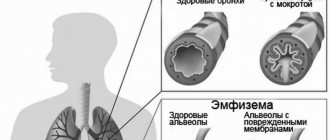
Colds in children are often complicated by pneumonia, which is difficult to detect and treat. This severe pathology can be different, it all depends on what area of inflammation it covers.
Children under three years of age usually suffer from a complex form of pneumonia that has an atypical course. With such an illness, the child cannot cough up phlegm and say exactly where it hurts. To avoid the negative consequences of the disease, it is important to identify pneumonia in advance. Symptoms in children 2 years of age are usually more pronounced than in schoolchildren.
How to avoid making a mistake with a diagnosis?
As soon as the baby develops a cough, and even a high temperature, many parents immediately make a diagnosis on their own and, moreover, it is not always correct. It is quite easy to confuse pneumonia with bronchitis, but these are two different diseases. Of course, they are not distinguishable externally, but inside the body itself the differences are clearly visible.
First of all, pneumonia is an infectious disease. Unlike inflammation of the bronchi, the infection affects the small alveoli and eventually they become inflamed. A child with a weak immune system is more susceptible to this disease, and the symptoms are very dangerous. The fact is that the alveoli play an important role in the exchange of oxygen and in the presence of an inflammatory process, fluid accumulates in them. This manifests itself as suffocation or other symptoms associated with impaired breathing.
How to treat inflammation in young patients?
It is important to diagnose the disease in time and prescribe effective therapy to avoid complications. First of all, the doctor determines whether the child needs hospitalization or not, and then prescribes a set of procedures and medications. But in most cases, treatment of children under 3 years of age is carried out in a hospital, since daily monitoring and, if necessary, emergency care are required. Children with rickets, weakened immunity and chronic respiratory diseases should also be under constant supervision.
As is already known, symptoms of pneumonia can be detected. In children 2 years of age, treatment consists of taking antibiotics. These are: Sulfamethoxazole, Amoxicillin, cephalosporins (Zeftera), macrolides (Clarithromycin) and fluoroquinolones (Moxifloxacin, Levofloxacin, etc.). Doctors carry out empirical treatment until they receive the results of the background examination.
If the little patient’s condition does not improve within two days, a new drug is prescribed. When the disease is caused by viral infections, antibiotics do not bring the desired result, so antiviral drugs are prescribed: interferons, Oseltamivir. If pneumonia is caused by a fungus, then drugs such as Diflucan, Flucanozol and other similar drugs must be used.
When a child experiences severe hypoxia, he is transferred to a ventilator in the intensive care unit. In case of dehydration, oral rehydration with saline solutions is performed, and possibly the use of infusions.
To treat pneumonia, antipyretics, mucolytics, anti-inflammatory and expectorant drugs, as well as bronchodilators are used.
Symptomatic treatment of the inflammatory process in the lungs involves physiotherapeutic procedures, breathing exercises, drainage massage, ultraviolet irradiation and physical exercise. In addition, doctors recommend consuming probiotics to normalize intestinal microflora, as well as sorbents to remove toxic substances from the body. For pneumonia, inhalations with a nebulizer are also used, immunomodulators and vitamins are used.
What causes the problem?
Very often, pneumonia is the second disease that develops due to primary infection with ARVI, influenza or any other viral infection. The pathogen accumulates in the upper respiratory tract, pharynx, nasopharynx, but with poor immunity, aggressive pathogens can descend lower, affecting the bronchi and then the lung tissue. This happens not only in the case of a weak protective function, but also in the event of incorrect or untimely treatment.
There are points that should be taken into account during a viral disease so that the disease does not worsen and become chronic:
- Forget about antitussives such as Stoptusin or Bronholitin. Coughing itself helps the body get rid of excess phlegm, mucus, viruses and toxins. Suppressing this reflex can only worsen the child’s condition. Sputum will accumulate intensively in the lower parts of the lungs, which will lead to their inflammation.
- In case of viral infection, it is not recommended to take antibacterial drugs. These drugs are completely powerless and useless for diseases of viral etiology and are prescribed only in case of severe complications or bacterial damage to lung tissue.
- It is not recommended to use vasoconstrictor drops, because they only contribute to the rapid penetration of microorganisms into the lower sections, especially in small children.
- It is important to give your child plenty of warm water, which is useful in removing toxins from the body. In a year or two this is very difficult, but if you don’t do this, the mucous membrane will dry out, plus dry air and a long course of the disease are guaranteed.
- Throughout the entire course of therapy (and it is very long, at least 3 weeks), wet cleaning should be carried out, the room should be ventilated and, if possible, humidified with special devices (for example, you can use a humidifier). Cool, fresh air better dilutes mucus and promotes its rapid removal.
Pneumonia in children is a complex disease, fraught with many consequences and even death. The smaller the baby, the more difficult the therapy, but any inaction or too active action can lead to complications. Only a therapist will confirm the diagnosis and prescribe correct and effective treatment.
What does Komarovsky say about pneumonia?
Dr. Komarovsky takes the issue of pneumonia quite seriously. According to a famous pediatrician, the cause of the disease can be anything. It is impossible to deny the connection of even the most minor illness and even physical injury with the further onset of pneumonia.
According to the doctor, the causative agent of pneumonia can be any microbe or virus that enters a child’s body . And often the parents themselves provoke the occurrence of this unpleasant disease with their excessive care.
According to Komarovsky, the alarm should begin to sound under the following circumstances:
- The child began to cough. If you have a cough, it means there is a problem.
- The baby was a little sick, and after a short course of therapy everything seemed to be getting better, and suddenly everything returned to normal.
