Progesterone is a steroid hormone in structure. The monthly cycle, pregnancy and embryonic development are under its influence. It is synthesized from cholesterol and is a precursor to other steroids:
- testosterone;
- estriol;
- cortisol;
- aldosterone.
Progesterone is involved in brain function as a neurosteroid. Based on it, other metabolites are produced that can influence various types of receptors in brain tissue (for example, GABAA receptor). Its activation leads to inhibition of the transmission of nerve impulses.
With a lack of allopregnanolone, a neurometabolite of progesterone, depressed mood and depression appear. This fact explains why women experience bad mood, sad thoughts and tearfulness due to PMS.
How does progesterone change during pregnancy?
Normally, progesterone constantly increases during pregnancy. Its concentration increases 20 times. Moreover, the increase begins already in the second half of the cycle, when conception has not yet occurred. After fertilization, it is this hormone that helps strengthen the fertilized egg, and then maintains the pregnancy throughout the entire pregnancy.
When the source of progesterone formation changes, it decreases. This corresponds to approximately 6-9 weeks of pregnancy. The main role in hormonal synthesis passes from the ovaries to the placenta. It is at this time that the risk of spontaneous miscarriage increases. A decrease in progesterone levels in the later stages is a sign of the onset of labor.
We recommend reading the article about hormones for endometriosis. From it you will learn which hormones are tested for endometriosis, which hormones are deficient and which will be increased, as well as hormones for treatment of endometriosis and fibroids. And here is more information about tests for female hormones.
How to take it
A blood test for progesterone during pregnancy involves taking venous blood. The procedure takes place in several stages. Preparatory:
- the medical worker enters the patient’s first and last name in the registration register or computer database;
- In front of the pregnant woman, the nurse puts on gloves and opens sterile packages (syringes, disposable alcohol wipes);
- the necessary tools are located within walking distance.
The patient should sit comfortably on a soft chair or couch. A woman should be as relaxed as possible. The arm (just above the elbow) is tied with a fabric tourniquet. To ensure maximum blood flow into the vein, the woman is asked to clench and unclench her fist for several seconds. The needle cap is removed immediately before sampling.
The needle is placed parallel to the skin. The intended puncture site is wiped with an alcohol wipe. After the biomaterial has been collected, the needle is carefully removed and cotton wool soaked in alcohol is applied to the injection site. The woman should bend her elbow to quickly stop the bleeding.
Why do you need progesterone during early pregnancy?
The main tasks of progesterone during early pregnancy are its protection, the successful continuation of pregnancy and the restructuring of the woman’s entire body to nourish the unborn child. For this hormone:
- relaxes the walls of the uterus, reduces its tone so that there is room for the growing fetus;
- weakens the immune defense, preventing the reaction of rejection of foreign (half) protein;
- stops ovulation and menstruation;
- creates a dense mucus plug in the cervix to prevent infection;
- stimulates the development of the mammary glands, the branching of their ducts, the proliferation of lobules for subsequent lactation, but restrains it until childbirth;
- changes mood and character - movements and thought processes slow down, the woman becomes relaxed and calmer, the need for rest and sleep increases;
- dilates arteries to accommodate increased blood volume;
- protects the mother’s skeletal system from destruction;
- increases metabolic rate and body temperature in the first 100 days of pregnancy.
Interestingly, the hormone itself has a predominantly positive effect on the woman’s body, and its metabolic products cause:
- swelling;
- engorgement and tenderness of the mammary glands;
- toxicosis;
- thickening of bile and destruction of liver cells;
- deterioration of carbohydrate metabolism - blood glucose increases after eating.
The last action is necessary for feeding the fetus. It is important that the incoming energy source is not immediately absorbed by the mother’s body. When the response to insulin is excessively reduced, gestational diabetes occurs.
Progesterone for the body of a pregnant woman
Progesterone is an important hormone that allows a woman to become pregnant and carry a child to term. The production of progesterone in women occurs in three stages:
- Under normal conditions, it is synthesized by the ovaries.
- After fertilization of the egg, the corpus luteum is responsible for the production of progesterone.
- Starting from the 2nd trimester, the placenta assumes responsibility for maintaining the required level.
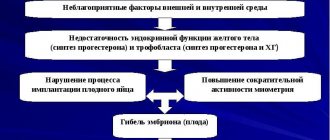
Deviation of the hormone level from the norm is dangerous for the fetus. If there is an initial lack of it, the zygote will not be able to attach to the wall of the uterus. The hormone relaxes it and reduces contractions, helping the embryo to securely attach. Lack of progesterone often leads to miscarriage, and its high value leads to various pathologies.
If there is a lack of progesterone in a woman’s body, the doctor prescribes medications that help artificially maintain pregnancy. Following the recommendations gives every chance for successful fetal development.
Test for progesterone during pregnancy
During pregnancy, a progesterone test is not considered mandatory; it is prescribed in the following cases:
- threat of miscarriage - pain in the lower abdomen and lower back, cramps, spotting or bleeding;
- previously there were spontaneous abortions, recurrent miscarriage;
- diseases of the adrenal glands, thyroid gland, infectious;
- suspicion of a frozen pregnancy or attachment of the fertilized egg outside the uterine cavity, postmaturity;
- Progesterone has been prescribed for treatment and its outcome needs to be assessed.
It has been established that a healthy woman’s blood contains 2 times more progesterone than with miscarriage. In the wall of the uterus, its level is two hundred times higher, and its reaction to the hormone is also stronger.
When to take it
Progesterone during pregnancy can be taken at 4 weeks. If a woman is just planning children, she needs to check the hormone level in advance. The biomaterial is collected on days 22-23 of the menstrual cycle. This scheme can be followed only if the cycle duration is 28 days. If it is irregular, you can independently calculate the “lucky” day for ovulation and add 8-9 days to it.
The doctor may order a laboratory test at 13-15 weeks if the patient:
- there is a threat of spontaneous abortion (sharp deterioration in condition);
- fetal growth retardation or placental insufficiency was detected.
During a normal pregnancy, no analysis is prescribed.
Symptoms of changes in hormone levels
Low progesterone leads to increased uterine tone in the early stages and spontaneous miscarriage. This is accompanied by pain in the lower abdomen and bleeding.
During a developing pregnancy, the doctor may suspect hormonal deficiency based on ultrasound data:
- discrepancy between the age and size of the uterus;
- insufficient amniotic fluid or polyhydramnios;
- abnormal fetal heartbeat - increased frequency as a sign of oxygen starvation;
- the placenta has changes in structure, the flow of blood to the fetus is disrupted.
Ultrasound during pregnancy
Excess progesterone can manifest itself as:
- edema, increased body weight due to tissue swelling;
- fatigue;
- nausea, vomiting;
- increased blood pressure;
- headache, migraine attack;
- yellowing of the skin, brown spots;
- pain in the right hypochondrium;
- engorgement and increased sensitivity of the mammary glands.
... and what is it for?
The biological effects of progesterone depend on the moment in a woman's life. Before pregnancy, its functions are as follows.
- Uterus. Increases the growth of glands and microvessels in the endometrium, prepares the mucous membrane for implantation. Reduces myometrial contractility to prevent expulsion of the embryo.
