Otitis in children is an inflammatory disease that occurs due to the passage of viral microorganisms through the Eustachian tube. Other reasons include: stagnation of fluid in the middle ear, hypothermia, and other diseases that provoke inflammation.
Children are more susceptible to the disease because their Eustachian tube is horizontal. The course of the disease becomes more complicated with heavy discharge, allergic reactions and various infections (for example, the upper respiratory tract). In particularly severe cases, the eardrum may become deformed, resulting in complete hearing loss.
Symptoms
Otitis media in children manifests itself in the same way as in adults:
- Temperature rises
- Nasal and ear congestion occurs
- Lost appetite
- Ear canal hurts
- Itching and peeling
Symptoms of otitis media in children may be characteristic only of their age:
- Constant crying
- Vomiting and throwing back of head
- Constant attempts to touch the sore ear
- Diarrhea, diarrhea
- Crying caused by pain during feeding
- Purulent discharge (in acute forms). When they appear, the temperature usually decreases and pain symptoms disappear.
Diagnostics
Older children may tell their parents about ear pain. If the child is not yet 2 years old, he will indicate pain by crying and severe anxiety, firm refusal to eat, and, less often, vomiting and diarrhea. To determine otitis media, you need to press on the tragus of the ear. The child’s increased crying unmistakably confirms the expected diagnosis.
Any suspicion of the development of the disease requires urgent consultation with a pediatrician or otolaryngologist.
How does a specialist make a diagnosis? He has an ear mirror - a specific device, thanks to which the doctor sees all the changes that have occurred in the external auditory canal and eardrum.
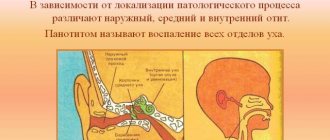
Types of otitis media in children
- External - occurs when the rules of cleaning the ear are violated; damage to the skin leads to infection. Itching, peeling, hearing loss, and redness appear. Cleaning a child's ears should be done with cotton swabs, carefully and not deeply.
- Medium – develops in children under one year of age with hypothermia. It is necessary to carefully wrap your baby before walks. Overheating and improper feeding are also not allowed. The inflammatory process can occur against the background of influenza diseases. That is why parents are not recommended to self-medicate. Pushing factors are allergies, adenoids and fluid stagnation in the nasal cavity.
- Internal - a dangerous type, leading to complete deafness. Otitis in children develops with prematurity, constant runny nose, against the background of a cold, and in advanced stages of the moderate form of the disease. The presence of tonsillitis doubles the possibility of this deviation.
Factors predisposing to the development of the inflammatory process
The main factors contributing to the occurrence of otitis media include:
- chronic diseases of the nasopharynx;
- frequent colds;
- improper hearing hygiene;
- mechanical damage to the ears;
- foreign body in the ear;
- penetration of moisture into the ears;
- allergens;
- anatomical features of the hearing aid.
In the absence of perforation of the eardrum, pathogenic flora penetrates into the middle ear through the nasopharynx; in extremely rare cases (blood poisoning and other serious diseases), the infection spreads through the circulatory system.
Course of the disease
There are many reasons that cause otitis media, depending on which its further course is determined. Feeding with artificial nutrition, mechanical damage, measles, scarlet fever - all this is very likely to lead to the development of otitis media.
Otitis in a child occurs quite quickly, and the temperature rises. When feeding, a pressure difference appears in the ear and mouth, which significantly increases the pain. Unilateral inflammation forces the child to roll over onto the affected ear to relieve unpleasant symptoms.
Acute forms lead to purulent discharge over a short period of time. The pus can deform or rupture the membrane, and the baby will lose hearing. If the first signs are detected, consult a doctor immediately.
Causes of the disease
While the child is small, his auditory tube is still short and wide, and, therefore, infectious agents can easily enter it from the nose, nasopharynx or oral cavity when coughing, sneezing or blowing the nose.
