What is tank smear culture
Bacteriological culture is an analysis to determine the provoking factor and how sensitive it is to a particular drug.
This research method is widely used in medicine.
Almost any liquid biological material can become a substance for study. Collection from the genitals is preferable.
Based on the results, correct and successful treatment can be prescribed.
If the cervical canal is dilated, what to do?
In cases where the patient has dilated the cervical canal, the doctor raises the question of the need for hospitalization.
This is the main symptom of isthmic-cervical insufficiency. During this period, the cervix dilates prematurely. As the fruit grows over time, it puts even more pressure on it, provoking its further opening.
If there is a multiple pregnancy, dilatation of the pharynx is observed in almost all cases.
To eliminate the pathology, medication and surgical techniques are used.
Medicines are prescribed to normalize hormonal levels or eliminate increased uterine tone.
Surgical treatment is used when cervical pathology is detected, its injuries or an existing polyp.
For polypous growths, a course of treatment is carried out and, if necessary, the formation is removed.
For the first time, a Pap test is recommended for girls three years after the start of sexual activity or at the age of 21, after which the examination should be carried out annually. However, if the test does not detect any changes in the cells of the cervix for three years in a row, then the doctor may recommend having this test done once every two to three years. If a woman’s Pap test results have been negative throughout her life, then after 65 years of age the test can be abandoned.
Women using hormonal contraceptives, suffering from infertility or uterine bleeding, obesity, genital warts or genital herpes, on the contrary, are recommended to have a cervical smear more often - up to twice a year.
An unscheduled cervical smear may be recommended for a woman who decides to undergo gynecological surgery or, for example, installation of an intrauterine device. It is also recommended to do a Pap test in preparation for conception, and then a smear is necessarily taken from a pregnant woman when registering with an antenatal clinic.
Ignoring the cervical smear recommended by doctors is strictly contraindicated, since cervical cancer detected in the early stages and timely treatment can prevent the development of a dangerous disease.
Objectives of the study
In the female reproductive system, the balance of the acidic environment plays an important role. It consists of protective microbes that prevent infections from entering.
Under the influence of negative factors, pathogenic bacteria multiply to huge numbers and exceed the indicators. A chain reaction of inflammation occurs.
A smear culture during pregnancy is prescribed to identify harmful bacteria. The doctor takes a smear from the genital mucosa, since then the most accurate results are obtained.
Bacteria are placed in a comfortable environment for them to develop and examined under a microscope.
Bacteriological culture plays a huge role in the detection of infectious diseases. Research methods may differ, but the goal is the same: to obtain indications and identify pathogens without foreign impurities.
Functioning of the cervical canal in pregnant women
During conception, the cervical canal changes color: before pregnancy, the hue of the space between the pharynx is bright pink, and after it is blue. With the appearance of blueness, the gynecologist determines the onset of pregnancy.
Mucus changes during pregnancy: it forms a dense plug. It protects the fetus by preventing pathogenic bacteria from entering the uterus. The time for the plug to peel off occurs individually: for some, 1.5 weeks before birth, for others, 2 hours.
Cervical fluid consists of elements:
- mucin;
- lysozyme;
- proteins;
- polysaccharides;
- electrolytes;
Moreover, 50% of its composition is water.
Estrogen and progesterone form cervical mucus. The first hormone causes the secretion to be produced abundantly during menstruation. Progesterone reduces this function to a minimum, making the mucus more dense.
During childbirth, the cervical canal begins to open up to 10 cm. This helps the woman easily endure the birth of the baby.
In some cases, the expectant mother is diagnosed with isthmic-cervical insufficiency. This means weak cervical support for the rapidly growing fetus. The development of pathology in pregnant women is recorded by the 18th week. The embryo grows and moves.
Sometimes, according to indications, surgery is prescribed to tighten the cervical canal. The seal is removed when it is time to give birth.
A woman should have a smear and culture done by a doctor. Both procedures are straightforward and completely painless. Timely testing eliminates the risk of developing infertility.
Interesting topic? Share your opinion in the comments.
Indications for analysis
What is the sowing tank used for? Biological material from pregnant women can be examined routinely at scheduled times at the discretion of the gynecologist. The fence is made from the cervical canal.
