Curettage of the uterus is a traumatic procedure for removing the endometrial layer using a loop or other surgical instruments. This procedure can be therapeutic or diagnostic; the first is usually more extensive. But regardless of the type and purpose of the procedure, the recovery period after such an intervention is quite long, and it must be carried out correctly so that no consequences or complications arise. How rehabilitation proceeds after cleaning (scraping) of the uterus will be discussed in this material.
Duration of the period
Strictly speaking, such an intervention is not considered a surgical operation, although in fact it is traumatic, and during it a large wound surface is formed. For example, after curettage to remove cysts or in case of endometriosis, almost the entire inner surface of the uterus becomes the wound surface, since the endometrium is removed from the entire surface.
For this reason, a fairly long recovery period after this procedure is recommended. It lasts, depending on the volume of intervention and the individual characteristics of the body, from three to four weeks.
Consequences
After the curettage procedure, almost the entire inner surface of the uterus is a fresh wound. It takes time for the endometrial layer to fully recover. This may take about a month.
Unpleasant consequences of such an operation may include:
- Pain and discomfort in the lower abdomen, radiating to the lumbar region;
- Feeling tired, drowsiness, loss of strength;
- Bleeding in the first few hours and spotting for 7-10 days.
If painful sensations cause you severe discomfort, you can take a painkiller tablet - ketanov, ibuprofen, etc. No additional treatment is required after cleansing.
Patients may experience delayed menstruation. If the cycle does not recover within several months, you should definitely consult a doctor. The help of a gynecologist may also be needed in case of prolonged spotting and increased body temperature.
Complications
The curettage procedure for hyperplasia is quite complex and dangerous. Incorrect medical procedures can lead to dangerous complications, namely:
- Uterine bleeding;
- The development of an inflammatory process in the patient’s genital organs;
- Significant accumulation of blood in the uterus.
If after surgery you notice a sharp increase in body temperature, deterioration in health, and the absence of any vaginal discharge, be sure to consult a doctor immediately.
Damage to healthy tissue by a gynecological instrument can lead to the formation of adhesions and scars, which in turn often causes the development of infertility.
Recommendations
Recovery after curettage has a number of normal characteristics. If there is a deviation from the norm, it is recommended to immediately consult a doctor. Normally, during this period the following may be present:
- Pain in the lower abdomen associated with contraction of the uterus after curettage;
- Minor bleeding;
- Feelings of nagging, aching pain in the back.
Such symptoms may be present only in the first few days. If it persists after a week, then you need to consult a doctor. You should also do this if there is heavy bleeding and excessively intense pain, or if you have a fever after cleaning the uterus.
During this period, it is necessary to reduce physical activity, which will have a good effect on your well-being. You cannot steam in the bathroom; hygiene must be maintained with the help of a shower. At the same time, it is better not to use chemical products for intimate hygiene, medications administered vaginally, tampons and douches. Avoid overheating - do not visit saunas, steam baths, solariums, the beach, do not swim in open reservoirs and pools, carefully observe hygiene.
Complications and treatment
In most cases, recovery after curettage of the uterine cavity is very quick. But in some cases, such treatment can have negative consequences. Complications of curettage include the following pathologies:
- bleeding;
- damage to the cervix;
- inflammation;
- intrauterine synechiae (adhesions).
Treatment is prescribed in each case individually, depending on the diagnosis and her general well-being. Recovery after curettage of a frozen pregnancy can take place in a few days, if there are no negative consequences in the form of abdominal pain or fever.
If the patient had hyperplasia, then further treatment depends entirely on the examination result. Hormone therapy is usually prescribed to restore the imbalanced hormonal balance. Endometrial hyperplasia is treated with combined oral contraceptives and a therapeutic intrauterine device. If frequent relapses occur, endometrial resection is recommended.
After gynecological surgery, some women experience heavy discharge, which is due to poor blood clotting. They occur as bleeding and can pose a threat to the patient’s health. Treatment includes taking medications to promote better blood clotting.
Every woman should undergo an ultrasound examination several months after treatment.
After cleaning, blood clots may accumulate in the uterine cavity, which increases the risk of developing infectious diseases. Treatment in this case consists of special injections and medications that relieve spasms and increase uterine contraction after curettage.
