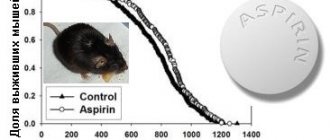
Aspirin is an effective drug that is widely used to relieve withdrawal symptoms during hangovers. The product has an analgesic and anti-inflammatory effect, and also thins the blood.
Thanks to these properties, the medicine eliminates the symptoms of poisoning caused by excessive alcohol consumption (headache, dizziness, nausea, thirst, weakness).
Description and composition
- The main active substance of Aspirin is Acetylsalicylic acid (ASA) , the main pharmacological feature of which is considered to be the ability to weaken platelet aggregation. In addition, Aspirin is used to reduce fever, relieve pain and inflammation.
Pharmacodynamics
- The mechanism of the therapeutic effect of the drug is to stop the occurrence of prostaglandins (prostacyclin and thromboxane A2) due to the inevitable decrease in the activity of cyclooxygenase-1, which takes part in their synthesis. The property of prostaglandins, which consists in enhancing platelet adhesion, inflammation in the lesion, the sensitivity of pain receptors and the affinity of hypothalamic receptors for pyrogenic components, is weakened when exposed to COX-1.
Pharmacokinetics
- After oral administration, the drug is completely absorbed from the digestive tract in a short period of time. After absorption, ASA is converted into salicylic acid. From 66 to 98% of ASA and SA are combined with blood proteins.
SA is able to cross the placental barrier with proteins and enter breast milk. Because of this ability, the medicine is undesirable for use during pregnancy and lactation.
- The maximum content of the drug in the blood is achieved 10-20 minutes after administration. In the liver, salicylic acid is converted into salicylphenol glucuronide, salicylacyl, as well as salicylic and gentisic acid.
- The half-life of the substance is 2-3 hours when using a small amount of the drug. With a significant dose, this time interval can increase to 15 hours.
- ASA and its derivatives are excreted from the body by the kidneys. If there are no kidney diseases, then the medication, taken once, is completely eliminated from the body in 2-3 days.
Composition of the drug
One Aspirin tablet contains acetylsalicylic acid (0.5 g), microcrystalline cellulose and corn starch.
Release form of the medicine
- The medication has the form of biconvex round tablets. One cardboard package contains 1 or 2 blisters with 10 contour cells. An alternative to Aspirin is Aspirin Upsa, available in the form of effervescent tablets for dissolution in water.
Manufacturer
The manufacturer of this drug is the German company Bayer Bitterfeld GmbH, located in Germany.
Conditions for dispensing from pharmacies
This medication is dispensed without a doctor's prescription.
Cost of the drug
The average price for the drug varies from 75 to 509 rubles.
Rules and terms of storage of the drug
Aspirin must be stored at a temperature of no more than +25°C out of the reach of children. The shelf life of Aspirin is 5 years from the date of production.
Scope of application of Aspirin
Thanks to its analgesic effect, the drug can be used to combat headache, muscle, dental, menstrual and joint pain. However, it is not recommended to use Aspirin during menstruation, since ASA can increase bleeding by weakening platelet aggregation.
The antipyretic and anti-inflammatory effect suggests the use of the drug for infectious and inflammatory diseases, rheumatic diseases and fever in patients over 15 years of age.
How does it affect the blood?
Acetylsalicylic acid and aspirin-containing drugs belong to the group of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. These substances reduce the formation of prostaglandins in the body, which, among other effects, promote platelet aggregation and sedimentation of blood clots on the walls of blood vessels.
There is an opinion that taking “acetyl” lowers cholesterol levels in the blood and inhibits the progression of atherosclerosis. This confusion is due to the fact that blood clots, the formation of which aspirin blocks, often form on atheromatous plaques. The medicine does not have a direct effect on cholesterol levels in the body.
The drug acts as a thinner, preventing platelet aggregation and slightly dilating blood vessels, which reduces the risk of blood clots. This is the antiplatelet property of the drug. The effect after taking a simple aspirin tablet occurs within an hour and lasts 24-48 hours.
In addition, long-term use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory substances causes a decrease in the number of leukocytes and other blood cells, which the doctor must take into account when prescribing tablets.
Rules for taking Aspirin
The drug should be taken 3 times a day with time intervals between doses of 4-8 hours. In case of problems with the liver or kidneys, it is advisable to increase the interval between doses or reduce the dosage. The maximum single dose of the drug is 1000 mg, the daily dose is 3000 mg.
The duration of therapy for the purpose of relieving fever should be no more than 3 days, for pain relief – no more than a week.
The tablets are taken orally after meals (this helps reduce the negative effects of the medicine on the gastric mucosa), with plenty of water. To further reduce the aggressive effect of Aspirin on the gastric mucosa, you can take the tablets with milk or jelly, which envelop the mucous membrane and thereby protect it.
Before you start taking the drug, you must carefully read the instructions.
