According to this information, it becomes clear that leukocyte infiltration of the cervix is a condition that develops in the presence of an inflammatory process in the tissues. Most often found in cervicitis and vaginitis.
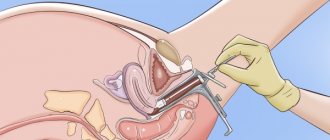
The diagnosis of leukocyte infiltration is made to women who have had a smear taken during a gynecological examination. The resulting material is sent to the laboratory for examination under a microscope. A smear is obtained using a Volkmann spoon after inserting a speculum into the vagina.
Where does the research material come from? The doctor takes tissue from the places where he sees pathological changes. The resulting material is applied to a glass slide and dried, only then the smear is checked in the laboratory.
Preparation
Only a comprehensive examination will allow us to detect the cause of leukocyte infiltration and cure the changes occurring in the cervix. An increased number of leukocytes is treated with antiseptic and antibiotic drugs, as well as lactobacteria and bifidobacteria.
Treatment of leukocyte infiltration also depends on the cause itself. Having gotten rid of the disease, the level of leukocytes in the epithelium of the cervix will be restored. It is possible to be sexually active in this condition if additional tests do not reveal a specific infection.
Cytology results
1. Quality of the drug:
2. Cytogram (description).
3. Additional clarifications.
Read 12 comments:
added after 16 minutes
added after 1 minute
Nival, well, everything is fine!
Leave a comment:
You must register or log in to be able to comment.
- Build a graph:
- Registration
- Remind password
- Information:
- Registered: 193362 people.
- BT charts: 374324 pcs.
- FAQ on working with charts
- Rules on BeTeshka
- Search for "Yasha" and Search for "Gosh"
- Help in deciphering gr. BT
- Help for newbies
- AzBuka BeTeshki for beginners
- Blog of communication between planners
- “Pregnant” BT charts
- Our rulers
- Contacts
New blog topics:
- · Mashulya Pregnancy planning:
- On line:
Visitors: 67
Registered: 19, guests 48.
Use of materials only with the permission of the administration, subject to an active link to the site.
https://www.my-bt.ru/talk/comments43019p1.html?
https://youtu.be/YIpfr51OM_g
Methods for studying atypical cervical cells
Before talking about methods for examining the cervical area, you need to know who needs to undergo these same examinations and how. So, the examination shows:
Laboratory research
- all women from 30 to 65 years old. It will be enough to carry it out once every three years.
- girls are supposed to undergo it three years after she begins to be sexually active
- girls who are not yet sexually active need to be examined more frequently, once a year
- women who suffer from any diseases of the genital organs of any nature should also be examined annually
A study to identify atypical cells of the cervix is carried out using cytology. To do this, a smear is taken from the vaginal area and sent for laboratory analysis.
If this analysis shows the presence of atypical cells, then most likely the doctor will want to better examine them using a special device called a colposcope. In addition, there is a biopsy test. It involves taking an area of the mucosa where atypical cells are found and studying it in order to establish further treatment.
Cytology results
Good day! Please help me decipher the cytology results. After 3 weeks, stimulation followed by incision is planned. All the tests are excellent and the last one came back like this:
Cytological examination of biomaterial from the cervix using the Papanicolaou method (PAP test)
1. Quality of the drug:
Exocervix - the quality of the drug is adequate.
Endocervix - the quality of the drug is adequate.
2. Cytogram (description).
Exocervix - the resulting material contained cells of superficial and intermediate squamous epithelium
Weak, sometimes moderately pronounced leukocyte infiltration.
Endocervix - elements of peripheral blood and squamous epithelial cells were found in the obtained material
superficial, intermediate layers and columnar epithelium.
Squamous metaplastic epithelium.
Moderate, sometimes pronounced leukocyte infiltration.
3. Additional clarifications.
In the obtained material, cells with signs of malignancy were not identified.
Read 12 comments:
The exocervix and endocervix are adequate, which means that there are no malignant cells.
Well, it seems like there is not much inflammation. I don't think it's scary. They'll treat you and everything will be fine!
added after 16 minutes
I’ll also add that I’m not a doctor, so only a doctor can be more specific.
With inflammation it is unlikely that they will take him for stimulation (
What could this even be? Everything tested clear for infection
Nival, I can’t say for sure about inflammation, but I was confused by the pronounced leukocyte infiltration in places. The girls will go to the blog and maybe they’ll say something.
Here is my test, the doctor said it was excellent and that everything was ok. But it’s true that you have written more than I have.
added after 1 minute
And so, mild leukocentral infiltration is the norm
Thank you very much for your answers! I made an appointment with the doctor tomorrow (lucky, a window appeared), then I’ll tell you what they tell me about it.
Nival, your question is about my work profile. smear is normal. What day of the cycle was it taken on? I don’t think they will ban stimulation
Nival, well, everything is fine!
Hermione, good afternoon! On the 7th day of the cycle.
Nival, good afternoon. The number of leukocytes is a dynamic value, it can change during the cycle, many factors influence it. What did they say at the consultation?
Hermione, today I went to two doctors with this question - the first one said everything is fine and don’t do anything, the second one prescribed Terzhinan suppositories. opinions differ
edited less than a minute ago
Nival, no, worry, the first doctor didn’t prescribe anything, because you have no complaints, and if you don’t, then there’s nothing to treat. And the second one prescribed Terzhinan as a safety net, it won’t make things worse, it can be used. Do what will make you feel calmer, because the main thing is your attitude.
Content
To maintain health, a woman is recommended to carry out timely preventive diagnosis and treatment of gynecological diseases with regular visits to the gynecologist. In the absence of complaints and chronic pathologies, a preventive visit to the doctor is recommended annually.
A gynecological examination is the basis for determining the normal microflora of the vagina and the cellular composition of the cervix.