If gynecological surgery was performed during an exacerbation of inflammatory processes in the cervix or endometrium, the woman may experience unpleasant discharge. Endometritis forms, which is accompanied by high fever and abdominal pain. Treatment consists of a course of antibiotics.
Advice: You must take medications strictly as prescribed by your doctor. In this case, you must comply with all requirements and recommendations. This will help avoid complications and shorten the recovery period.
Drugs
Treatment after curettage of the uterine cavity involves taking medications. They are not aimed at directly promoting the growth of the endometrium, since this is not necessary - this is a natural process that occurs physiologically. The medications are taken in order to improve the patient’s condition and well-being, avoid relapses of the disease, and also prevent the development of severe consequences and complications, such as infection.
Antispasmodics
Antispasmodics after uterine curettage should be prescribed with caution. This is due to the fact that after this procedure the uterus contracts, pushing out excess endometrium and rejecting its remains. This is a normal physiologically determined process in this situation, but it causes quite severe pain in the lower abdomen, which persists in the first days after the intervention.
It can cause quite severe discomfort to the patient, but it is not advisable to relieve it with antispasmodics, because if the uterus does not contract, the healing process may be delayed. In severe conditions, No-shpa and other drugs are prescribed.
Antibiotics
Antibiotics are always prescribed after curettage of the uterine cavity. They are taken in a course of five to ten days, one or two tablets per day, depending on the selected drug. Depending on the patient’s condition, the course may begin on the day of cleaning or a day or two earlier.
Why are antibiotics prescribed at all? It is necessary to drink them in order to avoid any concomitant infection. The fact is that with this intervention not only a wound surface is formed, but also local immunity is greatly reduced. All this together significantly increases the likelihood of developing an infection in the uterus. To prevent this, strong broad-spectrum antibiotics are prescribed, such as Tsiprolet, Ceftriaxone, Amoxiclav, etc.
Herbs
How to restore the uterus after curettage? In general, it is able to recover on its own; this is a normal process, similar to the restoration of the endometrium after menstruation, when it is almost completely rejected and renewed. The growth of the mucous layer within the cycle and after curettage occurs under the influence of the hormone estrogen produced by the ovaries. The more it is, the more actively the endometrium grows.
Estrogen preparations can cause hormonal imbalance, but the use of herbs rich in phytoestrogens (plant analogues of estrogen) has a very beneficial effect. You can drink decoctions and infusions from boron uterus and red brush. Borovaya uterus after curettage is especially indicated, as it contains more phytoestrogens than other herbs.
Anti-inflammatory drugs
Anti-inflammatory drugs are not always prescribed, but in most cases they are still indicated. They are needed for approximately the same thing that antibiotics are needed for - to prevent the development of the inflammatory process on the wound surface. Drugs such as Nurofen and Ibuprofen are prescribed, which are taken 2-3 tablets per day for a week, starting from the day of the procedure. For the same period, Diclofenac can be prescribed by injection. In addition to the direct anti-inflammatory effect, they are also good pain relievers.
If a temperature appears after curettage, this may indicate the onset of an inflammatory process. Therefore, it is necessary to immediately consult a doctor.
Pregnancy
Pregnancy after curettage is possible, and often even more likely if the pathological endometrium was removed. Usually, menstruation begins around the third week after the procedure, since during this time the mucous layer of the uterus has time to recover. In this case, the menstrual cycle is completely normalized and becomes regular after about 4 months. In general, it is possible to plan conception within six months after the procedure, but before starting attempts, it is better to consult a doctor.
When is curettage performed?
Curettage is prescribed when the thickness of the endometrium reaches 15-16 mm. With such thickness, a diagnosis is made: hyperplasia, and measures are taken to study and treat this layer of the uterus. During the operation, the superficial (functional) layer is removed, and over time it grows back. This is possible thanks to the lower (basalt) layer of the endometrium, which remains intact.
In addition, curettage is carried out in the presence of polyps in order to find out the nature of the tissue and remove it. Thus, the procedure is performed for 2 purposes: to perform a diagnostic and surgical operation. A biopsy does not allow achieving an absolutely accurate answer if the area of the changed mucosa is large. And polyps cannot be controlled by biopsy, since you can take a piece of tissue from some and skip others of microscopic size.
