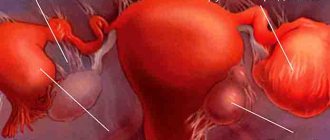
This disease is a benign limited growth, the foci of which grow on the mucous membranes of the uterus. A girl or woman can become pregnant with a polyp, depending on the shape and type of pathology.
The neoplasm reaches from 6 mm to 3 cm in size; it is not related to oncology.
Desired happiness
Types of polyps:
- growth of the cervical canal - between the vagina and the uterus, is rarely removed during gestation, as it does not interfere with the growth of the fetus;
- decidual type - formed from the reaction of the endometrium to conception;
- placental polyp - if a particle of placenta remains after childbirth, then a growth may appear;
- glandular - formed at the cellular level, has a loose body, is easily treated with hormones;
- polyp made of fibrous tissue - the structure is dense, requires removal due to the threat of developing into a malignant form;
- glandular-fibrous - consists of glandular cells, connective tissue, removal is desirable;
- angiomatous - has a developed vascular network with increased bleeding;
- adenomatous is the most dangerous precancerous condition; urgent surgical intervention is necessary.
It is impossible to get pregnant in the usual way with endometrial polyps when the cause of the neoplasm is hormonal levels.
If the etiology of the growth is non-hormonal in nature, then getting pregnant is realistic. Pathology does not affect the processes of the gestational period.
According to statistics, cervical polyp affects mature women. The disease can also occur in immature girls in the period before the onset of the menstrual cycle.
There is a possibility that menopause will resolve the polyp. The insidious disease is often asymptomatic.
Failure to treat the tumor can lead to excessive focal growth.
The polyp grows to a large size, so the egg will not pass through the genital tract to attach to the uterus.
If formations block access to the reproductive organ, then pregnancy is impossible.
Mechanical damage to the endometrium
As a result of curettage using the abortion method, tissue particles and blood clots sometimes remain, which leads to disruption of the normal growth of the mucous membrane.
Without repeated surgery, if left as is, growths will begin to form on the bottom of the uterus or in the folds. An intrauterine device that a woman uses for a long time also leads to the risk of mechanical damage to the endometrium.
After removing the IUD, to exclude possible violations, you need to check the uterine cavity for changes or growths. Usually, with an endometrial polyp, doctors recommend removal, believing that the pathology cannot be treated with medication.
Chances of getting pregnant with a polyp in the uterus
With this problem you can conceive and give birth safely.
There is a chance of getting pregnant with a uterine polyp. You need to come to your doctor or gynecologist-endocrinologist for an initial appointment. The specialist examines:
- an ultrasound scan is required;
- undergo an examination by a gynecologist;
- taking tests.
If polyps are found, the doctor will prescribe treatment or surgery to remove them. There are cases when growths in the uterine cavity do not interfere with pregnancy or embryo development.
Everything will work out
Gynecologists recommend removing the tumor before conception. Especially if the growth is large or small, but widespread. Find out the location of the polyp. It may be positioned poorly or inconveniently.
Women who are tested rarely need to take action to solve the problem. First, make an appointment and examination with a gynecologist.
Pregnancy after polyp removal
Removal of the tumor and subsequent hormonal therapy increases the likelihood of pregnancy. The attending physician gives permission to plan conception after completion of therapy, tissue healing and if the result is negative for oncology.
The rate of pregnancy depends on the individual characteristics of the body.
After childbirth, a placental type of polyp, consisting of placental tissue, is sometimes diagnosed. Removal is carried out by scraping.
https://youtu.be/XUQJoTEuwJM
The likelihood of conception and childbirth with polyps of the cervical canal
This is the connection between the cervix and vagina. Epithelial cells secrete secretions that prevent the entry of pathogenic agents.
A polyp that grows in volume shows a tendency to bleeding and inflammation. Therefore, the microflora of the cervical canal becomes contaminated, which creates a favorable environment for the development of microbes.
This fact is the first contraindication for fertilization, since there is a high risk of infection of the embryo. The appearance of a polyp in the cervical canal is accompanied by:
- leucorrhoea;
- cramping pain in the lower abdomen;
- spotting, bloody discharge with an odor.
They are especially noticeable during an examination by a gynecologist or during sex. If the polyp is less than 1 cm in volume and there are no signs of pathology, then do not touch such a neoplasm during the period of conception and gestation.
The large size of the growth and the inflammatory process are an obstacle to fertilization, but also the threat of miscarriage or damage to the cervix during childbirth. It is better to get pregnant after removal of the tumor.
Probability of pregnancy with a polyp
Growing into the cervical canal from the uterus, neoplasms create an obstacle to sperm. The more endometrial growths, the less chance of pregnancy. Even if the pathology did not prevent the sperm from fertilizing the egg, there is a high probability of its rejection by the uterine mucosa.