In newborns during childbirth, some amniotic fluid or the contents of their stomachs may enter the ear during regurgitation. Also, during the first year of life, a certain amount of embryonic myxoid tissue remains in the child’s tympanic cavity, which has not yet had time to transform into the mucous membrane. This tissue is an excellent breeding ground for the development of infection and symptoms of otitis media in children, which requires treatment. The causes of otitis in little ones can also be the predominantly horizontal position in which they are, as well as adenoids, prematurity, weakening of the body by various diseases or malnutrition, artificial feeding, sucking a pacifier, infectious diseases, acute respiratory infections, acute respiratory viral infections, fungal infections, allergies, heredity.
One of the most important factors that contributes to the occurrence of symptoms of otitis media in a child that requires treatment is insufficiently developed general and local immunity, unable to protect its owner from pathogenic microflora and inflammation.
Very often, acute otitis media in children, starting in one ear, spreads to the other, and bilateral acute otitis media appears in the child.
According to statistics, every second child in the first year of life had at least one episode of this disease in their anamnesis. Almost 90% of children under 3 years of age suffered from otitis media.
Repeated, that is, constantly recurring acute otitis occurs in 20% of children.
Symptoms of otitis media in a child
Typically, before the first symptoms of otitis media begin to appear, children first have a runny nose and/or cough that requires treatment.
Symptoms of inflammation of the middle ear in children of different age categories have some differences. Treatment for young and older children is also slightly different.
Symptoms of the disease in children under 1 year of age
Manifestations of the disease in newborns and children under one year of age:
- Frequent, causeless crying and sudden screams;
- Refusal to breastfeed is sometimes accompanied by consent to drink from a bottle, since sucking movements in this case cause less pain. Hunger and thirst cause an irritable state;
- The child rubs the sore side of his head or ear against his mother’s hand or pillow and makes pendulum-like movements with his head;
- In the first days of the disease, increased excitability and intermittent sleep are observed;
- After several days of illness, the child’s behavior changes dramatically - he is depressed, spends a lot of time sleeping;
- Symptoms of intoxication of the body and disturbances in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract appear - such as vomiting, loose stools;
- The child begins to lose weight;
- The temperature may not rise in the first days, but after 1-2 days of illness it rises to 39-40°C;
- After a few days, discharge from the ear appears;
When pressing on the ear, the child's response is unambiguous - from manifestations of noticeable anxiety to hysterical screaming in pain. Diagnosing otitis media in very young children is quite difficult, since there are diseases with similar symptoms.
Symptoms of the disease in children aged 2-3 years
Older children can more clearly indicate that they are bothered by ear pain. It is also easier for a doctor to differentiate otitis media in a child 2-3 years old from other diseases, since by this age, as a rule, there is already an anamnesis, the data of which the doctor can rely on during diagnosis.
Symptoms of otitis media in a child aged 3 years requiring treatment:
- The child clearly makes it clear that his ear hurts - he tugs, rubs, pulls his ear, points his finger at the painful area, complains in his “childish” language;
- The child becomes irritable, nervous, rude;
- Temperature above 38°C;
- Vomiting, diarrhea, lack of appetite, or inability to eat due to severe pain;
- Discharge from the ear may begin.
It is very important at the initial stage of the disease to separate the symptoms of otitis media from the manifestations of other diseases or problems that can cause discomfort or pain in the child’s ears.
For example, if small foreign objects get into the ear, the child does not have a fever or discharge. If water gets into the ear, it can cause not only discomfort, but temporary hearing loss on one or both sides, but there are no symptoms such as pain and fever. When wax plugs form, the child’s hearing quality decreases on one side. If blood, rather than pus, is released from the auricle, this cannot be a manifestation of otitis media. Bleeding from the ear occurs when there is a head injury or a scratch inside the ear canal.
