What is an ovarian dermoid cyst, how is it different from others, and how to get rid of it? A dermoid cyst is a non-malignant formation that develops in utero and is formed from fragments of embryonic tissues of the embryo.
The structure looks like a mobile capsule with a dense whitish shell, connected to the ovary by a long stalk. The capsule is filled with thick jelly-like contents with elements of various body tissues: fat, bones, nerve fibers, hair, teeth and cartilage, glandular organs formed during the development of the embryo.
Other medical terms (names) used to refer to this type of neoplasm are mature teratoma, dermoid or teratodermoid ovarian cyst.
It should be noted that a dermoid cyst is often considered a germinal tumor because, unlike cystic structures that are formed due to the accumulation of fluids, it is formed as a result of mitosis (cell division).
Structure Features:
- The size of the dermoid reaches 120 – 150 mm.
- The development of a mature teratoma is quite slow, so the pathology may not manifest itself for years.
- Among diagnosed cystic ovarian structures, this pathology accounts for 15–20%.
- Diagnosed at any age, starting from newborns. It is most often found in growing girls at the stage of puberty, in women of childbearing age and those in menopause.
- Malignancy (cancerous degeneration) of cells is possible (1 – 3%).
Ovarian dermoid cyst
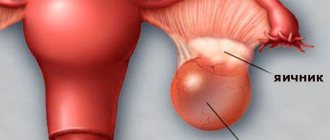
An ovarian dermoid cyst is a pathological formation of benign ovarian tissue that occurs against the background of impaired proliferation (the process of formation of new cellular structures) and differentiation (cells of a certain morphology perform specific functions in the body).
A benign tumor develops oval or round in shape and has a smooth surface on the outside.
The maximum dimensions of the compaction reach 13–15 cm, its cavity is filled with particles of sebaceous and sweat glands, fat, hair, teeth, muscle and nervous tissue; in extremely rare cases, fragments of more complex organs, for example, eyes, may be present inside the capsule.
This is due to the fact that dermoid cysts are formed from germinal embryonic layers, which are preserved in paired female endocrine glands when cell differentiation is impaired.
Tumor formation of ovarian tissue in the ovary can occur both in young girls and girls of the reproductive period, and in elderly women.
Causes of ovarian teratoma
The causes of dermoid cysts are being investigated. The main reason for the appearance of dermoid is a disruption of the intrauterine process of tissue formation during the development of the embryo. In this case, elements of the rudimentary organs of the embryo remain in the ovary, from which a mature teratoma can grow.
These tissue fragments include three germ layers:
- ectoderm (skin, neural tube, sensory organs, intestinal sections);
- mesoderm (bones, cartilage, muscles, kidneys, blood vessels);
- endoderm (intestinal mucosa, liver, pancreas, lungs).
This is where the name of the cyst comes from - dermoid.
However, the exact reasons for the occurrence of the abnormal process, in which conditions are created for the proliferation of embryonic tissues, have not been determined. Embryonic fragments are detected in the gonads of many women, but only in certain cases do they serve as material for the development of an ovarian cyst.
Provoking factors are considered:
- Hormonal changes, which is confirmed by the frequent detection of tumors during periods of hormonal surges: in girls 12–15 years old during the formation of menstrual function, in adult women - during pregnancy and menopause.
- Injuries to the reproductive organs and peritoneum.
Symptoms
Symptoms do not appear at the beginning of tumor formation. It is possible to detect a dermoid cyst only with a routine ultrasound examination of the pelvic area.
The clinical picture appears when the formation increases to 8 cm or more.
Symptoms that arise include:
- pain in the area below the navel;
- feeling of heaviness in the lower abdomen;
- severe pain during sexual intercourse;
- disorders of the functioning of the urinary organs;
- violations of the act of defecation;
- general weakness and lethargy;
- increasing body temperature;
- in the absence of timely treatment, twisting of the leg may occur, which causes the development of intense abdominal pain with subsequent irradiation into the rectum and lower extremities (to the right or left - depending on the location of the tumor), temperature readings rise to 39 degrees, a feeling of nausea occurs, vomiting is possible.