How to take aspirin to thin your blood correctly?
Acetylsalicylic acid is far from being a harmless drug, as it might seem at first glance. Therefore, it is not advisable to take pills on your own, especially for a long time. The exact regimen and dosage are prescribed by the doctor, who assesses the expected benefits and harms of use.
For preventive purposes, for heart disease and varicose veins, tablets should be taken regularly in low and medium doses, 75-150 mg, once a day. The daily dose is usually 100 mg, the maximum is 3 g.
According to the instructions, you should not take the medicine on an empty stomach. It is best to take the tablet 30 minutes after eating. Take it with a glass of water or milk, which has an alkaline pH and neutralizes the acidic environment of hydrochloric acid in the stomach.
It is best to take aspirin at night, since at night, when a person moves little, the risk of blood clots increases. Usually the course of treatment is long, at least 2-3 months. It should be remembered that only a doctor prescribes an individual regimen of use!
You should not drink alcohol during a course of treatment with aspirin, this can cause side effects and damage to internal organs!
The drug is also used for emergency treatment of myocardial infarction. To do this, the patient is quickly given a simple aspirin tablet to chew. It helps reduce the effects of the disease.
Contraindications for use
You should not take Aspirin if:
- Hypersensitivity to the main active ingredient, additional substances and other types of NSAIDs that can provoke an allergic reaction.
- Chronic heart failure 3-4 functional class.
- Combinations of signs of bronchial asthma, ASA intolerance and polyposis of the nasal mucosa and paranasal sinuses - the aspirin triad.
- Renal failure with creatinine Cl level less than 30 ml/min.
- Salicylate-induced bronchial asthma.
- Liver failure.
- Use of methotrexate in an amount of 15 mg per week.
- Age less than 15 years (in this case, there is a possibility of Reye's syndrome).
- Hemorrhagic diathesis.
- Breastfeeding.
- Acute stage of erosive and ulcerative processes in the gastrointestinal tract, the occurrence of bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract.
- First and third trimester of pregnancy.
Does Aspirin help with headaches?
Aspirin may be useful for severe headaches due to its powerful analgesic effect. Elimination of pain is due to blocking the synthesis of prostaglandins and suppressing the activity of pain receptors. Thus, the production of substances responsible for the occurrence of swelling, pain and inflammation stops.
According to the instructions for the drug, Aspirin can be prescribed to relieve headaches, in particular migraines. The drug can only be prescribed to patients over 15 years of age. The dosage taken depends on the intensity of the headache and is no more than 3 g per day. In older people, the maximum dose is reduced to 2 g.
Possible side effects of Aspirin
Below are the possible side effects of Aspirin on the body.
From the side of digestion
From the digestive side, the following may appear:
- increased activity of liver transaminases;
- ulcerative lesions on the mucous membranes of the digestive tract up to the appearance of a perforated ulcer;
- gastrointestinal hemorrhage;
- abdominal pain, nausea, heartburn, vomiting;
From the urinary system
Functional renal changes, as well as acute renal failure, may occur in the urinary system.
From the circulatory system
Inhibition of thromboxane A2 by acetylsalicylic acid negatively affects the mechanism of platelet aggregation, which leads to an increase in the amount of bleeding when using the drug. Hemorrhages often occur during or after surgical interventions, contributing to the emergence of surgical complications. Bleeding can occur in the genitourinary tract, mouth, nose, subcutaneous fat, and gastrointestinal tract.
The most dangerous thing is cerebral hemorrhage, especially with the simultaneous use of anticoagulants by patients suffering from arterial hypertension.
When bleeding, signs of posthemorrhagic iron deficiency anemia are observed:
- my head is spinning
- paler skin
- asthenia occurs.
Bleeding can be both open and latent, so it is better that during the period of use of the medication, doctors carry out physical and laboratory monitoring of the patient’s condition.
From the central nervous system
Excessive use of Aspirin can lead to headaches, hearing loss, ringing in the ears and dizziness.
Allergic reactions
When taking Aspirin, allergic reactions may occur, namely:
- bronchospasm (asthmatic syndrome);
- anaphylactic shock;
- rash on the skin, itching, Quincke's edema, urticaria;
- swelling of the nasal mucosa;
- cardiorespiratory distress syndrome, characterized by pulmonary inflammation with diffuse infiltration of lung tissue and a sudden decrease in blood oxygen levels.
