Children are a group of the population that is most sensitive to various types of infections. Until the age of three, when the baby does not yet go to kindergarten, viral diseases are less likely to occur to him. However, as soon as a child joins a team, he is increasingly exposed to such an unpleasant and highly contagious disease as rotavirus infection. The baby has a fever, stomach pain, diarrhea and vomiting . How to protect a child from rotavirus infection and prevent the occurrence of such reactions?
What do we know about rotavirus - its features, routes of spread and risk groups
In the middle of the last century, doctors did not suspect the existence of rotavirus. Although the disease was diagnosed quite often, it was mistaken for a type of gastroenteritis. It was only at the end of the 80s that scientists were able to establish that the cause of the disease was a virus.
Despite the name, the pathogen has nothing to do with the influenza virus and similar pathologies, although the first signs of rotavirus infection and the acute course are similar to most of them.
The cause of the disease is usually rotavirus A. It accounts for almost 92% of all cases of infection. Every year, up to 26 million cases of illness are registered worldwide. For 3% of them, the disease ends in death. This happens especially often in developing countries.
The pathogenic microorganism affects both children and adults. At the same time, in children the disease is more pronounced and acute. Rotavirus is most often transmitted through the oral-fecal route through contact with a patient or his things. Airborne infection occurs somewhat less frequently.
Preschool children are more susceptible to the effects of rotavirus infection. Babies get sick less often because they are protected by the mother's passive immunity in the first months of life. Most often, pathology is diagnosed during the cold season, although isolated cases of infection are also recorded during other periods. Despite the apparent similarity of rotavirus infection with respiratory and intestinal ailments, the disease has its own distinctive features:
- high resistance of virus virions to sanitary influences and the ability to mutate;
- lightning-fast development;
- simultaneous damage to the respiratory tract and digestive tract;
- affinity for the mucous membrane of the small intestine;
- seasonality of rotavirus gastroenteritis;
- lack of effective treatment aimed at destroying the pathogen.
The characteristics of the disease allow us to speak about the uniqueness of rotavirus and its insidiousness. Disguising itself as other diseases, it is capable of misleading both the patient and the inexperienced doctor.
https://youtu.be/QCg8GAUzdZY
Dangerous scratches
If a mother has scratches or cuts on her hands, then the pathogenic microorganisms that have settled in them will certainly end up in the food that is prepared for the child. The bactericidal patch does not help in such cases - put a glove on the injured hand, as when washing dishes. Most often, staphylococcus gets into food this way.
You can bring it into food and with droplets of saliva, and your throat does not have to hurt - after all, there are hidden carriers of staphylococcal infection who feel healthy, and there are quite a lot of them. So try not to talk while you're cooking!
Legion-Media
Poisoning caused by staphylococcus develops very quickly in children, literally in one and a half to two, maximum four hours, and is severe. Most often they are associated with the consumption of milk, cottage cheese, sour cream and other dairy and fermented milk products. The enterotoxin produced by staphylococcus is heat-stable, unlike most other microbial poisons. For it to collapse, heat treatment is needed for 1.5–2 hours! But many people think that by holding yesterday’s food on the fire, they reliably disinfect it. As you can see, this measure does not always work!
How does rotavirus gastroenteritis begin?
The disease is cyclical. It is customary to distinguish an incubation period lasting 2–5 days, an acute phase lasting 4–7 days (in severe cases more than a week) and a recovery stage.
The first signs of rotavirus infection appear on days 3–5 of infection. During this period it is most often observed:
- nausea and vomiting;
- diarrhea, flatulence;
- temperature increase;
- runny nose, redness and sore throat;
- lack of appetite;
- dehydration;
- lethargy, apathy, decreased performance.
Rotavirus is accompanied by respiratory signs and intestinal distress
Attention. On days 2–3 of the acute phase, the feces become gray-yellow or light, and the urine becomes dark. Such symptoms are characteristic of hepatitis, but the above signs of rotavirus disease will help you avoid making a mistake in diagnosis.
The manifestations of infection directly depend on the age of the patient, his state of health at the time of the disease and the strength of the immune system.
How does the disease progress?
Based on the high aggressiveness of this type of bacteria, it is impossible to effectively protect against rotavirus simply by keeping clean. As statistics show, strict adherence to sanitary and hygienic standards is not a panacea for infection. Every seventh child under the age of five gets rotavirus infection, and most of them are infants . Babies under one year old suffer from the disease in a particularly severe form. The initial entry of rotavirus into the body is considered the most dangerous. Main symptoms of the disease:
- vomiting, nausea, frequent loose stools, abdominal pain;
- redness of the tonsils, high body temperature, runny nose, sore throat;
- pale skin, dry lips, weakness, exicosis.
The acute phase of the disease initially shows itself as a cold or sore throat . The child complains of a sore throat, after which vomiting begins, the temperature rises, and then diarrhea begins.
