Increased echogenicity of the liver
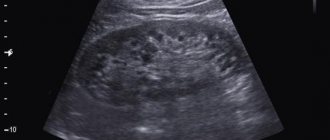
An increase in echogenicity indicates that the liver walls are thickened and difficult to transmit ultrasound waves. In this case, the cause must be identified immediately.
Causes
Increased echogenicity of the liver may be due to the following reasons.
| Disease | Peculiarities |
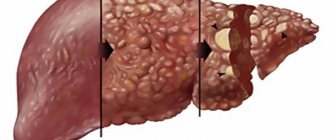
| Cirrhosis of the liver | Enlargement of the organ, followed by dystrophy and reduction in size; heterogeneous, granular structure. The echogenicity may be mixed, depending on the point of organ damage. |
| Liver abscess | First, the echogenicity is reduced - the inflammatory process begins. As the abscess grows, the appearance of increased echogenicity increases. |
| Chronic hepatitis (necrosis of the liver parenchyma) | The structure of the liver is homogeneous, and the echogenicity is moderately increased. |
| Dystrophy | The liver is slightly enlarged. Echogenicity increases with increasing ultrasound saturation from fatty inclusions in liver cells. |
| Chronic cholangitis | High echogenicity is manifested in the intensity of wave reflection from the walls of the dilated bile ducts. |
| Alveococcosis | Invasive and healthy liver tissues are blurred, the structure is reticular, and the echogenicity is diffusely increased. |
In addition, high echogenicity can be a consequence of:
- adenomas;
- hemangiomas;
- alcoholic fibrosis;
- obesity;
- sudden weight loss;
- diabetes mellitus;
- uncontrolled use of medications.
Alveococcosis
Tumor
Symptoms
Negative echogenicity may manifest as:
- sudden and causeless nausea and vomiting;
- yellowish skin tone;
- regular pain under the right breast;
- indigestion;
- overweight and obesity;
- heart problems;
- disorders in the immune system.
results
What's the norm?
In the absence of pathologies in the CT results, this parenchymal organ is located in the right hypochondrium and has dimensions corresponding to age indicators. A normal liver has clear boundaries and sharp corners. On the lower surface there is a gall bladder with ducts, of which there are normally 5. Healthy people should not have protrusions, depressions, round or irregularly shaped formations, or a decrease in the echogenicity of the structure.
Deviations
Pathology is diagnosed when abnormal elements appear on the tomogram. They can be detected at different depths of the organ parenchyma in the form of a cavity, cyst, or pathological tissue. If the organ is reduced in size, this means that normal hepatocytes have been replaced by connective tissue, which is the basis for the development of cirrhosis. CT reveals formations in the early stages of occurrence, features of their blood supply, relationships to neighboring organs and systems, the depth of invasion into hepatocytes and neighboring structures.
The echogenicity of the liver is reduced
Low echogenicity of the liver is the result of compaction of the liver tissues and the accumulation of fluid in them.
The liquid almost does not reflect ultrasonic waves, so on the monitor of an ultrasound machine, areas of the liver appear as dark dots.
Causes
The reasons for the decrease in echogenicity are:
- acute hepatitis;
- liver swelling;
- liver failure;
- tuberculosis metastases;
- parasitic diseases;
- liver abscess.
Symptoms
Signs of low echogenicity:
- skin itching and jaundice;
- lethargy;
- nausea and vomiting;
- intense pain under the right breast;
- enlargement and hardening of the liver;
- rapid and significant weight loss;
- darkening of urine.
What it is?
Echogenicity is a technical term used in echography to refer to the ability of organs to reflect sound waves.
The ultrasound machine converts sound waves reflected from tissues with different acoustic densities into a picture that is visible on the screen during the examination. Knowing the exact data on the echogenicity of each organ, the doctor states an increase or decrease. Deviation from generally accepted parameters means that negative factors provoked diffuse changes in the structures and functioning of internal organs: kidneys, pancreas, intestines, spleen, stomach and liver. Ultrasound makes it possible to visualize organs, identify the disease and monitor its dynamics.