Symptoms of acute otitis media in middle-aged and older children and adolescents usually appear suddenly, and the disease is accompanied by decreased hearing in one or both ears, and acute pain of varying intensity. The pain usually gets worse at night.
How and how to treat otitis in a child
Treatment of otitis media in children without the intervention of specialists is prohibited; the pain symptoms of a child can be reduced by freeing the nose from congestion and placing it in a warm environment.
Medicines are prescribed for acute forms of the disease. The antibiotic is taken orally or intravenously.
- The most common antibiotics prescribed to children: Cefuroxime, Amoxiclav.
- Nasal drops: Aquamaris, Salin, Nazivin (0.01%) and others.
- Temperature reduction is achieved by taking: children's Panadol, Calpol and Infanta.
Additionally, lamp heating is carried out - reflex, compresses and cotton swabs with medicine are applied. Hydrogen peroxide is sometimes used to clean pus.
In combination with physiotherapeutic procedures, recovery occurs faster. The main activities include:
- Ultraviolet irradiation
- Laser irradiation
- UHF
- Mud treatment
Compresses are applied only with the permission of a doctor (in the initial stages of development). To carry out the procedure, take a napkin and soak it in vodka or alcohol. Place special compress paper on a napkin, and cotton wool as a third layer, and apply it to your ear.
Drops - not intended for children under 1 year of age. For children, use cotton plugs soaked in the drug. Children older than one year are prescribed Otipax, the dosage is determined by the doctor. Otipax has analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects. The use of drops according to traditional methods is prohibited, as is the use of boric alcohol.
Pathology treatment methods
If otitis externa was diagnosed on time, the prognosis for recovery will be favorable and quick. It is important to show the child to the doctor in time, because the complexity of treatment directly depends on the neglect of the patient’s condition. The methods of prescribed therapy may consist of drug treatment and the use of physiotherapeutic procedures. If the prescribed treatment does not give the expected result, then surgical intervention is possible. Often, a puncture is performed with purulent otitis media, when the exudate does not come out.
Drug therapy
The range of drug treatment should perform several functions at once:
- relieve pain;
- normalize body temperature;
- relieve swelling;
- reduce the activity of pathogenic microorganisms;
- normalize hearing quality;
- increase the body's protective functions.
To reduce the pain of otitis externa, doctors prescribe painkillers. Such preparations can be in the form of drops, tablets, capsules or syrups. For children, it is acceptable to take Paracetamol, Ibuprofen, Neomycin in the form of drops. These medications will not only reduce pain, but also reduce high body temperature.
If otitis media is accompanied by discharge, the doctor must send the material for laboratory analysis to determine the causative agent. After this, antibiotics are added to treatment. Such drugs may be:
- Mycoheptin,
- Amphotericin B;
- Oxacillin;
- Ampicillin;
- Amphoglucamine (permissible for children over 12 years old), etc.
The type of antibiotic is prescribed depending on the type of pathogenic microorganism; in addition, the doctor takes into account the age, weight and individual characteristics of the child. It is prohibited to independently prescribe, cancel or increase the dosage of an antibiotic.
If otitis is caused by allergies, then antiallergic drugs are used. The choice of drug is carried out only after determining the pathogen:
- Suprastin;
- Telfast;
- Pipolfen;
- Tavegil.
To increase the protective function of the body, it is appropriate to take vitamin complexes and immunomodulators. Such drugs are especially relevant for viral external otitis.
Physiotherapeutic treatment
The range of physiotherapeutic services is also calculated for a certain form of external otitis; for example, with a purulent form, treatment with heating is strictly prohibited. The most common types of procedures are:
- UV therapy;
- UHF;
- Ear rinsing;
- Surgical opening of the boil.
UVR therapy involves the use of ultraviolet radiation, which fights microbes, relieves inflammation and increases local tissue immunity. The average course of treatment often consists of 10-12 procedures. UV therapy is carried out using a special device. The duration of one procedure is 10-15 minutes.