One of the standard gynecological procedures is the examination of the contents of the vagina and urethra for flora and oncocytology. Smears are taken from each woman.
A smear for oncocytology and flora is carried out annually in the absence of pathology, and an additional smear for flora in women with complaints from the reproductive organs.
What can a cytological analysis reveal?
How to interpret a smear for oncocytology? Decoding of data obtained in the laboratory is understandable only to a doctor. And the gynecologist does not always give a detailed picture of the disease, not wanting to waste time on explanations.
During the research process you can get 5 results:
- 1 type of cell change or negative indicator. This conclusion is made when a cytological examination does not reveal any abnormalities and the woman is healthy. Type 2 changes or inflammatory nature of the disease. In this case, additional tests are prescribed to accurately determine the nature of the changes and the reason causing them. After treatment, a repeat cytology smear is prescribed 3 months later. Type 3 changes or the presence in the epithelium of single cells with an abnormal nuclear structure. The patient is sent for detailed histological and microbiological examination. The final diagnosis is made on the basis of additional data, as well as on the basis of a cytology smear performed 3 months after the first. Type 4 changes or suspicion of malignancy. Morphological signs of cancer require urgent treatment, a full examination, including colposcopy and biopsy. Type 5 changes or detection of typical cancer cells in the epithelium in large numbers. Atypical cells found in the environment of the cervical canal and cervix, by all indications, suggest the presence of dysplasia and require immediate treatment by an oncologist. To determine the extent of the lesion, the nature of cell changes, a biopsy and histological examination are prescribed.
Types 2, 3, 4 of changes identified during cytology examination may be a sign of diseases:
- ectopia (erosion) of the cervix; papillomavirus infection; genital herpes; parakeratosis of the cervix; bacterial vaginitis; cercivit; vaginal candidiasis, etc.
Leukocytes and the cervix
Leukocytes are considered one of the main components of the human body, belonging to the white line of blood. The main function of white blood cells is to protect against harmful pathogens entering the body from the outside.
The protective function of leukocytes is:
- specific - from certain pathogens;
- nonspecific or general.
When inflammatory reagents enter the body, an inflammatory response develops, which is normally characterized by an increase in the concentration of leukocytes.
Leukocytes digest foreign agents. Normally, with a high concentration of pathogens, leukocytes begin to destroy, which is accompanied by an inflammatory reaction with the development of characteristic changes in the form of:
- hyperemia, or redness;
- swelling;
- local temperature rise.
A flora smear is a microscopic examination of scrapings from the urethra, cervix and vagina using bacterioscopy. To carry out the analysis, a disposable spatula with a rounded end is used.
The slide has 3 stroke designations:
- U - from the urethra;
- V - from the vagina;
- C - from the cervix or cervix.
In the laboratory, the dried smear is examined under a microscope, after which a conclusion is given about the composition of the microflora. The conclusion has visibility symbols:
- L — number of leukocytes;
- Ep—amount of squamous epithelium;
- Gn - the presence or absence of gonococci, the causative agents of gonorrhea, in the smear;
- Trich - the presence or absence of trichomonas in the smear, which are the causative agents of trichomoniasis.
Cytology, what is it?
Cytology is a method of examining tissue material taken from a patient to determine its cellular composition. After special treatment, the cellular structure of the area of the body being examined is studied to determine the presence or absence of pathological cells.
In gynecology, the oncocytology analysis method is widespread and is used to study the cervix for the purpose of early diagnosis of cancer. An analysis such as cervical cytology serves as a screening and allows you to detect pathology at an early stage.
Atypia
What is cervical cell atypia? This term means that for one reason or another, the normal cellular composition on the surface of the cervix in the vagina or in the cervical canal is disrupted.
Another name for this process is dysplasia. This condition has a complex development mechanism and is dangerous because it can cause cancer.
Causes
It is known that atypical cells appear in the cervical mucosa under the influence of various and often concomitant reasons. Development factors include:
- An infectious process caused by the human papillomavirus.
- Sexually transmitted diseases.
- Genetic predisposition.
- Adverse reactions to hormonal or other drugs.
- Promiscuous sexual intercourse.
- Smoking.
- Hypovitaminosis.
- Immunodeficiency.
It is no coincidence that the first place among the listed causes is the human papillomavirus (HPV). It is this infectious disease that is the main factor in the development of cancer in this anatomical region.
A vaccine against HPV has been developed and is being used, which is highly likely to prevent the development of atypia.
Degrees
In its development, cellular dysplasia has a number of successively changing stages. The following degrees of the disease are distinguished:
- Mild: there is a proliferation of cells in the deep layers of the cervix. Superficially located rows remain healthy.
- Moderate: hyperplasia of all layers of the mucosa. Sometimes single atypical cells are found.
- Severe: pronounced changes in the entire thickness of the mucous membrane. Structural elements increase in size, increased brightness of intracellular structures is observed - hyperchromia.
The last stages of the disease are defined by some experts as a group of cancer diseases that require urgent therapeutic measures.
Indications for smear cytology
A cytological examination of smears of the cervical mucosa is performed on all healthy women over the age of 18 years. In addition, the analysis must be carried out unscheduled in the following conditions:
- Preparing a woman for pregnancy.
- Identifying the cause of infertility.
- Deviations in the menstrual cycle.
- Sexually transmitted diseases, such as herpes in the genital area.
- Human papillomavirus infection.
- Before installing intrauterine contraceptive devices - spirals.
Even in the absence of the listed indications, cytological examination should be carried out regularly to exclude atypia of the cells of the cervical mucosa.
Material collection procedure
In order to examine the tissue being examined under a microscope, it is necessary to collect material - a smear or scraping. This is precisely the procedure for taking a section of the cervical mucosa for examination for oncocytology.
Many people have questions: how exactly does manipulation occur and should one prepare for it? It is worthwhile to dwell on these points in more detail.
