Furunculosis is a common inflammatory skin disease in which multiple boils can develop. According to statistics, deep pyoderma, occurring as boils or carbuncles, occupy one of the leading places in the structure of purulent-inflammatory diseases of the maxillofacial area.
Single boils most often affect the area of the nasolabial triangle and cheeks. However, with the development of furunculosis, multiple inflammatory infiltrates can be located on the skin of the face, back, neck, buttocks, thighs, legs, etc.
Furunculosis on the face is characterized by a severe course, the development of widespread swelling, severe pain and a high risk of complications.
When boils develop in areas of the body with a pronounced layer of subcutaneous fat (buttocks, abdomen), the size of the boils can reach a walnut. In the absence of timely treatment, such furunculosis can be complicated by the development of phlegmon, sepsis, etc. Attention. Due to the high risk of developing severe complications, only the attending physician should decide how to treat furunculosis.
Treatment of furunculosis is selected individually for each patient and depends on the severity of his condition, the number of boils, their location and the risk of complications, as well as the presence of diseases in the patient that complicate the course of the disease (diabetes mellitus, polycystic ovary syndrome, hypersecretion of androgens, immunodeficiencies, etc. .)
Furunculosis code ICD10 is L02 (a group of skin abscesses, boils and carbuncles).
What it is?
A boil is an acute skin disease with the formation of purulent contents in the damaged area in various parts of the body. As a rule, the process is purulent-necrotic in nature, in which not only tissue inflammation is observed, but also the process of inflammation of the hair follicle, where the entire pathological process begins.
The onset is folliculitis, with subsequent spread to the surrounding connective tissue. But a boil is distinguished from folliculitis not only by the extensive area of damage, but also by clinical manifestations.
What are boils
People call a boil a boil, a pimple or a boil. In medicine, this term refers to a pustular inflammatory skin disease. The process begins from the hair follicle. This is why boils never form in places where hair does not grow - on the heels or palms of the hands.
Most often, boils appear in places that are most susceptible to contamination and irritation. It could be:
- neck;
- eyes;
- forehead;
- head;
- chin;
- shoulder;
- cheeks.
Less commonly, the disease appears on the arms and legs, knee, lower back or abdomen. Furunculosis develops more often in men than in women.
If, for example, a boil appears on an intimate place, say, on the labia, and there are no other such manifestations on the human body, then it is customary to talk about local furunculosis. If the formations spread simultaneously in different places, for example, under the armpit, in the ear and on the chest, then they speak of a widespread form of the disease.
Stages of development
The development cycle of a boil consists of 3 phases:
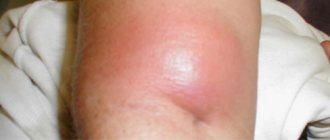
- Infiltration stage. The skin above and around the source of infection thickens, turns red, and swells. Painful sensations appear in this place. In the center of the infiltrate you can see the hair follicle. The common term is “boil ripening.”
- Stage of necrosis. Appears on days 3-4 of development. Around the hair with the inflamed follicle, a “core” is formed, consisting of necrotic (dead) tissue and pus. A white convex abscess appears on the surface of the skin. The thin tissue membrane covering it opens and the pus is expelled. The patient feels relief and pain reduction. Swelling subsides, redness decreases. A traditional medicine term meaning the process is “boil breakthrough.”
- Healing stage. The skin defect that forms after the “rod” is rejected, resembling an ulcer, heals. After large boils, scars remain.
On average, the full cycle of development and healing of a boil is about 10 days.
Why is the hair follicle involved in the purulent process?
To understand the mechanism of development of the disease, you should briefly examine the structure of the hair, follicle and sebaceous gland. Hair is keratinized skin cells modified by evolution, consisting of a shaft above the surface and a root located in the follicular sac. The follicle is immersed in the skin and subcutaneous fat and is surrounded by a connective tissue capsule. The lower part of the hair follicle resembles a club with an expanded lower pole. This “bulb” provides nutrition and innervation to the hair. The ducts of the sebaceous and sweat glands flow into it.
Sebum has the ability to neutralize pathological microorganisms that come into contact with the skin in abundance. The activity of the sebaceous gland is regulated by the adrenal glands and the hormone of the sex glands - testosterone.
Sweat glands are located in the armpits, around the nipple area, anus and genitals.
What does a boil look like: photo
You can say that you have a boil if you observe the following signs:
- redness of the skin area;
- the appearance of a tubercle with a compaction in the middle located in the hair follicle;
- subsequently, increased swelling of adjacent tissues, which become hot to the touch;
- pain at the slightest touch or movement of the body;
- a pustule with a rod is formed in the center, in which pus is located.
The photo below shows how the disease manifests itself in humans:
Click to view
[collapse]
Furuncle: symptoms
Boils on the face are most often located in the upper or lower lip area. Less commonly, a boil may occur in the ear or nose, or on the skin of the forehead. The most severe boils are those that form in the area of the upper lip, corners of the mouth, as well as in the nose and infraorbital areas (this corresponds to the area of the nasolabial triangle). These areas have a rich blood supply, and therefore thrombophlebitis of the facial veins develops here much more often, which can lead to thrombosis of the cavernous sinus, purulent meningitis and sepsis.
If you have a boil, treatment at the very first stage of inflammation can be carried out at home. At later stages, only surgical treatment is indicated. Next, we will analyze the clinical stages of boil development and the corresponding symptoms. So, if you have a boil, the symptoms of inflammation and patient complaints depend on the stage of the inflammatory process, of which there are three.
Stages of boil formation and their symptoms –
1) At the beginning of its formation, the boil simply resembles a swelling rising above the surface of the skin (soft tissue infiltration). At that stage of development, there is still no pus or necrotic core in it, but the tissues are very dense to the touch, tense, and painful when touched. The skin over the infiltrate has an intense red color (Fig. 8). The general condition of patients at this stage is usually satisfactory, and body temperature usually does not exceed 37.5 degrees.
2) At the second stage, which usually occurs after 3-5 days, symptoms of pus formation inside the boil already appear, which leads to an increase in its size. In addition to the increase in the size of the boil, patients note increased pain, which can become throbbing, as well as an increase in body temperature up to 38.0 degrees. In parallel with the formation of pus, a necrotic core is formed, and in this case, white or black dots can be distinguished on the surface of the boil (Fig. 9-10).