- Fallopian tubes. Increases the secretion of mucus, which serves as a nutrient medium for the embryo as it moves into the uterine cavity.
- Mammary gland. Stimulates the growth of mammary gland lobules and alveolar ducts. At the same time, progesterone suppresses the activity of prolactin and does not allow milk to be secreted.
- Sperm. Progesterone acts as a chemoattractant - a substance that stimulates cell movement.
During pregnancy, increased progesterone performs the following functions.
- Immunity. Reduces local defense reactions to ensure the safety of the embryo, which consists of 50% foreign DNA. But this leads to negative effects - pregnant women often develop vaginitis and vaginal candidiasis.
- Uterus. Relaxes the myometrium, which helps maintain pregnancy, reduces the risk of spontaneous abortion due to uterine tone. A decrease in progesterone facilitates the onset of labor.
- Mammary gland. Stimulates further growth of breast lobules, proliferation of ducts and alveoli.
Changes in progesterone concentration affect the pre-pregnancy stage. Low progesterone can lead to the following consequences:
- irregular cycle;
- discirculatory uterine bleeding;
- swelling;
- severe premenstrual syndrome;
- difficulties in getting pregnant.
Increased progesterone before pregnancy delays the onset of menstruation, makes the voice rough, increases skin greasiness and hair growth in unwanted places.
Reasons for deviations
To choose a treatment method, it is important to establish not only the fact of changes in the hormone in the blood, but also the cause of elevated or low levels.
Low progesterone during early pregnancy
Low progesterone levels are especially dangerous during pregnancy in the first months; in the early stages this can be caused by:
- threat of interruption,
- the beginning of a miscarriage,
- delayed fetal development,
- chromosomal abnormalities,
- ectopic pregnancy,
- insufficient formation of the placenta.
Threat of miscarriage
There are studies that have proven that reduced progesterone in the first months leads to increased blood pressure and edema (late toxicosis) in the second half of pregnancy.
The formation of the hormone can be disrupted due to diseases of the ovaries, adrenal glands, pituitary gland, and thyroid gland. The diagnosis is not made based on a blood test. The gynecologist takes into account the patient’s complaints, ultrasound data assessing blood circulation in the placenta, and recommends tests for human chorionic gonadotropin and estriol.
Increased progesterone during pregnancy due to medications
When treating with progestin drugs (Utrozhestan, Duphaston), it is important to prevent increased progesterone during pregnancy. This is due to the fact that this hormone is a source for the formation of male and female sex steroids. If their level increases, pregnancy is disrupted and there is a risk of fetal development abnormalities. Therefore, treatment with progesterone drugs is always monitored by tests.
Excess progesterone during pregnancy
For a successful outcome, not only a deficiency, but also an excess of progesterone is harmful, and during pregnancy it can be caused by:
- kidney disease (the excretion of the hormone is impaired, it remains in the blood);
- ovarian corpus luteum cyst (formation of a cavity filled with fluid);
- premature maturation of the placenta and its early “aging”;
- diseases of the adrenal glands;
- a tumor from the membrane of the embryo (chorionic carcinoma);
- hydatidiform mole - multiple blisters form instead of the fertilized egg, which happens with serious genetic defects.
A high level of hubbub after 16 weeks is a sign that the pregnancy is multiple.
... and excess
If a woman is pregnant with twins, then excess amounts of the hormone will be normal. In other cases, high progesterone requires medical attention.
Hydatidiform mole is a condition in which, instead of a full pregnancy, multiple blisters are formed from chorionic villi in the uterine cavity, and embryonic tissues are either grossly defective or absent. The danger of this condition is the possibility of metastases spreading to the lungs, brain, and germination through the wall of the uterus into the abdominal cavity. Therefore, the only treatment for hydatidiform mole is its removal.
Chorionic carcinoma is a malignant tumor of trophoblast tissue, germinal gonads, and chorionic villi. It often develops simultaneously with pregnancy, but can also appear after childbirth. Pathology is treated with chemotherapy and radiation therapy. Surgical treatment is used for:
- sepsis;
- bleeding;
- perforation of the uterus;
- large size of the lesion;
- failure of other treatment.
In case of renal failure or pathology of the placenta, supportive treatment is carried out, the purpose of which is to allow the woman to bear the child.
Progesterone for IVF
With IVF (in vitro fertilization), progesterone is reduced. This is the result of the introduction of hormones that stimulate the maturation of eggs. They create an advantage in favor of estrogens. The second reason is a puncture (puncture) of the follicle to collect the egg. This inhibits the formation of a full-fledged corpus luteum, which produces progesterone.
Therefore, all patients need to take synthetic analogues for the first 11-12 weeks. When the hormone-forming role passes to the placenta and it is well formed, such support will no longer be needed.
Progesterone and IVF
During IVF, progesterone preparations are necessary to create conditions for embryo implantation. The condition of the endometrium in the second phase is monitored using ultrasound. Women with various pathologies that do not allow pregnancy to develop resort to assisted reproductive technologies. The endometrium often suffers:
- with a thickness of up to 5 mm - implantation is impossible;
- with a thickness of 5-7 mm - implantation is likely;
- with a thickness of 7-12 mm - optimal condition.
It is possible to prepare the endometrium for implantation only with the correct prescription of hormonal drugs.
Progesterone testing during pregnancy is carried out according to indications. At a later date, such an analysis can be prescribed in case of postmaturity. Childbirth after 41-42 weeks is more traumatic for the woman and the newborn. Therefore, this sign serves as an indication for the gradual preparation of a woman for induced labor.
How to correct analysis indicators
To correct deviations, the cause of hormonal changes must be eliminated.
If elevated
If diseases that cause hormone growth (tumor, hydatidiform mole) are excluded, then in the early stages only symptomatic treatment is carried out:
- Magne B6 to stabilize emotions;
- adequate sleep and daytime rest;
- walks for at least an hour in the fresh air;
- refusal of salty and spicy foods;
- the use of natural laxatives and diuretics (pumpkin juice, decoction of dried apricots and prunes);
- reducing animal fats in the diet.
Elevated progesterone after the first trimester is often treated in a hospital, as it is important to prevent a lack of blood flow through the placenta. The doctor may prescribe vascular medications (Dipyridamole, Actovegin), vitamin injections, and drugs to dilate the arteries.
If lowered
Low progesterone in pregnant women requires the use of drugs containing it. At the same time, it is recommended to reduce stress levels. The stress hormone cortisol is formed from progesterone, depleting its reserves. This is possible using:
- listening to music;
- long walks;
- handicrafts;
- relaxing massage of the collar area;
- the use of sedatives, but they must be prescribed by a doctor.
It is important to include in your diet:
- raspberries (in the absence of allergies);
- avocado;
- bell pepper;
- pumpkin seeds and raw nuts (it is recommended to soak them overnight in water for better absorption);
- fish (mackerel is useful);
- cottage cheese 5-9% fat, milk cream.
You should not drink coffee or eat soy products. Excess sugar and white flour are harmful.