Preparation for the procedure
If you have been prescribed the described procedure, you should follow a few simple conditions in order to conduct the study painlessly and obtain reliable materials.
The following points are recommended:
- Abstain from sexual intercourse two days before visiting a gynecologist.
- 2 days before the procedure, you should not use vaginal forms of medications - gels, suppositories, creams, etc.
- Two hours before the gynecological examination and procedure, you should not urinate.
- If you experience unpleasant symptoms from the genital organs: pain, itching, discharge, you should inform your doctor. Some conditions may be a contraindication for a smear for oncocytology.
The optimal time for submitting material for cytology is the period after menstruation (approximately the fifth day of the cycle).
Taking technique
Cytology in gynecology involves taking material through a mucosal smear. The scraping is performed in a gynecological chair during a doctor's examination. Using special sterile instruments (cytological brush), a layer of tissue is taken from the vaginal part of the cervix and from the cervical canal. Cytology is a low-traumatic procedure, therefore it is used for mass diagnostics.
The gynecologist tries to take material at the border of healthy tissue and the expected site of atypia, so that the doctor in the laboratory can detect altered cells.
In most cases, the procedure lasts a few seconds and is absolutely painless for the patient.
Sometimes there is bloody discharge from the vagina, the appearance of which is associated with minor trauma to the mucosal area. This side effect of an oncocytology test usually lasts for two days and does not require special treatment methods.
Complications
The use of disposable sterile instruments, taking material from the very edge of the cervical canal, and compliance with the requirements for the manipulation reduce the risk of complications to a minimum. However, even such a safe procedure as cytology can lead to complications.
If after the procedure you experience pain and bleeding from the vagina for more than two days, you should consult a gynecologist for examination.
It is possible that the smear technique was violated when collecting material for oncocytology.
A serious complication of the procedure is stenosis of the cervical canal. This condition is characterized by overgrowing of the lumen of this anatomical area with adhesions. This reaction of the body is associated with extensive or deep trauma to the mucous membrane, in response to which healing occurs with the formation of scars. This condition can lead to infertility, as the cervical canal becomes obstructed.
The risk of complications is minimal, so cytology is the most important method in the primary diagnosis of cervical cell dysplasia.
Liquid cytology of the cervix
The most effective method of preparing the material taken for examination is liquid cytology of the cervix. This technique allows us to achieve a minimum frequency of false-negative cytological findings.
Indications for taking a smear
If a woman has no complaints, the indications for analysis include:
- annual preventive examination;
- registration for pregnancy;
- 18, 30, 36, 40 weeks of gestational age;
- cervical erosion;
- ectopia of the cervix;
- ectropion of the cervix;
- cervical dysplasia;
- cervical stump after surgery.
If there are complaints, a smear is taken for examination when:
- changes in the color or consistency of vaginal discharge;
- the appearance of an unpleasant odor of discharge;
- violation of the act of urination in the form of discomfort, pain;
- itching in the genital area;
- burning sensation;
- painful sensations in the lower abdomen;
- discomfort or pain during sexual intercourse;
- changes in the nature of discharge or discomfort while taking medications.
Normally, if a woman has complaints, a smear for flora is taken at the first visit to the antenatal clinic. During pregnancy, vaginal examinations and smears are performed more frequently if indicated.
Preparing for the study
On the eve of the smear test, a woman should toilet her external genitalia, in other words, wash herself with running water and put on clean underwear.
A smear is not taken:
After douching;
After inserting vaginal suppositories;
During menstrual bleeding (period);
After sexual intercourse for 2 days.
http://intimatehealth. ru/proczeduryi/czitologiya-mazka-iz-shejki-matki. html
http://lediveka. ru/zdorove/bolezni-i-lechenie/chto-pokazyvaet-mazok-na-citologiyu. html
http://vseomatke. ru/lejkotsitarnaya-infiltratsiya. html
Preparation and execution
To obtain a reliable result of a smear examination, it is necessary to properly prepare for a visit to the gynecologist. No special preparation required. However, simple rules should be followed.
- Avoid sexual intercourse for 48 hours before the smear test.
- Do not use lubricant gels, vaginal suppositories or creams 24 hours before the test.
- It is forbidden to douche 24 hours before seeing a doctor.
- On the day of the smear test, do not use any intimate hygiene products when washing your genitals.
- After the last day of taking antibacterial drugs, 10 to 14 days should pass.
- It is not recommended to do the test during menstruation. Particular attention is paid to heavy bleeding.
- The last act of urination before visiting a gynecologist should be performed 2 hours before the appointment.
Sexual activity, topical products, and douching can distort the reliability of the result due to changes in the microbiocenosis.
If there is bloody discharge, there will be red blood cells in the field of view of the microscope. With heavy discharge, other elements and pathogenic microorganisms may not be detected.
During the act of urination, urine can wash away cellular elements and microorganisms.
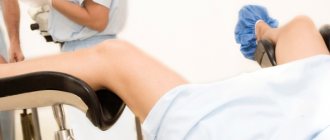
The research is carried out as follows.
- A woman is on a gynecological chair.
- The doctor inserts speculum into the vagina and exposes the cervix.
- A smear is taken from the cervix, urethra, and vagina for flora.
- A thin layer of material is applied to a glass slide under the designations: C, V, U.
- The material is sent to the laboratory, where it is stained with special dyes and examined under a microscope.
How to detect it in a smear?
This condition is detected by taking a routine smear from the vagina and examining it under a microscope. The smear is taken by a gynecologist with a special instrument called a Volkmann spoon. Material for research is taken during the examination of a woman on a chair after inserting a gynecological speculum into the vagina. A smear is taken from areas suspicious for pathological changes. The taken material is applied to a glass slide and dried.
An accumulation of leukocytes detected in this way may indicate focal inflammation of the cervix.
Taking a smear from one area does not provide information about the condition of the cervix as a whole and there is a possibility of missing pathology.