Consequences and complications
When a teratoma grows, the following negative consequences are possible:
- dermoid cyst tissue begins to replace ovarian tissue (ovary), disrupting its functions;
- the cyst compresses the vessels, preventing blood flow to the cells of the reproductive gland;
- the dermoid puts pressure on adjacent organs, including the bladder and intestines, preventing them from functioning normally;
- 1–3 women out of 100 who have a mature teratoma develop squamous cell carcinoma of the ovary.
Complications requiring emergency care
The most severe conditions that can be caused by a mature teratoma are:
- rupture of the cyst walls;
- twisting of the leg;
- suppuration of the cyst.
The first two complications often occur with severe physical stress, playing sports, active sexual intercourse, and in girls - during outdoor games, but can occur in the absence of external provoking factors.
Suppuration of a dermoid cyst occurs when microbes from foci of infection in the body invade it.
All three conditions are extremely life-threatening, however, their symptoms are often mistaken for signs of poisoning, inflammation of the appendix and other intestinal problems, especially if up to this point no examination of the ovary has been carried out and the woman does not know about the cyst.
Basic symptoms to watch out for:
- Acute, unbearable, long-lasting pain in the lower abdomen or on one side, often radiating to the groin, rectum, or leg. If the dermoid cyst has burst, the pain may subside after some time, indicating a state of false improvement.
- Soreness and hardening of the abdominal muscles when trying to palpate.
- Increased body temperature, which can reach 39-40 C.
- Overexcitation, panic, followed by severe lethargy and apathy.
- Perspiration, cold sweat, rapid pulse.
- General weakness to the point of exhaustion.
- Nausea, vomiting, urinary and stool retention.
- Severe decrease in blood pressure, loss of consciousness, shock, coma.
All these symptoms require immediate surgical care in a hospital or intensive care unit.
Diagnostics
The initial examination of a patient with suspected cystic formation of ovarian tissue begins with a recto-abdominal examination, which involves palpating the tumor simultaneously through the vagina and rectum.
During the diagnostic procedure, a mobile, round-shaped neoplasm is identified, the location of which is in front and to the side of the uterus.
On palpation there is no pain in the area of formation.
After a gynecological examination, instrumental and laboratory tests are prescribed:
- transvaginal (examination of the pelvic organs is carried out using a special sensor, which is inserted into the vagina) and transabdominal (through the abdominal wall, ultrasound - during diagnosis, the size of the seal, the thickness of its walls, the severity of the blood supply are determined, and the contents of the cavity are determined);
- if necessary, CT and MRI are performed;
- with a pronounced clinical picture and large sizes, laparoscopy and puncture through the posterior vaginal fornix are performed;
- testing for the tumor marker CA-125;
- differential diagnosis is carried out.
After receiving the results and making a final diagnosis, the doctor prescribes a treatment regimen.
Signs of dermoid formation of the ovary
If the cyst is small (up to five centimeters), then it does not manifest any symptoms, but is detected by chance, during an ultrasound examination of the pelvis or a manual (manual) gynecological examination. A specialist can identify a round formation with clear contours and suspect the presence of a mature teratoma.
Although the cyst grows rather slowly, its growth does not stop and can reach fifteen centimeters. When the tumor reaches five centimeters in diameter, mild nagging pain is noted. If its diameter is 10 centimeters or more, the cyst can put pressure on nearby organs and tissues. With significant volumes of neoplasm, the following signs are noted:
- nagging pain in the lower abdomen;
- unclear location of pain;
- a feeling of fullness, heaviness and squeezing appears in the lower abdomen;
- increased abdominal size (especially in thin girls);
- increased urge to urinate due to the pressure of the tumor on the bladder;
- pain when urinating;
- disorders of the gastrointestinal tract (intestinal dysfunction is manifested by constipation and indigestion, as the gastrointestinal tract is compressed);
- pain during sexual intercourse.
If mature teratomas become inflamed, the body temperature rises to 38-39°C, the patient feels fatigue, lethargy and discomfort in the lower abdomen. If the leg of the dermoid tumor is twisted, signs of irritation of the peritoneum appear, sharp pain sensations that radiate to the leg or rectum.
Treatment methods
A dermoid cyst of the right or left ovary, regardless of the size of the pathology, requires surgical treatment.