Gradually, the pressure of pus on the walls of the boil increases, and this can lead to the fact that it can spontaneously open. In this case, pus will begin to appear on the surface of the skin, and the necrotic core will begin to gradually emerge from the depths of the tissue to the outside (Fig. 11).
3) At the third stage, tissue regeneration begins. This stage begins after the emptying of pus from the cavity of the boil and rejection of the necrotic core. Tissue swelling and inflammation at this stage gradually decreases, and tissue healing occurs with the formation of a small scar. In the next section we will describe in detail how to treat a boil at different stages of the inflammatory process.
When should you definitely see a doctor?
Do not self-medicate; to establish a diagnosis and carry out treatment, you should definitely contact a dermatologist. It is especially impossible to treat yourself and only with folk remedies if:
- The boil appears again in the same place. Treatment may require removal of sweat glands that cause recurrent inflammation.
- Weakened patient - the patient has a severe concomitant disease (oncology, diabetes, etc.) or is taking drugs that suppress the immune system.
- Severe - in cases where the boil causes serious pain and is accompanied by fever, severe swelling, headache and other symptoms of a severe infectious disease.
Diagnosis of boils
Furunculosis can be diagnosed using both a visual examination and some laboratory tests. To determine the disease, the doctor only needs to examine the formation.
A blood test is performed only for complicated furunculosis. A sterility test may be required if blood poisoning is suspected due to improper removal of the abscess. If the disease appears due to diabetes mellitus, a glucose test may be performed.
If treatment with antibiotics is required, for example, for chronic recurrent furunculosis, an examination of the discharged pus may be performed. This allows you to accurately determine the type of microorganism that makes a person sick.
Detailed diagnostics are rarely carried out, since people with boils do not always turn to specialists.
The boil should not be squeezed out
As the boil fills, its surface begins to thin out, and for a faster recovery, the patient can try to pierce it with a needle or other sharp object to release the pus.
This cannot be done, because with a careless or deeper puncture, infected pus can penetrate into neighboring tissues or into the bloodstream, spreading throughout the body. It is also possible that the rod will partially remain inside, which will lead to a chronic process and frequent relapses of furunculosis. The boil should fill up and burst on its own. This usually happens within 1 - 2 weeks.
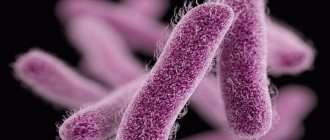
Staphylococcus is the main cause of furunculosis
As already written above, the main causative agent of purulent inflammation of the hair follicle is staphylococcus. There are many varieties of this microorganism. Only about 10% of them are pathogenic. The malaise develops when these particular forms begin to actively reproduce.
Factors leading to the development of boils
The development of purulent processes in the hair follicles is promoted by:
- increased sweating with impaired skin protection functions;
- minor traumatic injuries to the skin due to scratching, scratching, abrasions, through which infection enters the skin and hair structures;
- contact of the skin and pathological secretions during rhinitis, sinusitis and other inflammatory infectious diseases;
- hygienic problems, skin contamination;
- occupational factors: contact with chemical, construction, household dust, liquid harmful ingredients;
- altered or reduced immunity that occurs against the background of severe chronic pathologies;
- hormonal dysfunction that develops with diabetes mellitus and excess adrenal function. An imbalance leads to trophic disorders of the skin, a decrease in local protective reactions, which creates a favorable environment for the development of pathogenic microbes.
Treatment of boils at home
Single inflammations that are not on the face can be treated at home. For this purpose, ointments that draw out pus and folk remedies are used. If the recommendations are followed correctly, the boil should heal within a week.
Treatment regimen for boils at home:
- In the initial stage, it is necessary to regularly wipe the inflammation with a solution of aniline dye 3-4 times a day. At the same time, make sure that the boil is dry and change gauze dressings, which protect the inflammation from the penetration of infections from the outside.
- When the infiltration stage occurs, which is characterized by redness and swelling, ultraviolet irradiation is useful. You can sunbathe at home.
- In order for the abscess to mature faster, Ichthyol ointment is used once a day. It is applied carefully, trying not to injure the inflammation. Then they cover it with cotton wool, which is bandaged with gauze and keep the compress for 6-9 hours.
- After the abscess has opened, the wound is disinfected with hydrogen peroxide. Subsequently, until complete healing, the area with the boil is treated with a solution of sodium chloride several times a day.
View photos
[collapse]
How to treat a boil: ointment and antibiotics
If you have a boil, treatment at home can be effective only at the very early stage of the disease, when there is still only inflammatory swelling of the tissue, but without the formation of a cavity with pus. Only in this case can conservative treatment be carried out to prevent suppuration. How to cure a boil at this stage - you need to use a 2% alcohol solution of salicylic acid to treat the skin, and Ichthyol ointment for antiseptic dressings.
Also at this stage, blockades with weak anesthetic solutions (like infiltration anesthesia) are very effective, but for this you need to consult a dental surgeon or maxillofacial surgeon. Some types of physical therapy treatments may also be effective. But the treatment of a boil, in which a cavity with pus and/or a necrotic core has already formed, can only be carried out surgically.
Thus, we summarize... Treatment of a boil at home is possible only if it is small in size (up to 5 mm) and a cavity with pus or a necrotic core has not yet formed, and you do not have a high fever or concomitant diseases - such as diabetes mellitus, dermatological diseases, weak immunity, etc. In all other cases, the sick person should consult a doctor.
You need to see a doctor immediately –
Below we have indicated a list of cases in which you should immediately consult a doctor (even if you have not yet formed a cavity with pus), because this will prevent the development of serious complications. So,
- if you have severe throbbing pain,
- if body temperature is above 37.5 degrees,
- if the boil is localized in the nasolabial triangle (on the upper lip, nose, nasolabial folds, infraorbital areas), as well as in the ear canal,
- if the boil occurs in an infant or small child,
- when there are signs of infection spreading - the size of the redness around the boil increases, or red stripes appear around it, or if a necrotic core has not formed in 2 weeks, or when another boil appears nearby,
- if you have diabetes mellitus, oncology, rheumatoid arthritis, endocarditis, obesity, if you are taking prednisolone or its analogues, or have a reduced immune system (in addition, in all these conditions, treatment of the boil is carried out under mandatory systemic antibiotic therapy).
