Blood pressure is the most important indicator of the functioning of not only the heart muscle, but also the entire body. This term most often refers to blood pressure (BP) - the force with which blood presses on the walls of blood vessels and arteries - but the name includes several other types of pressure: intracardiac, venous and capillary.
If a person’s blood pressure deviates more or less from normal values, it is necessary to carry out initial diagnostic measures, as this may be a consequence of abnormalities in the functioning of internal organs. In order to understand in time that the body needs help, you need to familiarize yourself with the table showing what pressure is normal for a person depending on his age.
What is blood pressure
Blood pressure is a human biomarker that shows the force with which the liquid components of the hematopoietic system (blood and lymph) press on the walls of the vessels through which their flow is carried out. The pressure in the arteries is not a constant value and can fluctuate and change up to 5-6 times per minute. Such oscillations are called Mayer waves.
Normal blood pressure in an adult depends not only on the functioning of the heart and blood vessels, but also on external factors. These include stress, level of physical activity, diet, abuse of alcohol or drinks containing caffeine.
Taking some medications can also cause fluctuations in readings, but they should not deviate from the normal blood pressure of a person by age by more than 10%.
How to measure correctly
Blood pressure should be measured according to instructions. If you do this incorrectly, you can miss serious health problems or, conversely, sow panic if the incorrect result is too far from normal values.
There is a special device to measure blood pressure - a tonometer. Automatic instruments are more suitable for independent use at home - they do not require special skill when measuring, unlike manual ones. To ensure that the measurement error is minimal, the following rules must be observed:
- Before measuring blood pressure, you should avoid physical activity.
- Before the procedure, you should not smoke, it is advisable to avoid eating.
- You need to measure your blood pressure in a sitting position; be sure to lean your back against the back of a chair.
- You need to carry out the procedure while sitting at a table, placing your hand on the tabletop so that it is approximately at the level of your heart.
- When taking measurements, you should not move or talk.
- It is advisable to measure the pressure on both hands for more accurate indicators.
If all rules are followed, pressure readings should be accurate. If the discrepancies with the norm are significant, you need to contact a cardiologist. If there are doubts about the correctness of the procedure, you can measure the pressure under the supervision of a person who is better versed in the intricacies of the procedure.
Systolic and diastolic pressure is the force of blood movement through the vessels at the moment of contraction and relaxation of the heart muscle. To get reliable results, follow some recommendations when taking blood pressure measurements:
- 40 minutes before the measurement, avoid eating salty, spicy and fried foods, strong tea and coffee, and also do not smoke;
- the results are affected by excessive physical activity, so an hour before measurements you need to engage in quiet activities;
- take a comfortable sitting or semi-sitting position;
- the hand involved in the measurement is moved to the side and placed on a hard surface;
- To establish an accurate result, two measurements are taken with an interval of 2-3 minutes.
The measurement is carried out with a mechanical or electronic tonometer. The cuff is installed 6 cm above the elbow. The stethoscope is placed on the bend and the pulse is listened to at the moment of deflation. The first knock determines the upper limits. Gradually the intensity of the tones decreases, and the last sonorous blow marks the lower boundaries.
What does upper and lower pressure mean?
- When measuring blood pressure in a person, two indicators are recorded:
- systolic, upper indicator : the resistance force of the vascular walls to blood flow at the moment of compression of the heart muscle;
- diastolic, lower indicator : blood pressure on the walls of the arteries at the moment the heart relaxes.
For example, 120/80: 120 is the upper blood pressure indicator, and 80 is the lower blood pressure.
What pressure is considered low
Consistently low blood levels are called hypotension. This diagnosis is made to the patient if, for three consecutive measurements with an interval of one week, the tonometer readings do not exceed 110/70 mm Hg. Art.
Hypotension can occur for several reasons, some of which can be very serious, such as blood infections (sepsis) or endocrine pathologies (hypothyroidism, diabetes). A decrease in the resistance force of the vascular walls can occur with extensive blood loss, heart failure, or prolonged exposure to a stuffy room. In athletes, acute hypotension often develops against the background of injuries and fractures as a reaction to painful shock.
Treatment of hypotension includes a balanced diet, proper rest, moderate exercise, and massage. Procedures that have a positive effect on the elasticity of blood vessels (swimming, aerobics) are useful.