To clarify the diagnosis of leukocyte infiltration, the doctor may prescribe liquid-based cytology. This type of study is more informative than a regular vaginal smear. The material for this study is taken with a special brush, which is scrolled around the entire circumference of the uterine cervix. This eliminates the possibility of missing a disease.
White blood cell counts are normal
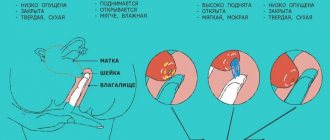
Normal leukocyte counts depend on the location of the material taken and are determined in the field of view of the microscope.
- Vagina or V. Leukocytes - 0 - 15, epithelial cells - 5 - 10, mucus - moderate. Gram-positive flora in the form of bifidobacteria and lactobacilli can be detected.
- Cervix or C. Leukocytes - 0 - 30, epithelial cells - 5 - 10, mucus in moderate quantities.
- Urethra or U. Leukocytes - 0 - 5.
Normally, the number of leukocytes does not exceed 15 per field of view. When their number increases, one can judge the nature of the inflammation: the higher the concentration of leukocytes is determined, the more pronounced the inflammatory reaction.
Squamous epithelium is the superficial layer of cells that is found at the entrance to the cervix and lines the vagina. Normally, it is always determined during childbearing age. As estrogen levels decrease, their quantity decreases.
Mucus is detected in material from the vagina. If it is found in material from the urethra, diseases of the genitourinary system should be differentiated.
Doderlein rods are lactic acid bacteria that create the normal acidic flora in the vagina. If there are enough of them, they speak of normal microflora.
Normally, the smear does not contain pathogenic microflora in the form of gonococci, trichomonas, chlamydia, gardnerella, yeast, and cocci.
During pregnancy and depending on the phase of the cycle
The number of leukocytes in a smear varies depending on the phase of the menstrual cycle and during gestation, which is due to hormonal fluctuations.
Normally, the number of leukocytes is higher in the cervical canal compared to the vagina.
The concentration of leukocytes increases in the middle of the menstrual cycle and increases before the onset of menstruation. To correctly interpret the result obtained, it is necessary to compare the ratio of leukocytes to squamous epithelium. Normally, there are 10 polymorphonuclear leukocytes per 1 cell of squamous epithelium.
During gestation, the normal number of leukocytes in the visual field increases. This is due to the fact that leukocytes and mucus provide protection to the fetus and uterus from infection in the form of a cervical plug, which is located in the cervix.
In the case of high white blood cell values during gestation, this may indicate a risk of gestational complications in the form of:
- IUI or intrauterine infection of the fetus;
- premature birth;
- spontaneous miscarriage;
- weakness of labor.
Reasons for the increase
Among the main reasons that lead to an increase in leukocytes in a smear are:
- colpitis or inflammatory lesion of the vagina;
- cervicitis or inflammatory disease in the cervix;
- endometritis or damage to the endometrium of the uterus;
- salpingoophoritis or inflammation of the uterine appendages;
- urethritis or inflammation of the urethra;
- malignant processes of the reproductive organs;
- STI;
- bacterial vaginosis;
- hormonal imbalance;
- immune disorders;
- severe stressful situations;
- frequent douching;
- anatomical features of the vulva;
- intestinal dysbiosis.
It should be noted that an increase in leukocytes and an inflammatory process in the vagina and cervix may be asymptomatic.
Regular gynecological examination allows timely elimination of the infectious and inflammatory process. Contents of the article:
A cytology smear or PAP test in women is of great diagnostic importance, since it makes it possible to identify a malignant process in the initial stage and prescribe therapy in a timely manner.
What is AK?
Atypical cells - what are they? Atypia is spoken of when, during a cytological examination, cellular structures that differ from healthy cells were identified in a sample of collected tissue. In other words, they are mutated. Their danger lies in the fact that they can “live” in the human body for a long period of time without revealing themselves.
So, is atypia cancer or not? AKs are not necessarily a sign of malignant oncology, but they may well develop into one. For a long time they are able to remain in a latent state, but when a person’s immunity weakens, they go on the “offensive” and begin to divide uncontrollably. In this case, the situation will develop according to one of two scenarios:
- a benign tumor will appear;
- a malignant, cancerous neoplasm will form.
Benign cell atypia - what is it? Typically, such a mutation occurs in the presence of sluggish inflammatory processes or other diseases, mainly of an infectious nature. In this situation, benign tumors form, which usually respond successfully to treatment.
Signs of malignant atypia - what are they? In this case, the situation is less favorable, and there are reasons for this. First of all, this leads to the formation of malignant, cancerous tumors. Of course, this process does not always take place, but it requires particularly close attention, since it is not always possible to identify it in the early stages. Typically, the tumor is diagnosed at a later stage; moreover, it often turns out to be inoperable and does not respond well to radiation and chemotherapy.
On a note. Cells with signs of atypia do not always lead to cancer. If the immune system is quite strong, then it may well destroy them without consequences for human health. The presence of chronic foci of inflammation interferes with this process, so all acute diseases must be treated on time, and be sure to be cured completely.
Atypical cells in gynecology
Atypia - what is it in gynecology? In gynecological practice, such a diagnostic procedure as a cytology smear is of great importance. We will consider further what this procedure is, when and why it is performed, but now we will briefly consider the question of what atypical cells are in gynecology.
Cytological examination in gynecology
Cytological analysis in gynecology refers to microscopic examination of samples taken from the vagina and cervical canal to determine the typical cellular composition. This diagnosis allows doctors to draw conclusions about the presence of inflammatory processes, precancerous diseases or cancer in the patient’s reproductive organs.
Unlike histological examination, the cytological method is non-invasive. That is, when taking biological material there is no need to perform a biopsy or puncture, and the integrity of the tissue is not compromised at all. Samples taken using a fingerprint or swab are analyzed. To obtain accurate results, you must carefully follow the rules for preparing for the examination. It is also very important that the analysis is deciphered by the woman’s attending physician, who will take into account her complaints and data from other diagnostic methods.