Heat compresses (not on the face!!!) –
Most small boils (no more than 5 mm) can be cured only with heat compresses, without antibiotic therapy or surgical opening. Heat compresses allow the flunculus to ripen faster and open on its own. Warm/hot wet compresses, increasing tissue temperature, increase blood circulation in this area, which leads to a more rapid transition of inflammation from the infiltration stage to the formation of a cavity with pus. Usually they are carried out 3-4 times a day, for 10-20 minutes.
Important!!! Heat compresses cannot be applied to the face; they can only be used when the boil is localized on the body. In addition, heat compresses cannot be used even on the body - with carbuncles, hidradenitis, lymphadenitis, festering atheroma or lipoma. Imagine that you suddenly made a mistake in your self-made diagnosis, and you actually do not have a boil, but a festering atheroma. You will get serious complications.
An alternative to conventional wet heat compresses can be bandages with Vishnevsky ointment. By the way, surgeons also periodically prescribe heat compresses if they see that it is too early to open the boil (a cavity with pus and/or a necrotic core has not formed). This is done to speed up the course of inflammation and perform surgery faster, thus reducing the overall duration of the disease (24stoma.ru).
Opening the boil (and draining it) –
At the second stage of inflammation, i.e. if a cavity with pus and/or a necrotic core has already formed, surgical opening of the boil is performed. If the boil occurs on the face and neck, this is done by a dental surgeon or maxillofacial surgeon, and a boil on the leg or in the armpit will be opened by a general surgeon. You should not try to treat boils larger than 5 mm without opening them, using only heat compresses, ointments and antibiotics.
The autopsy is performed under local anesthesia. A small incision is made, after which the necrotic core and remaining pus are removed from the wound. The abscess cavity is carefully scraped out and washed with antiseptics, after which a drainage made of rubber gloves is inserted into the wound. In the first days after opening, exudate will be released from the wound. The wound should be washed daily with antiseptics, and hydrophilic ointments with osmotic activity can be applied to the wound. Such ointments will improve the drainage of pus and speed up the cleansing of the wound.
Important : under no circumstances try to open the boil yourself by squeezing it, piercing it or trying to cut it. This can increase not only the risk of scarring, but also the penetration of infection deep into the tissue. Such self-medication, for example, on the face, can lead to thrombophlebitis of the superficial facial veins, sepsis and even death.
How to draw out pus from a boil -
You can use Levomekol ointment after surgical opening of the boil. Please note that dressings with it can only be done after the boil has opened on its own or has been opened by a surgeon. Levomekol ointment has an antiseptic and necrolytic effect, which will allow the wound to quickly cleanse itself of pus and necrotic tissue.
Treatment of boils with antibiotics -
Antibiotics for boils are not needed in all situations.
Antibiotic therapy may be recommended if the boil is large, located in a potentially dangerous area of the nasolabial triangle or infraorbital area, or in sensitive areas such as the groin, armpits or ear canal. Treatment of a boil with antibiotics is also mandatory in cases of acute intoxication of the body (at high temperatures), concomitant diseases, and a high risk of developing thrombophlebitis of the facial veins. However, the use of antibiotics for boils is often not effective. This is due to the presence of several pathogens at the site of inflammation, especially staphylococci and enterococci, which are often resistant to many antibiotics at once. Therefore, the drugs of choice are usually amoxicillin + clavulanic acid (Amoxiclav), ampicillin + sulbactam, cephalosporins, fluoroquinolones. In the presence of diabetes mellitus and immunodeficiency conditions, in which the risk of complications is high, imipenem and meropinem are prescribed.
- If there is no fever and the size of the boil is less than 5 mm, in this case no antibiotics are required, unless of course you have the concomitant diseases that we described above.
- If the temperature is low and the size of the boil is more than 5 mm, a course of oral antibiotic is prescribed for 5 to 7 days. These may be: trimethoprim, sulfamethoxazole, cleocin, vibromycin, minocycline and others.
- In patients with high fever or multiple abscesses, a course of antibiotic therapy in this case is at least 10 days. Antibiotics such as rifampicin, rifadin, rimactan and others are used.
Staphylococcus aureus has the ability to quickly become resistant to the most powerful antimicrobials, making treatment difficult. Therefore, you should never self-prescribe antibiotics. In the presence of MRSA (methicellin-resistant strain of Staphylococcus aureus), an antibiotic such as vancomycin is prescribed, and in case of multi-resistant strains of staphylococcus and vancomycin-resistant strains of enterococcus, linezolid is prescribed.
Important: in patients with a boil localized in the nasolabial triangle, infraorbital region, or with extensive lesions, in addition to antibiotics, anticoagulants must be prescribed to prevent thrombosis of the facial veins.
Ointments for furunculosis
For furunculosis, ointments containing antibacterial drugs are mainly used.
| Name | Instructions |
| Gentamicin | Description: Ointment in tubes, from 15 to 80 g. Gentamicin is an antibiotic that is effective against many types of infections, including staphylococcal. Directions for use: Apply to the location of boils 2 – 3 times a day. Usually the course of treatment lasts 7–14 days. |
| Levomycetin | Description. Levomycetin is a powerful antibiotic that has a pronounced effect in purulent processes. Available for local cutaneous use for furunculosis in the form of liniment (a thick mass like an ointment). Sold in tubes of 25 and 30 g, in cans of 25 and 60 g. Method of use: Make dressings with chloramphenicol liniment, change once a day. |
| Tetracycline | Description: Tetracycline is a broad-spectrum antibiotic. Effective against many types of microorganisms, including staphylococci. Available in tubes of 100 g. Method of use 1. Apply a small amount of ointment to the location of boils 2 - 3 times a day. |
| Levomekol | Description. Levomekol not only has pronounced antibacterial properties, but also stimulates tissue regeneration. Therefore, it is used for large opened boils for speedy cleansing and healing. Directions for use: Soak a sterile gauze pad in the ointment and apply it to the wound. Apply a bandage. Perform dressings daily. |
| Dimexide | Description. A medication belonging to the group of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Eliminates inflammation and pain. Directions for use: Moisten a sterile gauze pad with dimexide. Apply to the location of the boil and apply a bandage. Do dressings daily. |
| Sintomycin | Description. Syntomycin is an antibiotic, which in its chemical structure is very similar to chloramphenicol. Also available in the form of liniment, in 25 g cans. Method of application. Apply liniment to the area where the boil is located. Place a bandage over it. Perform dressings daily. |
Furunculosis - symptoms
The main symptom of furunculosis is the appearance of multiple boils. The inflammatory infiltrate has a characteristic appearance. In the center of the pustule (purulent inflammation) there is a black (necrotic) rod. The pustule itself is located on swollen skin and is surrounded by a rim of inflammatory hyperemia.
