Features of decoding a general urine test in adults, children and pregnant women
A general urine test is a clinical test necessary to make an accurate diagnosis. In laboratory conditions, the physicochemical parameters of this biological fluid are determined, and the sediment is diagnosed separately.
Disturbances in the functioning of the body are primarily manifested in the composition of urine. By noticing deviations from the norm in time, you can avoid severe forms of disease.
Features of urine collection
Submitting urine for analysis requires virtually no effort on the part of the person. The liquid must be collected immediately after sleep in a washed jar. The genital area must be washed before the procedure to prevent bacteria from entering.
For the most accurate results, you should not drink alcohol or diuretics the day before the urine test. Fresh fruits and vegetables can unduly change the color of the liquid. The medical restriction is that cystoscopy should be performed no later than a week before the test.
Women during their menstrual cycle should not allow menstrual blood to enter their urine.
The laboratory accepts a fixed volume of urine, the approximate norm is 50 ml. The collected test must be delivered to the clinic no later than 2 hours after collection.
- If you can’t get urine out within this period of time, you need to put the jar in the refrigerator. The analysis result can be obtained within the next day.
Why is it necessary to donate primary urine?
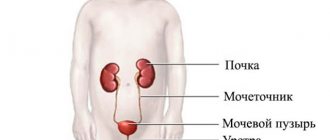
The formation and entry of urine into the bladder occurs through several stages. First of all, primary secretions are formed, which go from the kidneys to a network of capillary pathways.
This process occurs due to increased pressure, as a result of which blood and proteins cleanse the urine of harmful components. Next, it moves through the main structural and functional particles of the organ, that is, through the nephrons.
In the nephrons, urine undergoes the function of returning fluid back into the body, which means that due to the increased level of pressure, water will return to the channels again along with all the useful trace elements.
The level of primary secretions in the flask should not exceed 150-180 milliliters, which can be checked at home. But the density of urine needs to be examined in laboratories.
Relative density of urine
Most people know that doctors recommend taking tests in the morning and on an empty stomach (whether urine, feces or blood), but they do not understand the meaning of these rules at all. The explanation for this is quite simple.
During sleep, human breathing slows down, and sweat production is practically absent, that is, the fluid level does not replenish. That is why for laboratory research such urine is the most useful and exemplary indicator of the state of the body.
Interpretation of a general urine test in adults
The importance of a general urine test in clinical practice cannot be overestimated. To make it easier to decipher its results, use a table.
| Index | Norm |
| Volume | 100–130 ml |
| Color | Straw yellow |
| Smell | Specific, soft |
| Foaminess | When shaking the urine, there should be virtually no foam |
| Transparency | Transparent |
| Density | 1,000–1,025 units |
| Acidity | From 5 to 7.5 on the pH scale |
| Protein | Absent |
| Sugar | Absent |
| Bilirubin | Absent |
| Ketone bodies | Absent |
| Formed cells (erythrocytes and leukocytes) | Red blood cells - no more than 2 per field of view. Leukocytes – in men no more than 3, in women – 5 in the field of view. |
| Flat epithelium | In women there are large numbers, in men there are single cells |
| Transitional epithelium | Single cells in the field of view |
| Renal epithelium | None |
| Hyaline casts | None |
| Grainy cylinders | None |
| Wax cylinders | None |
| Red blood cell casts | None |
| Bacteria | None |
| Mushrooms | None |
| Salts | Absent or detected in small quantities |
It is advisable that every healthy person take a urine test once a year, as it provides enough information about the state of the body and allows you to diagnose some diseases at a latent stage, in the absence of any symptoms.
Quantity
A decrease in the amount of urine is observed with dehydration, acute and chronic renal failure. With a large volume of urine (polyuria), diabetes mellitus or diabetes insipidus can be suspected.
Color
Changes in the color of urine can be due to various reasons:
- orange-red – for diseases of the hepatobiliary system, accompanied by an increase in the level of bilirubin in the blood (cholestasis, cirrhosis, hepatitis);
- the color of meat slops indicates an admixture of blood (hematuria), is a sign of urolithiasis, tuberculosis or kidney cancer;
- reddish – often caused by eating beets the day before or foods containing large amounts of food coloring, as well as certain medications (Amidopyrine, acetylsalicylic acid);
- black is a sign of alkaptanuria, a hereditary disease associated with impaired tyrosine metabolism;
- grayish-white - with purulent inflammation of the kidneys or bladder;
- blue-green - associated with increased putrefactive processes in the intestines, accompanied by the formation of indoxylsulfuric acids, which are excreted by the kidneys and, decomposing in the urine, give it this color due to the formation of indigo;
- bright yellow-orange – taking vitamin B2, Furadonin, Rifampicin, eating large amounts of carrots;
- dark brown – Metronidazole therapy.