The most terrible consequence of the disease, which can lead to death, is dehydration, so the baby’s condition must be monitored most closely, because he cannot say what exactly is tormenting him. The baby needs to be protected, and if he is sick, then he should be constantly given water so that the water balance is not disturbed.
Symptoms of rotavirus infection in pediatrics
Intestinal flu is considered primarily a childhood disease. Breastfed babies become infected with rotavirus very rarely and tolerate it easily. Babies who receive various formulas instead of mother's milk are much more likely to suffer from infection.
In infants, the disease is especially acute: dehydration immediately develops, severe vomiting and diarrhea create a significant threat to the health and life of the baby. In this case, hospitalization is the best option.
Older children are characterized by a less dynamic development of intestinal flu, which does not require hospital treatment. If a child visits a child care facility, the likelihood of infection increases several times.
In children, rotavirus most often begins atypically. Respiratory symptoms appear first, and then signs of intestinal infection develop:
- The child complains of nausea, looks sleepy and lethargic, and is constantly capricious.
- Vomiting may occur on an empty stomach, often streaked with blood. After lunch, undigested food is found in the vomit. The reflex occurs after eating, after 10–15 minutes.
- The temperature rises and remains firmly at one level throughout the days of illness.
A baby sick with rotavirus becomes capricious
Since the intestinal symptoms of rotavirus infection are indistinguishable from signs of poisoning, dysentery or salmonellosis, it is impossible to make a diagnosis on your own. You need to call an ambulance or a doctor at home.
Advice. Before the doctor arrives, the baby should not be given painkillers and antibacterial drugs, so as not to blur the symptoms and thereby complicate the diagnosis.
Can children have rotavirus without fever? Yes, this is possible, but it is not typical for an infection and significantly complicates the diagnosis. Erased symptoms appear in the following cases:
- primary infection occurs against the background of weakened immunity;
- the child has already suffered a rotavirus infection previously.
With a favorable course of the disease and timely treatment, the symptoms of the disease begin to subside after 7 days, and recovery soon occurs. Rotavirus is very contagious and in a few days can spread to all relatives and family members, as well as to other children in the kindergarten group.
Self-medication of intestinal infection is dangerous
Unfortunately, young parents often have a frivolous attitude towards intestinal infections: they do not go to the hospital, they treat the child themselves.
Treatment of an intestinal infection with home remedies, and even more so self-medication, can harm the child and lead to a protracted, chronic course of the disease.
In this case, not only the small family member suffers, but also those around him, whom he can infect. If you suspect that your child is sick, contact your doctor immediately. To make a correct diagnosis, you will have to resort to laboratory tests. The doctor may recommend doing a bacterial culture of stool, a coprogram, a blood test (sometimes a serological test), and a bacteriological examination of the vomit.
Abdominal pain due to intestinal infection in a child
Correct diagnosis and timely treatment usually give good results. Of course, provided that you strictly follow all the doctor’s instructions. If necessary, the doctor can refer a small patient for treatment to an inpatient department. If your child shows signs of dehydration (lethargy, dry conjunctiva, oral mucosa), then hospitalization is required.
Signs of rotavirus gastroenteritis in adults
In older people, the infection occurs much less frequently and is milder. This is due to stronger immunity and high acidity of gastric juice.
The ways in which rotavirus infection spreads among adults are fundamentally different from the ways in which children are infected. The older generation is most often infected through the nutritional route, while children are faced with airborne spread of the intestinal group.
In adults, signs of rotavirus infection are as follows:
- symptoms of gastroenteritis or enteritis develop;
- secondary lactose deficiency appears;
- short-term diarrhea is observed.
In this case, there are no manifestations of respiratory distress. Often, rotavirus without fever goes completely unnoticed. The patient usually attributes a minor intestinal disorder to errors in nutrition.
Attention. The absence of external signs of disease does not negate the presence of pathogens in the body. A person becomes a virus carrier and is able to infect others.
The wide spread of the disease among adults is due to the amazing resistance of virus virions to environmental factors and sanitary measures.
Rotavirus is resistant to environmental influences and disinfection
It is often possible to identify signs of rotavirus infection in adults only during a medical examination. On palpation, pain in the peri-umbilical and epigastric zone is noted. Visual examination of the rectum will most likely show redness and swelling of the mucous membrane. Blood and protein may appear in the urine.
The cellular composition of the blood will also change: in the first days the level of leukocytes will increase, then leukopenia will develop. The erythrocyte sedimentation rate will remain unchanged. Using a visual examination and other diagnostic measures, it is possible to fairly accurately determine the presence of rotavirus in adults and prescribe treatment.
Rotavirus infection during pregnancy
It is impossible not to mention infection with intestinal flu during pregnancy. How easily the disease progresses depends on the health of the expectant mother and her immunity.
