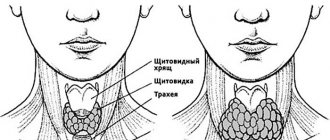
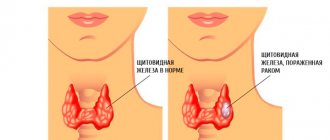
A thyroid cyst is a cavity filled with fluid. This type of benign neoplasm differs from thyroid nodules in structure (nodules, i.e. tumors are formed from glandular cells). Cystic formations of the thyroid gland can be single or multiple, they account for 3-5% of the total number of all neoplasms of the gland, most often appear in females over the age of 40 years
Cyst in the thyroid gland - is it dangerous? The prognosis depends on the type of formation. Benign cystic neoplasms can be completely cured, and sometimes resolve spontaneously. In some cases, relapses of the pathology are observed. In some cases, malignancy may occur, i.e. degeneration into a malignant tumor - then the prognosis worsens.
Thyroid cysts are more likely to develop in women over 40 years of age.
In order to prevent the development of cystic formations of the thyroid gland, it is recommended to consume iodine and vitamins to meet the body's needs, and to avoid exposure to ionizing radiation.
Symptoms of a thyroid cyst
Regardless of the lobe in which the neoplasm is diagnosed, the symptoms of organ damage by a disease such as a thyroid cyst will be more characteristic in the later stages of development, and one of the most striking is the presence of a feeling that there is a lump in the throat. It is quite possible to detect such a compaction yourself, with simple palpation. And over time, additional signs of a tumor will begin to appear in the form of:
- difficulty breathing, as the cyst presses on the larynx, thereby blocking the trachea;
- pain in the area where the tumor is located, which can radiate to the ear and jaw;
- discomfort and pain when swallowing;
- changes in voice timbre, which is quite rare, since the cyst affects a number of nerve fibers.
Types of pathology
- Simple cystic goiter develops when the thyroid gland begins to become covered with follicles. In this case, the formations are benign;
- Cystadenoma is a life-threatening disease, since as it progresses, benign formations become malignant. The oncological process is associated with impaired blood circulation in tissues. With the development of cystadenoma, the thyroid tissue becomes filled with blood and serous pus; the result is a malignant goiter;
- A cystic goiter can be located on the side or in the center of the organ. Here one can judge the innate characteristics of the organism;
- Colloid cystic goiter is often inherited;
- There are also parathyroid cysts. These formations “grow” on glandular tissue;
- Echinococcal formations are caused by exposure to parasites.
Causes of thyroid cysts
Thyroid cysts, or in other words, nodes in the neck, occur for reasons such as:
- frequent stress;
- disturbance of psycho-emotional state;
- long-term recovery after a serious illness;
- burn;
- hypothermia;
- overheat;
- hyperactive functioning of this organ;
- increased or decreased production of thyroid hormones by the pituitary gland.
In addition, the node develops either on the right or on the left lobe of the organ if:
- iodine deficiency;
- thyroid disease;
- poisoning of the body, regardless of type;
- disruption of hormones;
- living in an area with poor ecology;
- mechanical damage to the thyroid gland;
- congenital pathology in development and functioning;
- hereditary predisposition.
Most often, a thyroid cyst appears due to follicle dystrophy, which occurs due to iodine deficiency, as well as trauma and mechanical damage.
Stages of development
It is customary to distinguish three stages of cyst formation: initial, period of active growth and regression of formation.
Stages: initial, period of active growth and regression of education.
- The initial stage occurs unnoticed by the patient. The time may last for several months. Ultrasound during this phase usually reveals a small liquid inclusion up to 1 cm in diameter.
- At the growth stage, the cystic thyroid nodule is characterized by a gradual increase in size and accumulation of fluid inside the cavity. The period takes several years. At this stage, clinical manifestations increase, and laboratory abnormalities are possible.
- The regression phase occurs in less than half of the cases. It is characterized by a gradual reduction of the cyst, in the place of which an area of fibrosis forms. Resorption is achieved with normal thyroid function.