Cytological analysis usually takes no more than a day to complete. If a precancerous condition or an oncological process is discovered, invasive diagnostic techniques are used to clarify the diagnosis - biopsy.
Cytology is especially important when biopsy is contraindicated and when examining a large number of patients (when it is necessary to identify women at risk for developing malignant pathology).
A smear cytology (Pap test, Papanicolaou test) is a microscopic examination of a smear from the cervix for the purpose of early detection of cancer. This analysis is also called a hytological smear or oncocytology smear. This examination is easily tolerated by patients because it is completely painless and does not take much time.
A cytological smear not only makes it possible to timely diagnose cellular abnormalities, but also helps to identify the presence of unwanted microflora in the vaginal environment. At the same time, the test does not provide accurate data on the detected pathologies, and if an unfavorable result is obtained, the patient is sent for additional examination (smear for flora in women) and for testing for STDs.
Using the cytological method, which has been successfully used in gynecological practice for decades, it is possible to identify 5 types of changes in the cells of patients. Moreover, the research is very simple and affordable. Doctors advise all women aged 18 to 65 to undergo it at least once a year. Based on the results of the analysis, it is possible to reliably establish the presence or absence of any pathology.
Technique for performing oncocytology analysis
Gynecologists recommend performing a cytological analysis annually, starting at age 19. A smear for oncocytology is taken even if a woman under 25 years of age (and older) remains a virgin. But there are also exceptions. If cytology gives a negative result twice in a row, then the analysis can be done once every three years. And after 65 years, a woman can completely refuse cytological examination.
Women at risk (problems listed above) should have this test done more often. At the discretion of the attending physician, the examination can be carried out every three months or every six months.
A gynecological speculum is inserted into the uterus to visually examine its cervix and canal. Then the uterus is cleaned of secretions with a cotton swab. After this, a scraping is made from three different zones with a sterile spatula:
- from the side of the cervical canal (endocervix) to study columnar epithelial cells; from the vagina (exocervix) to study flat epithelial cells; from the vaginal vault.
The material taken for atypical cells is applied to a glass that is degreased and treated with a special solution in an even layer. In this case, it is allowed to apply all three samples to a common glass. To prevent the material from drying out, it is coated with a mixture of ether and ethyl alcohol or pure (96%) ethyl alcohol.
Some clinics use special aerosols for this. Then a scraping is made from the surface of the cervical canal for oncocytology, vaginosis and STI pathogens, using a sterile cervical brush (endobrush) or a cotton swab on a stick treated in saline solution. It is applied to a separate glass slide.
The procedure for taking a smear from the cervical canal for cytology is absolutely painless. After the examination is completed, the smears are sent to the laboratory for examination. It is usually performed under a microscope. But in some clinics they also use other methods of detecting pathologies in epithelial cells, for example, the Papanicolaou staining method (PAP test), the drying technique and other methods.
Liquid cytology is considered a more reliable method of testing for atypical cells. This analysis differs from the traditional one in that the taken material is first mixed with a special solution, and only then distributed over the glass. The solution cleanses the resulting material from unnecessary mucus and leukocytes, perfectly preserving epithelial cells for further research.
After taking a smear for oncocytology, some women experience small blood clots. There is no need to worry about this. This is a completely normal phenomenon and usually goes away the next day.
Indications for smear cytology
It is advisable for all women to have a smear for cytology. Before the age of 40, it is enough to undergo such diagnostics once a year. Representatives of older age groups need to be examined once every 6 months. Some cases are mandatory indications for the test. These include:
Inflammation in the cervical canal, cervix, especially if they occur chronically.
Menstrual irregularities.
Reproductive problems.
Preparation for surgical interventions and other medical procedures.
Pregnancy planning.
Preparing to install the spiral.
Taking hormonal drugs.
Diabetes.
2nd and 3rd degree obesity.
The presence of certain viruses in the body (human papilloma, genital herpes).
Frequent change of sexual partners.
How is the pathological process diagnosed?
So, having understood what cellular atypia is, let’s move on to consider the question of how they are detected and when it is necessary to carry out a diagnosis. To identify such structures, a Pap test is performed. This test is also called an atypia smear, a cytology smear, or a Pap test.
Usually there are no special reasons for performing the manipulation - gynecologists always do it as a safety net. But there are some situations when a sample is extremely necessary and mandatory. This:
- a woman being promiscuous;
- smoking;
- the presence of papillomavirus in the patient’s blood, manifested by the appearance of papillomas on the body, or genital warts on the genitals;
- earlier onset of sexual activity;
- absence of labor or complicated labor process;
- abortions, miscarriages in history.
A smear for atypical cells is also necessary if a woman has a genetic predisposition to cervical cancer. That is, if cancer cells were detected in the patient’s mother, aunt, sister or grandmother, the test must be performed regularly. And even if they have not developed into a full-fledged cancerous tumor, a smear for AK from the cervix is extremely necessary.
Like any pathological processes, cell atypia is also not causeless. One of the main factors is hormonal disorders in the body, which is confirmed by the fact that most often pathologies develop in women 40 years of age and older, whose bodies begin to prepare for the menopause.
No less dangerous is the presence of factors such as:
- frequent gynecological diseases;
- having promiscuous sex life;
- injury to female organs (numerous abortions, wearing an intrauterine device);
- the course of chronic inflammatory processes;
- presence of HPV in the body;
- weakened immune system;
- too early onset of sexual activity;
- heredity.
Gynecological diseases and disorders usually present with symptoms that disrupt a woman's life and cause significant discomfort. Depending on the degree of development of the pathological process, the characteristics of the disease and its development, signs of atypia may be:
- disturbances of the menstrual cycle, its frequency and duration of menstruation;
- bleeding;
- painful menstruation;
- the appearance of spotting in the middle of the cycle, as well as continuing long after menstruation or occurring after sexual intercourse;
- problems with conception (infertility).