If you have asymptomatic rotavirus, there is no need to worry too much. It is enough just to more closely observe the well-being of the woman and child. In severe cases of infection, the situation may be complicated by intrauterine developmental disorders of the baby and lead to miscarriage.
Attention. The danger of rotavirus during pregnancy lies, first of all, in the insidiousness of the disease. Disguising it as other diseases, in particular toxicosis, significantly complicates diagnosis and delays the start of treatment.
Details
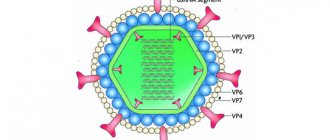
In terms of the frequency of diseases, rotavirus infection ranks second after ARVI. The causative agent of the disease got its name from the Latin word rota - “wheel”, because viral particles under an electron microscope look like small wheels with a wide “hub”, twenty short “spokes” and a circular rim.
Rotaviruses on various environmental objects remain viable from 10-15 days to 1 month. (depending on temperature and humidity), in feces - up to 7 months. Mostly children under the age of 1 year are ill, less often - up to 6 years; In adults, the disease is quite rare - in isolated cases.
Dzhanneta Jasitytė, consultant: Inna Danilova, pediatrician, Ph.D. honey. Sciences Article provided by the magazine “My baby and I”, No. 1 2007
Therapy for rotavirus infection
Before proceeding to the analysis of medications, it should be noted that there are still no specific treatment regimens for rotavirus. To combat intestinal flu, symptomatic therapy is used, aimed at eliminating the manifestations of the disease and alleviating the patient’s condition.
Only a specialist can diagnose rotavirus infection and prescribe proper treatment. The patient is prescribed strict adherence to quarantine, bed rest, diet and plenty of fluids.
Drug therapy for rotavirus
The basis for the treatment of rotavirus enterocolitis is the prevention of dehydration and restoration of water-salt metabolism. For this, the patient is prescribed Regidron and solutions containing sodium chloride. In addition, the treatment regimen includes the following drugs:
- Enterosgel. Collects and removes toxins and poisons from the body, helps restore microflora and gastrointestinal mucosa. Has contraindications.
- Enterofuril. It is an intestinal antiseptic and has antimicrobial activity. Prevents further development of rotavirus. During pregnancy, you should consult your doctor.
- Enterol. This probiotic effectively eliminates the symptoms of infection and helps break down food, in particular milk sugar. In addition, Enterol retains fluid in the body, preventing dehydration.
Enterosgel is included in the treatment regimen for rotavirus infection
Together with Enterol, it is recommended to take drugs that normalize the intestinal microflora: Bifidumbacterin or Linex.
Attention. If there are no obvious improvements 2 days after the start of therapy, you should stop treatment and consult a doctor to clarify the diagnosis.
Antiviral and antimicrobial drugs for rotavirus
Drugs in this group will help avoid secondary infections, so their prescription is completely justified. They are especially effective at the early stage of rotavirus enterocolitis.
The treatment regimen includes the following medications:
- Cycloferon. A drug with a wide spectrum of activity. Has contraindications.
- Kagocel. The medication is taken for no more than 4 days. Has immunomodulatory and antimicrobial effects. Prohibited for cases of genetic lactose intolerance.
- Ingavirin. Prevents the introduction of rotavirus into cells and its further reproduction. The therapeutic course is 5 days. During pregnancy, consultation with a doctor is necessary.
- Furazolidone. It has antimicrobial activity and improves immunity. Concomitant use of Furazoliidone and alcoholic beverages may lead to vomiting. It has a number of contraindications.
- Amiksin. The product activates the production of interferon and has an antiviral effect. Consultation with a doctor is required; there are contraindications.
Antiviral drugs are prescribed to treat rotavirus
In severe cases of rotavirus infection, intravenous administration of Trisol or Disol solutions is prescribed. Children are often prescribed intramuscular injections of immunoglobulin.
To improve the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, it is considered advisable to use enzymes: Pancreatin, Festal and others.
It should be noted once again that treatment for rotavirus is only symptomatic. It is not aimed at destroying the virus itself, but at eliminating symptoms and preventing complications.
Basic preventive measures
To reduce overall morbidity, a list of measures has been created aimed at protecting the population and preventing the epidemic. The concept of rotavirus prevention includes:
- after using the toilet, going outside and visiting public places, wash your hands thoroughly with soap;
- do not open your mouth while swimming in pools and public bodies of water;
- do not drink from untested springs;
- exclude contact with the patient, transfer patients to the infectious diseases department;
- when preparing dishes, take into account the temperature regime, process ingredients well, give preference to home cooking;
- regularly process children's things and toys;
- wash vegetables and fruits and, if necessary, pour boiling water over the peels.
A vaccine against rotavirus has been created. It is not included in the National Vaccination Calendar as mandatory for all children, but can strengthen the baby’s immune defense. When administered, there is a possibility of infection, however, the pathology will be mild or asymptomatic.