Aspirin: instructions for use
| pharmachologic effect | Aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid) belongs to the group of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). This medicine has analgesic, antipyretic and anti-inflammatory effects. It inhibits cyclooxygenase enzymes involved in the synthesis of protaglandins. Blocks the synthesis of thromboxane A2 in platelets and thus prevents these blood cells from sticking together. Many people take low-dose aspirin every day to prevent myocardial infarction and ischemic stroke. For pain, fever and symptoms of inflammation, this remedy is prescribed to be taken in increased doses for no longer than several days in a row. |
| Indications for use | The main use of aspirin in our time is to thin the blood and prevent cardiovascular diseases. Other indications: increased body temperature during colds and other infectious inflammatory diseases, inflammation and pain of various origins. People take acetylsalicylic acid voluntarily and as prescribed by a doctor for headaches and toothaches, PMS in women, and rheumatoid arthritis. This medicine can only be used by adults and adolescents over 15 years of age unless there are contraindications. It is not suitable for children! |
Read more:
- Aspirin for headaches
- Aspirin for blood thinning
- Aspirin for fever
- Aspirin and alcohol
| Contraindications | Children's age - up to 15-16 years. Only adults can be treated with aspirin unless they have the contraindications listed below. Bleeding or ulcer in the gastrointestinal tract, damage to the gastric mucosa. Previous hemorrhagic stroke. Hypersensitivity, allergy to aspirin and other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Bronchial asthma, especially if taking aspirin is known to worsen its course. Increased tendency to bleed due to vitamin K deficiency, hemophilia, anemia or other causes. Severe renal or liver failure. Alcohol abuse, alcoholism. |
| special instructions | If a patient has gout or high levels of uric acid in the blood, taking aspirin may make things worse. If the patient has arterial hypertension that cannot be controlled, then the administration of acetylsalicylic acid may increase the risk of hemorrhagic stroke. If you are planning surgery, tell the surgeon in advance that you are taking aspirin. Most likely, you will need to stop taking it several days before surgery. Aspirin is a medicine that thins the blood. Other drugs that have the same effect are antiplatelet agents, anticoagulants, thrombolytics. Together with them, acetylsalicylic acid can be taken only as prescribed by a doctor, but not on your own initiative. |
| Dosage | Aspirin can only be taken by adults and adolescents over 15-16 years of age. Children are not allowed. To prevent myocardial infarction, this medicine is prescribed 75-162 mg once a day. For the prevention of ischemic stroke - 75-100 mg per day. For fever and pain of various origins - 300-650 mg every 4-6 hours until the symptoms go away. Do not take more than 1000 mg at a time. The maximum daily dose is 3000-4000 mg. If a myocardial infarction is suspected, the patient should immediately take 160-325 mg of aspirin, and the tablets should be chewed. Acetylsalicylic acid is taken orally, during or after meals, with plenty of water. Some tablets can be split and chewed, others cannot. Read more in the instructions for use of your drug. If the fever does not go away within 3 days, and the pain does not go away within 7 days, consult a doctor and stop self-medication. |
Read about medications to prevent thrombosis, heart attack and stroke:
- Cardiomagnyl
- Thrombo ACC
- Aspirin Cardio
- Acecardole
| Side effects | Gastrointestinal tract: abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, heartburn. Aspirin rarely causes gastrointestinal bleeding and erosive and ulcerative lesions. Their symptoms are severe abdominal pain, bloody, coffee-colored vomiting, and darkened stools. If you notice the signs listed above, consult a doctor immediately. Central nervous system - dizziness and tinnitus, usually in case of overdose. Hematopoietic system - increased risk of bleeding during surgical operations, household injuries, nosebleeds. Allergic reactions - urticaria, anaphylactic reactions, bronchospasm, Quincke's edema. Read more about the side effects of aspirin here. |
| Pregnancy and breastfeeding | As a general rule, aspirin should not be taken during pregnancy, especially in the early and third trimester. In rare cases, doctors prescribe acetylsalicylic acid to pregnant women, despite the possible side effects. Read more in the article “Aspirin during pregnancy and breastfeeding“. This medication partially passes into breast milk if taken by a nursing mother. Talk to your doctor if you are pregnant, nursing, or planning a pregnancy. |
| Interaction with other drugs | Acetylsalicylic acid preparations can negatively interact with many medications. Before you are prescribed aspirin, tell your doctor about all the medications, dietary supplements, and herbs you take. It is not recommended to combine ibuprofen, ketorolac, naproxen and other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs with drugs. Aspirin enhances the effect of methotrexate, digoxin, insulin and drugs that lower blood sugar. Weakens the effect of many tablets for blood pressure and gout. Increases the concentration of lithium drugs in the blood. Concomitant use of acetylsalicylic acid with other blood thinning medications is possible, but increases the risk of bleeding and hemorrhagic stroke. Discuss with your doctor. |
| Overdose | Accidental or intentional overdose of aspirin tablets can have serious consequences, especially for children and the elderly. Symptoms: dizziness, tinnitus, hearing loss, increased sweating, nausea and vomiting, headache, confusion, hyperventilation. Urgent hospitalization is required. In the hospital's intensive care unit, doctors will begin detoxification measures. Gastric lavage and taking activated carbon can be done at home, before the emergency team arrives. |
| Storage conditions and periods | Store at room temperature 15-30 degrees Celsius, in a dry and dark place. Do not store at temperatures of 40 degrees Celsius or higher. Do not store in the bathroom. Keep medications away from children and pets. Different aspirin preparations have different storage conditions and shelf life. For more details, read the instructions for use of the medicine that was prescribed to you. Do not take acetylsalicylic acid tablets if they have spoiled - their color has changed, or a vinegar smell has appeared. |
Watch the video - an excerpt from the TV show “Living Healthy.” Find out how to take aspirin for fever, headaches, joint problems, to prevent heart attack, stroke and even cancer. The presenter is the famous doctor Elena Malysheva.