When the echogenicity of the parenchyma of an organ is increased, it means that at the moment its tissues are different from healthy ones. If echogenicity increases or decreases, or the homogeneity of the structure or contours of an organ changes, a targeted examination of the questionable area is carried out. Interpretation of ultrasound gives a clear idea of the condition and diffuse changes in the liver parenchyma and the entire digestive system. The manipulation allows the doctor to clarify the following questions:
what is the density and size of the organ; homogeneous or heterogeneous structure; are scars or nodes present; what is the concentration of metabolic products; infection with worms; are there tumor formations; condition (expansion or narrowing) of blood vessels and bile ducts; formation of stones and obstruction of veins; is it accompanied by increased echogenicity and enlarged lymph nodes.
Diagnostics
If the echogenicity of the liver parenchyma is increased or decreased, the doctor may prescribe additional diagnostic methods:
- CT (computed tomography). It is prescribed to confirm the increased echogenicity of the organ.
- Blood chemistry. With its help, you can clarify data about the processes occurring in the liver, as well as detect HIV and hepatitis markers.
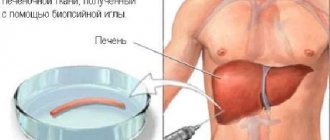
- Biopsy. Makes it possible to confirm or exclude malignant formations in a separate area of the liver if local heterogeneity of echogenicity is recorded.
The doctor makes the final diagnosis after combining the data from a medical study:
- general analyses;
- Ultrasound of the liver;
- patient complaints.
Ultrasound of the liver in a video from the author VitapowerTV.
Advantages and disadvantages
Liver CT has the following advantages:
Possibility of examination in different projections.
- speed of execution and obtaining results;
- easy preparation;
- a small number of adverse reactions;
- absence of pain;
- non-invasiveness of the technique;
- quality of images in 3 planes;
- comprehensive examination of the organ;
- diagnostics of the vascular and lymphatic system of the liver;
- Possibility of use for people with severe obesity;
- detection of diseases at early stages of development;
- examination of the gallbladder and ducts.
The disadvantages of computed tomography include:
- high price;
- the possibility of developing adverse reactions to the contrast agent;
- exposure to small doses of x-rays;
- the need to stay in a closed space for some time.
Treatment options
The specialist selects the treatment method for each person individually, based on:
- type of pathology;
- severity of the disease;
- accompanying illnesses.
In any case, you need to carry out a series of cleansing measures to remove toxins and waste.
Drug therapy
For effective treatment, doctors use symptoms relief techniques:
- antispasmodics suppress severe pain;
- choleretic agents prevent congestion in the hepatic ducts;
- diuretics help get rid of excess accumulations and abdominal cavity;
- disaggregants restore the functioning of blood vessels and enrich the organ with nutrients.
The doctor often prescribes hepatoprotectors to protect liver cells:
- Essentiale - contraindicated in case of hypersensitivity to the components, contraindicated in premature infants; adults and children are prescribed 5-10 ml per day intravenously;
- Hepa-merz - contraindications are individual intolerance, lactation period, renal failure, and childhood;
- Karsil - not used for celiac disease, individual intolerance to components, galactosemia and for children under 12 years of age.
Essentiale (price: 634 RUR)
Hepa-Merz (price: 729 RUR)
Karsil (price: 339 RUR)
Diet
It is important to limit the consumption of fats and focus on the vitamin complex, as well as medications with essential phospholipids.
The therapeutic diet includes:
- vegetables;
- vegetarian soups and soups with milk;
- steamed chicken (can be replaced with turkey or beef);
- dairy products;
- steamed lean fish;
- porridge;
- honey;
- homemade juices;
- lemon tea;
- jelly;
- compote.
Alternative liver cleansing techniques
Before using alternative methods, you should consult your doctor.
Methods for cleansing the liver have the following advantages:
- have a beneficial effect on the functioning of the organ;
- suppress stagnation and provoke the secretion of bile;
- It is better to remove sand from the bile ducts.