How dangerous is rotavirus gastroenteritis?
Rotavirus infection with early diagnosis and proper treatment occurs without any complications. It is important to ensure that young children do not become dehydrated or have too high a temperature. Lethal outcome is extremely rare and only if the disease develops against the background of reduced immunity.
The consequences of rotavirus infection are reduced to deterioration of digestion and the development of dysbacteriosis. This condition is not critical and can be easily eliminated by taking appropriate medications.
Some doctors believe that rotavirus can reduce immunity, especially if the disease recurs several times. This opinion is quite controversial and causes numerous disputes.
Indeed, rotavirus weakens the immune system. But with the right lifestyle and proper nutrition, it quickly recovers. To speed up this process, you should take vitamin complexes.
Important. After contracting rotavirus in childhood, the patient’s body develops a strong immunity to the disease. In people with low antibody levels, the disease recurs repeatedly.
Reducing the temperature during rotavirus
Rotavirus infection is almost always accompanied by an increase in core body temperature, on average up to 38 degrees. If the child tolerates this symptom satisfactorily, there is no need to resort to antipyretics. When the temperature rises to 39 degrees, doctors recommend Cefekon suppositories, suitable for children under 3 years of age. For older patients, Paracetamol is allowed, dosing according to the instructions. In some cases, when the temperature cannot be brought down to an acceptable level, it is possible to use Paracetamol with Analgin (a quarter of a tablet).
In addition to drug treatment, wet wipes with vodka or vinegar solution are added. The solutions must be applied to the child’s entire body, avoiding temperature changes between areas of the skin.
The drug Enterofuril has a good therapeutic effect. The product actively fights gastrointestinal dysfunction and stabilizes body temperature. If necessary, you can replace it with Enterol.
When a rotavirus infection is accompanied by pain in the gastrointestinal tract, the child is given 1 ml of No-shpa solution, first diluted with a teaspoon of water or tea.
Rotavirus infection is accompanied by a violation of the intestinal microflora. After the main treatment, you will need a course of drugs that eliminate dysbiosis. The following drugs are allowed for the treatment of childhood dysbiosis: Hilak forte, Linex, Normobact (allowed for infants).
Prevention of rotavirus infection
Intestinal flu is not a very serious, but rather unpleasant disease. In addition, the infected object is capable of infecting its immediate surroundings within a few days. How to fight rotavirus and protect yourself and your loved ones from the disease.
As nonspecific preventive measures, basic hygiene rules should be followed:
- Wash your hands after going outside and before lunch.
- Regularly carry out wet cleaning in the house.
- Provide separate bed linen, towels and personal hygiene items for each family member.
- Eat only thoroughly washed vegetables and fruits and boiled water.
Clean hands are the basis for preventing rotavirus
Attention. All these measures can only reduce the risk of rotavirus infection, but not eliminate it completely. A more effective method of prevention is vaccination. The procedure is very effective and reduces the risk of infection by 80%.
Vaccination against rotavirus gastroenteritis is given in the first weeks after birth. Today, two types of vaccines are used: Rotatek and Rotarix. The drugs are available in the form of a solution and are administered orally to the body.
How many days does rotavirus last?
In most children, with proper therapy, vomiting goes away within a day, and abdominal pain and diarrhea persist for 3–7 days. The immune system of the body receiving support begins to produce immunoglobulin A, which helps fight viral infection. But even on days 12–15 from the onset of the disease, the intestines are not yet cleared of viruses. Therefore, a child who is already feeling relatively well continues to remain dangerous to others for about 4 weeks.
To prevent other family members from getting sick, it is necessary to observe basic hygiene standards: wash your hands, boil children’s dishes and cutlery, and do not forget about wet cleaning of the apartment. At the end of the disease, a certain amount of antibodies will be formed in the body, which will help transfer the rotavirus much easier the next time.
Frequently asked questions about rotavirus
Rotavirus remains a little-understood disease, so it's no surprise that people want to know more about it. Young mothers especially have a lot of questions. For example, at a doctor’s appointment they are often asked whether rotavirus can occur without diarrhea? This happens extremely rarely. Diarrhea is a constant companion of the disease.
Another, no less frequent question is: is there always a fever with rotavirus infection? In approximately half of the cases, the disease may occur without pronounced symptoms. If there is a temperature and it is not very high, there is no need to bring it down. This will help fight infection. Rotavirus becomes inactive at temperatures of 38 °C and above. And only if the thermometer readings are more than 39 °C, you should take an antipyretic.
High temperature helps fight rotavirus infection
Many people try to treat rotavirus with antibiotics. Is it worth doing? The answer is clear - no. There will be no benefit from taking them, since the nature of the disease is viral, not bacterial.
How to fight rotavirus? This is a very persistent infection. Conventional disinfectants cannot cope with it. For example, in the feces of a sick person, virions remain active for up to 7 months.
