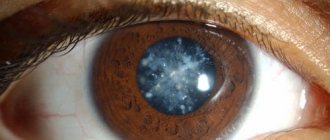
Astigmatism is a fairly common visual impairment. According to WHO, a quarter of the world's population suffers from it. Often this type of ametropia is diagnosed in children, often accompanied by parallel myopia or hypermetropia. How can it be corrected in childhood? Read more in the article.
Our eyes are a unique optical mechanism consisting of several lenses. Light rays pass through them and focus on the desired points on the retina, creating a clear image. With astigmatism, the surface of the cornea is curved or the lens is deformed. As a result of incorrect refraction, when light passes through them, the rays are not focused properly, and a person sees blurry, smeared, and the image may be stretched horizontally or vertically. Why can such a pathology appear in a child?
Causes of astigmatism in children
Astigmatism can be congenital or acquired. This eye disease is diagnosed in 46% of preschoolers and primary schoolchildren with varying degrees of severity. It is curable, but it is important to make a diagnosis in time.
Acquired astigmatism can be due to several reasons:
- various eye injuries;
- subluxation of the lens;
- pathologies during the formation of teeth and jaws.
Congenital astigmatism is much more common. It should be noted that most children are born with a small degree of this disease (up to 0.5 D). A weak degree, which is called physiological, does not affect the quality of vision and the development of normal binocularity. For many children, this type of astigmatism goes away within the first five years of life.
It happens that a child is born with more severe degrees, which are already caused by genetic disorders: alcohol syndrome (due to the mother's drinking of alcohol during pregnancy), retinitis pigmentosa, albinism. Due to the development of the visual organs, the curvature of the cornea may change in the first year of life, which is also a favorable factor for the onset of the disease.
Causes
A disturbance in the optical structure of the eye, leading to weakened vision, is called astigmatism. Abnormalities affect the cornea or lens of the eye. With this disorder, children see objects unclearly or confuse shapes; two optical foci are simultaneously present in the eye, located in the wrong places.
One of the most common diseases is congenital astigmatism in children; it is inherited. It may not manifest itself in any way at the beginning of the baby’s life; usually the diagnosis is made no earlier than 2 years. Astigmatism can manifest itself at any time as the child grows and develops. It is important to carefully monitor children's vision, especially if there are known cases of vision problems in relatives, and follow the instructions of an ophthalmologist.
The disorder can be a consequence of eye injuries. Visual impairment is caused by a pathological condition of the jaws and teeth, which can distort the walls of the eye sockets.
Important! In most children who are born with a congenital degree of astigmatism, it decreases by the age of one year (<1D), does not require treatment, and is called physiological.
What is the danger of astigmatism in children if it is not treated?
This pathology is more complex in nature than myopia or farsightedness. The child sees poorly both at close and long distances. It is difficult for him to accurately determine the distance to an object or between objects, and the sense of space changes.
If this eye disease is not corrected in time, it can further lead to strabismus, amblyopia, and in critical cases, blindness. In addition, astigmatism is often accompanied by headaches and discomfort in the eyes, causing discomfort to the child.
Treatment of astigmatism
When a child’s astigmatism occurs with a degree below 0.5 diopters, and there is no nearsightedness or farsightedness, then special treatment is not necessary. If such patients experience severe discomfort and pain, the doctor identifies the cause of their occurrence and prescribes appropriate therapy.
More often, astigmatism is treated with non-drug methods. In order to correct visual impairment, patients are prescribed special corrective glasses or lenses. Surgery or laser correction is most often resorted to after patients reach 18 years of age, since children under this age are still growing and developing their eyes.
Special glasses
Glasses are a common method for correcting visual impairment due to astigmatism in young patients. The selection of glasses is carried out on an individual basis. Thus, for children with farsightedness and myopia, special lenses are selected taking into account the cylindrical component of the optical power.
When writing a prescription, the doctor indicates in what position the cylinder axis should be and what its optical power is in diopters. This allows patients to use glasses with different refractions in different sections, with the correct refraction of rays passing through the eye and lens.