Overdose
Salicylate poisoning, depending on the dose and duration of use of the drug, can be acute or chronic. Acute intoxication occurs with a single dose of a toxic dose of 100 mg per 1 kg of body weight.
- The acute form is characterized by the occurrence of metabolic acidosis, that is, a violation of the acid-base state.
- A chronic form of salicylate poisoning occurs when a dose of 100 mg per 1 kg of body weight per day is consumed for 2 or more days.
Symptoms indicate primary damage to the nervous and digestive systems: dizziness, vomiting, nausea, ringing in the ears, hearing loss, and confusion. These signs of chronic intoxication disappear after stopping the use of Aspirin.
Severe poisoning is characterized by the appearance of ketosis, elevated body temperature, metabolic acidosis, respiratory alkalosis, hypoglycemia, respiratory failure, cardiogenic shock, and coma. In this case, the patient must be treated in a hospital setting using forced diuresis with alkaline solutions, lavage, dehydration, large doses of activated charcoal and symptomatic therapy.
Composition of Aspirin tablets
On sale there are effervescent and classic Aspirin tablets, as well as with the prefix “cardio”. All of them contain acetylsalicylic acid as an active component. The composition is indicated in the table:
| Factors | Classic Aspirin | Effervescent tablets |
| Concentration of acetylsalicylic acid, mg per 1 tablet | 100 | 500 |
| Description | White round | Biconvex, white, with a “cross” imprint and the inscription “ASPIRIN 0.5” |
| Auxiliary elements of the composition | No | Microcrystalline cellulose, corn starch |
| Format | 10 pcs. in a blister pack with instructions for use | 10 pcs. in blister, from 1 to 10 blisters per package |
Interaction with other drugs
Aspirin enhances the effect of the following drugs:
- Heparin and indirect anticoagulants (the antiplatelet effect of ASA, together with the weakening of coagulation by heparin, increases the likelihood of bleeding);
- Methotrexate (ASA damages its binding to proteins by reducing renal clearance, thereby causing hematopoietic side effects);
- Insulin and sulfonylurea derivatives: gliclazide, tolbutamide, glibenclamide, chlorpropamide (the hypoglycemic effect of these drugs is enhanced by displacing them from their bonds with proteins and the hypoglycemic effect of ASA).
- Other NSAIDs (the use of Aspirin with other NSAIDs increases the ulcerogenicity of both groups due to the unidirectionality of their effects).
Thus, it is necessary to reduce the dosage of these medications when taken simultaneously with Aspirin.
Aspirin, on the contrary, does not have an enhancing effect on some groups of drugs. A suppressive effect. Thus, Aspirin weakens the effect of the following drugs:
- Diuretics;
- Systemic glucocorticosteroids (except hydrocortisone);
- Uricosuric medications;
- Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors.
What can replace aspirin drugs?
Often people cannot tolerate aspirin-containing medications due to underlying medical conditions, such as asthma or stomach ulcers. Then doctors prescribe antiplatelet agents with a different mechanism of action and select medicinal herbs.
It should be remembered that each antiplatelet agent reduces platelet aggregation and can cause any bleeding, for example, from the nose.
Medications
Possible substitutes:
| Active substance | Representatives |
| Clopidogrel | "Agregal", "Lopirel", "Plavix". |
| Dipyridamole | "Dipyridamole", "Curantil", "Drisentin". |
| Ticlopidine | “Aklotin”, “Vazotik”, “Tiklid”. |
| Cilostazol | "Krurovit", "Plestazol". |
| Iloprost | "Ventavis", "Ilomedin". |
Well-known representatives of the group of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, to which acetylsalicylic acid belongs, are paracetamol, analgin, ibuprofen.
All these drugs have anti-inflammatory, antipyretic, analgesic effects, but are not capable of thinning the blood, so their use as antiplatelet agents is not advisable.
Medicinal plants
From the history of the discovery of acetylsalicylic acid, it is known that it was first isolated from the bark of white willow. There are natural aspirin, which also helps thin the blood.
It is found in the following plants:
- Willow bark.
- Horse chestnut.
- Ginkgo biloba.
- Sweet clover.
- Tribulus grass.
- Meadowsweet.
- Peony.
- Red clover.
- Chicory.
- Hawthorn.
- Sagebrush.
- Raspberry leaf.
