Cervical erosion: definition and types
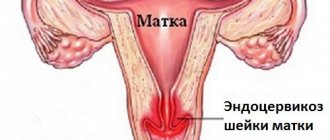
Cervical erosion is a pathology of the vaginal mucosa of the cervix, when the normal epithelium is replaced by columnar epithelium of the cervical canal.
There are several types of erosion:
- Congenital ectopia of the cylindrical epithelium of the cervical canal is a round-shaped formation with a bright red color, which appears in adolescence and often heals itself. It almost never leads to cancer.
- True erosion - when examined using mirrors, the doctor sees a red spot no larger than 1 cm in size, but with clearly defined edges. It lasts up to 2 weeks, after which it degenerates into ectopia.
- Ectopia is a pathological change in the epithelium when normal cells are replaced by cylindrical ones. Externally, ectopia is a red spot of different sizes that can exist for years, periodically changing size. In this case, treatment will be required, because with prolonged “ignoring” of the pathology, the likelihood of the formation of malignant tumors increases.
Causes and symptoms of cervical erosion
Before talking about treatment, it is worth dwelling on the causes of erosion and the symptoms that accompany it. This will allow us to understand in more detail the nature of this disease.
Among the reasons that lead to the formation of erosion are the following:
- infections (herpes virus, papilloma, ureaplasma, trichomonas, chlamydia, etc.);
- early sexual life;
- frequent change of partners;
- hormonal imbalance;
- difficult births or complicated abortions.
In most cases, this disease is asymptomatic. As a rule, a woman learns about the presence of the disease at an appointment with a doctor during a gynecological examination. It happens less often when patients themselves turn to the doctor with complaints of pain in the lower abdomen, burning sensation, purulent mucous and bloody discharge that appears after sexual intercourse.
You should not try to treat these diseases on your own, as this can only worsen the situation: other inflammatory processes will appear, problems with conceiving and bearing a child may arise, and there may be a threat of miscarriage. You should immediately consult a doctor who can diagnose the disease and prescribe appropriate treatment.
Description of the disease
This diagnosis is made when single-layer columnar epithelium from the cervical canal is displaced onto its surface, lined with stratified squamous epithelium.
Such a displacement can be called ectopia, and gynecologists of the Soviet school use the concept of “pseudo-erosion”.
Modern gynecologists call true erosion a condition when the mucous membrane is torn off from a small area of the cervix.
This is usually a consequence of mechanical damage (sexual intercourse, gynecological manipulation, chemical burns and improper use of contraception) or inflammatory processes caused by infections: chlamydia, trichomonas and others.
The damage usually heals within a few weeks . In its place, pseudo-erosion, or displacement of the epithelium, may appear. It’s easy to get confused in so many terms, which is what happens to patients.
Women of reproductive age, in the absence of complaints, should undergo a preventive examination by a gynecologist at least once a year.
A visit to the doctor should not be postponed if you are concerned about:
- bloody intermenstrual discharge and discharge after sexual intercourse;
- painful intercourse.
Gynecologists usually make the diagnosis of “cervical erosion” during an examination.
But to confirm the diagnosis and find out the reasons, a series of additional tests and studies should be done . This is a smear for flora, colposcopy, biopsy and subsequent cytological and histological studies, PCR diagnostics, including for the human papillomavirus, which is especially common in patients with this diagnosis, tests for HIV, syphilis, and hepatitis.
For treatment, it is necessary to find out the causes of the disease. All types of cervical erosion, except true, require their own method of treatment, which should be prescribed by a gynecologist.
Congenital erosion occurs in nulliparous women and usually goes away without any intervention by the age of 22-25.
You need to be regularly monitored by a specialist and minimize the risk of infection, monitor your hormonal levels. True erosion also goes away on its own.
Diagnosis of cervical erosion
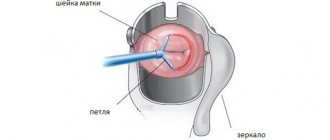
Very often, at a gynecologist’s appointment, you can hear about the presence of cervical erosion. But this information is not always true. The doctor, using a mirror, can only see redness on the cervix of a certain size. To verify the validity of the preliminary diagnosis, he prescribes colposcopy, which is a painless procedure and allows you to examine the damage under a microscope. If some areas are suspicious, a targeted biopsy will have to be done. During this procedure, a small piece (about 1-2 mm) is taken from the cervix for further examination.
If the doctor has suspicions that erosion has appeared as a result of infection, he will recommend doing a smear for flora, cytology, donating blood for HIV, syphilis, hepatitis B and C. In this case, treatment will be aimed at eliminating the existing disorders, because if the cause of the disease is not removed , then there is a high probability that erosion will form again. In addition, after the immediate cause is cured, cervical erosion may disappear on its own or significantly decrease in size.