UHF is an ultra-high frequency current that helps relieve swelling, remove inflammation, accelerate the removal of purulent masses and mucus, and increase immunity. Such currents also help accelerate tissue regeneration inside the ear, which is especially important in the purulent form of the disease. The duration of one procedure is from 8 to 15 minutes. You can see a noticeable result after 5-10 procedures, because it all depends on the severity of the disease.
Ear rinsing is most often done with furatsilin. This substance is a cheap but effective antiseptic. Using a syringe without a needle, 1 ml is injected into the ear canal. After introducing the required volume, the patient tilts his head and furatsilin is poured out along with earwax, pus and mucus. This procedure is unacceptable for children under 5-7 years of age.
If external otitis is accompanied by the formation of a boil, then it is opened on the 4-5th day. This procedure is carried out to speed up the breakthrough of the abscess. Everything is carried out under extremely sterile conditions. After the procedure, the tissues are treated with an antiseptic and a sterile bandage is applied.
ethnoscience
Folk lovers of alternative medicine have found their own recipes for combating otitis externa. The simplest and most affordable treatment options:
- Turunda with chamomile infusion. Pour 20 g of dry chamomile with a glass of boiling water and leave for 20 minutes. Soak the turunda in the infusion and squeeze well so that liquid does not drip from it. Place in the ear canal for 20-30 minutes. Repeat 3 times during the day. The method is acceptable for treating children.
- Turunda with vegetable olive oil. It is enough to heat the oil in a water bath and cool it to human body temperature. Soak a cotton swab in oil and place it in the ear overnight.
- Rubbing the ear with camphor alcohol. The method is safe, but it is important to ensure that the drug does not get inside the ear. Simply wipe the ear canal with a sterile cotton swab dipped in camphor alcohol. It is important to carry out such cleaning 2-3 times a day.
It is important to always discuss the choice of a traditional treatment method with your doctor first.
Prevention of otitis in children
The main preventive measures are to prevent influenza diseases. The baby should receive regular breastfeeding. Watch your nose, avoid stagnation of fluid and prolonged runny nose. Timely vaccination against Haemophilus influenzae, and then against pneumococcus, is necessary.
If you have a fever, do not use compresses or other warming techniques, and do not clean the ear canal too thoroughly with cotton swabs. When blowing your child's nose, do not block both nostrils. After feeding, place the baby only horizontally, because When a baby burps, milk can enter the Eustachian tube.
Immediately after the temperature rises, it is necessary to take antipyretic medications, and not wait until the body copes with the illness on its own.
Prevention of acute otitis media
With the classic course of acute otitis and the provision of timely medical care to the child, a period of recovery soon begins with complete normalization of hearing abilities. If the factors provoking the disease are not eliminated, otitis may recur or become chronic.
Prevention of otitis requires strengthening the immune defense, eliminating injuries to the external auditory canal and eardrum from foreign objects (cotton swabs, hairpins, etc.), and teaching the child how to blow his nose correctly. Mandatory treatment of existing diseases of the ENT organs is also required, including surgery, if a small patient suffers from adenoids, nasal polyps and other problems.
You cannot treat a child yourself, since otitis media is a serious disease that can lead to hearing loss. At the first signs of trouble, the child should be examined by a pediatrician or otolaryngologist.
What is otitis media?
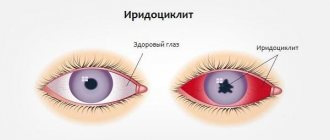
Otitis, including in children, is diagnosed if there is an inflammatory process of an acute or chronic nature in any part of the ear (or both ears - bilateral otitis). Otitis media can affect any part of the human ear and cause severe ear pain.
The main reason for the frequent occurrence of otitis (mainly inflammation of the middle ear) in childhood, doctors call the peculiarities of the anatomical structure of the child’s nasopharynx - the nasal cavity, ear and pharynx in children are reported. This is the reason for the infection from the nasopharynx to enter the ear cavity with the further development of otitis media.