Due to the high probability of degeneration of a benign process into a malignant one, it is necessary to remove the dermoid cyst exclusively through surgery; drug treatment does not bring the desired effect.
The extent of surgical intervention depends on many factors: the age category of the patient, the size of the formation, the rate of progression of the process and the clinical picture.
Emergency surgical intervention is required when inflammation or a complication in the form of twisting of the leg begins in the cyst.
Cyst surgery
During surgical treatment, they strive to prevent capsule rupture and preserve the woman’s reproductive function.
Dermoid cyst of the left and right ovary is treated using one of the types of surgical interventions:
- cystectomy – removal of the tumor formation of the ovary while preserving the healthy tissue structures surrounding it;
- resection – the teratoma and part of the damaged organ are removed;
- oophorectomy – removal of a neoplasm together with the affected organ (used when there is an accumulation of purulent contents).
Laparoscopy
As a rule, removal of an ovarian dermoid cyst is performed using laparoscopy.
The method is a low-traumatic operation, during which three small incisions are made in the abdomen to insert special instruments.
Using sensors on the monitor, the condition of the internal organs is visualized; accordingly, all manipulations are fully controlled by a doctor.
After laparoscopy, there are practically no scars left, the woman recovers quickly and returns to professional activities and her usual daily routine in a short time.
Laparotomy
Laparotomy is an operation during which an incision is made in the abdominal wall.
This operation can cause serious complications such as bleeding, so it is performed quite rarely. In addition, large scars remain after treatment, and the rehabilitation period may be delayed.
Dermoid and pregnancy
Mature teratoma and pregnancy are not mutually exclusive, since the pathology does not lead to impaired reproductive ability and hormonal disorders. A cyst can quietly exist in a woman’s body throughout pregnancy without showing any symptoms, but the tumor can grow under the influence of hormonal changes during pregnancy. If a dermoid neoplasm is detected during pregnancy, but its size is small and does not interfere with the normal development of the fetus, laparoscopy of the ovarian dermoid cyst is not performed. If complications develop, then, despite pregnancy, the question “should I remove the ovarian dermoid cyst?” doctors answer positively.
Forecast
With early diagnosis and removal of the cystic formation, complete recovery occurs with preservation of reproductive function.
Re-formation of teratomas is extremely rare. After surgical removal of a tumor, women should undergo an ultrasound scan once every six months.
If the teratoma is not removed in a timely manner, this can lead to complications.
Even minor physical activity (squats, bending, jumping) can be provoking factors. In addition, unremoved formations can degenerate into cancer.
Treatment
Depending on the stage of the pathology and the age of the patient, different methods of medical correction can be chosen:
— Waiting method. If a dermoid cyst is detected in a child or young woman, then this option is chosen. In this case, much depends on the size and location of the tumor. If it does not cause any discomfort and is small in size, then experienced doctors suggest simply observing the tumor. The patient is prescribed regular examinations and examinations using an ultrasound sensor. During them, cyst growth is noted.
— Conservative methods. This treatment method is based on watchful waiting. However, at the same time, the patient is prescribed medications that inhibit the production of certain hormones, as a result of which tumor development is inhibited.
— Surgical method of treatment. In most cases, if a dermoid cyst is found, surgery is inevitable. The only question that arises is when it will take place.
If the size is quite large, severe symptoms, infertility and other complaints, elective surgery is indicated. Tumor removal can be done in two ways:
- laparotomy;
- laparoscopy.
If a medical institution has all the necessary materials and equipment, as well as qualified surgeons, then the second type of surgical correction has an advantage.
MRI showed endometrioid cyst - what to do
A disease called endometriosis in women causes the formation of cystic cavities. There is no dependence between nosologies. Some representatives of the fair half develop endometrial cysts against the background of endometriosis with menstruation disorders, infertility, and abnormal pain in the lower abdomen.
MRI description of endometrioid ovarian cysts:
- High intensity signal in T1 weighted sequence;
- No shadow in hydrography mode;
- Adhesive conglomerates on both sides of the uterus with the formation of scars at the site of chronic inflammatory processes;
- Uneven thickening of the wall of the endometrioid cyst with inhomogeneous internal contours. Cyst size – up to 10 cm;
- The mode of uniform darkening on the T2 weighted pulse sequence is a differentiating feature that distinguishes endometriotic cavities from other hemorrhagic analogues;
- A similar MRI picture is formed with mucinous cystadenomas, but the latter type is larger. Gel-like internal contents, multi-chamber structure are specific MR signs of pathology. Mucinous cystadenomas can be traced using hydrography.
