What is eye pressure
Intraocular pressure reflects the pressure of the fluid inside the eye. The stable functioning of the retina depends on its indicator. A decrease or increase in value may indicate the development of diseases that affect the quality and acuity of vision.
All people experience eye pressure. Standard values are from 10 to 20. After 50 years, an increased rate is more common. According to statistics, the likelihood of developing glaucoma increases:
- 50-65 years – 20%;
- over 70 years old – 30%;
- over 85 years old – 40%.
Fluid outflow sharply worsens with age. If you have cataracts, drainage problems become worse. Against the background of weakened functioning of the visual system, serious ophthalmological diseases develop, including glaucoma.
After 40-45 years, the condition of the visual organs should be checked at least 1-2 times a year.
There are also other reasons for changes in IOP, which cause vision problems not only in older people. Among the main ones:
- severe stress;
- migraine attacks;
- nervous tension;
- hypertension;
- inflammatory eye diseases;
- hereditary predisposition.
With a slight change in eye pressure, symptoms do not appear. Pronounced signs indicate a significant deviation of the indicator from the norm.
Normal IOP in children
The normal intraocular pressure in children is the same in both sexes. For young patients, it is allowed to use tonometry to determine the indicator of eye functioning in question.
Parents need to pay attention to their child's behavior. When intraocular pressure changes, the child may experience heaviness in the eyes, pain in the head, and feel tired. Fatigue is especially noticeable in the evening.
At the first symptoms of increased ophthalmic tone in a child, he should be urgently shown to a pediatrician or ophthalmologist. After measuring the IOP value, he will develop further measures. It is necessary to pay attention to the fact that glaucoma develops extremely rarely in children. An increase in IOP in young children often indicates a malfunction of the thyroid gland.
We recommend reading: Eye pressure in children
Symptoms
After 45-50 years, women experience increasing disturbances in blood microcirculation in the eye. There are deviations in the optical properties of the retina. The changes are associated with hormonal characteristics and a lack of estrogen during menopause.
Cases of low blood pressure are less common. A common problem is increased IOP.
The pathology is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- rainbow circles before the eyes, goosebumps when focusing on the light;
- redness of the whites;
- rapid eye fatigue;
- feeling of pain;
- discomfort when reading books, working at the computer, watching TV;
- narrowing of the field of view;
- decreased visual acuity at dusk;
- pain in the temporal part, in the forehead area.
The symptoms of low blood pressure are more expressive:
- dry mucous membranes;
- loss of healthy shine in the eyes;
- prolapse of the eyeball.
The reasons for deviation of IOP from the norm are: age-related changes, congenital pathologies, ophthalmological diseases accompanied by an inflammatory process.
What it is
Every second a certain amount of fluid enters the organs of vision, then it flows out. Disruption of this process causes moisture to accumulate, which causes high eye pressure.
In this case, small vessels that regulate the outflow of fluid are deformed, and nutrients stop flowing to all parts of the eye, causing cell destruction.
This happens under the influence of many factors, including:
- heavy strain on the eyes (poor lighting in the room, watching TV);
- genetic predisposition;
- diseases of internal organs and eyes;
- chemical poisoning;
- hormonal disbalance;
- bad ecology;
- the use of certain eye drops and medications;
- damage to the integrity of the membranes of the eye;
- stressful state;
- disruption of the heart and blood vessels.
Pathology is often found in women during menopause.
Deviations from the norm may be the result of smoking and exposure to ethanol, high salt intake, and lack of minerals and vitamins. Changes in eye pressure are equally common in both sexes. Its increase is observed mainly in people after 40 years of age.
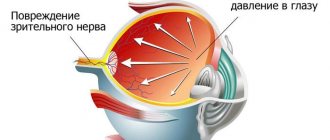
Increased IOP may cause damage to the optic nerve
Neglected pathology can lead to the development of diseases that modern medicine is not always able to overcome. Today, more than five million people in the world are blind due to high eye pressure.
Types of increased intraocular pressure
Experts recognize three types of ophthalmotonus:
- Stable – increased values are maintained on an ongoing basis.
- Transient - the IOP value increases once for a short time.
- Labile - periodic deviations of the pressure indicator towards increase are observed.
The first sign of glaucoma is stable ophthalmotonus. Pathology appears more often after 43-45 years or as a consequence of ophthalmological diseases.
In women, cases of glaucoma are diagnosed more often.
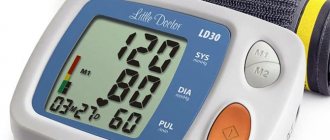
How is intraocular pressure measured?
IOP analysis is called tonometry. There is no need for special preparation before this examination. It is recommended to fulfill certain conditions:
- You must come to the examination in loose clothing;
- the patient does not need to worry before and during tonometry;
- 4 hours before the examination you do not need to drink a lot of liquid;
- contact lenses must be removed.
