05/22/2018 Category: Cervical erosionAuthor: Pomiome
Article last updated 12/07/2019
Cauterization is an effective way to treat erosion. But the risks of complications after surgery and restrictions after the procedure pose the woman the question of whether it is necessary to cauterize the cervical erosion or whether the operation can be postponed by carrying out maintenance drug therapy.
Indications for use
Only the attending physician can tell the patient whether or not to cauterize the erosion after the diagnosis has been carried out and the severity of the clinical case has been determined. Although cauterization using various technologies, as the only effective method, is used quite often in gynecology, it is prescribed only if there are absolute indications.
- Is there any pain when cauterizing erosion: reviews from patients
- What to do after cauterization of erosion: restrictions during the rehabilitation period
This method of surgical intervention cannot be called easy, therefore, if there are no acute indications, they try not to use it. It is mandatory to cauterize erosion if there are the following indications:
- development of dysplasia;
- mild neoplasia or cervical type;
- diagnosing leukoplakia;
- relapse of pathology after previous cauterization;
- the presence of foci of endometriosis;
- wide distribution of erosive foci on the tissues of the cervix.
Since these diseases will gradually worsen, leading to the development of severe complications and the rapid spread of pathological processes, the answer of doctors to the question of whether it is necessary to cauterize erosion is unequivocal - yes, it is necessary.
Why is erosion dangerous?
Erosion is dangerous due to the appearance of cells that should not be there. These cells do not yet lead to serious consequences for the body, but if, say, a virus gets in, destruction of the structure may begin. As a result, rebirth occurs. So erosion leads to malignant tumors. It is for this reason that this disease cannot be ignored.
Methods
After the doctor, based on the results of examining the woman, makes a conclusion whether it is necessary to cauterize the cervical erosion, a suitable technique is selected. The cauterization method is selected taking into account the severity of the clinical case, the patient’s age, and her history of pregnancies. Methods used:
- laser cauterization;
- exposure of tissue to argon;
- cryodestruction - a technique for destroying tissue under the influence of liquid nitrogen;
- radio wave method.
None of these methods will give a 100% guarantee that the pathology will not recur. This is one of the main reasons why many patients refuse to undergo such a medical procedure. If the pathology of the uterine cervix was detected in a timely manner, and the pathological process is in the early stages of development with minimal risks of complications, doctors do not rush with cauterization. This is especially true for women who do not have children, but are planning a pregnancy in the future.
First, conservative therapy is carried out, including mainly the prescription of anti-inflammatory drugs. If there is no positive dynamics for several months, and the inflammatory process does not decrease, they resort to cauterization.
Discharge
How does cauterization occur? In fact, there is an intensive effect on the epithelial area, including its vessels. It is the damage to the blood vessels that can lead to minor bleeding after the procedure.
Spotting and spotting within 2-3 days after the intervention is considered normal. If they persist longer, you should consult a doctor.
This is described in more detail in the article: Discharge after cauterization of cervical erosion.
Rescheduling
If there are indications for a gynecological procedure, the doctor will answer whether it is possible to cauterize the erosion after a thorough examination. Why is a preliminary examination necessary?
There are a number of contraindications, in the presence of which the pathology is not burned out due to the high risks of developing side symptoms and complications. These conditions include:
- there are inflammatory processes in the vagina;
- inflammation was diagnosed in the cervical canal;
- the patient has human papillomavirus;
- chronic infectious diseases transmitted through unprotected sexual intercourse;
- diagnosis of pseudo-erosion.
Should cervical erosion be cauterized or not in the presence of these contraindications? Yes, but only after the inflammatory processes are eliminated. This is achieved primarily through drug therapy, but surgical intervention is often required.
Price
How much does it cost to treat cervical erosion? This depends on the region and type of medical institution.
Cost of manipulation by city
| Type of procedure | Moscow | Saint Petersburg | Ekaterinburg | |||
| Radio wave treatment of cervical erosion | Central Clinical Hospital No. 2 named after. ON THE. Semashko JSC Russian Railways | 5050 rub. | SM-Clinic | 4700 rub. | Road hospital | From 1000 rub./session |
| Electrocoagulation of erosion | Family Clinic | 5000 rub. | Altermed | 8000 rub. | ASK | 1800 rub. |
| Cryodestruction | Family Clinic | 3000 rub. | Alpha Center | 1500 rub. | ||
| Laser treatment | MEDLUX | From 8000 rub. | Gynecology Center on Shuvalovsky Prospekt | 4500 rub. | Women's clinic | 8000 rub. |
| Electroconization | Family Clinic | 15,000 rub. | Sun Clinic | From 6500 rub. | New technologies | From 3500 rub. |
| Argon plasma ablation | Family Clinic | From 3500 rub. | Leka Farm | From 4000 rub. | Panacea | From 1500 rub. |
| Chemical exposure | Medic | 2500 rub. | Eleos | 2500 rub. (excluding drug cost) | Magnolia | 1000 rub. |
| Ultrasound treatment | Health. Center for Medicine and Cosmetology | 2000 rub./session | Liteiny Medical Center | From 650 rub./session | Your Doctor | 1300 rub./session |
Is it necessary to cauterize erosion? Most often, this procedure is necessary because it minimizes the risk of relapse (unlike drug treatment). But sometimes experts do not recommend resorting to it.