- Possible pneumonia is also indicated by a cold, from which parents cannot rid their baby for a week or more.
- You notice that the child wants to take a deep breath, but nothing happens. Instead, a debilitating dry cough without sputum appears.
- The first signs of a cold appeared with a low temperature, a runny nose, but on top of everything else there was added pallor and bluishness of the skin.
- The child appears to be healthy, but you notice shortness of breath.
- High temperature is not reduced by antipyretics.
The doctor reminds moms and dads to remember that they are not doctors. And only specialists who have modern methods for detecting pneumonia in children can treat the baby.
Symptoms
The main symptoms are high fever and whitish skin
The disease often begins like a common cold, parents can see the following picture:
- Runny nose and sinus congestion.
- Frequent sneezing, especially in the first days of illness.
- Weakness, drowsiness and lethargy.
- Complete or partial refusal of food.
- The skin is whitish.
- High body temperature, which can only be brought down by a dose of antibiotics.
It is the last two signs that clearly indicate the presence of our problem, but with the rest the situation is a little different. Since the body and age of babies are different, therefore, symptoms can manifest themselves differently.
It is important to understand that pneumonia in young children causes many unpleasant symptoms that interfere with a full life, so at the beginning of treatment, children may feel better. Even if the symptoms have completely disappeared, stopping therapeutic treatment is prohibited. You should complete the treatment process; in this case, listen to the advice of your pediatrician.
An important point remains an accurate diagnosis; remember, only an x-ray can confirm it.
Symptoms of pneumonia in a child 2–3 years old
- After a viral illness, there is no improvement, or after the symptoms of ARVI have decreased, the temperature rises again and the cough intensifies.
- Decreased activity, lack of appetite, and sleep disturbances persist for more than 7 days.
- Coughing.
- Dyspnea. The number of breaths exceeds 30 times per minute.
- The temperature is low and may not rise if the disease progresses sluggishly.
- There is obvious pallor of the skin.
- Signs of body intoxication.
- When the temperature rises, conventional antipyretics do not help. The fever lasts 4 days or longer.
If you suspect pneumonia, you can ask your child to take a deep breath.
If there is inflammation, the child will have a severe coughing attack.
Sometimes the disease is asymptomatic. Parents should be wary of a cough that persists for a long time.
Not even strong. The cough may only occur after physical activity or during sleep.
In case of suspicion, an x-ray of the lungs should be taken.
With viral pneumonia, the child’s skin is pink, with other symptoms of inflammation.
This disease does not require special treatment and goes away on its own after 4–6 days.
Blue color of the skin indicates the bacterial nature of the inflammation.
This condition requires treatment with antibiotics.
The nature of the disease and treatment tactics are determined by the doctor.
If the inflammation is chlamydial or mycoplasma in nature, the symptoms are different.
Sluggish development of the disease raises suspicion of an atypical course.
Symptoms of an atypical infection:
- A sharp rise in temperature to 39 degrees and above, then normalization or retention of 37–37.5 is observed.
- Dry cough, sometimes with shortness of breath.
- Symptoms of a cold.
- Blood tests show no significant changes.
Symptoms of pneumonia in children with and without fever
Pneumonia in children: symptoms with and without fever. Pneumonia in children - ... “Read more”
When should a baby be hospitalized?
An important point remains the doctor’s decision about the therapeutic approach, or rather where exactly it will take place, so the following factors should be taken into account:
- How serious is the condition and are there any complications? Respiratory dysfunction, blood poisoning, decreased blood pressure, purulent processes in the lung and other serious disorders indicate the need to hospitalize the baby.
- Double pneumonia. For example, focal inflammation can be treated at home; in most cases it gives positive results of therapy. But the lobar form of the disease is dangerous and treatment should be carried out within the walls of a medical institution.
- Social preconditions. If the surrounding living conditions make it impossible to follow all the doctor’s recommendations, the baby should be taken to the hospital.
- General indicators. If you have chronic illnesses or other problems, regardless of age, it would be advisable to go to a medical center.
Signs of pneumonia are in any case very dangerous and threaten the baby with the loss of the most precious thing - life. Therefore, listen to the opinion of a specialist and go where the medical staff will take care of you.
Duration of illness
If the pathology proceeds without complications, then the child will recover with proper treatment in 10 days. Sometimes doctors insist that medications be used for 2 weeks to consolidate the results. If after this time, the signs of the disease have not disappeared and the child’s condition has not improved, then the treatment regimen should be changed and antibiotics of a new group should be used.
You should not self-medicate or trigger the disease. It is necessary to carefully monitor the baby's condition. Of course, improvement does not occur immediately, but if there are no changes after a few days, it is better to consult a doctor again.
Diagnostics
An X-ray of the lungs primarily helps determine the diagnosis.
It is extremely difficult to detect this disease on your own, and sometimes it is impossible even for an experienced doctor without preliminary tests. Even Komarovsky, a famous pediatrician, talks about the need to conduct certain research methods, without which it will not be possible to accurately establish a diagnosis.
In addition to examination and history taking, the following research methods should be carried out:
- Take an x-ray of the lungs.
- General blood and urine analysis.
- Biochemical analysis.
- Auscultation or listening to the lungs.
If the baby is less than two years old, then the development of the disease will be much faster, in which case treatment should begin immediately and without delay.
Diagnostic procedures
Symptoms of pneumonia in a 2-year-old child will help you recognize them. Diagnosis of this disease is carried out only by a doctor. Moreover, in some cases it is quite difficult to detect this disease. After all, hilar pneumonia cannot always be seen even on an x-ray. That is why, if parents assume that the baby has this particular illness, they should insist on a more thorough examination.