To make a medicine, you need to collect plants, dry them and prepare a decoction or tincture.
special instructions
During pregnancy and breastfeeding
ASA helps to inhibit the formation of prostaglandins, which has a negative impact on the health of a pregnant woman.
- In the first trimester, the use of pain relief Aspirin in an amount of more than 300 mg per day can lead to congenital pathologies in the unborn child.
- In the second trimester, the use of Aspirin is allowed, but only if the benefits justify the possible complications.
- In the third trimester , the use of Aspirin is prohibited, as there is a possibility of intracranial hemorrhage in the fetus, suppression of labor, premature closure of the ductus arteriosus, and bleeding in the mother.
Taking salicylates during breastfeeding does not cause harm to the baby only if there is an occasional episode of ASA use. Long-term treatment with Aspirin is prohibited, since the drug passes into breast milk.
Under 15 years of age
- In case of viral diseases, children under the age of 15 years are prohibited from taking medications containing ASA, as it affects the brain and liver, which are damaged due to exposure to viruses. And this can provoke Reye's syndrome.
For liver problems
- The medicine is prescribed with strict dosage control and only in case of liver failure below class B on the Child-Pugh scale.
For kidney problems
- The medication is excreted from the body by the kidneys, so its prescription depends on the severity of problems in the functioning of the kidneys. Consuming large amounts of Aspirin can lead to acute renal failure.
Effect on driving a car and complex mechanisms
- As stated in the instructions, taking Aspirin does not have any effect on driving or operating machinery that requires special concentration.
Aspirin and alcohol
- You should not combine Aspirin and alcohol, as this increases the risk of stomach bleeding and allergic reactions.
Is it possible to take Aspirin during pregnancy?
The benefits of Aspirin for women are undeniable. The medicine is prescribed for various pathological conditions. Many pregnant women have a question about whether it is possible to take Acetylsalicylic acid during pregnancy. The possibility of admission depends on the gestational age.
The use of the product is prohibited in the 1st and 3rd trimesters of pregnancy. The harm is caused by an increased risk of birth defects in the child and weakness of labor. You can use tablets in the second trimester only after your doctor's permission.
Aspirin analogues
Below are the main analogues of Aspirin:
- Aspicor is a medicine containing 100 mg of ASA in one tablet, which dissolves under the influence of intestinal enzymes. The enteric coating reduces the ulcerogenic effect of the drug on the gastric mucosa. However, due to the presence of additional components in Aspicor, such as aerosil, lactose monohydrate, croscarmellose sodium, stearic acid and MCC, the likelihood of allergies increases. Other side effects are less pronounced, since the amount of active substance is 5 times less.
- Aspirin Cardio is a medicine containing 100 or 300 mg of ASA. The main indication for its use is the prevention of vascular complications in diabetes mellitus, hyperlipidemia, and arterial hypertension. In the case of varicose veins of the extremities, the medication helps normalize vascular tone, improve lymph outflow and prevent blood thickening.
- Acecardol is a medicine that contains ASA in a dosage of 300 mg. It is used to prevent heart attacks (primary and recurrent), arterial thromboembolism, angina pectoris, and deep vein thrombosis of the extremities. The drug has indications for use, side effects and contraindications similar to Aspirin Cardio.
Indications for use of the medicinal product
For what deviations is Aspirin C (effervescent tablets) prescribed? The instructions attached to this drug contain a list of the following indications:
- prevention (secondary) of myocardial infarction;
- relief of migraine attack (acute);
- rheumatic diseases;
- prevention of myocardial infarction in patients with unstable angina;
- treatment and prevention of ischemic transient cerebrovascular accidents;
- pain syndromes of moderate and weak intensity of various origins (including inflammatory);
- prevention of embolism and thrombosis;
- fever in infectious and inflammatory diseases.
Reviews about the drug
Marina Sergeevna, 45 years old, Ekaterinburg
. I always have Aspirin at home. It is able to reduce the temperature within an hour, and the price of the drug, unlike other antipyretics, is significantly less. By the way, Aspirin is good for helping your spouse and son-in-law with a hangover.
Ivan L., 43 years old, Minsk
. I fight high fever only with the help of these tablets. Aspirin is noticeably more effective than expensive fever medications. I rarely use a whole tablet; usually half a tablet is enough for me. It happens that your blood pressure drops a little after taking Aspirin. The huge advantage of the medicine is its low cost and constant availability in pharmacies. In addition, I once took Aspirin during a hangover, which quickly got rid of my headache.
Anna A, 23 years old, Krasnoyarsk
. Does Aspirin help? Definitely yes. And not only for high fever, toothache and menstrual pain. More recently, I started using an aspirin face mask, which helps fight various types of inflammation on the face. The recipe is simple: grind 3 Aspirin tablets into powder and add one tablespoon of water and honey, mix thoroughly and apply the product to the face for 15-20 minutes, then rinse with warm water.
