What is uterine endometriosis
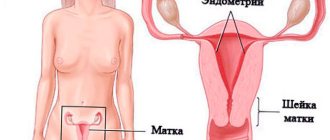
The endometrium consists of a functional layer, which is shed during menstruation, and a germinal basal layer, which forms the upper functional layer.
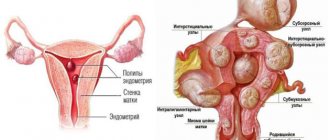
Endometriosis of the uterus is characterized by proliferation of glandular tissue of the uterus, called heterotopia. They tend to penetrate healthy tissue and form adhesions.
The growths increase in size, swell and bleed, which explains spotting outside of menstruation.
In addition, abnormal endometrial cells produce a specific fluid that is not excreted, the stagnation of which causes pain. Endometriosis of the uterus can be nodular, diffuse and focal.
According to the depth of penetration into the muscular layers of the uterus, the pathology is divided into four degrees. The lesions vary in size and shape: from a round formation of several millimeters to a shapeless growth of several centimeters in diameter.
Read more about what endometriosis is here.
Hysteroscopy, performed for diagnostic purposes, is accompanied by slight bloody or brown discharge, more like a smudge.
The first day or two you may feel a slight tug on your stomach. If the purpose of the manipulation was to operate on inflamed lesions, then bleeding continues from several days to a week, depending on the area of tissue affected.
Blood discharge after RDV is scanty, often disappears within a day if the patient complies with all the rules of the post-manipulation period.
What does it mean about pathology?
What discharge may indicate pathological processes in the reproductive organs that arose after vacuum aspiration? In addition to the absence of discharge, the following phenomena indicate pathologies:
- Light brown, yellow or greenish discharge that has an unpleasant, putrid odor. They indicate that an infection has entered the body and now an infectious-inflammatory process is developing in the genitals. Most often, the cause of infection is poor hygiene and too rapid resumption of sexual activity after the abortion procedure. A putrid odor indicates the proliferation of staphylococci, streptococci, and E. coli. Purulent clots or the smell of rotten fish are symptoms of sexually transmitted infections, which include chlamydia, mycoplasma, and trichomonas.
- Brown clots. They indicate pathology if they are accompanied by a rotten odor or the absence of scarlet blood. This disorder may be a symptom of endometriosis or polyps in the uterus.
- Stomach ache. Small cramps, like on the first day of menstruation, are the norm, because the woman has just undergone surgery. However, sharp cutting pains that last for several days and intensify indicate complications after an abortion. The woman needs to have an ultrasound to check if any particles of the fertilized egg remain inside.
- High temperature, nausea. A febrile state should immediately alert you, because it indicates acute inflammatory processes in the body. Internal bleeding, sepsis, peritonitis - this is how such complications manifest themselves.
After performing the vacuum, the gynecologist prescribes a control examination in a gynecological chair and an ultrasound. If a woman notices disturbances in the functioning of the body, she does not need to wait for her appointment and self-medicate. A timely visit to a doctor will help you get rid of the consequences of an abortion with minimal risk to your health.
https://youtu.be/KDYgCXwDD_U
The rehabilitation period after curettage
The rehabilitation period will depend on the level of complexity of the procedure performed. As a rule, bed rest does not last more than 2 days.
After a successful operation, the woman returns to full working capacity within a week. In the first days there is pain of moderate intensity, uterine bleeding with blood clots.
Normally, discharge should last a maximum of 10 days, with a gradual decrease in volume. Antibacterial therapy is prescribed to prevent infectious processes, hemostatic agents, and hormonal therapy to suppress the level of estrogen in the blood.
If the temperature rises or the discharge does not stop, you should seek medical help.
For two weeks after surgery it is prohibited:
- any physical stress;
- sexual intercourse;
- use intravaginal products;
- take medications that reduce blood clotting;
- take a hot shower, bath, visit a sauna, solarium;
- supercool.
The procedure of curettage of the uterus for endometriosis is dangerous.
There is a possible risk of uterine perforation, cervical tear, and removal of the basal layer of the endometrium. However, in some cases, the method turns out to be indispensable and allows you to save the uterus from amputation, preserving the possibility of childbearing.
If the operation is performed by a competent and experienced specialist, the risks of complications will be minimized.
To avoid complications after surgery, it is important to follow these rules:
- Stay in bed for at least 10 days.
- Do not lift anything heavy, avoid physical exertion, stress and hypothermia.
- Avoid drinking alcohol.
- Take all anti-inflammatory and restorative medications prescribed by your doctor.
- Avoid sexual activity for a while.
- Change your pads more often and wash yourself with natural products for special intimate hygiene.
- Do not delay the ultrasound appointment scheduled for you again in order to prevent complications in time.
Strictly speaking, such an intervention is not considered a surgical operation, although in fact it is traumatic, and during it a large wound surface is formed. For example, after curettage to remove cysts or in case of endometriosis, almost the entire inner surface of the uterus becomes the wound surface, since the endometrium is removed from the entire surface.
For this reason, a fairly long recovery period after this procedure is recommended. It lasts, depending on the volume of intervention and the individual characteristics of the body, from three to four weeks.