There are several ways to measure pressure. In the case of using the Maklakov method, the cornea is pre-treated with an anesthetic solution. Next, a medical load is placed on it. During tonometry, the eyeball sag and this area is colored with pigment.
The Goldmann method uses a slit lamp and an ophthalmic probe. An anesthetic is also instilled into the eyes. A paper strip is placed on the eye, then pressure is applied to it. A trace of pigment remains on the organ of vision and is analyzed.
An alternative diagnostic method is impression tonometry. It is carried out only in an eye hospital. Upon contact with the eyeball, the tonometer automatically records the tone, and the diagnostic results are displayed on the monitor screen.
During pneumotonometry, compressed air is released onto the eyeball. Based on the reaction of the cornea to the air stream, an increase or decrease in intraocular pressure is judged. This diagnostic method does not involve the use of painkillers. Most often it is used to diagnose blood pressure in children.
The simplest way to determine ophthalmic tone is palpation of the eye. The patient himself can do this. He needs to close his eyes, look down. Next, you should rest your forehead on your thumbs, and touch your eyelid with your index fingers and lightly press on it. If the pressure is increased, the eyeball will be elastic (and if it is significantly higher than normal, it will be hard as a stone). On the contrary, when IOP decreases, the sclera will seem to be “pressed through.”
The value of IOP indicators
Pressure limitsTrue, mm Hg. Art. Tonometric, mm Hg Art. Within normal limits 10—2012—25 Initial phase of glaucoma 21—22 to 26 Moderate glaucoma 26 to 36 Middle phase of glaucoma up to 33——Chronic glaucoma more than 33——Normal eye pressure in humans
The normal level of eye pressure depends on age and slightly on gender. For example, during pregnancy and menopause in women, indicators may change, and this is not considered a pathology.
The highest IOP is in newborns. It begins to gradually decline until the age of 10.
| Age | Men | Women |
| 20-30 years | 14,93+-2,47 | 14,97+-2,51 |
| 30-40 years | 15,17+-2,97 | 15,13+-2,82 |
| 40-50 years | 15,55+-2,96 | 15,71+-3,04 |
| 50-60 years | 15,89+-3,21 | 16,47+-2,89 |
| 60-70 years | 16,33+-3,8 | 16,79+-3,79 |
| 70-80 years | 16,14+-4,15 | 17,15+-3,83 |
Norms may vary slightly depending on the tonometer.
The norm is a very arbitrary concept, because the average indicators are scattered in the range from 11 to 21 mm Hg. In this case, the tonometer, the time of day and even the time of year matter, since all this causes the indicator to change slightly.
Useful video
Normal eye pressure:
Measurement methods
Patients cannot measure intraocular pressure on their own. This requires medical devices. Common values in numbers are a natural indicator of IOP or the result obtained using the Maklakov technique.
The process of obtaining data involves applying a certain force to the eye. Decoding the response of the organ of vision reflects the result. Measurement impact options:
- Contact - the ocular surface is in contact with the measuring device.
- Non-contact - air flow is used as a force to influence the organ of vision.
When conducting an examination in a clinic, the following tonometry methods are offered:
- electronograph;
- ICare tonometer;
- Goldmann device;
- according to Maklakov;
- non-contact tonometry;
- pneumotonometer;
- device "Pascal".
Pneumotonometry is a painless procedure. The patient does not feel any discomfort during IOP measurement. Taking accurate data is necessary for high-quality diagnosis and adequate prescriptions. Therefore, readings made by an ophthalmologist by pressing a finger on the eyeball are not taken into account. This information can only be used to make a preliminary diagnosis.
Ultra-precise IOP measurements are necessary to diagnose and treat glaucoma. Inaccuracies can have serious consequences.
The pressure inside the eye can be determined by performing daily tonometry. The analysis is carried out in two ways: according to Goldman, according to Maklakov. The devices take accurate measurements without causing any discomfort to the patient.
According to Goldman
The procedure is carried out in this order:
- An anesthetic and contrast liquid are injected into the eye cavity.
- The patient is asked to sit down at the slit lamp, on which the tonometer is fixed.
- The ophthalmologist applies a prism to the eye and applies moderate pressure with the object on the cornea.
- Using a blue filter, a specialist takes readings at the right moment, and then deciphers them using a special scale.
According to Maklakov
The procedure is carried out in a lying position in the following order:
- Injection of an anesthetic solution into the eye cavity.
- Contrast liquid is applied to glass plates.
- Lower the device onto the cornea so that the painted surface comes into contact with it.
- Press on the eyeball with a metal object.
- The resulting prints are placed on damp paper and measurements are taken with a ruler.