The pathogen can be neutralized by boiling the item for at least 3 minutes. But this method is not always suitable. What else does rotavirus kill? The most effective remedy that can destroy the pathogen is ethyl alcohol. With its help, you can reliably disinfect the patient’s room and belongings.
From the above, it becomes clear that rotavirus is not an ordinary microorganism. The pathology caused by it requires mandatory consultation with a doctor. If treated ineptly or untimely, the disease can lead to serious consequences.
Attention. The article is for reference only. Specialist consultation is required.
Additional information about rotavirus infection can be found in the video:
This disease causes inflammation in the upper respiratory tract and digestive organs. A child can become infected with rotavirus infection for various reasons, and an adult can also get sick from it. However, in children the disease is much more complicated than in parents.
How is rotavirus transmitted?
Another feature of rotavirus infection: if a child has had RVI three times in a year, then the disease begins to manifest itself not as an intestinal disease, but as a cold. The same applies to adults. Intestinal symptoms become less pronounced as the body has already adapted. The severity of the infection decreases, and respiratory manifestations come to the fore.
There are both pros and cons to this. On the one hand, the body no longer suffers as much from dehydration. On the other hand, if rotavirus infection occurs like a common cold, people no longer pay attention to it, especially adults. And if someone in a family gets sick with rotavirus, as a rule, all its members become infected within two days.
This is due to the characteristics of the pathogen - it is unusually stable in the external environment. For example, the virus can live on glass surfaces for up to 10 days. To become infected, a child only needs to receive 10 viral particles, while an infected person releases billions of such particles. In addition to airborne droplets, there is also a fecal-oral method of transmission of infection.
The majority of cases are children of the first or second year of life who do not attend child care institutions. According to world statistics, every child under 5 years of age, regardless of the sanitary conditions in which he is located and where he lives, suffers rotavirus infection on average up to 2 times.
Rotavirus infection is a year-round infection, but its incidence is slightly higher in the cold season. Our study showed that the maximum peak of RVI is observed when the temperature remains at a level of -15?C.
What is rotavirus infection in a child?
This disease in children is provoked by pathogenic viruses that infect the patient’s gastrointestinal tract. The acute form is characterized by the development of fever, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and increased body temperature. The diagnosis of intestinal flu (or rotavirus infection in children) is made on the basis of a whole range of laboratory tests and epidemiological data.
The therapeutic process for this disease includes:
- rehydration;
- special diet;
- detoxification;
- taking medications.
Rotavirus in a child is a disease that is included in the group of viral diarrhea. Theoretically, a person of any age can become infected with it, but in children this disease is registered more often. Gastroenterologists, pediatricians or pediatric infectious disease specialists deal with rotavirus infection in children. The susceptibility of children to this virus is very high. In the first five years of his life, every child experiences intestinal flu, sometimes multiple times. In more than half of cases, the infection develops in infants from 3 months to 2 years.
Infants (up to three months) develop passive immunity to viruses. However, for this, the baby must be breastfed. Otherwise, even a tiny baby can get sick. Relapses do not occur earlier than 6-12 months after the child suffered rotavirus. When re-infected, children tolerate symptoms much more easily.
Signs of illness
The first sign of the disease is usually a sharp increase in body temperature, chills, and flu-like aches. Then spasmodic pain in the abdomen appears, severe flatulence, accompanied by loose stools and nausea. At the same time, gurgling in the intestines is pronounced.
The development of symptoms occurs very quickly. The general condition of the patient is lethargic, activity and performance are reduced, and there is no appetite. Vomiting and diarrhea lead to dehydration, the skin becomes pale, the mucous membranes are not sufficiently moisturized, lips are cracked, and the tongue is coated with a white coating. But not all cases exhibit such obvious classic symptoms.
Causes of the disease
Rotavirus infection in children can be transmitted from other patients or carriers of influenza. When you notice the first signs of illness in your child, he becomes contagious. On the 5th day after illness, rotavirus is especially dangerous for others. It is easily transmitted by airborne droplets, through dirty hands, toys, door handles, etc. It is easy to get intestinal flu through foods that the sick person has come into contact with. If you drink unboiled water, there is also a risk of infection, because even chlorine does not kill the pathogens of intestinal flu.
Nonspecific prevention
Currently, infants are being vaccinated quite successfully with the Rotatek vaccine, certified in Russia. Vaccination is the only fairly effective method of combating rotavirus infection. Vaccination is convenient because it is prescribed in the form of drops and is carried out from the 6th week of a child’s life to 32 weeks with an interval of 4 weeks. Thus, rotavirus infection can be prevented at a very early age.
Children are a group of the population that is most sensitive to various types of infections. Until the age of three, when the baby does not yet go to kindergarten, viral diseases are less likely to occur to him. However, as soon as a child joins a team, he is increasingly exposed to such an unpleasant and highly contagious disease as rotavirus infection. The baby has a fever, stomach pain, diarrhea and vomiting . How to protect a child from rotavirus infection and prevent the occurrence of such reactions?