A patient with astigmatism who is prescribed to wear glasses should be under constant supervision by an ophthalmologist. If the dynamics of the disease changes, the specialist will prescribe the appropriate correction method for the child.
Contact lenses
Wearing lenses is more convenient than glasses, since they help create a single optical system with the eyes. Astigmatism is corrected using special soft toric lenses. The principle of their operation is no different from glasses, but such lenses allow patients to lead a more active lifestyle - attend sports clubs, a swimming pool, etc.
Some ophthalmologists recommend using disposable lenses to treat the disease in children, since such devices do not require special care.
Gymnastics for the eyes
Regular performance of special gymnastic exercises helps improve metabolism, activate blood circulation and saturate tissues with sufficient oxygen and nutrients. Exercises can also strengthen the eye muscles, increase accommodation, and improve the ability of the visual organs to adapt to light and darkness.
The most effective and simple exercises are the following:
- Rotate your eyes down, up and to the sides, then look at the bridge of your nose. Such movements allow you to warm up and stretch your eye muscles. The child should do this exercise smoothly and slowly.
- Raise your eyes upward, trying to stretch the muscles as much as possible, and fix your gaze in this position for 10 seconds. Then look down, then look to the right and left, fixing your gaze for 10 seconds each time. This exercise helps develop peripheral vision, as well as relax the lens and cornea.
- Bring the child to the window and invite him to alternately look from objects located in the distance to those located nearby. While performing this exercise, the child should try not to rotate his eyeballs.
Surgical intervention
Parents who are wondering whether astigmatism can be cured or not should know that if conservative treatment methods fail, this disease can be eliminated through surgery. However, as noted above, an ophthalmologist can recommend surgical intervention only when the child reaches the age of 18.
The operation is performed using laser correction, or using surgical techniques such as keratomy or thermokeratocoagulation.
Hardware treatment of disease in children
Hardware therapy methods are often used as a complex treatment along with wearing special corrective lenses or glasses. These techniques include:
- Laser therapy.
- Electrotherapy.
- Magnetotherapy.
The listed hardware techniques allow you to achieve the following results:
- Improve metabolism in tissues and saturate their cells with oxygen.
- Activate blood circulation in the organs of vision.
- Increase neural activity.
- Eliminate spasm of accommodation.
Types of astigmatism in children
Depending on the severity, changes in refraction, location of the focus and some other factors, this eye disease is divided into the following types:
- corneal In this case, the surface of the cornea is curved. In this case, stronger degrees of astigmatism are diagnosed, since the cornea has a high refractive power;
- lenticular. Caused by deformation of the lens, it is less common than the corneal one. Usually it is congenital, inherited;
- hypermetropic - astigmatism combined with farsightedness;
- myopic - astigmatism is accompanied by myopia;
- mixed - myopic astigmatism is developed in one eye, and hypermetropic astigmatism in the other.
Also, this disease can develop in one eye (simple) or in both eyes (complex). In addition, it is classified according to the degree of severity: up to 3 diopters - weak, from 3 to 6 D - medium, over six - strong astigmatism.
Types and classifications
Doctors distinguish 2 types of this pathology:
- Simple hyperopic astigmatism: involves the image in one of the meridians of the eye being focused on the retina (which is normal), and in the other behind the retina (farsightedness).
- Complex hyperopic astigmatism: farsightedness of varying degrees is diagnosed in both meridians.
Both types of astigmatism are most often caused by the aspherical shape of the cornea; in rare cases, the cause lies in a change in the shape of the lens. Due to a disorder in the cornea, rays refracted in the optical system of the eye are not collected at one point. In addition, the anterior surface of the cornea is usually more curved and refracts rays more strongly. Mild corneal astigmatism (up to 0.5 diopters) is common, is considered an acceptable norm and does not lead to changes in visual acuity.