Treatment of thyroid cyst
If a thyroid cyst or nodes in the neck cavity, resulting from iodine deficiency, are benign formations, then treatment is quite possible. It can also be ruled out that this will cause serious problems for the patient or cause an enlargement of the cyst body. After the cavity is emptied, special substances are injected into it to cause the cyst to dry out and prevent relapse.
Therapy includes an integrated approach and application of:
- medications that will control hormone levels;
- agents that remove inflammation and help normalize metabolism;
- decongestants;
- medicines to improve blood circulation;
- antibiotics to prevent the formation of a bacterial infection.
Surgery to remove a thyroid cyst is usually performed using laser coagulation. In other words, this method is called local hyperthermia. It is recognized as updated and one of the most popular. Using a laser, hyperthermia is created in the part where the cyst is located and due to this, cell destruction occurs. The operation lasts 5-10 minutes, after which, if necessary, antibodies are injected. Among the advantages of the operation are:
- no pain;
- outpatient implementation;
- non-invasive basis;
- no side effects;
- no scars.
Possible complications
A common complication of a simple cyst is the addition of a bacterial infection. In this case, the walls of the formation thicken, adjacent tissues are infiltrated, pus and inflammatory secretions accumulate inside the cavity, destructive cystic degeneration develops, and regional lymph nodes are involved in the process. Upon external examination, redness of the skin, increased body temperature, general weakness and other symptoms of intoxication are noted. In advanced cases, a fistula tract is formed through which the contents are drained.
Also, a cyst can be complicated as a result of traumatic impact, when a tear or rupture of its wall occurs. The most serious complication is the degeneration of the cyst into a malignant tumor.
Prevention of thyroid cysts
To prevent such a process as the development of cyst cells and, accordingly, its occurrence in general, they resort to a preventive system in the form of:
- regular examination by an endocrinologist;
- elimination of any pathologies in the thyroid gland;
- consuming sufficient amounts of vitamins, minerals and iodine;
- limit exposure to ultraviolet radiation.
Even if a thyroid cyst, the symptoms and treatment of which can only be determined by a specialist, occurred in someone who has not previously encountered this organ in principle, it means that there is a hereditary predisposition or other factors were present, and therefore regular examination of the endocrine system by a doctor is not will hurt anyone.
Pathology in the left lobe
With such a neoplasm, a compensatory mechanism is often observed. In other words, the left lobe is active and the right lobe is hypoactive or normal. In this case, education does not pose a threat to life.
If the cyst of the left lobe of the thyroid gland enlarges, it is recommended to empty the cavity with the introduction of Sclerosant. This drug “glues” the walls of the formation and prevents the accumulation of colloidal contents. In case of purulent or inflammatory process, puncture determines the causative agent of infection. As a result, the doctor can prescribe adequate antibacterial therapy.
If, after sclerotherapy, a cyst of the left lobe of the thyroid gland reappears, the patient is recommended to undergo surgical intervention - resection.
Therapeutic treatment is based on iodine-containing drugs and a special diet. The prognosis of the pathology is favorable if all doctor’s prescriptions are followed.
Thyroid cyst in adolescents and children
In adolescents and young children, it is also possible for problems with the thyroid gland to form in the form of a cyst and, as a rule, the reason for this is:
- hereditary predisposition;
- iodine deficiency;
- presence of hormonal imbalance;
- staying for a long period in conditions of inadequate temperature, which can cause hypothermia and overheating;
- presence of thyroiditis;
- prolonged psycho-emotional stress;
- contact with harmful toxic substances;
- living in a polluted environment;
- thyroid injury;
- congenital pathologies, the removal of which has not been performed previously.
It is worth noting that congenital anomalies are very common and there are many factors that can provoke this. What a thyroid cyst is and what the prognosis for treating a child can be answered only by a specialist in the field of pediatric endocrinology after a thorough diagnosis.