The nature of the course of otitis - the duration of the inflammatory process, its manifestations, the prognosis for cure, including the presence or absence of complications, depends on the timeliness of seeing a doctor and starting treatment; the speed and strength of the immune response of the patient's body is also an important factor.
Among the pathogens that provoke the appearance and development of otitis media may be viruses, fungi and bacteria.
Folk remedies
Uncomplicated otitis media of moderate severity can be cured using the following traditional methods:
- A small amount of boric alcohol is applied to a clean gauze pad and applied to the affected area.
- Then a plastic bag is placed on top.
- The compress is secured with a scarf or bandage.
- After 15-30 minutes, the compress must be removed.
Aloe leaves are also good for treating inflammation. A thick piece of paper is cut lengthwise and applied to the sore ear on both sides. Everything is secured with adhesive tape.
For otitis of fungal etiology, wiping with soda solution is used. With the help of soda, an alkaline environment is created, which has a detrimental effect on pathogens. It should be noted that soda is not able to replace drug treatment.
Treatment of otitis media
What else is important if otitis media is being considered? Symptoms and treatment are the most important information. How can you cope with this type of disease?
- The patient needs complete rest. This is the only way to avoid increased pain and complications.
- Antibiotics. In this case, the doctor may prescribe the following drugs: Vilprafen, Amoxicycline.
- If your temperature rises, you can take an antipyretic such as Aspirn.
- In case of severe pain, the doctor may prescribe painkillers such as Ibuprofen and Paracetamol.
- Ear rinsing will be required to remove pus.
Sometimes, for otitis media, the doctor may prescribe surgical intervention. What procedures can we talk about in this case?
- Myringotomy. In this case, the patient's eardrum will be slightly incised.
- Tympanostomy. A tube will be installed in the patient's ear to drain the pus out.
- To prevent otitis media, the patient may have his adenoids and tonsils removed.
Only if the patient strictly follows the doctor’s instructions and carefully follows his recommendations, will it be possible to cope with the disease in the shortest possible time.
Causes
In medicine, otitis externa in a child is classified by origin as follows:
- infectious: caused by pathogenic microorganisms;
- non-infectious: provoked by others, including trauma, allergies.
The most common causative agents of external otitis in a child are:
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa;
- streptococci and staphylococci;
- fungi.
The main causes of the disease are:
- improper hygiene of the outer ear: lack of proper hygienic care for the ears;
- disturbances in the formation of earwax: if there is insufficient amount of it, the natural protective mechanisms of the ear are weakened, which leads to the appearance of pathogenic microorganisms. If there is an excess of it, plugs form, which increase the risk of infection;
- getting water or a foreign body into the ears: this leads to injury to the skin, causing irritation, swelling and, as a result, penetration of the infectious process;
- decreased immunity;
- the effect of cold wind;
- severe and chronic diseases;
- frequent infections;
- infectious diseases of neighboring organs (skin infections);
- taking medications that suppress the immune system (immunosuppressants, cytostatics);
- incorrectly prescribed antibiotics (in different forms);
- dermatological diseases.
The doctor will be able to determine the cause of the disease, having the research results in hand. Treatment of external otitis in a baby is usually carried out on an outpatient basis.
Improper hygiene of the outer ear.
The main thing in treatment
What should be said when it comes to a disease such as otitis media? Symptoms and treatment - this is what is important to focus on. First of all, I would like to say that if the first signs of this disease appear, you should immediately see a doctor. This is the only way to find out an accurate diagnosis and receive competent treatment. Otherwise, serious complications may arise, which are very difficult to cope with. If you self-medicate, the result may be similar.