The color of urine depends on existing diseases, eating and drinking habits, as well as medications used.
Smell
Immediately after urination, urine has a specific, mild odor. After some time it intensifies, which is normal. The appearance of other odors indicates pathologies:
- the smell of acetone - appears as a result of the formation of ketone bodies and is observed in decompensated diabetes mellitus, prolonged fasting, and uncontrollable vomiting;
- smell of feces - for infectious and inflammatory diseases of the urinary tract caused by E. coli;
- foul odor - its cause is usually a fistula between the bladder and intestines or a purulent cavity;
- musty or mousey smell - observed with phenylketonuria, a hereditary disease associated with impaired phenylalanine metabolism;
- the smell of sweaty feet - isovaleric or glutaric acidemia (hereditary metabolic disorders);
- the smell of hops or cabbage – hop dryer disease (methionine malabsorption);
- maple syrup smell – for maple syrup disease (an inherited disorder of branched-chain amino acid metabolism);
- rancid fishy smell – tyrosinemia (congenital metabolic disease);
- the smell of rotting fish – trimethylaminuria (a rare pathology associated with the accumulation of trimethylamine in the body).
It is not advisable to take a urine test on the days of menstruation or any illness accompanied by an increase in body temperature, as well as within a week after bladder catheterization or cystoscopy.
Foaminess
Normally, when shaking, a small amount of unstable foam forms on the surface of the urine. The formation of abundant white foam is observed with proteinuria, yellow - with jaundice.
Signs of health
Before directly submitting the material for examination, it is necessary to take into account the temperature in the room. It should not be higher than 15 degrees, otherwise the relative density of urine changes its volume and concentration.
If the conditions are met, then we proceed to study the collected secretions. They must meet all indicators:
- Hue . Yellowish urine of a brightly saturated color indicates the presence of dissolved components in it. In case of possible malfunctions in the body, the shade may change to light, transparent or dark yellow. In addition, the color changes if a person has taken antibiotics or other medications.
- Transparency . The absolute norm is complete transparency and purity of the discharge. However, cloudiness of the urine is often observed if it contains salt deposits, mucus or bacterial microorganisms. In its complete absence, we can talk about the formation of an infection.
- Smell . Without a sharp and specific smell - another plus. If you notice an unpleasant ammonia or other odor, you should consult a doctor immediately.
- Reaction . In laboratory studies, the optimal reaction is acidic. When alkaline, one can argue about infectious contamination.
For adults, the normal level of daily excretion is a little more than a liter. Urine leaves the child's body in smaller volumes, which is normal for this age.
When a child reaches 12 years of age, the specific gravity of urine reaches the level of an adult. This indicates the excellent development of the teenager.
It does not matter how much water a person drinks per day, because the structural components of the kidneys remove all existing elements.
If a person has not consumed enough fluids, his urine will be rich in minerals. This symptom is called hypersthenuria.
Factors affecting color
What determines the color of urine? First of all, the shade can be affected by the diet of the previous day. Many foods - carrots, cherries, blackberries, beets - often change the color of urine to orange or red.
The intensity of the yellow color depends on the amount of water consumed. People who drink a lot always have lighter, almost clear urine. The use of medications has a great influence on the shade. Many of them color urine blue, pink or green.
All these natural causes of urine discoloration do not have a significant impact on health and act for a short time, after which they disappear without a trace. Otherwise, it is recommended to seek help.
How is the material analyzed?
In laboratories, urine diagnostic procedures are carried out using a specialized device - a urometer. To determine the volume level, you need to fill the cylinder with liquid material.
It is necessary to carefully remove the foam formed on the surface using filter paper. Next, the urometer is immersed in the liquid and observation occurs. It is important that the device does not touch the cylinder itself.
After the urometer stops oscillating and sinking, the research laboratory worker should highlight the position of the lower meniscus on the scale. The available result is an accurate indicator of the normal specific gravity of urine or its deviation.