How to return progesterone to normal
As in many other cases, the cause is easier to prevent than to treat. Doctors believe that the problem needs to be solved comprehensively . For the purpose of prevention, doctors can immediately prescribe progesterone in the early stages for the following indications:
- with obvious progesterone deficiency;
- with systematic miscarriage (2 miscarriages or more);
- with artificial insemination;
- Prophylactic administration of progesterone for a short cervix reduces the risk of miscarriage by almost half.
Both deficiency and excess of progesterone require professional treatment with special drugs, such as Duphaston or Utrozhestan. Artificial analogues of the hormone are prescribed orally or vaginally. In severe cases, hormone injections are used intramuscularly.
Is it dangerous to take hormone tablets while pregnant?
The use of progesterone itself does not pose any danger to the woman and child. This is proven by more than 50 years of successful use. The drugs prescribed by gynecologists are made from wild yam, that is, they are close to natural remedies. All the effects that are noted after taking them completely replicate the effect of natural progesterone. They can:
- prevent miscarriage;
- improve metabolism;
- reduce the risk of late toxicosis.
Duphaston does not stimulate the formation of blood clots and does not disrupt the formation of the fetus. Side effects of use include:
- headache,
- nausea,
- swelling,
- increased blood pressure.
In the USA and a number of European countries, progesterone preparations are not used to maintain pregnancy up to 12 weeks. This is not due to their danger to pregnant women, but to the fact that in this period miscarriage is often caused by chromosomal diseases.
Video about progesterone during pregnancy
In the short video below, an obstetrician-gynecologist talks about the main misconceptions associated with progesterone and who should really be prescribed this hormone.
When carrying a child, expectant mothers are very worried and try to do everything necessary so that the little man is born healthy. The modern availability of almost any information, on the one hand, helps to better prepare and understand what is happening. On the other hand, it often leads to unnecessary worries. Some people scrupulously study all available tables, keep track of weight gain by week, while others believe that it is enough to follow the doctor’s instructions and regularly take prescribed tests. But in any case, your own experience will always be the most interesting and valuable.
Share your stories and comments about what happened to you. Perhaps it will help someone else get through a time of big change calmer and happier.
Why is progesterone low when planning pregnancy?
The reasons for low progesterone when planning pregnancy are:
- congenital developmental disorders of the ovaries and pituitary gland;
- changes in hormone metabolism, enzyme activity;
- polycystic ovarian tissue;
- injuries, operations, frequent diagnostic procedures in gynecology (for example, laparoscopy);
- hormonal imbalance due to diseases of the pituitary gland or hypothalamus of the brain;
- renal diseases: pyelonephritis, glomerulonephritis;
- liver dysfunction;
- diabetes;
- increased function of the thyroid gland (thyrotoxicosis), adrenal glands (Itsenko-Cushing syndrome);
- excessive exercise;
- obesity;
- strict, monotonous diets;
- smoking, frequent drinking of alcohol;
- long-term continuous use of hormonal contraceptive pills;
- growth hormone treatment.
It is important that they are detected before pregnancy, since treatment will be more effective and hormonal levels can be radically improved. It should be borne in mind that conception itself is possible with a lack of progesterone, but the chances of a favorable pregnancy are quite low. Progesterone deficiency after pregnancy is an indication for the use of drugs to prevent miscarriage.
Progesterone levels by week
The concentration of progesterone in the blood of a pregnant woman constantly increases. The increase occurs every week, almost evenly from the moment of conception until childbirth. The indicators are individual for each woman, the main thing is that they are within the normal range. The results of the analyzes can be independently compared with the indicators in the table. It is important to accurately determine the number of weeks so that the values are as accurate as possible. In case of deviations from the norm, it is recommended to take the test again to track the growth of progesterone over time.
Table of normal indicators in the first trimester
| Obstetric week of pregnancy | Normal hCG level (nmol/l) |
| 5-6 | 16,57-20,57 |
| 7-8 | 29.42-36.54 |
| 9-10 | 33.81-42.01 |
| 11-12 | 38.19-47.41 |
| 13-14 | 39.62-49.92 |
Table for the second trimester
| Obstetric week of pregnancy | Normal hCG level (nmol/l) |
| 15-16 | 41.69-51.81 |
| 17-18 | 52.86-65.7 |
| 19-20 | 64.04-79.56 |
| 21-22 | 66.99-83.71 |
| 23-24 | 70.6-87.7 |
| 25-26 | 74.26-93.52 |
| 27-28 | 81.63-101.41 |
Progesterone table for the third trimester of pregnancy
| Obstetric week of pregnancy | Normal hCG level (nmol/l) |
| 29-30 | 90.41-112.35 |
| 31-32 | 101,5-126.6 |
| 33-34 | 105,7-136,3 |
| 35-36 | 132,6-172 |
| 37-38 | 195.83-243.33 |
| 39-40 | 245.55-301,1 |
Are high readings dangerous?
Elevated progesterone interferes with the normal course of pregnancy. In the fetus, high levels of the hormone can cause malformations of internal organs and the endocrine system. Conditions that cause an increase in progesterone are especially dangerous:
- renal failure is accompanied by the accumulation of metabolic products in the blood, causing poisoning of the body;
- particles of hydatidiform mole can spread to the brain, lungs, and abdominal cavity;
- a tumor from the villi of the embryo membrane tends to metastasize, complications such as bleeding are possible;
- premature development of the placenta disrupts the supply of nutrients to the developing fetus.
All these conditions occur regardless of the use of drugs with progesterone. They are quite rare and require emergency medical attention.
We recommend reading the article on how to take hormonal supplements correctly. From it you will learn about the time of taking pills, what time to take hormonal pills for thyroid diseases and during pregnancy, as well as how to quit hormonal pills and how to reduce your appetite while taking medications. And here is more information about hormone tests when planning pregnancy.
Progesterone helps conception, implantation of the fertilized egg, and prevention of fetal rejection. With progesterone deficiency, miscarriages occur, so if they threaten, habitual miscarriage, Duphaston and Utrozhestan are prescribed after IVF. Treatment is always carried out under the control of tests. A high rate occurs with hormonal therapy, multiple pregnancies, and is also a symptom of dangerous diseases.
To restore normal progesterone levels, diet, lifestyle changes and medications are used.
What are the dangers of deviations from the norm for the fetus?
The danger of insufficient or too high levels of progesterone for the fetus arises from the first weeks after conception.
The main threat with a low concentration of the hormone is that the fertilized egg simply will not be able to gain a foothold in the uterus and the pregnancy will be terminated at the very beginning. An increase in the level during this period threatens the appearance of pathologies in the fetus, which can also lead to miscarriage. Lack of progesterone in the second and third trimester can lead to intrauterine growth retardation and premature birth. In this case, the woman requires hospitalization and medication support.
At the end of pregnancy, when the preliminary date of birth has passed, a decrease in progesterone in the blood often occurs. This indicates the need for delivery, since the baby no longer receives enough nutrients.
Progesterone is an important hormone for women, without which pregnancy is impossible. Monitoring its level throughout the entire period of bearing a child allows you to make timely adjustments with the help of medications, preventing negative consequences for the child.
Useful video
Watch the video about progesterone during pregnancy:
Similar articles
- Hormone tests when planning a pregnancy...