We suggest you read: Is it possible to cure a kidney cyst with saline dressings?
Dynamic observation of endometrioid cystic cavities allows for timely diagnosis of the tumor. The presence of nosology requires oncological alertness.
A protrusion into the mucous membrane of the posterior wall of the nasopharynx is an anatomical structure called the “bursa of Thornwald.” If the outlet is clogged and separated from the nasopharynx, the preconditions for the development of an inflammatory process are created.
The formation of a cyst in the area contributes to the accumulation of pus and damage to the surrounding soft tissue. There are no clinical manifestations until purulent degeneration. The consequences appear after the colonization of pyogenic flora.
Only magnetic resonance imaging reveals a small Thornwaldt cavity.
Magnetic resonance imaging evaluates the anatomy (location, structure of organs) of the ovaries and fallopian tubes, contents in the ovaries and fallopian tubes, and pathological changes. MRI shows changes in ovaries smaller than 1 centimeter, which is especially important for endometriosis.
In order for the diagnosis to be as accurate as possible, it is important that the patient provides his medical history to the MRI doctor. This will help to carry out MRI studies in the required protocols and sequences, which in turn guarantees the correct diagnosis.
The doctor will identify the dominant follicle, count the number of follicles in the ovary, evaluate the corpus luteum in the ovary, and evaluate the patency of the fallopian tubes.
MRI of the pelvis. Hyperintense lesions indicate fluid in a woman's fallopian tubes
Prevention
A dermoid cyst is a congenital disease caused by impaired fetal development in the embryonic period. Over the past year, the percentage of patients with dermoid cysts has doubled. Perhaps a big role in this is played by the influence of the environment, or the incorrect lifestyle of a pregnant woman, whose fetus subsequently suffers from this disease.
It is very difficult to determine the presence of inflammation before the disease manifests itself. That is why there is no prophylaxis to prevent the development of cysts.
In order to avoid serious consequences, you should undergo regular examinations by doctors. If a dermoid is detected at an early stage, then the consequences of its removal have virtually no effect on the patient’s future life. If a growth is detected in the body, you must follow all the doctor’s instructions and be sure to agree to the operation. Under no circumstances should a dermoid cyst be treated using traditional methods, since an effective result can only be achieved surgically.
Preventive actions
Unfortunately, it is impossible to protect the body from the occurrence of dermoid, because the true reasons for its appearance have not been determined.
A woman needs to visit a gynecologist regularly
Prevention comes down to timely detection of the problem. For this it is recommended:
- Visit a gynecologist regularly (2 times a year).
- Carefully monitor your health and treat all diseases in a timely manner.
- To undergo a full medical examination for those women who are planning to conceive a child.
- Eliminate unhealthy habits (drinking alcohol, smoking).
- Provide adequate nutrition, enriched with vitamin A, selenium, and minimize the amount of animal fats.
Classification by type of cyst in newborns
Newborn brain cysts are classified according to certain parameters.
Some of them have a congenital etiology, appearing during fetal development, or as a result of childbirth, aggravated by suffocation and oxygen starvation of the child. Other cysts appear after injury or inflammation as a complication. A vulnerable period when multicystic brain disease with multiple necrotic areas can occur, in which the prognosis is unfavorable, is the period between the twenty-eighth week of pregnancy and the first week after birth.
Depending on the location where these hollow structures are located, several varieties are distinguished. Cysts located in the pituitary gland, which controls growth and metabolism, most often cause developmental disorders in the corresponding area.
Cystic cavities are also found in the cerebellum, also known as lacunar cavities. They are quite rare and usually affect male children, causing motor dysfunction.
In the pineal gland, which is responsible for endocrine processes, pineal formations are formed due to improper movement of the cerebrospinal fluid. This also includes a pineal gland cyst.
In the arachnoid mater, due to mechanical damage, intracranial bleeding, and infection, a newborn may develop an arachnoid cyst of the brain, which is prone to enlargement, to which boys are also more susceptible.