First signs and symptoms
After contact with a carrier of the virus, signs of rotavirus infection in children develop within 13-95 hours (the period depends on the body’s ability to retain the virus). There are several different ways in which stomach flu develops. In the first case, the baby complains of:
- sore throat;
- dry cough;
- runny nose;
- conjunctivitis.
In the second case, the following symptoms can be found:
- nausea;
- diarrhea;
- signs of poisoning;
- gastroenteritis;
- pain in the abdomen.
Another variant of the course of the disease is typical for young children:
- the child is lethargic or, conversely, capricious;
- refuses to eat;
- presses his legs to his tummy.
How can I help before the doctor arrives?
The provision of first aid to your baby largely determines his condition and the course of the disease. If a child complains of nausea, abdominal pain, and has a fever, then the first thing to do is put the baby to bed. Position the pillow so that your head is significantly higher than your body and legs. From time to time you can wipe your baby’s forehead and temples with a handkerchief dipped in cold water. If the temperature is above 38.5ºC, give your child an antipyretic drug that you have already used before. A child’s weakened body needs a special diet.
But, under no circumstances force your child to eat!
After all, it is extremely undesirable to overload the body during illness. Even when the little one gets better, the daily amount of food should be 30-50% less than usual. But, on the contrary, increase the number of feedings.
At this time, offer your child crackers, rice, and liquid porridge with water. Avoid black bread, whole milk, dishes made from legumes, beets, cabbage, and juices. Such products increase fermentation in the intestines. Particular attention should be paid to the drinking regime, because with vomiting and diarrhea, dehydration occurs. Pharmacy rehydrating solutions, dried fruit compote, and blueberry juice will help restore the balance. Drinks should be given in small portions: 10-15 ml every 5-10 minutes.
Incubation period of rotavirus infection
Take care of your health - save the VKontakte link
After infection, rotavirus infection lives in the body for several days, and becomes acute later. How long the incubation period lasts in children depends on the characteristics of the body. As a rule, it is 1-5 days. At this time, virus particles actively multiply and accumulate. Sick children may not express complaints and feel normal. However, by the end of the incubation period, the child will develop weakness, nausea, diarrhea and a temperature of 38 degrees.
To avoid complications and speed up recovery, parents can begin treating their children’s rotavirus infection at this stage. To do this, it is worth strengthening the diet, giving the sick baby vitamins and minerals. However, it is worth noting that this period may go unnoticed by parents due to the absence of symptoms, so preventive measures will not be superfluous if there is an outbreak of intestinal flu in a kindergarten or a healthy baby has had contact with infected children.
Rotavirus survival rate and how it is transmitted
Bacteria of the genus Rotavirus have high survival rates. Literally nothing takes them away - neither disinfection, nor boiling, nor freezing .
They feel great and reproduce in both severe frost and sweltering heat, and also live for a long time in different habitats: on the surface of household items, in water, on food. At the same time, rotavirus infection is also very contagious and is transmitted by the fecal-oral route. If one of the family members is sick, then, as a rule, everyone will get sick, and newborns are especially susceptible to infection, since it is enough to touch the door handle, on which bacteria remains after the touch of the sick person, and infection is ensured. Adults tolerate this disease much easier and catch it less often . This is due to the fact that the body produces antibodies to rotaviruses, but such immunity does not last long, especially if a person has been ill only once.
How and with what to treat rotavirus in children
There is no specific treatment for stomach flu. Therapy is aimed at eliminating symptoms. Diet for rotavirus infection is very important, because the baby needs strength to fight the disease. In addition, the doctor will prescribe medications: antispasmodics, immunotropic, antipyretic. It is very important to take children's antibiotics to kill the virus particles.
How to treat rotavirus infection:
- Antibacterial suppositories are prescribed: Viferon or Lipferon. The dose should be calculated taking into account the age of the patient, the course of administration is from 5 days.
- Fighting dehydration or rehydration. The patient is provided with plenty of warm fluids, which can replenish lost fluid and maintain normal kidney function. Start giving liquid from a teaspoon, gradually increasing the volume. Special solutions (Oralit, Regidron, Humana), chamomile decoction, boiled water, rice broth, unsweetened dried fruit compote are suitable for this.
- To cleanse the body of toxins, take White Coal or Smecta.
- To reduce body temperature, you can take Nurofen syrup, children's paracetamol or Cefekon suppositories.
- It is recommended to wipe a sick baby with a solution of table salt (1 part water to 1 part salt). This will protect him from seizures due to high body temperature.
- If the baby has a stomach ache, then they give No-shpu, the probiotic Lacidofil, Riobal.
