The human body is inhabited by many microorganisms invisible to the eye. Some bacteria coexist peacefully with humans and even bring benefits, while others are pathogenic and cause pathological processes.
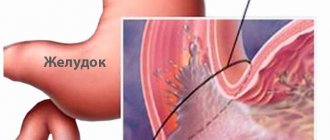
The bacteria Helicobacter pylori can cause diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (GIT). These microorganisms are very tenacious and extremely contagious, that is, they are highly infectious. For example, if one of the family members was diagnosed with helicobacteriosis, then in 95% of cases the people living with him will be infected.
A breath test is a medical test for the presence of the bacterium Helicobacter pylori in the body. The infectious agent can enter the human body through kissing, sharing utensils, and through mucus and saliva. Upon penetration into the stomach, the bacterium begins to actively multiply and destroy the cells of the organ.
It is Helicobacter pylori that is the main cause of gastritis, peptic ulcers and even cancer. However, not all carriers of this infection suffer from gastritis and ulcers. The state of the immune system plays a big role here. Poor nutrition, stressful situations, bad habits - all this creates favorable conditions for the activation of bacteria.
Important! Every third inhabitant of the earth is infected with Helicobacter pylori.
Helicobacter pylori produces ammonia gas, which essentially serves as a capsule for it, protecting it from the aggressive action of the gastric environment. Experts have learned to detect infection using blood tests, stool tests, and biopsies, but these methods have a number of disadvantages.
The Helicobacter breath test is a modern, and most importantly, safe research method that can be used in the diagnosis of pregnant women and young children. In this article, we will take a closer look at the principle of operation of this analysis, and also learn how to properly prepare for it.
How is the helic test performed to identify Helicobacter pylori?
The helic test is carried out according to the same scheme as the 13C-urease breath test. The only difference is that instead of isotope-labeled urea, a person receives a solution of urea. Air is taken in 2 samples: before taking the solution and after taking it.
The undoubted advantage of the study is its complete safety for human health. This is the best test for detecting Helicobacter pylori in pregnant women and children. However, a number of experts question the accuracy of the results obtained. Therefore, the helic test is carried out only in Russia.
conclusions
The hydrogen breath test is included in diagnostic standards when looking for carbohydrate absorption disorders and bacterial overgrowth syndrome. Its reliability strongly depends on proper preliminary preparation. The research method is informative, but difficult to interpret independently. It is recommended not only to consult with a doctor based on the results of the analysis, but also to visit him before the study. The doctor will help you draw a conclusion about the feasibility of the study and explain the reasons for the results obtained.
Interpretation of the results of a breath test for Helicobacter pylori
A breath test can give two results: positive or negative. The patient either has Helicobacter pylori in the body or has not been infected.
Also, using a special device called a mass spectrometer, the quantitative values of Helicobacter pylori in the body are determined.
The data obtained can be interpreted as follows:
If the stabilized isotope in the exhaled air contains from 1 to 3.4%, then the degree of infection is mild.
When the isotope concentration is in the range of 3.5-6.4%, they speak of an average degree of infection.
Severe Helicobacter pylori infection will be indicated by rates of 6.5-9.4%.
Extremely severe is indicated by values greater than 9.5%.
As a rule, the accuracy of the test is beyond doubt. It is possible to obtain a negative result only if the conditions for preparing for the study are not observed. Some drugs can reduce the activity of gastric juice production, which will make it impossible to break down urea.
Test results will be available 1-2 days after the test. The storage period for collected samples is 10 days, but no more.
Analysis results and normal indicators
The Helic breathing test is very effective - the reliability of the result can range from 75 to 97 percent, depending on the equipment used and how carefully the patient has prepared. The great advantage of the method is that immediately after the procedure the doctor will be able to tell whether such a bacterium was detected or not, that is, you will not have to wait a long time for results. If the study is carried out using a different method, using a mass spectrograph in the laboratory, then the waiting time for the result can range from 1 to 10 days - the maximum shelf life of patient samples.