There are contraindications. Specialist consultation required
© 2019 – 2019, Bunata Dmitry. All rights reserved.
Precautionary measures
The occurrence of side effects can be avoided if the dosage is calculated correctly and the rules of administration are followed. Always remember that any drug should be used as prescribed by a doctor, or under his supervision. Below we provide a list of contraindications to the use of aspirin:
- Pregnant women are contraindicated from taking aspirin, especially in the last 3 months of pregnancy, as the drug can cause health problems for the unborn child;
- Elderly people should take aspirin with caution, as it can cause stomach and intestinal problems;
- You should not combine aspirin with alcohol and tobacco, as this may increase the risk of stomach bleeding.
Aspirin has a wide spectrum of action, and is a salvation from pain, cramps, and colds, but do not forget about its side effects. Always use aspirin only in recommended doses, and preferably only after consulting a doctor, and then unpleasant consequences will bypass you!
Blood thickening and drug intake
Blood is one of the main substances in the body, its components and quality characteristics directly affect human health. One of the parameters that determines the proper functioning of the circulatory system is blood viscosity.
Mechanism of blood thickening
This term refers to the level of blood resistance to its own movement, that is, its internal friction, or fluidity. Normally, this figure is 4-5 mPa-s (millipascal seconds). Changing it is not so easy, but if this happens, it means that we are talking about a serious disruption of the cardiovascular system.
Causes
Blood thickening can occur under the following conditions:
- problems with the liver, pancreas;
- the presence of infectious processes;
- chronic dehydration;
- unhealthy lifestyle (abuse of alcohol, smoking, unhealthy diet, stress);
- unfavorable environmental conditions;
- pregnancy;
- taking hormonal medications and diuretics.
It is important to remember that blood viscosity cannot be determined visually. To do this, you need to take the appropriate test (D-dimer).
If, however, an increase in this indicator is confirmed, most often this indicates a change in the cell membranes of red blood cells and platelets, which leads to “gluing” of cells. To return your blood to normal consistency, you need to balance your diet and adhere to the drinking regime.
But these measures are not always enough, so doctors prescribe ASA, which, even in small doses, prevents platelets from settling on the walls of the endothelium and the formation of blood clots that close the lumen of blood vessels.
Mechanism of action of a blood thinner
Speaking from a scientific point of view, the question of whether Aspirin thins the blood or not, paradoxically, must be answered in the negative. In fact, the drug does not directly affect blood consistency, but blocks the formation of the vasoconstrictor thromboxane A2 (an oxidized derivative of fatty acids), which is the main cause of platelet aggregation (that is, the ability to unite into conglomerates) and the appearance of blood clots.
The formation of thromboxane A2 ceases throughout the life of the platelet (7-10 days), and within 5-6 days of taking ASA, the platelet component of hemostasis (the ability of blood to circulate through the vascular bed) is restored. In addition, ASA enhances fibrinolysis (dissolution of blood clots and clots by splitting fibrin strands) and reduces blood clotting.
Site of action of aspirin
ASA also acts at the level of endothelial cells, inhibiting the metabolite of arachidonic acid - prostacyclin (which naturally suppresses platelet aggregation), but much weaker and for less duration than in the case of thromboxane A2, especially when taken in low doses. This fact is decisive when choosing a dose in antiplatelet therapy of ASA.
Drug overdose
During treatment, you must strictly monitor compliance with the dose prescribed by the doctor. If it is exceeded, a dangerous condition can develop, including coma. Therefore, in case of accidental overdose, the patient requires hospitalization. He undergoes gastric lavage, infusion therapy, hemodialysis, and diuresis. This is necessary to prevent the dangerous consequences of acetylsalicylic acid poisoning. This condition can be determined by the following symptoms:
- nausea, vomiting;
- tinnitus, hearing loss;
- dizziness, confusion;
- feverish condition;
- ketoacidosis, hypoglycemia;
- hyperventilation or respiratory alkalosis;
- cardiovascular and respiratory failure.
Risks
Why these particular periods? Everything is explained quite simply. In the first trimester of pregnancy, the formation of the baby's internal organs occurs, so aspirin can harm this process. In the third trimester, the risk is due to the fact that it thins the blood, as a result of which there may be a large loss of blood during childbirth.
Some doctors do not recommend that their patients take this drug, so they find a less dangerous replacement for it. Why? Because aspirin has an aggressive composition and has many side effects. Regarding the question: “The benefits of aspirin and harm, what is more?” - it's up to you to decide. We will present the reverse side of aspirin below.
In a shell or without?
Coated aspirin tablets are designed to pass through the stomach without disintegrating until they reach the intestines. The protective coating is thought to allow aspirin tablets to be gentler on the stomach lining, and may be useful for people with a history of gastritis or ulcers who take aspirin daily.