What pressure is considered high
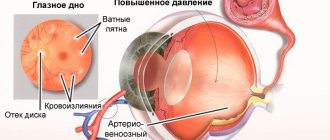
Arterial hypertension is a persistent increase in blood pressure above 140/90 mm Hg. Art.
Not only internal factors related to the work of the heart and other internal organs, but also external ones, for example, short and restless sleep, increased salt consumption, poor climatic and environmental living conditions, can contribute to the development of hypertension.
In older people, these indicators may increase due to chronic stress, consumption of low-quality foods, as well as deficiency of vitamins and minerals, primarily B vitamins, magnesium, and potassium.
Treatment includes medication correction, therapeutic and preventive nutrition (limiting spices and salt), and giving up bad habits. It is important for working people to create a work and rest regime that is favorable for the body, as well as to properly organize work activity so that it is not associated with a negative impact on the heart muscle or nervous system.
Table of blood pressure norms by age in women, men and children
A person’s blood pressure (the age norm will be indicated in the table) has different acceptable values.
| Age | The average normal blood pressure is mm Hg. |
| 0 – 14 days | 55/35 – 90/45 |
| 14 – 30 days | 75/35 – 108/70 |
| 1 – 12 months | 85/45 – 108/70 |
| 1 – 3 years | 95/55 – 108/70 |
| 35 years | 95/55 – 112/72 |
| 5 – 10 years | 95/55 – 118/74 |
| 10 – 12 years | 105/65 – 124/80 |
| 12 – 15 years | 105/65 – 134/84 |
| 15 – 18 years old | 105/65 – 128/88 |
| 18 – 30 years old | 124/76 – 125/74 |
| 30 – 40 years | 128/78 – 130/82 |
| 40 – 50 years | 136/80 – 140/85 |
| 50 – 60 years | 140/82 – 145/86 |
| 60 – 70 years | 145/85 – 147/88 |
| 70 years and above | 147/87 – 150/92 |
In case of any deviations from the norm, it is necessary to consult a doctor to identify the cause and treat the body to prevent further development of the disease.
At birth, the child has low blood pressure (55/35 – 90/45). This is due to the vessels not yet developed. As you get older, your blood pressure gradually increases. In an infant, it may differ from the established norm and may not increase for some time. The reason for this may be the slow development of the cardiovascular system.
The figure shows the normal blood pressure according to a person's age.
This complication is not serious unless accompanied by other pathologies. Parents are advised to force their child to move more. At the age of 5–10 years, a child may have high blood pressure. This may be caused by physical activity.
If the pressure does not decrease for a long time, then you need to reduce the child’s physical activity. As you grow older, your upper blood pressure will constantly increase, and your lower blood pressure will decrease. If the indicator changes by no more than 15 units, this will be considered within the normal range.
Pressure, the so-called pulse pressure, is determined by measuring blood pressure. The difference between a larger and a smaller number is the PD. Using these indicators, the doctor is able to determine the condition of the aortic valves, myocardial function, and blood flow through the human arteries. PD also has a table showing the norm by age.
Low PD can cause:
- anemia;
- headache;
- fainting.
Otherwise, it will signal diseases such as:
- heart sclerosis;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- inflammatory damage to the myocardium;
- anemia.
If PD decreased and quickly recovered, this may signal the initial stage of the disease. After such leaps, you need to monitor the further functioning of the body. If falls in PD begin to become more frequent, then you should immediately consult a doctor and undergo an ECG. An increase in PP can occur during physical activity. Such jumps happen to every person.
However, if the increase in PP becomes more frequent, this indicates disorders in the body:
- renal failure;
- iron deficiency in the body;
- intracranial pressure;
- fever;
- ischemia.