There is also a mixed type of astigmatism, which is manifested by the following disorder: myopia is noted on one of the meridians, and hypermetropia is noted on the second.
Hypermetropic astigmatism of the eyes in children comes in several degrees of severity:
- A mild degree causes virtually no symptoms.
- Moderate degree is characterized by the appearance of fog in the eyes and headache.
- In severe cases, the child may complain of a sharp decrease in vision, and from the outside, adults may notice the baby’s strabismus. The child suffers from pain and pain in the eyes, as well as tearing. Children with severe astigmatism become nervous and irritable, and their mood often changes.
How to recognize symptoms of astigmatism in children?
Parents should carefully monitor the development of the child’s visual organs and pay attention to the peculiarities of visual perception. He should be taken to the doctor immediately if the following symptoms are noticed:
- the child squints when looking at both long and short distances;
- complains of eye fatigue while reading or writing;
- has difficulty reading text, cannot identify some letters;
- tilts his head to the side in an attempt to get a better look at the object.
If such signs are present in children, you can also conduct a mini-test at home to check for astigmatism. To do this, experts advise doing the following. You need to take a sheet of paper with a clear graphic black and white design, then place it in front of the child’s face at arm’s length and ask him to close one eye. Next, check how well he sees all the lines or strokes (by pointing to them), find out if any of them seem lighter than the rest.
If the answers to the questions are affirmative, this may indicate the presence of astigmatism with some degree of probability. During the examination, the ophthalmologist will use instruments to identify the degree and type of this disease.
Preventive measures
It is impossible to avoid the manifestations of congenital pathology, but it is possible to prevent the development of the acquired form.
How to carry out prevention:
- ensure proper lighting in the house;
- alternate visual and physical activity (allow the child to take breaks during school lessons and homework);
- perform eye exercises;
- massage the eyelids;
- Healthy food;
- protect eyes from injury and infection;
- Carry out an annual examination with an ophthalmologist.
Vision is very important for a person. When a child sees well, he can study normally and play sports without experiencing discomfort. Wearing glasses can be a real tragedy for a teenager. Be attentive to children, listen to complaints, take care of their health in advance.
Diagnosis of childhood astigmatism
To determine the nature of the disorder, the same research methods are used as for adults. The most common method is autorefractometry. A beam of infrared light passes to the retina through the pupil and, reflected from the fundus of the eye, returns. The sensors record the parameters, and then the program compares them with the initial ones, thus determining the clinical refraction.
Using a keratometer, you can calculate the degree of curvature of the meridians of the outer surface of the eye. The method of computer keratotopography also makes it possible not only to determine the degree of deformation of the cornea, but also its thickness and shape (in complex cases). Ultrasound of the eyeballs, skiascopy and some other methods may also be prescribed. It is important to identify astigmatism at the earliest stages, as in children it often leads to strabismus and amblyopia.
Definition of disease
Hypermetropic astigmatism is a vision disorder characterized by changes in the shape of the lens or cornea.
In a healthy person, the lens has a smooth spherical surface. With farsighted astigmatism, a violation of the sphericity of the lens is observed, the shape of the eye itself is elongated vertically, which is why the focal point is located outside the macula - the center of the fundus. Astigmatism bifurcates this focal point, resulting in severe distortion of visual information. Children with this disease cannot focus their eyes on close objects, so they see the picture blurred and unclear.
Hypermetropic astigmatism is sometimes called hypertrophic astigmatism, since they are the same disease. It causes visual impairment and farsightedness in the child.
Correction with astigmatic glasses
The most common and generally the only method of correction is up to the age of 9-10 years (starting from this age, contact lenses can become an alternative to glasses). To correct astigmatism, you need special lenses that have a complex design and are called cylindrical. They make it possible to correct the difference in refraction of the two main meridians of the eye. Their main feature is the axis, which has no optical effect. In the opposite direction from it there is a focus, due to which the lens has the same effect as a spherical one. Optics with cylindrical lenses are prescribed for refractive error in a separate meridian. If the astigmatism is mixed, then toric lenses are needed - a clearly calculated combination of cylindrical lenses with spherical ones. They refract the light flux along two meridians at once.