If polyps in the cervix occur due to hormonal imbalance, ovulation (the part of the cycle during which conception is possible) may not occur for a long time. In this case, the possibility of pregnancy is excluded.
In medical practice, there are cases of pregnancy and successful pregnancy with this disease, which means that it is possible to become pregnant with an endometrial polyp.
If the lesions were discovered after pregnancy, do not panic: a polyp in the uterus and pregnancy are quite compatible. Formations in the uterine cavity that do not interfere with conception, in most cases, do not interfere with the birth of a healthy child.
A polyp on the cervix during pregnancy can cause inflammation, bleeding and other complications.
Treatment of polyps
Treatment methods for endometriosis are chosen according to three schemes:
- constant monitoring of tumor growth;
- drug treatment;
- surgical excision.
The choice of tactics depends on the type and size of the polyp, the patient’s age, symptoms, and wishes regarding pregnancy. The main method of treatment is surgery. Doctors admit that hormonal therapy does not provide lasting results.
To remove the growth, it is necessary to remove the vascular pedicle that feeds the tumor. There is a risk that the tumor will grow again. And in the worst case, the growths will turn into hyperplasia.
Surgical methods:
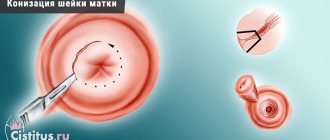
- hysteroscopy or hysteroresectoscopy;
- electrocoagulation;
- cryodestruction;
- radio wave method;
- laser polypectomy (removal of electric loops);
- curettage (scraping);
- in case of malignant degeneration of polyps, trachelectomy (cervical amputation) and hysterectomy are performed.
A more gentle operation is hysteroscopy.
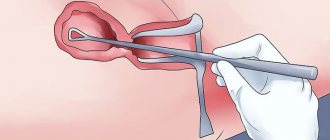
Scraping process
Curettage of the uterine cavity
The procedure is performed blindly.
It does not cut off the stalk of the polyp without damaging adjacent surfaces. Diagnostic curettage is a useless procedure in the treatment of growths in the uterus. Among the methods of treating polyps, hysteroscopy is first performed, then cauterization of the stem. Only after these procedures is curettage performed.
They are used not to remove growth, but to take remnants of the endometrium to study the quality of the material. Curettage is sometimes done in extreme cases, for example, with a polyp or hyperplasia, severe bleeding occurs.
In such circumstances, it is urgent to stop it, then curettage is the only, but forced, action.
Electrocoagulation
Removal or cauterization of the growth is carried out using electrodes through which high-frequency current is transmitted. They come in different sizes and shapes - in the form of a needle, knife, straight or curved loop, ball.
A crust forms on the affected area, protecting against infection and bleeding. The method is available to all women.
In the treatment of polyps, electrocoagulation is used as cauterization after hysteroscopy.
Cryodestruction
This is an alternative to operation using liquid nitrogen.
Treatment is carried out by freezing the affected tissues, in place of which new ones are regenerated. The method is contraindicated for infections, inflammation, endometriosis, and scars on the cervix.
When treating polyps, it is suitable for cauterization after excision of the stem.
Hormonal drugs
Conservative therapy is suitable for the following purposes:
- prevention of recurrence of formation;
- revitalization of hormonal levels;
- restoration of regularity and elimination of menstrual irregularities.
Women under 35 years of age are prescribed COCs (combined oral contraceptives) with a balanced content of hormones, for example, Janine or Regulon.
For older patients, gestagens are prescribed to regulate phase 2 of the cycle, for example, duphaston, norkolut or utrozhestan.
Hormonal therapy is carried out for 6 months without interruption.
What does a polyp look like?
Polyp during pregnancy: how it affects, what is the danger, is it possible to get pregnant
Having learned that she will soon become a mother, a woman understandably begins to worry whether certain deviations in her well-being and physical health will affect the normal development of the fetus. And these fears are not unfounded. For example, with an endometrial polyp, this may not have any effect on the interesting situation, but may cause a spontaneous miscarriage.
Pregnancy and the occurrence of polyps
At different phases of the menstrual cycle, a woman’s body produces either progesterone or estrogen. As a rule, the body reacts to the fertilization of an egg with rapid hormonal changes.
However, it happens that the balance of hormones is disturbed. As a result, the cells begin to grow excessively - hyperplasia is formed.
As a consequence of this, a growth forms on the walls of the cervical canal or on the cervix.
When the endometrium grows, conception is difficult. Often it is the uterine growth that causes infertility. The neoplasm leads to blockage of the fallopian tubes, reducing their patency.