As for the results, the norm is 0 or less (the difference in results between the first and second stages). If the bacterium is present, regardless of the size of the colony, the result will be greater than zero:
- trace value – from 1.5 to 3.5 (bacterium not in the active phase);
- low level – 3.5–5.5 ppm;
- low level – up to 7;
- most often, when bacteria are active in the human digestive system, test results range from 7 to 15 ppm;
- high level of contamination - up to 70.
What to do if the test is positive?
If the test for Helicobacter pylori is positive, then the patient will need to undergo a comprehensive examination of the digestive system. The patient must be sent for an FGDS, which will provide information about the condition of the stomach and duodenum. He will also donate blood for biochemical and general analysis; other studies may be required.
Helicobacter pylori requires treatment. Depending on the severity and nature of the damage to the inner wall of the stomach, a therapeutic regimen is selected. However, to eliminate bacteria, antibiotics are always used, which are combined with proton pump inhibitors. In this case, two antibacterial drugs will be prescribed. This may be Amoxicillin, Levofloxacin, Metronidazole, Clarithromycin, etc.
During treatment or after its completion, the doctor may suggest that the patient take another test for Helicobacter pylori. This is required to monitor the effectiveness of ongoing therapy or to evaluate treatment already performed. A gastroenterologist treats diseases of the digestive system.
What is Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori)?
This is a spiral-shaped gram-negative bacterium, which is found in 90% of cases in patients with diseases of the stomach and duodenum. To date, the connection between H. pylori infection and the occurrence of these diseases has been proven. The bacterium enters the body with food, or by contact - from one person to another (through shared dishes, household items, etc.). Having penetrated the stomach, H. pylori quickly multiplies, injures the mucous membrane, causes inflammation (gastritis), and after a few years leads to the destruction of the mucous membrane and the formation of ulcers.
It is believed that, in the absence of treatment, H. pylori colonizes the gastric mucosa and can exist throughout a person's life, despite the host's immune response. The ability of H. pylori to colonize the mucous membrane and cause gastritis or gastric ulcers depends not only on the state of the host’s immunity, but also on the individual characteristics of a particular strain of the bacterium. H. pylori infection may be accompanied by symptoms or be asymptomatic (without any complaints from the infected person). It is estimated that up to 70% of infections are asymptomatic and about 2/3 of the world's population is infected with Helicobacter, making this infection the most common in the world. The percentage of infection in the Russian population, according to various sources, reaches 60–80%.
Rapid tests for Helicobacter pylori
To determine whether you have pathogenic flora, there is no need to go to the laboratory. You can purchase rapid tests at the pharmacy that are intended for home use. When used correctly, the reliability of the results reaches 100%.
There are two types of rapid tests, the biological material for which is blood or feces.
To perform a test to detect Helicobacter pylori in the blood at home, you will need to follow the following algorithm:
Wash your hands thoroughly and treat them with an antiseptic solution.
Remove all dough components from the packaging and place them on a clean and dry surface.
Breath test for Helicobacter pylori - what is it?
This is a quick and painless way to detect a pathogenic microorganism, which consists in the ability of the bacterial enzyme urease to decompose urea, releasing CO2. This analysis is also called the urease test.
The European Association of Gastroenterologists recognizes this test as the “gold standard” in diagnosing bacteria.
Carbon dioxide is released by the lungs during breathing and its amount is recorded when the examined patient exhales with a special device.
Indications for its implementation are the following symptoms and conditions:
- gastritis
- erosions, peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum
- complaints from the digestive system: heartburn, belching sour or airy, abdominal pain, nausea, discomfort in the stomach and intestines, stool disorders.