It is not recommended to take medications to normalize blood pressure without a doctor determining the cause. This may worsen your health condition.
| Age, years | Minimum normal blood pressure, mm Hg. Art. | Maximum normal blood pressure, mm Hg. Art. | ||
| men | women | men | women | |
| 1-10 | 100/60 | 120/78 | ||
| 10-20 | 115/70 | 110/70 | 134/83 | 138/85 |
| 20-40 | 117/77 | 110/75 | 137/87 | 132/83 |
| 40-60 | 120/82 | 112/79 | 144/90 | 137/87 |
| More than 60 | 145/78 | 144/82 | 147/83 | 159/91 |
| Age, years | Pulse is normal, beats/min | |
| men | women | |
| 1-10 | 70-120 | |
| 10-20 | 60-130 | 70-110 |
| 20-40 | 50-90 | 60-70 |
| 40-60 | 60-85 | 75-83 |
| More than 60 | 70-90 | 80-85 |
In children
| Age scale | Blood pressure is normal, mm Hg. Art. | Pulse is normal, beats/min |
| up to 2 weeks | 55/40 – 95/50 | 100-150 |
| 2-4 weeks | 79/41 – 113/75 | 100-150 |
| 2-5 months | 89/48 – 113/75 | 90-120 |
| 5-12 months | 89/48 – 113/75 | 90-120 |
| 1-3 years | 98/59 – 113/75 | 70-120 |
| 3-6 years | 98/59 – 117/77 | 70-120 |
| 6-10 years | 98/59 – 123/79 | 70-120 |
A high heart rate in newborns and infants is due to the growing body’s great need for energy. The minute volume of blood during this period is lower than required. To compensate for the insufficient delivery of oxygen and nutrients to the tissues, the heart needs to contract more often. As minute blood volume increases with age, the pulse decreases. In infants, vascular tone and resistance are also reduced.
As the body develops, the walls of the arteries thicken and become stiffer. The muscle cells of the heart and blood vessels function more intensively. Blood pressure gradually increases as you get older. The indicators for children of school and preschool age are close in value, but the maximum permissible limits are expanding. Entering school and the associated psychological and physical stress have a great impact on the body.
In teenagers
| Age, years | Blood pressure norms by age, mm Hg. Art. | Pulse is normal, beats/min |
| 10-12 | 110/70 – 127/83 | 70-130 |
| 13-15 | 110/70 – 137/88 | 60-110 |
| 15-17 | 110/70 – 131/89 | 60-110 |
For high school students, puberty and hormonal changes come first. Heart mass and volume increase rapidly. During puberty, sex differences in cardiac function appear. In young men, the myocardium is able to contract more strongly and powerfully. In girls, with the onset of menstruation, systolic pressure rises and heart rate decreases.
In adults
| Age, years | Normal blood pressure, mm Hg. Art. | Pulse is normal, beats/min | |
| men | women | ||
| 18-29 | 126/79 | 120/75 | 60-100 |
| 30-39 | 129/81 | 127/80 | |
| 40-49 | 135/83 | 137/84 | |
| 50-59 | 142/85 | 144/85 | |
| 60-69 | 145/82 | 159/85 | |
| 70-79 | 147/82 | 157/83 | |
| 80 and older | 145/78 | 150/79 | |
By the age of 25, the cardiovascular system matures. Further changes in function are associated with aging. With age, heart rate and minute blood volume decrease. The formation of cholesterol plaques narrows the lumen of blood vessels. The contractility of the heart decreases. Atherosclerotic changes cause an increase in blood pressure and the risk of developing hypertension.
With age, blood pressure increases until old age, then decreases. In older people, the heart muscle weakens and cannot contract with sufficient force. The blood becomes more viscous, flows more slowly through the vessels, and stagnation occurs. The elasticity of the walls of arteries and veins decreases. Vessels become fragile and brittle. The development of hypertension at this age causes heart attacks and strokes.
Normal human pressure
Monitoring blood counts is especially important for people in the older age group, since their risk of pathologies of the cardiovascular and endocrine systems exceeds 50%. In order to notice existing deviations in time, you need to know what a person’s normal blood pressure is and how it can change depending on his age.
By age (table)
Below are tables showing blood pressure norms by age for women and men. Based on these data, you can monitor vascular health and promptly seek medical help if the need arises.
Some experts deny the theory that an increase in upper and lower blood pressure in a person with age is a physiological norm, believing that even at 50-60 years old this figure should not rise above 130/90 mm Hg. Art.
Despite this, the percentage of elderly and senile people capable of maintaining indicators at this level does not exceed 4-7%.