If after colposcopy the doctor is convinced that the patient really has erosion, then two solutions are possible:
- removal of uterine erosion;
- dynamic observation by a gynecologist with control colposcopies (every 3-6 months).
Is the procedure always necessary?
Before cauterization of cervical erosion, the need for the procedure is always assessed. WHO recommends such treatment only in the presence of a certain, fairly narrow range of indications - an ulcer that is not amenable to conservative therapy, cervical deformity and grade 2-4 dysplasia for any type of erosion.
Before cauterization occurs, the doctor assesses the condition of the affected area and determines the type of erosion. In most cases, at the first stage, anti-inflammatory therapy is prescribed and dynamic monitoring of the dysplastic process of the mucosa is carried out.
In the countries of the former USSR, cauterization is not always carried out according to indications. Any unusual or increasing discharge or the patient’s wishes often serve as the basis for surgery.
Conservative therapy
This technique involves identifying the cause of the disease and directing treatment to eliminate it. As practice shows, in most cases, after eliminating the cause of the pathology, erosion disappears.
In this case, the patient is prescribed a course of antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs or immunomodulators. The doctor can also recommend traditional medicine recipes that are a complement to treatment.
This method is universal and suitable for all women, including nulliparous girls. Its only drawback is the likelihood of relapse.
Examination of a woman
Most women have a negative attitude towards the examination procedure. Metal speculums are inserted into the vagina for examination. They are cold, so the muscles narrow and the instrument enters tightly. Then it is better to use plastic mirrors. A light is then directed to the cervix and examined. If redness or uneven color is detected, the doctor performs a colposcopy and takes smears for the flora.
To make an accurate diagnosis, you need to undergo cytological and histological examinations. To check for malignancy, a small piece is cut off from the damaged area. Next, after receiving the biopsy result, the doctor will prescribe the correct treatment. First you need to take a smear. When infections are detected, they are treated, and then the erosion itself. It happens that after the infection is cured, the problem disappears on its own.
Diathermocoagulation
This is a method of tissue cauterization, which uses a high frequency current of up to 3-5 amperes. This allows for extensive and deep coagulation of the affected area. This technique can also be used for endometriosis, condylomas and early and moderate dysplasia.
The advantages of the procedure are its accessibility and prevalence. Almost every specialized clinic has equipment for treating erosion using current. But the doctor’s competence plays a very important role in the procedure, since it is he who controls the depth of tissue destruction. If diathermocoagulation is carried out incorrectly, a number of difficulties may arise :
- bleeding (both during surgery and during the rehabilitation period);
- development of endometriosis;
- exacerbation of inflammatory processes;
- the appearance of scars;
- menstrual irregularities.
Cryotherapy
This is one of the new techniques, the essence of which is to burn out the affected areas of the uterine mucosa using liquid nitrogen. Using a special cryoprobe apparatus, the gynecologist applies liquid nitrogen to the affected area for 2-3 minutes, after which he takes a break for 5 minutes to thaw. If necessary, he carries out the next stage of freezing and allows time to thaw. The procedure is quick and painless, there is no bleeding, and no scars form on the cervix. Copious liquid discharge is possible - hydrorrhea, but this symptom is normal, although it causes slight inconvenience.
This operation to remove cervical erosion has a number of contraindications, which also need to be emphasized. So, this procedure is not performed if the patient:
- uterine fibroids;
- dysbacteriosis;
- any inflammatory processes of the genital organs;
- cicatricial deformities on the cervix;
- endometriosis;
- somatic diseases;
- pregnancy and lactation period.
Main methods of treatment
Now there are many methods for cauterizing erosion. The specific method should be selected by a specialist. Let's look at the most common types of cauterization of cervical erosion.
Diathermocoagulation
The most outdated way to combat erosion, which involves cauterizing it with electric current.
Its advantages include accessibility and efficiency - that’s why it still exists.
Before starting treatment, the vagina is sanitized, any infectious and inflammatory processes are eliminated.
The essence of the method is that the electrode delivering current discharges points to the affected area until the entire erosion is covered with a scab. at this site , covered with a crust .
The scab comes off in about 10-12 days. Since instantaneous coagulation of blood vessels does not occur during the procedure, the woman will experience spotting and bleeding throughout the entire rehabilitation period.
A serious drawback of the method is the formation of a rough scar from connective tissue, which can affect the course of labor in the future.
Therefore, this method is categorically not recommended for nulliparous girls.
Diathermoexcision
A common method that involves cutting out the affected tissue with an electric knife.
This method can be used to treat ectropions, and it is supposed to be carried out on days 7-9 of the menstrual cycle.
But the procedure has a number of complications: bleeding, poor wound healing, scar formation, endometriosis, and cervical deformation.