An intermediate velum cyst may often occur. Its location is the fold of the inner lining of the brain, where its third ventricle is located. Detected primarily on MRI.
A tumor in the subarachnoid space can appear as a consequence of injury, inflammation, or as a postoperative complication. This appearance is not typical for infants.
Cystic formations also form in the lateral ventricles of the brain; as they grow, they cause an increase in intracranial pressure.
Most often found in infants are subependymal cysts filled with cerebrospinal fluid, which occur after intracranial bleeding due to vascular damage.
It can be a consequence of injuries received by the child while passing through the birth canal. SECs can be of different sizes and have a negative impact on the baby’s health.
Retrocerebellar formations occur in the tissues of the gray matter of the brain when its cells die, provoked by infections, bleeding, and wounds. These cysts can be severe and require treatment.
Such a type of cyst as porencephalic is almost never detected in childhood.
In this case, several cavities in the brain replace necrotic areas of the brain.
Periventricular damage to the white matter is caused by disturbances in intrauterine development or exposure to infection, which can result in paralysis of the baby.
According to the cellular structure, the cyst can be:
- colloidal. It appears during fetal development and increases as the baby grows, causing fluid accumulation in the brain. Requires removal;
- dermoid. A rare formation located in the corners of the eyes, behind the ears, in the back of the head, on the lips or on the nose. It consists of cells of dental, bone, glandular tissues, and hair follicles. It needs to be disposed of promptly;
- an epidermoid cavity filled with flat epithelium and keratinized particles, which should also be removed;
- a choroid plexus cyst, also called a pseudocyst, filled with cerebrospinal fluid. It is diagnosed in the fetus by ultrasound examination and usually disappears by 28 weeks on its own, but may persist after birth. Manifestations are directly related to the place where it originated.
Classification of a brain cyst is made based on its location or the period of life in which it formed. There are the following main types of brain cysts in an infant:
- One of the most severe forms of this disease is a subependemal cyst. May appear due to cerebral hemorrhage or due to oxygen deprivation. Often, the cyst can disappear on its own, so it does not require serious treatment in the future. But otherwise, urgent surgery is necessary. Of course, with proper monitoring of the child and implementation of preventive measures, such measures will not be required.
- An arachnoid cyst is a formation that can be located in the arachnoid membrane of the brain, mainly filled with cerebrospinal fluid. There are two main types of cysts: primary and secondary. Most often, such cysts occur in boys. The cause of the formation may be a previous inflammatory disease, head injury or hemorrhage in the brain. A distinctive feature of this type of cyst is its rapid growth, which can lead to some complications. But with timely treatment, this will not affect the further development of the child.
- A retrocerebral cyst is one of the most common types of formation. Can lead to necrosis of brain cells or complete disruption of its functions. It may appear due to surgery in the skull area, insufficient blood circulation in the brain, injuries or a stroke.
Depending on the type of tissue from which the cyst is formed, as well as its structure, a brain cyst can be:
- Arachnoid (enlarged sphere filled with cerebrospinal fluid).
- Colloidal (formed at the embryonic stage, during the formation of the central nervous system).
- Dermoid (forms in the early weeks of fetal growth when cells destined for the face are isolated in the brain or spinal cord).
- Epidermoid (formed similarly to dermoid, when cells from skin tissue, nails and hair enter the spinal cord or brain).
- Pineal (formed in the pineal gland of the brain).
Types of cysts
The classification of cystic formations is carried out based on their location, as well as with mandatory consideration of the dangerous consequences of the further development of the disease.
The disease develops in utero (during pregnancy itself) and can be diagnosed starting from the 28th week of fetal development. In medical practice, the neoplasm is classified as a cerebral pseudocyst.
In medicine, such a formation can also be called cerebral or intracerebral. The disease is typical for small patients who have disturbances in the functioning of the circulatory system (in the head area) or have suffered cerebral ischemia or internal hemorrhage. Often the neoplasm is a consequence of prolonged hypoxia.
The neoplasm forms on the surface of the tissue, between the membranes of the brain, and most often does not manifest itself with any characteristic symptoms. The internal filling of the formation is usually cerebrospinal fluid. An arachnoid cyst is much less common and is considered less dangerous. Lack of treatment is dangerous because the child will lag behind in his psychomotor development.