- preventive examination, when a microbe is detected in family members or close contacts (the microorganism is extremely contagious and is easily transmitted by oral, fecal-oral, contact routes)
- control of cure after treatment for Helicobacter pylori infection
The advantages of this test include:
- painlessness
- no endoscopic intervention
- rapidity
- high accuracy
- Possibility of diagnosis in elderly, debilitated patients and young children, as well as in persons for whom FGDS and other invasive tests are contraindicated
How is the urease breath test for Helicobacter performed?
The patient is given a tube or plastic tube, which he places in his mouth so that the tongue and palate do not touch it, and breathes calmly for several minutes. It is important that no saliva gets into the tube, which could distort the test results.
If saliva has accumulated in the mouth during breathing, you can remove the device from the mouth, spit or swallow the salivary gland secretions, and then continue breathing.
The patient drinks an aqueous solution of urea, which contains labeled 13C. After which he receives another tube and breathes in the same way as the first time: calmly, without touching it with his tongue, without allowing saliva to get inside.
It is advisable to take four samples of exhaled air after swallowing an aqueous solution of urea after fifteen minutes over an hour. But in some clinics, 1-2 samples are taken. This largely depends on the recommendations of the test system manufacturer.
Some manufacturers have improved examination devices so that even the ingress of salivary gland secretions does not distort the examination results.
All samples of exhaled air are analyzed by the concentration of carbon dioxide, namely the labeled 13C atom in the exhaled air: the presence of Helicobacter in the patient’s body increases the percentage concentration of 13C due to urease activity. The enzyme quickly breaks down urea, and the release of 13C is significantly enhanced.
If there is no microbe in the body, then the concentration of carbon dioxide in the air will be equal to its concentration before taking an aqueous solution of urea. There will be no deviations from the norm in the composition of the gas.
Rapid urease test
During gastroscopy, the endoscopist performs a biopsy of the gastric mucosa in the area of the pylorus and altered areas. To detect urease in a piece of stomach tissue, it is necessary to place the material in a special medium that contains urea and an indicator. In the presence of Helicobacter pylori enzyme, urea breaks down into carbon dioxide and ammonium ions. The pH of the environment will deviate towards the alkaline side and the indicator will display this by changing color.
Preparation
Two weeks before the diagnosis, you should stop taking bismuth drugs (De-Nol), proton pump inhibitors (Omeprazole, Pantoprozole, Omez, Kvamatel), and antibiotics.
On the eve of the lung examination, have dinner 8 hours before the gastroscopy. Do not drink water after midnight.
Methodology
The quick urease test or “CLO-test”, “De-Nol-test”, “HELPIL-test” is carried out according to the following algorithm:
- using forceps at the end of the endoscope, a tissue biopsy is performed - pinching off a piece from the area of the fundus and body of the stomach;
- the material is placed in a medium containing urea and phenol red indicator;
- a positive result is recorded if the color of the indicator changes from yellow to bright red.
Decoding indicators
The result is based on the color intensity of the indicator. The endoscopist evaluates the coloring as a plus.
+ — 1 degree of urease activity, low level of Helicobacter, color appears within 24 hours.
++ - degree 2 of urease activity, moderate level of bacterial infection, the indicator turns red within two hours.
+++ - 3 degree of urease activity, significant level of infection, bright red color of the indicator within an hour of the test.
What is a negative urease test? This is when the indicator does not change its color within 24 hours from the start of the study.
An example of a urease test
Advantages
The rapid urease test with gastric biopsy has the following advantages:
- quick diagnostics - on average about 30 minutes;
- low cost;
- does not require specific expensive equipment.
How to prepare for a Helicobacter breath test
The reliability of the urease microbial test largely depends on proper patient preparation. If you do not follow the preparatory medical recommendations, the analysis will not be informative.
Basic rules for preparing for a breath test:
- The last meal before the analysis should be no later than 22.00 pm. A light dinner is allowed in the evening; it is recommended not to eat anything in the morning. You can drink 50-100 ml of pure non-carbonated water 2 hours before the test.
- During the day, it is contraindicated to consume foods that contribute to increased gas formation: legumes, cabbage, fresh baked goods, carbonated drinks.