Cases when cauterization is not performed
The lack of need to cauterize cervical erosion does not mean that a woman should not treat it. Drug therapy is prescribed aimed at maintaining the normal condition and functioning of the uterine cervix. Do not cauterize cervical erosion in the following cases:
- the pathology is congenital, the presence of a symptomatic picture is due to hormonal imbalance, the condition is corrected with medication;
- true erosion, in which the soft tissues of the organ recover on their own, drug treatment is carried out only to eliminate signs of the disease;
- the pathological process is benign in nature, in which there is no likelihood of dysplasia;
- the development of pathology is caused by mechanical damage to the cervix, so it is worth waiting for their natural healing.
Only the attending physician can say whether it is worth cauterizing erosion in such clinical cases. But, as a rule, this procedure is not resorted to, since the likelihood of independent tissue restoration is high, and there are no risks of complications.
Hyaluronic acid for treatment
Almost all women know about such a substance as hyaluronic acid. It is included in various skin cosmetics. Due to this substance, moisture is retained, a protective film is formed and the skin heals quickly. Previously, the product was used only in dermatology and cosmetology. Today it is also used in gynecology. It has been proven that hyaluronic acid restores the mucous membrane and maintains water balance.
More recently, pharmacists have released Cicatridine vaginal suppositories, with their help you can heal the vaginal mucosa, moisturize it and restore it. The candles contain:
- Hyaluric acid.
- Centella asiatica extract, which is used to treat wounds. With its help, you can quickly restore tissues and speed up their healing.
- Calendula extract is the main feminine herb. In ancient times, calendula was used to treat trichomoniasis and candidiasis. This is the best antibacterial agent.
- Aloe vera extract has a wound healing effect.
- Tea tree oil has an antimicrobial, disinfectant, and anti-inflammatory effect. This component will help destroy pathogenic microflora, which aggravates the inflammatory process during erosion.
It is not recommended to use suppositories on your own, only after a doctor’s prescription.
Myths about moxibustion
There are many myths about the treatment of pathology, because of which women are afraid to resort to this method of treating the pathological process:
- Using the cauterizing method is painful . No, all procedures to remove pathological erosive lesions are carried out using local anesthesia to reduce the severity of the pain symptom. It is possible that a slight, nagging pain will appear in the lower abdomen during the procedure, but it is mild and quite easily tolerated by women.
- Removal of affected soft tissues leads to the development of complications . Like any type of surgical intervention, there are risks of complications after cauterization of the cervix. However, in most cases they are associated with poor quality work by the doctor or the woman’s failure to comply with medical instructions during the recovery period. If all the rules are followed, there is practically no chance of consequences developing.
- There will be some restrictions after the operation . Yes, after surgery, a woman will be prohibited for 1-2 months from entering into intimate relationships, visiting public pools, swimming in open water, going to a bathhouse, and using tampons during menstruation. Any violation of these rules will inevitably lead to complications.
- Is it necessary to cauterize the erosion and why do it if a relapse is still possible after the procedure ? Indeed, the likelihood of recurrence of the pathology is high, but this does not mean that surgery is not necessary. Without timely removal of pathological tissues, the risks of developing severe complications, including the appearance of cancer, are high. A relapse may or may not occur after 10 years, it all depends on whether the woman follows preventive measures.
- The procedure may have a negative impact on pregnancy in the future . This is not entirely true. Modern cauterization methods can minimize the risks of consequences, in particular, damage to adjacent soft structures, which can further negatively affect the condition of the reproductive system. If the operation is performed well, there will be no risk of complications in the future with pregnancy.
Modern methods of treating cervical erosion in nulliparous women
All methods of therapy must meet the following requirements:
- Efficiency: low relapse rate;
- The ability to capture the entire affected area at once and perform all manipulations in one step. Sufficient depth of penetration into the mucous membrane;
- Safety: low risk of complications, including bleeding, infection;
- No scars on the cervix after the procedure;
- Possibility to take material for a biopsy (relevant if a malignant tumor is suspected).
If these conditions are met, manipulation is considered safe and can be used to treat cervical erosion in women planning pregnancy. The following therapy methods meet all these requirements:
Chemical coagulation
The essence of the method: the use of various medications for direct application to the cervix.
For treatment, Solkovagin, Vagotil and other drugs are used. The drug is applied to the lesion, has a cauterizing effect, and does not leave scars. After using the medicine, a scab forms, which disappears after 5–7 days. It also allows you to fight concomitant infections, which is important for erosion complicated by inflammation of the cervix.
Chemical coagulation is actively used for small erosions (up to 2 cm in diameter and up to 2 mm in depth). Not used for deep and extensive lesions of the cervix, as well as for severe inflammation.