Before the procedures for ridding the liver of harmful elements, you need to undergo several preparatory measures that last 4 weeks.
During these days it is necessary to do a cleansing enema:
- Every day for the first week.
- Over the next week - every other day.
- During the third week, do it once every three days.
- In the last week, give an enema once.
During the preparatory month, it is recommended to eat cereals and vegetables, and exclude meat and dairy products from the diet. Thanks to this diet, the intestines will completely get rid of unnecessary elements.
After the preparatory month, the action plan is as follows:
- Drink fresh apple juice for three days in a row, which will successfully dissolve stones in the bile ducts.
- In the evening on the third day, prepare a solution of lemon juice (200 ml) and a teaspoon of olive oil. Apply a heating pad to the liver, and in the meantime drink 3 tablespoons of the solution every 15 minutes.
- Keep the heating pad for about two hours so that the organ warms up well.
- After the morning procedures, you can do an additional enema.
- After completing the cleansing procedures, it is recommended to maintain a light dairy-vegetable diet for 7 days.
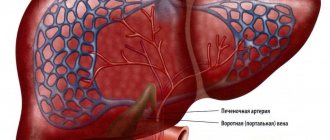
What are the features of segments
The right lobe of the gland consists of a lateral as well as a paramedian zone. The left lobe has two components. The diagram of liver segments on CT divides the organ into eight separated from adjacent elements, as indicated in the table.
| Segment | Location |
| №1 | It is fully a reflection of the caudate part. |
| №№ 2,3 | They are components of the left lobe of the organ. |
| №4 | Located in a square lobe. It is separated from the first segment by the hilum of the organ, and from the third segment by the hepatic groove. |
| №5 | The area is located near the gallbladder (its bed), but a little to the side - laterally. |
| №6 | Located below the previous segment. May occupy up to a third of the entire area of the right lobe. |
| №7 | The boundaries of this section are the diaphragmatic contour, that is, it is located even lower than the previous segment. |
| №8 | This area is reed. Its surface meets the diaphragm and differs only slightly from it. |
The anatomy of the liver is of great importance in the activity of the organ. Between the segments there are membranes (a kind of border between segments that do not allow the spread of pathology), thanks to which the risk of complications is reduced.
Prevention
To ensure that the echogenicity of the organ is always in order, you need to follow the rules:
- eliminate the use of alcohol and tobacco products;
- take medications only as prescribed by a doctor;
- it is recommended to reduce the consumption of fatty and fried foods, smoked meats, pickles, legumes and sweets;
- undergo a medical examination once a year;
- follow safety rules when working with toxins;
- communicate carefully with infected patients;
- do injections, tattoos and piercings only in special rooms.
Carrying out the procedure
CT with contrast
The use of additional substances for visualization of vascular and lymphatic networks is performed if hemangioma or other tumor diseases, abnormalities of the arteries and veins of the hepatobiliary system are suspected. CT scan of the liver with contrast involves the intravenous administration of special agents that are displayed on the screen under the influence of X-rays.
To speed up the removal of contrast after the examination, it is recommended to drink plenty of water.
By segment
High information content of the study.
Computed tomography based on the anatomical criteria of the liver is capable of depicting in detail the ductal system, the nature of the spread of pathological formations, cysts, and abscesses. Each segment is examined separately and together with neighboring ones, so the cause and path of pathology can be determined. A detailed study of the segments also includes visualization of each groove of the organ under study.
The nature of diffuse changes in the parenchyma
In case of disease of the liver, as well as other organs directly related to it (gall, bladder, intestines, pancreas), degeneration processes of various types can occur in the parenchymal tissue:
- Fibrous changes are associated with the proliferation of scar tissue. This pathology can manifest itself due to alcohol or toxic poisoning, or infection with parasites;
- Hypertrophic – thickening of the parenchyma;
- Sclerotic – with damage to the liver vessels;
- Dystrophy - when the liver tissue is gradually replaced by a fatty layer (with hepatosis);
- Changes associated with tissue swelling due to traumatic or inflammatory edema.