Among women
| Age | What pressure is considered normal (mm Hg) |
| 18-22 years old | from 105/70 to 120/80 |
| 23-45 years old | from 120/80 to 130/85 |
| 46-60 years old | from 120/80 to 140/90 |
| over 60 years old | from 130/90 to 150/95 |
In men
| Age | What pressure is considered normal (mm Hg) |
| 18-22 years old | from 110/70 to 125/80 |
| 23-45 years old | from 120/80 to 135/85 |
| 46-60 years old | from 120/80 to 145/90 |
| over 60 years old | from 130/90 to 150/100 |
In children
Regular measurement of blood pressure in childhood is necessary for children at risk for heart disease, diabetes mellitus and pathologies of the genitourinary system. Children born with malformations of the heart muscle should be registered with a pediatric cardiologist, and if there is any significant deviation of blood pressure from normal values, such children should be hospitalized for a comprehensive diagnosis.
Monitoring the indicators of this biomarker is also necessary for healthy children, since many serious diseases (including kidney cancer) begin with an increase in blood pressure. In order not to miss time and start treatment on time, parents should know what the child’s blood pressure should be normally, and what can cause it to change up or down.
The table below shows normal blood pressure in children under 12 years of age:
| Age | What pressure is considered normal (mm Hg) |
| from the first day of life to two weeks of age | from 60/40 to 80/50 |
| from two weeks to two months | from 90/40 to 90/50 |
| from 3 months to 1 year | from 100/50 to 100/60 |
| from 1 year to 6 years | from 100/60 to 110/70 |
| from 7 to 10 years | from 100/60 to 120/80 |
| over 10 years old | from 110/70 to 120/80 |
The norm of blood pressure in children 10 years old is already approaching the ideal pressure in an adult and is 120/80 mm Hg. Art. If this figure is slightly lower, there is no need to worry, since the individual characteristics of the functioning of the hematopoietic system and heart muscle are of great importance. If the child’s blood pressure is higher than these values, consultation with a cardiologist and pediatrician is necessary.
In teenagers
Normal blood pressure in a teenager is no different from normal blood pressure in an adult.
| Age | What pressure is considered normal (mm Hg) |
| from 12 to 18 years old | from 110/70 to 120/80 |
Pressure is a very important indicator that reflects the condition of blood vessels and the degree of blood supply to organs. To prevent pathologies associated with the hematopoietic system, it is necessary to know what blood pressure a person should have and take all measures to maintain sufficient tone and elasticity of blood vessels.
Chronic hypertension or hypotension is equally dangerous at any age, therefore, if the arterial biomarker regularly deviates from the age norm, it is necessary to seek medical help.
Author of the article: Sergey Vladimirovich, a supporter of reasonable biohacking and an opponent of modern diets and quick weight loss. I’ll tell you how a man aged 50+ can stay fashionable, handsome and healthy, and how to feel like 30 in his fifties. Read more about the author.
How can you raise blood pressure at home?
What pressure is considered normal? Have you found out what can provoke a sharp drop in blood pressure?
- A critical decrease in glucose concentration in the bloodstream;
- A drop in hemoglobin levels in the blood;
- Chronic lack of sleep or other type of overwork;
- Problems with digestion, gastrointestinal tract performance;
- Changes in climate zone and weather conditions;
- Thyroid dysfunction;
- Critical days and premenstrual period;
- Hypocaloric diet.
If blood pressure is consistently low, it is important to balance the diet, diversify the diet with fatty meats and fish, hard cheese and other high-fat dairy products.
Various seasonings and dried fruits are useful - pepper, ginger, raisins, figs
Measuring indicators
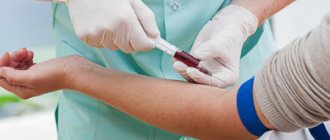
In order to determine the indicators, its determination is carried out. In order to determine a person’s blood pressure, it is recommended to use universal equipment - a tonometer. They are produced in several varieties. At home, the most common use is an automatic tonometer. Using this device, not only the simplicity of the procedure is ensured, but also the accuracy of the results obtained.
To determine blood pressure, certain coefficients are used - millimeters of mercury. After the determination, two numbers appear on the tonometer screen. The first of them displays the upper pressure, and the second – the lower. In accordance with the obtained figures and established standards, conclusions can be drawn about the state of human health. In this case, it is recommended to take into account the individual characteristics of the person.
Treatment
You need to determine ways to normalize blood pressure together with your doctor.