If the provided material is not enough for analysis, then during surveys several study parameters are used in terms of quality and quantity:
- Together with drops of urine, the following substances are sent into a cylindrical flask: benzene and chloroform.
- If the patient has hyposthenuria, the mixture is distributed and comes to the surface; with hypersthenuria, it sinks to the very bottom.
- By mixing these 2 substances, experts ensure that the provided material is exactly between benzene and chloroform.
In the presence of various inflammatory diseases of the urinary system, urine is collected from the bladder using a catheter.
Colorless
When drinking a large amount of liquid, the normal color of a healthy person's urine becomes almost colorless. Excessive consumption of alcohol, coffee drinks and green tea also causes discoloration.
Clear urine is a byproduct of diabetes. This disease occurs when the body does not produce enough insulin, glucose levels begin to rise, and excess sugar is excreted in the urine. A complete blood count will also confirm abnormal glucose levels.
A colorless tint can also indicate the occurrence of such a rare disease as diabetes insipidus, which affects the disruption of the production of antidiuretic hormone, which regulates fluid retention in the kidneys. People with these conditions often develop extreme dehydration and electrolyte imbalances.
Factors that change density indicators
The result of the specific volume analysis depends on the performance and functioning of the kidneys. You can determine the correct urine value by diluting it or examining its concentration.
The density of human liquid secretions is a constantly changing value. Patients are interested in what it means if the relative density of urine is increased. Certain factors can change its condition:
- Frequent consumption of fatty, fried, salty or spicy foods.
- Change in amount of daily fluids.
- Increased sweating due to changes in body temperature or other diseases.
- Increased amount of salivation, presence of phlegm or snot.
A healthy adult should have a normal measurement between 1.015 and 1.025 U.V.
What does a general urine test show?
Before we talk about how to decipher the results of a general analysis, we should list the parameters included in it. These include:
- organoleptic indicators (color, smell, volume, transparency, foaminess);
- physical and chemical parameters (density, acidity);
- biochemical indicators (protein, sugar, urobilin, ketone bodies);
- microscopic examination of sediment (erythrocytes, leukocytes, epithelial cells, casts, salt crystals, bacteria and fungi).
Only a doctor can evaluate the results obtained and their compliance with the norm, taking into account all the characteristics of the patient’s condition. For example, with many diseases of the biliary tract and liver, the color of urine changes. However, it happens that the color remains normal, but it is still impossible to exclude one or another pathology of the hepatobiliary system based on a number of other parameters.
If there is an increase in level
Hypersthenuria occurs in any person, regardless of gender, weight or lifestyle, due to the following factors:
- Vomiting, increased diarrhea, or other reasons that cause the body to lose fluid.
- Intestinal disorders and obstructions.
- Abdominal injuries.
- Toxicosis at the time of pregnancy.
- Acute or chronic disease of the urinary system.
- High doses of antibiotics or similar medications.
There is a wide list of possible causes of increased urine density and diseases of the genitourinary system, which lead to an increase in the mass of dry residues in urine.
Experts name several groups of causes of hypersthenuria: pathological (endocrine problems) and physical changes (sweating, salivation).
Other possible pathologies
The reasons for the color change may lie in the development of other dangerous diseases:
- Diabetes mellitus is an endocrine disease of autoimmune origin. It is accompanied by severe thirst, weight loss, and a general deterioration in well-being. The yellowish tint of urine becomes completely pale.
- Chronic renal failure. Accompanied by serious loss of organ functionality. They are not able to fully filter liquid. There is a significant change in urine during such an illness. It takes on a pale yellow tint.
- Renal lymphostasis. The problem is associated with the accumulation of lymph in the tissues. The most common cause of its development is inflammatory kidney disease. During this illness, the urine changes, it becomes white and begins to look like milk. This is the result of a large amount of lymph entering it.
- Hypercalcemia. The disease is hereditary. It is associated with increased calcium concentration in the body. This becomes one of the reasons why urine takes on a bluish tint.
- Viral hepatitis. With this pathology, gradual destruction of liver cells occurs under the influence of a viral infection. Bilirubinuria develops. Urine is distinguished by the presence of rich yellow foam in it.
- Pyonephrosis is the formation of an abscess in the kidney area. Urine is observed to be colored in three colors at once: a thick white substance is visible on top, the middle layer is milky, and salts and fats precipitate.