Boils are sharply painful. The severity of swelling around them depends on the location of the boil. The most pronounced swelling is observed with furunculosis of the face and genitals.
For reference. There is also an increase in lymph nodes close to the source of the infectious process. With facial furunculosis, the cervical, submandibular, and parotid lymph nodes become enlarged. With furunculosis of the buttocks or genitals, the inguinal lymph nodes become enlarged.
With boils in the nasolabial triangle, there is a high risk of complications. Symptoms of the development of complications will be the appearance of rapidly increasing swelling, pain and hardening of the veins during palpation, the appearance of symptoms of severe intoxication, fever, and the appearance of a purple tint to the skin of the face.
Attention. With the development of inflammation of the meninges, photophobia, vomiting, and stiff neck appear.
Antibiotics
Antibacterial drugs for the treatment of furunculosis:
- “Tseporin” (taken twice a day, one tablet, has traditional contraindications for antibiotics, is used in the treatment not only of ulcers on the surface of the skin, but also eliminates internal boils);
- “Erythromycin” (it is recommended to take one tablet twice a day; the effectiveness of the drug may decrease as a result of the body’s rapid adaptation to the components; not recommended if you have diseases of the digestive system and kidneys, or individual intolerance);
- "Cefalexin" (the dosage is selected in accordance with the instructions, helps fight boils; it is recommended to carry out a certain course of treatment; it has typical contraindications - individual intolerance, some diseases).
The method of treating furunculosis with tablets differs in some nuances. Any means with the desired effect can be used as an antibiotic, but if chronic formation of ulcers occurs, the use of such drugs is supplemented with vitamins or agents that strengthen the immune system. Long-term treatment with potent drugs can cause dysfunction of some body systems.
Multiple boils
When a significant number of boils appear, a disease occurs - furunculosis. Most often, multiple boils are located in limited areas of the skin surface.
By prevalence it should be noted:
- localized furunculosis, in which infiltrates are located in one area;
- disseminated furunculosis. Painful lesions are distributed over many parts of the body.
But sometimes ulcers spread to different parts of the body. Furunculosis often recurs, and new boils develop in place and next to the old ones.
Therefore, the following phases of the disease are distinguished:
- acute form of furunculosis. With it, many boils simultaneously appear on the skin, going through all stages of development, ending with recovery;
- chronic form of furunculosis. It is characterized by the constant appearance of new lesions arising in already healed areas.
Surgical removal
Surgical intervention is indicated when purulent infiltration spreads into the subcutaneous tissue with the formation of a voluminous abscess. In this case, surgical opening of the lesion and sanitation (cleaning the abscess cavity) is necessary. The intervention is carried out in a hospital operating room.
Antibiotics for boils are selected only by a doctor, depending on the sensitivity of the staphylococcal infection to them, as well as taking into account the patient’s tolerability. Also, antimicrobial drugs are used topically during a long healing process.
Treatment of a boil in a child is carried out according to the same scheme as in an adult.
Signs of boils appearing in other places
Boils may appear in the armpit area. In this case, hidradenitis occurs - a purulent process of the sweat gland. The complaints accompanying this pathology are similar to those that arise with a regular boil. Additionally, pain appears during movement of the shoulder joints.
In the groin area, a boil can cause complications on the lymph nodes and vessels, which is manifested by the appearance of painful subcutaneous cords and lumps (regional lymphadenitis and lymphangitis).
In women, specific boils of the labia majora occur, complicated by infection in the Bartholin glands. Bartholinitis occurs, accompanied by severe swelling of the labia, pain and severe redness.
The largest boils form on the skin of the buttocks and thighs.
Folk remedies
Boils are often treated with folk remedies. And they give quite a good effect, especially if the inflammatory process begins to be treated at the very beginning.
- Medicinal honey cake. Mix a teaspoon of chicken yolk, a dessert spoon of honey (not candied), 5 grams of butter (without salt) and knead into a soft dough, gradually adding wheat flour. The cake is applied to the boil and secured with a bandage or plaster. The dough for the procedure is prepared and applied daily until the pyogenic masses are completely removed.
- Drawing out pus with aloe or agave. The young tender leaf is cut, the spines are removed and kneaded. Apply a bandage to the boil, which is changed 5-6 times a day. With a ripening boil, all processes accelerate, and the abscess opens faster. Apply at any stage. If the boil does not break out in the early stage, the inflammatory phenomena may completely subside.
- Onion. The peeled onion is baked in the oven until soft and cut in half. The warm half is applied to the boil treated with hydrogen peroxide and secured with a gauze bandage. The bulb needs to be changed once a day until the pus completely drains from the wound. When changing the dressing, do not forget to treat the affected tissue with peroxide.
- Buckwheat porridge on water. Boiled buckwheat is also used to treat boils. Spread a spoonful of very thick porridge on gauze and apply it to the inflamed area, replacing it with a fresh mixture after 4 hours.
Complete disappearance of the boil takes from 3 days to several weeks. If you have a fever, severe pain, or existing chronic diseases, consult a doctor. Home treatment is designed only for uncomplicated forms of the disease and is especially effective in the initial stage of inflammation.
View photos
[collapse]
What causes abscesses?
Contact with pyogenic microbes on the skin does not always lead to the formation of boils. Many bacteria, including staphylococci, are part of the skin microflora and coexist peacefully with humans.