However, some researchers believe there is no evidence that coated aspirin reduces the risk of gastrointestinal bleeding. Moreover, there are a number of publications that such aspirin is less effective for preventing heart attacks.
From the history
This type of acid has been known for a very long time. How to get it? From willow bark. Its healing and analgesic properties were noticed by Hippocrates and medieval herbalists. But willow was a valuable raw material for light industry, so in the pharmaceutical field it was forgotten for several centuries.
Who should we thank for the re-introduction of aspirin? The triumphant return was organized by Napoleon during the blockade of Europe. The problem was that they stopped importing quinine, which was popular as an antipyretic. Then treatment with aspirin replaced it, only at that time it was known as acetylsalicylic acid. But the taste of this product left much to be desired, and it had an irritating effect on the mucous membranes.
How did the name “Aspirin” come about? It all happened in 1899. Felix Hofmann obtained a pure derivative of salicylic acid. Then a German company patented it and gave it the name “Aspirin”.
Why do pregnant women need aspirin?
If you are used to using this drug for headaches or fever, then it’s time to give it up. A good replacement would be paracetamol, which is safe during pregnancy.
However, some people simply need to take aspirin if, for example, blood clotting is increased. In these cases, the baby does not receive enough oxygen, which threatens miscarriage. If a woman is diagnosed with this problem or is at risk, then a quarter of an aspirin tablet is prescribed per day.
It is also prescribed for varicose veins, but there are also less dangerous drugs, for example, Curantil. If the situation is not critical, then instead of drug treatment it is recommended to use foods that thin the blood: cranberries, carrots, beets.
What type of drug thins the blood?
There are several types of medicine:
- Cardio;
- American;
- regular aspirin.
In most cases, aspirin Cardio is prescribed to elderly people as a preventive measure for the development of pathologies of the heart and blood vessels.
It must be taken with extreme caution and only with a doctor's prescription.
For younger people, with thickening and increased viscosity, it is better to use plain or American aspirin. However, you still shouldn’t get carried away with pills. It is better if the drinking regime is adjusted . In case of excessive loads, it is permissible to take the drug in small doses.
Analogs and price
The cost of the drug “Lospirin” is about 220 rubles for 30 tablets with a dosage of 75 mg. It is very difficult to find this medicine in the pharmacy chain, so it is advisable to replace it with analogues.
A pharmacist can offer a foreign drug “Aspirin Cardio”, which has the same main active ingredient. The price for 28 tablets with a dosage of 100 mg is 130-150 rubles.
An analogue of the drug is “Acecardin”, the cost of which is 200 rubles for 50 tablets with acetylsalicylic acid 75 mg.
Indications and restrictions
Before you start taking the medication, you need to understand what it helps with and for what conditions it is strictly forbidden to use it.
Indications for use and side effects
Main indications for taking Aspirin:
- Pain syndromes (mild or moderate).
- Colds (in adults and children over 15 years of age).
- Arthritis (rheumatoid).
- Inflammatory process in the myocardium.
- For the heart, ASA is used in the prevention of myocardial infarction.
- Preventing blood clots.
Contraindications
Like all medications, ASA has a list of contraindications that you should pay attention to first. Taking the medicine is prohibited under the following conditions:
bleeding (intestinal/stomach);
- “aspirin” asthma;
- hypersensitivity to the components of the drug;
- vitamin deficiency K;
- aortic dissection;
- hemophilia;
- gout.
During pregnancy, experts strongly do not recommend using drugs, especially in the third and first trimester. Its components can have a negative effect on the development of the fetus by penetrating the walls of the placenta.
The substance also passes into breast milk in moderate quantities. In this regard, it is better to stop taking pills during breastfeeding. If there is an urgent need for treatment, it is better to interrupt lactation.
With maximum caution and under the supervision of the attending physician, the use of drugs is allowed for:
- stomach ulcer;
- hyperuricemia;
- heart failure (decompensated).
Can it be given to children?
Since ASA is a universal and well-known remedy, the question often arises whether it can be taken in childhood. Most experts agree that this medication can be prescribed to adolescents over 15 years of age.
This is explained by the fact that at a young age children have not yet developed protective functions, and the use of ASA can provoke Reye's syndrome. Substances can cause brain intoxication, kidney or liver failure.
Reye's syndrome
In younger children, the drug may be prescribed only in extreme cases when other drugs cannot cope with the pathology. The course of treatment is carried out under the continuous supervision of a specialist.
Similar means
ASA has several medicinal properties, which has allowed it to become a universal, easy-to-use remedy. There are many substitutes for effervescent Aspirin:
- Aspirin Cardio is an antithrombotic drug based on ASA (100 mg per tablet). It is used as a preventive therapy for blood clots and embolisms, as well as during the recovery period after myocardial infarction and coronary artery disease. Rarely causes adverse reactions, since the concentration of salicylates is quite low.