Very often, descriptions of cases of atypia in gynecology note that this is a phenomenon that can be asymptomatic. In the early stages, the absence of signs is almost always observed, so the disease can be detected only by diagnostic results.
To diagnose the pathological process, a gynecological examination is performed with colposcopy and smear collection for atypia. In the first case, we are talking about a visual study of the surface of the organ through a special optical device - a colposcope, and in the second - a laboratory study of scraping the epithelium from the affected areas, which is taken using a gynecological spatula or brush directly during examination with mirrors. Both procedures are completely painless.
Taking an analysis to identify the presence of pathology
The taken smear is sent to the laboratory for cytological examination. To establish for sure that this is cervical atypia, an assessment method such as PAP (or Papanicolaou cytogram) is used. The biomaterial is stained and then examined under a microscope for its cytoplasmic and nuclear structure:
- the type of pathological process is initially determined (it can be inflammatory, malignant);
- then the severity of atypia is determined;
- then differentiation is carried out between epithelial fragments.
Preparation for a smear for cervical cytology
To get the most accurate result, you need to follow a few simple rules:
Do not douche.
Do not use topical medications (suppositories, ointments, etc.).
Wait until your period ends.
Do not urinate three hours before taking a smear.
Abstain from sexual intercourse for two days before the study.
If there is an inflammatory process in which a lot of secretion is released, the disease must be treated and a control smear done to confirm recovery. And only after this does it make sense to perform a cytological analysis.
An oncological smear is taken by a gynecologist when examining a patient. First, using mirrors, the doctor examines the condition of the vagina, examines the entrance to the cervical canal and the mucous membrane of the cervix. Then, material is taken for analysis from three areas (vagina, cervical canal, cervical inlet) using a special brush. The procedure takes very little time and does not cause patients any pain. The collected material is placed on a glass slide, evenly distributed and, after drying, transferred to a medical laboratory. There, the smear is stained with special substances and examined under a microscope.
In this case, the following characteristics are assessed:
Cell sizes and their structure.
Number of cells (per specific unit area).
Mutual arrangement.
The shape of the epithelium.
The presence of pathological changes in cells.
Structures of multilayered squamous epithelium of the vaginal mucosa
A - basal layer (a - basal cells, b - parabasal cells) B - intermediate layer, C - superficial layer; on the right are individual cells of the corresponding layers of the vaginal epithelium.
After the material collection procedure, the patient can immediately return to her normal activities. Normally there should not be any discomfort, since the brush cannot injure the tissue. True, there is a possibility that a small blood vessel will be affected. Then, within 1-2 days after the analysis, slight bleeding (streaks) will be observed. This phenomenon should not cause concern to a woman.
The cervix of a healthy woman is covered with columnar epithelium, and the vagina is flat. As for the vaginal microflora, it is not cocci, but rods. Some indicators depend on the phase of the cycle - karyo-pyknotic and acidophilic indices, basal and parabasal cells, the number of leukocytes. They provide information about the functioning of the ovaries.
Pap test interpretation
Depending on the condition of the epithelial cells, vaginal smears subjected to cytological examination are divided into five classes (Papanicolaou technique):
Class 1.
Absence of pathological changes in the studied material. The cells are of normal size and shape and are correctly located.
Class 2.
The morphological norm of some cellular elements is reduced, which is a sign of inflammation or infection. This result may be a sign of vaginosis. In such cases, further diagnostics are indicated to make an accurate diagnosis and select adequate therapy.
Class 3.
The material contains single cells with disturbances in the structure of the nucleus and cytoplasm (dysplasia or hyperplasia). The number of such pathological cells is small. The patient is sent for repeat cytology.
Class 4.
The examined smear reveals cells with malignant changes in the nucleus, chromatin and cytoplasm. These pathological changes indicate that the patient has a precancerous condition.
Class 5.
The presence of a large number of atypical cells in the smear (much more than normal). In this case, the initial stage of cancer is diagnosed.
Deciphering a smear for cytology using the Betsed method
Cytological analysis of material taken from the cervical canal is deciphered using the Betsed method. This takes into account the location of cells and dyskaryosis (changes in the nucleus). The results of the study may be as follows:
Norm. The absence of pathology does not have any special designation.
Vaginosis, koilocytosis – HPV.
- Cervical dysplasia depending on the degree - CIN I, CIN II or CIN III.
Cervical cancer - Carcinoma (pax).
Terms in diagnosis for cytological analysis of a cervical smear
In gynecological practice, it is customary to use the following designations and terms to describe the results of cytological studies:
CBO. Normal indicators, no pathological changes.
Cytogram of inflammation. Indicators indicating the development of the inflammatory process (cervicitis).
Leukocyte infiltration – increased number of leukocytes. This is a sign of vaginosis, exocervitis or endocervitis.
Koilocytes – the presence of cells indicating HPV.
Proliferation is the acceleration of cell division. This condition is typical for the inflammatory process in the uterus. With strong proliferation, advanced inflammation occurs.
Leukoplakia - pathologically altered (but not cancerous) cells are present in the smear.
Metaplasia - one type of cell is replaced by another. It is considered normal for patients who were treated for non-cancer pathologies of the uterus during menopause. In addition, this condition is normal for women who have been in menopause for more than 6 years.
Dysplasia is a precancerous pathology.
The following abbreviations are used to describe the results of an analysis of a smear containing atypical cells:
—ASC-US
– the presence of altered squamous epithelial cells of unknown etiology. It most often occurs in patients over 45, when estrogen production decreases.
—AGC
– changes in cylindrical cells, which may indicate vaginosis or some other diseases. This result requires additional clarifying diagnostics.
