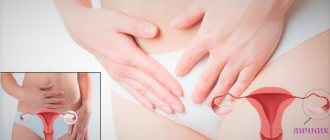
The ovary is a paired organ of the woman’s reproductive system, which is responsible for the production of hormones - estrogens, progestins, androgens, FSH and LH. If it functions normally, then the menstrual cycle is regular, as is ovulation. If there are malfunctions in the functioning of the ovary, this can lead to various diseases, which are usually accompanied by pain.
Can the ovaries hurt when there are no pathologies? The results of observations and studies show that they can, but doctors strongly recommend not to hope for a lucky break, but to undergo an examination.
The ovaries are located in the pelvis, so pain may be felt on the left or right side of the lower abdominal segment.
The localization of pain depends on the cause that caused it: sometimes the pain is clearly defined on one side of the peritoneum, and in some cases the entire lower abdomen hurts equally.
The nature can also be different: the pain can be pulling, shooting, cutting, aching or cramping. Treatment methods are also different: in one case medications are prescribed, in another, urgent surgical intervention is required, and sometimes examinations show that therapy is not needed at all.
Why do the ovaries hurt?
Why do my ovaries hurt?
This question is asked by many girls when they first understand what cramping sensations in the ovaries in women are. When a patient says that she feels pain in the ovaries, it is necessary to find out if there are other symptoms that would indicate a disease or inflammatory process. Why does the ovary hurt in women? There are several reasons. These may be inflammatory processes or hormonal imbalances. In addition, you can indicate some pathologies, such as abnormal development of the uterus and genital organs, as well as disruptions in the menstrual cycle. Pain in the ovaries has a direct connection with the menstrual cycle, and this is called ovulatory syndrome.
We recommend you find out:
Why does it occur
pain in the ovary during ovulation
Infection provokes swelling in the organ area. Bacterial infection causes changes in organ morphology and fluid accumulation.
The pain is different:
- localization in the groin, lower back and pubic area;
- unilateral manifestation;
- impermanence.
Diagnosis of ovarian diseases
The main diagnostic method is ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs. It can be used to visualize changes in the size and structure of the ovaries, and follicular disorders. Before performing an ultrasound, the doctor studies complaints and anamnesis, and conducts a gynecological examination. In some cases, other diagnostic methods are required - hysterosalpingography, organ biopsy.
Yes, the ovaries can respond with pain to many other diseases of the body.
During such a pregnancy, the fertilized egg does not move from the ovary to the uterine cavity, but is attached inside the fallopian tube. Despite this, the zygote continues to grow, causing tube rupture and severe internal bleeding.
The main symptom is a nagging painful sensation to the right or left of the pubic bone. When a rupture occurs, the pain becomes acute, bloody vaginal discharge may appear, nausea, dizziness appear, and the temperature rises.
Due to the high risk of fallopian tube rupture, a woman with an ectopic pregnancy requires emergency hospitalization.
Endometriosis
A disease in which the endometrium (the mucous membrane of the uterus) grows not only inside the uterine cavity, but also outside it (including into the fallopian tubes). Manifests itself through pelvic pain. When the endometrium is detached during menstruation, a spasmodic acute pain occurs in the area of the uterus, which can radiate to the area of the appendages.
Unpleasant sensations may appear during sex and going to the toilet. Endometriosis can cause anemia (as a result of excessive blood loss) and infertility.
Thrush
A fungal infection of the vagina that causes burning and itching in the genital area. A characteristic feature of thrush is a white discharge with a cheesy texture.
If complications occur, cervicitis (inflammation of the cervical canal) may develop, causing the woman to feel unpleasant symptoms in the area above the pubic bone.
Appendicitis
Pain in the right ovary can occur with appendicitis, since the ovary is physiologically located next to the cecum.
Appendicitis can be recognized by other symptoms:
- increasing pain syndrome (gradually moves from the navel to the right side of the abdomen and decreases when lying on the right side),
- nausea,
- problems with bowel movements and gases.
The right ovary may continue to hurt even after surgery for appendicitis, but if the pain intensifies, you should visit a gynecologist.
Adhesive disease
This is a pathological condition when adhesions form between the internal organs and the walls of the peritoneum. If they cover the uterine appendages, the girl may feel pain like during menstruation.
With adhesive disease the following are also observed:
- digestive problems,
- frequent vomiting,
- low-grade fever,
- weakness.
They occur as a result of bacterial infection or as a result of surgery.
Manifest through:
- pain in the lower abdomen,
- unusual and foul-smelling vaginal discharge,
- burning and pain when going to the toilet and having sex,
- cycle disturbances, increase in temperature.
In addition to the acute inflammatory process, inflammation in the pelvis can provoke complex destructive tissue changes, including the formation of malignant tumors.
Radiating pain in the female ovaries can occur with urolithiasis, cystitis (inflammation of the bladder), STIs (chlamydia, gonorrhea, syphilis), the formation of tumors on the organs of the urinary system and in the rectum, and the development of hemorrhoids.
Therefore, if not only the ovaries hurt, but other unusual symptoms are also observed, you should definitely visit a doctor.
Pain syndrome during periods of natural hormonal imbalances
Nagging pain in the ovary can be avoided, but to do this you need to know how they arise. Pain in the ovarian area appears in many patients after 30 years. For the most part, it can be associated with the onset of ovulatory syndrome. This is a very common occurrence. After a girl has her next period, a corpus luteum forms in place of the follicle in the ovary. It is a collection of cells that is responsible for the production of progesterone.
Can the ovaries hurt with this condition? In order to exclude any pathologies, consult a specialist. Most often, the ovary hurts after ovulation. In this case, severe pain occurs in the second part of the cycle, after two weeks. It is part of the ovulatory syndrome. In this case, aching pain in the ovaries in women is especially noticeable.
If the corpus luteum has not formed, the ovary and follicle will secrete a small amount of progesterone. As a result, damage and rejection of the uterine mucosa may occur. As a result of this, the woman’s ovaries hurt a lot, sometimes they pull, and her lower back also ache.
This manifestation of ovulatory syndrome has the following symptoms: periodic sharp pain in either the right or left ovary, weak vaginal discharge, elevated temperature, pain during discharge.
Please note: What can cause ovarian pain in women during ovulation? The ovary is pulled at the moment when the egg leaves its limits. Minimal rupture occurs and some blood spills into the abdominal cavity. The spilled blood irritates the nerve endings of the peritoneum, so aching pain in the ovary is normal.
Since it occurs in the middle of the cycle, it is easy to calculate the moment of its occurrence. For example, if your cycle is twenty-eight days long, then pain in the ovaries appears on the thirteenth to fourteenth day. Most women at this time note a shooting pain that lasts for several hours.
A woman may also feel discomfort if the ovary ruptures. This condition leads to heavy bleeding into the peritoneum, resulting in peritonitis - a severe inflammatory process. In order to restore the integrity of the ovary, urgent surgical intervention is necessary.
During menstruation, pain in the ovarian area under normal conditions cannot bother a girl. What many patients write off as pain in the ovary is actually pain in the uterus. When the uterine lining is shed, it must get rid of its contents, so it begins to rapidly contract.
My ovary hurts, what should I do, many women ask. If this phenomenon occurred after menstruation, then such a picture is not characteristic of ovulatory syndrome. The girl should not lift weights or engage in physical activity. Contact your gynecologist to rule out the possibility of complications.
We recommend you find out: Why
Colitis of the ovary after ovulation
Pain in the left ovary can be present with a natural hormonal imbalance. These periods include adolescence, postpartum and premenopausal. Discomfort experienced during this time rarely requires treatment and usually goes away on its own.
Puberty
During adolescence, the formation of the menstrual cycle occurs. This may be accompanied by pain in the lower abdomen. The left and right appendages gradually increase in size and begin to produce the first follicles, which results in minor discomfort.
Pain can persist until the menstrual cycle reaches full regularity. For prevention, it is recommended to show the girl to a doctor. Pathologies discovered at this stage are easily treatable and do not cause complications in the future.