Symptoms will help detect pneumonia in a 2-year-old child; diagnostic methods are aimed at performing a full examination:
- X-rays of light.
- Biochemical research.
- Blood analysis.
- Interview with parents and child.
- Tapping the chest.
In babies under one year old, this pathology can develop quickly, so in their case you should not hesitate if rapid breathing appears and the temperature rises.
Therapy for two-year-old children
Antibiotics are the mainstay of treatment for pneumonia, and refusing them is extremely dangerous, because such a decision can lead to the death of the child. Parents should listen to the recommendations of doctors, give plenty of fluids and feed the baby healthy foods, as well as:
- Taking antibacterial agents. In this case, it is important to adhere to the time schedule for taking the drug. If the doctor prescribes it twice a day, then at least 12 hours should pass between doses of the medicine. Penicillins and cephalosporins are prescribed for one week, then macrolides for five days. The effectiveness after taking antibiotics is noticeable already on the third day from the start of therapy.
- Remedies for fever. Antipyretic drugs are used only when the thermometer shows a temperature above 38 degrees. An increase means that the baby’s body is resisting, so if he is able to withstand it, do not rush to stuff the child with pills.
- Dieting is an important point, manifested by complete refusal of food. You should not force feed; the child should eat light food and only if he wants to.
- Using Regidron to improve water-salt balance. It can be easily added to juices, teas or simply mixed with water.
- Taking vitamins and other complexes rich in microelements will help the body's overall resistance to pathogens.
How to care for sick children?
When doctors have diagnosed pneumonia in a child, the symptoms of which were discussed above, it is necessary to provide him with a cozy and favorable environment. On top of everything, the baby needs complete rest. During this period, you should add more vegetables and fruits to your diet. To avoid dehydration caused by illness, it is necessary to ensure that your child drinks plenty of fluids.
Complications of the inflammatory process
Complications of this disease occur only in cases of neglect or inappropriate treatment. If the inflammation spreads to the pleura, pleurisy and a croupous rash may develop. The most dangerous is considered to be pulmonary destruction, in which the child dies.
If the therapy is chosen incorrectly, the baby’s cardiovascular system may suffer, and this happens most often in the two-year-old category of children. This process begins due to prolonged poisoning of the body with toxins.
Classification of pneumonia in children
In medical practice, several classifications of pneumonia are used, which make it possible to accurately determine the nature and location of inflammation, the severity of the disease and the causes of its development.
By origin, pneumonia in a child can be:
- Intrahospital or otherwise hospital. This form of the disease is spoken of if pneumonia in a child is diagnosed three days or later after hospitalization in a hospital or at least three days after his discharge from the hospital. Hospital-acquired pneumonia is more severe, since children are infected with those pathogenic organisms that are endowed with increased resistance to most antibiotics;
- Out-of-hospital;
- Congenital. These types of pneumonia include inflammation of the lung tissue that occurs in a newborn baby in the first three days after birth;
- Neonatal – pneumonia that develops in babies in the first month of life.
Based on X-ray morphological signs (changes in X-ray images), pneumonia in children is classified into:
- Focal – the formation of infiltrated foci with a diameter of up to 1 cm in one or several segments of the lung;
- Segmental - pathological changes cover entire segments of the lung;
- Croupous - inflammation proceeds violently, accompanied by tissue necrosis, due to which toxins enter the bloodstream, causing severe intoxication of the body;
- Interstitial - inflammation covers the walls of the alveoli and parenchyma, fibrous restructuring of the pulmonary structures is possible.
According to the severity of its course, pneumonia at an early age is divided into complicated and uncomplicated. Complications of the disease often include respiratory failure, pleurisy, lung abscess and tissue gangrene, and a negative effect on the cardiovascular system cannot be ruled out.
Pneumonia is divided into:
- Acute – symptoms appear clearly in the first 2-3 weeks, complete recovery takes about 6 weeks;
- Prolonged - clinical signs of an inflammatory reaction of the lung tissue and their radiological confirmation are determined for more than 6 weeks.
The severity of the condition of a child with pneumonia determines the need for his hospitalization in pediatric departments for treatment.
Prevention
Vitamins and fresh air are good prevention of all diseases
It is easier to prevent infection than to treat the baby later; taking antibiotics, high fever and intoxication are dangerous friends for young children. Therefore, by following basic preventive measures you can protect your baby:
- When a baby is born prematurely, he should be checked by a pulmonologist very often, since his lungs have not opened well.
- You should try to protect young children (especially in the off-season) from possible infections with viral or colds.
- Drainage massage is a kind of prevention of the accumulation of phlegm in the lungs. Performing light tapping daily will help protect the respiratory system from inflammation.
- Strengthen and protect your baby's immune system, supply it with vitamins and microelements. Walk more in the fresh air and feed your baby in a balanced manner.
- An important element is nervous calm, less stressful situations and neuroses.
Prevention is an important detail, but it often receives the least amount of time and effort. Parents should not take such things lightly; they should listen to the pediatrician's recommendations.
Preventive measures
Symptoms help identify pneumonia in a 2-year-old child, but prevention helps avoid the occurrence of this disease. Preventing pneumonia is key to reducing child mortality. Prevention consists of hardening the baby, breastfeeding, combating dust and gas pollution in the room, and playing sports.
It is important to protect your child from passive smoking and observe basic personal hygiene standards. You should also respond quickly to any signs of illness. If your beloved child suffers from pneumonia too often and for a long time, it is better not to risk it and get vaccinated. Of course, it will not be able to protect against all pathogens, but it will form stable protection against streptococcus and pneumococcus.