- 2 weeks before testing, it is not recommended to take antibacterial drugs, and a week before testing, avoid antacids, NSAIDs, analgesics, and bismuth preparations.
- You must not drink alcohol three days before the test or smoke on the day of the test.
- Before the examination, you should not use chewing gum; in the morning before the analysis, you should brush your teeth well and rinse your mouth with water.
Compliance with these rules will allow you to obtain reliable test results and correctly interpret them. If you ignore the recommendations before urease analysis, then exhaled air samples will be uninformative.
How to choose a laboratory?
Modern test systems are automated, and the test is assessed not by a person, but by a machine. In addition, there are systems whose indicator tubes are protected from saliva entering them. This makes the procedure more comfortable. And the research itself takes less time.
Before choosing a laboratory where you are going to do a breath test for Helicobacter, you should find out what method is used for this and what equipment will be used for the study.
The cost of the test can be quite high. This depends on the comfort of the patient and the accuracy of the study. Hardware tests are more accurate.
Breath test results for Helicobacter pylori
The test results are based on determining the percentage of 13C in exhalation before and after loading with a urea solution. Typically, isotope abundance is calculated using a mass spectrometer.
Normally, the content of 13C during exhalation is no more than 1% of the total amount of carbon dioxide. If the result obtained is as follows, the test result is negative, the examined patient does not have H. pylori.
If the percentage of 13C isotope exceeds 1%, then there is infection with the bacterium. There are 4 degrees of infection:
- Less than 3.5% - mild degree
- 3.5-6.5% - average
- 6.5-9.5% - pronounced
- More than 9.5% - extremely pronounced
The analysis can show not only the presence/absence of a microbe, but also the severity of contamination of the gastric mucosa and the degree of activity of the bacterial process.
Many breath tests have test strips placed in the tubes of the device. When exhaling, depending on the concentration of CO2, the indicator changes color - it turns blue, the length of the blue indicator strip is directly proportional to the concentration of carbon dioxide in the air.
The medical worker uses a ruler to measure the length of the blue indicator in two samples: before ingesting an aqueous solution of urea and after, then calculations are made and the result is interpreted.
A breath test for Helicobacter pylori is a quick and safe test that allows you to identify the bacterium that causes chronic gastritis and stomach ulcers. After entering the body, the bacterium moves along the gastric mucosa using flagella and attaches to its walls. The microorganism produces substances that destroy epithelial cells of the gastric mucosa and releases toxins that cause immune diseases. Trying to protect itself from a parasitic microorganism, the stomach increases the secretion of hydrochloric acid and substances that destroy its walls. However, the bacterium is able to survive for a long time in an acidic environment thanks to the enzyme it secretes, urease, which protects the microorganism from the effects of gastric juice.
Decoding
Normally, the indicators of the first and second samples are identical. If the indicator is above zero, this indicates the presence of helicobacteriosis. The study indicators directly indicate the activity of the infectious process:
- up to 3.5 – indicates an inactive phase of the disease, which is usually not difficult to get rid of;
- up to 5.5 – low level of helicobacteriosis;
- up to 7 – low level;
- up to 15 – an active process that is difficult to treat;
- over 15 high level of contamination of the digestive tract.
The breath test for Helicobacter pylori can be performed on both children and adults.
A rapid urease test for Helicobacter pylori is taken during gastroscopy. For the study, you will need a small amount of mucosal tissue. The sample is placed in a special medium with urea and phenol red indicator. Helicobacter pylori secretes urease, which in turn converts urea into ammonia. The presence of bacteria is indicated by a sample turning red.
Where is the test done? You can take the test in modern laboratories or clinics. You can do a urease breath test in the Invitro laboratory. So, the bacterium Helicobacter pylori is a dangerous microorganism that can cause gastritis, peptic ulcers, cancer, and allergic reactions.