Similar actions are performed with the second eye. You can get the most accurate results by taking measurements 2 p. in a day. This approach is due to the fact that throughout the day the ophthalmotonus changes within three units.
How to measure?
To determine whether the symptoms that appear are a consequence of ophthalmic pathologies, it is necessary to measure the pressure in the eyes. It is impossible to do this at home, since there is no universal device capable of measuring the pressure force of the intraocular fluid without the use of additional methods.
Most public medical institutions use the method proposed by Maklakov , in which IOP is measured using weights painted with a special solution. This procedure is quite unpleasant, but in most cases it allows you to obtain accurate results (accuracy - up to 96.7%) and evaluate the full clinical picture of the health of the visual system.
To reduce discomfort, before the procedure the doctor instills an anesthetic in the form of drops into the eyes. After the medicine begins to act, small weights are placed on the cornea using tweezers, after which they are immediately removed, and the doctor can evaluate the result obtained by the degree of coloring.
- More modern and comfortable diagnostic methods are:
- pneumotomography - determination of the strength of intraocular pressure using air flows;
- electronography – measurement of the rate of production of intraocular fluid and its outflow.
The most accurate method for diagnosing high eye pressure is considered to be Maklakov tonometry.
Ways to reduce pressure
Particularly severe cases require surgical restoration of normal eye pressure. Without surgical intervention, glaucoma will lead to complete loss of vision. With timely treatment, drug therapy and auxiliary measures are used. These include: proper diet, folk recipes, eye exercises.
Drugs
You can normalize eye pressure at an early stage of the disease with the help of medications. Medicines are prescribed by the attending physician, taking into account the condition of the visual organs and related health problems. Among the effective remedies: Timolol, Travatan, Azopt, Xalatan, Pilocarpine, etc.
Timolol
The therapeutic result is achieved thanks to the properties of the active substance of the drug - timolol maleate. Reducing eye pressure is achieved by suppressing the production of intraocular fluid. The product takes effect within 20 minutes. The effect lasts for 8-24 hours. The classic treatment regimen involves instilling 1 drop twice a day. After stabilization of the IOP, a transition to single instillations in the same dosage is carried out. The cost of the bottle is 21 rubles.
Pilocarpine
The basis of the composition is pilocarpine hydrochloride. The active substance penetrates well through the corneal layer. A decrease in IOP occurs against the background of an increase in the permeability of the trabecular diaphragm and the opening of the anterior chamber angle. The achieved effect lasts for 4-6 hours. It is recommended to administer the product 1 to 3 times a day. Single dosage – 1 drop. To relieve an acute attack of angle-closure glaucoma, treatments should be carried out every 15 minutes of the first hour, 30 minutes of the second and third hours, 60 minutes of the next 4-6 hours. On the second day, they switch to 3-6 times eye drops. The cost of the bottle is 53 rubles.
Xalatan
A medicine was made based on the substance – latanoprost. The principle of operation is to stimulate the outflow of intraocular fluid, which helps to reduce the IOP value. After administering the drops, the effect is observed after 3-4 hours and persists throughout the day. A single dose is 1 drop. Carry out procedures more often than once. per day is not recommended. The product has virtually no contraindications; restrictions apply only to allergies. The cost of the bottle is 546 rubles.
Gymnastics for the eyes
Moderate physical activity will help stabilize eye pressure. It is worth considering aerobics classes, cycling, jogging. Training duration is 30-40 minutes. You can arrange them from 3 to 5 times a week.
Gymnastics for the eyes will help bring IOP back to normal. The exercises do not take much time, and mastering the technique is accessible to everyone. Women over 50 simply need such exercise.
How can I reduce IOP?
You can reduce intraocular pressure with eye drops. However, they provide only a temporary effect. Glaucoma is treated with surgery. There are several ways to quickly reduce IOP. All of them are based on increasing the rate of outflow of intraocular fluid.
Increased ophthalmotonus can cause severe visual impairment. Also, this symptom may be a contraindication to laser correction or wearing contact lenses. At the first symptoms of glaucoma and other diseases accompanied by an increase in IOP, it is recommended to be checked by an ophthalmologist. After 40 years of age, you need to check your vision for signs of presbyopia. With increased ophthalmotonus, problems may arise with the selection of correction agents.
Exercise for the eyes
Purpose of the exerciseExecution techniqueTime costsRelaxing muscles, relieving tension. Close your eyes with your palm. After relaxing, blink a couple of times. Repeat blinking at 5 second intervals. 2 minutes. Increasing the flexibility of the eye muscles. Draw an infinity sign with your eyes, imagining it mentally. Movements are performed exclusively by the pupils. 2 min. Strengthening muscles, improving vision. Select 2 objects in the room: close (30 cm) and distant. Focus your gaze on one and the other object alternately. For 1-1.5 minutes. on every subject. Change the position of the eyes 10-15 times. Improving focus Focus your gaze on your arm extended forward. Bring the phalanges closer to the nose, not reaching 8 cm. Move your hand back. For 2-3 minutes. keep your finger on your finger.Eye exercises improve visual function, normalize the outflow of tear fluid, and reduce stress on the optic nerve.