It is highly advisable to take hormone tests when planning a pregnancy. They especially need to be checked for those who have been unable to get pregnant for a long time. Indicators of the thyroid gland in the blood, as well as pituitary hormones, are important. Read more - Hormones for endometriosis: what tests are needed...
Hormones are always analyzed for endometriosis. They are analyzed to prescribe treatment. And to delay the spread of the disease, they choose the IUD and contraceptives. Which hormones are elevated and which are deficient in fibroids and endometriosis? Read more
- How to take hormonal hormones correctly, quit pills...
If you know how to take hormonal hormones correctly and also quit pills, you can avoid complications. It is important to consider the timing of administration, especially for the thyroid gland. During pregnancy, the schedule will also help preserve the fetus. How to reduce appetite while taking hormonal medications? Read more
- Hormones of the first phase: which ones are given in the first phase...
Hormones of the first phase play a significant role in the menstrual cycle and the ability to become pregnant. If the norm is established in the indicators, then you should look for the causes of the problems elsewhere. What hormones are released in the first phase? Read more
- Tests for female hormones: when, on what days...
It is necessary to take tests for female hormones if you suspect a hormonal imbalance or when planning a pregnancy. It is important to know exactly which exams to take and on what days, and how to prepare properly in order to get accurate results. How long does it take to prepare tests? Which are considered normal, interpretation of results for female sex hormones. Read more
Preparation
A test for progesterone during pregnancy, the weekly norm of which is determined depending on the phase of the cycle, must be taken in the morning on an empty stomach (from 8 to 11 am). To get the most reliable results, a woman must properly prepare for the procedure. Necessary:
- discuss in advance with your doctor the abolition of drug therapy;
- repeat the analysis after 7-10 days to check the reliability of the study;
- carefully monitor compliance with antiseptic rules;
- relax as much as possible during the collection of biomaterial;
- completely eliminate harmful foods from the diet 2 days before the expected analysis;
- completely stop drinking alcoholic beverages and tobacco products;
- maintain psycho-emotional balance.
A woman planning a pregnancy should avoid visiting the sauna and bathhouse before donating blood. Before collection, you need to tell the healthcare worker the exact day of your menstrual cycle. Pregnant women indicate the due date.
Why are the numbers increased?
Progesterone levels increase sharply at the onset of labor. The increase also occurs every trimester, week by week during a normal pregnancy, and if a woman is carrying twins, then progesterone increases significantly.
In some cases, elevated standards indicate pathology:
- if in the early stages of pregnancy a hydatidiform mole occurs, when the chorionic villi grow in the form of blisters filled with fluid;
- delayed maturation of the placenta;
- impaired adrenal function;
- use of hormonal drugs.
Signs of increase
Increasing hormone levels causes side effects:
- Constipation. Progesterone relaxes the smooth muscles of the intestines, making it difficult for food to move through.
- Mood swings and depression.
- Headache. Increasing levels of the hormone increase blood flow to the brain, relaxing blood vessels, which lowers blood pressure.
- Drowsiness.
How else is pregnancy regulated at the initial stage?
You should not think that progesterone alone will make it possible for the expectant mother to cope with the many months of work. The activity of the body in any period of life and position cannot be accomplished without the management of other substances. In anticipation of a new addition to the family, many of them change quantitatively. Hormones during early pregnancy are produced not only by the endocrine glands and reproductive organs.
At the initial stage, the following changes are recorded:
- The pituitary gland works more intensely, suppressing the production of FSH and LH. During the entire period of pregnancy, the new reproductive cell does not mature, and there are no menstruation. But the production of prolactin increases. The substance is responsible for the subsequent production of breast milk, which contributes to changes in the mammary glands from the very beginning.
- The hormones that ensure the functioning of the thyroid and adrenal glands also increase quantitatively in the early stages of pregnancy. And they determine the healthy gestation and development of the embryo.
- The placenta adds free estriol and lactogen to the blood. Their level determines the likelihood of the baby developing chromosomal abnormalities, blood supply to the uterine tissue, and dilation of the mammary gland ducts.
- The amount of estradiol increases, which allows you to carry a child to term normally. It is now produced not only by the ovaries, but also by the placenta. At the initial stage of pregnancy, estradiol must be present in the body in the required quantity, otherwise it will not be possible to carry it through, despite the optimal amount of progesterone.
HCG and early pregnancy
Based on the results of the analysis, a new substance is discovered - human chorionic gonadotropin. This hormone helps to accurately determine pregnancy in the early stages. It is produced by the fetal membrane immediately after implantation of the fertilized egg in the uterine cavity. The amount of progesterone and estrogen largely depends on the amount of hCG. If there is a deficiency, the likelihood of interruption becomes closer than ever.
The longer the pregnancy, the higher the hCG values should become. Therefore, throughout the entire period of time, one has to take a hormone test more than once. Thanks to this feature, a specialist can easily establish not only the fact of the existence of a new life, but also the period.
HCG also makes it known about irreparable defects in the formation of the fetus, which will allow it to be interrupted in time. Its differences from normal values may be evidence of multiple pregnancy, diabetes mellitus in a woman, which sometimes manifests itself against the background of a new condition, or ectopic pregnancy.
Timely monitoring of hCG and progesterone hormones in the early stages of pregnancy will help assess the general condition of the body and choose the right treatment methods if necessary. You should not prescribe therapy on your own - you can aggravate the situation and provoke various kinds of complications (including miscarriage). Following the doctor's recommendations will help improve the well-being of the pregnant woman and prevent unwanted consequences.
More about estradiol
This substance, in fact, makes a woman such. It participates in the formation of her reproductive system, the outline of her figure, regulates the menstrual cycle and sexual desire.
Estradiol is so necessary during early pregnancy that the placenta also joins its production by the ovaries. The growth of the uterus and optimal blood circulation in its vessels to nourish the fetus depend on it. A special feature of estradiol is that adipose tissue can also produce it.
If a woman is overweight, it is natural that its indicators will be noticeably higher than normal. But this is not so scary for pregnancy, although it makes you feel worse due to the retention of fluid and salt in the tissues.
Low estradiol in early pregnancy is much more dangerous. It means a problem with the fetal membrane, which is needed to protect and nourish the embryo. And this leads to a shortage of necessary compounds, oxygen. The most negative consequence of low estradiol is miscarriage. The placenta, not receiving sufficient nutrition, exfoliates, and the fetus is brought out.
All these reasons require maintaining the required volume of estradiol during pregnancy; the table norms will help you know it exactly:
| Duration (in weeks) | Hormone amount (pg/ml) |
| 1-2 | 210-400 |
| 3-4 | 380-680 |
| 5-6 | 1060-1480 |
| 7-8 | 1380-1750 |
| 9-10 | 1650-2290 |
| 11-12 | 2280-3120 |
| 13-14 | 2760-4300 |
It is easy to notice that as the period increases, the indicators of the substance become higher. Therefore, loved ones should not be surprised that as the pregnant woman approaches childbirth, her nervous excitability also increases. This is a peculiar manifestation of the maternal instinct at an early stage, for which estradiol is also to a significant extent responsible.