The peculiarity of the disease is that the cavity itself forms inside the brain, which increases the risk of death of the gray matter. As the cyst develops, a serious deterioration in the child’s well-being is observed, and specialist intervention is also necessary.
Neoplasms are localized in the periventicular region of the white matter. They are formed during intrauterine development of the fetus. The need for surgical intervention in such cases is determined solely by the doctor. If the formations themselves are relatively small, then with conservative complex treatment they can decrease in size and resolve on their own.
A porencephalic cyst is characterized by the simultaneous formation of multiple formations of different sizes. The pathology is quite rare, but requires immediate intervention from doctors.
Hollow formations with internal fluid of this type can be found in the area of the pia mater near the third ventricle. It is possible to confirm or completely refute the doctor’s suspicions about the presence of a disease such as a cyst of the intermediate velum only after a thorough magnetic resonance imaging.
A subarachnoid cyst is usually localized in the subarachnoid space and is a consequence of head trauma, for example due to an accident. With a rapid increase in the size of the cyst and complex manifestations of symptoms, surgical intervention is necessary.
Dermoid cyst
The main difference between the dermoid type of cyst is the fluid filling of the cavity, which consists of embryonic particles. The disease is diagnosed extremely rarely and only in children of the first year of life.
The development of pathology can lead to the formation of mental retardation, partial or complete loss of vision and hearing, as well as disturbances in gait and coordination of movements.
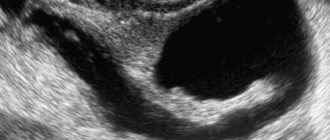
This is what a brain cyst looks like on an MRI.
We have already mentioned that a cyst can be a congenital pathology, or it can appear after the birth of a baby:
- In the first case, the neoplasm appears as a result of developmental disorders of the child while he is in the womb. It is also possible that an inflammatory process may occur after asphyxia, which occurred at birth.
- In the second case, cystic formation may occur as a complication after injury or an inflammatory process. Next, we will consider the types of these pathologies.
Reviews from women about the treatment of mature teratoma
Three years ago, a dermoid cyst was operated on at the Nizhny Novgorod Clinical Diagnostic Center.
There was laparoscopy. There were two centimeter-long scars, practically invisible, and there was one stitch through the navel. The cyst was discovered at the age of 18, and the operation was performed at the age of 30. It was on the right ovary, it was not possible to save it, it was my own fault - it lasted so long. The sooner you have surgery, the better!!!! Don't be afraid of anything! They also cut out my fibroids and removed a bunch of adhesions. Don't delay. This year I will try to get pregnant with one ovary. The doctors said that everything would be fine! And I believe. Vasilyeva Svetlana https://deti.mail.ru/forum/v_ozhidanii_chuda/planirovanie_beremennosti/u_kogo_byla_dermoidnaja_kista_ili_teratoma_kak_lechili_i_posledstvija/
Dermoid cysts do not resolve in any way.
The doctor suggested that I “observe.” They observed me until I was taken to the emergency room with a torsion, and was successfully operated on in the hospital. My operation was difficult, but now 3 years have passed, I carried the pregnancy, gave birth myself, only three tiny scars on my stomach remind me of the operation. So it’s okay, but it’s better to have surgery right away. She https://www.woman.ru/health/woman-health/thread/4369629/
Women who have been diagnosed with a dermoid cyst need to take their health very carefully and seriously. However, there is no need to panic. Modern surgery will quickly and efficiently eliminate this problem. And if the patient does not delay the operation, then the doctors manage to completely preserve the woman’s reproductive function.
Reasons for education
Cerebral cyst
The reasons for the appearance of a brain cyst in a newborn can be very diverse, let’s now try to figure them out:
- As mentioned above, a cyst can appear in a child in the womb. This is considered normal, since during some periods of pregnancy these formations can appear and disappear quickly, so you should not worry about this.
- A child may also develop a cyst due to infection. This can be observed during a difficult pregnancy or difficult childbirth. Often the appearance of a cyst can be triggered by the presence of the herpes virus in the mother’s body.