Curettage is prescribed based on ultrasound. It is important that ultrasound is performed after menstruation. If an ultrasound was done before your period, you need to do it again after it, since the polyp may disappear on its own, and curettage will not be necessary.
Conclusion
Curettage is a traumatic but necessary procedure. You cannot avoid it if it was prescribed by a doctor, as it can have unpleasant health consequences. Provided that the recovery period is carried out correctly, complications after curettage are extremely unlikely, and this procedure only has a positive effect on health.
The period after curettage of the uterine cavity requires a special approach on the part of the doctor and responsible implementation of all recommendations on the part of the patient. The reproductive and physical capabilities of the female body are not limitless, therefore, an important task of the gynecologist who has performed uterine cleansing is considered to be complete, careful observation and provision of a protective regime.
In the period after cleansing the uterus, experts identify three main areas of work for complete rehabilitation:
- Prevention of infections.
- Restoration of the endometrium and menstrual cycle.
- Restoring physical and mental health.
To achieve these goals, gynecologists give recommendations in terms of taking antibacterial drugs, oral contraceptives, limiting physical activity, maintaining sexual rest and performing general strengthening measures.
How you feel after cleaning
Not everyone is able to quickly get into the usual rhythm of life, resume sports and exercise. Recovery time largely depends on the individual characteristics of the body.
After curettage, moderate abdominal pain, mild anesthesia-related dizziness, and moderate bleeding are usually noted.
Restoration of the uterus after curettage, both therapeutic and diagnostic, lasts one menstrual cycle, the whole body - from 2 to 6 months.
General health after curettage:
- Body temperature up to 37.2-37.3 is considered normal in the first 2-3 days.
- Moderate abdominal pain lasts up to 7 days.
- Slight dizziness is acceptable.
Discharge after cleaning procedure:
- The first few days there is discharge from the genital tract in the form of fresh blood, as during menstruation.
- A week after the curettage, the discharge takes on a sanguineous character: it becomes mucous and has a brown color due to the admixture of altered blood.
- The restoration ends with yellowish discharge, which gradually takes on a classic appearance: scanty, mucous discharge, which, when dried, takes on a yellowish tint.
- The normal duration of discharge during the recovery period is 10-12 days.
Normally, the first day of menstruation should occur after a period of time equal to the length of the cycle before cleaning (provided that it is regular).
What you should pay attention to and when you need to seek help from medical professionals if a woman has undergone curettage:
- Long-term (more than 20 days) bloody discharge.
- Scanty or heavy menstruation, spotting not associated with menstruation in the long term after curettage. These symptoms may indicate the development of cervical endometriosis or hormonal imbalance.
- Unpleasant smell of discharge.
- The discharge looks like “meat slop”.
- Increased discharge with light physical activity.
- Pain in the lower abdomen that lasts more than a week after curettage.
- An abrupt cessation of discharge after uterine curettage, which may indicate the accumulation of clots in the cavity of the organ (hematometer).
- Heavy bleeding.
- Increased body temperature.
- Loss of consciousness.
The above symptoms may indicate the development of endometritis.
That is why it is extremely important to be under the supervision of a doctor if there are even minimal signs of infectious complications.
How dangerous is the period after the procedure?
The uterine cavity after cleaning is an extensive wound surface. The lion's share of recommendations after curettage will be aimed at preventing microorganisms from entering the cavity of the operated organ. Gynecologists are aimed at preventing the development of inflammation of the reproductive organs and its chronicity.
Experts identify two groups of risk factors for the development of infectious complications after uterine curettage:
- Main group. This category includes women with a history of endometritis, chronic recurrent chlamydia, urea and mycoplasmosis, candidiasis, human papillomavirus infection, and persistent vaginal dysbiosis. In such patients, the likelihood of developing purulent-inflammatory diseases in the gynecological area during curettage is most likely. Patients are subject to the closest attention from doctors. This also includes emergency cases of curettage.
- Additional group. Patients who had uterine cleansing due to bleeding (endometrial hyperplasia), miscarriage, curettage of placenta or ovum remnants have a lower risk of infectious complications compared to the main group.
Women who have undergone diagnostic curettage have the lowest risk of developing infectious complications. Typically, this type of study is carried out in cases of infertility of unknown origin, in preparation for IVF, suspected polyps and subserous fibroids, and menstrual irregularities.