Traditional treatment
Treatment of estrogen-progesterone deficiency with folk remedies is effective if the conditions and their application are met. The following drugs are used to increase estrogen levels:
- Aroma oils. They normalize the general condition of a woman. Geranium, lavender, fennel and basil oils will be beneficial.
- Hibiscus tea.
- Flax seeds. They can be consumed with food or on their own. The seeds contain a large amount of useful substances that improve the general condition of the body and also stabilize hormonal levels. You need to eat half a cup of them. After consultation with your doctor, the dosage can be slightly increased.
- Aloe juice. The leaves need to be placed in the refrigerator for several days. After a few days, you need to squeeze out the juice and drink a teaspoon three times a day.
- Young nettle. It must be collected in the spring. The dried raw materials need to be crushed, poured into a thermos and filled with boiling water. The product is infused throughout the day. The liquid is consumed three times a day by sip.
Progesterone can be increased using the following means:
- Raspberry leaves. Pre-dried raw materials in the amount of 2 tbsp. l. you need to pour 2 cups of boiling water. It will take 1 hour to infuse. The medicine should be taken in small sips throughout the day.
- Wild yam. It should be mixed with raspberry leaves in equal proportions. Next, 1 tbsp. l. The mixture is poured into a glass of just boiled water. The liquid is infused for several hours. The medicine is taken three times a day, one tablespoon at a time.
- Plantain seeds and mantle grass. Requires 1 tsp. first component and 1 tbsp. l. second. This mixture is steamed 1 cup. boiling water and take a tablespoon three times a day.
- Red brush. To prepare the medicine, you need 100 g of raw materials and 1 liter of vodka (you can use moonshine). The product should be infused for a month in a place where access to direct sunlight is blocked. It should be taken three times a day, 40 drops. For ease of use, the tincture is diluted with a small amount of water. During infusion, the mixture must be shaken periodically.
- Borovaya uterus. You need to pour 50 ml of raw material into 0.5 liters of vodka or alcohol and keep it in a dark place for 2 weeks. The dosage is 30 drops three times a day. Take the medicine half an hour before meals.
- Cinquefoil goose. You need to pour boiling water over 20 g of crushed raw materials and simmer over low heat for an additional 15 minutes. After this, the product should be left covered until it cools completely. After filtering the medicine, you need to drink half a glass 4 times a day before meals.
You can also use the following to normalize your overall hormonal levels:
- Hop cones. The raw materials must be washed thoroughly, pour cold water and cook over low heat for 20-30 minutes. After the product has cooled, you can use it 0.5 cups up to 4 times a day.
- Rose hips and lemon balm leaves. Both components are combined in equal quantities, poured with hot water and cooked over low heat for 40 minutes. You can drink the product instead of tea twice a day.
Treatment with folk remedies should be started if the patient has no contraindications. You should not use herbal medicines if a person has:
- There is an allergic reaction or intolerance to certain components by the body.
- Period of pregnancy or breastfeeding.
- Chronic pathologies in the acute stage.
- Long-term use of hormonal drugs.
- Pathologies of the intestines or stomach.
- Presence of blood clots in blood vessels.
You should not use herbs if a woman has been diagnosed with a hormone-dependent tumor or unstable blood pressure.
Treatment at elevated concentrations
A slight increase in the hormone can be corrected with diet. To do this, normalize weight, limit the consumption of nuts, hard cheeses, flour and fried foods.
Mifepristone. It is used to stimulate labor in the case of a normal full-term pregnancy. The drug is over-the-counter, but should be taken only after consultation with your doctor. Do not take if intrauterine pregnancy is suspected.
To stimulate labor, drink 1 tablet of 200 g, 1 time per day. After 24 hours, another 1 tablet is taken. After this, the condition of the woman in labor is assessed, and prostaglandins are prescribed if necessary.
In addition to medications, it is suggested to give up bad habits, adjust your daily routine, reduce the proportion of protein foods, and give up foods containing a high percentage of saturated fats.
Magnesia during pregnancy and other medications
What else is prescribed to a pregnant woman because of reinsurance? Noshpu, viburkol, magnesium sulfate (magnesia) and a number of other drugs, sometimes in large doses, although these drugs do not help maintain pregnancy and do not improve the prognosis.
I want to say a few words about magnesia . Its use at the beginning of pregnancy is not only ineffective, but also dangerous to the woman’s health. At rest, the muscles of the uterus are insensitive to this drug. Only when cramp-like contractions begin in the third trimester of pregnancy can the muscles of the uterus become sensitive to magnesium sulfate and respond to it with temporary relaxation. However, not always and not for everyone.
In modern obstetrics, this drug is used to prevent and relieve seizures and partly to lower high blood pressure during such serious complications of pregnancy as preeclampsia and eclampsia. Magnesia has many side effects, which is why it is used only with strict control of the electrolyte (salt) metabolism of a pregnant woman.
Necessary treatment
Based on the above symptoms, you should not delay visiting a qualified specialist in order to receive medical care at a very high level. You should understand the seriousness of this type of disease, since treating symptoms is a very long and complex process.
You should not self-medicate; before using any medications, you should first consult your doctor. Many people know that this disease can be very successfully cured with the use of hormonal drugs, but only under the strict supervision of a specialist.
To do this, it is worth significantly reconsidering your daily routine; pregnant women should pay increased attention to their healthy sleep; as a rule, it should be at least eight hours. Among all the methods and recommendations, the following are the most basic:
Among all the methods and recommendations, the following are the most basic:
It is worth taking care of proper nutrition, with mandatory adherence to a regime in which the intake of fats, carbohydrates and proteins should be balanced; It is worth learning to behave with restraint when any stressful situation arises, and if possible, of course, it is better to avoid them; Engaging in light sports will minimize the occurrence of all symptoms, due to which the overall tone of the body will be increased; You should definitely eliminate bad habits from your life such as: smoking and drinking alcoholic beverages; It is necessary to normalize your daily routine, rest and sleep should be increased. It is very important to rest and sleep as much as a specialist recommends to you; When carrying a fetus, it is very useful for the expectant mother to walk a lot in the fresh air; It is important to pay attention to the use of important vitamins; if the necessary vitamins in the required quantities do not enter the body with food, experts prescribe their analogues in tablets; You should definitely consult with a qualified specialist on the choice of contraceptives.. https://www.youtube.com/embed/s4oXuUUTWbY. https://www.youtube.com/embed/s4oXuUUTWbY
All the methods listed above very favorably contribute to increasing the concentration of the hormone in the blood, resulting in a long-awaited pregnancy. The most important thing is to understand what sad consequences can result from a reluctance to timely contact a medical institution to receive qualified assistance and attempts to self-administer medications, since a critically low level of the hormone is incompatible with maintaining a pregnancy and will inevitably only lead to an abortion.
It doesn’t matter whether the hormone is increased or, on the contrary, decreased, in any case, this means the development of a pathological process, which is important to stop in time. Adhering to simple preventive measures and recommendations from your treating doctor will help you experience a happy feeling of motherhood in the near future, and you will be able to watch how your baby grows and develops
Phases of the menstrual cycle
Childbirth is a natural ability of the female body, the implementation of which requires the coordinated interaction of all its organs and systems. The main role here belongs to hormones. To be able to get pregnant, gonadotropins produced by the pituitary gland are necessary. They influence the functionality of the ovaries, which, in turn, produce estrogen and progesterone.