The endometrium is completely restored within one menstrual cycle. This time is enough for the uterus to fully recover and begin to “work” in its usual way.
In the vast majority of cases, discharge upon completion of curettage is observed for several days - like normal menstruation. If bleeding lasts more than 7 days, then it makes sense to consult a doctor. Normally, after cleansing, the walls of the uterus should gradually contract, and when this process occurs slowly, it may be accompanied by spotting and spotting. There may be some complications.
But when the bleeding is profuse and prolonged, then most likely pathological disturbances in the functioning of the uterus have occurred after cleansing. It is also worth paying attention to prolonged pain in the lower abdomen: if it bothers you even after the bleeding has stopped. This is not normal, so it makes sense to see a doctor.
The norm can be considered pain that is observed only during the discharge, and after that the patient’s general well-being should only improve.
Consequences of scraping
All manipulations are performed blindly using special tools, so violations are possible. It is important to be able to distinguish between natural discharge and pathological bleeding after curettage.
Like any operation, curettage can have complications. This depends on the doctor’s experience, the duration of the manipulations, the reasons for curettage, diseases of the genital organs, compliance with the rules of asepsis (processing of materials, instruments, doctor’s hands), and the quality of the operation performed. In addition, bleeding after curettage may occur in women with poor blood clotting. Prolonged bleeding may be associated with hormonal imbalances.
Symptoms of the disease
In the early stages, endometriosis may occur without significant symptoms.
In the second and third degrees, the disease manifests itself:
- Menstrual irregularities - the cycle itself is shortened, the duration of menstruation increases.
- Constant or periodic pain in the lower abdomen, lower back.
- Severe premenstrual syndrome.
- Pain during sexual intercourse.
- Heavy menstrual flow.
- Spontaneous miscarriage, infertility.
With a long course of endometriosis with heavy menstruation, signs of anemia begin to appear: general increasing weakness, dizziness, pale skin.
The first mention of the disease was found in ancient Egyptian manuscripts, which Hippocrates described in his writings.
There is no discharge after curettage of the uterus for only one reason - the formation of a hematometra. Removal of the endometrial layer is associated with significant trauma to the organ. A hematometra after cleaning the uterus can form as a result of the accumulation of unremoved fragments of the mucous membrane and wound blood joining them. In addition, fragments of the fetus may remain in the uterine cavity after curettage to terminate the pregnancy.
The signs become:
- Severe pain. The discharge accumulated in the uterus after cleaning it causes overstretching of the walls, which greatly irritates the nerve endings. The organ responds to this with increased contractions. That is why, with the development of hematometra - the pathological cessation of discharge after curettage of the uterus - a woman experiences nagging pain localized in the lower abdomen. In their strength they can resemble labor pains.
- Abrupt cessation of discharge after cleaning the uterus. It is this symptom that helps the gynecologist make a preliminary diagnosis.
- Development of local inflammation. Since blood is an ideal environment for the proliferation of bacteria, thanks to this hematometer it accompanies the development of local inflammation. This is also facilitated by a decrease in immune defense caused by curettage. In the absence of bleeding after cleansing, body temperature rises, general health becomes worse, and pain intensifies. After infection of the secretions accumulated in the uterus, the hematometra becomes pyometra.
Regardless of how long the bleeding continues, a woman should be alerted to certain symptoms. It will indicate a deterioration in general condition and the need for urgent medical attention.
These signs include:
- the formation of severe pain of a cramping nature, spreading not only to the lower abdomen, but also to the area of the entire abdominal cavity;
- nagging pain localized in the lower abdomen, radiating to the lumbar region, hips and groin;
- sudden cessation of bleeding (of any intensity) - this can be a sign of the development of hematometra and, in the absence of qualified medical care, threatens the development of serious complications;
- a rapid rise in body temperature to high levels indicates the development of an infection;
- the inability to eliminate severe pain even by taking strong antispasmodics;
- severe bleeding that does not decrease even several hours after completion of the procedure - filling one pad per hour;
- the appearance of an unpleasant odor in the genital discharge;
- deterioration in general health.
If such symptoms develop, the woman is recommended to undergo urgent hospitalization.
Discharge as normal and pathology
Normal discharge after curettage of the uterine cavity is considered to be those that last from 5 to 7 days (maximum 10) without an unpleasant odor and not too abundant, without clots. Pain during this period is normal. This is due to the fact that the uterus begins to actively contract. Curettage can also occur; this usually occurs 5 days after the operation. This is explained by the fact that the blood already has time to clot due to the small amount of secretions. Gradually they become smearing and end completely.
In cases where abrasion was performed before the next menstruation, bleeding usually lasts in proportion to normal discharge.
If during surgery there were errors in terms of asepsis or it was performed poorly, then the nature of the discharge may acquire signs of pathology. Yellow discharge after cleansing may indicate the proliferation of bacteria in the genitals and the development of diseases such as trichomoniasis and chlamydia.