If the index is increased, treatment consists of taking the following medications, which will be prescribed by a cardiologist:
- diuretics;
- alpha and beta blockers;
- calcium antagonists;
- Sartanov.
To restore normal blood pressure, it is recommended:
- lie down and calm down;
- douse yourself with cool water or soak your limbs in cold water;
- take a walk in the fresh air in the morning or evening;
- iron the dampened towel and apply it to the neck;
- take a bath in a hot bath (this helps dilate blood vessels);
- exclude physical activity.
To increase blood pressure, it is recommended to drink coffee. This method will help if the pressure has dropped sharply, although the effect is short-lived. In addition to coffee, salty foods help increase the rate. To do this, eat a piece of lard, a pickled cucumber, and salted nuts.
However, it would be a good idea to consult a doctor.
During pregnancy
In pregnant women, both external changes and changes in blood pressure levels are observed under the influence of changes in hormone production.
In the early stages of pregnancy, blood pressure is usually slightly reduced. This depends on toxicosis, in which there is a weakening of the general vital tone, which provokes a decrease in blood pressure standards. In addition, the index in the 1st trimester of pregnancy may change due to an increase in progesterone levels, which leads to vasodilation.
In the 2nd trimester, an increase in blood pressure is observed, since already at 20 weeks the pregnant woman’s blood flow volume begins to increase, which is why the indicator increases.
During pregnancy, changes in pressure are an indispensable indication for determining the condition of the expectant mother and baby. If your blood pressure deviates from the norm, you should consult a doctor.
Let's consider what the mean arterial pressure (MAP) should be when carrying a baby:
Where is the deviation and where is the norm, only the doctor decides based on the results of additional examination and diagnosis. When blood pressure increases excessively, the baby develops hypoxia.
In a teenager
At 15 years of age, the blood pressure norm is almost the same as that of adults (although this category of patients often experiences abnormalities in the index, which is due to hormonal characteristics during puberty).
When a teenager suffers from high (or low) blood pressure, a detailed diagnosis of organs such as the heart and thyroid gland is prescribed. In the absence of diseases, there is no need to be treated - in the future the condition will return to normal by itself.
The following indicators are considered normative for adolescent children:
A slight increase in heart rate in adolescents is normal, as the heart continues to adapt to the rapidly developing body.
A low heart rate is observed in adolescents involved in sports, since their heart functions in an economical manner.
What diseases can we talk about?
As a result of the decrease in pressure, blood flow slows down. Internal organs receive oxygen and nutrients in limited quantities. The brain and heart suffer the most from this condition.
Hypotension can develop against the background of:
- cardiac pathologies: arrhythmia, cardiomyopathy, myocarditis;
- lesions of the endocrine system: hypothyroidism, hypocortisolism;
- vascular tone disorders: vegetative-vascular dystonia, stroke, tumors;
- allergic exacerbations;
- poisoning of the body.
A patient whose blood pressure has dropped may experience dizziness, weakness, drowsiness, headache, and nausea. The skin turns pale, the pulse quickens or weakens. If hypotension is a consequence of the disease, then other characteristic signs are added.
When is medical help needed?
More often, people with chronic blood pressure diseases take medications prescribed by a specialist to increase or decrease blood pressure, depending on the pathology.
But there may be situations when you need urgent medical help:
- the help of a specialist will be required after a sharp rise in blood pressure and the inactivity of treating medications;
- for pain in the heart area;
- with numbness of the face or body;
- with numbness of the hands and pain in the shoulder joints;
- when fainting;
- with constant weakness and drowsiness;
- with deterioration of hearing and vision.
If the above symptoms occur, it is recommended to call an ambulance. The doctor will measure your blood pressure and order an ECG. For quick treatment, the patient is placed on bed rest and takes medications. In this case, the specialist checks the pressure readings every 20 minutes. to monitor their changes.
Advice is worth its weight in gold
When diagnosing a patient with problems with the cardiovascular system, blood pressure should be monitored daily in the morning and before bedtime.
When a deviation of parameters from the norm is noticed, for normalization it is recommended to maintain the principles of healthy life - nutrition should be balanced, muscles need alternating physical activity with rest, and emotions should be as positive as possible.
Experienced tourists advise communicating more with nature, moving, and relaxing actively. This helps improve blood circulation in the body and normalize blood pressure.