Postpartum period
The main process of recovery of a woman’s body after childbirth takes place within six months. During this time, the ovary begins to function fully, and the menstrual cycle is restored. Pain in the left ovary can be throbbing or dull and is physiological in nature. It indicates the normalization of reproductive function and the process of preparing the body for a new conception.
If you are breastfeeding, pain in the ovaries may occur only after the end of lactation. In some women it occurs earlier, in others the menstrual cycle is absent throughout the entire period of feeding the baby. This is explained by the fact that prolactin, produced during lactation, stops the functioning of the appendages, protecting against a new pregnancy. However, women who are breastfeeding need additional contraception.
Menopause
Closer to 40-50 years, a woman’s menstrual cycle is disrupted. This is facilitated by low follicle maturation and lack of ovulation. The functionality of the left ovary decreases, which leads to a decrease in its size and the appearance of pain in the organ. The onset of menopause is accompanied by other symptoms - hot flashes, mood swings, changes in blood pressure, and deterioration in well-being. Some women tolerate this process easily and feel almost no changes in the body.
At the onset of menopause, the ovaries reach their minimum size. The menstrual cycle stops. All unpleasant symptoms, including pain in the lower abdomen, also disappear.
Pain in the lumbar region and lower abdomen
Pain in the right ovary can lead to serious consequences, including infertility, if the situation is not resolved promptly.
In addition, when pain occurs in the area of the right ovary, age and lifestyle should be taken into account. And now we are not talking about a teenage girl with a polygamous attitude towards intimate relationships, but about women, girls, girls in general. Pain in the right ovary can occur even in a girl who has not reached puberty. Most often, this is due to an inflammatory process due to hypothermia. This is also possible for a grandmother who experienced menopause 20 years ago, and the reasons for this may be different, including inflammation and infections. We will look at the specific causes of pain below.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=UVpo4Q_RvF0
In 90% of cases, girls and young women complain of simultaneous pain in the ovarian region and at the lumbar level. Banal prolonged hypothermia is the first reason for the occurrence of such unpleasant sensations. If hypothermia is excluded, then this indicates the presence of one or more pathologies of the genitourinary system, for the diagnosis of which the nature of the pain, frequency of occurrence, and also its duration are of great importance.
As you know, all women of childbearing age have their own individual menstrual cycle. It consists of 3 phases. In each period of the menstrual cycle, a woman may complain that the ovaries are pulling. Ovulation is accompanied by pain quite often. It is characterized by the release of an egg into the abdominal cavity.
This process is accompanied by changes in the gonads. The dominant follicle ruptures when the egg is released. During this period, some women experience unexpressed nagging pain in the right or left groin area. Unpleasant sensations occur on the side where the follicle ruptured.
Ovulation occurs in the middle of the menstrual cycle. In addition to discomfort in the ovarian area, it is accompanied by other symptoms. Among them are increased sexual desire and the release of clear, thick mucus from the vagina. Ovulation lasts only 1 day, during this period the probability of conceiving a child reaches its maximum.
Ovarian apoplexy
Pain in the ovarian area is caused by apoplexy - rupture of the ovary. The pathology can also occur in adolescence, but is more often diagnosed in women over 25 years of age.
Apoplexy is a hemorrhage in the ovary caused by damage to the vascular walls.
The state is called:
- the presence of a cyst;
- physical activity;
- sexual intercourse during ovulation.
The pathology causes sudden, acute pain.
Signs of the disease include:
- asthenia;
- weakness;
- dizziness;
- nausea;
- loss of consciousness;
- pain in the area of the sacrum of the coccyx and lower back.
The severity of the pathology depends on the volume of blood lost. Treatment of the disease is carried out in a hospital setting. In extreme cases, surgery is indicated. Often there is a disturbance in the morphological structure of the corpus luteum due to pathologies in the vessels against the background of inflammation. The process occurs during ovulation.
There are several forms of pathology:
- Painful. There are acute pains.
- Anemic. Accompanied by fainting and asthenia.
- Mixed. Includes features of previous types.
Treatment
Treatment for pain in the right ovary is prescribed taking into account the disease that causes this symptom.
For inflammatory or infectious diseases, antibacterial treatment, immunostimulants and physiotherapy are prescribed.
If there are problems with the balance of sex hormones, a course of appropriate medications will be prescribed. After completing the course, an examination will be carried out again and all changes will be studied.
Various surgical interventions are prescribed if the cause of ovarian pain is adhesions, cysts, neoplasms and similar pathologies that are difficult to treat with medications.
For almost any disease, sedatives can be prescribed to calm the patient.
If the right ovary hurts during ovulation, then no special treatment is required. However, a gynecologist may recommend vitamin preparations containing magnesium to reduce the intensity of all manifestations during this period.
Pain in the ovaries after surgery
The reasons may be physiological or pathological.
Physiological ones include:
- uncomfortable position during sex;
- presence of depressive or hysterical disorders;
- individual structure of reproductive organs;
- ovulation process;
- rough sexual intercourse.
Pathological provocateurs include:
- the presence of an inflammatory process in the pelvic area;
- endometriosis;
Depending on how the ovaries hurt in women, you can understand the reason.
- ovarian apoplexy;
- the presence of an oncological tumor;
- cyst formation;
- stagnation of blood in the veins of the genital organs;
- ovarian infection;
- the presence of adhesions in the pelvic area;
- dryness in the vaginal area;
- inflammation of the uterine cervix.
Pain in the postoperative period bothers women quite often.
Among the most common surgical methods are:
- puncture;
- laparoscopy;
- laparotomy;
- laser treatment.
Ovarian punctures
The surgeon can evaluate how the ovaries hurt in women during follicle puncture. The procedure involves puncture of organs, resulting in the formation of hematomas. This causes pain. Such a symptom after the manipulation is considered normal.
Complications often occur after cyst removal. In this case, the type of operation performed plays an important role. Usually, discomfort after laparoscopy ceases to bother the patient after 2-3 days. During laparotomy, which is an abdominal operation, they may bother you for 7-10 days.
Certain risks arise when removing a large cancer tumor, the presence of injuries or open bleeding. Removing a cyst using laser beams has many similarities with laparoscopy. In this case, the operation is performed not with a scalpel, but with a laser beam. This is a bloodless method, as problem areas are cauterized with a laser.
If after the above interventions pain occurs in the area of the cyst, this can be explained by:
- the presence of adhesive formations;
- lack of personal hygiene;
- inflammatory process;
- physical fatigue;
- rupture of the ovarian membrane;
- divergence of seams;
- infection.
When performing a laparotomy, which is an abdominal operation, a woman’s ovary may hurt for some time, which is considered a normal sign. But if the pain does not go away within 10 days, then this is evidence of complications that have arisen that require urgent treatment.
What to do if your ovary hurts? First, go through the diagnostics. If the doctor discovers a malignant tumor, he may prescribe urgent surgery. Since any operation traumatizes the body to a certain extent, it is not surprising that pain may appear in the ovarian area. It is a mandatory reaction of the body that appears after a puncture.
Typically, women experience ovarian colitis, abdominal bloating, and vaginal discharge. These signs appear because the injection into the ovary caused minor injury. In addition, a microscopic bleeding wound appears at the injection site, which irritates the abdominal cavity. Typically, pain does not leave a woman for a week after surgery.
Pain after cyst removal may be associated with the occurrence of adhesions in the pelvic cavity, bleeding and the development of pelvioperitonitis. Do not forget that the more extensive the operation, the more pronounced the pain syndrome will be.
How to protect yourself
It is worth talking a little about the prevention of painful abdominal syndromes in the area of the left ovary, because it is also used after treatment to prevent relapse. In addition, topical prevention will help maintain overall health and avoid contracting many ailments:
- Don't get too cold. Especially try to keep your feet warm, because hypothermia has a detrimental effect not only on women's diseases.