If during the procedure all elements of the discharge were not removed, i.e. placenta, fertilized egg, the development of the inflammatory process begins:
- Endometritis. This disease, caused by a complication after curettage, is an inflammation of the uterus. The penetration of infection can occur from poorly sterilized instruments, violation of asepsis at the time of manipulation, or if elements of discharge (fetal egg, endometrium or placental remains) were left in the uterine cavity. Discharge after such an operation may be profuse, with blood or accumulations of clots. It is difficult not to notice the presence of an unpleasant odor. The color of the discharge often resembles a decomposed substrate. The patient herself may be accompanied by an increase in body temperature and nagging pain in the lower abdomen.
- Prolonged bleeding. If the discharge lasts more than 10 days, then the reason is a hormonal imbalance or incomplete removal of the area. Bleeding is prolonged when curettage was performed in the first half or middle of the cycle.
- Presence of hematometra. This is the process of accumulation of blood clots in the uterine cavity. Removing them is problematic due to premature closure of the cervical opening. If this fact occurs, a woman may notice a sudden cessation of bleeding of any kind. This usually happens a couple of days after curettage. In addition to stopping the discharge, sharp, contraction-like sensations of pain and an increase in body temperature are characteristic.
Recommendations
After curettage, the woman experiences bleeding. They remain especially strong during the first few hours or days. Then the bleeding subsides. The total duration of the “daub” is no more than 21 days.
If the bleeding suddenly stops, but pain appears in the lower abdomen, this is a sign of the formation of a hematometra or other dangerous condition. The cause is spasm of the cervical canal, as a result of which blood accumulates inside the uterus. Pathology is diagnosed only with the help of ultrasound examination.
In order to prevent the development of hematomas, a woman is prescribed No-Shpa.
If a woman has a pathology of the blood coagulation system, the doctor takes this into account when managing the postoperative period, monitors the hemostasiogram and prescribes appropriate medications.
In addition, in order to avoid the development of complications, it is recommended to take a course of drugs from the category of antibiotics, which prevents the development of inflammatory processes.
The results of histological studies of tissues are ready 10 days after the curettage procedure. They will allow the gynecologist to identify the true cause of uterine bleeding and prescribe adequate drug therapy.
Recovery after curettage has a number of normal characteristics. If there is a deviation from the norm, it is recommended to immediately consult a doctor. Normally, during this period the following may be present:
- Pain in the lower abdomen associated with contraction of the uterus after curettage;
- Minor bleeding;
- Feelings of nagging, aching pain in the back.
Such symptoms may be present only in the first few days. If it persists after a week, then you need to consult a doctor. You should also do this if there is heavy bleeding and excessively intense pain, or if you have a fever after cleaning the uterus.
During this period, it is necessary to reduce physical activity, which will have a good effect on your well-being. You cannot steam in the bathroom; hygiene must be maintained with the help of a shower. At the same time, it is better not to use chemical products for intimate hygiene, medications administered vaginally, tampons and douches. Avoid overheating - do not visit saunas, steam baths, solariums, the beach, do not swim in open reservoirs and pools, carefully observe hygiene.
Complications after the procedure
Any violation of the integrity of the body can lead to a number of complications, in the case of curettage these are:
- Cervical rupture. This is possible when the surgeon's forceps rebound. That is, the weak elasticity of the fabric provokes the tool to fly off at the moment of tension. Sharpness causes damage. If the tears are small, they may heal on their own, but in the case of a large tear, stitches will be required.
- Deformation of the uterus. This is possible for two reasons:
- looseness of organ tissues and their puncture with minimal pressure on the uterine wall;
- weak reaction of the cervix during dilation (the doctor’s effort transfers the load to the organ, it is injured);
Small injuries can heal on their own under medical supervision; in other cases, sutures are required.
- Development of hematometra. If there is a spasm of the cervix after abrasion, this will cause hematometra - an accumulation of blood clots in the uterine cavity. The type of treatment for this pathology is medication. As a preventive measure, taking the drug No-spa or its analogue Drotaverine gives good results.
- Violation of the integrity of the uterine mucosa. This happens with rough or excessive curettage, when the main layer of the uterine mucosa is deformed. This is a serious pathology. Its frequent consequence is infertility due to the lack of a new endometrial layer.
In addition, inflammation of the uterus often occurs. However, the occurrence of this disease can be prevented by strict sanitization.
These complications can significantly complicate a woman’s life, even leading to dire consequences.
For prevention purposes, doctors prescribe antibiotics immediately after curettage. This helps reduce the risk of complications and speed up the recovery process.
Of course, it is important that the operation is performed by a surgeon with extensive experience, efficiently and effectively.
Popular treatments
To treat uterine endometriosis, complex treatment is used. It is obligatory to take hormonal drugs, which causes a medicated menopause, as a result of which the formation of an egg and the development of the endometrium do not occur.
The treatment course lasts 6 months. During this time, foci of endometriosis shrink and atrophy.
Hormonal therapy does not help restore your own hormones and does not always give positive results; it has a number of side effects.
Surgical methods of treatment:
- Laparoscopy is a low-traumatic manipulation that allows you to remove endometrioid lesions and adhesions; laser and electrocoagulation are used. Cauterization stops the growth process and reduces the risk of relapse. Organ-preserving surgery is performed for moderately severe disease. For successful treatment, laparoscopy is combined with medications.
- Curettage or cleaning of the uterine cavity is a radical method, used to stop uterine bleeding in the infiltrative pathological form of the disease.