- L-SIL
– the presence of a small number of atypical non-cancerous cells. In this case, the patient is referred for further examination (biopsy and colposcopy).
-ASC-H
– pathological changes in cells that indicate precancerous pathology or an incipient oncological process.
—HSIL
is oncocytology (altered flat cells are present). Such patients are given immediate treatment to prevent degeneration into a malignant tumor.
— A.I.S.
– This abbreviation indicates that cylindrical malignant cells have been identified. With such results, urgent treatment is necessary.
If pathologically changed cells are detected in a smear, the laboratory assistant will definitely indicate this in a written report specifying the type of changes. If there are no special designations in the analysis transcript, then, in all likelihood, the smear corresponds to the norm. An accurate diagnosis cannot be made based on this test alone. To determine the nature of the pathology, the gynecologist needs to compare the results of different examinations.
How the analysis is carried out
A cytological smear (Pap test, Papanicolaou smear, oncocytology smear) is performed during a gynecological examination. The doctor uses a mirror to examine the vagina, the entrance to the cervical canal and the cervical mucosa. If there is a suspicion of an anomaly, cells are collected with a special brush from 3 areas: from the walls of the vagina, the cervical canal, and the entrance to the cervix. The procedure is comfortable, painless and does not require special preparation.
- cell structure; cell size; epithelial shape; mutual arrangement; number of cells per unit area; pathological changes in cell structure.
A cytology smear allows you to identify most inflammatory diseases, precancerous pathologies of the epithelium (dysplasia), and malignant tumors.
After taking a smear, spotting is often observed for 2-3 days, which is normal. Extremely rare - severe bleeding, abdominal pain, chills, increased body temperature. In this case, an urgent examination by a gynecologist is required. Important advice from the editors!
If you are experiencing problems with the condition of your hair, you should pay special attention to the shampoos you use. Frightening statistics - 97% of shampoos from well-known brands contain components that poison our body. The substances that cause all the troubles are designated in the composition as sodium lauryl/laureth sulfate, coco sulfate, PEG, DEA, MEA.
These chemical components destroy the structure of the curls, the hair becomes brittle, loses elasticity and strength, and the color fades. Also, this nasty stuff gets into the liver, heart, lungs, accumulates in organs and can cause various diseases. We recommend that you avoid using products that contain this chemical. Recently, our experts conducted an analysis of shampoos, where products from the Mulsan Cosmetic company took first place.
The only manufacturer of completely natural cosmetics. All products are manufactured under strict quality control and certification systems. We recommend visiting the official Mulsan online store. ru. If you doubt the naturalness of your cosmetics, check the expiration date; it should not exceed one year of storage.
How many days does a smear cytology test take?
Cytological analysis of a smear usually takes from 1 to 5 days.
It is important to remember that the oncological process does not occur in a few days. Quite a long time passes from the first pathological changes to malignant degeneration. Therefore, timely detection of atypical cells in a woman’s body makes it possible to prevent the development of cervical cancer. For these purposes, an accessible and simple method for the early diagnosis of malignant cells was introduced everywhere - a cytological examination of a smear.
A smear is taken during a gynecological examination using a cytobrush, and then the material is placed on glass (for liquid oncocytology, a removable cytobrush is used, which, together with the material, is immersed in a bottle with a special medium).
Oncocytology of the cervix, as a rule, is not limited to one smear (vaginal portion of the cervix), since there is a need to study the epithelium of the cervical (cervical) canal. This is because the most problematic area in relation to the oncological process is the junction zone (transformation zone) - the place of transition of the multilayered squamous epithelium of the vaginal part of the cervix (ectocervix) into the single-layer prismatic (cylindrical) epithelium of the cervical canal (endocervix).
Of course, it is unacceptable to “slap” both smears on one glass during diagnosis (this is only possible during a medical examination), because they can get mixed up and the smear will turn out to be inadequate.
In a smear from the cervix of a young healthy woman, you can see cells of the superficial and intermediate layer (in various proportions) of non-keratinizing four-layer squamous epithelium growing from the basal cell, which is normally located deep and does not enter the smear, as well as cells of the prismatic epithelium of the cervical canal.
The PAP test is a fast, inexpensive, informative method for diagnosing diseases of the vagina and cervix.
The main task of cervical smear cytology is: - identification of atypical cells; - diagnosis of precancerous changes (dysplasia) and cervical cancer (CC).
Cervical screening (mass examination of cervical smears) is a method of secondary prevention of cervical cancer.
Primary prevention of cervical cancer is vaccination against the human papillomavirus HPV.
Read more about the symptoms of human papillomavirus infection in women and the treatment of HPV here: Condylomas acuminata.
The main task of cytological analysis of cervical smears is to identify atypical cells.
Atypical cells are morphologically altered cells: precancerous, cancerous.
- In malignant atypical cells, oncogenic mutations affect both the nucleus and the cytoplasm.
Cytological signs of malignant atypia: - increase in nuclear size; - change in the shape and color of the kernel; - abnormalities in the cytoplasm of cells.
The severity of atypia can suggest the level of precancerous changes (degree of dysplasia) of the cervix. But! Cytology does not determine the depth of tissue damage and does not distinguish dysplasia from non-invasive cancer (carcinoma in situ) or invasive microcarcinoma. Histology solves these problems.
Decoding the result
Deciphering test results is a simple matter for a doctor, but for a patient it is incomprehensible letters and terms.
- Latin letters U, C, V are a symbol for collecting secretions from the urethral, cervical canal and vagina, respectively. The number of leukocytes – a number of up to 15 units is considered normal. The presence of trichomonas, gonococci, and fungi indicates an infection of the genital organs that needs to be treated. Gardnerella in combination with fungal mycelium are signs of vaginal candidiasis, which can cause inflammation. The presence of glandular, flat, columnar epithelium in large quantities with signs of atrophy and pathological changes indicates possible signs of the development of cancer. Such cells are carefully studied and described in detail in the comments. The type and nature of changes are established. Degree of purity - 1, 2 degrees indicate a good vaginal environment, 3, 4 requires additional research and treatment. Flat epithelium normally comprises up to 10 units. An excess indicates a possible disease of hyperkeratosis - a benign formation of the cervix. Mucus in moderate quantities is a normal state of the vaginal environment.