Factors that indirectly influence the period after curettage:
The above diseases have an indirect effect on the course of the recovery period of curettage, but their presence significantly reduces physical strength, the body's resistance to infections and slows down the healing processes of the wound surface in the uterus after curettage.
The causative factor of the disease is the opportunistic vaginal flora (staphylococci, streptococci, E. coli), as well as representatives of the pathogenic flora, if the patient before the operation had untreated sexually transmitted infections - chlamydia, ureaplasmosis, mycoplasmosis, gardnerellosis and others. That is why, in the period after therapeutic curettage, gynecologists recommend taking antibacterial drugs without fail, regardless of the infectious history. After diagnostic cleaning, you can limit yourself to taking sulfonamides.
According to statistics, the incidence of endometritis after uterine cleansing is 20%.
Purulent-inflammatory diseases of the genital area do not always appear after curettage due to non-compliance with the doctor’s recommendations. Nosocomial infection is still relevant today. A woman should choose modern clinics with rich obstetric and gynecological experience.
Poor quality cleaning can result from the penetration of endometrial cells into the cervical tissue, which leads to endometriosis.
Doctors' recommendations
- Sexual activity is excluded for 3 weeks after cleansing. The goal is to prevent infectious complications and bleeding. In addition to bacteria, semen contains prostaglandins that relax the uterus.
- It is recommended to use a condom for 6 months after curettage to prevent pregnancy.
- You should not take a bath or visit the pool for a month.
- It is not recommended to use tampons to absorb blood after curettage. This can provoke the development of inflammatory processes in the uterine cavity.
- After curettage, physical activity should be limited as much as possible.
Recommendations for taking antibiotics and other medications during curettage:
- Antibacterial medications must be taken strictly at regular intervals.
- Minimum duration of taking antimicrobial agents: 3 days for Azithromycin and 5 days for other drugs.
- The dosage of the drug should correspond to the patient’s weight.
- Drinking alcohol while taking antibiotics is not recommended.
- To relieve pain, you should take Ibuklin or Diclofenac.
- To prevent the formation of adhesions, enzyme preparations (Wobenzym, Longidaza) are usually prescribed.
If the recommendations of the gynecologist have not been announced, then the above advice must be followed.
Indications
With a disease called hyperplasia, the patient experiences accelerated pathological growth of the mucous surface of the inner layer of the uterus. This disease must be treated, since its progression has extremely negative consequences for a woman’s life. At a later stage, the disease can degenerate into oncology.
In modern medicine, there are several main types of this disease:
- Glandular hyperplasia - endometrial cells grow equally throughout the uterus.
- Focal hyperplasia - pathological areas of cells accumulate in separate places, forming slight thickenings.
- Combined hyperplasia of the glandular-cystic type is a simultaneous combination of the first and second types of the disease.
- Atypical hyperplasia is the most dangerous form of pathology. With this disease, cells in all layers of the uterus grow at an accelerated pace. There is a possibility of the disease degenerating into oncology.
Most women with this diagnosis ask themselves the question: “Is it necessary to do curettage for endometrial hyperplasia?” A gynecologist will be able to answer this question after carefully studying the diagnostic results. It all depends on the form and degree of development of the pathology.
The main indications for performing an instrumental procedure for cleaning the uterus can be considered:
- Prolonged bleeding during menstruation;
- Irregularities in the menstrual cycle (cycle period more than 40 days);
- Unsuccessful attempts to conceive a child within 6 months;
- Spotting bloody discharge from the vagina;
- Severe pain in the lower abdomen and lumbar region, accompanied by an increase in body temperature.
To determine the most effective method of treating endometrial hyperplasia, mandatory diagnostic curettage is performed. The physician must send the seized biomaterial for histological examination. This diagnosis will allow not only to accurately determine the type and form of the disease, but also to identify the presence of dangerous cancer cells.
Curettage of the uterine cavity is carried out not only to diagnose pathology, but also for therapeutic purposes. Indications for cleaning in case of endometrial hyperplasia include:
- Polyps on the cervix or in the uterine cavity;
- Chronic endometritis;
- Myoma;
- Difficult childbirth;
- Ectopic conception;
- Frozen fruit;
- Spontaneous incomplete miscarriage.