- In severe cases of the disease, a total hysterectomy is performed - complete removal of the organ and appendages. Preservation of the ovaries will provoke relapses of endometriosis.
Physiotherapy is used as prescribed by a doctor in the absence of contraindications:
- Electrophoresis of zinc and iodine has an analgesic, sedative effect, and normalizes hormonal levels.
- Magnetic therapy calms the nervous system and improves tissue microcirculation.
- Ultraviolet radiation anesthetizes, relieves inflammation, and has a biostimulating effect on endometriotic lesions.
Balneotherapy includes radon and iodine-bromine baths, vaginal irrigation, and microenemas. The procedures have analgesic, anti-inflammatory and sedative effects.
Eliminate hormonal imbalance, normalize thyroid function. A long course of treatment ensures a reduction in pathological endometrium.
Computer reflexology is a method based on the restoration of neuroendocrine connections, immune regulation of the female body, using ultra-weak direct current. The result of therapy is the normalization of uterine functions, restoration of hormonal balance, improvement of immunity and strengthening of the nervous system.
Intrauterine devices are used to treat stage 1 endometriosis. Installed by a specialist after undergoing diagnostic procedures.
Treatment of hematometra - a condition in which discharge stops after cleaning - consists of restoring the mechanisms for evacuation of uterine contents. Quite often, the outpouring of liquid contents occurs independently during diagnostic probing.
But even after the uterine cavity has been emptied of accumulated secretions, there is a possibility of their re-accumulation if the true cause of the formation of hematometra has not been eliminated.
If the delay in discharge after cleaning is caused by the retention of fetal particles, then the woman is prescribed repeated curettage or vacuum aspiration.
When the cessation of bleeding after cleaning is facilitated by polyps of the cervical canal or submucosal (submucosal) myomatous nodes, they are removed. They can create conditions for relapse of the pathology.
After the uterus is freed from blood accumulation, therapeutic measures are taken to restore the tone of its muscle wall and improve contractility. For this purpose, special drugs are used, in particular Oxytocin, as well as drugs from the category of antispasmodics.
Regardless of whether a woman has symptoms of inflammation or not, she is prescribed antibiotics.
Do not forget that prolonged presence of bloody discharge in the uterine cavity can cause the development of sepsis.
How to prevent complications from occurring
Complications during the rehabilitation period arise against the background of decreased immune defense, as well as hormonal imbalances. To protect yourself as much as possible from a long recovery period, you must follow simple rules:
- Do not leave the hospital for at least 24 hours after cleaning.
- For 7 days after curettage, observe bed rest.
- Avoid excessive physical activity.
- Protect yourself from stressful situations.
- Don't freeze.
- Follow all recommendations of the gynecologist.
- Use therapy aimed at maintaining the body's protective resources.
- Promptly undergo repeated ultrasounds to assess repair processes.
Women who are periodically observed by a gynecologist after surgery are maximally protected from complications. Therefore, it is so important not to ignore the need to visit doctors. Patients who went to the hospital for a consultation may not have to worry about their health in the future.
Curettage of the uterus is an unpleasant but necessary operation, which is sometimes impossible to do without. The procedure, which is performed by highly qualified specialists, very rarely causes complications that require appropriate treatment. However, discharge after cleansing is a natural and completely normal process that cannot be avoided.
The task of every woman is to control the nature, color and duration of the discharge. Many people do not know what to do if their health changes for the worse during the recovery period. In such a situation, there is only one way out - to seek help from specialists. Only a doctor can give a real assessment of the state of women’s health, as well as prescribe adequate therapy.
https://youtu.be/EY3oPCAhizw
Gynecological curettage is a complex procedure that is very stressful for the female body. It is carried out after a miscarriage, abortion, frozen pregnancy and in the presence of certain other medical indications. A woman should know how much blood flows after cleaning the uterus. Although this is normal, excessive bleeding may indicate a pathology. It is important to detect the problem in time.
Drugs
Treatment after curettage of the uterine cavity involves taking medications. They are not aimed at directly promoting the growth of the endometrium, since this is not necessary - this is a natural process that occurs physiologically. The medications are taken in order to improve the patient’s condition and well-being, avoid relapses of the disease, and also prevent the development of severe consequences and complications, such as infection.
Why is there blood?
Bleeding after curettage is normal. If a woman prepares in advance for the consequences of the procedure, it will be easier for her to bear it physically and mentally.
In the process of curettage, a layer of the endometrium is removed from the uterine cavity, which normally leaves the woman’s body during menstruation. This mucous membrane is penetrated by blood vessels, so when it is removed, many miniature bleeding wounds are formed on the walls of the uterus.
The general condition of the body in the period after curettage of the uterine cavity is similar to that in the days of menstrual bleeding. During the procedure, the same processes are performed, only artificially. Some women have noticed that, in comparison with their usual periods, they feel slightly worse after the surgical procedure.
After this surgery, blood should bleed. The absence of discharge indicates pathology and causes alarm. An immediate medical examination is required. If there is no bleeding after the procedure, this indicates the probable formation of a hematoma in the cervical area. In this case, blood accumulates inside, which poses a danger to the woman’s life.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis is established on the basis of anamnesis, gynecological examination and diagnostic studies:
- Ultrasound examination determines the shape and localization of endometriosis, increased size of the uterus, thickening of the walls of the organ.