Also prescribed according to some indicators:
- when a woman plans to become a mother in the near future;
- with inflammation of the female genital organs and
- microflora disorders;
- if the results of the previous smear are questionable;
- in cases where the uterus is constantly susceptible to infection.
The various visible manifestations of infectious diseases are also taken into account. For example, unpleasant vaginal discharge, itching, burning, irritation.
Using this diagnostic method, you can determine why the menstrual cycle is delayed.
For pregnant women, the test is prescribed if a genitourinary infection is suspected, or for the purpose of its prevention.
The development of pathogenic infectious parasites in the uterus cannot be ignored. This can lead to miscarriage or infection of the fetus.
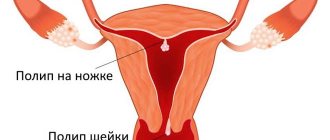
What is the cervical canal and what is its significance?
The cervical canal is the transition from the vagina to the body of the uterus; it has a conical shape with a hole in the center through which the vagina communicates with the uterus.
Normally, the length of the canal is 3–4 cm; it is part of the cervix. The external os of the canal exits into the vagina, and the internal os into the uterine cavity. One of its main functions is protecting the uterus from infections and pathogenic microorganisms; cells located inside the canal produce mucus, its consistency is determined by the stage of the cycle. Mucus at the beginning and end of the menstrual cycle is more viscous with increased acidity; most microorganisms do not survive in such conditions.
If pregnancy occurs, under the influence of the hormone progesterone, a plug is formed from the mucus in the cervical canal, which protects the fetus from infections from the outside.
A culture tank is the same as a smear, only it is taken not from the walls of the vagina, but from the opening of the cervical canal. This type of test is not preventive; it is prescribed by a doctor due to elevated white blood cells in a regular smear.
An increased number of leukocytes is a sign of an infectious disease occurring in a woman’s body and requiring immediate treatment.
Also, sowing is required when planning a pregnancy, if sexually transmitted diseases are suspected, in case of infertility, or when registering for pregnancy.
The inoculation is taken using a sterile brush and placed in a flask, into which no foreign microorganisms from the external environment should get. After this, the analysis is sent to the laboratory.
There is no need to be afraid of this procedure; it is not painful at all and is safe. This test is also safe for pregnant women.
IMPORTANT! To obtain a reliable test result, you must abstain from sexual intercourse, do not use vaginal contraceptives, douche, or use perfume gels for intimate hygiene for at least 24 hours. If you have taken antibiotics, the test is prescribed no earlier than 2 weeks after you stop taking the medications.
The canal is a through hole that connects the top of the vagina directly to the uterus. It is located inside the cervix.
- The length of this channel is about 4 cm.
- Width - about 8 mm, during childbirth - 10 cm.
- It has 2 narrowings: internal and external pharynx.
The external one is usually examined by a gynecologist using medical instruments. Nulliparous women have a pinpoint pharynx. And those who gave birth have a slit-like pharynx.
A smooth, pale pink canal is characteristic of young, healthy women. And during menopause, the mucous membrane is very pale, and almost no secretion is produced.
The main purpose of the canal is to protect against infectious diseases and facilitate the penetration of sperm into the uterus. Blood clots also pass through this channel during menstruation.
At the very beginning and after the end of the menstrual cycle, mucus from the cervical canal has an acidic environment. The mucus from the cervical canal is very viscous and blocks the passage like a plug.
Harmful microorganisms die in this acidic environment. And spermatozoa in such an environment become incapable of fertilization. The level of estrogen can be determined by stretching the mucus; the longer the thread, the more hormones in the body.
Already in the middle of the monthly cycle, estrogen levels increase significantly, and the mucus becomes thin and alkaline. And sperm gain access to the eggs of the uterus.
But after conception, the ovaries produce progesterone, and the mucus in the cervical canal becomes more viscous. A thick mucus plug forms. It protects the fetus from pathogenic bacteria. Before birth, this plug comes out of the canal.
Tank culture is a bacteriological analysis that is used to determine what kind of microorganisms inhabit the cervical canal.
What is it used for:
- If the study reveals pathogenic microflora, the doctor prescribes specific antibiotics to destroy the infection. After all, the results of the analysis provide a detailed picture of the organisms inhabiting the cervical canal and what medications need to be taken to combat the disease.