All of the above conditions and pathologies can be successfully cured using a fairly simple curettage procedure. However, the physician must take into account the fact that the patient may have contraindications to curettage.
It is not recommended to carry out such manipulations if an infectious or inflammatory disease develops in the body, and in particular in the woman’s genital organs. Instrumental intervention in this case can only aggravate the situation and will contribute to the spread of the inflammatory process to the uterus.
What is endometrial hyperplasia - causes and symptoms of the disease
The endometrium is the inner lining of the uterus, or more precisely, the mucous layer lining the uterine cavity. It creates the necessary conditions for implantation of the fertilized egg and its normal development.
In other words, the mucous membrane “holds” the fertilized egg inside the uterus, provides it with nutrition, and participates in the formation of the placenta.
The endometrium consists of supporting connective tissue (stroma), embedded uterine glands and numerous blood vessels.
All structures of the uterine mucosa develop and function under the “guidance” of sex hormones. In the first half of the menstrual cycle (in the phase of estrogen influence), the uterine glands and the functional layer of the endometrium grow.
In the second - under the influence of progesterone - this growth stops. The endometrial stroma swells and accumulates useful substances. The uterine glands begin to secrete a nutritious mucous secretion. Every month, the endometrium prepares to “accept,” “feed,” and store the fertilized egg in the uterus.
If pregnancy does not occur, the “overripe” functional layer of the endometrium is destroyed and rejected with menstrual blood.
In the next monthly cycle, according to the balanced influence of sex hormones, the uterine mucosa is restored from the basal “germ” plate.
Location of the uterine mucosa - endometrium
When there is a “breakdown” of the balanced hormonal influence, more precisely, estrogen, the uterine glands multiply beyond measure and the uterine mucosa thickens.
The cause of endometrial hyperplasia is a general or local hormonal imbalance: excessive influence of estrogen on the uterine mucosa with insufficient action of progesterone.
Dangerous consequences of hyperplasia:
- Uterine bleeding leading to anemia
- Infertility
- Malignancy
Signs and symptoms of endometrial hyperplasia:
- Spotting bloody discharge from the genitals, not associated with menstruation.
- Menstrual irregularities:
- amenorrhea,
- hyperpolymenorrhea,
- Irregular menstrual cycle.
Diagnostics
- Ultrasound – ultrasound examination of the uterus reveals signs of endometrial hyperplasia by increasing the size of the M-echo.
- Hysteroscopy with separate diagnostic curettage of the endometrium - confirms or refutes the ultrasound diagnosis.
- Histological examination of removed tissues establishes the final diagnosis.
An accurate diagnosis of endometrial hyperplasia and determination of its form (typical benign or atypical precancerous) can only be made by histological examination of tissue obtained by curettage of the uterine mucosa. Return to contents
Indications for curettage of the uterine mucosa
- Suspicion of endometrial hyperplasia based on ultrasound results:
- In reproductive age: the M-echo value during the first 7 days of the menstrual cycle is more than 7-8 mm.
- In postmenopause: the M-echo value is 6 mm or more.
- During childbearing age: uterine bleeding, spotting not associated with menstruation.
- In postmenopause: bloody discharge from the genitals of any nature.
- Sometimes uterine curettage is done to evaluate the effectiveness of hormonal treatment for endometrial hyperplasia or other uterine pathology.
The purpose of separate diagnostic curettage of the mucous membrane of the cervical canal and the body of the uterus is to assess the condition of the mucosa in various benign and/or malignant processes in the uterus.
Curettage of the walls of the uterine cavity for endometrial hyperplasia is both a diagnostic and therapeutic procedure.
Therapeutic effect of scraping:
- Removal of unhealthy endometrium along with possible pathological formations (glandular polyps, etc.)
- In some cases: emergency stop of uterine bleeding.
Curettage of the uterine mucosa or “cleaning” for endometrial hyperplasia should be carried out under the control of hysteroscopy. “Blind” (without visual control) curettage is not justified in the conditions of modern development of operative gynecology.
What is hysteroscopy?
Under the visual control of hysteroscopy, many therapeutic surgical procedures are performed, including curettage of the walls of the uterine cavity.