Citramon is a combination drug that consists of acetylsalicylic acid, paracetamol and caffeine. Available in the form of white tablets, it is used as a pain reliever. It is used more often than other medications for mild headaches. Thanks to the caffeine in the composition, it has a stimulating effect on the nervous system and helps fight drowsiness.
- Acecardol - tablets contain 50, 100 and 300 mg of ASA. Prescribed for the prevention of blood clots, myocardial infarction, stroke and coronary artery disease. The drug is most often taken by patients with excess weight, bad habits, and people in the older age category, as they belong to a risk group for the development of cardiovascular diseases and the formation of blood clots.
Can I take aspirin before donating blood?
The process of donating blood is a very serious process. Almost all medications must be stopped before donating blood. You also need to adhere to a number of other recommendations.
- Indeed, doctors insist that before such a procedure, medications must be stopped. An exception can only be made in emergency cases, and then it takes into account what medications were taken previously.
- Experts recommend stopping taking aspirin and drotaverine approximately 5 days before donating blood.
- In principle, everything is clear without explanation. Since aspirin thins the blood and can also cause bleeding, taking it before such a procedure is simply dangerous.
- Do not neglect this recommendation, because this can lead to very negative consequences.
Therapeutic effect
The properties of the drug "Aspirin", from which it helps to relieve fever and pain, depend on the action of the active element. Acetylsalicylic acid has an antiplatelet effect, stops the functioning of enzymes that excite pain impulses, increase temperature, and provoke the inflammatory process. Thus, the drug eliminates the symptoms of pain, inflammation and heat, regardless of what area of the body they appear in.
Due to the lack of impact on pain centers, the medication is included in the group of non-narcotic painkillers. In small quantities, Aspirin exhibits antiplatelet properties. By reducing blood clotting, it prevents the formation of blood clots in blood vessels. When using large dosages, in addition to the antiplatelet properties, antipyretic, analgesic and anti-inflammatory properties are added, which are side effects in case of thrombosis.
Symptoms of drug overdose
Drug overdose most often occurs in older people. The main signs of the pathological condition are:
- Dizziness.
- Attacks of nausea and vomiting.
- Confusion.
- Noise in ears.
- Acute intoxication.
- Hemorrhage.
- Respiratory failure.
- Decreased hearing acuity.
- Hypoglycemia.
The toxic effect of the main substance develops as a result of long-term therapy or exceeding the recommended daily dosage. Moderate intoxication is observed during repeated administration of increased doses of the drug. If the concentration of salicylates in the blood plasma exceeds 300 mcg/ml, there is a possibility of acute intoxication, expressed in a change in the acid-base balance.
A patient with symptoms of overdose should be sent to a medical facility as soon as possible, where the body will be cleansed and the acid-base and electrolyte balance will be restored.
Drug interactions
The instructions for use of Aspirin indicate possible drug interactions between acetylsalicylic acid and other medications:
- The drug increases the toxic effect of Methotrexate, narcotic analgesics, other NSAIDs, and oral hypoglycemic agents.
- The drug increases the activity of sulfonamides and reduces the activity of antihypertensive drugs and diuretics (Furosemide).
- In combination with glucocorticosteroids, alcohol and drugs containing ethanol, the risk of bleeding and damage to the gastrointestinal mucosa increases.
- The drug increases the concentration of Digoxin, lithium preparations, barbiturates.
- Antacids with magnesium or aluminum hydroxide slow down the absorption of the medication.
Side effects
Lospirin, although absorbed in the intestines, can cause abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, heartburn, and bloating. Sometimes doctors observe inflammation of the gastrointestinal mucosa and ulcers in their patients.
During therapy, problems with the vascular system may arise, manifested in the form of bleeding, asthenia, pallor of the skin, and hypoperfusion.
Sometimes during treatment, patients’ blood counts change - thrombocytopenia, anemia, hemolysis begins, so it is important to monitor blood counts during treatment.
In some cases, allergic reactions are observed in the form of rash, itching, swelling, and rhinitis. Possible problems with the kidneys, nervous system, and hearing organs.
Cancer
The results of a study by American scientists revealed another beneficial property of acetylsalicylic acid. They describe how to take aspirin to prevent cancer. If you use this drug for a year, the disease does not progress, the tumor decreases, and the risk of metastases is significantly reduced.
There is one caveat: research on aspirin in this area is not yet sufficiently supported by evidence, so it cannot be included in anti-cancer therapy.
Cardiovascular diseases
Aspirin helps with a large number of diseases, not limited to influenza and acute respiratory infections. For example, let’s take cardiovascular diseases, which are very common in our country. Aspirin is often used to thin the blood. We will describe how to take it and how long the course of treatment lasts a little later.
The thing is that acetylsalicylic acid can thin the blood, thereby reducing the risk of blood clots, and as a result significantly reduces the risk of heart attacks and strokes. Note that a large dose of aspirin can also help with a heart attack that has already occurred. It reduces mortality by twenty-three percent.