagonist of endogenous muscarinic receptors, so a systemic effect does not develop, the effect affects only the intestines. The drug is available in tablets and suppositories, which significantly accelerates the onset of the therapeutic effect.
Diet
Nutrition needs to be given special attention, since it is impossible to recover without normalizing it. Regular meals are required, always at the same time, without long breaks, in small portions.
| Recommended Products | Not Recommended Products |
|
|
Exercises
During periods between pain, walking, climbing stairs without an elevator, and other physical activity that improves intestinal motility are useful. Exercises for strengthening the abdominal muscles are very useful:
- "bike";
- twists - straight and reverse;
- hanging leg raises;
- bar;
- training on simulators;
- push ups.
Massage
Massage improves blood and lymph flow, activates metabolic processes, strengthens and warms muscles.
Massage movements are performed with warm hands. The main ones are:
- stroking around the navel clockwise;
- “mill” - palms are placed across the abdomen, movements from the ribs to the pelvis alternate;
- stroking from the ribs to the pelvis with both palms at the same time.
Self-massage is not difficult to master, and its benefits are undeniable.
Folk remedies
An ancient folk remedy is dill seeds boiled in milk. For a glass of milk you need to take 1 tablespoon of dill seeds and boil for no more than 5 minutes. Cool, strain and drink in small sips throughout the day.
Read more: Using dill water for colic
Traditional medicine offers a variety of herbal remedies. The peculiarity of all is to take it for a long time, at least a month, since the concentration of the active substances is low. The following are used:
- chamomile, calamus root and oak bark;
- motherwort grass;
- oregano herb (motherland);
- lavender tea;
- alder decoction;
- ginger tea;
- wormwood decoction.
Read more: The use of herbs for colic and abdominal pain
Folk remedies have to be selected by trial and error, but each person has the opportunity to find his own, most effective remedy.
We recommend reading:
Absorbents: names of drugs and their use to cleanse the body
Diet for intestinal colic
A special place in the treatment of intestinal colic is given to diet. It is almost always prescribed and is an integral part of treatment.
If you have intestinal colic, you need to avoid fatty, fried, spicy, pickled, salty and smoked foods. It is also not recommended to use seasonings in dishes, eat canned food, or drink carbonated drinks. Products made from yeast dough and sweets are prohibited. You should reduce your consumption of meat dishes.
It is better to give preference to cereals, low-fat fish, and vegetable dishes. It is useful to drink herbal teas and fermented milk drinks.
| You can eat | Prohibited |
| Chicken, rabbit, lean beef, chicken eggs - boiled | fatty meat, pork, sausages, frankfurters |
| Wheat crackers | Fresh baked goods, rye bread, |
| Low-fat cottage cheese, kefir | Whole milk, other full-fat dairy products |
| Vegetable, unrefined fats | Animal fats |
| Beets, carrots (juice from them), boiled pumpkin | Cabbage, cucumbers, sweet peppers, radishes, corn, radishes, turnips |
| Buckwheat porridge, semolina on water | Millet, pearl barley, oatmeal |
| Juices | Sugar, sweets |
| Apples | Legumes |
Preventive measures
In order to prevent the development of intestinal spasms, it is necessary to adjust the diet and diversify the menu. For normal food movement and good motor skills, plant fiber is needed all year round. Also, such fiber does not require large amounts of digestive enzymes and bile acids. This means that such products do not burden the digestive organs.
To avoid convulsive contractions of the intestinal muscles, you should not overeat. It is especially harmful to overeat at night. Fractional meals in small portions are the best option for digestion. The digestive organs will have time to join the process. Enzymes and bile are produced in sufficient quantities. Digestion proceeds without problems.
It is also necessary to promptly treat diseases, the complications of which are digestive problems. Try to avoid depression and increase stress resistance.
Classification
There are several types of intestinal spasms.
Hepatic
The cause is cholecystitis and cholelithiasis.
This condition is accompanied by a pronounced pain syndrome in the area of the right hypochondrium, radiating to the upper limb. The patient begins to complain of attacks of nausea and vomiting, a bitter taste in the mouth.
Rectal
The place of localization is the rectum. Accompanied by severe pain and false urge to defecate.