How long does the disease last?
In the case of normal development of the pathological process (without complications), recovery will occur on the 10th day. In many cases, doctors prescribe antibiotics for at least two weeks. If after the specified period the baby does not feel better, it is worth changing the drugs to others; perhaps they are not suitable for this pathogen.
Self-medication should not take place in this case, since the life of a very young patient is at stake. Try to constantly monitor the baby’s health and at the slightest suspicion, immediately consult a doctor.
Author of the publication: Irina Ananchenko
Remember! Self-medication can cause irreparable consequences for your health! At the first symptoms of the disease, we recommend immediately contacting a specialist!
Symptoms of pneumonia in a child under 1 year of age
- The onset of the disease is often characterized by a clear decrease in the baby’s activity. The child sleeps constantly and reacts poorly to external stimuli. There may be a different picture. The child is capricious, does not eat, and cries. You need to pay attention to a clear change in the child’s behavior.
- In infants, the temperature may not rise above 37.1–37.5. Sometimes the temperature does not rise at all.
- Indigestion, vomiting, loose stools, frequent regurgitation are signs of intoxication.
- Runny nose, sore throat, cough.
- When coughing, yellow sputum is produced, sometimes green - purulent.
- Shortness of breath or increased number of breaths (more than 50–60 per minute). When breathing, the child puffs out his cheeks and stretches out his lips. Foamy discharge from the nose or mouth is possible, more often in children under 3 months.
- If you undress a child, you can notice how the skin is retracted from the side of the diseased lung when breathing.
- Breathing may become difficult and may stop due to advanced inflammatory processes.
- A characteristic sign is blue discoloration of the skin of the nasolabial triangle - cyanosis. Particularly visible when sucking.
In children under one year of age, a state of intoxication quickly sets in.
Therefore, at the slightest suspicion of inflammation, you should seek medical help.
Symptoms of pneumonia in infants, signs and treatment
Pneumonia in infants: symptoms, signs, treatment. Pneumonia is unpleasant and even dangerous in... “Read more”
Symptoms of the disease
Lung damage occurs in two types: unilateral and bilateral, i.e. localization of the disease in one or both lobes of the pulmonary system. Pneumonia is distinguished:
- focal, with damage to a small area of lung tissue;
- segmental with damage to the entire segment;
- confluent, affecting several segments of the pulmonary epithelium;
- lobar with damage to the entire lobe of the lung.
The main symptoms that indicate the development of an infectious disease and require immediate intervention are:
- general malaise, weakness, drowsiness;
- increased work of sweat glands;
- severe cough, runny nose, watery eyes;
- heat;
- aching joints;
- difficulty breathing, often with pronounced wheezing;
- Intoxication of the body may occur, which is manifested by vomiting or regurgitation.
If one of the symptoms appears, you should definitely consult a doctor. Often the disease occurs without fever and only a persistent cough, accompanied by vomit, is observed.
Disease prevention
Many components of a healthy and correct regimen are in themselves a prevention of bilateral pneumonia in children. Temper and strengthen children from the first days of life.
This contributes to the formation of strong immunity, the development of the respiratory system and lungs in children. Provide them with a nutritious, varied diet. Always try to identify and completely treat any inflammatory process in a timely manner.
Vaccinate your kids. Maintain a healthy atmosphere at home: perform wet cleaning, provide an influx of fresh air, and humidify it if necessary. It will be useful to have a massage, often stay outside, in parks. Clothing must be appropriate for the season so that the child does not get cold or sweat excessively.
Make sure your baby does not have close contact with sick people. An active life position and a quick response to incipient ailments will help to cope with the pathology without sad complications.
Kinds
By type of distribution it is divided into:
- Focal - with the formation of foci of infiltration, up to 1 cm in size, which are located in random order. Later they can grow and merge with each other (focal-confluent appearance).
- Segmental – affects an entire segment of the lung. Signs of pneumonia in children, such as high fever, cough and wheezing, may be absent at the initial stage of the disease. The following come to the fore: weakness, nausea, dizziness, refusal to eat. Then tachycardia, pallor, and microcirculation disorders begin.
- Croupous – more often observed in patients over 5 years of age. It is characterized by the development of fibrinous inflammation of the lung lobe or 2–3 segments of the lobe, with pronounced symptoms. From the first days the following symptoms appear: fever, cough, shortness of breath, difficulty breathing, weakness, signs of general intoxication of the body (vomiting is possible), tachycardia, rapid breathing (in children over 5 years old - more than 40 breaths per minute), pallor.
- Interstitial – damage to the connective tissue of the lung. This species is dangerous due to its severe disease and high mortality rate. Characterized by a sharp, acute onset. The temperature rises up to 40 degrees and is almost not reduced by antipyretic drugs, and can last up to ten days. Shortness of breath and rapid breathing up to 60 breaths per minute. Myocarditis and pulmonary edema may occur.
Chlamydial
The name of the disease according to the type of pathogen, the main one is chlamydia pneumoniae or chlamydophila pneumonia.
Children over 5 years of age are most often infected. The infection of the body by this parasite is asymptomatic for some time, but later the consequences of a deep destructive process in the internal organs begin to appear.
By the end of the third week, signs of normal malaise include a rise in temperature to 38 degrees and a dry cough. Chronic diseases of the body become more active.
The following symptoms are characteristic of chlamydial pneumonia: rash, neurological abnormalities, joint pain, gastrointestinal disorders.