Diagnostics
Biopsy
In order to make a correct diagnosis, it is necessary to undergo a whole range of diagnostic measures. First of all, this is a visual inspection, as well as palpation. After this, a blood test is performed to determine the hormones that are synthesized by this organ. To determine the nature of the pathology, a biopsy is performed, which makes it possible to take material for histological examination. Based on the information received about education, the attending physician makes a decision on what his further treatment will be.
Worth knowing! Puncture of thyroid nodes is the most basic diagnostic method today. This is due to the fact that the obtained biological material from the cyst is subsequently examined for the presence of various pathogens and malignant cells. And this is already necessary in order to correctly prescribe further treatment.
Why do tumors appear on the thyroid gland?
More often, a cyst is a benign neoplasm. Among all pathologies of the endocrine system, a thyroid cyst can be diagnosed only in 4-6% of all cases. The size of the cyst is measured in mm.
Elena Malysheva live. “My dears, do not remove the thyroid gland! Better..." Read more »
A large cyst is visible to the naked eye.
The hormones produced by the organ are contained inside a colloid, a substance that has a gel-like state. The colloid is located in follicles, which are voluminous round formations. When tumors form, the outflow of colloid from the follicles, of which there are about 30 million in the human body, becomes difficult, as a result of which fluid accumulates in the follicles and their size increases.
The following factors can provoke formation in the thyroid gland:
- iodine deficiency;
- inflammation in the organ;
- negative effects of toxic substances;
- organ damage;
- hormonal imbalance;
- hereditary factor.
Pathogenesis
This cyst, unlike other cystic formations, is capable of changing its “behavior”, that is, it can decrease or increase over time, disappear and make itself known with renewed vigor.
A person may not be aware that he is sick for a long time, since the symptoms of this disease may occur unnoticed by him.
The patient begins to feel primary discomfort when the cyst increases significantly in volume.
In this case, the symptoms of the pathological condition become quite obvious:
- external neck deformity;
- problems with breathing and swallowing;
- hoarseness of voice;
- pain in the neck due to the pressure of the cyst on the nerve tissue.
In addition, the follicular cyst can become inflamed and then symptoms of suppuration in the thyroid gland begin.
The body reacts to this condition with increased temperature, soreness of the entire neck area, swelling, and inflammation of nearby lymph nodes.
A follicular cyst does not exhibit hormonal activity because it cannot produce any additional hormones.
Because of this reason, laboratory tests in this case will be within normal limits, that is, they will not indicate that the functional activity of the thyroid gland is impaired due to the pathology present in it.
Diagnostic measures
To identify the disease, a physical examination is necessary: this is palpation of the neck. By palpation, the doctor determines how enlarged the lymph nodes are. It is worth noting that a goiter may not cause symptoms. This happens if tissues grow slowly. If a person has identified one of the above symptoms, he should consult an endocrinologist.
In addition to a physical examination, the doctor will prescribe tests that will confirm the pathology. It is important to say that treatment at an early stage gives a comforting prognosis and also reduces the risk of cancer. During the diagnostic process, the doctor finds out the patient’s complaints, finds out after what and when exactly the symptoms appeared. The patient donates blood for analysis and undergoes instrumental diagnostics. It is necessary to carry out:
- Ultrasound;
- Radiography;
- Biopsy (if a malignant process is suspected);
- Scintigraphy of the thyroid gland.
Other methods can detect the level of thyroid hormones.
How is therapy carried out?
Depending on the size of the goiter, the doctor prescribes conservative therapy or surgery.
If cystic formations of the thyroid gland are actively growing, you cannot do without surgery!
If their size is less than 9 mm, no special treatment is required, but the patient undergoes examination once every 4 months. Regardless of the nature of the therapy, its goal is to restore the thyroid gland. Drug treatment is the use of:
- Antibiotics;
- Medicines to relieve inflammation;
- Preparations with iodine;
- Medicines with synthetic hormones.
When selecting medications, the doctor takes into account the nature of the disease and the severity of symptoms. To confirm the diagnosis of thyroid goiter, an endocrinologist may prescribe a cytological analysis. The study will help identify the nature of the disease, and it is also necessary to exclude oncology. Treatment is required if the nodes grow slowly. A malfunction of the thyroid gland can cause a lack of hormones. In this case, the doctor prescribes medications with these hormones. The operation is prescribed if the size of the formations exceeds 9 mm.