Hysteroscopy with curettage is performed:
- in the hospital,
- in a specialized operating room,
- under general, mainly intravenous anesthesia,
- without a single incision on the patient’s body: the hysteroscope device and surgical instruments are inserted into the uterine cavity through the cervical canal.
Hysteroscopy
Optimal timing of hysteroscopy with curettage for endometrial hyperplasia:
- If the rhythm of menstruation is maintained: 3-4 days before the expected menstruation.
- For oligomenorrhea with metrorrhagia: on the first day of the appearance of acyclic bleeding.
Contraindications to hysteroscopy with curettage for endometrial hyperplasia:
- Acute inflammatory process in the genitals.
- “Bad smear”: 3-4 degree of vaginal cleanliness.
- Acute general infectious disease.
- Severe non-gynecological pathology.
Return to contents
Preventive actions
The best prevention of endometritis is refusal to terminate pregnancy, pregnancy and natural childbirth. If it is impossible to continue the pregnancy, it is advisable to perform a medical abortion, which does not require curettage of the uterine cavity. In any case, if you need to have surgery, you must listen to the following doctor’s recommendations:
- a complete preliminary examination to identify all foci of infection followed by a course of treatment;
- performing the operation only in a specialized medical institution (gynecological department of a hospital);
- mandatory course of antibacterial therapy after the procedure;
- refusal of intimacy for a month after surgery;
- implementation of all necessary hygienic measures at all stages of the postoperative period with refusal to use tampons (in case of bloody discharge, pads must be used);
- refusal to visit the bathhouse and take hot baths (you can wash in the shower);
- the use of medications to rapidly contract the uterus;
- selection of rational contraception.
https://youtu.be/zZRYHY40YIY
It is impossible to completely eliminate the risk of endometritis formation after traumatic curettage of the uterine mucosa. A repeated operation performed after a short period of time is especially dangerous. It is necessary to minimize the danger by strictly following the advice of a specialist and avoiding surgical methods of terminating an unwanted pregnancy.
Preparation for hysteroscopy with endometrial curettage
What tests need to be taken:
- Vaginal smear “for flora”: examination of vaginal discharge to determine the degree of purity.
- PAP test: cervical smear for cytology.
- General urine analysis.
- Determination of blood group and Rh factor.
- Complete blood count with leukocyte formula.
- Blood chemistry:
- total protein,
- creatinine,
- urea,
- ALT, AST
- total bilirubin, direct, indirect,
- PTI
Methodology
How is curettage done for endometrial hyperplasia? There are three ways to carry out the intervention:
- Blind cleaning with a curette;
- curettage with hysteroscopy;
- separate diagnostic curettage.
All methods are considered surgical operations, so the woman must be prepared accordingly for them. In the first phase of the menstrual cycle, the size of the mucous layer is determined using ultrasound diagnostics. Then the patient undergoes a vaginal smear “for flora” and a PAP test (cytology) from the gynecologist.
If there are no contraindications, the doctor will set a date for the procedure. By this time, the woman must undergo a general and biochemical blood test, blood for syphilis, HIV markers, hepatitis, group affiliation and Rh factor. Be sure to undergo fluorography and electrocardiography, visit a general practitioner or cardiologist, and also talk with an anesthesiologist.
On the eve of the intervention, you should take a shower, carefully shave your external genitalia, and also remove all jewelry. The last meal and drink should be no later than 6 hours before anesthesia.
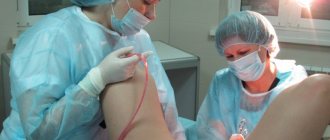
In modern gynecology, blind cleansing is rarely performed due to the high probability of trauma to the uterine cavity. Most often, curettage is performed under the supervision of a hysteroscope - a miniature video camera that allows you to assess the condition of the endometrium and monitor all movements of the doctor.
How is endometrial curettage performed?
Anesthesia: Intravenous anesthesia is preferred.
Duration of the operation: Total time of the entire procedure: approximately 20 minutes.
After registration in the hospital and the necessary preparation, the health worker invites the patient to the operating room.
The woman is placed on a gynecological chair for intrauterine operations.
The external genitalia and vagina are disinfected with an iodine-containing agent. Urine is drained by a catheter. Blood pressure is measured and pulse is counted.
Pain relief is given (short-term general intravenous anesthesia).