Mycoplasma
A common type of disease, occurs in 20% of cases, typical for people under 15 years of age. The Mycoplasma pneumoniae virus is transmitted by airborne droplets.
The incubation period can last from one to three weeks. During this time, mycoplasmas actively multiply and spread between cells and on mucous tissues. The course of the disease itself with clinical symptoms of pneumonia in children lasts about 2 weeks.
The first symptoms are an increase in temperature to non-critical levels, sore throat, runny nose, chills, dry cough, pain when swallowing. These symptoms are usually mistaken for the flu, which makes timely diagnosis of this type of inflammation difficult. Later, pain in the chest area and difficulty breathing appear.
Atypical
This term combines all types of diseases that are caused by rare pathogens. This disease often occurs latently, without pronounced symptoms. Therefore, diagnosis is difficult. True, most of these diseases proceed without complications, but there are exceptions; they are aggravated by the lack of adequate treatment due to diagnostic errors.
Therefore, you should be extremely careful and, if you have any suspicions, seek help from a medical facility.
You should pay attention to the duration and nature of the course of ARVI and influenza. If the patient's condition improves and then worsens again, it is time to consult a doctor. If the cough remains dry for a long time and does not go away, residual effects after the illness persist for a long time - you need to seek advice from a medical institution.
If atypical pneumonia is viral in nature, then treatment methods may be sufficient even if the diagnosis is incorrect, since the therapy includes immune-modulating, antiviral, antipyretic drugs and mucolytics.
Acute bronchitis and bronchiolitis - differences from pneumonia
The bronchi are the main routes through which air enters the lungs. With bronchitis, mucus accumulates in them, which makes breathing difficult. Bronchiolitis is a blockage of small bronchial passages by mucus.
Bronchitis is considered a less dangerous disease that is easier to treat. With bronchitis, the baby may not have a fever at all, he may feel relatively normal. And with the standard course of pneumonia, an inflammatory process with a strong reaction of the body is a standard set of clinical manifestations.
Pneumonia in children may be accompanied by coughing up blood; this does not happen with bronchitis.
A characteristic sign of any of these diseases is a cough with wheezing. When it appears, you should immediately contact a pediatrician who will listen to the child’s chest and determine the affected area of the body. The diagnosis is confirmed by x-ray.
Reasons for appearance
Bilateral pneumonia often occurs in children under 15 years of age. In adults, this disease is diagnosed extremely rarely. Many factors lead to the appearance of this disease, such as:
- bacterial infections;
— weakened protective functions against the background of viruses;
- complications after illnesses;
- heart failure;
- persistent diseases of the respiratory system (sinusitis, bronchitis, asthma);
- bad ecology;
- hypothermia or, conversely, overheating.
Symptoms and diagnostic methods
Signs of bilateral pneumonia are as follows:
- elevated body temperature (above 38 degrees) for a fairly long period of time;
- the appearance of shortness of breath;
- cough (first dry, then wet);
- blue lips and fingertips;
- general weakness;
- lack of appetite.
If these signs appear in a child, you should immediately call a doctor, since acute bilateral pneumonia can permanently disable a child’s body.
When diagnosing the disease, the following methods are usually used:
- X-ray of the lung area in two projections. This diagnostic method is used when bronchopneumonia is suspected. From this x-ray, the doctor will be able to tell where exactly the source of inflammation is located, whether the roots of the lungs are expanded.
- Sputum examination. Based on sputum analysis, it will be possible to determine the pathogen that caused the development of the disease, and on this basis, select the necessary antibiotics.
- General blood analysis. Based on it, you can monitor the course of the disease and detect the first signs of inflammation.
- Specific blood tests are also used that can identify the causative agent of pneumonia.
Such diagnostic methods will allow timely detection of the disease and prevent its further development.
Pneumonia at 3 years old
From a medical point of view, this age in children is considered special. From the age of three, the number of leukocytes in the blood begins to increase in children and at the same time the volume of lymphocytes decreases. In this regard, at this age, immune factors often weaken, which significantly increases the risk of an inflammatory disease.
How does double pneumonia manifest itself in a 3-year-old child? It usually begins with an increase in body temperature. In this case, parents should pay attention not to the height of the mercury column, but to the duration of the fever. With pneumonia, it lasts more than three days, even with proper treatment of the viral infection.
The most serious sign indicating the presence of bilateral pneumonia in a 3-year-old child is the appearance of shortness of breath (up to 40 inhalations and exhalations within a minute), as well as tension in additional muscles. These symptoms are more important in determining pathology than listening to wheezing.
In addition, three-year-old children with pneumonia are certainly tormented by a cough. At the initial stage of the disease, it can be dry, and after the resolution of acute inflammation, it can become productively moist.
The disease manifests itself as cyanosis of the nasolabial triangle, as well as general intoxication syndromes (pallor and drowsiness).
If a pediatrician called to see a small patient diagnoses pneumonia, he will immediately send him to the hospital.
How to get rid of fever?
It is allowed to reduce the temperature after consultation with a pediatrician . He will prescribe the necessary effective medications. You can try to reduce the fever using traditional methods.
There are good ways to help lower your fever, but they should be used with extreme caution. The patient is wiped with a towel soaked in water at room temperature. Vodka and vinegar are also used for wiping.
If your baby has a fever, he needs to sweat well. To do this, you can drink self-prepared teas from raspberries, linden flowers, thyme, and chamomile. Cranberry juice, red currant and lingonberry juices will also help.
You can offer the patient to eat a grapefruit, 2 oranges, half a lemon and the temperature will drop. Thanks to vitamin C, the condition can be stabilized.