Important point
An allergic reaction to the components of the drug is possible. If severe itching and burning occurs after the procedure, you should consult a doctor.
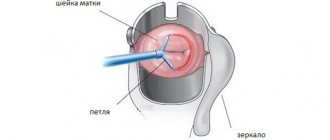
Radio wave therapy
The essence of the method: the use of radio waves to cauterize erosion.
An effective non-contact method that guarantees getting rid of a defect on the mucous membrane without damaging healthy tissue. Does not require anesthesia and is performed on an outpatient basis. It is considered one of the best ways to treat erosion in women planning pregnancy.
On a note
After radio wave exposure, no scars remain, the cervix is not damaged, conception, gestation and birth of a child proceed without any problems.
Radio wave coagulation is carried out using the Surgitron apparatus. During the procedure, the doctor acts on the lesion with the pathology with high-frequency radio waves. This method is recommended for nulliparous women, as it does not leave scars on the cervix.
Laser coagulation
The essence of the method: cauterization of the pathological focus with a laser beam.
It is used for the treatment of erosion, as well as the removal of condylomas, nabothian cysts and other formations on the cervix. Allows you to precisely remove only the affected tissue without touching healthy areas. Penetrates to a depth of 3–5 mm, so it is not used for deep defects.
Argon plasma ablation
The essence of the method: the effect of argon on a defect in the mucous membrane.
It is a contactless and improved version of DEK. Unlike electrocoagulation, it does not leave scars and does not provoke bleeding. Effective for shallow lesions of the mucous membrane (up to 3 mm).
On a note
Numerous positive reviews of modern methods of destructive treatment indicate that laser and radio wave coagulation are the preferred treatment options. Both procedures are painless. Recovery after manipulation takes 3–4 weeks. Reviews indicate that women tolerate these procedures quite well and subsequently do not experience problems with having a child.
In modern gynecology, DEC (diathermoelectrocoagulation) is not used to treat cervical erosion in nulliparous women. After this procedure, rough scars often remain, which subsequently interferes with conceiving and bearing a child. Natural childbirth after DEC is also not always possible, which significantly limits the use of this method in young girls.
Gynecologists have not come to a consensus regarding cryodestruction. The use of liquid nitrogen in nulliparous women is possible, but the method has its limitations. Cryotherapy is effective only for shallow mucosal defects, and often the doctor is unable to cover the entire affected area. The high frequency of relapses, a long recovery period, discomfort during and after the procedure - all this makes cryodestruction not the most suitable method of therapy for nulliparous women.
Consequences of untreated pathology in a timely manner
By postponing surgery to remove cervical pathology in a timely manner, a woman exposes herself to the risk of developing serious complications. In addition to the gradually increasing intensity of the symptomatic picture, hormonal imbalance and cycle disorders, the greatest danger is the risk of degeneration of a benign process into a malignant tumor.
Cervical cancer is a common complication of untreated erosion. It occurs predominantly in women of reproductive age who have neglected the need to visit a gynecologist in a timely manner. Therefore, cauterization of erosive foci of the cervix should be carried out as soon as the diagnosis has been made.
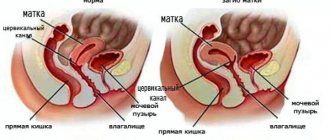
Types of erosion
The diagnosis given to a woman by a gynecologist may imply three different conditions of the cervical mucosa. This:
- true erosion, in which bleeding wounds and microcracks are found on the cervix, when pressed, drops of blood or ichor are released;
- ectopia, or the appearance of red areas on the cervix. They can be of different sizes and, if severe, cover the entire cervix. Red spots are formed by a specific cylindrical epithelium, characteristic of the internal (cervical) canal of the cervix;
- congenital ectopia, which is a feature of the development and formation of a woman’s internal genital organs and is considered a physiological, natural condition that disappears on its own after reaching the age of 20.
The areas of red epithelium on the cervix are formed by cylindrical cells, which are arranged in one layer. Their functions differ from those performed by ordinary cells of the integumentary pink epithelium, tightly connected to each other and arranged in several rows.
The cervical epithelium is single-row and is unable to protect the cervix from mechanical damage that may occur during sexual intercourse. Normally, the mucous membranes of the cervix and vagina secrete a small amount of liquid mucus, the purpose of which is to remove dead epithelial cells and bacteria.
The purpose of the cylindrical cells is different - they must ensure the targeted movement of sperm to the uterus. The thick mucus they produce hermetically seals the cervical canal, preventing foreign fluids and infections from entering the cervix.
Areas of red epithelium that appear in the wrong place begin to produce atypical mucus, which becomes a breeding ground for various pathogenic microorganisms, which, under certain conditions, can provoke the appearance of inflammatory processes.
The condition of true erosion is diagnosed quite rarely - wounds and damage are detected within 10-14 days and tend to heal on their own. For various reasons, the affected areas are covered not with flat, but with cylindrical epithelium, i.e., ectopia is formed.