Infection can occur through kissing or even sharing utensils. A bacterial infection damages the cells of the mucous membrane, causing their complete destruction. Early diagnosis will help avoid dangerous complications. One of the modern diagnostic methods for helicobacteriosis is a breath test. This is a safe, painless and highly effective study.
Indications for a breath test
A breath test for Helicobacter pylori is performed in the following cases:
- early diagnosis of H. pylori-associated chronic gastritis;
- complaints of a dyspeptic nature (discomfort in the stomach and intestines, pain in the stomach and duodenum, bad breath, heartburn, nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, feeling of heaviness after eating, increased gas formation, rumbling in the stomach, stool disorders);
- determination of the risk of gastric and duodenal ulcers;
- epidemiological studies (detection of infection of family members or persons in close contact with the patient);
- screening before endoscopy;
- monitoring the patient after treatment for Helicobacter pylori infection.
How to detect Helicobacter pylori - modern diagnostic methods
There are various diagnostic options that help detect Helicobacter pylori. These include:
13C-urease breath test
- Credibility. The 13C-urease aerotest has a very high level of sensitivity (up to 95%) and specificity (95-100%), it is recommended by both Russian and European gastroenterologists. Only this test, in addition to the presence of bacteria, also determines its quantity. This test is ideal for quantitatively assessing the level of infection of a patient before and after anti-Helicobacter therapy and drawing conclusions about the effectiveness of treatment.
- Speed. The test is carried out within 40-45 minutes, the patient receives its results within 1-2 days. The result of the 13C-urease test is a conclusion with a graph in which the patient’s data is compared with normal and limit values, the presence and amount of the Helicobacter Pylori bacterium is determined (from the absence or insignificant amount to a pronounced or high level of infection).
- Methodology and conditions. The test is absolutely safe and does not cause any discomfort to the patient. The 13C breath test should be performed in the morning on an empty stomach or in the daytime after 4-6 hours after eating.
- Preparation. Conditions for obtaining an accurate result: conducting the test 6 weeks after using antibiotics and bismuth preparations; 2-3 days before the test it is necessary to avoid drinking alcohol; no later than two weeks before the test, you must stop taking proton pump inhibitors (omeprazole, rabeprazole, lansoprazole, esomeprazole, pantoprazole) or type 2 histamine receptor blockers (ranitidine, famotidine, nizatidine, roxatidine), in consultation with your doctor.
- Contraindications. There are no absolute contraindications. Consult your doctor about performing the test if you have a history of gastric surgery.
For analysis, the patient's exhaled air is collected 2 or 4 times: the first time as a control sample, and three times every 10 minutes after the patient takes a drug containing 75 mg of 13C-labeled urea. A high-precision infrared analyzer determines the composition of the air and, accordingly, the amount and activity of bacteria.
Breathing Helic test
- Credibility. The helic test provides identification of bacteria. This aerial test for Helicobacter can be prescribed for primary diagnosis.
- Speed. The test takes 15-30 minutes. The conclusion is given to the patient immediately after the test.
- Methodology. The Helicobacter Pylori breath test (Helicobacter pylori test) is a quick, easy and painless way to diagnose the Helicobacter Pylori bacterium. The test is a non-invasive method, i.e. does not require endoscopic examination or blood sampling, and does not cause any discomfort. It is safe for patients of all ages and for use during pregnancy.
Preliminary preparation is required to carry out the test. The aerotest is taken on an empty stomach; smoking and chewing gum are prohibited before the test. The test is performed 2-4 weeks after the end of antibiotic therapy.
The analysis of exhaled air is carried out twice: on an empty stomach and after the patient drinks a special solution of urea. In this way, the urease activity of the bacterium Helicobacter Pylori is assessed, which indicates the presence of the bacterium.
Test for Helicobacter during FGDS
- Credibility. Taking a biopsy specimen for analysis directly from the stomach is considered the most reliable method for diagnosing Helicobacter pyloriosis.