The fertilized egg cannot enter the uterine cavity. Even if a fertilized egg manages to penetrate the uterus, it cannot attach to its wall as a result of the altered structure of the endometrium.
The likelihood of miscarriage increases.
In some cases, endometrial growth interferes with ovulation.
When planning the birth of a baby, you need to get rid of the growth and only then make attempts to conceive.
Types of uterine polyps
In gynecology, it is customary to distinguish polyps:
- Neoplasm in the cervical canal. This type of outgrowth does not interfere with fruiting, so such pathologies are rarely removed. With hormonal changes in the body due to a new condition, they often disappear on their own without medical intervention.
- Polyp in the gallbladder. Gallbladder polyposis does not threaten the mother and child, provided the function of this organ is preserved.
- Decidual polyp is a consequence of pregnancy. Against the background of hormonal changes, the structure of the endometrium changes, a decidual growth appears, which is easily confused with a number of other varieties. After childbirth, the structure of the uterine endometrium normalizes - it disappears.
Polyp of the cervical canal during pregnancy
Pathology of the cervical canal is the main cause of sudden arrest of fetal development. Symptoms indicate a problem:
- brown or bloody discharge with an unpleasant odor;
- severe pain resembling contractions;
- leucorrhoea;
- discharge of white mucus from the vagina with an unpleasant odor;
- spotting after intercourse, physical activity or gynecological examination;
- there were disruptions in the menstrual cycle;
- unsuccessful attempts to conceive a baby through IVF;
- bleeding in the middle of the cycle;
- aching pain in the lower abdomen;
- nagging pain in the lower back.
Causes of pathology
The exact etiology of this pathology is under study. Provoking factors are:
- incomplete removal of the placenta from the uterine cavity during childbirth;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- hormonal abnormalities and endocrine diseases;
- metabolic disease;
- excess body weight;
- genetic predisposition;
- weak immune system, presence of sexually transmitted diseases;
- diabetes;
- excessive growth of the vascular network, arterial hypertension;
- carrying out the procedure of curettage of the uterine cavity for specific gynecological indications;
- medical abortion;
- inflammatory process and bacterial diseases of the female reproductive system;
- mechanical damage to the female internal genital organs as a result of medical manipulations;
- using an intrauterine device as a method of contraception.
What to do if you have a cervical polyp during pregnancy
If a polyp is found in the cervical canal during pregnancy, you need to:
- Determine the type of tumor through medical diagnostics. If this is a decidual type of pathology without signs of isthmic-cervical disorders, and the size of the growth is no more than 1 cm, there is no need to treat or remove the tumor: after childbirth it will go away on its own.
- If the neoplasm is large or multiple, there are signs of an inflammatory process, surgery is required to preserve the pregnancy and prevent the likelihood of injury to the cervix during childbirth.
Will it be possible to get pregnant with this pathology?
Gynecologists cannot give a definite answer to the question of whether it is possible to get pregnant with a polyp in the uterus. Much depends on the individual characteristics of the woman, her age, the presence or absence of concomitant diseases of the genitourinary system.
Medical statistics contain facts of conception and successful childbirth with growths. However, stopping the development of the fetus due to a polyp is also a common occurrence. In cases where the pathology grows, the woman will not be able to give birth on her own.
Planning a pregnancy
When there is growth in the endometrium, a woman needs to carefully plan her pregnancy. She should:
- go for an ultrasound;
- undergo a gynecological examination;
- pass the necessary tests;
- treat the growth and, if necessary, remove it.
Nulliparous women need to know: if women become pregnant with a small tumor in the uterine cavity, it is necessary to register with the antenatal clinic as early as possible in order to maintain the pregnancy and give birth to a healthy baby.
Dangers of pathology during pregnancy
The presence of a foreign tumor in the uterine cavity can negatively affect the early stages of pregnancy:
- there is a high risk of placental abruption;
- high risk of miscarriage;
- the placental layer experiences a lack of blood supply - the child receives less nutrients than he needs;
- the fetus receives insufficient oxygen (this is dangerous due to the onset of hypoxia);
- the consequences of a uterine growth can be detected both in the first trimester and after childbirth in the form of developmental delay.
Subsequent complications after detection of pathology
A woman should know that a polyp not only affects pregnancy, but can also lead to complications in the postpartum period. Due to the growth, the following happens:
- ovarian dysfunction;
- endometriotic inflammation of an acute or chronic nature;
- sepsis;
- infertility;
- uterine oncology;
- ectopic pregnancies;
- uterine rupture;
- uterine bleeding.
Bleeding polyp during pregnancy
Endometrial formations in the female genital organs are easily injured. In case of mechanical damage, it bleeds. An infection can penetrate through the thin membrane of the neoplasm, threatening the life and health of the fetus.