Colloid goiter: features of manifestation and treatment methods
Prevalence of the disease
Nodular colloid goiter is a disease that is most common in 5% of adult patients, while women suffer from this disease 5 times more often than men. In the general structure of thyroid diseases, colloid goiter accounts for 90% of all goiters.
In recent decades, this disease has become increasingly common in children and adolescents; this is due to insufficient iodine intake in the young body.
Characteristics of the disease
The thyroid gland is an organ of endocrine secretion, consisting of many follicles in which the formation of thyroid hormones - thyroxine and triiodothyronine (T3 and T4) occurs. The follicle contains cells that produce a special jelly-like substance called colloid. It fills the lumen of the follicle, then direct synthesis of hormones occurs.
With colloid goiter, excessive accumulation of colloid occurs, and the proliferation (reproduction) of glandular cells also increases.
Clinical forms
There are several forms of the disease, which differ in histological structure and extent of the process. They can transform into one another, which indicates the progression of the process.
Forms of pathology:
- 1. The first and most common is the nodular form. Due to the proliferation of glandular cells, individual follicles begin to grow and nodes form, as a result of which the thyroid gland enlarges. First, one node appears, then their number increases, and a multinodular colloid goiter develops.
- 2. The next form is diffuse colloidal. There is an increase in the number of nodes that spread throughout the gland tissue, all of them filled with a large amount of colloid.
- 3. The third form is colloid cystic. In the formed nodes, the colloid begins to become covered with capsules with the formation of cysts. As a result, cystic degeneration of glandular tissue develops, and the level of hormones changes, both upward and downward.
The outcome of the disease may be regressive changes in the thyroid gland, and it ceases to fully perform its functions.
The presence of an immune reaction indicates the presence of inflammatory changes in the tissues of the gland and the activity of the process.
There are three degrees of goiter based on size:
- 1. In the first degree, the enlargement of the thyroid gland is not externally visible; nodes are detected only by ultrasound.
- 2. In the second degree, you can visually notice that the gland has grown in size when tilting the head back.
- 3. In the third degree, the thyroid gland is so large that it is visible to the naked eye even with the head positioned vertically.
According to changes in the formation of hormones, they are distinguished:
- Goiter with hypofunction - the amount of thyroxine and triiodothyronine in the blood decreases, clinical signs of hypothyroidism appear.
- With hyperfunction - the production of thyroid hormones increases, and symptoms of hyperthyroidism occur.
- Colloid goiter with normal levels of hormones in the blood is called euthyroidism; symptoms develop only when the organ is large and is associated with mechanical compression of surrounding tissues.
Reasons for the development of the disease
The causes of colloid goiter are not fully known. But the following possible predisposing factors are identified:
- Insufficient intake of iodine into the body through food is the so-called endemic goiter. With iodine deficiency, the thyroid gland tries to eliminate this deficiency and captures freely circulating iodine in the blood to a greater extent. And in order to produce the missing hormones, it begins to synthesize more colloid, and for this, more glandular cells are formed, and the gland increases in size. Today this is the most common theory of the formation of nodular colloid goiter.
- Hereditary factors also play a role; the presence of the disease in close relatives increases the likelihood of the disease occurring in children.
- Age - in people over 50 years of age, the incidence increases significantly; it is believed that this is due to a disruption of neuroregulatory processes in the aging body.
- The female sex is more susceptible to the development of nodular colloid goiter; every second woman over 50 years of age has nodular formations in the thyroid gland. This is due to the fact that thyroid hormones and female sex hormones have a direct relationship. With the onset of menopause and a decrease in estrogen and progesterone levels, women lose the balance between these hormones, and the risk of thyroid diseases increases. The same process occurs during pregnancy, the usual menstrual cycle is disrupted and the likelihood of thyroid pathology increases.
- External factors such as stress, bad habits, poor environmental conditions and occupational hazards play an important role.
Treatment of the disease is more symptomatic, since it is not possible to find out its exact etiology.