Reasons for deviation from the norm
An increase in intraocular pressure occurs due to the influence of such pathogenic factors:
- increased stress on the organ of vision (for example, prolonged viewing of TV shows or reading in poor lighting conditions);
- unfavorable family predisposition;
- pathological changes in the organ of vision;
- diseases of internal organs;
- chemical intoxication;
- imbalance of hormones;
- unfavorable environmental conditions;
- using certain eye drops;
- violation of the integrity of the eye membranes;
- prolonged stress;
- heart and vascular diseases;
- in women – menstrual irregularities, menopause;
- smoking;
- drinking large amounts of alcoholic beverages;
- insufficient intake of vitamins and minerals into the body.
Reasons for decreased IOP:
- hypotension;
- retinal disinsertion;
- inflammation of the iris;
- dehydration;
- keratitis;
- conjunctivitis;
- blepharitis.
If low pressure inside the eye persists for more than a month, the nutrition of the eye may be disrupted, retinal detachment, optic nerve dystrophy and, as a result, complete blindness. The patient needs to urgently come to see a doctor if a halo appears when looking at a bright light.
Nutrition
Some adjustments are made to the diet. The amount of foods that contribute to the rise of insulin is reduced. This applies to potatoes, pasta, sugar, bakery products, and cereals. It is recommended to consume more dark-colored berries (blackberries, blueberries), as well as vegetables that contain lutein (spinach, Brussels sprouts, broccoli).
Omega-3 fatty acids should be included in the menu. They can be consumed in the form of dietary supplements or natural products - seafood (salmon, tuna, salmon, herring).
Increased pressure level
Increased intraocular pressure
Ophthalmohypertension is an extremely rare but serious pathology that can lead to a marked decrease in visual acuity or amorosis (lack of vision). If the pressure level is constantly high, a diagnosis of Glaucoma is made. This term will combine more than 80 diseases of different causes and pathogenesis, which have a number of common features:
- intraocular pressure is always above normal or intermittently;
- the presence of optic neuropathy leading to atrophy of the branches of the optic nerve;
- vision pathology.
Congenital glaucoma, corneal edema
A similar disease is observed in 3-4% of the population over 65 years of age and in 30% of those who live to 90 years of age. The pathology can also occur in newborns, the incidence is 1 in 22,000 births.
Folk remedies
Alternative medicine can be used to supplement the treatment prescribed by your doctor. There are simple but effective recipes that have stood the test of time.
Aloe decoction
Used to wash eyes. Aloe (about 5 leaves) is poured with boiling water (250-300 ml). Boil the product for 5 minutes. After cooling, the decoction is ready for use.
Decoction of nettle and lily of the valley
Used for lotions. Nettle and lily of the valley (2 tsp each) are poured with boiling water (200 ml). Cover the container with a lid and let the product brew for 9-10 hours. Cotton pads soaked in liquid are applied to closed eyes (for 5-7 minutes).
Potato compresses
The raw root vegetable is grated on a fine grater. Combine it with apple cider vinegar (5 ml). Let it brew for half an hour. The pulp is applied to gauze napkins and placed on closed eyes. You need to keep the compress for 10 minutes.
Regardless of which prescription is chosen to stabilize eye pressure, the course duration is at least 1 month. Regularity of procedures – 2-3 rubles. in Week.
Briefly about intraocular tone
Intraocular pressure is an indicator characterizing the pressure of the fluid located inside the organ of vision on all membranes and structures of the eye. The indicator varies significantly and depends on the following criteria:
- activity of the ciliary body, which ensures the production of jelly-like liquid;
- trabecular system for drainage of intraocular fluid through a special network of trabeculae, its components are located in the anterior corner.
Schematic representation of the fluid dynamics pathways of the eye
Pressure can be quantified using this formula:
IOP= f/c + PV,
where f is the intensity of moisture synthesis, c is the rate of fluid removal from the eye, PV is the episcleral pressure of the veins. The ratio of these factors determines the value of intraocular pressure.
Glaucoma - increased intraocular pressure
Prevention measures
It is always easier to prevent diseases, so experts recommend adhering to the following rules in everyday life.
- Time for work and rest should be balanced. The body (including the visual system) needs at least 8 hours a day to rest.
- You need to take breaks throughout the day. At this time, you can allocate 3-5 minutes to perform eye exercises or massage.
- Before going to bed, it is recommended to massage the eyeballs with your fingertips, making circular movements clockwise and counterclockwise.