If atypical cells are found in the smear, the laboratory technician will write about this in the conclusion and also determine the type of changes. Therefore, if the transcript of the cytology smear does not contain any special notes, then, most likely, no pathologies were found.
The time required for a smear test for cytology is from 1 to 5 days. Pathological changes in the cells of the cervical canal and cervix on the way to the diagnosis of cancer go through several stages, and not in 1-2 days. Cytological examination makes it possible to identify atypical cells at the initial stage and begin treatment, which in most cases leads to complete recovery. Therefore, cytological examination has been widely introduced into medical practice as a quick, painless and inexpensive way to diagnose cancer cells at an early stage.
Cytology smear: interpretation
Oncocytology involves microscopic analysis (study of the cellular composition and state of cell organelles) of material suspicious of an oncological process and taken from any accessible place.
In this regard, patients should not be surprised by smears for oncocytology, prepared not only from scrapings of the female genital organs, but also fine-needle aspiration biopsy (FNA):
- Enlarged regional lymph nodes (cancer of the larynx, nasal cavities and paranasal sinuses, salivary glands, penile cancer, eye tumors, etc.);
- Tumors of the pancreas, liver, gallbladder and extrahepatic bile ducts;
- Seals and nodes of the mammary and thyroid glands.
It might be useful to read:
- Causes and treatment of uterine subinvolution after childbirth;
- Online test “What kind of cat are you? Test how much of a cat you are;
- We take an Igm immunoglobulin test; what kind of test is it?
- “For health you need cold and movement”;
- Peony officinalis Peony flowers in folk medicine;
- Headache and pressure on eyes - what to do? ;
- Healing properties, uses and contraindications of peony petals Peony flowers medicinal properties;
- Blood after constipation Frequent constipation; bloody stool;
Why do atypical cervical cells appear?
There are a great many reasons that can provoke this disease, so it is important to know them in order to prevent the development of a malignant tumor in time:
Cervical cancer
- Mechanical damage to the uterus, trauma.
- Changes in the vaginal mucosa, which later spread to the uterine area.
- Processes of keratinization of the cervix and internal genital organs. In medical language, this disease is called leukoplaxia.
- Damage to the cervix during childbirth or during a procedure that requires cleaning the uterine cavity, including abortion.
- Injury to the uterus by means of contraception such as coils and caps, damage to it due to inept insertion of a tampon or the use of sex toys.
- Disturbances in the functioning of the endocrine system, hormonal imbalances and imbalances of hormones in a woman’s body.
- Infection of a woman with the papilloma virus, including in the intimate area.
- Having promiscuous sex with more than three sexual partners at the same time, or having sex with a partner who is not faithful to his partner.
- Losing your virginity too early in adolescence.
- Bad habits, and smoking especially affects the condition of the female genital organs.
- Weak immunity, due to which a woman is exposed to serious diseases.
- Incorrect treatment of previously occurring diseases of the genital organs.
- Infectious diseases that are sexually transmitted.
Attention! Atypical cells are present in varying quantities in any organism, but if it works correctly and smoothly, then there is nothing to worry about. The immune system destroys these cells in time. Cancers occur only when this system fails and abnormal cells are not destroyed. They mutate and turn into so-called oncological ones. The worst thing is that this process is very slow, and a person can understand that he has cancer only after several years, when he can no longer be helped.
Preparing the patient for the procedure
It is optimal to do a smear for cytology after the end of menstruation and before the middle of the next menstrual cycle.
— Refrain from sexual contact. — Do not use vaginal products (suppositories, creams, gels, etc.). — Do not douche.
- Biomaterial is collected using sterile disposable instruments.
1. The patient undresses to the waist and lies down in the gynecological chair.
2. To visualize the cervix, the doctor uses a Speculum speculum.
It is rational to take scrapings for histology under colposcopy control.
3. The doctor inserts a cervical brush into the cervical canal to a depth of 1.5-2 cm, takes a sample of endocervix tissue and places (imprints) it on a prepared glass slide with appropriate markings.
4. Then, using an Eyre spatula, scrape from the junction (from the transformation zone) of the epithelium and place it on the designated part of the first slide or on the second glass.
5. If necessary, with another spatula, the doctor makes a targeted scraping from the suspicious area of the ectocervix and places the taken biomaterial on another glass with the appropriate marking.
6. Smears are immediately treated with a fixative, dried and sent for examination.
7. In the laboratory, first of all, the adequacy of the cytological smear is assessed: - are there enough cells on the glass for analysis; — is the biomaterial applied too thin/thick; - how well the fixation is done; — whether the smear is contaminated with mucus, blood, semen or inflammatory exudate.
- Satisfactory quality of the biomaterial (adequacy of the smear) is a key factor in the effectiveness of smear analysis for cytology for decoding.
If your doctor asks you to retake the PAP test, don’t be alarmed. Practice shows that up to 20% of smears are not performed adequately and must be repeated.
The procedure for taking a smear is short-term, low-traumatic, safe and in most cases painless. Sometimes the patient may feel mild, transient discomfort.
How to behave after the procedure: - Refrain from sexual contact for 1-2 days. — Otherwise, lead a normal life. — If necessary, the doctor gives individual recommendations.
Contraindications to cytology: - Acute genital infection (itching, profuse, purulent, with a strong odor, foamy vaginal discharge). - Pregnancy. - Virginity. - Menstruation.
For minor patients who are sexually active, cervical scraping is done in the presence of their parents (guardian).
After childbirth, you can take a cervical smear no earlier than 3 months later.