- Follow complete treatment and all medical recommendations
- Try not to become overtired, both mentally and physically
- Do not wear clothes that are too tight in the pelvic area (trousers, skirts, etc.)
- Support your immune system so that it can cope with various inflammatory processes that can also cause pain in the area of the left and right ovary.
Only a doctor can determine why the left ovary hurts. Without diagnosis, examination and certain tests, the full clinical picture cannot be seen.
Important! If you do not pay attention to any manifestations of pain syndromes in the area of the left ovary for six months, then the picture will necessarily become chronic.
Visit your local gynecologist in a timely manner, take smears, undergo examinations and simply monitor your women's health on your own. Listen to your body’s signals and be sure to respond to them in order to avoid many irreversible consequences. Be healthy, beautiful and young!
Pain syndrome during periods of natural hormonal imbalances
Menopause
Before menstruation, the ovary hurts due to ovulatory syndrome - a normal physiological state of the female body.
Hyperstimulation syndrome occurs when the female body is exposed to hormonal drugs used to provoke artificial ovulation. Medicines are also used in infertility therapy and donation. In this condition, the female gonads begin to increase the production of steroid hormones.
High levels of progesterone and estrogen negatively affect the endothelium. Symptoms develop 2-5 days after taking the medicine. Most often, the leading symptom is intense pain in the ovarian area. At the same time, other signs of pathology are ignored.
These include:
- accumulation of fluid in the peritoneum;
- difficulty breathing;
- pain in the lower abdomen;
- vomiting;
- flickering of flies before the eyes;
- difficulty passing urine;
- swelling in the legs;
- decrease in blood pressure.
Possible complications
In the absence of adequate therapy, pain in the ovaries can cause various, sometimes irreversible, consequences.
Why is pain in the ovarian area dangerous?
- internal bleeding;
- adhesions;
- ectopic pregnancy;
- miscarriage, difficult childbirth, fetal pathologies;
- disturbances in the functioning of the digestive, urinary, and endocrine systems.
The main consequence of ovarian pathologies is infertility.
If you ignore pain in the ovaries, adhesions in the uterus may begin
Interrupted tubal pregnancy
Pain in the ovaries is often triggered by pregnancy.
The main reasons include:
- threat of interruption of pregnancy;
- presence of a cyst;
- cyst rupture.
If there is continuous dull pain, a tubal pregnancy is diagnosed. The fetus grows and the risk of pipe rupture increases.
If there is continuous dull pain, a tubal pregnancy is diagnosed. The fetus grows and the risk of pipe rupture increases. A pipe rupture is indicated by pain that spreads to the lower back.
In addition to pain in the ovarian area, discomfort occurs in the anus. A woman feels pressure before defecation. Bloody discharge occurs when blood comes out of the tube. They are distinguished by their smearing character. Usually the discharge is scarlet in color.
There is an opinion among women that if the ovary pricks during pregnancy, then this is normal. But statistics show that pain during pregnancy does not occur without an obvious reason. When the uterus significantly increases in size, the ovaries, along with the fallopian tubes, move above their normal location.
Often, women experience pain in their ovaries during early pregnancy due to overstretching of the ligaments that support the uterus, ovaries and tubes. Tension arises in them as they suffer from increased stress. You can get rid of this symptom by normalizing your diet and sleep patterns. Get plenty of rest and do gymnastics and breathing exercises.
Every gynecologist will tell you that during pregnancy the function of the paired glands is almost completely turned off. Therefore, pain cannot arise in them. It’s another matter if the discomfort began even before pregnancy, and only intensified during this period. A pregnant woman may suffer from inflammation as well as ovarian tumors.
The best option is to take preventive measures before pregnancy. If you notice pain in the ovaries in the early stages of pregnancy, contact your gynecologist. Otherwise, complications such as abortion, hypoxia, placental abruption and others may occur.
We recommend you learn: How to recognize
ovarian cyst pain
Pregnancy
Painful sensations of a pulling nature may occur after ovulation. During this period, a large amount of the hormone progesterone is released. In the absence of pregnancy, a woman’s body prepares for the rejection of the endometrium - menstruation. Women during this period often complain that the left ovary is pulling (or the right, depending on the location of the dominant follicle).
The ovary is a glandular organ of the female reproductive system, in which changes occur constantly. Pain can not only accompany ovulation, but also continue for several days after it. After all, the gland tissue undergoes physiological damage during follicle rupture. Healing occurs in a short period of time and is not accompanied by severe pain.
If the discomfort continues for a long time, you should consult a gynecologist. In addition, indications for consulting a doctor are nagging pain of high intensity that is constant. They may indicate the occurrence of cystic formations, an inflammatory process, or the onset of an ectopic pregnancy. All these pathologies require immediate treatment.
A condition in which you should especially carefully monitor your health is pregnancy. Many women have retracted ovaries during this period. Most often, this symptom occurs at the beginning or end of pregnancy. In fact, the unpleasant sensations that a woman perceives as pain in the ovaries are associated with stretching of the uterine ligaments.
The fact is that while carrying a child, significant changes occur in the entire body, including the genitals. Often patients go to the doctor with a complaint such as ovarian tugging before menstruation. For many women, this symptom indicates the development of pregnancy. Changes associated with carrying a child occur already in the first trimester.
In most cases, discomfort in the lower abdomen is caused by sprained ligaments. They are located in the same place as the ovaries. For this reason, pain is easily confused with the discomfort that is observed with adnexitis and other pathologies of the gonads. Despite this, there is a possibility that the woman actually has an ovarian pull.
Pain in the appendage area in pregnant women is quite dangerous. If the ovary pulls in the early stages, you should pay attention to the intensity of the discomfort. Mild pain may indicate implantation of the embryo into the uterine tissue. However, such discomfort quickly passes. If the pain lasts for several days or gets worse, you should consult a doctor immediately.
One of the life-threatening conditions is ectopic pregnancy. This means that the fetus is attached to the tissue of the appendages. Most often, tubal pregnancy is diagnosed, but its development in ovarian tissue is also possible. The development of the embryo leads to stretching and rupture of the appendages. In this case, signs of pregnancy are observed, such as increased levels of hCG in the urine, nausea, delayed menstruation and an enlarged uterus.
If the left ovary pulls for a long time, this may indicate adnexitis. The inflammatory process during pregnancy is particularly dangerous, as it leads to complications. In addition, many medications are contraindicated while carrying a child. Pain in the left half of the abdomen can be observed with constipation due to stretching of the sigmoid colon.
A nagging pain in the ovaries is observed for several days after drug manipulation. These include procedures such as in vitro fertilization, removal of cystic formations, tubal ligation, etc. The recovery period after any surgical intervention on the appendages is accompanied by pain.
Normally, this lasts for 2-3 days. In this case, there should not be a pronounced increase in temperature and other inflammatory symptoms. One of the stages of the IVF procedure is the transfer of embryos into the uterine cavity. This process is accompanied by a hormonal reaction from the ovaries. Therefore, slight nagging pain is considered normal in this case.
Treatment for nagging pain in the ovarian area depends on the cause of its occurrence. To temporarily relieve discomfort, antispasmodics are prescribed. These include the drugs “No-shpa” and “Drotaverine”. Ovarian cysts are an indication for hormonal therapy. Oral contraceptives “Jess”, “Janine”, etc. are used.
If you have pain in the side of your lower abdomen, this is not necessarily a sign of problems with the ovaries. Soreness of the organs of the female reproductive system can be provoked by completely harmless factors.
Ovulation
This is the process of the release of a mature egg from the ovary, which occurs in women approximately in the middle of the menstrual cycle. Before the egg enters the fallopian tube, the follicle in which it was located ruptures, which causes pain during ovulation.
In each cycle, pain usually occurs either on the right or on the left, it all depends on in which ovary the egg has matured. General discomfort may persist 1-3 days after ovulation.
During ovulation, a woman may experience not only painful symptoms, but also slight malaise, sometimes an increase in temperature by two or five degrees (such symptoms are called “ovulatory syndrome”).