Dangerous forms of pneumonia
The latent form of pneumonia is characterized by mild symptoms. It is the most dangerous type of the disease. It is necessary to carefully monitor the child's behavior. With pneumonia, his condition worsens significantly; usually parents notice whims and crying, but no cough or runny nose occurs.
Treatment of pneumonia
A latent form of pneumonia can appear when immunity deteriorates. The risk of this disease increases if parents do not monitor the dosage and frequency of taking medications. These drugs negatively affect human immunity and are especially dangerous at an early age. Antibiotics often have a negative effect together with antitussive drugs, since by blocking the process that regulates the release of sputum along with mucus, the risk of infection and spread of infection increases. Children who suffer from immunodeficiency from birth have an increased risk of pneumonia.
On a note! Atypical pneumonia is caused by chlamydia and mycoplasma. Strong structural changes in the lung tissue may occur, while general signs do not reflect the symptomatic picture.
The main signs of atypical pneumonia:
- Severe intoxication that does not go away for no apparent reason.
- Headache.
- Unpleasant sensations in the muscles.
- Hyperhidrosis.
- Increased body temperature (this symptom may be absent).
- The amount of food consumed per day is significantly reduced. The child may completely refuse to eat.
- Enlarged lymph nodes.
Indications for hospitalization for pneumonia
With atypical pneumonia, the disease can be detected by retraction of the skin in the area of the inflamed area when breathing. If pneumonia occurs as a result of mycoplasma activity on the skin, a polymorphic rash may form. It is possible that the spleen and liver may increase in size, which is most often noted only at a doctor’s appointment. Pneumonia often occurs with an erased symptomatic picture, which is why people confuse it with pharyngitis, a persistent sore throat. It is necessary to identify the disease as early as possible to eliminate the risk of complications.
Video - How to suspect pneumonia?
Definition of disease
The main respiratory organ of a person is the lungs, where oxygen is absorbed into the blood and carbon dioxide is removed from them. This happens in the alveoli - the smallest sacs at the ends of the bronchioles, the branches of the bronchi. The alveoli are penetrated by numerous capillaries that supply the lungs with blood. It is blood that is the carrier that is responsible for the normal nutrition of all tissues and organs.
However, the function of the lungs is not only gas exchange. Toxins, decay products formed when inflammatory processes or infectious diseases occur in the body, can be eliminated through the lungs. In case of any injuries, surgical interventions, food poisoning, colds, the lungs along with the gastrointestinal tract, liver, kidneys, and skin receive additional stress, which invariably leads to a decrease in immunity.
As a result, fluid and even pus begin to accumulate in the alveoli, which leads to disruption of gas exchange and the spread of inflammation to neighboring areas.
In most cases, pneumonia in children begins against the background of incorrect or interrupted treatment of acute respiratory viral infections and acute respiratory infections. As a primary disease, pneumonia occurs very rarely and is associated with severe hypothermia, which most parents, as a rule, do not allow.
Reasons for development
Factors that cause bilateral pneumonia differ in children of different ages. Newborns and infants can become infected with respiratory pathologies due to:
- premature birth;
- immunodeficiency;
- congenital anomalies;
- lack of weight;
- constant regurgitation;
- asphyxia;
- birth injuries;
- intrauterine hypoxia.
Asphyxia
In the student's medical history, pneumonia appears as a result of exposure to the following factors:
- colds (sore throat, sinusitis);
- hypothermia;
- harmful addictions;
- influence of allergens and harmful impurities;
- emotional stress;
- unbalanced diet;
- lack of vitamins, minerals, micro- and macroelements.
This list is supplemented by cardiovascular diseases, autoimmune pathologies, chronic lack of sleep, and allergic reactions. Herpes simplex, rubella, chickenpox and influenza are significant causes for concern. The disease affects the lungs unevenly. The causative agent of pneumonia in childhood is most often pneumococcus. The list of microorganisms that provoke the disease includes legionella, chlamydia, and pneumocystis. Treatment of a child for pneumonia should occur in a hospital setting.
Complications
Being a dangerous infectious disease, pneumonia can often lead to the development of complications. In this case, treatment may take up to several months. The most common complications observed are:
- lung abscess with the development of an abscess in the lung tissue;
- destruction of lung tissue, which leads to its melting and the formation of a cavity;
- dry or exudative pleurisy with damage to the pleural layers;
- broncho-obstructive syndrome with obstruction of the bronchi, often accompanied by the appearance of spasms;
- pulmonary edema, which threatens respiratory failure;
- infectious-toxic shock is also observed;
- inflammation of the heart muscle, damage to the inner or outer lining of the heart;
- sepsis, which threatens damage to many internal organs;
- inflammation of the meninges or medulla;
- blood clotting disorder;
- anemia.
With timely and correct treatment, most complications go away along with the disease itself. The main driver of their development is bacteria.
What is the fever associated with the illness?
When faced with inflammation of the respiratory system in a baby, every parent is interested in what temperature is normal for pneumonia. There is no definite answer, due to the individual characteristics of each organism. Of course, there are indicators that occur more often, but the situations are still different.
The temperature is considered normal if it is 37.7-38 degrees. It lasts for 2 weeks. An increase can be seen in the evening. In the morning the temperature will stabilize.
It is possible to raise the indicator to 39-40 degrees. This indicates a weak defensive function of the child’s body; the process of inflammation is quite complex. The fever can last for 2 days or 2 weeks. It all depends on the immune system, how long the body will fight the virus.
The temperature must be constantly monitored, as the healing process depends on it.