But there are many factors that provoke a purulent inflammatory process:
- decreased immunity, as a result of which the body lacks protective antibodies to fight pathogenic bacteria;
- the presence of chronic diseases, as well as infectious diseases;
- metabolic disorders, including diabetes;
- hormonal imbalance – often during adolescence, in pregnant women and during menopause;
- hyperhidrosis – excessive sweating promotes the growth of bacteria;
- active functioning of the sebaceous glands;
- vitamin deficiency as a result of improper, unbalanced nutrition;
- overheating and hypothermia, which disrupt the regenerative functions of the skin;
- various skin injuries, including during shaving, depilation, irritation of the skin by tight clothing, items made of synthetic fabrics;
- neglect of personal hygiene;
- skin contamination under hazardous working conditions;
- overwork, stress.
The risk of developing boils increases significantly in people suffering from alcohol and nicotine addiction. Bad habits are one of the reasons for the appearance of unpleasant skin problems.
Complications
Most boils heal without medical intervention or complications. However, in rare cases, a boil can lead to serious consequences, such as sepsis. This complication can lead to severe infectious damage to the heart, lungs, kidneys, bones, joints, brain and even death. Also, a boil can lead to scarring after healing.
Improper use of antibiotics can cause MRSA (methicellin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus). In this case, treatment can be very difficult and lengthy, and the risk of infection spreading throughout the body increases many times over.
With ineffective treatment or prolonged self-medication, a large amount of pus can accumulate inside the boil, which can lead to the development of an abscess boil. If this occurs on the face, then thrombophlebitis of the facial vein or angular nasal vein may develop. This condition can threaten the patient's life.
Measures for the treatment of furunculosis
Independent intervention in the case of existing furunculosis does not bring success. Long-term outpatient and inpatient treatment with repeated preventive courses is required.
Local methods of influencing boils are used, which are identical to cases of single lesions. The main attention is paid to stimulation of the immune system and general measures of influence on pathological foci.
For these purposes the following is used:
- ultraviolet irradiation;
- laser therapy;
- immunostimulation (T-activin);
- treatment with immunoglobulins, interferon, rhinoleukin;
Antibiotics for the treatment of furunculosis are prescribed only after determining the sensitivity of the isolated pathogen to them. The patient's reaction is also taken into account.
Important: the boil opened on its own, what should I do? In this case, it is necessary to thoroughly wash your hands, rinse off the released necrotic masses with furatsilin solution and gauze swabs, then rinse the cavity several times with hydrogen peroxide. Seek medical help if necessary.
Antiseptics
Such medications are prescribed to prevent rotting and disinfection. Potassium permanganate is usually used when treating wounds. But alcohol tinctures are also used for boils. Antiseptics kill germs and painlessly disinfect the skin. To process chiri, the following are suitable:
- "Chlorophyllipt";
- Vinilin”;
- "Fukortsin";
- salicylic acid;
- "Betadine";
- potassium permanganate;
- "Magnesia".
"Chlorophyllipt"
Available in the form of an oil solution or as an alcohol tincture. Sometimes there are capsules. The effective product contains chlorophylls, which are released by eucalyptus leaves. The plant is famous for its bactericidal and antiseptic properties. But for furunculosis, the medicine is used as a compress on the site of inflammation or wiped on the face for prevention.
"Dimexide" for boils is used for external treatment.
"Dimexide"
It is better to apply the drug precisely to the source of inflammation in the form of a compress. This way, it will better relieve swelling and resist the spread of infection, because absorption begins within 10 minutes after application. The main component of the medication is dimethyl sulfacite, thanks to which the drug is used when it is necessary to numb a boil. The action of the drug is aimed at destroying varieties of staphylococcus.
Why do boils appear?
The bacteria Boils - Treatments, Causes, and Symptoms, more precisely staphylococci, are to blame for everything. They live on the skin of each of us and in most cases do not cause much trouble. However, under certain conditions, a violation of the peace treaty is possible.
With injuries, mechanical damage (for example, constant friction) or decreased skin immunity (it is caused by a variety of reasons: from vitamin deficiency to diabetes), staphylococci can penetrate the skin. Specifically, the hair follicle is the sac from which hairs grow.
Inflammation develops in the hair follicle, so there is always hair in the center of the boil.
In response to aggression, the body sends leukocytes—white blood cells—to the same pouch, whose task is to absorb and digest insolent microbes. By destroying the infection, the leukocytes themselves die - this is how pus is formed.
When dying, defenders release substances that cause a local inflammatory reaction. Therefore, the skin around the battlefield swells, turns red and becomes hot.
Redness and soreness persist until the boil opens and empties. The stages of this process look something like this:
Photo of furunculosis
Read here! Meniere's disease: clinical picture of the disease and advice on choosing a treatment method (95 photos)
Please repost
0
2
Operative methods of getting rid of chiries
Surgical intervention is used at the stage of the formed purulent-necrotic core of the boil. After its removal, there is a rapid decrease in swelling and tissue tightening, and an improvement in well-being.
The surgical treatment technique is as follows:
- lysis of the skin over the abscess using acids and installation of drainage for the outflow of pus;
- mechanical method of removing the rod with tweezers or a clamp with drainage;
- tissue incision above the boil, cleaning of necrotic tissue.
The first treatment option involves artificially opening the boil using salicylic acid crystals. After the breakthrough, independent rejection of necrotic masses begins, and clinical manifestations decrease. To speed up the process, latex drainage is introduced. It is removed after complete cleansing of the wound. Carry out daily dressings with antiseptic treatment.
The second method of treating a boil is performed without the use of an anesthetic. The hair follicle and surrounding tissues have rotted away; removal should be painless. Further actions are similar: dressings, antiseptic treatments.
The third method of treatment is used when an abscess forms, when the accumulation of pus is significant. After treating the skin with antiseptic solutions and administering local anesthesia, tissue dissection is performed in the area of greatest softening. A culture is taken for sensitivity to antibiotics. Wash the wound after a boil with antiseptics. Drainage is installed and covered with an aseptic bandage.
Related factors
In order for the picture of the disease to take on a characteristic clinical character, a combination of exogenous (external) and endogenous (internal) factors and causes is necessary that contribute to the colonization and survival of staphylococci in the body. Exogenous predisposing factors may be the following:
- permanent mechanical damage to the skin;
- presence of harmful production conditions;
- insufficient hygiene for skin infections;
- severe hypothermia or hyperthermia.