- MRI diagnoses pathology in 90% of cases.
- With the help of hysteroscopy, the altered relief of the uterine cavity and the formation of scars are revealed.
- Laparoscopy is performed to confirm the diagnosis and take scrapings for histological examination.
- Hormonal levels are analyzed.
- The level of tumor markers is determined.
The modern level of operative gynecology with the introduction of laparoscopic instruments makes it possible to get rid of endometriosis, followed by pregnancy.
If a woman does not have discharge after therapeutic or diagnostic curettage, then a hematometra becomes a preliminary diagnosis.
The diagnosis is confirmed during a gynecological examination and ultrasound. Signs of pathology include a painful, enlarged and soft uterus on palpation.
Additionally, probing is prescribed. The procedure looks like this:
- the woman is located in the gynecological chair;
- the doctor carefully inserts a thin probe made of special medical metal into the uterine cavity.
If there is accumulated discharge, either blood or pus will be released from the uterine cavity.
In addition to probing, the woman is prescribed an intravaginal ultrasound examination. An ultrasound examination can reveal the presence of liquid contents. But the equipment is unable to determine its type.
Laboratory tests are mandatory. These will be:
- smears from the vagina and cervix for microflora;
- bacterial culture;
- PCR.
Tests are necessary to confirm infection, which in almost all cases accompanies the cessation of bleeding. But clinical symptoms of inflammation of the hematometer are not always accompanied.
In severe cases, a woman is prescribed a hysteroscopy procedure. The technique allows you to perform a visual examination of the uterus. The doctor will be able to examine the walls of the organ and assess the condition of the cervical canal mucosa. In addition, during the procedure - if such a need arises - treatment can be carried out.
Menstrual cycle after mini-abortion
Abortion is a serious physiological and hormonal stress for the body, no matter how it is carried out, which is why the menstrual cycle is disrupted. It is impossible to predict how long the discharge will be, when a new menstrual cycle will begin and how long it will take for the female body to recover and enter a normal physiological rhythm.
The beginning of secondary discharge after vacuum aspiration in gynecology is considered the beginning of the female cycle, but you should not expect that the next menstruation will begin at your standard time. Menstruation may start early or late.
After the abortion, the patient should spend 30-60 minutes lying on her stomach and under the supervision of a doctor. During this period, she may experience discomfort and pain. Further, such symptoms should disappear. Due to hormonal changes, a woman may experience mood swings, depression, irritability, and even a deterioration in general well-being, discomfort in the groin area and mammary glands.
If a mini-abortion was not done for medical reasons, but with the aim of terminating a pregnancy, then the doctor will probably prescribe contraceptives for several menstrual cycles. Sometimes an antibiotic is also prescribed. It is important to remember that after vacuum aspiration, the woman’s body recovers very quickly and the onset of the next pregnancy is possible even before the first menstruation begins after the operation.
The vacuum aspiration procedure is the least dangerous of all aborted procedures, however, it may have consequences that are worth considering:
- partial retention of the fertilized egg (incomplete removal);
- trauma to the inner surface or cervix with instruments, which can lead to bleeding;
- introduction of infection;
- hormonal disorders;
- infertility.
Intimate life
When can you have sex after a uterine curettage procedure? This should be addressed by the attending physician after examining the patient. The uterus must be cleared of blood, tissue particles, and clots. And this requires at least 7-10 days. But the average period is about 2 weeks, although in some cases the doctor sets limits for 1-1.5 months.
You must use a condom. This will not only avoid infection of the delicate mucous membrane, but will also prevent unwanted pregnancy. Fertilization becomes possible approximately 2 weeks after the procedure.
Some women are reluctant to resume sexual activity. Especially if the curettage was associated with the loss of a child. For them, sex is an opportunity to conceive and lose a baby again. This is already a psychological problem, and to solve it, a consultation with a gynecologist is required.
You can have sex a week after the procedure, but it is better to coordinate this with your doctor. In addition, if the patient experiences pain during sexual intercourse, she should immediately consult a specialist. It is important to carefully maintain hygiene and use barrier methods of contraception to prevent various infections from entering the uterine cavity.
Causes of discharge after a vacuum
You need to figure out which discharge is normal. Primary vaginal flows that are brown in color are the result of damage to the uterine tissue. The healing period depends on the individual characteristics of the body, and lasts from 1 to 4 days. Such discharge begins immediately after surgery. After they end, new ones appear, which can easily be mistaken for menstrual bleeding, but this is a response to hormonal changes in the body. Vaginal discharge includes blood and mucus. Gradually, the quantitative composition changes in favor of mucus. This is due to the completion of the healing stage of damaged tissue.
Important!
Serious complications rarely occur after vacuum aspiration and, therefore, the appearance of atypical vaginal discharge, pain, or fever indicates the need to immediately consult a doctor. If there is no discharge, then this is also a bad sign, possibly indicating a hormonal imbalance or other abnormalities.
In the next week after surgery, it is necessary to avoid physical and emotional stress. It is better to spend this time at home, calmly and freeing yourself from homework. It is the lack of proper postoperative rehabilitation that causes complications.
In what cases is curettage required?