When wearing glasses to correct astigmatism, you need to visit a doctor at least once every six months so that he can check what changes have occurred in the eyes during this time and, if necessary, write out a different prescription for glasses, for example, with smaller diopters.
Treatment
In order for the treatment of simple and complex variants of hypermetropic astigmatism in children to be effective, it must be started as early as possible, taking a whole range of measures.
Optical correction
The doctor usually prescribes glasses for children under 7 years old, and lenses for older children. The lenses of the glasses are not simple, but spherocylindrical. Contact lenses are selected strictly individually for each patient. A line of toric contact lenses has been developed to correct astigmatism. The degree of damage and possible concomitant pathology are taken into account.
How to choose glasses for astigmatism, read here.
Glasses and lenses for astigmatism are exclusively vision correction. If you remove the optics from your eyes for a long time, your vision will begin to deteriorate again.
Surgical intervention
To permanently get rid of farsighted astigmatism, it is necessary to correct the shape of the cornea. Only microsurgery doctors can do this. At this stage, the most effective ways to influence the cornea are:
- Laser thermokeratoplasty;
- Laser keratomileusis.
Read more about laser keratomileusis here.
Laser thermokeratoplasty.
These procedures change the shape of the cornea, making it convex and flat in the central part. Visual acuity is restored.
As a rule, modern medicine uses surgical intervention for patients over 18 years of age. However, in severe cases of hypermetropic astigmatism, doctors also perform laser surgery on young patients.
Other treatments
Conservative treatments include:
- Eye muscle training;
- Proper nutrition;
- Swimming;
- Massage.
Eye exercises to improve vision are described at this link.
To treat astigmatism, ophthalmologists often prescribe special exercises for children. The complex may include the following exercises:
- The child needs to look into the distance, then fix his vision on some object located nearby, at a distance of 20-30 cm.
- Eight. The young patient needs to make a figure eight with the pupils of his open eyes.
- Alternately closing the organs of vision while fixating the open eye on a nearby object.
- Index finger exercise. The baby needs to look closely at the index finger, slowly bringing it closer to the nose.
- Massaging closed eyes with thumbs.
Gymnastics for the eyes
After performing gymnastics, you need to close your eyes and let them rest.
Gymnastics, taking various medications, wearing glasses, as well as surgical intervention are prescribed only by an ophthalmologist after a thorough diagnosis.
Contact lenses
Starting at about 10 years of age, a child can already use toric contact lenses. Children often choose this type of correction. It is more convenient to engage in active recreation and play while wearing lenses, and this eliminates ridicule from peers, because many teenagers are embarrassed to wear glasses. It is important for parents to ensure that their child properly cares for optics and follows hygiene rules. It is best to choose daily lenses for the first wear.
Modern manufacturers produce toric lenses in a wide range. For example, the monthly replacement model SofLens 66 Toric from the manufacturer Bausch + Lomb has optimal characteristics. Also popular is the Air Optix for Astigmatism model from Alcon, which has the highest level of oxygen permeability of 138 units. These lenses provide eye comfort all day long.
Possible complications
Childhood hypermetropic astigmatism can cause amblyopia and strabismus. Visualization of the image by parts of the retinas is disrupted as a result of blurriness in one of them, which leads to the formation of amblyopia, which is often a consequence of this eye disorder. This complication can occur when the difference in refractive power is more than ± 1.5 diopters in both eyes simultaneously.
Read the material on how to treat strabismus in children.
Complex farsighted astigmatism diagnosed in both eyes can be complicated by albinism.
If hypermetropic astigmatism detected in a child is not treated in a timely manner, then after the age of 10 he may develop convergent strabismus.