Lead
Occurs against the background of lead poisoning. It is characterized by bleeding gums, tension in the abdominal muscle tissue, increased body temperature, and the formation of a gray coating on the tongue.
Appendicular
This is the first sign indicating acute appendicitis. The pain is increasing in nature and localized in the iliac zone.
Renal
The cause of the disease can be tumor formations, urolithiasis, pyelonephritis. The patient begins to complain of pain, which is also localized in the lower back.
There is an increase in body temperature and a decrease in blood pressure . When pain first appears, some patients may lose consciousness.
Pancreatic
Description
Colic is a sharp, cramping pain that occurs in the abdominal cavity.
Colic occurs due to spasm of the muscle fibers of organs located in the abdominal cavity and retroperitoneal space. Depending on the location of the spasm, there is a certain classification. Colic is of the following types:
- intestinal;
- hepatic (bilious);
- renal;
- pancreas (pancreatic).
Colic is not considered as a separate disease, but is a symptom of a disease that has a spasmodic reaction of the body in response to an irritant.
Intestinal colic:
- eating fatty, fried, smoked meats;
- lack of regular, rational and balanced nutrition (eating on the go, eating too much, consuming coarse fiber or, conversely, for a long time the absence of foods containing fiber in the diet);
- poisoning: food poisoning (poisonous mushrooms, poor-quality or expired food);
- medicinal;
- chemicals (for example, lead during its mining and smelting, during the manufacture of battery plates, paint components, electrical and cable products);
Renal colic:
- blocking the excretion of urine due to an attack of urolithiasis (a sign is the presence of stone fractions of urates, oxalates inside the hollow structures of the kidney, as well as in the bladder);
- pyelonephritis;
- kidney tuberculosis;
- neoplasms in the kidneys.
Hepatic colic:
- cholelithiasis;
- acute inflammation of the biliary tract.
- acute pancreatitis;
- pancreatic neoplasms.
The prognosis for colic in the absence of treatment for the disease that initiated its occurrence is unfavorable. Therefore, if pain occurs, you should immediately consult a doctor, who, in turn, will determine the cause of its occurrence and prescribe appropriate treatment.
Cabbage juice will improve bowel function
A developing infection in the intestinal cavity or the onset of inflammatory processes in the intestinal cavity will be eliminated by cabbage juice.
Despite its specific and not entirely pleasant aroma, the drink is useful to drink not only for people with problems with colic in the intestines. Twice a day, a glass of cabbage liquid diluted with water or carrot-beet juice should be drunk to maintain the body's immune strength and resistance to colds.
Colitis and flatulence have long been treated with enemas and temporary fasting. A person suffering from intestinal spasms was allowed to drink only herbal decoctions and infusions of thyme, dandelion, coltsfoot, marjoram and blueberries.
Popular herbal “cocktails”
When it’s not just colic in the intestines in adults that causes discomfort. How to treat (tablets that have been trusted for many years - No-Shpa) concomitant diarrhea at home is a fairly common question. The herbal mixture, represented by thyme, alder cones, St. John's wort, lemon balm and stinging nettle in equal quantities, is poured with boiling water overnight, and the medicinal drug is infused in this way until the morning. For 10 grams of dry herbal “mix”, 250 ml of boiling water is enough.
Another recipe that helps with the same problem is another collection of medicinal herbs. It is prepared from three main components (snake knotweed, valerian root and chamomile inflorescences), but arnica or chestnut leaves are often added. A quarter liter of hot water is enough for a tablespoon of herbal tea. Before taking the medicine, it should be infused in a thermos, and it is recommended to drink it on an empty stomach.
Many people do not know how to overcome intestinal colic in adults or how to treat it. Medicines prepared independently will bring no less benefits than potent pharmaceutical medications. For example, a decoction of alder bark boiled over a fire for a couple of minutes is one of the most effective remedies against intestinal colic.
Chemical poisoning of the body and worms
Quite often, in people whose professional activities are directly related to the use of lead, colic in the intestines can be detected.
In adults, treatment in this case will be aimed at quickly cleansing the body of heavy metal chemical poisoning. It is often easy to notice a characteristic dark plaque between the teeth of those who have been poisoned.