Among internal factors, an important role belongs to diseases of various organs and systems, as well as reasons associated with lifestyle errors. Pathologies of the body that have a significant impact on the state of the immune system can be the following:
- obesity;
- diabetes;
- diseases of the thyroid gland and other endocrine glands;
- hypo- and vitamin deficiencies;
- chronic infectious processes in the tonsillar tonsils, teeth, physiological cavities;
- physical and psychological exhaustion;
- lability of the autonomic nervous system.
Disease detection
Diagnosis of the disease consists of conducting the following medical studies:
- Medical examination.
- Dermatoscopy.
- Examination of the boil contents for the presence of microorganisms.
Additional research methods include clinical tests of urine and blood, ultrasound, computed tomography, x-ray of the sinuses, and rhinoscopy.
What to apply for boils
The main thing in the treatment of ulcers is the rapid maturation of the boil.
Photo 5 – It is important that the boil matures
To do this, apply a bandage, as well as apply lotions to the area where the boil occurs with a variety of medications, which leads to better cleansing of the wound and a reduction in inflammation.
Photo 6 – Lotions and dressings with medicines will help the boil to mature
In order for the abscess to mature faster, ointments are used, most often NSAIDs (anti-inflammatory drugs). They reduce skin inflammation and lead to an improvement in a person’s condition.
Photo 7 – Use anti-inflammatory drugs
Medicines for boils
Antibiotics, antiseptics, anti-inflammatory and painkillers are always used against boils from specific therapy after surgery.
Photo 8 – Furuncle removed surgically
Which drugs are effective, and what to treat or numb the skin with, you should definitely ask your doctor, since self-medication is strictly contraindicated and can lead to complications.
Photo 9 – The doctor will select an effective treatment
In any pharmacy you can find the necessary groups of drugs that are used when a boil occurs.
Photo 10 – The pharmacist at the pharmacy will tell you what to use against the boil
Antibiotics are drugs that act on a specific type of bacteria, and knowing the spectrum of their action, we can actively prescribe them to a particular pathogenic flora. Based on this, they are divided into certain groups for the treatment of boils.
Photo 11 – Antibiotics are divided into groups
The causative agents of this disease can be different, so different groups of these drugs :
- cephalosporins (cephalexin, cefotaxime, ceftriaxone, ceftazidine);
Photo 12 – Ceftriaxone for infections - tetracyclines;
Photo 13 – Tetracycline - penicillins (amoxicillin, ampicillin, amoxiclav);
Photo 14 – Amoxiclav - macrolides (erythromycin, azithromycin, spiramycin);
Photo 15 – Spiramycin - fluoroquinolones (ciprofloxacin, ciprolet, tsifran);
Photo 16 – Ciprofloxacin - metronidazole, clotrimazole;
Photo 17 – Metronidazole - lincomycin;
Photo 18 – Lincomycin - aminoglycosides (baneocin - ointment);
Photo 19 – Baneocin - fucidin (fusidic acid);
Photo 20 – Fusidic acid - zinerite (erythromycin + zinc).
Photo 21 – Erythromycin
Anti-inflammatory drugs: Dimexide, Salicylic acid, Celestoderm (glucocorticoids), Nimesil, Boric acid.
Photo 22 – Dimexide – an anti-inflammatory drug
Photo 23 – Celestoderm – anti-inflammatory drug
To solve the problem of how to cauterize a boil, as well as after opening the resulting wound, antiseptics can be used:
- Ichthyol. Ichthyol ointment is one of the most common and effective drugs against boils. It has a large number of properties that are excellent for affected skin. These include: regeneration, improvement of blood circulation in affected skin, antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, thickening and drawing out of pus.
Photo 24 – Ichthyol will help the boil to mature - Chlorhexidine.
Photo 25 – Chlorhexidine – kills germs - Furacilin (furacilin alcohol).
Photo 26 – Furacilin – prevents germs from spreading - Chlorophyllipt.
Photo 27 – Chlorophyllipt - Vitaon.
Photo 28 – Vitaon - Dioxidine.
Photo 29 – Dioxidine - Sulfuric acid (sulfur for boils is not often used).
Also, magnesium sulfate can be used as an anti-inflammatory agent for skin lesions, in particular with the development of a boil, which, due to rapid absorption by the skin, has a faster effect.
Photo 30 – Magnesium sulfate for boils
All these remedies are excellent for treating boils. They destroy the pathogen, relieve the inflammatory reaction, and disinfect the wound.
Photo 31 – There are many remedies for treating boils
There are other less specific, but still used medications for the development of furunculosis. These include hydrogen peroxide, magnesia, calendula (especially used when pus is leaking), “rescuer” cream and others.
Photo 32 – Rescue cream is less effective in combating boils
There are also folk methods that patients use at home:
- warm compresses from horsetail, onions, cabbage leaves, cottage cheese. These ingredients soften the abscess and help cleanse the cavity of pus;
Photo 33 – Folk remedies help against boils - Arnica montana, hibiscus root, chamomile decoction contribute to the maturation of the boil.
Photo 34 – Chamomile decoction promotes ripening
Plasters for boils are also used, which contain antibiotics, anti-inflammatory agents, and disinfectants. At home, patients can still cauterize boils, but this only works at the beginning of the process, and even then, it is not advisable to do this, as it may have further side effects and complications (burn, sepsis).
Photo 35 – You can cauterize a boil only at the very beginning
Attention! You should not self-medicate and squeeze out boils, as this can lead to the development of adverse consequences, including septic conditions.
What drugs are used?
Many remedies have been developed for the treatment of furunculosis. The inflammatory process is a complex combination of internal and external factors; to eliminate it, you need to act from different angles. The type of therapy depends on three components: stage, size, cause.
Furunculosis: treatment with the following drugs:
- Antibacterial drugs have a detrimental effect on living cells - beneficial and harmful microorganisms. Quickly and effectively suppresses the pathogen - staphylococcus.
- Anti-inflammatory. Any medication from this group quickly reduces and stops inflammation. In the vast majority of cases, the doctor prescribes the medicine in the form of an ointment. It is applied pointwise to the boil, which accelerates the absorption of active substances. Popular drugs: Rescuer, Diclofenac, Dimexide. Tablets may be prescribed - Nimesulide, Voltaren, Aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid), etc. They provide an analgesic effect and alleviate the patient’s condition.