- Observe personal hygiene rules.
- Stick to a balanced diet. Include more fresh fruits, berries and vegetables, and foods containing Omega-3 acids in the menu.
- Use vitamin complexes, which include microelements beneficial for eye health.
- When performing exercises, you should not put too much pressure on your eyeballs. Heavy physical exercises involving heavy lifting and other overexertion are also not recommended. This automatically increases the IOP.
- Spend more time outdoors on weekends. Active games and hikes are the best cure for all diseases.
Periodically you need to visit an ophthalmologist for a preventive examination. This will help identify the problem at an early stage, which will simplify treatment.
How to reduce eye pressure without using drops?
Eye pressure can be reduced without the use of medications. Long walks in the fresh air help reduce eye pressure by saturating the body with oxygen.
Proper nutrition with foods containing Omega-3 fatty acids, vitamins and minerals normalizes the pressure inside the eyes. Also, to feel great, you need to limit your salt intake as much as possible.
Folk remedies are also an excellent way to reduce eye pressure. Decoctions of meadow clover and golden mustache quickly normalize eye pressure. Stressful situations and nervous overload significantly increase eye pressure, so they should be avoided as much as possible.
Prevention of deviations
It is better to prevent any disease in time than to treat it for a long time. One of the preventive measures is, first of all, regular visits to an ophthalmologist, who will measure eye pressure.
The main ways to prevent deviations in eye pressure:
- Daily exercise for the eyes.
- Regular exercise.
- Quality rest.
- Complete nutrition.
- Taking vitamin complexes.
- It is necessary to rest your eyes and not strain your eyesight too much.
- Moderate consumption of drinks with high caffeine content.
- Complete abstinence from alcohol.
Laser correction
The most effective treatments for high blood pressure in glaucoma are iridectomy and trabeculoplasty.
Iridectomy
This is a surgical operation during which laser exposure is used. A thin hole is artificially created near the iris of the eye, through which the outflow of excess intraocular fluid is ensured. The procedure does not leave scars and does not require a long recovery period.
The operation can be performed on an outpatient basis and does not require lengthy preparation. However, the patient must undergo examination the day before. A few days before the iridectomy, miotic eye drops are prescribed, which constrict the pupil. They should be used strictly as prescribed by the doctor, avoiding omissions.
After surgery, antibiotic drops are prescribed. This prevents the spread of the infectious process.
Trabeculoplasty
This is another effective procedure that helps lower IOP. It can be performed without hospitalization. But for two hours after the operation, the patient must be under the supervision of a doctor.
Before the procedure, the specialist instills drops with an anesthetic effect. He then directs the laser beam to the channels, where the outflow of fluid occurs. Next, small burns are made. At the end, special drops are instilled into the patient to avoid an increase in IOP immediately after surgery. The procedure does not cause any pain. Sometimes people with high sensitivity notice some pressure on their eyes, but no more.
Complications after trabeculoplasty are quite rare. Most often, there is a repeated increase in intraocular pressure.
IOP parameters can be corrected using laser irradiation
Medicines
Drug therapy has three main objectives:
- reduce IOP levels;
- improve blood supply to the eye structures, including the optic nerve;
- · normalize metabolic processes to avoid the development of dystrophy.
Using eye drops to reduce blood pressure is very simple. But to achieve the maximum therapeutic effect, you should adhere to some rules:
- wash your hands thoroughly with soap;
- throw your head back;
- gently pull back the lower eyelid;
- Inject the medicinal substance into the formed conjunctival sac without touching the mucous membrane;
- close your eyes for five minutes.
First, let's talk about drugs that reduce the production of intraocular fluid. Let's highlight a list of popular drops belonging to this group:
- Timolol. Refers to beta-blockers. The active substance reduces the volume of aqueous humor. Timolol is used in the treatment of adults. Doctors usually prescribe one drop twice a day;
- Betoptik. Reduces IOP levels as quickly as possible. Drops are an analogue of Timolol. The difference between them is that Betoptik does not reduce the production of moisture, but creates a barrier to its increased separation. The active component of the drug is betaxolol;
- Okupres-E. The active ingredient blocks beta-adrenergic receptors. The therapeutic effect lasts throughout the day. Okupres-E reduces both normal and elevated IOP.
The development of ocular hypertension is also based on impaired fluid outflow, which is why doctors prescribe drops that improve it. Consider the popular drops of this group:
- Xalatan. Latanoprost is the active ingredient of the drug. This component guarantees positive dynamics in the treatment of visual hypertension and open-angle glaucoma. Xalanthan has a gentle effect and rarely causes side effects;
- Travatan. It has a powerful therapeutic effect in the treatment of ophthalmotonus. Drops have the ability to slow down the development of glaucoma.