- Hemoglobinuria. This concept includes several forms of hemolytic anemia, which occur with the penetration of hemoglobin into urine, as well as intravascular hemolysis of blood cells. The color of the urine may change to black.
For these deviations, complex long-term treatment is required. The sooner the problem is diagnosed, the greater the chance of maintaining health.
Symptoms
It is possible to identify such a disease in the body only with the help of laboratory tests, but based on general symptoms, a person can independently suspect hypersthenuria:
- A small number of visits to the toilet, accompanied by a decrease in the volume of fluid coming out.
- Darkening and change in odor of discharge.
- Swelling throughout the body or in certain areas.
- Reduced performance, rapid fatigue.
- Pain in the abdomen and lower back.
In completely undeveloped children under the age of 5-7 years, increased urine density is often associated with congenital or acquired pathologies.
Normal indicators
A urine analysis for relative density does not involve examining the biological fluid that is excreted from the body after a night's sleep, as is the case with general diagnostics. Urine collection should be performed starting from the second urination after waking up, and then at intervals of 3 hours.
In total, you need to collect 8 servings per day. Each sample will be examined separately and its specific gravity or density determined. There is no need for special preparation for collecting biological material. You just need to maintain your usual diet and also indicate the amount of liquid taken.
Zimnitsky test norms for each portion of urine. Source: etopochki.ru
Depending on the age of the patient, the density in the urine test will be increased or decreased:
- In children who are just born and during the first 10 days of life - from 1.008 to 1.018;
- At the age of 2-3 years – 1.010-1.017;
- From 4 to 5 years 1,012-1,020;
- Patients aged 10-12 years – 1.011-1.025;
- In adulthood – 1.010-1.025.
In situations where, during the study of the parameters of the obtained sample, an increase in specific gravity was detected and it was 1.035, the patient is diagnosed with hypersthenuria. It is this concept that determines the increase in urine density. It is also worth noting that at different times of the day, the parameter may fluctuate.
Indications for prescribing a urine test
A referral for a clinical urine test issued by the attending doctor should not cause any concern to the patient. This procedure is recommended for everyone (both adults and children) once a year as a preventive examination - the study provides information about the absence of health problems.
If a pathological process is suspected of developing in the patient’s body, a general urine test can confirm or challenge the assumption.
Practitioners recommend urine testing for:
Is it possible to donate evening urine?
- initial diagnosis of any disease in a patient;
- suspicion of impaired functional activity of the bladder (cystitis) and kidneys (glomerulonephritis, pyelonephritis);
- infectious and inflammatory processes;
- metabolic disorders;
- intoxication with drugs or toxic substances;
- the patient has symptoms of diabetes mellitus, hepatitis;
- monitoring the effectiveness of prescribed treatment.
Biochemical examination of urine
This study is also called a urine analysis for trace elements. Many people are interested in what a urine test for microelements gives? With the help of this study, it is possible to diagnose inflammatory and rheumatic processes, determine the quality of the liver and kidneys, disorders of water-salt metabolism, and establish an imbalance of microelements in the body. An imbalance of microelements can provoke the development of many pathologies. Therefore, it is very important to identify it at an early stage and eliminate it in a timely manner.
biochemical urine analysis allows you to determine the quantitative content of proteins, enzymes, carbohydrates, lipids, pigments, low molecular weight nitrogenous substances, inorganic substances (iron, calcium, potassium, sodium, chlorine, phosphorus, cobalt, selenium, magnesium) in the human body.
Preparation for the study and methods of conducting it
Many people have had to collect urine repeatedly for various laboratory tests. However, not everyone knows that obtaining accurate analysis results depends on following certain rules for preparing for the study. Here are the basic requirements:
- 2 days before the analysis, you must give up salty, smoked and spicy foods, avoid drinking alcoholic beverages, stop taking multivitamins and medications (if this is not possible, you must notify the laboratory assistant).
- OAM must be passed before an instrumental examination of the urethra or bladder (urethroscopy or cystoscopy).
- On the eve of the urine test, you should avoid eating those foods that can change the color of the urine. These are beets, carrots, rhubarb, spinach, carbonated drinks containing dyes.
- It is not recommended to visit a sauna or bathhouse before donating urine. These health procedures promote the release of large amounts of fluid through the pores of the skin, as a result of which the concentration of urine increases.