- Antiseptic. They prevent relapse, stop rotting, disinfect, kill germs. For the treatment of boils, the following are used: potassium permanganate, Fukortsin, Betadine, Magnesia, Vinylin, Chlorhexidine, Baneocin ointment, Furacilin, salicylic acid, Chlorophyllipt, Miramistin.
- Antihistamine. Reduces tissue swelling.
- Preparations to strengthen the immune system. Bacterial infection attacks more often at times when the body's defenses are weakened. An immunomodulator will help strengthen it. To treat furunculosis, it doesn’t matter what it is - a capsule, a drop or a tablet, the main thing is the result. The duration of the course depends on the patient's condition. A good therapeutic effect is given by: Galavit, Immunal, Timalin, Polyoxidonium. Lykopid helps to increase local immunity.
- Vitamins and homeopathy act as aids in the chronic form of the disease, for preventive purposes. The homeopath selects herbs and describes the scheme for their use. When treating furunculosis with homeopathy there are no contraindications; it can be used even if the patient is a child. Vitamin preparations are taken in courses; they must contain substances beneficial to the skin.
The doctor conducts an examination and then makes recommendations for treatment.
The first stage of the disease involves treatment with alcohol solutions and antiseptics: Miramistin spray, medical diluted alcohol (diluted with boiled water), Chlorhexidine, Furacilin solution. Apply gently to the boil, working around the area.
After self-opening, disinfection is carried out. A compress is applied, under which there is a drug with anti-inflammatory and disinfectant action.
If the abscess does not open on its own, surgery should be performed in a hospital setting. First, an injection of antibiotic and painkiller is given, then the lump is cut with a scalpel. After surgery, local or extensive antibacterial therapy is carried out.
In the chronic course of the inflammatory process, it is important to pay attention to strengthening the body. If the cause is a helminthic infestation, Dikaris and its analogues are prescribed. If the intestinal microflora is disturbed, probiotics are needed - Lactofiltrum, Diflucan. If the protective mechanisms fail, immunomodulators, vitamins, herbal infusions, and preparations are prescribed.
Where else does a boil occur?
The face is not the only place where unpleasant symptoms can appear. Sometimes, relatively infrequently, furunculosis can be localized in the armpit, groin area, lower extremities, genital area and buttocks. In some cases, the lymph nodes may be affected along with the disease. The most severe symptoms accompany boils located in the thighs and buttocks. It should be noted that in such places the pimples themselves are the largest.
Therapeutic procedures
Cryotherapy for boils is a physical procedure using cold. As a result of the sequential narrowing and dilation of blood vessels under the influence of low temperature, their tone is restored. This reduces exudation, swelling and pain. Tissue trophism improves, tissue resistance to infection increases.
Need advice from an experienced doctor?
Get a doctor's consultation online. Ask your question right now.
Ask a free question
Autohemotherapy is a method based on the intramuscular injection of the patient’s own blood. The technique has a stepwise scheme. Blood is injected, gradually increasing the volume to 10 ml. Treatment with autohemotherapy is indicated for furunculosis. Nonspecific stimulation of the immune system occurs.
Hijama - bloodletting treatment. A puncture is made and a jar is installed in its place. Periodic bloodletting stimulates the proliferation of bone marrow cells, which increases the body's nonspecific defense. Used for furunculosis.
UHF is a method of physiotherapy. By creating an electromagnetic field, tissues are heated. Heat stimulates regeneration, increases blood flow at the site of application, increasing the influx of immune cells and antibodies, and promotes the resorption of infiltrate. A contraindication to treatment is the presence of pus.
Plasmapheresis is a method of detoxifying the body. The plasma is purified from toxins and metabolites. It is used in surgery for severe forms of furunculosis, sepsis, and as part of complex therapy.
Boil causes
There is no doubt about the bacterial origin of the boil, since the main cause is said to be a staphylococcal infection. Normally, staphylococcus is part of the microorganisms living on human skin. And only about 10% of all bacteria of the Staphylococcaceae family are capable of causing infection.
Patients suffering from furunculosis have an imbalanced ratio of pathogenic and beneficial microflora. So the number of harmful microorganisms on their skin can reach 90%. The reasons for the predominance of pathogenic microorganisms can be: injuries followed by infection due to decreased immunity, ignoring the rules of skin hygiene.
Malfunctions of the immune system are often caused by the presence of foci of chronic infections in the body, such as:
- infectious and inflammatory disease of the paranasal sinuses (sinusitis);
- inflammation of the maxillary sinus (sinusitis);
- inflammation of the tonsils (tonsillitis).
Furunculosis is also provoked by various metabolic disorders, such as diabetes and endocrine pathologies. Corticosteroids and cytotoxic drugs are used in the treatment of these diseases. They suppress the immune system and have a number of other side effects, which also provokes the formation of boils.
Maceration of the skin with a tendency to sweat profusely can provoke injury and the entry of pathological flora into the hair follicle.
The skin loses its protection and pathogenic microorganisms can easily penetrate it if the following diseases occur:
- itching of the skin as a symptom of dermatological diseases;
- chronic allergic dermatitis
- seborrhea;
- eczema;
- dermatomycosis;
- scabies.
The formation of a boil in the ear or nose can provoke chronic otitis media, rhinitis, and other nasopharyngeal inflammations with the release of purulent contents.
Signs
A thickening appears on the skin. Very quickly, literally within the first hours, the following are noted:
- redness;
- severe pain;
- purulent contents.
Once the head becomes visible, the pain intensifies . Due to the accumulating purulent contents, the head of the abscess appears whitish-yellow.
As the boil matures, the following may appear:
- increased body temperature;
- enlarged lymph nodes;
- local change in blood circulation.
After the boil breaks out, the pus flows out and the recovery stage begins. After healing, a scar may remain in its place .
Features of boil treatment
Boils not only cause discomfort with constant pain, but also do not look aesthetically pleasing. Many people have a desire to squeeze out the pus, but this should not be done. Yellowish masses can be removed using special medications. When treating a boil at home, it is necessary to take into account the location of the abscess and the stage of development of the boil.
- Causes of boils on the genitals of women - signs and treatment regimen
- How and how to treat paraproctitis - subcutaneous, chronic, purulent
- What is an abscess: symptoms and treatment
On the butt
Occurring in some areas of the skin, boils can cause significant discomfort. For example, a boil on the butt (and on the labia, including the pubis) is constantly in contact with clothing. This nuance directly affects the healing process of inflammation. It is recommended to combine the use of ointments with regular sealing of the abscess with a plaster to reduce friction with underwear or other items of clothing.