Subscribe to our INSTAGRAM account!
Menstruation is the process of shedding the endometrioid layer of the uterus. After it ends, the first phase of the cycle begins. At this stage, oocytes mature. The importance of estrogen in a woman’s body at this stage is very high.
In the middle part of the cycle, ovulation occurs - the release of a mature egg. During this period, the concentration of gonadotropins reaches its peak. Then the second phase begins: the luteal phase. The bladder from which the egg was released turns into the corpus luteum, which ensures the development of pregnancy at first. Here the main role belongs to progesterone.
Estrogen and progesterone ensure not only the onset of pregnancy, but also its development in the early stages. Thanks to these hormones, the ability to lactation appears.
What is progesterone?
Progesterone is a hormone that affects human reproductive function. It is produced in the ovaries, placenta (during pregnancy) and adrenal glands, helps prepare the body for conception and bearing a child, regulates the menstrual cycle, and affects libido. If a woman's body does not have enough progesterone, problems with conception may occur.
Pregnancy and menstruation are largely controlled by hormones, and one of these hormones is progesterone. It belongs to the class of progestogens, secreted by the corpus luteum, a temporary endocrine gland that the female body produces after ovulation in the second half of the menstrual cycle.
Progesterone affects the function of the endometrium and prepares the uterus for the implantation of the egg. If fertilization does not occur, the corpus luteum disappears and progesterone levels drop.
In medicine, synthetic steroid hormones called progestins are used. In combination with estrogen they are used in the development of contraceptives. Progestin is also useful in the treatment of disorders during menorrhea and menopause.
The influence of the hormone on the onset and gestation of pregnancy
Progesterone is the key hormone that determines the possibility of conceiving a child. It creates all the conditions so that the egg can meet the sperm and be fertilized. Progesterone prepares the bed for implantation - the introduction of a fertilized egg into the uterus. The hormone also helps ensure that pregnancy proceeds safely - from the moment of conception to childbirth.
The progesterone level in the second phase of the cycle should be 7-56 nmol/l. It is this concentration of the hormone that allows a woman to become pregnant . Lack of progesterone levels interferes with fertilization, implantation and gestation.
In most cases, a woman simply cannot conceive a child due to progesterone deficiency in the second phase of the menstrual cycle. Even if fertilization occurs, such a pregnancy is often terminated early.
History of the study of the hormone
They first learned about progesterone back in the 30s of the last century. This happened during the study of the corpus luteum, located in the ovaries. Scientists conducted a large number of experiments on animals before they saw a connection between this substance and the ability to produce offspring.
The name of the hormone comes from the Latin word, which when translated sounds like “to bear.” Progesterone is produced by the corpus luteum, which is located in the ovary. The process of its production begins after the egg leaves the follicle. Until the onset of menstruation, progesterone levels rise. With their onset, its amount in the body decreases significantly.
What does elevated hormonal levels mean?
Such indicators are not often found, but sometimes this indicates multiple pregnancy. If not one, but several embryos develop in the female body, then the amount of the hormone should be large.
If there is no multiple pregnancy, then elevated progesterone levels indicate various kidney pathologies, impaired formation of the placenta, and poor functioning of the adrenal glands. So there is no need to worry about accumulating hormonal reserves; high levels require clear adjustment.
If a woman has too much of this substance in her body, then she begins to experience the following symptoms:
- headache;
- a person gets tired quickly;
- the uterus is greatly enlarged in size, profuse bleeding is observed;
- a person constantly feels sleepy, even if a lot of time is devoted to sleep;
- feels sick for no apparent reason;
- food is poorly digested, heartburn is tormented, the stomach is bloated;
- Problems with stool begin.
How to test progesterone?
Tests are prescribed in the following cases:
- To determine the causes of infertility.
- In the absence of the secretory phase of the menstrual cycle.
- When the luteal phase of menstruation is too short.
- Bleeding from the uterus when there is no apparent reason for this.
- Presence of hormonal imbalance.
- If there is a possibility of premature termination of pregnancy.
- The presence of symptoms that appear during menopause.
- For detection of ovarian and adrenal tumors.
- If adverse reactions occur when taking progesterone as a medicine.
- If you need to monitor the general hormonal levels in order to stimulate ovulation.
- To monitor the placenta.
Tests for hormone levels do not require special preparation
You usually do not need to undergo special training to take the tests. It is recommended not to eat food eight hours before the procedure.
If the menstrual cycle lasts a little longer than usual, then blood should be donated around day 28.
To obtain the correct results, the total duration of menstruation plays an important role. Therefore, before drawing blood, the nurse always asks when you last had a discharge and what your period is.
Usually the study is carried out in the morning. The best option is the day of the cycle when the level of the hormone in a woman’s blood is the highest.
If you have an irregular cycle, then the procedure must be completed several times to calculate the exact value. First you need to determine the presence of ovulation. Usually, special tests are purchased for this or basal temperature is measured. After this, the date for the analysis is determined. This usually happens a week after ovulation.
Tests are taken on any day convenient for you if you are pregnant or have started menopause. Before conducting any research, you should consult your doctor. You must tell him if you are taking any medications. This can significantly affect test results.
Test results may be different: the hormone may be in short supply or in excess. Let's take a closer look at each of the cases.
Treatment for hormone deficiency
Increased uterine tone and spotting are not a reason to use hormonal medications. Sometimes it is enough for a woman to rest, change her diet, and all problems will be resolved. If it is necessary to use hormones, therapy should be carried out only under the supervision of a physician, based on the results of hormonal studies.
Prescribed medications are discontinued gradually; abrupt withdrawal can lead to miscarriage.
The issue of using hormonal drugs is sometimes decided by a doctor without taking into account the level of progesterone. If it is necessary to prescribe drugs, the obstetric history, complaints of the pregnant woman and an assessment of her condition after the ultrasound are taken into account.
Hormone therapy
If progesterone levels are low, the doctor prescribes hormonal therapy:
- Utrozhestan. The drug is based on the active ingredient progesterone, which is identical to the natural hormone. Reduces excitability and contractile activity of the uterus. Prescribed in case of threatened miscarriage or premature labor. 400 mg is prescribed every 8 hours. The duration of use is determined by the doctor; withdrawal from the drug is carried out gradually. Pregnant women should monitor their liver function.
- Duphaston. A gestagenic drug containing the active substance dydrogesterone. Prescribed for progesterone deficiency. The drug is quickly absorbed by the gastrointestinal tract and metabolized in the liver. Prescribed in cases of threatened miscarriage due to a decrease in progesterone levels. In this case, it is taken 2 times a day until the 20th week of pregnancy, and then the dose is gradually reduced.
- Crinon. The drug is used in the first trimester with insufficient functioning of the corpus luteum. It is not recommended to use the drug in subsequent periods. Doses are agreed with the doctor.