In complex therapy of glaucoma, doctors often prescribe tablets:
- Anaprilin. The drug reduces the level of vascular and intraocular pressure, and also improves heart rhythm;
- Prozerin. The drug fights ophthalmic hypertension, improves the functional activity of the muscle fibers of the bladder and uterus. In general, the tablets increase muscle tone in the body;
- Clonidine. The tablets reduce the level of intraocular and blood pressure and reduce the heart rate. Clonidine has a general calming effect;
- Cavinton. Dilates the blood vessels of the brain, increases the level of blood circulation in the blood vessels and increases the amount of oxygen received by the brain. The tablets do not affect cardiac function and blood pressure levels;
- Hypothiazide. These are diuretic tablets that are designed to remove fluid from the body. Due to the diuretic effect, IOP and blood pressure levels are reduced.
Injections into the eyeball are an effective method of treating ophthalmotonus
Injecting drugs into the eyeball that lower IOP is an effective method of solving the existing problem. The procedure is carried out by a qualified specialist in a specialized institution. It is not permissible to carry out injections at home, as there is a risk of infection and damage to the structures of the visual apparatus.
Experts distinguish four types of injections for ocular hypertension:
- Parabulbar. The drug is injected into the fatty tissue located around the eye.
- Retrobulbar. The injection is given directly into the eyeball.
- Subconjunctival. The drug is injected under the mucous membrane;
- Intravitreal. The drug substance enters the vitreous substance.
Typically, injections are prescribed when there is a sharp deterioration in the condition and progression of glaucoma. Injections are prescribed in treatment courses, between which there are breaks of several months. This allows you to reduce clinical symptoms, stop destructive changes in eye structures and the active progression of the pathological process.
How to lower eye pressure at home
How to relieve eye pressure at home without resorting to medications? If the pathology has just begun to manifest itself, then by taking simple preventive measures, you can eliminate the risk of complications. To do this, you need to avoid wearing clothes that block the flow of blood from the veins of the head (do not wear ties, do not wear tight collars). In addition to restrictions on physical and mental activity, you can lower eye pressure at home in the following ways:
- do not tilt your body down;
- give up alcohol and cigarettes;
- exclude coffee, tea, salt;
- do not drink a lot of liquid;
- light massage on the upper eyelids.
Measuring intraocular pressure in adults
In medical institutions, doctors use proven techniques with which they get the right results. These include tonometry according to Maklakov and Goldman. These are effective methods that have been used for many years.
| Measuring intraocular pressure: | Description of the procedure |
| according to Maklakov | The essence of the procedure is that a weight moistened with paint is placed on the eye. After this, an imprint is made on the paper and special measurements are taken. The higher the IOP, the less paint is washed off from the plates. This is explained by the fact that the cornea is flattened quite a bit under the weight of the weights. Therefore, contact with the surface of the convex part of the eye is minimal. |
| according to Goldman | In modern ophthalmology, a non-contact Goldmann tonometer is more often used to measure indicators. With this type of pressure level determination, the norm is approximately 11-13 mm Hg. The Goldmann tonometer releases a certain volume of air at a given pressure. Using a special sensor, the device reads the tension of the cornea, which changes shape under the influence of air flow. After this, the level of intraocular pressure is calculated. The design of the Goldmann tonometer is complex, so you cannot use this device yourself. |
How is intraocular pressure measured without the help of instruments?
Of course, this technique allows you to assess the condition of the eye very roughly, but still doctors advise every person to master it. The eyeball is felt through closed eyelids with one finger. In order to evaluate the result, you need to apply slight pressure. Normally, your finger should feel an elastic ball that is slightly pressed.
IOP measurement result:
- If the eye is hard as a stone and does not deform at all when pressed, then there is a high probability that intraocular pressure is increased.
- If it is completely impossible to feel the spherical shape, and the finger easily “falls” inside the eye, then this indicates a strong decrease in intraocular pressure.
According to medical recommendations, every person should visit an ophthalmologist at least once a year. If discomfort occurs in the eyes or the quality of vision deteriorates, it is necessary to make an unscheduled visit to the ophthalmologist's office. Many serious illnesses can be prevented if the cause of changes in blood pressure is diagnosed in a timely manner and appropriate treatment is started.
How to relieve eye pressure with folk remedies
After consulting an ophthalmologist, treatment with folk remedies can be carried out in conjunction with the main one, but only at the initial stage of the disease. How to reduce eye pressure? For effective treatment you will need patience and adherence to preventive measures. Folk remedies for eye pressure are contraindicated in case of individual intolerance and allergic reactions. List of proven recipes for adults for high IOP:
- An infusion of nettle, sleep herb and wild pear shoots. Drink 3 times a day before meals.
- Drops of mint oil (1 drop), distilled water (100 ml).