Catarrhal otitis media
This type of otitis is considered an infectious disease that can provoke the development of a purulent form of inflammation in the ear. Therefore, you should know the main symptoms of catarrhal otitis in order to be able to quickly and professionally help your child:
- pain syndrome. It is always very strong, so children cry incessantly - this applies to those babies who do not yet know how to speak and express their emotions/feelings only by crying. Older children will simply point out the location of the pain;
- pain in teeth. Very often, a child aged 2 years or older complains of pain in the teeth with developing catarrhal otitis - this occurs due to irradiation of ear pain;
- hearing loss. It will be insignificant, but easily recognizable - the child turns on the TV louder, reacts poorly to speech addressed to him;
- general deterioration of condition. The child becomes lethargic, capricious, refuses to eat and walk;
- increase in body temperature. It may be critical or not - it all depends on the child’s immune system.
Types of treatment
Acute otitis media
Treatment is as follows:
- Nasal drops. This treatment is prescribed due to the anatomical features of a person, which provide a direct dependence of the nasal passages on the auricles. The use of nasal drops is designed to constrict blood vessels and eliminate a runny nose. The following drugs can be used: Nazivin;
- Rhinostop.
Nazivin
Rhinostop
- Ear drops. The purpose of ear drops is a direct impact on the source of inflammation; their purpose is to remove bacteria from the middle ear cavity. Such drops can also provide an analgesic effect. These drops can also be used in the treatment of newborns. Drops such as: Otipax;
- Otofa.
Otofa
- Warm treatments. This treatment involves the use of special warm compresses, which ensure blood flow to the compress site and accelerate the production of protective cells by the body.
- Antibiotics. Most often, this type of treatment is used in an advanced stage of the disease or in the presence of pus. Antibiotics are rarely prescribed to newborns. These medications should be taken under strict supervision; if you have any questions or concerns about the child’s condition, you should immediately contact your doctor. Drugs that may be prescribed include: Augmentin;
- Amoxiclav;
- Ceftriaxone;
- Amoxicillin
Ceftriaxone
Amoxiclav
Amoxicillin
Augmentin
Bilateral otitis media
Treatment tactics:
- Antipyretic. Taking this type of medication not only provides a decrease in temperature, but can also eliminate the child’s pain, which is aggravated by the general condition of the body in the form of weakness and body aches. Antipyretic treatment consists of taking medications that contain paracetamol: Paracetamol suspension;
- Panadol (suppositories or syrup);
- Efferalgan syrup.
Efferalgan for children
Panadol for children
Paracetamol for children
- Warming up. In the absence of purulent manifestations, one of the possible methods of treating this disease may be the use of a special blue lamp. Warming the ears is allowed only if there is no elevated body temperature.
- Compresses. One of the types of treatment for bilateral otitis is the use of special compresses. This treatment improves blood circulation in the area of inflammation, which causes the child’s body to produce protective cells. The most commonly used types of compresses are: alcohol, fir, camphor.
- Physiotherapy. If it is necessary to restore auditory function and reduce the resulting pressure in the Eustachian tube, doctors prescribe physiotherapy, which is manifested in the use of UHF, ultrasound and phonophoresis. Please note that to obtain lasting results you must undergo at least 5 procedures. A complete treatment consists of 10-14 physiotherapy procedures, which can be combined with each other.
- The use of ear drops is permissible for a period of 7 to 14 days, 3-4 times a day.
- Regarding nasal drops , you should consult your doctor.
Folk remedies
Folk remedies that can be used only after consultation with a doctor, and only in symbiosis with other types of treatment, include:
- Walnut oil. To do this, take an oil tincture (for at least 3 months) and lubricate the area outside the ear.
- Sagebrush. The tincture of wormwood in alcohol must be kept for at least 10 days, after which the liquid is injected into the child’s ear at night.
Surgical intervention
Surgical intervention is performed in rare cases; this type of operation is performed by an otolaryngologist.
There are two main types of operations used for otitis media:
- Removal of adenoids . In case of enlargement of the tonsils and adenoids, disturbances in the functioning of the child’s hearing system may be observed. This procedure is performed under local anesthesia and does not carry complications. In addition, it is a preventive measure for children prone to sore throat.