- Another reason that provokes the appearance of this disease is poor blood supply to the newborn’s brain, which can lead to tissue death and, as a result, to the formation of a cavity filled with fluid.
- A cyst can also appear after illness, for example, meningitis, encephalitis.
- Also, any injury can cause a brain cyst to appear in a newborn.
What can cause tremors in a newborn and is it worth worrying about the peculiar trembling of the baby’s limbs and head? A diagnosis of glioblastoma of the brain has been made - you can lie down and die, or there is still a chance and it must be used 100 percent.
Tumor marker CA-125 in ovarian cyst: norm and pathology
Modern oncology has the latest diagnostic methods that allow early detection of various pathologies in the human body. These include a blood test to determine tumor markers, which indicate the presence of tumors. It also reveals the nature of the formation and helps plan treatment in a timely manner.
Tumor marker CA-125 for ovarian cysts has an important role in a woman’s life, because it indicates the presence of a tumor not only of the uterine appendages, but also of other organs.
Ca-125 with an ovarian cyst is normal from 0 to 30 IU/ml. At the same time, 0-15 IU/ml is absolutely healthy, and 15-30 IU/ml is the upper limit of the acceptable value.
The borderline value is 30-40 IU/ml - observed during pregnancy or menopause.
Elevated CA-125 with an ovarian cyst - more than 40 IU/ml. Indicates an ovarian cyst, inflammatory causes, endometriosis, liver diseases (40–100 IU/ml). Over 100 IU/ml - possible development of an oncological process.
Most women with pathology of the appendages, in whose analyzes CA-125 is elevated due to an ovarian cyst, begin to read reviews on forums and thereby set themselves up for the worst scenario. A tumor marker test alone will not make a definitive diagnosis.
Such a study only signals the onset of an inflammatory process. A tumor marker shows a discrepancy with the norm, which is not always the cause of the disease. The numbers in the analysis will not accurately indicate the reason for the deviation, so additional research is necessary.
The importance of tumor marker diagnostics lies in identifying the disease even before the appearance of pronounced symptoms.
Tumor marker HE 4 for ovarian cysts is used for screening diagnosis and evaluation of the effectiveness of treatment of ovarian tumors.
As a result of numerous studies, the purpose of which was to compare the sensitivity and specificity of tumor markers HE4 and CA-125 in women with various forms of benign and malignant neoplasms of the reproductive organs.
All scientific papers provided percentage data that indicated that HE 4 has higher sensitivity and specificity compared to CA-125. This is an innovative discovery in the diagnosis of tumor diseases of the internal genital organs.
Diagnosis of the disease
When examined in a gynecological chair, the doctor defines a dermoid as a mobile round formation that is localized in the uterine appendage and does not cause pain.
To conduct a differential diagnosis, the following studies are prescribed :
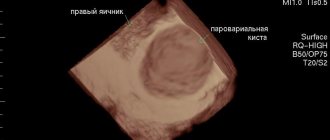
- Ultrasound , preferably vaginal - such a study allows you to evaluate the parameters of the tumor - wall thickness, size, state of blood supply, presence of inclusions, density of the contents of the cyst cavity, and so on.
- MRI – is prescribed to clarify the data provided by ultrasound.
- Pregnancy test – necessary to exclude ectopic pregnancy.
- A tumor marker is needed to be sure that the tumor is not malignant.
- Laparoscopic examination is required to make an accurate diagnosis, as well as to obtain biomaterial for laboratory research.
The essence of pathology
Any cyst is a capsule or sac-like formation, inside of which there is liquid content.
Growths formed in the ovary can be true or functional. The latter tend to resolve on their own, and the true ones, although benign, must be removed through surgery.
A dermoid cyst is a true cyst - its contents are the result of cell division of its capsule-shaped membrane.
This cyst is also called dermoid, the shape of the dermoid is oval or round, the walls are thin but strong.
Most often, single-chamber formations are found, but sometimes multi-chamber ones can be observed. A mature cyst has a mucous fluid inside it, sometimes you can find sebaceous glands, adipose tissue, and even hair and teeth in it.
The dermoid does not grow quickly, however, if there are factors that provoke its growth, it can reach up to 15 cm in diameter.
As for the age group, a dermoid can form at absolutely any age of a woman, including a newborn girl.