- Use aloe vera liquid (pour 3 leaves with a glass of boiling water, cook for 6 minutes) to rinse your eyes 4 times daily.
- Ingredients for oral administration: motherwort herb (15 g), hot water 250 ml. Leave for an hour, strain through cheesecloth, take 1 tbsp. l. 3 times.
- You can make eyelid ointment from crushed dandelion and honey (proportions 1:1).
Diagnosis and treatment
Eyes are delicate organs, and when it comes to medical procedures related to them, most people tend to experience anxiety, if not fear. How eye pressure is measured in a clinic is not clear to everyone. Let's try to figure it out.
There are a number of ways to determine the IOP value:
- Palpation method.
The ophthalmologist, by pressing on the eyelid of the subject's closed eye, examines the degree of elasticity of the eye. Normally, the eyeball should be quite soft. An apple that is too hard indicates higher than normal blood pressure. In many ways, the level depends on the adaptability of the sclera. The analysis of indicators is carried out using the Bowman scale. The results of such an examination depend on the doctor’s skill level and his ability to analyze the circumstances.
- Applanation tonometry.
This method involves measuring by squeezing the cornea of the eye. The simplicity and accuracy of the method ensure wide popularity of its use in ophthalmology. Measurements are carried out using a Maklakov tonometer.
- Impression tonometry, or Schiotz method.
The measurements are carried out by studying the elasticity of the eye using a special rod, the mass of which is constant. This procedure requires the use of an anesthetic solution. The unit of measurement is a linear quantity, which is integrated into millimeters of mercury using a special nomogram.
- Non-contact method.
An electronic tonometer provides the most painless way to measure IOP. The procedure is simple for both the doctor and the patient.
How to treat ophthalmological abnormalities will become clear after a detailed analysis of the condition of the whole organism, since complex therapy is the most effective. It is imperative to identify the reasons that led to unwanted changes. Treatment is prescribed after analyzing eye pressure.
An intraocular pressure tonometer is a small device equipped with a measuring ruler.
Taking into account IOP standards, the doctor must determine whether the patient has high or low eye pressure and, depending on the scale of the problem, may prescribe eye pressure drops or prescribe additional tests. The first thing to do if eye pressure is elevated is to identify the cause. Otherwise, there is a risk of getting rid of the symptoms without solving the problem.
Negligence during examination and incorrect course of treatment lead to blindness. The patient's condition in this case is assessed as critical.
Chronic ophthalmotonus cannot be considered a direct cause of the development of severe eye diseases, but it is precisely this that indicates the presence of problems in the human body that can lead to dysfunction of the visual organ, when neither lenses nor other types of devices to improve the quality of vision are able to change the situation.
Symptoms of increased intraocular pressure
The clinical manifestations of the pathology are multifaceted. In the early stages, the disease does not manifest itself in any way. Initial signs develop when the pathogenic process has led to irreversible changes in the fibers of the optic nerve. The manifestations include the following.
Signs of glaucoma of the eye
- Hyperemia of the sclera.
- Signs of eye discomfort. There are episodes of dryness and decreased focusing on distant objects. When using computer devices or reading for a long time, the eyes quickly begin to water, and pain appears when blinking.
- Narrowing of visual fields. Peripheral areas begin to disappear. Gradually, the field of view turns into a small dot located in the center. The final stage is complete blindness.
Dynamics of changes in visual fields
- Pain syndrome. Against the background of overload of the receptor, conductive and central parts of the visual analyzer, headaches appear (usually of the migraine type). Chronic pain develops in the area of the brow ridges.
- Adaptation disorder in the dark. The organ of vision is rebuilt when the light is suddenly turned off for 10-15 minutes (normally 2-3). Gradually this figure increases and can be 60 minutes or more.
- The appearance of visual pseudohallucinations. Ischemia of the optic nerve and retina leads to the development of all kinds of goosebumps, spots, and flickering dots before the eyes. Rarely, a whitish veil (as in fog) can be observed.
Symptom of "pressure in the eyes"
Low intraocular pressure: treatment
With reduced IOP, treatment measures are aimed at eliminating the cause; they may include the following measures (and more often, a combination of several of them):
- opening of the suprachoroidal space;
- fistula closure;
- anti-inflammatory therapy;
- therapy of a general disease.
In addition, the treatment regimen must include drugs that improve metabolic processes in the tissues of the eye (ATP, angioprotectors, vitamins).
In the absence of the necessary treatment, the outcome of eye hypotony is complete and irreversible loss of vision.
Both increased and decreased IOP are dangerous for vision function. Therefore, any deviation of eye pressure from the norm must be promptly identified, and the patient prescribed the necessary treatment.