- OAM should not be taken by women during menstruation. This physiological condition will bias certain analysis parameters.
A general clinical examination of the morning urine sample is performed; it must be collected in a special sterile container purchased in advance from a pharmacy chain
OAM is performed in clinical laboratories of public medical institutions and private medical centers.
To collect biological material, it is important for the patient to fulfill certain conditions:
- perform a thorough toilet of the genitals;
- release a small amount of urine into the toilet;
- Without interrupting urination, place the sample collection container and fill it 2/3 full.
The biomaterial must be delivered to the laboratory center no later than two hours after collection - long-term storage of urine affects the analysis results
Now is the time to find out what exactly a urine test shows?
Treatment with traditional methods and prevention
Some preventative methods will help maintain the excretory system, internal organs and pelvic muscles in a healthy state:
- proper nutrition;
- physical exercise;
- regular examinations by doctors.
If a woman eats right, eats fresh fruits, herbs and vegetables, meat and fish, and maintains a water-salt balance, then she will not have problems with urination. Constant physical activity - gymnastics, aerobics, Kegel exercises - will help strengthen the pelvic muscles.
Although there are a lot of medications for therapy, some women prefer traditional methods. Herbal teas and decoctions, compresses and lotions help.
- To prepare the healing liquid, you need to mix 1 tsp. cherry stems and dried corn hair, pour 1 tbsp. boiling water After 15 minutes, the mixture must be drunk.
- A mixture of centaury and St. John's wort helps. You need to brew 1 tsp of boiling water. dried herbs and drink the infusion three times a day, half a glass.
- An onion compress will help with pain in the lower abdomen when urinating. One onion needs to be grated on a fine grater and placed in cheesecloth. The compress should be applied to the lower abdomen in the evenings for 3-5 days.
Light urine is a sign of various pathologies of the excretory system. The reasons for women may depend on their condition and actions. In any case, this factor is a reason for examination.
Article design: Vladimir the Great
Daily biochemical analysis
In this case, all the urine that the patient’s body excreted during the day is studied. To achieve this, it is usually believed that the fluid intake regime should be the same as always. Urine is collected from seven in the morning one day until seven in the morning the next.
The subject of the study is to study the content of the following substances in urine provided for analysis:
- uric acid;
- amylase;
- creatinine;
- glucose;
- protein;
- urea;
- calcium, sodium, chlorine, magnesium in the form of electrolytes.
Urine color during pregnancy
When expecting a child, the female body experiences maximum stress, as it performs functions for two. During this period, doctors regularly examine the woman and prescribe a number of tests that help determine the presence of developmental pathologies in the woman or fetus. One of the available and reliable assessment methods is urine analysis. The tone of the discharge indicates the general health of the expectant mother and child.
Causes of decreased specific gravity of urine
If the density of the biological fluid is below normal, they speak of hyposthenuria . This does not necessarily mean that the person is sick. Doctors know of cases where such a deviation was a consequence of the patient consuming an excessive amount of liquid shortly before taking a laboratory test.
The use of any diuretic drugs also leads to hyposthenuria. The doctor must be warned about this factor in advance so that the data obtained are not misinterpreted.
Collection of general urine analysis
After all preparatory steps have been completed, biological fluid is collected for further laboratory testing. The following standards for urine collection for general analysis are distinguished:
- They check only morning urine, which accumulates in the bladder cavity throughout the night;
- in the first 3 seconds you need to urinate into the toilet to allow natural rinsing of the urethra from mucus and epithelial cells, and only after this the patient can direct the stream into a container for collecting biological material;
- immediately before urinating, you must take a warm shower, thoroughly wash your genitals with soap, and then wipe them with a dry, clean towel (failure to comply with this rule for collecting urine may result in the appearance of an excess number of leukocytes in its composition, or the specialist conducting the analysis may detect an infection, located on the surface of the foreskin in men or around the urethra in women);
- the container where urine is collected must be prepared in advance and sterilized (it is best to initially purchase a plastic container from the pharmacy intended for collecting urine for general analysis);
- the optimal volume of biological material that can show the most accurate biochemical composition of the test fluid is 100-150 milliliters of urine (it is important to remember that at the moment of urine outflow, the surface of the genital organs should not touch the container for collecting it);
- urine for general analysis should be stored for no more than 2 hours at an air temperature of 5 to 17 degrees Celsius (biological material that was outside the laboratory for longer than the specified time, or was not stored in a refrigerator, is not suitable for research);
- newborns need to wear special urine bag bags, they are sold in pharmacy chains, are sterile and provide urine collection for general analysis without irritating the baby’s skin surface (for older children who go to the toilet on their own, the rules for collecting urine are exactly the same as for adult).