- Myringotomy. This action is performed only in the case of exudative otitis media. It involves the introduction of a special shunt made of titanium, which ensures normalization of the functioning of the hearing aid while restoring the function of fluid outflow.
Types of disease (otitis media)
Otitis media - symptoms in adults have already been discussed, I would also like to say that patients may have the following types of this disease:
- Purulent otitis media. In this case, the disease causes purulent inflammation that occurs in the eardrum. In this case, the ear may “leak”, that is, pus will come out, possibly with blood.
- Adhesive otitis media. Occurs when otitis media recurs too often. In this case, scars form in the eardrum, and a gradual decrease in hearing occurs. The situation can only be corrected through surgery.
Otitis externa: treatment
Consider the disease otitis externa: symptoms and treatment. If everything has been said about the signs of this subtype of the disease, now I would like to pay attention to curing this problem. So, first of all, it needs to be said that the doctor will open the boil surgically. All you need is local anesthesia. The procedure itself will take no more than 20 minutes. After this, the doctor will prescribe the following medications:
- Drops. This could include medications such as Normax and Candibiotic.
- Ointments. Such products as “Celestoderm-B”, “Levomekol”.
If the patient has diffuse inflammation, then rinsing the ear canal will be necessary. This can be done using disinfectant solutions. In this case, the swelling can be relieved with the help of conventional antihistamines: Suprastin, Claritin. You can cope with pain with the help of medications such as Nimesulide and Diclofenac.
Types of external otitis
There are also two main types of otitis externa:
- Limited. In this case, we are talking about the occurrence of a boil or inflammation of the hair follicle, which is located precisely in the ear canal. Painful sensations are concentrated in the area where the formation occurs. After a while, the abscess should open, after which all discomfort will go away.
- Diffuse. In this case, the inflammation affects the entire ear canal of the patient. The first and signal symptom of otitis in this case is an increase in temperature to 39 °C. Appetite also decreases and chills may appear. In this case, the auricle itself swells and turns red. Blisters may appear on the skin upon release.
What causes middle ear inflammation?
Inflammation in the middle ear does not appear out of the blue. Its root cause is a change in pressure in the tympanic cavity. Why can this happen? Firstly, with sudden changes in pressure on the eardrum - for example, when diving or when ascending (descending) during air travel. Secondly, and this is the most common reason, for various inflammatory diseases in the nose and pharynx, when the patency of the Eustachian tube is disrupted. In short, if we put aside all sorts of rare causes of otitis, the following will become clear: otitis is almost always not an independent disease at all and, again, is almost always a complication of inflammatory diseases of the nasopharynx, primarily acute respiratory viral infections (ARI). Every adult is well aware that with any colds in the nasopharynx, there is an increased formation of mucus. Repeated sniffing, especially active sniffing (no matter whether into or out of oneself) contributes to the entry of mucus into the lumen of the eustachian tube; In addition, viruses and bacteria that cause acute respiratory infections can directly cause inflammation of its (Eustachian tube) mucous membrane. Both of these factors, together or separately, cause a sufficiently long-term disruption of the ventilation of the tympanic cavity, and the pressure in it becomes negative. Under these conditions, the cells lining the tympanic cavity begin to secrete inflammatory fluid. Already at this stage, very specific symptoms of otitis media arise - pain in the ear(s), hearing impairment. Later (sometimes after a few hours, but more often after 2-3 days), bacteria enter the tympanic cavity (all through the same eustachian tube) and begin to multiply - otitis media becomes purulent. The pain increases, the body temperature rises, the pressure in the tympanic cavity often increases so much that the eardrum ruptures and purulent fluid begins to be released through the resulting hole through the ear canal.