Pain in the ovaries before menstruation is provoked by a sharp drop in estrogen hormone levels and partial detachment of the endometrium (therefore, before menstruation, a woman may experience slight brown discharge).
During a girl's menstruation (if she is healthy), the ovaries should not hurt, but a similar sensation may occur due to soreness of the uterus.
Pregnancy
During pregnancy (both in the early stages and later), the ovaries should also not hurt, since during pregnancy their function is practically switched off (they become active when the menstrual cycle and ovulation resume). However, painful discomfort can be provoked by changes in the size of the uterus and a shift in its position inside the abdominal cavity.
Therefore, during pregnancy, many women perceive sprained muscles and ligaments as problems with the ovaries (especially in the early stages, when all these sensations seem very unusual).
Sometimes pain in the groin area accompanies sexual intercourse or occurs after sex.
Similar sensations can be caused by:
- excessively strong or deep penetration of the partner into the vagina, in which his head strongly presses on the cervix of the female uterus;
- insufficient amount of natural vaginal lubrication, which causes painful friction;
- convulsive contraction of the vaginal muscles before and after sex, provoked by orgasm or psychological experiences of the woman.
At the same time, it is worth considering that discomfort and pain in the lower abdomen during and after sexual intercourse can also cause inflammatory or infectious diseases of the genitourinary system (you can learn more about these diseases in the following sections).
Therefore, be sure to consult a doctor if, in addition to pain during/after sex, you experience:
- burning in the vagina and urethral area;
- burning sensation when going to the toilet;
- unusual vaginal discharge (especially if it has an unpleasant odor);
- elevated temperature (around 37˚C).
Any external interference with the integrity of the ovaries often leads to pain on the side of the pubis.
So, a similar condition can occur after:
- puncture sampling;
- cyst removal;
- manipulation of the fallopian tubes (for example, removal of the endometrium for endometriosis or tubal ligation for contraception);
- surgical operations on the uterus.
The course of some gynecological and non-gynecological diseases can be rapid.
Therefore, be sure to call an ambulance if you observe the following symptoms in yourself or someone close to you:
- Persistent or increasing pain in the ovarian area or lower abdomen (may radiate to the lower back).
- Unexpected deterioration in health – weakness, nausea.
- A sharp rise in temperature.
- The appearance of spotting or heavy bleeding.
Bleeding is especially dangerous for women, as it can lead to death within just a few hours.
During pregnancy, complaints of pain in the lower abdomen and lumbar region are due to an increase in the load on the spinal column. But in the early stages of pregnancy, when the weight of the fetus and the weight of the woman herself have not yet increased significantly, such complaints may signal a threat of miscarriage.
If the pulling sensation does not cause pain, but is quite uncomfortable and occurs after the 20th week, false Braxton-Hicks contractions can be suspected. The reason for this phenomenon is considered to be increased excitability of the uterus, which does not require special treatment and goes away after taking warm water procedures and walking at a calm pace.
Adnexit
Adnexitis is an inflammatory process in the ovaries. It is accompanied by cutting and stabbing pain. The patient experiences pain periodically. They are localized in the lower abdomen.
The intensity of pain varies. Sometimes the pain spreads to the back and legs. Adnexitis is treatable, but subject to adequate and timely treatment. Otherwise, the pathology may become chronic, and pain in the ovaries will bother the woman throughout her life.
In the ovaries, sharp pain in women is caused by adnexitis, an inflammatory disease that is caused by infections. Young ladies over 20 years of age are at risk.
Diseases of the reproductive system
If the right ovary hurts badly, then the causes of this symptom in women may be the presence of various diseases. At the same time, pain in the ovary is not temporally related to ovulation or menstruation, and a woman may notice strange discharge and other associated symptoms.
- With inflammatory and infectious diseases, the most common of which are oophoritis and adnexitis, pain in the right ovary occurs quite severe. Moreover, such diseases can begin in other organs of the reproductive system, and only then spread further.
- With hormonal imbalance, women notice not only a dull and aching pain, but also a disruption of the menstrual cycle, as well as symptoms that usually appear with premenstrual syndrome... During an ultrasound, the ovaries may look like blackberries, although normally they are smooth. This ovarian condition is also called polycystic disease. Each of the cells, which looks like a small ball, is a cyst.
- Adhesions formed due to inflammatory diseases or after surgery in the reproductive system.
- If endometriosis has spread to these organs, the ovary on the right side often hurts. Accompanied by a delay in menstruation and increased pain before the onset of menstruation.
- After surgical interventions, including abortions, inflammation may occur, which will cause pain.
- Various neoplasms. They can be asymptomatic for a long time, but when pain appears, the menstrual cycle is almost always disrupted. With cysts, a pulling sensation in the lower abdomen is often observed. If there is a torsion of her leg or a rupture of the body itself, then the symptoms are very vivid and strong. In this case, it is necessary to urgently call an ambulance, since this condition is deadly for the woman.
- Hemorrhage into the ovary followed by its rupture is apoplexy. In this case, the pain is sharp, stabbing. The disease requires surgical intervention, as it threatens the development of peritonitis.
- Various diseases of nearby organs. Sometimes it is very difficult to determine the source of pain when a woman simply feels that her right side hurts. For example, severe pain due to inflammation of the appendix does not have a clear localization. Therefore, if the right side hurts, the ovaries are not always the cause.
- When treating infertility with hormonal medications, ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome may occur. In this case, they increase in size and a tingling sensation is felt. At the same time, the woman notes weight gain.
- Psychological problems can also cause pain in the right side. Most often these are so-called “phantom” pains that appear during depression or neurosis.
Pain in the ovaries associated with the menstrual cycle: causes, signs
Without instrumental and laboratory tests, it is difficult to identify the cause of organ pain. There are two types of pain in the left ovary - physiological and pathological. The first ones can be distinguished independently; to do this, just listen carefully to your own body.
Physiological
| Cycle day | Causes |
| 1-3 | The course of menstruation. Due to temporarily increased blood circulation during menstruation, there is pain in the left ovary. The symptom is especially acute in the presence of functional cysts. |
| 8-13 | Stage of follicle maturation. Their increase may be accompanied by slight nagging pain in the woman’s left ovary. |
| 14-15 | Ovulation. When the Graafian vesicle ruptures and the egg is released, there is sometimes a short-term acute pain of low intensity in the left lower abdomen. The duration of the symptom is from several hours to 1-2 days. |
| 26-28 | Preparing for the start of menstruation. |
A physiological symptom may be completely absent. Its presence is determined by the individual characteristics of the body. Often women who feel such pain in the left ovary experience severe discomfort in the lower abdomen during menstruation.
Pregnancy
Pain of natural origin includes pain during pregnancy. Successful conception may be manifested by unpleasant sensations in the left lower abdomen. The sign appears from the first days of a missed period. Its absence cannot exclude pregnancy, since its occurrence is individual.
The symptom is caused by the growth of the corpus luteum, which produces progesterone. This is explained by the body’s increased need for this hormone during gestation. Pain in the left ovary is often accompanied by nausea, dizziness, weakness and drowsiness. All these signs are a consequence of increased progesterone levels.