- Speed. The FGDS procedure lasts 2-5 minutes, and a conclusion on the results and the presence of Helicobacter pylori infection is issued immediately after the study. In general, the examination and conversation with the endoscopist takes 30-40 minutes.
- Methodology. In cases where a gastroenterologist prescribes an FGDS to a patient, especially in the case of gastritis and peptic ulcers, a simultaneous test for Helicobacter will make a significant contribution to the diagnosis. In this case, the patient will receive two conclusions from one study. During FGDS (endoscopic examination - fibrogastroeuodenoscopy), the endoscopist sees with his own eyes the condition of the mucous membrane of the stomach and duodenum, identifies the affected areas and takes samples from them for research (biopsy).
Blood test for antibodies to Helicobacter pylori
- Credibility. The presence of antibodies in the blood indicates that the immune system once encountered the bacterium, recognized it and responded. This means that the analysis does not directly detect Helicobacter, but only indirectly indicates its presence in the past or present. Antibodies to the bacterium appear 3-4 weeks after infection, and also remain in the blood for about 1 month after treatment. Sometimes antibodies remain in the blood for life, regardless of the presence of Helicobacter. Therefore, the result of the analysis is not always reliable: it can be either false positive or false negative, and a number of more tests may be needed to clarify the results.
- Speed. The analysis takes 2-3 days.
- Methodology. Blood is drawn from a vein. Blood is donated on an empty stomach; before donation, you should not eat for 8 hours.
Preparing for a breath test
Diagnosis is carried out in the morning.
In preparation for the study, the patient must adhere to the following rules:
- stop taking antibiotics a month before undergoing a urease breath test;
- 14 days before the examination, avoid taking antisecretory and antihistamine drugs, and a few days - antacids, bismuth preparations and analgesics;
- 3 days before the examination do not drink alcohol;
- During the day before the test, it is recommended not to eat fatty, fried foods, pickles, sweets and legumes;
- at least eight hours must pass between the last meal and the breath test;
- on the day of the test you need to stop smoking and chewing gum;
- Before the procedure, you should thoroughly brush your teeth.
H. pylori detection methods:
There are several methods to confirm or refute the presence of infection. Endoscopic examination (FGS) with the removal of fragments of the gastric mucosa (biopsy) makes it possible to detect H. pylori bacteria during microscopic examination of a biopsy of the gastric mucosa or when cultured on nutrient media. Non-invasive (not requiring endoscopy) tests for the presence of Helicobacter pylori infection include determining the titer of antibodies in the blood to H. pylori antigens, as well as the urease breath test or HELIC test.
How to perform a breath test for Helicobacter pylori
The labeled urea urea breath test is based on detecting the concentration of urea. The test allows not only to confirm or exclude an infection, but also to determine the quantitative indicators of bacteria in the body: the greater the number of bacteria, the higher the urease activity.
The duration of the HELIC test is approximately 15 minutes, the result can be obtained directly during the study.
To perform the analysis, the patient is asked to hold his breath for a few minutes and exhale air into a container or plastic tube. This sample is used as a control (base) sample. After this, as a load, the subject takes a urea solution, which contains a non-radioactive stable labeled isotope of carbon 13 C. After some time, the patient exhales air into another test tube.
Analysis of the base and loading levels of the 13 C isotope in exhaled air is carried out using a diagnostic gas mass spectrometer or a less sensitive infrared IR spectrometer.
The disadvantages of the method include the high cost of diagnostic equipment and the isotope for the test.
A less expensive method of analysis is the ammonia rapid breath test (HELIK ® test system with a digital analyzer). The level of urease activity in the stomach in this case is assessed by changes in the concentration of ammonia in the exhaled air. The method is based on recording the increase in ammonia concentration in the oral cavity, which increases in the exhaled air after taking urea. Gas appears in the oral cavity within 6-7 minutes after taking the load. In this case, the indicator tube connected to the device changes its color. During the examination, it is necessary to ensure that no saliva gets into the tube.