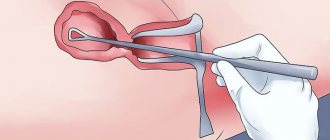
Uterine curette - a surgical instrument for curettage of the endometrium
The vagina is expanded with a gynecological “mirror”. The cervix is fixed with special instruments. The cervical canal is gradually “opened” by Hegar dilators. Then, using a uterine curette No. 1-2, curettage (curettage) of the surface of the cervical canal is performed.
Curettage of the cervical canal
The resulting scraping of the cervical mucosa is placed in a separate bottle with formaldehyde.
Then, a survey diagnostic hysteroscopy is performed using a hysteroscope device.
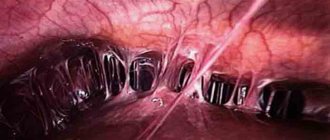
Hysteroscopy. Endometrial hyperplasia: thickened endometrium in the form of folds
After visual assessment of the mucous membranes of the uterus. Curette No. 4 is inserted into the uterine cavity and curettage of the uterine walls is performed: consistent, careful scraping of the functional layer of the endometrium from all internal surfaces of the uterus and the area of the uterine angles.
Endometrial scraping
The thoroughness of endometrial removal is assessed by hysteroscopy.
All tissue collected from the walls of the uterine body is placed in a second bottle with a preservative.
After completion of curettage and control hysteroscopy, the endoscopic device and surgical instruments are removed. The vagina is cleaned with a dry cotton swab to remove any remaining blood and tissue. The cervix is treated with iodine tincture. The vaginal specula are removed.
An ice pack is placed on the patient's lower abdomen. If necessary (in case of decreased uterine tone), an injection of oxytocin is given, which contracts the uterus.
Both containers with samples of the endocervix and endometrium are labeled and sent to the histology laboratory.
Features of scraping
The uterus is a hollow organ lined with endometrium. This fabric consists of two layers - functional and base. The first grows and develops, creating a favorable environment for the fertilized egg. If pregnancy does not occur, it is rejected and excreted from the body along with menstruation. Hyperplasia causes the proliferation of hyperplastic cells of the functional layer of the endometrium.
The most common cause of pathology is hormonal imbalance. If the disease is not treated, it will lead to serious complications such as infertility and cancer. An integrated approach to treatment can prevent such consequences. Doctors often use a proven treatment regimen - cleansing and a course of hormones. Endometrial hyperplasia goes away in most cases after curettage and treatment. If therapy does not help or blood tests reveal the presence of atypical cells, a radical method is used in gynecology - hysterectomy (removal of the uterus).
Procedure
Endometrial curettage is carried out today in one of two ways - curettage or hysteroscopy. The first option is used less and less often, because the operation is performed blindly, and there is a high risk of damage to healthy tissue. The procedure is performed under anesthesia. It lasts no more than half an hour. Discharge after curettage may last for 1-2 weeks.
Hysteroscopy is an innovative method. An optical device and instruments are inserted into the uterine cavity. The camera displays the image on the screen, which allows you to control the entire process.
After curettage of hyperplasia using a hysteroscope, the rehabilitation period requires much less time. The final stage of the operation is cauterization of the blood vessels, so the discharge after curettage in this way lasts only 3-7 days.
On what day of the cycle should I take a Pipelle biopsy?
Regardless of how the uterus is cleansed, before the procedure the patient will have to undergo a series of tests, limit sexual intercourse, and have an enema. You also need to take into account existing contraindications: it is forbidden to carry out cleaning in the presence of infections, exacerbation of chronic diseases, severe inflammatory processes.
Postoperative period
After the operation, the patient is under medical supervision in the hospital room for 2 hours. Then, after assessing her general condition and receiving individual recommendations from the attending surgeon, she can be sent home.
Curettage of the uterus - norms of the postoperative period
- Pain: unpleasant pulling sensations in the lower abdomen for the first hours after surgery. Minor pain is reminiscent of menstrual pain.
- Discharge: bloody, non-intense, spotting, bloody - can be observed for 5-10 days after surgery.
- Body temperature: in the first three days after surgery, an evening increase in body temperature to 37.3 degrees is considered normal.
- Antibacterial therapy: antibiotics, anti-inflammatory, painkillers after uterine curettage are prescribed by a doctor according to individual indications.