Pathological
Pain associated with the course of diseases of the left ovary appears regardless of the day of the menstrual cycle. They can have a pulling, stabbing, cutting or aching character and are more intense than physiological pain syndrome.
| Disease | Description and symptoms |
| Inflammatory processes in the uterus and appendages | Nagging pain in the lower abdomen, painful menstruation. Possible disruption of the monthly cycle. With an acute type of organ inflammation, body temperature rises. |
| Infectious lesions of the genital tract | Pain syndrome occurs only when the infection is widespread. Accompanied by pathological vaginal discharge with an unpleasant odor, itching and burning of the external genitalia. |
| Hormonal disbalance | Pain in the left ovary due to hormonal imbalance often indicates its multifollicularity or the occurrence of functional cysts. At the same time, there are frequent delays in menstruation, probably their complete absence. Menstruation is characterized by high profuseness and pain. |
| Tumors | In the first stages of development of any tumor, there are no symptoms. Pain occurs only when the tumor reaches a size of more than 4-5 cm. Large tumors are manifested by asymmetry of the abdomen, with pain radiating to the left ovary and lower back. During the course of the malignant process, the menstrual cycle is disrupted, health deteriorates, weakness appears, and performance decreases. |
| Endometriosis | Initially it affects the uterus, then through the fallopian tubes the ovaries. It is determined by nagging pain in the lower abdomen, intermenstrual uterine bleeding, and interruption of menstruation. |
| Rupture of the appendage or its cyst | It manifests itself as acute severe pain in the left ovary; over time, its focus becomes impossible to determine due to the spread of pain throughout the entire abdomen. Distinctive signs of apoplexy are cold sweat, drop in blood pressure, increased heart rate, loss of consciousness or faintness. |
| Ovarian torsion or cysts | The symptoms are similar to a rupture, but are much less intense. Prolonged presence of an organ in a state of torsion can lead to its necrosis. |
| Adhesive process | It occurs as a result of a long course of inflammatory processes, endometriosis, as a postoperative complication. If the left ovary is affected by adhesions, there may be pain in the lower abdomen and disruption of the menstrual cycle. |
| Ectopic pregnancy | Until 6-8 weeks it manifests itself only as a delay in menstruation. Subsequently, the fertilized egg causes severe sharp pain in the area of the left ovary or fallopian tube. Surgery is required to eliminate it, otherwise the fallopian tube may rupture. |
The type of pathology cannot be determined independently. To make a diagnosis, a comprehensive examination of the body is required.
Pain in the left ovary can occur after gynecological operations and other similar manipulations. These include:
- laparoscopy or laparotomy in the pelvic area;
- abortion;
- spontaneous miscarriage;
- curettage of the uterus.
After all of the above, the functioning of the ovary is temporarily impaired. This is caused by artificial intervention during the menstrual cycles, in the case of miscarriage - sudden termination of pregnancy. The functionality of the appendage is restored within several months, during which pain may be present.
There are many diseases of the right ovary that manifest as discomfort. By the type of symptom, you can determine the severity of the disease and the likelihood of its spread to the left paired organ, uterus and fallopian tubes.
These types of pathologies include oophoritis and adnexitis. As they progress, inflammation affects the appendages, causing them to enlarge and swell. This is accompanied by nagging pain in the area of the right ovary, which can spread to the lower back.
Pain due to inflammation is constantly present. In the acute form of the disease, it occurs suddenly and is characterized by high intensity, which decreases as recovery progresses. Chronic oophoritis is accompanied by periodic mild pain in the right ovary.
Infections, fungi and other microorganisms cause inflammation of the affected organs. Infection of only the right ovary is rare because penetration of pathogenic bacteria into the genitals usually occurs through the vagina. Most often, the appendages become infected after the uterus and fallopian tubes.
Infectious processes in women are manifested by aching pain in the right ovary. Pathology can be present without pain. A characteristic sign of the presence of pathogenic microorganisms in the genital tract is a change in the appearance of vaginal discharge, which acquires a yellowish or greenish tint and an unpleasant odor.
Adnexitis is an infectious inflammation of the right ovary and its fallopian tube. The causative agents of the disease are candida, mycoplasma, ureaplasma, chlamydia. Pain during the course of the pathology manifests itself in the area of the affected organ and is aching in nature, often spreading to the lower back. The symptom may periodically weaken and intensify again. This indicates an advanced course of adnexitis.
If pain occurs on the right side of the ovary and body temperature rises above 37 degrees, acute or subacute adnexitis is diagnosed. Its treatment should be started immediately, otherwise it can develop into a chronic form of the disease.
Organ apoplexy
The rupture of the right ovary is accompanied by severe acute pain in its area. Additionally, the appearance of cold sweat, a drop in blood pressure, and increased heart rate are noted. Possible lightheadedness or fainting. Some time after apoplexy, the pain syndrome spreads to the entire abdomen, which makes it difficult to diagnose the pathology.
When the first symptoms of epididymal rupture appear, the woman should be immediately taken to the hospital. If treatment is refused or medical care is not provided in a timely manner, peritonitis is likely to develop, which threatens the life and health of the patient.
Sometimes, to prevent the development of negative consequences, it is necessary to remove the ovary. This is done during laparoscopy or laparotomy. The last type of intervention is necessary when the woman’s condition is serious. During the rehabilitation period after removal of the ovary, there is pain in the right side, which normally should not last more than a month.
The non-standard location of the ovaries can be either a congenital feature or an acquired pathology. If pain occurs in the appendages, there is a high risk of torsion of their legs or rupture during pregnancy, surgery is required.
The pain syndrome with an atypical location of the right ovary is sharp. It can intensify during physical activity and when lifting weights. Often, the abnormal location of organs manifests itself during sex in the form of pain in the right side in the area of the ovary.
Cysts and tumors
Small ovarian neoplasms are often asymptomatic. Their increase causes a nagging pain in the right lower abdomen. Often, cysts of a functional nature provoke disruption of the menstrual cycle - long delays in menstruation.
With a tumor or large cyst of the right ovary, pain is often present, which intensifies with physical activity, sexual intercourse, and heavy lifting. A formation larger than 10 cm can cause acute pain radiating to the leg or sacrum - this is caused by compression of the nerve endings. In some patients, the pain in the area of the right ovary becomes so severe that they lose their leg and the process of walking becomes difficult. This is true for tumors more than 20 cm in diameter.
Apoplexy cyst
Acute pathology most often requires surgical intervention. Symptoms of cyst rupture are the same as with ovarian apoplexy. The condition is dangerous due to the development of an extensive inflammatory process resulting from internal bleeding and the entry of cyst contents into the peritoneum.
Accompanied by acute pain in the right lower abdomen. Symptoms are similar to a ruptured cyst, but less pronounced. Twisting of the capsule leg requires emergency medical attention, otherwise there is a high risk of apoplexy of the formation or the ovary itself.
Prevention methods
It is impossible to prevent physiological pain. If they are present, it is allowed to take painkillers. There is likely to be a slight decrease in their intensity when leading an active lifestyle - regular exercise, a balanced diet.
Measures to prevent pathological pain in the left ovary include preventing diseases of the genital organs. Experts recommend the following to women:
- visiting a gynecologist once every six months, during natural hormonal imbalances - once every 3-4 months;
- refusal to take medications without a doctor’s prescription;
- use of barrier methods of contraception;
- balanced diet;
- taking vitamins in the spring and winter;
- Immediately consult a doctor if pain occurs in the lower abdomen and changes in the nature of the monthly cycle;
- timely treatment of all pathologies.
It is impossible to prevent the development of diseases with one hundred percent probability. Prevention measures are aimed at reducing the risk of diseases and improving sexual health.
If pain occurs in the left ovary, a woman should consult a doctor. The help of a specialist is not required only in the event of pain of a physiological nature. In other cases, after undergoing a comprehensive diagnosis, the doctor prescribes treatment for the appendage. The earlier the disease was detected, the faster a complete recovery will occur.
Primary diagnosis and pain relief
As mentioned earlier, if a girl feels discomfort in the left ovary, then there are various reasons for this. Some do not pose a threat to health and disappear on their own in the near future. Others appear periodically and with varying intensity. It is these symptoms that should alert you, as they can lead not only to a deterioration in your general health, but also to infertility. What to do in this situation? The first thing you need to do is contact a specialist and undergo a gynecological examination. Using palpation, the gynecologist will palpate the ovaries, determine their size and localization of pain. This pressure on different areas of the lower abdomen makes it possible to find out the main cause of discomfort in the left ovary and will direct you to an ultrasound to confirm or refute the diagnosis. To determine the cause for sure, a specialist may also prescribe tests.