The HELIC test is highly sensitive and accurate; it does not require complex equipment or the use of isotopes of altered composition. The duration of the analysis is approximately 15 minutes, the result can be obtained directly during the study.
Test procedure
The procedure for performing each test is slightly different, due to the characteristics of the reagents.
We recommend reading:
Blood test for Helicobacter: normal and pathological indicators, interpretation
The research is carried out in a laboratory setting. The sequence is:
- The patient sits on the couch and breathes calmly into the test system tube. It is important not to put the tube in your mouth or touch it with your tongue or lips. If saliva gets into the tube, the test will have to be repeated no earlier than an hour later. Breathing should be measured and shallow - normal.
- A capsule of carbon-labeled urea is dissolved in 50 ml of water and the solution is allowed to drink.
- The patient lies down on the couch and lies on each side for 5 minutes so that the solution is evenly distributed.
- After 10 minutes, the patient gets up and breathes into the tube again - if C14 carbon was used, then once is enough, and if C13, then twice more every 10 minutes.
- The tubes or bags containing the breath samples are sealed, labeled and sent to the laboratory for testing.
- Reply the next day or the next day.
Helic test
Can be carried out in any convenient place, including at home. Order of conduct:
- The patient takes a comfortable sitting position.
- Breathe at a calm pace into the plastic test tube for 6 minutes - it is important that no saliva gets into it, otherwise the test will have to be postponed for 40 minutes.
- If an automatic analyzer is not connected, then the result of the first half of the test is recorded manually - the initial color is simply noted, and if there is an automatic analyzer, the recording occurs automatically.
- Next, 0.5 mg of urea is dissolved in 50 ml of water and the solution is given to drink.
- Then the patient breathes into the tube again, but from the other side, also for 6 minutes.
- The doctor compares both results and makes a conclusion about whether there is an infection, right on the spot and immediately.
The most popular method of diagnosing Helicobacter in modern medicine is the breath test. The urease helic test is based on the biochemistry of urea hydrolysis. Helicobacter produces urease during its life. This enzyme accelerates the conversion of urea into ammonia and CO2. Urease helps bacteria live and multiply in the aggressive environment of the stomach.
The patient is given a solution of carbamide (urea) to drink, the hydrolysis of which produces gas that enters the oral cavity. The level of gas entering the test tube before and after drinking urea allows you to determine the presence of bacteria.
The test shows the presence of helicobacter pylori and the level of contamination of the gastric mucosa. Repeated tests evaluate the dynamics of the disease.
Decoding the results
Analyzing the information received, the doctor makes a conclusion that the patient is infected.
The breath test is based on measuring the concentrations of urea and its breakdown products in exhaled air.
If there are no bacteria in the body, then the concentration of carbon dioxide with carbon 13 C in the exhaled air will be equal to its concentration before taking an aqueous solution of urea. If the stress test contains a lot of carbon dioxide with labeled carbon 13 C, this means that the patient is infected with Helicobacter Pylori.
Video from YouTube on the topic of the article:
What affects the reliability of the results
The results of the helic test may be distorted due to non-compliance with the preparation rules and violation of the test technique (saliva entering the tube). Physical activity can distort the results, so the patient should not move during testing.
The following medications cause the greatest sampling error:
- antibiotics;
- bismuth preparations;
- proton pump inhibitors (Pantoprazole, Lansoprazole, Rabeprazole, Esomeprazole);
- type II histamine receptor blockers (ranitidine, nizatidine, roxatidine, famotidine).
Any medication you take may affect the test samples. A week before the test, you should stop taking medications.
Test results are influenced by eating foods that cause flatulence: cabbage, beans, garlic, fruits. Alcohol vapor also causes errors in helic test data. We are talking not only about alcoholic beverages, but also alcohol-containing mouthwashes. On the day of the test, after brushing your teeth, rinse with water; mouthwash should not be used.
The test cannot be done after FGDS (fibrogastroscopy) - at least 24 hours must pass.