- In addition, this analysis helps determine the nature of the positive bacteria that are involved in metabolism. The study helps determine the presence and type of fungi living in the genitals.
- With its help, thrush is identified, and methods of treatment for this disease are selected.
- The analysis helps to identify microorganisms that cause inflammatory processes (citrobacteria, enterococci, staphylococci).
Tests are carried out on the basis of a scraping from the cervical canal; it is absolutely painless. And biomaterial with microorganisms taken in this way can also be examined for reaction to antibiotics. Analysis is required for complications during pregnancy and inflammatory diseases of the cervix.
Analysis steps:
- When taking scrapings, only a sterile brush is used. With its help, the secretion of the glands located there and desquamated cells containing microorganisms are taken from the cervical canal.
- The taken biomaterial is immediately placed in a glass tube with a nutrient medium.
- All kinds of bacteria and fungi placed in such favorable conditions begin to multiply. The main thing is not to let them die, because in this case it will be impossible to identify the causative agents of dangerous infections.
- For this purpose, a glass tube with biomaterial for research is placed in a thermostat in which a constant temperature of 37 degrees is maintained.
- When the test tube gets to the laboratory, its contents are applied to another nutrient medium, which is located in a Petri dish.
- The bowl with microorganisms is placed in a thermostat for a few more days so that the process of bacterial reproduction begins.
- A few days later, when there is sufficient material for research, the types of microorganisms are determined, the number of units within each type is counted, and tests for antibiotics are carried out.
Culture tests are prescribed to take a biological sample from the walls of the cervix for further examination in the laboratory. A sample is taken if the doctor suspects an infectious disease of the genital organs.
That is why the gynecologist first prescribes a bacterial examination of the cervical canal, and then prescribes treatment.
When conducting a bacterial study, you can identify:
- various fungi;
- enterococci;
- Trichomonas;
- epithelial cells;
- leukocytes;
- staphylococci;
- gonococci.
This type of analysis is one of the most informative methods for identifying dangerous bacteria.
The data obtained through research is deciphered, and then treatment is prescribed. But it is possible to carry out bacterial analysis for preventive purposes.
Analysis of biomaterial from the cervical canal should be taken:
- for infectious diseases of the female genital organs;
- annually as a preventive study;
- when there are coccal bacteria in a vaginal smear for microflora;
- leukocyte counts are increased in the smear;
- with frequent inflammation of the genital organs;
- for any uncharacteristic vaginal discharge;
- during and during expected pregnancy.
How the research is carried out
Tank seeding from the cervical canal during pregnancy is carried out quite often. With normal gestation, this occurs at 30 weeks.
If there are specific complaints or there have been previous miscarriages, infection of the fetus in the womb, and so on, a smear is given as prescribed by a doctor.
The collection of material is carried out by a midwife or nurse from the antenatal clinic.
In this case, preparation for tank sowing includes:
- exclusion of water hygiene procedures;
- you cannot douche and use antiseptics;
- do not insert suppositories or other medications;
- if during planning the procedure coincides with menstruation, then a smear cannot be taken; it is taken 2 days after the complete end of menstruation;
- tank analysis is not taken immediately after colposcopy;
- Any treatment that includes antibiotics or drugs interferes with reliable results.
The patient is positioned on a gynecological chair. The health care provider inserts a speculum into the vagina and then uses a sterile probe with a small loop to take a swab.
The procedure is absolutely painless and safe for the child.
Preparation for the procedure and interpretation of data
The patient needs to be well prepared for vaginal bacterial culture. To do this, you must follow certain rules. Neglecting them can lead to unreliable data, which means that the analysis will have to be repeated.
So how to prepare for a cervical canal test? Follow these guidelines:
- the day before the scheduled procedure, you must stop douching;
- do not use vaginal suppositories, including hormonal contraceptives;
- refuse sexual contacts one day before the study;
- within 48 hours after colposcopy, culture from the urethra in women is not given.
Note. If before the study you took antibiotics or other potent medications, then the culture test must be rescheduled to another day. Under the influence of antimicrobial drugs, the properties of biological material from the cervical canal change somewhat, which may lead to false research results.
What results are not normal?