Regime and nutrition for pneumonia
If the temperature rises significantly, you need to put the child to bed and wait for the doctor to arrive. After the examination, the doctor will give all the necessary recommendations for maintaining bed rest. As a rule, there are no strict requirements for keeping a child in bed. Better sputum discharge is observed with physical activity.
Nutrition does not require strict measures. It is better to feed your child small portions and light foods. It is often recommended to increase the amount of fluid consumed; you can include compotes and fruit and berry juices in your diet. It is advisable to exclude dairy products at the initial stage of the disease, as they can cause a gag reflex.
As for feeding newborns, it is recommended to choose a more comfortable body position when feeding, change the thickness of food and increase the size of the hole in the nipple.
Causes of the disease
In children, viruses, bacteria and fungi can cause bilateral lung damage. The main route of penetration of these microorganisms is through the air, and less often through the hematogenous or lymphogenous route. Through blood or lymph, a child becomes infected, for example, from the mother, during the prenatal period of its development.
In accordance with age, it is possible to distinguish the characteristics of the course of infection in a child, depending on the type of pathogen:
- From birth to six months, the main reason is the penetration of viruses into the body, as well as infection with staphylococci, chlamydia, and E. coli.
- From 6 months, the risk of bacterial pneumonia increases due to staphylococci and pneumococci entering the lungs.
- At school age, the main causative agents of inflammation are pneumococci, but they are also associated with the risk of infection with atypical forms of pneumonia.
The disease occurs when the body is affected by the following reasons:
- weak immunity;
- lack of vitamins;
- lung and heart defects;
- improper treatment of ARVI;
- birth injuries.
Often, the development of bilateral inflammation becomes a complication of acute bronchitis and inflammation of the paranasal sinuses.
Important! The diagnosis is often made in children under 15 years of age, and in adults, bilateral pneumonia is detected much less frequently.
Consequences and complications
When we talk about the consequences and complications of pneumonia, we mean advanced inflammatory processes, the treatment of which was not carried out in a timely manner, which served as the basis for the development of other infectious, as well as pathological processes in the body. The most dangerous consequence of suffering from complicated pneumonia is death. Death occurs due to the rapid proliferation of pathogenic microbes in the lungs, which are carried by blood throughout the body, forming widespread inflammatory foci.
Mortality due to pneumonia most often occurs in persons with compromised immunity, or those whose immunity has not been fully developed. Thus, children under one year old and elderly people over 60 years of age are at risk. In 60% of deaths due to pneumonia, pneumococcal microbes are to blame.
The following functional and pathological forms of diseases that can occur as a result of pneumonia are distinguished:
- infectious-toxic shock;
- sepsis (bacterial blood infection);
- abscess, as well as pericarditis;
- various purulent-inflammatory processes.
Traditional medicine against pneumonia
Along with medications, the doctor may prescribe the use of traditional medicine. The choice of herbal medicine depends on the results of the main treatment. But the prescription of decoctions and mixtures does not imply refusal to take medications used to treat the disease. Folk remedies act as an additional method of fighting for the patient’s health.
- Among the most popular antiviral drugs, onions and garlic should be noted.
- To prepare infusions and decoctions, raspberry berries and leaves, coltsfoot leaves, linden blossom, plantain leaves, nettle leaves, and licorice root are used. By the way, some of them are sold in pharmacies in the form of ready-made preparations and syrups.
- Elderberry and rosehip fruits are also popular.
- Honey and propolis can be used only in the absence of allergic reactions to bee products.
- For drinking, you can cook dried fruit compotes with the addition of black currants. These berries are known for their high content of vitamin C. They can also be eaten fresh.
- Pharmacies offer ready-made herbal mixtures for the treatment of pulmonary diseases. There are also breast preparations that are used as an expectorant. They are produced either in the form of a herbal collection or in ready-made filter bags. Brew as tea and drink throughout the day. Don't forget to consult your pulmonologist.
How to recognize different types of disease?
Pneumonia has various forms and some of them differ in symptoms or have different dynamics and severity of clinical manifestations. Let's look at it in more detail below.
Bronchopneumonia is inflammation of the walls of the bronchioles. under three years of age are at risk . The symptoms are as follows:
- cough;
- dyspnea;
- arrhythmia;
- temperature above 40°C ;
- dizziness;
- fatigue;
- wheezing.
Left-sided pneumonia. This type is more dangerous than others; it occurs when the body is exhausted as a result of a previous illness. The left-sided process announces itself:
- sudden increase in temperature and chills;
- pain when taking a deep breath;
- wet cough, sputum production, shortness of breath;
- pain in the left side of the chest;
- nausea, vomiting, weakness.
Right-sided inflammation is the most common type in children aged 1 to 3 years . The clinical picture is as follows:
- sweating;
- high body temperature;
- cyanosis of the nasolabial area;
- cough with sputum production;
- increased heart rate and breathing.
With the segmental form of the disease, there may be no cough in the first days, which makes it difficult to determine before visiting the hospital. But at the same time there is a high temperature that does not decrease.
Also, the disease can occur without an increase in body temperature. This can be due to viral pneumonia. In this case, the main signs are:
- dry cough;
- drowsiness;
- muscle pain;
- After the disease develops, a wet cough appears and the temperature rises.
Bilateral pneumonia is localized in the lower parts of the lungs. Expressed by the following symptoms:
- the temperature does not decrease within three days;
- wheezing, cough;
- there is difficulty and rapid breathing;
- When breathing, you can hear whistling and groaning.
There is also a hidden form. It occurs without pronounced symptoms, which usually signal pneumonia. In such a situation, the disease can easily be confused with a common cold. Common symptoms of a cold include:
- dry cough;
- skin rashes;
- muscle weakness;
- a sharp increase in temperature to 39°C , and then a decrease to 37-37.5°C .