Most often, a neoplasm is diagnosed in the right ovary, since it has a larger volume and is better supplied with blood, therefore ovulation is more frequent there.
Expert opinion
Dmitrieva Elena Yurievna
Gynecologist-endocrinologist, 40 years of experience
Scientists do not yet know exactly why a dermoid develops; the formation of a cyst occurs in utero and is stored in the ovaries. Therefore, a neoplasm can be detected in childhood. However, not all dermoids reach mature forms; this requires certain factors, such as hormonal changes or abdominal trauma. Sometimes doctors choose observational tactics and conservative methods to treat dermoid formation, and quite often the tumor disappears on its own. If a woman experiences complications or negative symptoms that manifest themselves when the cyst is large, it is removed.
MRI diagnosis of arachnoid cyst: consequences
The use of magnetic resonance imaging makes it possible to distinguish between primary and secondary types of formation. The first option is formed in utero. Causes of arachnoid cystic cavities of the second type:
- Brain concussion;
- Strong blows to the head;
- Major strokes;
- Severe road traffic accidents.
Differentiation of primary and secondary types of arachnoid cystic cavities using MRI is based on studying the wall. The wall of the primary lesion consists of the arachnoid membrane, the secondary one - scar fibers.
Tomograms show the localization of the arachnoid brain cavities:
- Lumbar spine;
- Around the sheath of nerve fibers;
- Posterior cranial fossa;
- Frontal or parietal parts of the head.
We suggest you read: Fluid cyst in front of the ovary
The causes of the primary subarachnoid lesion are inflammation, meningitis of the newborn, brain injury to the baby during movement through the birth canal.
Methods for effective treatment of brain cysts
Treatment of a cyst located in the brain is performed using conservative and surgical methods. Conservative therapy involves taking pills and other forms of medication. Surgical method - surgery is prescribed. In the absence of indications for surgery to remove a cyst located in the brain, drug therapy for the disease that caused the appearance of tumors is first performed.
The brain has a great compensatory ability and often copes with such pathologies without therapy. If the functioning of one part of the brain is disrupted, another part of the organ can take over and perform its functions. The operation is indicated in cases where there is an increase in the strength and frequency of attacks, and serious pathologies develop - hydrocephalus, pre-stroke conditions.
Conservative therapy
For a cyst that remains stable in size in the brain, the patient is treated with anti-inflammatory and antiviral drugs. Taking into account the type of underlying disease, immunomodulators and medications are prescribed to restore normal blood supply to the tissues of the head and to resolve adhesions.
Surgical method
The doctor compares what the initial dimensions of the cyst were and how its geometric parameters change over time. If the spherical cavity grows progressively, removal of the cyst that is growing in the brain is indicated. In case of manifestation (increased clinical manifestations after an asymptomatic course) of the disease, therapeutic methods are used to ensure decompression of surrounding tissues. Surgical methods include:
- Radical surgery. Trepanation of the skull followed by excision of the tumor with its walls and contents.
- Shunting (expansion of the lumen of blood vessels) in the subdural space.
- Laparoscopic fenestration. Opening the cyst cavity using endoscopic and laser equipment, removing liquid contents, excision of part of the walls, treatment with coagulation.
- Drainage using needle aspiration.
Ventricular drainage is urgently performed in emergency cases when the patient has severe disturbances of consciousness - coma, stuporous state. The procedure is performed to reduce intracranial pressure and eliminate compression on the tissue.
What is a cyst localized in the brain?
Cysts, common in different areas of the adult brain, are spatial cavities hidden behind impenetrable dense walls and filled with fluid. The neoplasm looks like a spherical inclusion against the background of the brain matter or its membranes. Many people who are faced with a similar problem are concerned about the danger of a cyst localized in the brain. If a benign formation does not grow, the person’s health does not deteriorate.
As the size of the tumor increases, the risk of complications increases - impaired fluid outflow, the development of hydrocephalus. The consequences of a cyst located in the head of an adult are predicted individually based on observations and research results. It is impossible to answer the question of how long people live with a cyst. The duration and quality of life depend on the individual characteristics of the body and the specific course of the pathology. A person with a small foreign formation that does not change in size can live to an old age.