Symptoms of the disease
In the initial stages, the disease does not manifest itself in any way. As the process progresses and the size of the thyroid gland increases, clinical symptoms develop. Manifestations of the disease will depend on the type of goiter and the functional capacity of the organ.
With hyperfunction, patients are concerned about the following complaints:
- mood disorders;
- increased heart rate;
- increased sweating;
- sometimes fever.
Patients become irritable, aggressive, they quickly get tired, due to increased appetite they lose weight, and due to increased metabolism they are bothered by frequent diarrhea and urination.
With hypothyroidism, when the secretion of thyroid hormones is reduced, patients complain of weakness, impaired memory, attention and thinking, appetite decreases, but patients gain weight due to a slower metabolism, the skin becomes dry, flaky, sweating decreases and swelling of the extremities is also a concern.
If there are no changes in the amount of hormones in the blood, then patients complain only in the later stages, when the gland reaches a large size.
Nonspecific symptoms that apply to all types of goiter include manifestations of the disease associated with an enlarged thyroid gland. Its size puts pressure on surrounding tissues, resulting in the following complaints:
- First of all, this is an aesthetic problem; the neck seems to swell. This is what forces many patients to undergo surgery.
- The large gland puts pressure on the airways, and patients feel shortness of breath, especially in a horizontal position.
- There is difficulty swallowing and a feeling of a lump in the throat due to mechanical pressure on the esophagus and pharynx.
- Compression of nearby vessels and nerves leads to hoarseness (damage to the recurrent laryngeal nerve), dizziness and tinnitus.
- Sometimes there is pain at the site of the node, due to rapid progression, the occurrence of an immune reaction and the development of the inflammatory process.
- If there is one large node, more than 1-1.5 cm in size, then the patient can palpate it independently.
Treatment of colloid goiter
The choice of treatment option depends on the type of hormonal secretion of the affected organ and the size of the thyroid gland. In the initial stages, nodular goiter is relatively safe. When this disease is detected, active drug therapy, much less surgical intervention, is not indicated.
Patients in the initial stages of the disease without clinical symptoms are subject to clinical observation by an endocrinologist and are required to undergo ultrasound examinations twice a year to monitor the dynamics of the process.
Such patients are prescribed therapy with herbal preparations to normalize endocrine function and stop cell proliferation. The main medicinal plant used for this purpose is Cinquefoil white, which is part of such drugs as Zobofit and Alba.
If there are significant deviations in hormone levels, more serious medications are prescribed.
For hypothyroidism, thyroid hormone preparations (Euthirox, Thyroxine) are used to compensate for the lack of T3 and T4.
Hyperfunction requires the prescription of antithyroid drugs that inhibit the production of T3 and T4 - Mercazolil, Tyrozol.
If the blood contains a normal amount of hormones, iodine preparations are used - Iodomarin, potassium iodide.
In what cases is surgery indicated?
Conservative therapy does not always have the expected effect. There are a number of cases when surgical treatment is necessary:
- If the gland presses on surrounding tissues and interferes with swallowing and breathing.
- If family members have thyroid cancer.
- Hyperfunction that is not amenable to conservative therapy.
- If within a short time from the onset of the disease the condition has significantly worsened and the nodes have become more than 3 cm.
Use of folk remedies
Alternative medicine uses a whole arsenal of medicinal plants to combat goiter. Treatment with folk remedies only allows you to stop the development of the disease and use them better in combination with traditional methods.
Medicinal plants for the treatment of goiter:
- 1. Cherry bark is indicated for any level of hormones; an alcohol tincture is prepared from it and taken a tablespoon three times a day.
- 2. Gorse is prescribed for hypothyroidism; a decoction is made from the dried herb and taken a tablespoon 2 times a day.
- 3. Potentilla is used for elevated hormone levels. Make an infusion, which is consumed 100 ml three times a day.
- 4. Chokeberry, in addition to treating the thyroid gland, is used as a sedative.
- 5. Use fresh berries, which are ground with sugar and stored in a cold place. They are made into tea twice a day and consumed for 3 months.