You can relieve painful symptoms yourself. However, this should only be done after consulting a doctor. To do this, you must adhere to the following recommendations:
- pause training and avoid other intense physical activities;
- eat well and add as many vitamins as possible to your diet;
- do not drink or smoke;
- avoid conflict situations and stress;
- take painkillers.
Thus, the appearance of even minor pain in the left ovary requires a mandatory examination and compliance with all the instructions of a specialist.
Often women experience pain in the lower abdomen. However, sometimes there are no deviations in health status. It also happens that only the left ovary “pulls.” If there are other symptoms, then we can assume the presence of hormonal imbalances in the body or some kind of disease. Often the sensation is weak, and the woman puts up with it instead of going to the doctor. But sometimes acute pain forces you to immediately call an ambulance. Any complication in the functioning of the ovaries is fraught with serious complications, so it is necessary to carry out timely diagnosis and treatment.
- Inflammatory diseases
- Endocrine diseases
- Pathologies resulting from changes in the structure of the ovaries
- Ovarian dysfunction
- Complications, signs of pathological conditions
- Causes of pain in the ovary at different periods of life
- How to avoid complications, diagnosis
Nagging pain after medical procedures
A nagging pain in the ovaries is observed for several days after drug manipulation. These include procedures such as in vitro fertilization, removal of cystic formations, tubal ligation, etc. The recovery period after any surgical intervention on the appendages is accompanied by pain. Normally, this lasts for 2-3 days. In this case, there should not be a pronounced increase in temperature and other inflammatory symptoms. One of the stages of the IVF procedure is the transfer of embryos into the uterine cavity. This process is accompanied by a hormonal reaction from the ovaries. Therefore, slight nagging pain is considered normal in this case.
Answers to basic questions
The main questions that worry women and to which you need to know the answers so as not to miss a serious illness or complication.
When to call a doctor
You should call an ambulance in case of sharp, sudden, throbbing pain, accompanied by nausea, vomiting, fever, and general weakness. With these symptoms, the patient requires mandatory hospitalization.
If there is throbbing pain on the side of the left or right ovary, this may indicate torsion of the cyst stalk.
An increase in temperature, spotting, pulsation in the lower abdomen after hysteroscopy or ablation (curettage) of the uterine mucosa requires immediate medical intervention.
There is throbbing pain, nausea, vomiting, abdominal tension, bleeding - the main symptoms of a ruptured tube during an ectopic pregnancy, spontaneous miscarriage (abortion), ruptured appendix - you urgently need to call an ambulance.
Important: Such conditions, which doctors call “acute abdomen,” are dangerous to health and life. Therefore, you should not hesitate to see a doctor.
Pulsation radiating into the leg is a consequence of diseases such as complications of a hernia, femoral or inguinal, purulent inflammation of the appendages, acute appendicitis. The best decision is to call an ambulance for immediate hospitalization.
Which doctor should I contact for pain in the ovary?
If you experience mild pain that does not require urgent medical intervention, you need to make an appointment with your local gynecologist and undergo an examination. If there is an assumption that the symptoms are caused by other concomitant pathologies, the doctor will prescribe consultations with the appropriate specialists.
What tests can doctors prescribe for pain in the ovary?
The list of studies depends on the presumptive diagnosis, the possibilities of outpatient or inpatient treatment.
- general or detailed blood and urine tests;
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs;
- intravaginal gynecological examination.
If infectious inflammation of the reproductive organs is suspected, vaginal smears or bacterial culture of microflora, sexually transmitted infections (mycoplasma, chlamydia, ureaplasma, gardnerella, gonococcus, candida) are prescribed.
If syphilis or HIV is suspected, an appropriate venous blood test is prescribed.
To identify endocrine disorders of the reproductive glands, blood tests are prescribed for the following hormones:
- LH – luteinizing;
- FSH – follicle stimulating;
- testosterone, estrogen, prolactin, progesterone;
- TSH – thyroid stimulating;
- SHBG – sex hormone binding globulin;
- DEA-S04 – dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate.
If a thyroid disease is suspected, additional tests for hormone levels are prescribed:
- T4-thyroxine;
- T3 – triiodothyronine;
- AT-TPO and AT-TG – antibodies to thyroid peroxidase and thyroglobulin.
If viral pathologies are suspected, blood tests are prescribed to possibly detect cytomegalovirus, papilloma viruses, herpes, and Epstein-Barr.
To clarify the diagnosis and simultaneous treatment, puncture and laparoscopy may be prescribed.
Can the ovaries hurt?
Of course they can. But it is impossible to independently determine whether the glands or other pelvic organs are suffering. Only a doctor can make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe treatment. If pain occurs, it is not recommended to take analgesics on your own, so as not to blur the clinical picture of a possible disease.
When the ovaries hurt
Pain syndrome in the lower abdomen, on the right or left, can manifest itself in various diseases of both the pelvic organs and the abdominal organs. Therefore, in such cases, differential diagnosis is necessary to exclude concomitant pathologies.
Why does the ovary hurt?
Tingling in the ovary is not always a sign of pathology. Symptoms such as aching, stabbing pain, aggravated by walking, can be observed after ovulation, when the contents of the follicle enter the abdominal cavity.
Tingling in the area of the right ovary occurs during pregnancy, as the growing fetus puts pressure on the glands and fallopian tubes.
In any case, only a specialist can make an accurate diagnosis.
How to understand that it is the ovary that hurts
It is impossible to answer unequivocally the question of why women’s ovaries hurt without a full examination. If the ovary is pulled for a long time, after menstruation, you definitely need to consult a gynecologist.
Why does my right ovary hurt?
The right ovary hurts and pricks when the egg matures in it. This is the so-called ovulatory syndrome, which does not require emergency treatment. The right ovary can be pulled before, sometimes during menstruation, during rough sex. The pain may be due to a developing cyst, benign or malignant tumor. Infections, hormonal disorders, endometriosis, apoplexy, ectopic pregnancy, torsion of the pedicle of the cyst, appendix provoke pain on the right side.
Why does my left ovary hurt?
Accordingly, similar causes of pain in the right ovary may appear in the left. But the left ovary hurts and stings less often than the right. The reason is that on the right side there are more arteries supplying the female organ. The gallbladder and appendix are located on the same side. Pain on the left side can be caused by the sigmoid colon, which is stretched due to untimely bowel movements.
Why do ovaries hurt in women?
Ovarian pain can be a natural physiological reaction of the body that occurs before and after menstruation, or it can be caused by pathological processes. Another reason is the abolition of long-term use of oral contraceptives. After stopping the medications, the functioning of the glands is restored, which is accompanied by aching symptoms, tingling, and nagging pain. Discomfort also occurs after surgery, which goes away after complete healing of the operated organ.
Causes and types of inflammation
Even if a girl dresses warmly and has no infections, there is still a risk of inflammation.
Poor immunity, poor diet, bad habits - all this provokes inflammatory processes. We already know why the ovaries hurt - because of inflammation. There are two types - adnexitis and oophoritis. With adnexitis, the ovary itself is inflamed, and with oophoritis, its appendages are inflamed. The girl will not be able to independently determine what type of disease it is. The symptoms are very similar to each other: pain, sharp or wave-like, throbbing or constant. Girls often ask why their ovaries hurt on the first day of menstruation. This is a common occurrence for nulliparous young women.
The reasons why pain occurs can be associated not only with inflammatory processes. If a girl experiences pain depending on her position and movement, this often means that a cyst is beginning to form. Then an operation is necessary to remove the formation that is causing the ovaries pain.
Factors in the development of pain
If the ovary on the left hurts, the reasons for women may be different. Let's take a closer look below at the factors that contribute to the development of such pain in the ovaries.
Stopping the development of an embryo outside the uterus
Due to a violation of the patency of the tubes, the presence of adhesions, pregnancy could begin in the fallopian tube itself.
Such pregnancy outside the uterus can lead to two forms:
The sensations in these two cases will be similar. The girl feels excruciating pain in the abdomen, spreading to the uterus.