It often happens that uncomfortable colic in the intestines is a consequence of helminth infection. Worms are detected during clinical laboratory tests of stool. In the contents, experts find eggs of one or another type of helminth. However, intestinal colic is not the only sign of uninvited “guests” appearing in the body. In addition to painful spasms, the following is observed:
- rapid weight loss;
- nausea;
- complete lack of appetite;
- constant itching around the anus;
- the presence of more than 4 eosinophils in the blood parameters of the clinical analysis.
Motherwort, oregano and lavender
Among chronic diseases that cause constant colic in the intestines, acute colitis occupies one of the first places in terms of prevalence. You can relieve irritation of the intestinal walls with the help of an infusion of motherwort and stinging nettle. Finding a dry collection of motherwort in a pharmacy is not difficult, and pour two tablespoons of dry herb with two glasses of hot water at home, after 30-40 minutes the infused drink can be filtered and used for medicinal purposes. You need to drink this drug for three weeks.
Oregano herb is another effective remedy that helps overcome intestinal colic in adults. Many supporters of alternative medicine know how to treat and how to get rid of spastic pain. They found their salvation in an infusion of a dry plant. To get a healing drink, you will need 3 tablespoons of dry inflorescences of the plant, poured with a liter of boiling water. You do not need to infuse this drug for a long time; after ten minutes you can begin treatment.
“Mountain lavender,” sung in songs, can quickly calm the intestines and relieve spasms. A plant prepared as a simple tea that does not need to be specially infused helps. The recipe is simple - a teaspoon per glass of boiling water. However, it is extremely important not to overdo it with traditional therapy and drink no more than three cups of tea per day.
Stomach cramps: what to do? Causes and symptoms of periodic pain
The main sign of muscle contraction is rapidly developing pain in the upper abdomen, and the person’s general condition worsens. Spasmodic contractions may also be accompanied by nausea or vomiting, and weakness. With severe cramps and pain in the abdominal area, a person usually takes a bent position. Thus, there is a decrease in discomfort.
Other signs include increased gas production and tense abdominal muscles.
Gastric spasm can occur differently in each person. Symptoms depend on the causes of the disease.
Usually, most people suffering from this disease have a question: what to do with stomach cramps? First you need to figure out why and why this happened.
Why does pregnant women have stomach pain?
As a rule, during the period when a girl is pregnant, she often has difficulties with the digestive system. Mostly these problems occur in the second and third trimester. This circumstance is explained by the fact that the growing uterus puts pressure on the digestive organs, thereby causing pregnant girls to experience stomach pain with cramps and attacks.
One of the most common troubles that befalls pregnant women is flatulence and heartburn.
An increase not only in the weight of the fetus, but also in size leads to a displacement of the digestive organs, which provokes constipation. In addition, all this is accompanied by bloating.
In this situation, experts advise following a diet and diet, not eating too much food at one sitting, and drinking more fermented milk drinks. Taking medications such as laxatives is not recommended. Because their use can lead to hypertension. This phenomenon is considered unfavorable for the fetus.
Medications
Among medications in the treatment of spasms, antispasmodics occupy a leading place. But you need to keep in mind that they only eliminate the symptom, but do not remove the cause of the pathology; long-term use without a doctor’s prescription can lead to dire consequences. Usually they are used either for a one-time dose or as prescribed by a doctor in courses.
- No-shpa. The most recognizable drug among antispasmodics. The recommended one-time dosage is 80 mg. Causes relaxation of smooth muscle tissue not only of the digestive tract, but also of other muscles, as a result it can cause a decrease in pressure and weakness.
- Papaverine. Available in suppositories and tablets. An old drug with many side effects, rarely used.
- Duspatalin. A more modern medicine that selectively targets stomach and other spasms of the digestive tract.
- Buskopan. The most fast-acting antispasmodic. Specializes in gastrointestinal pain. Contraindicated during pregnancy.
- Meteospasmil. Complex drug, a strong antispasmodic and carminative.
It is important to know that antispasmodics and painkillers are contraindicated in acute conditions until the cause is determined.