- Menstruation after surgery: occurs after 28-31 days (on time) or with a slight (week) delay.
When to see a doctor immediately
- Body temperature rose above 38 degrees.
- Profuse uterine bleeding began.
- Severe pain in the lower abdomen and/or discharge with an unpleasant odor appeared.
Security mode after scraping
- Driving: It is prohibited to drive any vehicle after applying anesthesia - for 24 hours.
- Physical activity: limit lifting weights of more than 3 kg for 1 month.
- Sexual activity is prohibited for 2-3 weeks.
- You cannot use sanitary tampons, douche, or visit a sauna, bathhouse, or swimming pool for 1 month.
- Replace bathing with a hygienic shower - within 2 weeks.
With good histology results, pregnancy after separate diagnostic curettage is allowed after 2-3 months. Return to contents
Endometrial scraping - consequences
Correctly performed diagnostic curettage of the uterine cavity for endometrial hyperplasia does not have any negative consequences.
This minor operation does not affect a woman’s fertility, and in some cases improves the reproductive prognosis.
But, like any operation, curettage and hysteroscopy for endometrial hyperplasia in rare cases does not exclude complications.
Possible complications of uterine curettage:
- Infectious and inflammatory processes of the endometrium and cervix.
- Exacerbation of chronic inflammatory diseases of the genital area.
- Mechanical trauma to the cervix, uterine perforation.
- Uterine bleeding.
- Hematometra.
- Surgical complications associated with anesthesia, etc.
- Formation of intrauterine adhesions.
If the patient follows all the recommendations of the attending physician, adequate preoperative preparation and appropriate qualifications of medical personnel, the risk of developing negative consequences of diagnostic uterine curettage is negligible.
Contraindications for surgery
It is strictly unacceptable to scrape from the uterine cavity if any inflammatory manifestations are detected in the area of the external genitalia. The doctor will not perform surgery if the following gynecological diseases are present:
- vulvovaginitis,
- colpitis,
- bartholinitis,
- cervicitis,
- erosion of the cervix with bright inflammatory manifestations,
- bacterial vaginosis.
It is unacceptable to perform the curettage procedure against the background of an infection of the internal genital organs:
- acute and subacute endometritis;
- chronic endometritis in the acute stage;
- salpingitis and oophoritis in the acute stage;
- adnexitis with typical symptoms of inflammation.
Contraindications for any type of surgical intervention are general infectious diseases with high fever, acute inflammation in the urinary system and gastrointestinal tract.
At the stage of preparation for the operation, the specialist will find out what the risk of complications is and what the consequences may be. Even if the danger is minor, it is advisable to postpone the procedure until infectious diseases are eliminated.
Treatment after curettage of endometrial hyperplasia
The tactics of patient management in each case are individual and depend on the form of hyperplasia, the age and reproductive plan of the patient, concomitant gynecological and somatic pathology.
Typical hyperplasia is most often treated with monophasic low-dose COCs or pure gestagens (Duphaston, Utrozhestan, Provera, etc.) for a course of 3 to 6 months.
The effectiveness of treatment is assessed every 3 months using ultrasound and/or pipell biopsy of the endometrium.
Hyperplasia with atypia requires continuous hormonal therapy for 6 months or more.
Hysteroscopy. Atypical endometrial hyperplasia or precancer
Atypical endometrial hyperplasia in menopause after curettage is treated radically: the uterus is removed. Read about this in detail in the article: Atypical endometrial hyperplasia
Glandular cystic endometrial hyperplasia - treatment after curettage
There is no uniform algorithm for the management of patients under the age of 48 years with typical glandular cystic hyperplasia.
In some cases, after curettage, dynamic observation with ultrasound control is carried out, because endometrial curettage in itself is a therapeutic procedure. In others, hormonal therapy is prescribed with monophasic COCs or gestagens.
International recommendations for the treatment of glandular cystic endometrial hyperplasia after curettage read in detail: Glandular cystic endometrial hyperplasia
The treatment tactics for hyperplasia during perimenopause are aimed at achieving a permanent cessation of menstruation using GnRH A drugs or injectable gestagens (Depo-Provera).
In older women suffering from obesity, hypertension, diabetes, glandular cystic endometrial hyperplasia (after curettage and histological confirmation) is treated surgically.