Constant colds, difficulty breathing through the nose, an incessant runny nose - all these are accompanying signs of adenoids. Almost 50% of all children experience this disease. What are adenoids and where are they located? Why do they increase? How to understand that pathology is developing? How are adenoids treated and is it possible to cope with the disease without surgery? Let's figure it out together.
What is this?
Photos and signs of adenoids in children are included in this article. But what is it? This is the name for overly enlarged, overgrown pharyngeal tonsils. If, in addition, they are inflamed, then we can talk about a disease called adenoiditis.
The pharyngeal tonsil itself is a small gland that can be found on the back wall of the larynx. It is further divided into several lobes. This organ is part of the immune system. Its main task is the reproduction of lymphocytes. That is, cells that protect the human body from viruses, bacteria and other harmful foreign agents.
But when the pharyngeal tonsil grows, it turns from a useful organ into a pathological one and is a threat to health. Why do many parents strive to find out how to determine adenoids in a child? The fact is that overgrown pharyngeal tonsils are a typical childhood problem. Moreover, it is quite rare in children under 2 years of age and in adolescents. The peak incidence of adenoiditis occurs between 3 and 12 years. Statistics show that for every one thousand children here, 27 suffer from this disease.
Features of the anatomical structure
Adenoids in a child’s nose are a nasopharyngeal tonsil, part of the pharyngeal ring. It is located in the place where the pharynx and nose connect. In newborn babies, the tonsils are still underdeveloped. But by the age of three they are fully functional.
The tonsils have an important job in the body. They are a kind of barrier that prevents the entry of infections and viruses. Having penetrated the nasal passage, microorganisms immediately encounter the pharyngeal tonsil. Lymphocytes are also formed in the tonsils, these are cells that protect the immune system.
Adenoids are actively functioning until the age of seven. Most often they become inflamed in children aged 3 to 7 years. Gradually they become smaller in size. And by the age of 15-16 they become tiny, without affecting the breathing of adults.
The tonsil increases in size when a child gets a viral or bacterial infection. Some time after the illness (from two to three weeks), it again becomes its previous size. But if the child gets sick again, the enlarged adenoids become larger again, not having time to return to their previous size. Then they do not return to their original size. Gradually they grow and become like cushions and make it difficult for the baby to breathe. Sometimes inflammation of the adenoids is diagnosed.
Causes
It is important to know how to identify an adenoid in a child. But you also need to imagine why children can develop such a pathology. Its main reasons are as follows:
- Frequent colds and infectious diseases that somehow affect the condition of the mucous lining of the nasopharynx. For example, measles, rubella, mononucleosis.
- Poor environmental conditions in the area where the child lives.
- Genetic predisposition. Therefore, parents who suffered from this problem in their childhood should definitely know how to identify an adenoid in a child.
- Tendency to allergies, presence of bronchial asthma. It is these pathologies that are observed in 65% of children who have been diagnosed with adenoiditis.
- Unfavorable both climatic and microclimatic conditions. Something like: dryness or gas pollution from air exhaust, the presence of a large amount of suspended dust in it. This all leads to drying out of the mucous membranes, which makes them very vulnerable.
What are the complications of adenoids?
If the disease is not treated, it leads to serious consequences. Neighboring organs suffer, oxygen starvation is diagnosed, since breathing through the mouth cannot provide the baby’s body with a sufficient amount of oxygen.
Complications include:
- Increased incidence of viral and colds;
- Frequent inflammation of the middle ear;
- Children's hearing decreases;
- Deformation of the structure of the skull, the child develops an adenoid type face;
- The chest develops incorrectly;
- Developmental inhibition in contrast to peers and speech impairment.
Prevention
A number of preventive measures will help minimize the risks of developing the disease. These include regular hardening of the baby, a balanced diet and walks in the fresh air. You should also strengthen the body with courses of vitamins and immunomodulators, and avoid communicating with children suffering from viral infections. By following these rules, parents can avoid frequent viral infections and inflammation of the adenoids.
Development of the disease
How to identify adenoids in a child's nose? The best way is to contact an ENT specialist at the slightest alarming symptoms. After all, the disease is constantly progressing and it is dangerous to ignore it.
There are several stages of adenoid development, each with its own individual characteristics:
- The tonsil has grown slightly. It blocks only a certain part of the nasal passage. There are not many specific signs of a problem at this stage. Only the child has some difficulty breathing, especially at night.