Radio wave methods
These include radiosurgery and the use of the Surgitron device.
Radio waves imply pinpoint, local destruction of deformed tissues and the formation of a wound surface. The wound heals, and healthy squamous epithelium forms on the surface of the cervix.
The wound heals completely within 1.5-2 months, which is twice as fast as with the two previous methods.
The procedures rarely lead to complications and do not provoke the formation of scars on the cervix, so they can be used to treat erosion in women who have not given birth or in those who want to have more children.
Laser vaporization
Using a carbon dioxide laser, a specialist cauterizes or excises pathologically altered tissue in the area of erosion, and a wound is formed in its place.
After it heals, normal flat epithelium forms on the cervix.
This method is one of the most modern and effective.
It practically does not provoke complications, does not lead to the formation of scars on the cervix and assumes rapid healing (within 1-1.5 months).
Cryodestruction
In this case, pathologically altered tissues of the cervix are treated with liquid nitrogen . Due to low temperatures, they die off, and normal tissues form in their place, the cervix is covered with squamous epithelium.
Cryodestruction is performed on days 7-9 of the menstrual cycle. Everything will heal completely in 2-3 months, the risk of complications is very low, scar tissue does not form.
Among the disadvantages of the method, there is a fairly high risk of relapse , the cause of which is insufficiently deep freezing of the affected tissues.
Chemical coagulation
The procedure involves treating the eroded surface with medications .
Previously, Vagotil was mainly used to cauterize cervical erosion, but today it has been replaced by a more effective and modern treatment - Solkovagin.
The doctor first dries the damaged area with a cotton swab. Another tampon is thoroughly soaked in the selected product and the eroded area is treated with it.
The treatment lasts for three minutes. Residues of the drug are removed with a clean, dry swab. In order to increase the accuracy of application, the session is carried out under the control of colcoscopy.
The procedure is completely painless and does not even require local anesthesia. It is suitable even for a woman who has never given birth.
But this method is not used if the diameter of the erosion is more than one centimeter.
Because medications are more gentle than other treatments, multiple treatments may be required to completely eliminate the problem.
Is it possible to cure cervical erosion without cauterization? We will talk about:
- how to get rid of cervical erosion at home;
- Is it possible to cure the disease with folk remedies?
- how to use sea buckthorn suppositories for treatment;
- what other suppositories can be used for this disease.
Laser therapy
This operation to remove cervical erosion is considered the best today. Cauterization of erosion with a laser is carried out using a special device: a laser beam in the form of a strong light flux is pointedly directed at the affected tissue. Local anesthesia may be used during the procedure, but this is not required.
Laser coagulation, compared to other methods, has the following advantages:
- simplicity and speed of implementation;
- eliminating the possibility of damage to healthy tissues;
- no bleeding;
- During its passage, the laser beam has a positive effect on the vaginal microflora, killing pathogens;
- the rehabilitation period is only 1 month (longer for complex erosions);
- no scars.
For complex forms of erosion, laser treatment takes place in several stages, since it is difficult to determine the depth of the affected tissue. Therefore, it is more effective to do several cauterizations over a certain period. When “burning out” large areas, transparent, white and yellow discharge is possible.
This equipment should not be used if a woman has any inflammatory processes or infections of the reproductive system.
Indications and contraindications
Cauterization of erosion is necessary in the following cases:
- Large affected area.
- Growth of the affected area.
- Unpleasant symptoms, for example, pain during sexual intercourse, using a tampon, and bleeding.
- Repeated occurrence of inflammatory processes.
- Human papillomavirus.
- Weakened immunity.
Despite the fact that cauterization is necessary in most cases, sometimes there is a chance to do without it. Sometimes a doctor may prescribe medication or no treatment at all.
This happens if there is a chance for the erosion to heal on its own.
No cauterization needed:
- If the patient plans to become pregnant in the near future.
- If a woman has a strong immune system, but a small area is affected (there is a chance that the body’s defenses will cope on their own).
- Pseudo-erosion often does not require removal.
- Congenital erosion in a patient younger than 25-27 years old - at this age it often goes away on its own.
- Absence of acute or chronic inflammatory processes, viruses, fungi.
There are contraindications for which removal cannot be performed.
These include the following:
- Inflammatory processes in the genitourinary and reproductive systems.
- Untreated sexually transmitted diseases in acute and chronic form.
- Oncological processes.
- Nervous system disorders.
- Diseases of the cardiovascular system, hematopoiesis and blood clotting disorders, certain genetic abnormalities.
- Endocrine system disorders, such as diabetes.
- Metabolic disorders.
- Polyps in the canal.
- Dysplasia, leukoplakia and other diseases of the cervix.
Pregnancy, lactation, recent childbirth will be a relative contraindication. But everything is determined by the severity and nature of the pathology, so the doctor must make the decision.