- The patient becomes pale, powerless, a headache appears, and the woman may faint.
- Against the background of what is happening, the patient develops a state of shock: the pressure becomes low, the pulse becomes frequent.
- The blood of the uterus flowing from the tubes can even enter the space between the organs.
Important! Under no circumstances should such symptoms be ignored.
Severe pain symptoms are also felt in the anus. Pain arising from pregnancy stopping outside the uterus will be severe upon examination.
The current condition is considered dangerous. Immediate surgical intervention is necessary, otherwise this condition may threaten the woman’s life.
Torsion
An acute condition when the ovarian ligaments are twisted, interrupting the flow of blood to the gland. The ligaments that support the ovary become twisted for one reason or another, disrupting its normal functioning.
What happens to a woman when her left ovary is torsioned:
- sudden pain in the appendage;
- discharge mixed with blood;
- nausea and vomiting;
- rapid heartbeat;
- problems with urination;
- increased body temperature and others.
Ovarian torsion poses a huge danger to the female body. This pathological condition can affect not only the ovary, but also pose a danger to other organs of the abdominal region. And this can ultimately result in peritonitis and death.
Therefore, in order to maintain her health and reproductive function, every woman should know that if any suspicious symptoms appear, she should go to the hospital for qualified help.
Apoplexy
Apoplexy is bleeding that opens inside the ovary. This is profuse bleeding into the peritoneum. It occurs most often when the girl is not yet 40 years old. The patient feels unexpected pain in the gland.
The disorder can take two scenarios due to accompanying symptoms:
- The first case is painful. This state is accompanied by powerful, undying feelings directly at the site of the glands. The skin color begins to turn gray, the patient’s blood pressure drops, and powerlessness sets in. Other signs are not expressed as clearly as painful feelings. Shock is added to this situation. The patient may lose consciousness.
- The second variation is hemorrhage. It is expressed not only in pain, but is also accompanied by signs of large blood loss. Blood pressure drops significantly. There is pale skin, a feeling of powerlessness and dry skin. The girl may experience a state of shock. Sometimes such an attack may not be accompanied by pain.
Cyst formation in the ovary
A cyst is a formation on the appendage, which is filled with contents of various structures, similar to a sac with a thin shell. The cyst can be of different types. In the vast majority of cases, this is a functional cyst.
That is, the follicle in which the egg grows must burst every month for the egg to be released, and in its place a corpus luteum will form, secreting hormones. It persists throughout pregnancy, if conception has occurred.
A neoplasm is formed if the follicle has not burst and begins to fill with fluid. This often goes away after a month, then the cyst resolves.
A neoplasm occurs against the background of hormonal imbalance. But you should definitely consult a doctor if you have persistent pain symptoms.
The cyst can also be hemorrhagic, when blood vessels burst inside the follicle or corpus luteum, bleeding occurs and unpleasant pain occurs.
Another type of cyst is dysontogenetic. Appears directly during the growth of glands in adolescence
The greatest danger is posed by a tumor cyst, leading to carcinoma, or, as we used to call it, cancer of the appendage.
A woman should know that any cramps, colic, excruciating pain in the appendages, lower abdomen, dizziness and other ailments become urgent reasons to make an appointment with her gynecologist to maintain health.
Groaning pain with andexitis
Andexitis disease is accompanied by aching pain. Caused by chlamydia, candida and other sexually transmitted infections. The presence of pathologies can be determined by certain symptoms: the groin area will sting when touched, and the lower back will hurt.
Soreness can be localized in more than one place. If the functioning of the female reproductive glands is disrupted, the sacrum may also suffer.
Oaphoritis is a disease that is expressed instantly in two ovaries. Formed if the body is very overtired. If the patient falls ill due to hypothermia, then his resistance decreases. This condition causes enormous discomfort and pain.
A competent doctor will quickly detect the disease and tell you what actions need to be taken in the presence of apoplexy or bleeding directly into the internal pelvic cavity.
How to avoid complications, diagnosis
If the pain is constant or occurs regularly during sexual intercourse, you should visit a doctor to get a diagnosis. The presence of inflammation and infections is determined using blood tests and a vaginal smear. Changes in the size and shape of the left ovary will be visible on an ultrasound.
When prescribing treatment, the nature of the symptoms, the duration of the pathological condition, and the woman’s age are taken into account. If necessary, consultations with an endocrinologist, urologist, and surgeon are carried out.
Under no circumstances should you self-medicate or use a heating pad to relieve pain. Heat will provoke the development of an inflammatory process or increased bleeding. Any medications (even painkillers) must be taken as prescribed by a doctor. Temporary improvement sometimes masks the symptoms of serious illnesses.
If there is unidentified pain in the ovary, it is necessary to avoid physical activity and avoid stress.
Video: Why does the left lower abdomen hurt?
Benign and malignant tumors
We must not forget that the ovary on the right can hurt due to a tumor. At the initial stages of its development, it does not reveal itself in any way. Most often, women become aware of the problem only when the formation grows to a large size and begins to put pressure on neighboring internal organs - the rectum, bladder, uterus. Blood circulation in the abdominal cavity and pelvic area is disrupted, and severe spasms occur.
We also recommend viewing: What consequences does ovarian rupture entail?
Side symptoms that are observed in the presence of a benign tumor:
- constipation and difficulty urinating;
- prolonged absence of menstruation;
- in some cases, an increase in waist size due to the accumulation of a large amount of excess fluid in the abdominal cavity (ascites);
- pain in the ovary radiates to the leg or lower back.
The female body also does not react in any way to the appearance of a malignant tumor for a long time. Then a sensation appears as if the right ovary is being pulled, but since the painful discomfort does not last long, it is rarely paid attention to. Then the pain becomes more frequent, the stomach begins to grow, and the same symptoms appear as in the presence of a benign formation. A malignant tumor can be recognized by general health: weakness, increased fatigue, and sudden weight loss. To diagnose ovarian cancer, a whole range of measures is carried out: ultrasound, puncture, blood test for the presence of tumor markers.
Causes of pain
Regular ovulation, which occurs every month, can cause pain. Such pain will be aching in nature. If it becomes strong during ovulation, you can take a painkiller. There are other reasons why the ovary hurts before menstruation.
But you need to be careful and exclude the presence of any pathology. Therefore, if the pain does not go away, be sure to consult a doctor.
Unusual sensations in the left appendage may appear when using hormonal drugs to protect against unwanted pregnancy or treat hormonal disorders. They affect the functioning of the ovaries.
In this case, it is better to stop taking it or change the drug. In any case, you need to resort directly to the help of a qualified specialist. The doctor will examine you and give recommendations.
Most often, these unpleasant feelings arise as a consequence of the inflammatory process, due to the attachment of a fertilized cell outside the uterus, apoplexy, twisting of the appendage leg or the formation of a cyst, and others.
Note! Due to inflammatory outbreaks, not only the ovaries ache, but also all internal organs without exception.
Functioning of the ovaries
The ovaries are located to the right and left of the uterus and are connected to it by the fallopian tubes. These organs are the “producers” of eggs and female sex hormones. A woman’s fertility level depends on the health of the ovaries, i.e. ability to conceive and bear a child. The normal size of the ovaries is 30-41 mm in length, 20-31 mm in width, and the normal thickness of the organ is about 14-22 mm. Any deviations from these parameters are a reason to contact a gynecologist and identify the causes of the violations.
With normal functioning of the paired gonads, women do not experience severe pain, and the monthly cycle is regular. Various pathologies of the reproductive system can cause discomfort in the ovaries.
How to treat a pain symptom
Without doctors, it will not be possible to simply get rid of the problem. Initially, during the consultation, the patient is given standard recommendations: be at rest, take pain medication, reduce physical activity, stress, and encounters with troubles and stress to a minimum. You need to watch your food during this time, and also refrain from smoking and alcohol.