- The adenoids practically double in size and already cover up to 2/3 of the nasal passage. How to identify adenoids in a child’s nose at this stage? They, of course, cannot be seen with the naked eye. The child constantly complains of difficulty breathing, suffers from snoring, and breathes with his mouth slightly open.
- The tonsil completely blocks the nasal lumen. At this stage of the disease, breathing through the nose becomes impossible.
Causes of adenoid development
The main reason for the appearance of adenoids in the nose in children is a weak immune system. Hypertrophy of lymphoid tissue is designed to improve the protective function of the tonsil and increase the number of immune cells. However, with an increase in the size of the nasopharyngeal tonsil, the process of breathing through the nose worsens, since the organ covers part of the vomer, as a result of which local immunity is further weakened. The result is diseases of the ENT organs associated with impaired nasal breathing.
Causes and predisposing factors to the development of adenoids:
- genetic predisposition;
- frequent ARVI;
- allergic reactions;
- too dry air;
- “childhood” infectious diseases – chickenpox, measles, scarlet fever;
- chronic diseases of the upper respiratory tract;
- weakened immunity.
One of the most common reasons is genetic predisposition. It has been proven that children of parents who experienced adenoids in childhood are more susceptible to this disease.
A predisposing factor is a decrease in general immunity. This may be due to various reasons - from long-term use of antibiotics to chronic diseases. Also one of the reasons is the presence of a focus of infection in the body, for example, in the case of chronic tonsillitis.
One of the factors that indirectly affects the development of adenoids is the air that the child breathes is too dry or polluted. This is explained by the fact that the nasopharyngeal tonsil acts as a kind of filter, purifying all the air entering through the nose. If it fails to cope with its functions, the process of proliferation of lymphoid tissue begins and adenoids form.
Signs of enlarged tonsils
Signs of adenoids in a child at an early stage of the disease are usually nonspecific. Parents sometimes think that their children have a common runny nose or cold. But there are also specific symptoms that should never be ignored:
- Difficulty breathing through the nose.
- The child begins to snore in his sleep.
- The patient has difficulty swallowing food. Sometimes he even chokes on it while eating.
- The child may complain that there is a foreign body in his nose. In this case, when you blow your nose, nothing is detected.
- Children's voices become quiet and dull. All the time I feel like they are talking “in my nose”.
- The child periodically or constantly breathes through his mouth.
- You notice his constant irritability and chronic fatigue.
Symptoms and treatment of adenoids in children
- difficult or impossible breathing through the nose;
- the child breathes through his mouth;
- adenoids in young children (infants) cause problems with the sucking process (the baby does not eat enough, is capricious and does not gain weight well);
- anemia;
- problems with smell and swallowing;
- feeling of a foreign body in the throat;
- the child speaks quietly;
- nasal voice;
- snoring during sleep, sleep disorder;
- recurring otitis media, chronic runny nose;
- hearing problems;
- complaints of headaches in the morning;
- overweight, excessive activity, decreased performance at school.
A child with chronic disease (in addition to the classic symptoms) is characterized by slightly bulging eyes, a protruding jaw, an overbite (the upper incisors protrude forward), a half-open mouth and a deviated nasal septum. Pay more attention to what your child looks like.
If you notice several of the above signs in your child, this is a reason to contact an otolaryngologist to diagnose the problem and choose an effective treatment method with an integrated approach to solving the problem.
Symptoms of adenoiditis
The review presented photos, symptoms and signs of adenoids in children. We know how enlarged tonsils manifest themselves. Now let’s imagine the symptoms of the stage of the disease when it turns into inflammation - adenoiditis:
- A runny nose, against which conventional medications are virtually powerless.
- Heat.
- Headache.
- Constant sleepiness.
- General weakness.
- Decreased appetite.
- Complaints of nausea.
- Chronic cough.
- Pain in the nose, ears, throat. In some cases, there is a slight deterioration in hearing.
Drug treatment
Drug treatment is divided into local and systemic. Local methods are more gentle and have a local therapeutic effect. But in cases of purulent acute adenoiditis, a protracted course, one cannot do without prescribing systemic drugs.
Methods of local therapy:
- Sanitation of the nasal passages. At home, this is rinsing the nasal cavity with saline solutions. They either use ready-made liquids (Humer, Salin, Aquamaris) or prepare their own. For the last option, add a teaspoon of sea or medicinal salt to 200 ml of warm water.
- Using nasal drops. The direction of the drug depends on the leading symptom. These can be vasoconstrictors (Naphthyzin, Nazospray, Farmazolin), antimicrobials (Protargol, Isofra), steroids with anti-inflammatory effects (Nasonex).