Traditional medicine also advises, in case of thyroid disease, to apply a mesh of iodine solution to the location of the diseased organ.
Forecast
With a benign course of the process, the prognosis for the development of cysts is positive. Correctly selected treatment will relieve the patient of the tumor without unpleasant consequences for him. It often happens that it will be enough to simply observe the cyst and not need to do anything with it.
If there is a more severe cyst in the thyroid gland, treatment is necessary, especially with malignant degeneration of the neoplasm. The greatest risk of malignancy is with the development of a glandula thyreoidea cyst in children (from 14 to 40% of cases, versus 5% in adults).
If the cyst has a malignant course, then in the early phases of its development a favorable treatment prognosis is observed in 80% of cases. A decrease in this indicator is caused by the appearance of metastases and germinations in the tissue of surrounding organs.
What is cystic degeneration?
Cystic degeneration of an endocrine organ is a cystadenoma, in which nodular changes of a benign nature become malignant, as a rule, this occurs due to disruption of the circulatory process in the tissues of the gland.
As a result, more and more cavity formations are formed in the organ, the inner layer of which is lined with altered epithelial tissue, and they are filled with either serous liquid contents or blood.
Approximately 30% of nodular changes transform into cystadenomas.
This disease may be accompanied by congenital dystrophic changes in the thyroid tissue, microscopic hemorrhages, and hyperplasia of the thyroid follicular tissue.
Sometimes cysts grow extremely slowly, and there are situations when their growth is too active and the cyst grows significantly even in a few weeks.
Cystadenoma is characterized by dystrophic changes in the tissues of the thyroid gland, as well as its uneven growth.
In some cases, cysts fill the entire tissue of the gland, displacing all its healthy areas.
At the same time, they exert pathological pressure on nearby nerve fibers, blood vessels and normally functioning tissues, which causes an increase in the degenerative process in the organ.
In addition, cysts uncontrollably produce thyroid hormones and release them into the blood, which can soon cause thyrotoxicosis.
Prevention of cystic goiter
To prevent cystic degeneration of the gland, the following measures are recommended:
- A nutritious and regular diet that ensures a sufficient supply of vitamins and minerals, especially iodine;
- Taking vitamin and mineral complexes in winter;
- Regular visits to health resorts, especially for people living in regions with iodine deficiency;
- The use of preventive physiotherapy (for example, magnetic and laser therapy);
- Sufficient (but not excessive) sun exposure in the summer;
- Frequent exposure to fresh air;
- Preventive use of mineral waters.
In order not to miss the occurrence of cystic changes in the gland, it is important to undergo an ultrasound examination of this organ every year. For the same purpose, it is recommended to periodically take tests for the level of thyroid hormones.
A nutritious and regular diet that ensures a sufficient supply of vitamins and minerals, especially iodine;
Taking vitamin and mineral complexes in winter;
Regular visits to health resorts, especially for people living in regions with iodine deficiency;
The use of preventive physiotherapy (for example, magnetic and laser therapy);
Sufficient (but not excessive) sun exposure in the summer;
Frequent exposure to fresh air;
Preventive use of mineral waters.
In order not to miss the occurrence of cystic changes in the gland, it is important to undergo an ultrasound examination of this organ every year. For the same purpose, it is recommended to periodically take tests for the level of thyroid hormones.
Dynamic ultrasound examination of the gland with an interval of 1 year; Healthy balanced diet; Taking multivitamin complexes and iodine preparations (dosage is selected by an endocrinologist);
Sanatorium-resort treatment, especially for persons who live in endemic areas; Physiotherapy, for example: magnetic laser therapy of the thyroid gland;
Avoidance of direct ultraviolet rays, moderate tanning in the summer; Refusal from various types of radiation, including tanning in a solarium; Physical exercises, walks in the fresh air; Preventive intake of mineral water.
For prophylactic purposes, it is not recommended to independently take both iodine-containing drugs and hormonal drugs used to treat the thyroid gland.
Similar amateur activities
can result in serious problems in the functioning of the endocrine system.