Those test results according to which enterobacteria were detected in a smear in women are considered unfavorable. These are microorganisms that often infect the human intestines. If they get on the mucous membranes of the genital organs, quite unpleasant symptoms can occur: pain in the lower abdomen, increased body temperature, copious mucous, purulent, bloody discharge, etc.
However, the list of pathogenic bacteria does not end there, so the presence in a smear may indicate serious health problems:
- coli;
- yeast fungi in large quantities;
- different types of staphylococcus;
- bacteria citrobacter;
- Proteus bacteria;
- gonococci;
- trichomonas;
- gardnerell;
- leptothrix.
Be careful! The presence of diphtheroids in the smear should be of particular concern. It indicates the development of vaginal dysbiosis, which is accompanied by itching, burning of the genitals, pain in the lower abdomen, and deterioration of well-being. This disease is similar to intestinal dysbiosis, and although it is considered relatively safe, disruption of the normal vaginal microflora can have extremely serious consequences.
Some pathogenic microorganisms are not detected during culture of the cervical canal for flora. In this case, the polymerase chain reaction, or PCR, method is used.
Data decryption
To begin with, let's figure out how much it takes to smear the flora and culture the culture medium. In the first case, the results can be prepared either within a few hours or within a couple of days. This directly depends on the employment of medical personnel.
The same cannot be said for bacterial culture. Its results are issued 5 days from the date of submission of the material for research. During this time, the bacteria will have time to grow, which will enable the laboratory assistant to indicate their exact number. These data are important for prescribing therapy for the patient.
Now a little about decoding the received data. In healthy women, there are no fungi in the smear, and the level of lacto- and bifidobacteria is at least 10 to 7 degrees. The norm for E. coli is 1 to 2 CFU. The presence of single enterococci is allowed.
What does the results show?
The female genital organs have many microorganisms in their flora. Some of them do not pose a danger, and some are not the norm for beneficial gestation.
Normal tests should show the presence of: lactobacilli, bifidobacteria. Other microorganisms that are inherent in the intestines should not be detected, except in a single quantity.
If the culture shows a large accumulation of them, this indicates that the genitourinary system is inflamed.
Norms
The contents of the cervical canal are not sterile. In any case, the vagina and cervix are inhabited by microorganisms.
If microbes are classified as opportunistic or facultative, then they do not pose any danger.
According to the standard, culture from the cervical canal should reveal many lactobacilli and bifidobacteria - microorganisms beneficial for women's health, representatives of the natural vaginal flora.
The presence of a large number of intestinal inhabitants is undesirable: enterococci, Escherichia coli.
In single quantities, these bacteria do not threaten women's health, but when found in large numbers in cultures from the cervical canal, they are symptoms of inflammation of the genitourinary system.
Even one single bacterium of staphylococcus, gonococcus, trichomonas, leptothrix, found in culture from the cervical canal, indicates infection of the cervix with dangerous pathogens. Such infections pose a particularly great threat to pregnant women.
Normally, bifidobacteria and lactobacilli in the culture from the cervical canal should be at least 10 * 7. Only a specialist can decipher the culture from the cervical canal.
People without medical education will not be able to independently determine whether the microflora is normal or there are deviations.
Each woman has individual indicators, so it is not enough to simply compare the numbers obtained as a result of culture from the cervical canal with the reference interval.
A slight deviation from the norm may be natural for a particular patient. After bacterial culture, the doctor comprehensively analyzes the results of the vaginal smear and culture from the cervical canal.
This is necessary to compare the flora found immediately after taking the biomaterial and the bacteria grown on the nutrient composition.
But there are criteria that definitely do not belong to the norm - pathogenic microbes that are at the stage of intensive development.
Culture from the cervical canal helps to detect not only the presence of pathogenic microbes, but also, no less important, to determine the stage of their development:
- the initial stage is weak growth of microorganisms, which can only take place in a liquid medium;
- second stage – bacteria multiply more actively, are able to master solid media, and form no more than 10 colonies on them;
- the third stage - the number of colonies on solid compounds increases to 100 - this indicates the presence of an inflammatory process;
- the final stage – the number of colonies exceeds 100.
The norm of microorganisms in culture from the cervical canal is disrupted for hormonal, immune, and hygienic reasons.
In addition, deviations in the composition of the microflora are a symptom of female ailments of an infectious nature.