Separate diagnostic curettage of the uterus is carried out for therapeutic purposes, to remove the overgrown endometrium, as well as to remove scrapings for histological examination. During curettage, the outer layer of the uterus is removed without affecting the basal layer.
The procedure is prescribed when conservative treatment is ineffective and there is an existing risk of complications.
Indications for uterine curettage are:
- Prolonged uterine bleeding leading to the development of anemia.
- Increased pain syndrome.
- Formation of endometriotic cysts in the ovaries.
- Formation of adhesions in the uterine cavity.
- Infertility.
- Hyperplasia.
No discharge
What to do if the discharge that the gynecologist warned about is absent? This is an alarm bell that requires you to see a doctor. If there is no bleeding after an abortion or it suddenly stops, this may indicate that particles of the fertilized egg remain in the uterus.
Remains of the embryo, endometrium and blood clots accumulate in the uterine cavity. The cervical canal becomes blocked and the natural outflow of dead tissue is disrupted. The woman experiences increased pain in the abdomen and lower back, which turns from aching to cutting. Brown, foul-smelling clots are periodically released.
This pathological condition is called hematometra. It is characterized by the accumulation of blood in the uterine cavity and is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- decreased blood pressure;
- tachycardia;
- dizziness;
- pain radiating to the tailbone;
- fever.
If hematomas occur, you should immediately consult a doctor. Without timely treatment, this pathology leads to inflammation of the genital organs, peritonitis, and infertility.
Indications for surgery
To quickly restore the endometrium, the operation is performed 2-3 days before the onset of menstruation. Curettage is a simple but painful procedure that requires anesthesia.
The choice of anesthetic is determined taking into account the specifics of the pathology: most often general anesthesia or spinal anesthesia is used.
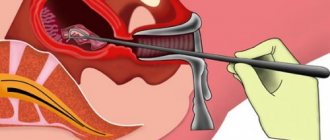
Currently, the curettage procedure is performed using a hysteroscope. After anesthesia, a dilator is inserted into the vagina, pushing apart the vaginal walls and forceps that fix the uterus.
Next, a hysteroscope and curette are inserted into the cervical canal. The video device provides control over the process and makes it possible to evaluate the work done. Cleaning begins from the cervical canal, then proceeds to curettage of the uterine cavity.
The top layer is scraped off with a surgical instrument, and the collected material is sent for histological examination.
On average, the operation lasts from 20 to 40 minutes.
There are very often discussions on the forum about why there is no discharge after curettage or it stops the next day, but cramping pain remains, sometimes accompanied by fever. In this case, we can talk about a hematometer - an accumulation of blood clots in the uterus, the cervical canal of which is already closed, and their expulsion is impossible. These clots literally burst the reproductive organ, causing sharp spasms. They can provoke sepsis of adjacent tissues.
Therefore, if after curettage or cleaning of a frozen pregnancy there is no discharge, immediately consult a doctor for a re-examination and evacuation of bloody concentrations. The lack of medical intervention in this situation leads to serious consequences. It’s worth thinking about if the blood loss was minor and lasted only one day, but the pain continues to cause discomfort.
This gynecological procedure is prescribed in the following cases:
- The need to obtain an endometrial analysis.
- Removal of pathological formation.
- Termination of pregnancy - for medical reasons or at the will of the patient.
- Removal of frozen fetus, cleaning after miscarriage.
Curettage is prescribed after an ultrasound examination of the uterus and the collection of certain tests. Many patients complain that after curettage is completed, they experience heavy bleeding from the vagina for some time, which is often accompanied by painful sensations.
Read on, how long does bleeding last after cleaning the uterus normally?
Opinion of gynecologists
Any abortion must be treated with great responsibility, because the possibility of planning a new pregnancy in the future will depend on this procedure.
The most important indicator of the success of the surgical intervention is the discharge after vacuum cleaning, so every woman should monitor the intensity, color and smell of the discharge.
Normally they should:
- be abundant only in the first 24 hours;
- after 5–7 days decrease to a minimum;
- have a normal odor similar to that of menstrual fluid.
If after a vacuum-aspiration abortion the patient feels general weakness, her temperature is elevated, the mucus discharge has an unusual color and smells bad, you should definitely seek medical help.
Some women, immediately after finding out about their pregnancy, begin to read information on forums about how to provoke a miscarriage. This should not be done under any circumstances - all kinds of traditional methods are unsafe, and when women come to the hospital after such attempts, they cannot do without curettage.
It must be remembered that timely vacuum aspiration is an effective and reliable way to terminate a pregnancy.
Correctly performing such an abortion, as well as monitoring the discharge and general well-being after the intervention, will help the woman recover very quickly and without any serious consequences.
«>
Diet example
For a quick recovery, it is important to properly balance work and rest modes. Ideally, you need to sleep at least 8 hours a day, work no more than 8 hours, and rest at least 8 hours. At the same time, if the work involves physical activity, then you need to take sick leave for at least a few days after the procedure. If the work is not physically difficult, then, usually, you can return to it the next day. But this must be agreed with your doctor.