What to feed a child with rotavirus infection:
- rice porridge;
- mashed potatoes;
- bananas;
- crackers, bagels;
- infants are transferred to lactose-free formulas;
- exclude dairy products, sauces, fried, fatty, vegetable and meat additives.
Invisible danger
Rotavirus causes an acute infectious disease that affects the gastrointestinal tract. It is sometimes mistakenly called “stomach flu” because in addition to diarrhea and vomiting, the disease may be accompanied by fever, runny nose and sore throat. If an adult who gets sick usually recovers after a few days, then for young children - who, according to statistics, get sick most often - the disease can be fatal. Lenta.ru tells you what you need to know about rotavirus to avoid negative consequences.
Rotavirus was first described in 1973. But it received its name only the following year, 1974, when virologist Thomas Henry Flewitt, studying the virus under an electron microscope, noticed that its particle resembled a wheel (Latin rota - “wheel”).
There are several main types of rotavirus, but more than 90 percent of all cases of the disease are caused by rotavirus A. Almost every child under the age of five experiences rotavirus infection at least once in their life. According to the latest data, only among children under five years of age in 2020, up to 258 million cases of diseases caused by rotaviruses occurred worldwide, of which 128 thousand were fatal.
The peak of the spread of rotavirus infections in both Europe and Russia is the cold months of the year, that is, from December to May.
A child becomes infected from a sick person through contaminated water or food. The virus gets there through unwashed hands due to poor hygiene when preparing food or violations of food storage conditions.
The main carriers of rotavirus infection are children attending kindergarten or other children's groups. Rotavirus is transmitted through household contact through objects and dirty hands, so hygiene should be carefully observed when in contact with a sick person.
Photo: Depositphotos
Parents may have a reasonable question - so what, if you wash your hands thoroughly, will this protect your child from illness? Unfortunately no.
The incubation period, that is, the time from infection with the virus to the appearance of the first signs of the disease, ranges from a couple of hours to several days - usually 1-2 days.
Most often, rotavirus infection manifests itself as enteritis (inflammation of the small intestine) or gastroenteritis (inflammation of the stomach and small intestine).
The disease begins acutely. Most children have a temperature of up to 38 degrees, but it can reach 39 and even higher. The child may experience abdominal pain combined with nausea, vomiting, diarrhea and flatulence. Abdominal pain, as a rule, appears from the first days of illness, is diffuse in nature or localized in the upper half of the abdomen. Of course, in children who cannot yet complain, it will not be possible to find out the characteristics of abdominal pain.
In addition to intestinal disorders, rotavirus infection may also cause general cold symptoms: runny nose, redness and sore throat, enlarged cervical lymph nodes. Against the background of high temperature, young children may even develop seizures.
The duration of diarrhea on average ranges from three days to a week, but it can, especially in young children, persist for a longer time, up to 10-14 days.
Photo: Depositphotos
The main danger of rotavirus infection in children is rapid dehydration due to vomiting and frequent diarrhea. At the same time, it is often impossible to replenish fluid loss with regular drinking - a sick child may refuse water, and due to an increased gag reflex, fluid is not retained in the body.
The main goal of treatment is to combat dehydration, since there are no effective antiviral drugs aimed at combating rotavirus. Doctors call this therapy rehydration therapy.
Depending on the severity of the child’s condition, replenishment of fluid loss is carried out either by drinking water or by drips with saline solutions in the hospital. Drinking is carried out in fractions, every 5-10 minutes, 5-10 milliliters of liquid in any way convenient for the child - from a cup, bottle, spoon, syringe.
The need for hospitalization also depends on the severity of the condition: children with moderate and severe forms of the disease are usually treated in a hospital.
Symptomatic treatment is also used - antipyretic drugs for fever, enterosorbents, drugs to combat flatulence, and so on.
Doctors at the American Gastroenterological Association believe that taking certain probiotics may help combat diarrhea caused by rotavirus gastroenteritis.
Nutrition during treatment should be adjusted. Dairy products from whole milk and gas-forming products (for example, cabbage, rye bread, legumes, soda) are completely excluded from the child’s diet.
It is recommended to eat small portions 5-6 times a day. For a child, porridge with water, lean chicken, meat or fish, and vegetable soups are suitable.
Breastfeeding during rotavirus infection can and should be done. Mother's milk contains antibodies that help the baby fight the virus and disease.
Photo: Depositphotos
It is known that rotavirus infection is one of the “diseases of dirty hands”, therefore the main methods of preventing the disease are associated with strict adherence to the rules of personal hygiene, improvement of the environment, compliance with sanitary standards and other preventive measures. The rules of hygiene are well known to everyone, but given the importance of such a problem as rotavirus infection, it would not be amiss to briefly recall them:
—If your baby is breastfed, continue breastfeeding. —Sterilize all utensils used to feed your baby. —Wash your child’s toys thoroughly every day. —For drinking, use only boiled water. — Thoroughly wash absolutely all fruits that you give to your baby. Even if you usually don’t wash bananas or oranges - “after all, you still have to peel them,” then during a period when there is a danger of infection, it is better to play it safe.