Hormone deficiency can be compensated for by increasing foods rich in zinc, magnesium, and protein foods. Abstaining from stressful situations, normalizing your daily routine with the right combination of sleep, rest and work - all this will help restore hormonal levels.
The role of the hormone during pregnancy
With the help of progesterone, the lining of the uterus (endometrium) is renewed monthly and prepares to receive a fertilized egg. Progesterone affects the contractions of the uterus, preventing its muscles from rejecting the egg. It also protects the body from miscarriage and is involved in stretching the uterus to accommodate the growing child.
During pregnancy, it affects the increase in subcutaneous fat on the woman’s abdomen, thus protecting the baby from mechanical bruises, and prepares the pelvic bones for subsequent childbirth.
Progesterone (the norm during pregnancy increases week by week in the second half of the menstrual cycle) is a hormone whose level in the female body is not constant. Its increase affects the uterine mucosa, which, under the influence of progesterone, secretes special proteins.
If the lining of the uterus is not thick enough, implantation does not occur, then estrogen and progesterone levels drop, the uterine lining is destroyed, and menstruation occurs.
In the event of fertilization, the placenta begins to develop, which at 8–10 weeks of pregnancy takes on the function of the corpus luteum. At the same time, estrogen levels decrease. The placenta provides nutrition and oxygen to the unborn child and begins to produce progesterone. From this moment, the production of the hormone begins at a faster rate, so it remains elevated throughout the entire 9 months.
The combination of high levels of estrogen and progesterone suppresses ovulation during pregnancy. Progesterone promotes breast growth during pregnancy. The hormone also reduces the mother's immune response to accept the embryo.
Progesterone belongs to the group of neurosteroids; it also affects other parts of the body:
- brain structures;
- nervous system;
- water-electrolyte metabolism;
- skin condition;
- protects against bone loss.
Diet
To normalize hormone levels and prevent malfunction of the body, you need to eat right. If you eat legumes daily, you can increase the level of female hormones.
Natural sources of estrogen are fruits and vegetables. It is better to include in the menu those foods that contain vitamins E and C. The diet includes tomatoes and pumpkin. Phytoestrogens are present in spinach and strawberries. Grapes have a positive effect on the hormonal system.
Subscribe to our Yandex Zen channel!
Dairy products, regardless of their type, will help improve the condition of a woman’s body. You should take flaxseed oil in your food. It contains phytoestrogens.
Natural soy products give a good effect. They activate the work of the ovaries and reduce cholesterol levels in the blood. But it is now difficult to find non-genetically modified products on the market.
To increase estrogen levels, you can use the following products:
- Chicken, rabbit, turkey.
- Hard varieties of cheese.
- Nuts.
- Green tea.
- Chicken egg yolk.
- Vegetable oil: olive, sesame.
- Seafood.
Proper nutrition is one of the components of pathology therapy.
Normal indicators
After ovulation, progesterone is secreted by the corpus luteum. After fertilization, a special layer of cells is formed in the embryo - the trophoblast. It secretes human chorionic gonadotropin, which further stimulates the corpus luteum, and it increases the secretion of the hormone. By 8-9 weeks of pregnancy, the developing placenta is included in the process of hormonal secretion. The main amount of the substance is produced in it.
The level of the hormone varies by week of gestation. It gradually increases, reaching a maximum at the time of birth.
Progesterone levels may vary depending on individual characteristics. The given table is not the only variant of the norm. Different laboratories may use their own methods for determining the hormone, which can be calculated in other indicators, for example, ng/ml is used.
The analysis should be deciphered by the obstetrician-gynecologist who is leading the pregnancy. He will be able to correctly correlate the research data, the patient’s complaints and clinical symptoms.
The role of progesterone in a woman’s body
The hormone progesterone is often called the pregnancy hormone. This is due to a significant increase in the concentration of the substance during pregnancy. The synthesis of the hormone in the female body is carried out not only by the ovaries and adrenal glands, but also by the placenta. Among the main functions of progesterone it is necessary to highlight:
- Preparing the uterus for implantation in early gestation.
- Stopping cyclic, menstrual flow during pregnancy.
- Decreased uterine muscle tone.
- Stimulation of growth of the reproductive organ.
- Participation in the formation of tissues.
- Stimulation of mammary gland growth.
In addition to the main function of ensuring normal implantation, progesterone (the norm in women is indicated below) performs a number of others:
- prevents the formation of fibrous cysts;
- helps transform adipose tissue;
- Helps normalize blood viscosity and sugar levels.
Symptoms of pathology
This is not to say that identifying the problem on your own is easy. You need to listen carefully to your body. Symptoms of estrogen-progesterone deficiency are:
- Permanent underdevelopment of the endometrioid layer. As a result, conception cannot occur.
- Frequent spontaneous abortions.
- Constant weakness, loss of strength.
- Decreased body temperature.
- Flatulence.
- Headache.
- Depressive state.
- Sleep problems.
- Increased irritability.
- Violation of skin tone.
- Dryness in the vagina, pain during intercourse.
- Osteoporosis.
- Painful sensations in the joints.
- Hair loss.
- Frequent bloating.
- Menstrual irregularities, painful or scanty periods. With a lack of progesterone, women experience heavy menstrual bleeding.
- Pathologies of the functioning of the mammary glands.
- A few days before the onset of menstruation or in the middle of the cycle, spotting appears.
A risk factor is excessive physical activity and inflammation in the brain tissue. Frequent stress, emotional outbursts, and infectious pathologies of any origin can also provoke the problem.
Preventive measures
The level of progesterone in the blood of a pregnant woman changes every day, the test is carried out taking into account weekly readings. The doctor will prescribe treatment, but the woman herself in an interesting position will be able to at least partially influence the situation:
- You should eat only fresh foods. It is necessary to give up fast food, forget about peppered, salty, fried foods, and excessive amounts of sweets. Their place should be taken by vegetables, fruits, herbs, meat, fish, dairy products, as well as those rich in vitamins B, A, C, E, D, etc.
- It is important to make time for sleep - at least 8-9 hours a day. If necessary, you can take a nap during the day.
- You should walk more in the fresh air.
- It is necessary to monitor the water-salt balance. Drink enough fluids and monitor the condition of the body. If swelling occurs, you should consult a doctor. This may be evidence of problems with the kidneys, an organ that also affects the production of progesterone.
- You should not visit places with large crowds of people - this is fraught with infection, especially in cold weather, and stress.
- Don't be nervous about trifles. Anxiety affects hormonal balance, so don't be nervous.
Do not think that progesterone alone is responsible for a woman’s condition during pregnancy and childbirth. There are other “responsible” ones, including hCG, free estriol, prolactin, inhibin A, insulin, TSH, T3 and T4, testosterone. The indicators of these hormones should also be found out in the presence of problems and pathologies.