- Sanitation of the nasopharynx includes the procedures of gargling, irrigation with sprays, and sucking lozenges. Preparations for the treatment of the throat - Chlorophyllipt, Orasept, Lisobakt, Givalex.
Vitamin complexes (Multi-Tabs, Pikovit, Alphabet) are used as general strengthening agents. If the infection does not respond to previous procedures, then oral antibacterial drugs are used. Medicines from groups with broad antimicrobial activity are prescribed.
Among the most effective antibiotics, the following are recommended:
- semisynthetic penicillins - Amoxil, Amoxiclav, Flemoxin, Flemoclav.
- macrolides - Sumamed, Azithromycin, Erythromycin.
- cephalosporins - Ceftriaxone, Ceftum, Cefodox.
The course of treatment averages from 7 to 10 days. The dosage is selected by the doctor based on the child’s weight and the severity of the disease.
How to recognize?
How to determine adenoids in a child at home? Compare his condition with the symptoms described above. If they coincide, there is a reason to urgently make an appointment with an ENT specialist. Only a doctor can absolutely accurately determine whether such a pathology is observed.
How to recognize adenoids in a child? A special examination is required. As part of this, the pharynx is examined in mirrors. A special device with a small round mirror (no more than 10 mm) in diameter is used. With its help, the tonsil area starting behind the soft palate is examined.
How to recognize adenoids in a 3-year-old child? With the help of this mirror device, which helps to examine the pharynx where it cannot be seen with the naked eye. Next, the doctor determines the stage of progression of the pathology. Based on observations, he can identify the cause of the disease.
In addition, the mirror device helps to discern the condition of the enlarged tonsil itself. It may be inflamed, covered in mucus, pus, or swollen due to an allergic reaction.
Using Home Methods
Folk remedies for the treatment of adenoids help in the initial stages of the disease. But apply treatment after consulting with your doctor.
- Take a glass of boiled water, add a quarter of a teaspoon of soda to it. Pour in 15 drops of propolis tincture. Choose 10% products. Rinse your nose three times a day. The water should be warm so as not to burn the mucous membrane.
- Grind dry St. John's wort, pour warm water into it. Then set aside for 5 hours, during which time it should brew, then strain. Rinse your child's nose with this product 3 times a day. The ratio of St. John's wort and water is 1 to 5 parts.
- Take a tablespoon of olive oil, add five drops of thuja essential oil. Place two drops in each nostril before going to bed. But first clear your nose. solution.
Attention! Treatment with folk remedies can begin after making sure that the baby is not allergic to the herbs or essential oils used.
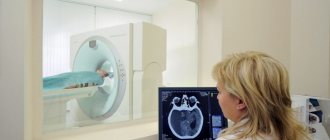
Endoscopic examination
How to recognize adenoids in a 2-year-old child? The most recommended method is endoscopic examination. What it is? Inspection using a miniature device with a camera and a light at the end. It is administered through the baby's nose. Everything that the camera records is broadcast on the monitor screen. The doctor and parents can immediately see the condition of the adenoids.
A similar procedure is not carried out at the stage of exacerbation of the disease, only during remission, in order to obtain a more informative and accurate picture. But even during an exacerbation, endoscopy will help determine hypertrophy of the tonsils, the presence of mucus, swelling or pus on their surface.
To make a more accurate diagnosis, after an endoscopic examination, the child is also sent for a blood test - general and biochemical. This diagnostic measure helps to identify an allergic predisposition or the presence of inflammatory processes.
Diagnostics
Before you figure out how to treat adenoids in the nose, you should find out the degree of proliferation of lymphoid tissue. To do this, you need to contact an otolaryngologist and undergo an examination.
First, the doctor will simply examine the patient. Rhinoscopy is performed - a small metal funnel is inserted into the nose, allowing you to visually examine the nasopharynx. To obtain a more detailed picture, endoscopic examination, radiography or CT of the nasopharynx is used.
Additionally, a general and biochemical blood test is prescribed to identify a chronic inflammatory process.
Diagnostic methods not recommended
Previously, the so-called digital examination of adenoids was popular among ENT specialists. It was very simple: the doctor placed his fingers in the child’s throat and felt the enlarged tonsils. This made it possible to determine both their size and consistency. Which provoked deep shock and vomiting in young patients.
Of course, such an examination was more informative than the same examination in the mirrors. After all, by palpating you can determine the degree of pathology, as well as palpate the tonsils themselves. If they are soft, it means that an inflammatory process is developing. If they are dense, then this indicates hypertrophy, which can only be dealt with through surgery.