Unfortunately, even the strictest adherence to all hygiene rules does not guarantee protection against infection. There are at least two reasons for this.
First, the rotavirus itself is considered highly contagious. Secondly, there is a concept - “asymptomatic carrier”. A person whose disease does not manifest itself in any way, but he himself is a walking source of infection.
Therefore, vaccination is currently recognized as the most effective method of controlling the incidence rate. The World Health Organization strongly recommends the inclusion of rotavirus vaccine in national immunization programs in all countries of the world. It has been proven that in countries that followed this recommendation, the frequency and severity of rotavirus infection has decreased significantly. Moreover, WHO recommends administering the first dose of rotavirus vaccine as early as possible - from the sixth week of a child's life, so that the immune defense is ready for the first contact with rotavirus. Information provided with the support of MSD Pharmaceuticals LLC, 119021, Russia, Moscow, st. Timur Frunze, 11, building 1 tel. +7-495-916-70-94 Consultation with a healthcare professional is required. RU-ROT-00062, 01.2020
Possible complications and consequences
Intestinal flu if not treated correctly leads to many complications:
- Dehydration, which can be fatal. To prevent this, you need to start desolating the baby in a timely manner or go to the hospital where a drip will be prescribed.
- Acetonemic state of the baby. At the same time, ketone bodies accumulate in the patient’s body, which negatively affect the brain. This complication is provoked by a lack of carbohydrates, which are consumed during the disease process.
- Convulsions can develop due to high temperature. To prevent them, the baby’s body is constantly cooled and rubbed with a salt solution.
Rotavirus: the effect of infection
A viral infection can seriously ruin the holiday experience, especially for a child. As a rule, the infection affects the body quite harshly, causing a number of unpleasant symptoms. Once in the child’s body, the infection goes through an incubation period, in most cases short - 1-2 days. After this time, parents may observe the following signs of the disease:
- an infectious child complains of nausea and vomiting;
- change in bowel movements - diarrhea;
- discomfort, colic in the intestines;
- weakness, increased body temperature, lack of appetite.
The main localization of pathogenic microorganisms is the upper parts of the small intestine. The virus infects intestinal cells, thereby provoking the development of a pathological process.
Prevention of rotavirus
To avoid infection with rotavirus infection, it is recommended to practice good hygiene. In addition, you should feed younger family members only with fresh, heat-treated foods. Humidify the air in the children's room and constantly ventilate the rooms in the house. If someone in the family has a cold, then limit the baby’s contact with him. There are intestinal flu vaccinations that are given only upon request (not included in the vaccination plan). This method is especially effective for children under 2 years of age.
https://youtu.be/Qt7TUuADHmo
How to protect yourself from rotavirus
To avoid becoming infected with rotavirus from a patient, you must follow certain rules:
- Provide the patient with separate dishes, towels and other items.
- Wash the infected person's dishes with warm running water and then pour boiling water over them or boil them.
- The towel is washed often; before washing, it is pre-soaked in a disinfectant solution.
- The person caring for the sick person should wear a gauze mask, change and wash their clothes regularly, and wash their hands frequently with soap.
- The bathroom and especially the toilet bowl are often washed with the addition of bleach.
- Floors and all surfaces are wiped many times a day with the addition of chlorine-containing products.
These measures prevent you from becoming infected with rotavirus infection, which greatly weakens the immune system.
Why is my child's immune system weakened?
Many people are familiar with these situations:
- As soon as the cold season begins, your child will definitely get sick
, and then the whole family. - It seems like you are buying expensive drugs, but they only work while you drink them, and after a week or two the baby gets sick again
. - You worry that your child’s immunity is weak
, very often illnesses take precedence over health. - You are afraid of every sneeze or cough.
It is necessary to strengthen YOUR CHILD'S IMMUNITY!
Next, you need to pay attention to the bed linen, because as a rule, when parents and children come on vacation, they rent hotel rooms. Unfortunately, not all hotels use linen disinfection methods, so it is better to take your own kit.
What else you need to know about rotaravirus infection is a disease of “dirty hands,” so teach your child to wash them thoroughly after going outside. It would be a good idea to use antibacterial agents (gels, wipes), especially after swimming in the sea or playing with sand.
Basic rules for protecting a child from rotavirus
You can talk about preventive measures to protect against rotavirus for quite a long time. Therefore, experts have identified a number of rules that must be followed while on vacation with a child in order to avoid getting sick:
- try not to dive headlong into the water to prevent it from being swallowed;
- after contact with the sea, sand, outerwear (swimsuit/swimming trunks), wash your hands thoroughly with soap and apply an antibacterial agent;
- use your own set of linen or carefully steam the provided one;
- Remind your child about hygiene rules as often as possible and keep his hands clean.