In the ear
If a boil occurs in the hearing organs, it is recommended to consult a specialist. The disease can cause otitis media. The treatment process does not differ from traditional methods, but the abscess must be constantly sealed with a bandage or a bandage worn to eliminate the risk of dust and contaminants.
On the eye and face
If boils appear on the facial area, it is not recommended to use cosmetics. It is not worth warming up a boil on the eye, as some traditional healers advise. Heat will negatively affect the pus, and furunculosis will begin to develop at an accelerated pace. The optimal treatment methods in this case are ointments, antibiotics, and traditional medicine methods.
In the nose
A boil in the respiratory system can lead to the development of dangerous ENT diseases. Such ulcers must be treated with maximum attention. Squeezing out pus is prohibited, and all hygiene procedures are carried out carefully. Treatment is based on the use of ointments, antibiotics and traditional medicine.
On the foot
Blood circulation of the lower extremities has its own characteristics. Boils on this part of the body are classified as the most dangerous diseases. It is not recommended to wet areas of inflammation. Ulcers must be constantly covered with a bandage or a bandage. Infection can cause diseases that negatively affect the arteries or musculoskeletal system.
Under the arm
The main problem in treating a boil under the arm is sweating. This nuance can cause significant discomfort and cause burning of the skin. During the period of development of the abscess, you should not play sports or exercise. Friction of the boil on clothing is prevented by a bandage or plaster.
Diagnostics
Characteristic local manifestations, patient complaints and examination data allow the doctor to easily make a clinical diagnosis. In a general blood test, a pronounced increase in the number of leukocytes (including segmented and band forms) and an acceleration of ESR are noted.
If the disease persists, a bacteriological analysis of the discharge from the boil is carried out to isolate the causative agent of the disease and determine its sensitivity to antibiotics. Such an examination allows you to increase the effectiveness of treatment.
If there is no effect from the therapy, immunological and other necessary examinations are performed to identify systemic internal diseases (diabetes mellitus, anemia, blood diseases, etc.).
How to distinguish a boil from a regular pimple?
The reader should understand that there are distinct differences between a regular pimple and a boil. This is necessary to know in order not to inadvertently injure the purulent core of the boil and thereby not introduce a staphylococcal infection into the blood. If the purulent core in the subcutaneous space is destroyed, staphylococcus bacteria will spread along with the bloodstream throughout the body. Here it is possible to develop furunculosis (the appearance of boils on the surface of the body anywhere) or purulent meningitis (if the boil was located on the neck or head area).
Important: under no circumstances should you squeeze the boil. Especially on the face or neck.
The main differences between a pimple and a boil:
Instructions for the use of Taktivin injections and analogues
- A pimple is a mild stage of the inflammatory process in the skin. Furuncle is an inflammatory purulent process in its deep layers at the base of the follicle;
- Redness for a pimple is often not typical or may be mild. At the site of boil formation, redness reaches a diameter of 1-3 cm;
- Pain is not typical for a regular pimple. At the site where the boil forms, the pain is pronounced and can even spread throughout the body or nearby tissues;
- A standard pimple is sebum that has not come to the surface and has accumulated in a clogged sebaceous duct. When ripe, the pimple breaks out on the 3rd day. The boil takes 6-8 days to mature;
- When a pimple breaks out, the wound is not as significant as when a boil breaks out;
- In addition, a common pimple does not leave scars on the skin, while a boil may leave obvious cosmetic marks in the form of deep scars.
How to cure boils in children at home?
Treating boils in children at home should be treated with great caution.
Folk remedies are not a substitute for professional medical intervention.
But, in exceptional cases, it is permissible to carry out home therapy. But, only if there is no temperature, no signs of intoxication, and no spread of the inflammatory process to tissues adjacent to the boil.
To speed up the maturation of the abscess, a still warm hard-boiled egg is applied to the affected area.
Compresses made from oils are also used - fir, sea buckthorn, camphor. Ulcers in children can be removed with the help of baked onions, which draw out pus well.
It is good to treat the affected areas with herbal decoctions and infusions - use chamomile, eucalyptus, and string.
In the treatment of boils in children, honey cakes, plantain ointment, beet juice are used, and brewer's yeast can be taken.
The child’s body is more vulnerable and defenseless against infections, so you should consult your doctor about home treatment.
If you are interested in why a cold in the nose appears and how to treat it, read this publication and find out.
You can learn about what the diet for seborrheic dermatitis should be, which foods are allowed and which are contraindicated, from this article.
Treatment of furunculosis with local and systemic drugs
Furunculosis, treatment with drugs is prescribed only after confirmation of the diagnosis, must be subjected to complex therapeutic effects. You are allowed to use products for local treatment of affected areas yourself. In this case, the most effective drugs are considered to be ichthyol ointment and liniment according to Vishnevsky.
Preparations for external use are used in cases of boil maturation or for treatment after removal of purulent-necrotic masses:
- Vishnevsky ointment. The product contains birch tar, castor oil and xeroform. Reduces inflammatory reactions and has antibacterial properties. Helps speed up regeneration processes. Treatment of the affected area is carried out as prescribed by the doctor.
- Ichthyol ointment. Used as an antibacterial and analgesic. Promotes accelerated maturation of formation, helps draw out pus.
- Tetracycline ointment. Used for various types of staphylococcal infections.
- Levomekol. It is prescribed to suppress the vital activity of staphylococcus and prevent the development of secondary infection.
To suppress pathogenic microorganisms and prevent the development of secondary infection, Baneocin is prescribed, a combined antibacterial agent in powder form for local treatment.
Healing of the boil
The healing stage of the boil is characterized by the formation of connective tissue in the hole left after its breakthrough. A scar forms at the site of the boil over several days. At first it is very noticeable and has a bluish-red color, and then gradually lightens and becomes almost invisible.
In some cases, the course of the disease may be more subtle and not accompanied by the appearance of a necrotic core. If a boil forms in the auricle, then severe ear pain, radiating to the jaw and temporal region, is added to its general symptoms. Sometimes complaints of a general headache may appear. A boil can impair hearing by blocking the ear canal.