Treatment of polyps during pregnancy
Treatment of small tumors is not required: the mother and child do not suffer from them. A polyp during pregnancy is dangerous in the following cases:
- it has been established that the growth is of an oncological nature (it must be removed surgically);
- the neoplasm provokes infectious processes (the woman is prescribed antibacterial drugs);
- the growth causes dilatation of the cervix and threatens premature onset of labor (the woman is inserted a pessary or the cervix is sutured).
Treatment of polyps in the early stages
If neoplasms in the uterine cavity or in the cervical canal bother a woman, the following options for a medical solution to the problem are possible:
- Removal of the tumor surgically for a period of 12-14 weeks. Indications are the presence of an inflammatory process, rapid growth of the polyp, and its bleeding.
- Antibacterial treatment. Indicated in the early stages of fruiting with an active increase in cervical growth.
- Prescribing drugs with progesterone to prevent the tumor from increasing in size.
As preventive measures in the early stages of bearing a child, women are advised to refrain from intimacy with a partner, excessive physical activity, and to monitor the activity of the growth and the condition of the fetus through systematic ultrasound monitoring.
Polyp removal during pregnancy
Performing surgical procedures on pregnant women is undesirable - it can harm the fetus. But in some cases, the benefits of surgery outweigh the risks. Indications for surgical intervention for cervical canal disease are:
- large and multiple growths;
- a persistent tendency towards an increase in the size of neoplasms (the polyp increases in size by more than 2 mm per month);
- severe bleeding, creating a threat of miscarriage;
- threat of infection in the membranes.
The operation is done through hysteroscopy.
In the endometrium of the uterus, surgical removal of growths is incompatible with pregnancy.
Planning pregnancy after polyp removal
After surgical removal of the growth, the woman is prescribed a course of hormonal treatment. She needs to follow all clinical recommendations, undergo tests, and undergo an ultrasound scan to identify the risk of relapse of the pathology.
You can become pregnant 2-3 months after finishing treatment. You should not delay conception, as there is a risk of new anomalies.
Source: //onko.guru/termin/polip-pri-beremennosti.html
Consequences if polyps are not treated?
At an advanced stage, when the necessary therapy is not carried out, pathologies can pose a serious health hazard:
- uterine bleeding - the growth gradually acquires its own vascular network, only its membrane is quite thin, so any injury can provoke bleeding, which sometimes cannot be stopped on its own;
- difficulties with conception - large polyps can block the female genital tract, so when the egg leaves the follicle it will not reach its target;
- complications during pregnancy - threat of miscarriage, placental abruption, possible ectopic conception, rapid growth of tumors;
- development of chronic infections - when pathogenic agents penetrate, they will spread to the area affected by the polyp;
- malignancy is the biggest threat when a benign growth degenerates into a malignant formation.
Who is prescribed surgical removal?
Emergency intervention is required in cases where hormone therapy is ineffective.
Who is at risk:
- women over 40 years of age during premenopause, when, against the background of severe hormonal changes, any neoplasm can sharply develop into a cancerous tumor;
- a polyp with a volume of more than 1 cm can provoke a lot of complications;
- reproductive disorders;
- blockage of the genital tract;
- bleeding;
- ectopic pregnancy;
- severe pain during menstruation and during sex;
- the risk of complications for fetal development, the birth of a child with a huge number of diseases is possible.
It will take a few months
Planning pregnancy after polypectomy
It has been statistically confirmed that in the vast majority of cases, pregnancy after removal of a polyp, if it occurs, goes quite well. In some cases, premature termination occurs.
Pregnancy occurs almost immediately after stopping contraceptives. The question arises, when is the best time to plan conception? It is not recommended to postpone pregnancy planning for a long time. Polyps often recur and there are cases where pregnancy proceeded along with a new polyp.
Young patients who have not given birth are wondering: is it possible to get pregnant with a polyp? In some cases, pregnancy in the presence of a polyp may well occur. Doctors have determined that the polyp will not significantly affect the course of pregnancy and childbirth. It does not pose any threat to the fetus. It is removed after childbirth in the usual manner.
Thus, neither the presence nor removal of a polyp is an absolute contraindication for planning pregnancy.
Expert advice
To avoid serious problems, you should listen to the recommendations of doctors:
- Regularly undergo gynecological examinations, especially important for girls with a hereditary predisposition.
- Try to avoid stress, take care of your nerves.
- Strictly monitor the hormonal balance - any disruptions, sudden changes in body weight, abortions, etc. must be excluded.
- If you have menstrual irregularities, contact your gynecologist immediately.
- Avoid unwanted pregnancy; approach the birth of your baby consciously.
- Get a full medical examination before conceiving.
- If polyps are detected, you must abstain from sexual intimacy and heavy exercise for the duration of treatment.
Be optimistic