Analysis of biomaterial from the cervical canal during pregnancy is often prescribed to expectant mothers, which rightly raises concerns among women - will the collection of biomaterial harm the fetus?
In order not to worry, it is enough to know the anatomy of the pelvis. The cervical canal is closed by a mucous barrier through which no pathogenic bacteria can penetrate.
But the color of the cervical canal changes already in the early stages of pregnancy, which can become an additional symptom of the presence of an embryo in the uterus.
Before childbirth, the mucus leaves the cervical canal, so it is imperative to treat the microflora in order to achieve the desired degree of purity of the smear in the early stages of pregnancy.
In addition, there is a pathology in which the cervix, under the pressure of the growing fetus, begins to open not before childbirth, but starting from the second half of pregnancy - in such cases, improving the vaginal microflora in the later stages will be impossible.
Pathogenic and opportunistic microorganisms will penetrate into the prematurely dilated cervix and the inflammatory process of the cervical canal will begin - cervicitis, which poses a direct threat to the gestation of the fetus.
The canal is populated by various microorganisms; it cannot be completely sterile. Lysozyme contained in the secretion of the canal has an antimicrobial effect.
Beneficial bacteria must be present in the cervix. But just one harmful bacteria, for example, staphylococcus, indicates an infection and the need for treatment.
The composition of the microflora depends on:
- on the age of the woman;
- presence of infection;
- hormonal levels;
- taking antibiotics;
- various pathologies.
The analysis provides data on the microorganisms inhabiting the cervix. A normal indicator should not contain any fungi or bacteria.
However, there must be beneficial bifidobacteria and lactobacilli, but not less than 10.7. Indicators of E. coli – 10.2 enterococci. Leukocytes are normal up to 30. Flat epithelium – 5-10. There should be a moderate amount of mucus.
Pathological is a condition in which a large number of E. coli, gonococci, yeast fungi, staphylococci, and trichomonas are found. This analysis is not able to detect chlamydia and ureaplasma.
The gynecologist interprets the results obtained from the laboratory. The analysis shows the name of the microorganisms inhabiting the cervix, as well as one of the 4 levels of cleanliness of the canal.
There are 4 levels of channel purity:
- Microorganisms show little growth. They are present in liquid media, but not in solid media.
- Bacteria of one type show growth of up to 10 colonies on a hard surface.
- The number of bacteria is up to 100 colonies on a solid medium.
- The number of different colonies is more than 100.
The first two degrees indicate contamination of the canal, and the third and fourth degrees indicate inflammatory processes.
And the reasons for the increased number of bacteria in the cervix are decreased immunity, hormonal imbalances, taking antibiotics, hereditary diseases, poor hygiene, infection during sexual intercourse, infection due to medical procedures.
Tank culture for the presence of bacteria can also determine sensitivity to various antibiotics. Bacteria whose sensitivity needs to be determined are placed in a dish with a nutrient medium. Discs soaked in antibiotics are placed on the surface of the medium.
This antibiotic penetrates the environment and affects the growth of microorganisms. The bowl should stand for some time at room temperature, and then it is placed in a thermostat for several hours.
After the required amount of time has passed, the diameter of the growth inhibition zone is measured and the suppression of bacterial growth is assessed:
- the absence of growth inhibition indicates bacterial resistance to the drug;
- zone diameter up to 1.5 cm – weak reaction, low effectiveness of the product;
- zone diameter from 1.5 to 2.5 cm – moderate sensitivity;
- diameter greater than 2.5 cm – hypersensitivity to antibiotics.
It is important to determine sensitivity to antibiotics, because in different women, bacteria react differently to certain medications. You cannot prescribe medications based only on textbook recommendations. It is necessary to find out which antibiotic can cope with the disease.
Normal analysis indicators include only the presence of beneficial microflora. It consists of bifidobacteria and lactobacilli. They can be present in the analysis in any concentration.
A normal result allows for the presence of small amounts of E. coli. But its concentration should not exceed 10*2 degrees of colonies. There should be no fungal flora in a normal bacterial culture from the cervical canal.
The appearance of Staphylococcus aureus, Klebsiella, enterococci, streptococci in the analysis is an indication for mandatory treatment. In this case, doctors also determine the reason that caused the appearance of these pathogenic microbes in the cervical canal.