This pathology causes discomfort to the teenager and is an unpleasant cosmetic defect, due to which the teenager may develop complexes and psychological problems. That is why it is so important to undergo regular examinations by an ophthalmologist and, when such a diagnosis is made, to promptly treat the pathology. The parents’ task is to follow absolutely all the doctor’s recommendations.
Convergent strabismus in a child is a complication due to hyperopic astigmatism
Prevention of astigmatism
It is very important not only to treat astigmatism, but also to take measures to maintain good eye health from childhood. Here are a few rules every parent should follow. Don't skip mandatory eye exams. The doctor can notice vision problems in time and prescribe therapy. Make sure that your child does not spend too much time on the computer or with gadgets, but rather plays active, educational games more often. It is important to create a diet so that it includes foods that are good for vision, and periodically take courses of children's multivitamins. Avoid overstraining your child's eyes. The optical system begins to strengthen only at 7-8 years of age. Before this time, you should not burden your baby with reading and writing, and you should also ensure that he spends no more than 3-4 hours a day in front of the TV or with a tablet.
Unfortunately, this is the problem of our time - the excessive passion of children and teenagers for gadgets. Doctors note a very rapid increase in eye diseases under the age of 18.
Astigmatism in children is a disease that needs to be diagnosed in time and correction begun in order to prevent the development of other serious disorders. To do this, it is important to monitor the state of your child’s visual function and follow all doctor’s recommendations.
How it manifests itself
It is almost impossible to determine the presence of a deviation in young children without an examination by an ophthalmologist, since children almost never focus on visual deviations. This happens because the baby simply does not know about the existence of problems. He gets used to what he sees, he doesn’t know what the norm is and what a deviation from the norm is.
Symptoms of the disease:
- the image blurs, doubles;
- dizzy;
- constant headache;
- irritability, increased fatigue under any type of stress;
- refusal to read books, look at pictures, or write work;
- tilting the head, squinting.
You should not expect that astigmatism will go into the physiological phase. The long-term influence of the projection of a blurred image on the retina will prevent the formation of correct visual functions or worsen existing ones.
Attention! Often parents do not attach importance to children's complaints and refusals to read books, considering them lazy and capricious. Be attentive to your child; it is better to visit an ophthalmologist more often than to deal with complications in adulthood.
It is especially difficult to detect astigmatism in children under one year of age, although a good specialist can detect the disease as early as 12 months. Parents should rely on a family history of the disease. Another sign of visual impairment up to one year is the child’s squint, which often accompanies infants.
Symptoms
The disease manifests itself in different ways, depending on age. A newborn sees this world in the form of spots of different sizes and colors. By the age of one year, his vision is established, and he can already clearly see objects. You can recognize the symptoms of this disease by his behavior.
Astigmatism in newborns manifests itself in the form of redness of the eyes, tearing; The baby often rubs his eyes, conjunctivitis may occur. To examine the toy, he brings it very close to his face. The baby cannot play for a long time, he begins to be capricious and cry.
At 2 years the disease manifests itself in the same way. He may miss when placing an object on a table, bed and other surfaces, crashing into furniture, corners in the house or in unfamiliar places.
Astigmatism in a 3-year-old child is accompanied by headaches or painful sensations in the eyes. A similar situation occurs at 4 years of age. He squints, concentrates on an object for a long time, cannot do one thing for a long time or play with one toy, and is often capricious.
Children aged 6 years and older experience a lot of strain on their eyes. Preparations for school are underway, children are learning to read and write. This leads to rapid eye fatigue, the baby may often rub his eyes, adjust his eyelids to improve vision, conjunctivitis, redness of the eyes, and swelling occur.
Preschool children often have congenital visual pathology, while schoolchildren and adolescents “acquire” astigmatism. The symptoms of the disease are almost the same, the only difference is age. When the baby can already speak, it is easier to diagnose the disease, since he can say what exactly is bothering him.