Radiography was also previously used to make a diagnosis. Today this method is recognized as ineffective. It risks unnecessary radiation exposure to the child. And, besides, it does not always give accurate results that correspond to reality.
With the help of x-rays, one could actually only see the shadows of enlarged adenoids. It was extremely difficult to know whether it was hypertrophy, inflammation or swelling.
Treatment
The goal of treatment of adenoids and adenoiditis is to normalize the general condition, restore adequate nasal breathing, and reduce the frequency of inflammatory processes in the nasopharynx. Children receive treatment on an outpatient basis, ENT departments or in-patient departments of infectious diseases hospitals. There are two types of therapy: conservative and surgical.
There are no universal remedies for the treatment of adenoids. The complex consists of the following areas:
- antimicrobial agents;
- anti-inflammatory drugs;
- immunocorrection;
- physiotherapy;
- symptomatic care;
- adenotomy.
Among surgical interventions, minimally invasive methods of removing the pharyngeal tonsil are widely used. Below we will dwell in detail on the various methods.
How to treat the disease?
You now know how to determine whether a child has adenoids. Of course, diagnosis is quite difficult for a non-specialist. There is always a risk that you will confuse this serious illness with a cold or runny nose. Therefore, in no case should you diagnose your child yourself, much less treat him with over-the-counter medications for adenoiditis!
Perhaps you will achieve some relief. But after a while, the symptoms of the disease will return and it will continue to progress. There is no need to wait for the moment when overgrown adenoids completely block the nasal lumen, and the child will not be able to breathe normally at all. This is the case when a visit to the doctor cannot be postponed!
How to determine if a child has adenoids? To answer this question, ENT specialists carry out precise diagnostics: endoscopic examinations, urine and blood tests. In some cases, an x-ray of the nasopharynx is indicated.
The main methods of treating this problem in children are mainly medicinal and conservative. Especially in the early stages of the disease (1.2). It is possible to get rid of adenoids here by taking medications and attending physiotherapeutic procedures. The surgical method is used only if conservative treatment has had no effect.
Complex treatment
What to do when a child is diagnosed with adenoids? Most people immediately think about removing them. However, you may not have to resort to surgery. Removal is carried out only in extreme cases when conservative treatment methods do not produce results. The treatment regimen usually includes vasoconstrictor and antiseptic medications, nasopharyngeal lavage, and sometimes antibiotic therapy.
Vasoconstrictor and drying drops
In case of severe swelling in the nose, which prevents the patient from sleeping and eating normally, as well as before therapeutic and diagnostic procedures, the doctor will recommend instilling drops of a vasoconstrictor and drying effect into the nose. It should be borne in mind that they do not treat adenoids, but contribute to temporary relief of the condition:
- Young patients are usually prescribed Nazol-baby, Sanorin for children, Naphthyzin for children (we recommend reading: instructions for using the drug "Nazol-baby" for children). There are restrictions - you cannot use these funds for more than 5-7 days in a row.
- If the adenoids are accompanied by copious mucus secretion, then drying drugs are prescribed, such as Protargol (silver-based drops for children with instructions).
Rinsing the nasopharynx
Rinsing the nasopharynx is a useful procedure, but only if parents know how to do it correctly.
If you have doubts about your own strengths and skills, then it is better to sign your baby up for rinsing with a doctor - if the procedure is carried out incorrectly, there is a risk of infection in the middle ear and, as a result, the development of otitis media. For rinsing you can use:
- Aquamaris solution;
- still mineral water;
- saline;
- saline solution (1 hour (we recommend reading: how to make your own saline solution for rinsing a child’s nose?). L. salt per 0.1 boiled water);
- decoctions of medicinal herbs (calendula, chamomile).
Antiseptic drugs
To disinfect the surface of the mucous membranes of the inflamed nasopharyngeal tonsils, eliminate pathogenic microorganisms, reduce swelling and reduce inflammation, the doctor will prescribe antiseptic drugs. When treating adenoids in children, medications such as:
- Miramistin;
- Derinat (we recommend reading: how to drip Derinat into the nose of children?);
- Collargol.
Antibiotics
When treating adenoids, antibacterial drugs, including topical agents, can be used only as prescribed by a doctor. Antibiotics are included in the therapeutic regimen in cases where the patient has developed adenoiditis.