You need to eat natural, healthy foods, avoiding fried, fatty and smoked foods. An example diet could be like this:
- Breakfast - yogurt or cottage cheese, egg, whole grain bread, weak coffee;
- Second breakfast - fruit;
- Lunch – vegetable or low-fat meat soup, side dish of cereals and white low-fat fish, tea;
- Afternoon snack – fruit lard, kefir, or yogurt;
- Dinner – vegetable side dish and chicken breast, rosehip decoction.
It is advisable to include foods rich in phytoestrogens in the diet - corn, soybeans, yams.
How to avoid negative consequences
Bleeding after curettage in most patients goes away without complications. However, some have encountered the following unpleasant consequences:
Uterine bleeding after gynecological curettage occurs extremely rarely. This problem may arise in a patient who suffers from poor blood clotting. This complication is life-threatening. If one pad fills with blood per hour, the woman needs immediate help. In most cases, doctors use Oxytocin injections and hospitalize the patient.
Hematometra is a complication that occurs due to the natural contraction of the cervix after cleaning is completed. When the spasm is particularly strong, a clot begins to form in the organ cavity. It does not have time to get out, which leads to the accumulation of blood inside. The condition threatens the development of an infectious disease. The woman notices that the blood has stopped flowing, and sharp pain has appeared in the lower abdomen.
Endometritis is an infectious pathology that occurs as a complication after gynecological cleansing of the uterus. The disease is inflammatory in nature and develops due to the penetration of microbes into the organ cavity. A woman can suspect the onset of the disease based on her general health. The first negative symptoms occur a few days after the surgical procedure. The temperature rises, general weakness and fever occur.
You can protect yourself from some complications. A woman should carefully follow all recommendations of the attending physician who performed the surgical procedure. It is necessary to notice the changes occurring in the body in order to adjust the therapy at the right time.
You can protect your body from the possible consequences of gynecological curettage if you follow the following recommendations:
- before surgery or immediately after it, take Drotaverine or No-Shpu to prevent excessive contraction of the cervix;
- use antibiotics prescribed by a doctor to prevent infection of the organ;
- do not overload yourself in the days following the intervention, rest more, get enough sleep;
- eat right, take vitamins, replenish lost blood.
It is important to choose the right doctor. Whether there will be negative consequences from the procedure or not largely depends on how well the manipulations are performed.
If the uterus is not completely cleaned, there is a risk that the bleeding will not stop. Using unsterile instruments increases the risk of infection. A good specialist is the key to effective curettage.
You can reduce the duration of bleeding from cleaning if you choose the right day for the procedure. Since gynecological curettage has much in common with the natural processes during menstruation, the closer to these days the intervention is carried out, the easier it will be for the body to recover. After the bleeding stops, the next period will come only when the cycle is restored.
https://youtube.com/watch?v=L6g04h53o0I
If a woman knows how many days blood should normally bleed after gynecological cleansing of the uterus, what it should be like and how to protect herself from negative manifestations, there will be no complications. Proper curettage will help get rid of the disease.
How to prepare
Before the procedure, your doctor may prescribe hormonal medications. Clinical and biochemical blood tests, cytology smears, and ultrasound are examined to determine the functional layer of the endometrium.
Three days before curettage, the following are prohibited:
- sexual intercourse;
- douching;
- use of vaginal suppositories and tampons.
Endometriosis at an early stage of development can be successfully treated. That is why regular preventive examinations with ultrasound diagnostics and other tests are so important.
As a rule, curettage is performed a few days before the start of menstruation - this helps reduce blood loss and speed up the recovery of the uterus after the procedure.
Due to the fact that curettage is a surgical procedure (that is, an operation), in order to ensure your safety, before it is performed, the doctor may prescribe a number of examinations for you: a general blood test, a coagulogram (blood clotting test), a bacteriological smear from the vagina, tests for sexually transmitted infections.
2 weeks before your curettage: Stop taking any medications or dietary supplements (including herbal supplements) that you have not previously discussed with your doctor who will be performing the curettage. Some medications can change blood clotting and increase the risk of bleeding. If you are taking medications for a serious illness (for example, hypertension, arrhythmia, epilepsy), do not stop treatment, but be sure to tell your doctor about the medications you are taking.
2-3 days before curettage:
- Avoid sexual intercourse.
- Do not douche and refuse to use any intimate hygiene products. To toilet the genitals, use only warm water.
- Stop using any medications in the form of vaginal suppositories, tablets, or sprays unless their use has been discussed with your doctor in advance.
On the eve of curettage, refrain from eating and drinking 8-12 hours before the procedure. This is necessary for safe anesthesia.
Possible complications
A common complication after cleansing is uterine bleeding. It can begin due to a puncture in the wall of the organ, an incorrectly performed procedure, hormonal imbalance, or low blood clotting. A complication should be suspected if there is heavy discharge that does not subside for several days after curettage of the uterus, during which it is necessary to change the pad or tampon every 0.5–1 hour. Consequences: massive blood loss, tissue hypoxia, development of anemia.
Violation of the integrity of the functional layer of the mucosa is fraught with long-term complications. The main one is endometriosis. Its development can be assumed by regular brown spotting before menstruation or in the middle of the cycle. The growth of the functional layer of the endometrium outside the uterine cavity is sometimes accompanied by cramping pain.