Causes
The main reasons why the disease can develop are identified:
- congenital pathology associated with the inheritance of a pathological gene formed in an autosomal dominant manner;
- pathology of the cornea - a thorn, malnutrition through blood vessels, erosions, ulcers, inflammatory process;
- pathology of the lens - clouding of the internal structure, coloboma;
- postoperative complications that cause various pathologies of the cornea and lens (most often, astigmatism develops due to improper suturing);
- mechanical damage to the eyeball, which leads to its deformation (penetrating injury, scar formation), this results in improper passage of the beam through the internal structures of the eye.
The doctor must not only identify the disease, but also establish the root cause. If this is not done, relapse is possible after treatment.
Symptoms of the disease
In the case of congenital visual defects, it is extremely difficult to recognize them at an early age without the help of a doctor. The thing is that the child initially sees poorly, and believes that this is how it should be, so he does not complain. Only a sensitive and attentive attitude will allow you to suspect something is wrong. You should contact a specialist if your child:
- He squints, looks closely,
- Stumbles, often falls,
- Complains of a headache
- Gets tired quickly
- He rubs his eyes and complains of pain and discomfort.
At an early age, it is impossible to completely get rid of astigmatism. But correction with glasses will make life much easier for the baby and his parents.
Myths
1. Glasses are forever.
With some types of astigmatism, in many cases children can get rid of constant wearing of glasses. If the degree of astigmatism is high, then after amblyopia is cured, excimer laser correction is used, allowing teenagers to get rid of glasses.
2. Astigmatism is completely cured.
Since there is a congenital defect of the cornea, the defect cannot be corrected using conservative methods. Visual acuity can be improved by mobilizing the structures inside the eye that are responsible for focusing the image. That is, astigmatism is compensated. The disease can be cured only with the help of excimer laser correction.
3. Laser vision glasses.
With regular wearing of poly-diaphragm glasses, their manufacturers promise to get rid of all eye diseases. But the therapeutic effect has not been proven, although there is no harm either.
4.Preparations with blueberries.
Typically, these tablets are dietary supplements or multivitamin sets. This means that they have not undergone clinical trials. Therefore, they are not used in pediatric ophthalmology.
Source https://tvoelechenie.ru/oftalmologiya/astigmatizm-u-detej-lechenie.html
Prevention
Congenital astigmatism cannot be prevented. But you can eliminate the possibility of its development using the following methods:
- classes for the child only in a well-lit room;
- when standing or sitting, the child should keep his back straight, his head should look only forward, but not down;
- proper nutrition with the intake of all useful substances into the body; if this is not enough, it is necessary to use multivitamin preparations;
- timely visit to the ophthalmologist with all diagnostic tests for timely detection of the disease.
If a child has a congenital form of astigmatism, or it appeared in early childhood, the pathology can gradually worsen the quality of vision. Therefore, it is recommended to undergo an annual examination by an ophthalmologist and use the prescribed treatment.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of astigmatism is carried out during an ophthalmological examination, which allows assessing visual function and eye condition. It includes the following methods:
- visometry;
- ophthalmoscopy;
- biomicroscopy;
- Ultrasound examination of the eyeball.
The diagnosis of astigmatism is made during an ophthalmological examination of the child.
To assess refraction, perform:
- computer keratotopography;
- keratometry (ophthalmometry);
- autorefractometry;
- skiascopy (shadow test) with cylindrical or spherical lenses.
Based on the data obtained, a conclusion is made about the presence of astigmatism in children, the form and degree of the disease, and possible complications are determined.
What to do with astigmatism?
Astigmatism must be corrected! Correction is especially important in children of primary, preschool and school age, since their visual system is just developing. If correction is not started, this can lead to a delay in the development of the visual system as a whole, as well as to the occurrence of strabismus and other dangerous complications.
Astigmatism is corrected with glasses or contact lenses. For spectacle correction, complex cylindrical lenses or spherocylindrical lenses are used, combining spherical and cylindrical glass.
At school age, contact lenses can be used. Soft lenses that correct astigmatism are called toric lenses. But it is important to remember that contact lenses require careful handling and special care.