As soon as the urine collection process is completed, it is immediately delivered to the laboratory department, where its general analysis will be carried out. If it is not possible to promptly send biological material, then it is necessary to comply with all storage rules described in the above paragraphs.
What does a urine test show? Urine is the final product of human life, it contains 95% of water filtered by the kidneys, and in the remaining 5% you can find toxins, dead epithelial cells, red blood cells, leukocytes, dead hepatocytes, and various chemical compounds.
Urinalysis is a very informative method for studying the human body.
What other colors can there be?
- Colorless. Urine should have a certain color. The absence of a clear color of urine, when it is transparent and colorless for a long time, indicates an increase in urination, and this is a pathological deviation. Factors often include diabetes mellitus, as well as long-term use of diuretic medications. Absolutely colorless urine is a sign that the kidneys cannot cope with the increased load and do not have time to remove excess fluid from the body. This is dangerous due to a violation of the water-salt balance.
- Green and blue. When the color of urine changes to green, this is a rare “exotic” phenomenon that occurs when treating children with brilliant green. When a substance stains the mucous membrane of ulcers, it enters the body and is excreted by the kidneys, which is why the child’s urine is colored. The urine of a patient with liver pathologies will look like this when it stands in sunlight. A blue-green tint appears when using Triamterene. Yellowish with green is the result of taking Alexandria leaf.
- Blue. A blue tint is also possible. It occurs in case of infection of internal organs. In children, this phenomenon is observed with hypercalcemia. In adults, pseudomonas infections become a factor.
- Honey. A honey-colored urine often indicates a fluid deficiency. To prevent this condition, you need to control your daily water consumption. It is important to remember that toxic elements and breakdown products leave the body with urine, so dehydration can cause poisoning and intoxication.
- Violet. Purple urine is rare, but possible. This happens when tryptophan metabolism fails. In order for urine to turn purple, you need to be exposed to several phenomena at once. This is an increase in the intake of tryptophan, alkaline urine, and the presence of chronic diseases of the urinary system. However, these factors do not directly affect the color of urine. It becomes colored already when standing in daylight.
Women's urine often changes color during pregnancy. This is due to increased secretion of cervical fluid, which mixes with urine, making it cloudy. This is not a violation, and therefore should be taken into account in the analysis.
Urine clarity
A change in the level of transparency and the appearance of impurities are often associated with infectious pathologies and the presence of urolithiasis. This is accompanied by painful urination, which may immediately indicate the development of cystitis. It is also necessary to pay attention to symptoms such as fever, constant feeling of thirst, changes in appetite, increased blood pressure, weight loss, and changes in the color of stool.
Considering the normal color of urine, you should determine the level of transparency:
- cloudy - it can be a manifestation of inflammatory processes in the genitourinary system, impurities are caused by an increase in the level of epithelium and leukocytes, that is, purulent exudate is formed in the urine;
- an abundance of foam is a factor in the increased protein content, which indicates problems with the hepatobiliary system.
Decoding
Only a specialist should interpret test results based on existing assumptions about the diagnosis. Changes in the same indicator can occur in various pathologies. Thus, a drop in the number of red blood cells occurs with anemia or lack of oxygen, and also with tumor processes.
ESR responds to many conditions: pregnancy, infectious diseases, trauma, menstruation, myocardial infarction. And even when taking medications, the erythrocyte sedimentation rate changes.
Exceeding the reference values does not always indicate illness. It could simply be an unhealthy diet or an overly active lifestyle with overwhelming loads and stress. If blood and urine tests are normal, but you are not feeling well, then additional examination and consultation with a specialist will be required.
We have reviewed basic information about general blood and urine tests. Why are they needed and what should the results be for a healthy person. There is no need to get carried away with regular testing unless your doctor requires it. A considerable number of processes take place in the body during the day and all of them are reflected in blood and urine indicators, so the results change and can be misleading or cause panic.