If the level of these microbes in the analysis is increased, then this not only can pose a threat to the development of pathologies of the female genital organs, but can also lead to the development of pneumonia or other diseases of the internal organs in an infected woman.
What do deviations mean?
The results do not always show normal values. Poor culture during pregnancy is not uncommon.
Depending on the identified pathology, possible treatment options are considered.
The absence of squamous epithelium indicates a decrease in estrogen; an excess of these components indicates inflammation.
Yeast-like fungi indicate characteristic diseases, for example staphylococcus in the cervical canal in pregnant women.
Abundant mucous discharge also indicates inflammatory processes.
In connection with the detection of any deviations from the norms, additional procedures are prescribed. A pregnant woman undergoes tests to examine vaginal discharge.
First of all, they consider options for harmful bacteria acquired through sexual contact.
Treatment is prescribed based on the timing of pregnancy.
The preferred treatment option during this period is topical remedies without antibiotics. Medicines should not adversely affect the fetus.
In the second trimester, more radical methods are allowed, but in case of urgent need.
Important! There are infections that do not manifest their existence openly in the body. That is, they develop in a latent form and affect the development of the child while in the womb. Therefore, even without any apparent reason, it is advisable to take this test.
Controversy surrounding analysis
Expectant mothers are wary of bacterial testing. After all, the brush is inserted deep into the vagina and a smear is taken from the cervical canal. But taking a smear test cannot lead to a miscarriage.
DID YOU KNOW? The downside of most drugs is side effects. Often medications cause severe intoxication, subsequently causing complications in the kidneys and liver. To prevent the side effects of such drugs, we want to pay attention to special phytotampons. Read more here.
The study is completely safe, but it is prescribed only when absolutely necessary. When assessing the state of the vaginal microflora, gynecologists use a special concept - the degree of purity.
There are 4 degrees of vaginal smear purity:
- Acidity is normal, lactobacilli predominate, there is no inflammation.
- Acidity is normal, a small number of leukocytes, the number of lactobacilli is reduced, diplococci are present.
- The environment is slightly acidic or alkaline, an increased number of leukocytes, a reduced number of lactobacilli, many coccal organisms.
- The environment is alkaline, a large number of leukocytes, the absence of positive and the presence of a huge number of dangerous microorganisms.
If a vaginal smear indicates problems, and the degree of purity is 3 or 4, then pregnant women are additionally prescribed a culture test from the cervical canal.
A normal culture of a pregnant woman should contain only beneficial microorganisms: lacto and bifido. A small amount of E. coli is allowed. There should be no yeast or bacteria present.
If an increased content of dangerous microorganisms is detected, then treatment is necessary. Therapy in the early stages of pregnancy gives good results.
Degrees of quality and growth of bacteria
There are microorganisms that live without actively manifesting themselves. At the time of immune and hormonal disorders, they are activated and begin to actively multiply. Each of the parasites finds its own habitat, where it is more comfortable. That is why one or another flora is used for analysis.
The results of the readings are based on the possibility of rapid development of harmful microorganisms.
The following options are possible:
- first degree. This is when there is a slight growth of bacteria and only relative to its environment;
- the next step is about a dozen colonies in another solid medium;
- at the third stage there is an increase to 100 colonies;
- in the last stage, more than 100 colonies of the same type are observed.
The primary two degrees of proliferation of microorganisms indicate clogging in the microflora, and the latter show inflammation.
These changes do not exclude the possibility of development associated with the interesting position of a woman during which hormonal changes occur, immunity decreases, and medications are used.
The entry of an infection into the body and its rapid reproduction can bring not only physical discomfort to the expectant mother in the form of itching, burning and discharge. For this reason, miscarriages, infections of the child during passage through the birth canal, and many other troubles occur.
To ensure a successful pregnancy, take care of your health in advance.
Author: Daria Andreevna, neonatologist
Especially for the site kakrodit.ru
Staphylococcus in bacterial culture
During pregnancy, there is an increased risk of transmission of infections from mother to baby. Therefore, it is very important to monitor the condition of the expectant mother. A frightening symptom is the detection of staphylococcal bacteria in the contents of a smear from the cervical canal. These bacteria can cause serious harm to the still developing child's body. One of the most dangerous bacteria that causes complex diseases is Staphylococcus aureus. If it is present in the patient’s body, the specialist determines individual therapy depending on the extent of the disease and taking into account the general physiology of the patient.