Pneumonia can be viral, bacterial or fungal. The causative agent of the disease can be identified using a blood test. Viral pneumonia is the most common and has a mild form. The most dangerous is bacterial pneumonia.
Treatment
Often, treatment of pneumonia in children 2-3 years old with an uncomplicated course is allowed to be carried out at home. A child may be transferred to a hospital in the following cases:
- child's age up to 1-1.5 years;
- a blood test showed decreased leukopenia or increased leukocytosis;
- airway aspiration;
- the child loses consciousness and is delirious;
- severe symptoms of sepsis;
- complication with exudative pleurisy;
- suspected lung abscess;
- antibacterial treatment does not give results;
- pneumonia is combined with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
Mechanism of bronchial obstruction
Drug therapy
When treating pneumonia in children from one to three years of age, antibiotics are prescribed if the main cause of the disease is bacteria. Antibacterial drugs remain effective:
- The group of penicillins - ampicillin and amoxicillin with clavulanic acid (Flemoxin Solutab, Amoxiclav).
- Cephalosporins 2-3 generations (Cefazolin, Cefuroxime).
- If you are allergic to penicillin medications, then antibiotics from the macrolide group (Azithromycin, Clarithromycin) are suitable.
- In case of severe pneumonia and the presence of concomitant pathologies, antibiotics from the group of 3-4 generation cephalosporins (Cefotaxime, Ceftriaxone) are prescribed in a hospital setting.
- If the disease developed against the background of immunodeficiency, the presence of destructive processes in the lungs, then reserve antibiotics (Linezolid, Meropenem and Vancomycin) are effective.
The duration of antibacterial therapy is 7-10 days. But there are situations when the doctor extends treatment to 3 weeks . In a hospital setting, antibiotics are used in the form of injections.
To relieve symptoms of pneumonia in children 1-3 years old, the doctor prescribes the following medications:
- If the body temperature is above 38.2°C, antipyretic drugs are used. Children are prescribed Paracetamol and Nurofen.
- For hypertension and pale fever (increased body temperature in the armpit, pale skin, cold palms and feet), a lytic mixture is prescribed - a combination of Analgin, Papaverine, Diphenhydramine. The dosage is calculated by the doctor individually, taking into account the age and body weight of the child.
- You can relieve pain from pneumonia with Ibuprofen.
- Mucolytics will help improve sputum discharge: ACC, Ambroxol, Lazolvan.
- For bronchial obstruction, bronchodilators are prescribed - Berodual.
The viral form of pneumonia in children 1-3 years of age most often occurs against the background of a common ARVI. The pathological process occurs along with ARVI, so usually only symptomatic drugs and immunomodulators are prescribed. Such cases account for approximately 60% of all cases of pneumonia in children. But the danger is that a bacterial infection occurs against the background of the virus and this requires more serious treatment.
Physiotherapy
Important! It is IMPOSSIBLE to carry out physiotherapy for fever, neoplasms, heart and vascular diseases, bleeding and hypertension of 2-3 degrees!
1. Electrophoresis. This method involves the administration of medicinal substances through the skin using electrodes. For therapy, electrophoresis with the following drugs is used:
- aminophylline;
- lidase;
- calcium chloride.
The peculiarity of the method is that the drugs presented act directly on the source of the inflammatory process. All medicinal substances accumulate, and their therapeutic effect is prolonged.
2. UHF (ultra high frequencies) . This procedure has a thermal effect. UHF improves microcirculation in the area of inflammation, has a resolving and anti-inflammatory effect.
3. SMV and DMV therapy. This treatment method is based on the use of an ultra-high frequency magnetic layer in the centimeter and decimeter range. An anti-inflammatory and bronchodilator effect is achieved.
4. Massage. This is one of the auxiliary methods of treatment and rehabilitation of pneumonia in children 1-3 years old, in which chest massage is performed. It improves blood and lymph circulation, promotes the evacuation of bronchial secretions. Both specialists and parents can provide massage. First, stroking movements are performed, then rubbing and vibration, and finally stroking again. More details about the types of massage here.
Drainage massage
Look in another article for other equally effective physiotherapeutic procedures.
Folk remedies
1. Radish with honey. Use only black radish. Cut it so that the upper part is smaller and resembles a lid. Make a hole in the radish and remove the pulp with a spoon. Place 20 ml of honey into the cavity. Cover with the cut top and wait 5 hours. This time is enough for juice to form. Give it to the baby 2 times a day, 10 ml. The general course of therapy should not exceed 5 days.
2. Decoction with bergenia. Pour 20 g of bergenia roots with 1 cup of boiling water. Leave for an hour, filter, use to gargle 3 times a day. You can take 5 ml 3 times a day.
3. Infusion of pine buds. Finely chop coltsfoot and plantain (30 g), combine with 40 g of pine buds. Pour 750 ml of boiling water. Take 1/4 cup 5 times a day.
4. Compress with plantain. Wash the plantain leaves and let them dry. Heat a towel with an iron and place plantain leaves there. Then place a warm napkin on the baby’s chest and wrap a scarf on top. Put the child to bed and remove the compress only in the morning.
5. The magical properties of propolis. Combine propolis and butter in the proportion of 100 g and 15 g. Give the child 5 ml 45 minutes before meals. Carry out treatment 3 times a day.
Important! You can use folk remedies only after consulting a doctor, as the child may have allergies! In addition, use them only in combination with medications, because folk remedies are only an auxiliary method of therapy.