Prevention of glaucoma
You can prevent an increase in intraocular pressure and the development of ocular glaucoma if you follow the following preventive measures:
- limit your time working at the computer;
- eat properly, balanced;
- stop drinking, smoking;
- avoid physical or emotional stress;
- drink at least 1.5 liters of water per day;
- do not lift heavy objects;
- do eye exercises regularly;
- to live an active lifestyle;
- prevent eye fatigue;
- do not read or work at the computer in the dark.
An important point in the prevention of glaucoma is periodic visits to an ophthalmologist, regular measurement of intraocular pressure, as well as timely treatment of ophthalmological pathologies.
Author of the article: Kvasha Anastasia Pavlovna, specialist for the website glazalik.ru Share your experience and opinion in the comments.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter.
How to regulate blood pressure
In a healthy person, eye pressure should average 15-16 mmHg. Art. But sometimes, under the influence of a number of factors, intraocular fluid stagnates, resulting in increased pressure on the walls of the eyeball. The more advanced the pathological process, the greater the tension and the worse the vision. If the disease is at the beginning of its development, then IOP regulation occurs by instilling special eye drops.
How to reduce eye pressure with glaucoma
For people with glaucoma, Xalatan, Pilocarpine or Betaxolol drops are usually recommended. In more advanced cases, in addition to drops, adrenomimetics, osmotics, as well as intravenous administration of Urea or Mannitol are prescribed. In addition to drug therapy, to regulate IOP it is necessary to change lifestyle, wear special glasses and do special eye exercises. Sometimes a doctor may recommend a herb that restores blood pressure. In the most difficult cases, surgery is performed.
Diagnostics
Measuring intraocular pressure is one of the methods for diagnosing eye health, used in ophthalmology. The disease is diagnosed by ophthalmologists using special devices:
- Maklakov tonometer;
- electrotonography;
- pneumotonometer.
In addition, the therapist can refer the patient to specialized specialists: cardiologist, neurologist, etc.
Combating increased intraocular pressure is a key task in the fight against glaucoma, otherwise if the indicators are not stabilized in a timely manner, the person faces irreversible loss of vision.
Characteristic symptoms of increased and decreased pressure in the eyes
Previously, we have already listed the main reasons for the development of both high and low pressure in the eyes. Now it’s time to move on to characterizing the symptoms most characteristic of these pathologies. According to ophthalmologists who regularly work with patients suffering from increased or decreased pressure, the most characteristic signs of ophthalmotonus may be such unpleasant sensations as, for example:
- increased fatigue, regardless of the number of hours worked;
- frequent headaches and inability to relieve pain;
- redness of the scleral area of the eyes for no obvious reason;
- pressure in the temples and brow ridges that occurs before bedtime;
- blurred vision in low light levels or at night;
- hardening of the eyeball upon palpation by an ophthalmologist;
- the appearance of a rainbow halo when looking at a bright light source.
So, we have discussed with you the main causes of so-called eye hypertension. Now let's take a closer look at the most striking and characteristic signs of the reverse state, that is, a decrease in intraocular pressure. Experts include the following symptoms:
- decrease in visual functions and deterioration in their quality;
- dryness of the scleral and cornea of the visual organs;
- decreased density of the eyeball upon palpation by a specialist.
However, according to the doctors themselves, it is not particularly worth focusing on these signs. Since a decrease in intraocular pressure can be completely asymptomatic, this significantly slows down the progress and possibilities of treatment. What to do in such a situation? Surely this question has been asked by many people who know first-hand about such a phenomenon as ocular hypotension. In this case, doctors only recommend being examined more often in order to be able to find out the level of ophthalmotonus using devices specially designed for this.
Causes of IOP violation
If intraocular pressure readings deviate from the norm, then the causes of this pathological phenomenon may be different. Increased ophthalmotonus (ocular hypertension) is a common phenomenon that is mainly observed in elderly people suffering from the following diseases:
- chemical poisoning;
- VSD;
- thyroid dysfunction;;
- traumatic brain injuries;
- hypertensive crisis;
- heart defects, heart failure;
- ophthalmological diseases;
- obesity.
The following factors can provoke a decrease in eye pressure:
- diabetes;
- liver failure;
- pathologies of an infectious nature;
- inflammation of the eyeball;
- retinal detachment;
- low blood pressure;
- damage to the eyeball.
Ocular hypotension can develop due to complications after surgery on the organs of vision. If a deviation from the norm has been identified, then the first step is to determine the cause of this pathological phenomenon, and then select treatment.
Which doctor should I contact?
An ophthalmologist can help solve vision problems.
The specialist conducts tonometry, studies the medical history and, if necessary, prescribes additional consultations with other doctors:
- neurosurgeon;
- neurologist;
- therapist;
- endocrinologist.
The need for examination by a specific specialist depends on the reason that led to changes in eye pressure.