Parents should know that glasses and contact lenses do not cure, but only correct astigmatism, improving visual function and quality of life. It is necessary to understand that the child will need to wear glasses all the time, and not just while reading or drawing. It will take some time to get used to them; on average, the period of adaptation lasts about two weeks. The task of parents at this stage is to choose comfortable, bright and fashionable frames for their baby. If you like the glasses, your son or daughter will wear them with great pleasure and will get used to them faster.
Surgical treatment of astigmatism, laser correction, is recommended after the age of 18, when the visual system is fully formed.
Children with astigmatism should be observed by an ophthalmologist and undergo a routine examination twice a year, since at this age there is constant growth of the eye, therefore, it is necessary to monitor the timely change of optics.
Back to contents
Description and reasons
To understand what astigmatism is, let’s look at the structure of the eye. The normal cornea has an almost spherical shape. Its function is to collect light rays into one point. With astigmatism, the curvature of the cornea is disrupted, resulting in an image with unclear contours. Blurred vision of objects in children forms an incorrect worldview, and cognitive processes are disrupted.
Astigmatism is often accompanied by refractive errors such as hypermetropathy (nearsightedness) and myopathy (farsightedness). Most often it manifests itself to a small extent, which does not need to be corrected. In the remaining 10% of cases, vision correction is needed to prevent strabismus.
Just heal and see the world
Early diagnosis builds a reliable bridge to correct vision correction. Since a child’s eye continues to grow until the age of 18, performing surgery would simply be the wrong decision. Before reaching this age, there are other conservative treatment methods. How to distinguish allergic conjunctivitis from bacterial conjunctivitis can be found here.
Special glasses
The simplest and most unpretentious method of vision correction. The glasses have cylindrical lenses. At first, they do not bring joy to the child, but after 5-10 days the situation changes for the better. Headaches are possible, but this cannot be avoided in any case. Gradually the lenses do their job. Older children are embarrassed to wear them, but this is hard work for parents. How to treat myopia at home, read our article.
Contact lenses
special glasses - a quick way to correct vision for astigmatism
This method, called keratology, involves the use of hard contact lenses. They are worn during night sleep and their task is to correct corneal deformation. The method can really help in correcting astigmatism up to 1.5 diopters.
Correction using laser technology
The entire process takes no more than 15 minutes. To ensure that the child feels calm and does not interfere with the doctor, drip anesthesia is used. Within 1 – 2 hours there is a noticeable improvement in vision. There is no postoperative period required, no stitches or bandages are needed. What stages of glaucoma exist can be found on the pages of our website.
You can return to your normal activities immediately after surgery, but it is better to give your eyes a little rest.
What other vision problems occur in children?
In addition to astigmatism and farsightedness, vision in children often deteriorates towards myopia. With this disorder, the child has difficulty distinguishing between objects that are distant from him. The causes of congenital myopia and farsightedness are similar and may lie in hereditary factors or pathological processes. Other causes of myopia are poor accommodation of the eye, long work at close range, visual fatigue, certain diseases, and changes (due to some factors) in the shape of the eyeball.
Sometimes farsightedness leads to myopia, which was not corrected in time with glasses or contact lenses. To treat myopia in children, a set of therapeutic measures, as well as glasses or contact correction, can be used.
Preventive actions
To prevent the development or progression of astigmatism in a child, follow these recommendations:
- Provide your baby with good lighting while reading, writing or drawing.
- Make sure that visual stress is periodically replaced by active rest. After prolonged visual stress, perform a gentle massage of the eyelids with your thumbs together with your baby.
- Teach your child to do eye exercises. For these purposes, exercises such as turning the eyes (left-right, down-up) and alternating fixation of the gaze on distant and near objects are suitable.
- Limit your child's time on TV and computer.
- Don't let your baby read while lying down.
For preventive purposes, parents should make sure that the baby’s diet contains all the vitamins and minerals necessary for the child’s body. In consultation with your doctor, you can also take vision vitamins that contain lutein.