Causes, symptoms and consequences of excess and deficiency of progesterone from normal during pregnancy
An excess of progesterone in the blood above normal can be caused by the following reasons:
- hydatidiform mole (incorrect fertilization result with concomitant chariocarcinoma);
- disruption of the development of the placenta (accompanied by symptoms such as a decrease in the size of the abdomen, low activity of fetal movements);
- chronic and/or congenital hyperplasia of the adrenal cortex (pathological functioning of the adrenal glands, excess tissue mass, which leads to hormonal imbalance in the body);
- renal failure (kidney functioning below normal);
- several fetuses in the womb (multiple pregnancy requires more resources from the body for gestation, which causes an excess of pregnancy hormone);
- hormonal therapy (injections of hormonal drugs during pregnancy can either increase or lead to a lack of progesterone in the blood).
An excess of the hormone in the mother’s body, on the one hand, indicates good development of the placenta. But, on the other hand, excess progesterone indicates the development of pathologies that can negatively affect the course of pregnancy.
Accordingly, it is very important to consult a doctor about the test results to prescribe therapy. It is also important to monitor the symptoms of possible diseases of the reproductive system.
What ways are there to lower progesterone in the blood?
Drug reduction is designed to neutralize the excess of the hormone during pregnancy by taking hormonal drugs in the form of tablets or injections. Medications include clomiphene, mifepristone, valproic acid, tamoxifen and synthetic progesterone analogues. The disadvantage of such drugs is the long list of side effects (the list of symptoms for side effects is also long)
Let us remind you that these drugs should be taken with great caution and only with the direction of a doctor. If you take pills or give injections of the above-mentioned medications during pregnancy, you will need to undergo additional tests during therapy.
This will help to control the treatment, monitor the development of symptoms of deviation and respond in time to the nuances of the body’s behavior. In severe cases of hormone excess, the patient should be immediately hospitalized, followed by injections and pills under the supervision of a doctor to reduce the risk of miscarriage. With a special diet, you can neutralize excess progesterone during pregnancy. In this case, it is necessary to significantly reduce the intake of certain foods in your diet: cheese, milk, cottage cheese, pumpkin seeds, nuts, legumes, beef. During therapy, it is recommended to regularly donate blood for analysis.
A lack of progesterone in the blood during pregnancy can occur due to the following factors:
- threat of miscarriage (high risk of premature termination of pregnancy);
- ectopic pregnancy (development of the fetus outside the uterine cavity, accompanied by symptoms such as severe pain in the abdominal area, internal bleeding);
- non-developing pregnancy (stopping the development of the fetus after any disturbances);
- delay in fetal development during pregnancy;
- the occurrence of pathological conditions that complicate the course of pregnancy (gestosis, fetoplacental insufficiency);
- post-term pregnancy (carrying the fetus for too long);
- diseases of the genital organs in women.
Treatment of progesterone deficiency is also based on tablets and injections of hormonal drugs. After hormone deficiency, the following may occur: unfavorable outcome of pregnancy, premature termination, deviation in the development of the child.
You can take care of your health and the health of your unborn child in advance: consult a doctor and undergo the appropriate tests. It is sometimes too late to receive treatment after pregnancy.
When planning a pregnancy, pay attention to the indicators of important biologically active substances. By normalizing blood biochemistry even before conception, the risk of pathologies can be significantly reduced
Is progesterone in injections or tablets dangerous?
To compensate for the lack of hormones during pregnancy, medications are prescribed. However, the doctor takes into account possible risks, which are especially typical for the first four months of gestation. From taking pills or injections, deviations from the norm in the development of the fetus may be observed. But a reduced amount of the hormone also poses a threat, so the doctor will have to assess the risks and the woman’s health status before prescribing the medicine.
Some women voluntarily take progesterone before conceiving to prepare their bodies. However, this is a dangerous activity, since increased levels of the substance provoke various pathologies. The risk of developing an ectopic pregnancy increases significantly.
Any medications should be used only if there are appropriate indications and recommendations from a doctor. Self-medication is dangerous for the health of the mother and the unborn baby!
What hormones need to be controlled?
The leading doctor usually tells you which hormones to take early in pregnancy. But sometimes a gynecologist can be overly optimistic and not prescribe the necessary research. Then it is better for a woman to play it safe and, in addition to progesterone in the early stages of pregnancy, as well as the already mentioned hCG and estradiol, insist on determining the amount:
| Hormone | What will it point to? |
| Free estriol | He will talk about the process of formation of the placenta, its blood supply and the condition of the umbilical cord, which serves to deliver nutrition to the embryo. A low indicator means there is a danger of problems in its development. |
| Prolactin | This substance not only stimulates the production of breast milk in the future, but its level can reveal deficiencies in the feto-placental system. |
| Inhibin A | This is a product of the placenta and ovaries. The hormone increases during the first 10 weeks, then decreases. By its elevated value, one can recognize Down syndrome in the fetus or identify oxygen deficiency. |
| Placental lactogen | Normally, it rises from 5 weeks to 34. Its low value indicates insufficient placental function and the risk of rejection of the fertilized egg. |
| Insulin | Impaired carbohydrate metabolism is the main cause of gestational diabetes mellitus. In most cases, it is detected during multiple pregnancies and goes away after childbirth, but it is necessary to fight it from the first manifestations. |
| T3 and T4 | These hormones are the result of the thyroid gland. The absence of the likelihood of miscarriage, stillbirth and mental disabilities in the child depends on its quality. In the first weeks, his heart, blood vessels and brain are formed. The intelligence of the unborn baby largely depends on the amount of thyroxine and triiodothyronine in the mother's blood. |
| TSH | This substance, produced by the thyroid gland, preserves the function of the hypothalamus and the supply of nutrition to the fetus. Excess and deficiency are dangerous primarily for him, since at this stage the embryo does not have a formed endocrine system and does not receive iodine on its own. And its deficiency is a potential threat to mental development. |
| Testosterone | The male hormone is also present in some quantities in the female body. But exceeding its normal concentration during pregnancy is dangerous due to the possibility of miscarriage. |
It is necessary for women who have had miscarriages, problems with conception, or premature birth to check their levels of these hormones. It doesn’t hurt to find out the composition of hormones beforehand, but it’s also important to control this at the initial stage.
Elevated progesterone levels
An increase in hormone levels during pregnancy is also a pathological process that requires adjustment and research. However, pregnant women do not always notice this condition! Among the main reasons for deviations from the norm of progesterone during pregnancy are the following processes:
- Dysfunction of the kidneys and adrenal glands;
- Improper formation of the placenta;
- Multiple births. To bear several fruits - two, three or more - will require more hormone than if one child is expected.
These conditions also require adjustment, and in the case of multiple births, even closer monitoring. Often, such ladies who are lucky enough to be carrying twins or triplets will have to undergo more tests much more often than other pregnant women.
Symptoms
The following symptoms indicate an excess of the hormone progesterone during pregnancy:
- Excessive fatigue and drowsiness, constant loss of strength;
- Headache;
- Constipation and heartburn, other problems with the digestive system;
- Bleeding and enlarged uterus. This may indicate abnormal development of the placenta, which is rare.
It is important to understand that the symptoms described above can be personal, that is, they can appear even in the absence of hormonal abnormalities. That is why it is important to contact your doctor with your suspicions and complaints about your health. After the examination, the doctor suggests taking several tests, including a hormonal panel. The interpretation of the results obtained should be carried out by an experienced specialist. You should not study the indicators on your own and draw premature conclusions.