Damage to the cervical mucosa during dilatation before curettage often leads to subsequent erosive changes leading to ectopia or dysplasia of the epithelium. Such disorders occur asymptomatically or with leucorrhoea. The condition may be complicated by impaired elasticity of the cervix and rupture during subsequent births. The formation of an oncological process is likely.
The most serious complication is infertility. If the instrument cuts the mucous membrane to a great depth, completely removing the functional layer, a scar is formed in this area. This reduces the chances of successful implantation of the embryo in the future.
Pregnancy
Pregnancy after curettage is possible, and often even more likely if the pathological endometrium was removed. Usually, menstruation begins around the third week after the procedure, since during this time the mucous layer of the uterus has time to recover. In this case, the menstrual cycle is completely normalized and becomes regular after about 4 months. In general, it is possible to plan conception within six months after the procedure, but before starting attempts, it is better to consult a doctor.
How many days does it bleed
The duration of bleeding after curettage is an important indicator for assessing the patient’s condition during the surgical procedure. The duration of discharge may vary depending on the woman’s health status and her characteristics.
Most patients bleed after curettage from several hours to several days. After completion of the procedure, the uterus begins to contract intensively, which helps reduce the intensity of bleeding.
Possible danger
Although minor uterine bleeding after curettage is normal, these days a woman should especially carefully monitor her well-being and the nature of the discharge. If problems arise, thanks to attentiveness, you can solve them at the very beginning, preventing dangerous consequences.
Recovery after cleaning the uterine cavity
Generally speaking, uterine curettage does not globally affect the functioning of a woman’s body; it is rather a psychological problem. Yes, of course, there are complications and difficulties during recovery, but all of these can be solved and with the proper quality of the procedure, the female body recovers quickly.
However, it should be remembered that after curettage the uterus is open, very vulnerable and is a bleeding wound of a fairly large size, because a whole layer of functional endometrium was removed from it:
- This condition is akin to what happens at the end of the menstrual cycle, that is, the endometrium peels off and leaves the uterine cavity.
- That's why you shouldn't be afraid of this procedure, because every woman experiences a similar condition every month.
If everything went well, then after the operation the woman may be discharged the next day, or may be offered to stay for another 2-3 days.
At the same time, she is prescribed anti-inflammatory, painkillers and hormonal drugs. She can easily take all this at home on her own. Hormonal ointments and suppositories are often used as additional treatment.
Attention! It is recommended to spend the first day after surgery lying in bed so as not to provoke even more bleeding. In the room, pain should stop after 2-3 days, and before that you need to take painkillers.
It is forbidden to have sex for a month after the operation . And after this time, you should strictly protect yourself. Pregnancy in this situation can only worsen the woman’s condition.
What is uterine curettage and what are the features of the procedure is described in the video:
Resumption of menstruation
Appears after 4–5 weeks. The timing largely depends on the general condition of the body and the speed of recovery of the cervix and endometrium. After abortion, there is often a delay. This is due to the fact that in this case it takes a little more time to restore reproductive function.
The menstrual cycle is fully restored after curettage only after three months. In some cases, this takes about six months. In the first few months, intense contractions of the uterus lead to pain during menstruation. Regula often become scarce or excessively abundant.
Changes that should alert you include severe abdominal pain, acyclic bleeding, and an increase in body temperature. In this case, postponing a visit to the doctor is strictly prohibited. A reason to visit a gynecologist is also a prolonged absence of menstruation.
When is conception possible?
Gynecologists advise waiting to conceive after an abortion or a frozen pregnancy for at least six months. Why so long? The body needs this period for rehabilitation. It is important to wait until the menstrual cycle is restored and the reproductive system is functioning properly. This time can be used for active preparation for pregnancy, including giving up bad habits, taking folic acid, and leading a healthy lifestyle. In this way, you can increase the chances of conceiving again as quickly as possible and bearing a healthy child.
So, curettage of the uterus is a procedure that in many cases cannot be avoided. With proper preparation for the procedure and following all the gynecologist’s recommendations, the procedure will only bring benefits and no complications will arise. Discharge after therapeutic cleansing of the uterus ends within 10 days. If this does not happen, hemostatic drugs are prescribed. Restoring the menstrual cycle takes several months, and you can start conceiving six months after an abortion or curettage.
Curettage is a serious operation during which the mucous layer of an organ is excised. Sometimes complications may occur after cleaning the uterine cavity. For this reason, an ultrasound is prescribed. In addition, the doctor gives recommendations, following which you can reduce the risk of undesirable consequences.
Curettage is performed for therapeutic and diagnostic purposes. During the operation, only the superficial mucous layer is removed, due to which the organ is restored quite quickly. In this case, pain appears in the first hours after curettage. Over time, they become less pronounced and disappear completely.
For therapeutic purposes, surgery is performed to remove the remains of the embryo after spontaneous abortion and if cancer is suspected. Abortions are often performed this way. In addition, indications for cleaning are frozen pregnancy and severe uterine bleeding.
Appointed. The cause of this pathology is hormonal imbalance. The danger of the disease lies in the fact that there is a risk of cells degenerating into malignant ones. When it develops, separate diagnostic curettage is performed.
Tissues obtained during the operation are sent to a histology laboratory to exclude oncology.