If a woman suspects some dangerous disease, she should not take independent measures or self-medicate. The therapy complex is prescribed directly only by the gynecologist.
If the condition is acute, you need to call an ambulance. You should not take any painkillers irresponsibly, this may not help, and the condition will only worsen. Any medications must be prescribed by a qualified specialist.
Ovarian cyst
Depending on which ovary is affected by the cystic neoplasm, pain may occur on the right or left. When both ovaries are simultaneously affected by cysts, painful sensations occur throughout the lower abdomen.
With cysts, most often the pain is of a pulling or aching nature.
If the cystic formation is small, then it does not cause any concern or pain and the woman finds out about them by chance, for example, during an ultrasound examination. It should be recalled that a woman also has functional cysts, for example, the corpus luteum, which do not require treatment.
Cysts on the legs are especially dangerous, since with any load, heavy lifting, or sudden change in the position of the woman’s body, torsion or twisting of the legs of the cyst can occur - a condition characterized by a clinical picture of an acute abdomen (severe pain with characteristic symptoms). If the patient is not provided with timely medical care, malnutrition of the cyst, inflammation, peritonitis, sepsis and death may develop.
Gynecological pathologies of the ovaries
Gynecological pathologies include acute and chronic salpingoophoritis, cystic formations in the ovaries, as well as sexually transmitted diseases. Most often, women develop inflammatory processes. They are caused by hypothermia, urinary tract infections, poor personal hygiene, etc. If the right ovary hurts, adnexitis should be differentiated from inflammation of the appendix of the cecum (appendicitis). Unpleasant sensations in the lower abdomen during salpingoophoritis are accompanied by other symptoms. These include: increased body temperature, menstrual irregularities, and the appearance of vaginal discharge.
Symptoms of ovarian pathologies
One of the main criteria by which physiological pain can be distinguished from pathological pain is the presence of accompanying symptoms. Discomfort observed normally is not accompanied by other signs of pathology. If, in addition to nagging pain, there are other symptoms, you should contact a gynecologist as soon as possible. Manifestations of diseases of the female reproductive system include:
- Increased temperature and general weakness.
- Menstrual irregularities.
- Increased pain during sexual intercourse and physical activity.
- The appearance of vaginal discharge of an unusual color and with an unpleasant odor.
- Pain when urinating.
If these symptoms appear, you should be examined by a gynecologist. In some cases, consultation with other specialists is necessary - an infectious disease specialist, nephrologist, endocrinologist, oncologist.
Physiological reasons
In the ovaries, follicles with eggs mature and the female sex hormones estrogen and progesterone are produced. The condition of these organs determines a woman’s reproductive ability, her general health and age-related characteristics of the body. The maturation of the egg and related processes most often occur alternately in the left and then in the right organ. The causes of pain in the ovaries are both ongoing physiological processes and various pathologies.
Natural reasons for pain in the groin area are:
- Menstruation. If the left ovary begins to hurt, this means that it is the one that is active in this cycle. Nagging pain is observed in most women, even without any pathologies in the condition of the genital organs. The regular occurrence of such ailment a few days before menstruation allows many women to predict their onset. Painful sensations continue during menstruation and even after it ends. The reason is changes in hormonal levels during the cycle.
- Ovulation. Around the middle of the cycle, a mature egg breaks the follicle membrane and leaves it, moving into the fallopian tube. In this case, the nerve endings are irritated, resulting in pain. Their intensity depends on the sensitivity of the body.
- Pregnancy during its normal course. The cause of mild pain in the left groin may be a natural hormonal shift that changes the structure of the ovaries and endometrium.
- Postoperative healing of the left ovary.
- During sexual intercourse, there may be an impact on the lower abdomen, which sometimes causes an aching sensation of mild pain and tingling. However, pain in the groin after sexual intercourse in most cases is a sign of serious illness. You should pay attention to how often it occurs and what other symptoms appear. An examination by a gynecologist helps to determine the nature of the pathology.
- Emotional experiences, heavy physical exertion.
What pathologies can cause discomfort in the left ovary
If the left (right) ovary hurts, in most cases there is a serious reason for this: pathologies associated with hormonal imbalance, infectious and inflammatory diseases, disruption of the structure of the organ.
Inflammatory diseases
Oophoritis and adnexitis. The inflammatory process that occurs in the ovarian appendages is called oophoritis. If it spreads to the fallopian tube, then adnexitis (or salpingoophoritis) appears.
The cause of inflammation can be the entry of pathogens of sexually transmitted infections into the appendages. In this case, the spread of infection occurs from the external genital organs to the internal ones. Another option is also possible: under certain conditions (hypothermia of the lower part of the body, decreased immunity), the opportunistic microflora present in the internal genital organs is activated.
More often, such diseases occur in the right ovary, located closer to the appendix and small intestine, from where the infection easily enters the ovary with the blood. Right-sided adnexitis is often mistaken for appendicitis, which is manifested by the sudden onset of sharp pain in the groin and abdomen.
Left-sided inflammation is accompanied by gradually increasing paroxysmal pain. The blood supply to the left ovary is not so intense, and inflammation occurs less frequently here.
Endocrine diseases
The work of the ovaries is regulated by pituitary hormones, the deficiency of which is caused by diseases of this organ. Hormonal imbalance also occurs when the thyroid gland and adrenal glands malfunction.
Pathologies resulting from changes in the structure of the ovaries
Apoplexy. Severe pathologies include rupture of the membrane of the left or right ovary, which can cause dangerous internal bleeding. In this case, the ovary hurts unbearably on the left or right side.
Twisting of the base of the organ leads to the cessation of its blood supply and the formation of necrosis. Both of these conditions are manifested by sharp, sudden pain and signs of blood loss. If they occur, you must urgently call a doctor. Surgery is required.
Cysts and tumors. Pathology is caused by compression of nerve endings and neighboring organs when the tumor reaches a significant size. Damage to the cyst and its contents entering the abdominal cavity are also possible. The occurrence of severe pain from a damaged ovary can also be associated with twisting of the stalk with which it is attached to the ovary.
Dysplasia and ovarian cancer lead to the destruction of its tissue.
Adhesions between the ovaries and tubes, as well as the walls of the abdominal cavity, prevent the free movement of organs, which causes constant nagging pain.
Endometriosis. In this case, particles of the mucous membrane of the uterine cavity enter the ovary, from which an endometrioid cyst can form. It may further degenerate into cancer.
Video: What threatens inflammation of the appendages, the causes
Ovarian dysfunction
Violation of ovarian function can occur both as a result of their diseases and for other reasons:
Complications, signs of pathological conditions
Complications of the disease may include infertility, the occurrence of acute conditions that are dangerous to health and life, and the appearance of malignant neoplasms.
Signs by which disease can be suspected are cycle disruptions, urination problems, constant pain in the groin, fever, and weakness. If the lower abdomen hurts on the left or right side, and a condition of “acute abdomen” is observed, emergency hospitalization of the patient is required.
Why does the ovary pull before menstruation?
Painful sensations of a pulling nature may occur after ovulation. During this period, a large amount of the hormone progesterone is released. In the absence of pregnancy, a woman’s body prepares for the rejection of the endometrium - menstruation. Women during this period often complain that the left ovary is pulling (or the right, depending on the location of the dominant follicle). Sometimes discomfort indicates pregnancy. In this case, nagging pain occurs due to the implantation of the fertilized egg. If pregnancy does not occur, then discomfort occurs due to rupture of the follicle.
The ovary is a glandular organ of the female reproductive system, in which changes occur constantly. Pain can not only accompany ovulation, but also continue for several days after it. After all, the gland tissue undergoes physiological damage during follicle rupture. Healing occurs in a short period of time and is not accompanied by severe pain.
If the discomfort continues for a long time, you should consult a gynecologist. In addition, indications for consulting a doctor are nagging pain of high intensity that is constant. They may indicate the occurrence of cystic formations, an inflammatory process, or the onset of an ectopic pregnancy. All these pathologies require immediate treatment.