Depending on the presence of various microorganisms in the contents of the cervical canal and their concentration, several stages of bacterial contamination of the female genital organs are classified:
- Microorganisms develop exclusively in liquid habitats
- The development of microorganisms is observed in particular on solid media at concentrations of up to ten colonial species.
- The concentration of microorganisms on solid media is 10 – 100 colonial species.
- The concentration of microorganisms on solid media is more than one hundred colonial species.
The genitals contaminated with bacteria are a consequence of infection during sexual contact or after medical procedures involving intervention in the vagina and cervical canal.
The spread of infection in the body is helped by disorders of the immunological and hormonal system, resulting inflammation of neighboring organs, treatment with antibiotics, and insufficient maintenance of genital hygiene.
Microbiological examination of the cervix and cervical canal
When conducting a cytological examination, it is possible to simultaneously carry out microbiological diagnostics. Based on this, a final diagnosis cannot be made, but infectious diseases of the genital tract can be suspected.
- Trichomonas colpitis - when trichomonas are detected;
- Candidiasis (better known as thrush) - when fungi of the genus Candida are detected;
- Bacterial vaginosis – decrease in lactoflora (normal vaginal flora), detection of cocci, gonococci, rods or mixed flora;
- Chlamydia – chlamydia detected;
- Changes in the epithelium under the influence of HPV.
- Microbiological method – sowing of flora with subsequent determination of the type of pathogen and its sensitivity to antibacterial drugs;
- PCR diagnostics (polymerase chain reaction) is a modern diagnostic method based on determining the DNA of pathogens of infectious diseases.
Norms of indicators during pregnancy
Gynecological analysis of a smear of the obtained biological material is carried out as prescribed by a doctor in childhood and adolescence. The norms for a healthy child are shown in the table.
| Indicators assessed | 1-5 years | 6-10 years | 11-15 years | 16-17 years old | Teenagers who are sexually active |
| Leukocytes | 0-2 | 3-5 | 5-7 | To 10 | To 10 |
| Slime | 1-2 | 1-2 | 1-2 | 1-2 | 1-2 |
| Epithelium | 1-3 | 4-6 | 5-6 | To 10 | To 10 |
| Flora | Kokkovaya | Kokkovaya | Mixed | Rod | Rod |
Norm for smear analysis in gynecology (read the explanation below)
The indicated parameters correspond to the number of visible cells of certain microorganisms that fall into the field of view when studying the material under a microscope. In women of reproductive age and older age, the norms depend on where the mucus was obtained from.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with Garlic against worms in adults and children
| Indicators | Vagina (V) | Cervical canal (C) | Urethra (U) |
| Leukocytes | 0-10 | 0-30 | 0-5 |
| Flat epithelium | 5-10 | 5-10 | 5-10 |
| Gonococci | None | None | None |
| Trichomonas | None | None | None |
| Key cells | None | None | None |
| Yeast | None | None | None |
| Microflora | Multiple Dederlein rods (gram-positive) | Absent | Absent |
| Slime | Moderate amount | Moderate amount |
In patients of reproductive and childhood age, not only the quantitative content of certain cells differs, but also the list of parameters by which the condition of the organs of the genitourinary system is assessed.
During the period of bearing a child, the hormonal background in a woman’s body changes significantly, more progesterone and estrogen begin to be produced. This affects the state of the vaginal microflora. Therefore, during pregnancy, the test is performed three times: at registration, at 30 weeks and before birth.
A gynecological smear analysis, the interpretation of which shows an increased content of lactobacilli (beneficial microorganisms), indicates that the patient is healthy. There is also an increase in the volume of mucus enriched with glycogen.
Normally, microscopic diagnosis shows the following:
- epithelium – no more than 15;
- leukocytes – within 10;
- mucus - in the form of /;
- fungi – make up 104.
It is possible to identify cells that are atypical for the area being examined. They are often determined when a smear is taken from the surface of the cervix. This condition indicates the development of dysplasia. To exclude the development of cancer, a cytological examination is additionally prescribed.