Prevention
There are some simple tips to help protect your child from the harmful effects of otitis media:
- make sure that the child does not scratch his ears;
- teach children how to properly clean their ears;
- ensure that foreign bodies do not get into the ear;
- protect your ears from water when swimming in pools and reservoirs;
- reduce the ingress of shampoo and other cleaning products;
- After taking water procedures, carefully wipe your ears.
If parents see the first signs of inflammation in the child’s ear, they should immediately take him to the doctor for a diagnosis and a speedy course of treatment. If you start recovery on time, the result will be visible after two days, and within 10 days the pathogen will be completely eliminated.
Don’t forget about preventive measures; they help reduce the risk of infection to a minimum.
Treatment
Treatment of otitis depends on the type and complexity of the disease. In case of acute otitis in a child, recovery can take up to three weeks. After treatment, hearing loss persists, which recovers within 3 months.
- Treatment of otitis media. As a rule, it takes place at home. The following drugs can be used during therapy: antibiotics, painkillers, vasoconstrictor drops, phytotherapeutic procedures. In particularly difficult cases, surgery is prescribed.
- Treatment of external otitis. It takes place in an outpatient clinic. Until the pus from the boil comes out, compresses with alcohol and antibacterial agents are used for treatment. After the rod has formed, the doctor performs an opening and subsequent rinsing with an antibacterial solution. Subsequently, an antiseptic ointment and bandage are applied to the sore spot. The bandage and ointment must be applied until complete healing. If otitis media causes fever and enlarged lymph nodes in a child, antibiotics are prescribed.
Important advice! Heating should not be used to treat any form of otitis media. This can cause swelling of blood vessels and further spread of infection!
Medicines
- Antibiotics for otitis in children. Drugs are prescribed if the cause of otitis is a bacterial infection. They should be used in the following cases: inflammation is localized bilaterally, complicated symptoms are expressed, the disease is diagnosed in a child under 1 year of age. Typically, antibiotics are given by injection.
- Local medications. To treat otitis media, ear drops are prescribed, which relieve pain and eliminate the causative agent of the infection. If there is purulent discharge, the first step is to thoroughly clean the canal and treat it with antibacterial solutions. Dr. Komarovsky, when treating otitis media in children, emphasizes that ear drops should not be used before the auricle is examined by a doctor. If the eardrum is damaged, drops into the middle ear can damage the auditory nerve. This may cause hearing loss.
- Nasal drops. With otitis media, children often have a stuffy nose. To facilitate nasal breathing, vasoconstrictor drops should be used. They also normalize ventilation of the middle ear and reduce swelling of the mucous membrane.
- Surgery. It is required quite rarely. But if the pus does not come out on its own, it is necessary to make an incision through which it will come out.
Traditional medicine recipes
- Pour 5 laurel leaves with 1 tbsp. boiling water, wrap in a warm towel and let stand for 3 hours. You need to drink the infusion 3 times a day for half an hour before meals. 5-6 drops should be instilled into the ears three times a day.
- Lemon juice. Squeeze the juice of one lemon. Apply drops to your ears 2 times a day. You need to add 5 drops at a time. The product relieves pain very quickly, inflammation goes away after a few days of treatment.
First aid for otitis media
If for objective reasons it is not possible to immediately show the child to a doctor, it is necessary to provide him with first aid. The first step is to numb the ear. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are suitable for this, they will relieve pain, reduce fever and inflammation. Drops can be instilled into the ears only if there is no damage to the eardrum. If there is a fever, it is necessary to give the baby an antipyretic drug.
How to instill drops correctly?
For infants, 2 drops are instilled into each ear. Children 3-4 years old can instill 3-4 drops. Before instillation, the bottle must be warmed to room temperature. You can pour the drops into a warm spoon and then pipette them. The child should be placed with his ear up, the auricle should be slightly pulled back, straightening the ear canal. Even if one ear is affected, drops should still be instilled into both ears. If your baby is sucking on a pacifier, it should be removed before the drops are instilled.