Antibiotics do not help reduce the size of the tonsils; in addition, when used uncontrolled, microorganisms develop resistance to the drugs.
| Drug name | Active ingredient | Release form | Age restrictions, years |
| Sorphadex | Gramicidin, dexamethasone, framycetin | Drops | from 7 years old |
| Amoxiclav | Amoxicillin, clavulanic acid | Tablets, powder for suspension, solution for intravenous administration | from 12 years/ no restrictions/ from 12 years |
| Sumamed | Azithromycin dihydrate | Tablets 125, 500 mg, capsules, powder for suspension | from 12 years / from 3 years / from 12 years / from 6 months |
| Suprax Solutab | Cefixime | Water soluble tablets | from 6 months (with caution) |
Physiotherapeutic treatment
Treatment of adenoids should be comprehensive. Physiotherapeutic methods complement drug treatment. Doctors often prescribe a nasal quartz procedure.
Ten-day courses of laser therapy also help young patients. Another effective way that helps improve nasal breathing after the second lesson is breathing exercises using the Buteyko method.
Folk remedies
Before using any traditional medicine, it is recommended to consult a specialist. Some recipes can harm inflamed nasopharyngeal tonsils if treated incorrectly. In addition, the selection of a suitable composition will depend both on the individual characteristics of the patient’s body and on the stage of the disease.
Popular home remedies include:
- Salt rinsing. 1 tsp Pour sea salt into a glass of boiling water, stir thoroughly until the crystals are completely dissolved. Add 2 drops of iodine. Cool to room temperature. Rinse the nasopharynx twice a day for 10 days.
- Mix oak bark (20 g), St. John's wort (10 g), mint leaves (10 g). Pour a glass of boiling water and cook over low heat for 3 minutes. Let it brew for 1 hour. Strain through cheesecloth. For 14 days, instill 4 drops of the decoction into each nostril into the patient’s nose (repeat the procedure twice a day).
- Antiseptic oils. Treatment consists of three consecutive courses, each lasting 14 days (42 in total). In the first two weeks, 3 drops of eucalyptus oil are instilled into each nostril of the patient three times a day. Sea buckthorn oil is used for the next 14 days. Complete the treatment with a course of cedar oil or tea tree oil.
Surgery
Adenoid vegetation is sometimes subject to surgical removal. It is carried out at stages 2-3 of the disease, when pathological changes pose a threat to the life and health of the patient, as well as in the absence of effect from the use of conservative treatment methods.
Adenotomy is performed using laser resection. This technique has a number of advantages:
- fast recovery;
- low level of trauma;
- excision is highly accurate;
- the ability to carry out endoscopic control;
- the laser has a cauterizing effect, due to which the risk of bleeding becomes minimal;
- less painful way.
Conservative therapy
How to determine the degree of adenoids in a child? Refer to the description above - individual symptoms are highlighted for each stage of pathology development. As for treatment, the most common would be drug therapy.
For the most part, children are prescribed antihistamines, immunomodulators, vitamin supplements, and other drugs that stimulate the body's immune defense. To relieve inflammation and facilitate breathing through the nose, special nasal drops with anti-inflammatory components are used.
Vasoconstrictors are prescribed with caution - they cannot be used for more than 3-5 days in a row! In some cases, rinsing the nasal passages with salted solutions or similar medications has a good effect.
As for physiotherapeutic procedures, the following are usually prescribed:
- Medicinal electrophoresis (with prednisolone, potassium iodide or silver nitrate).
- UHF therapy.
- High frequency magnetic therapy.
- Mud applications.
- Ultraviolet treatment.
Breathing exercises are also of great importance here. After all, a child, especially at an advanced stage of the disease, gets used to breathing through his mouth. Re-developing the habit of nasal breathing in such cases is very important.
The whole complex of these methods is in most cases enough to get rid of adenoids. But if the disease is at the third stage, the child’s condition does not improve, and surgical intervention has to be resorted to.
Why are adenoids dangerous?
Due to constant mouth breathing, the child’s body does not receive enough oxygen.
It is necessary to treat adenoids in the nose in a timely manner, otherwise complications cannot be avoided. The danger is not the proliferation of lymphoid tissue itself, but the diseases associated with it. Among the complications:
- chronic otitis;
- chronic sinusitis (sinusitis);
- hearing impairment;
- the appearance of speech defects;
- hypoxia;
- stopping breathing during sleep.
Chronic otitis is a sluggish inflammatory process in the middle ear. It is dangerous due to perforation of the eardrum and hearing loss. Otitis media does not lead to deafness, but a person with a chronic form hears about 20% worse than healthy people.
Chronic sinusitis, in particular sinusitis, is another common complication of adenoids. The disease manifests itself as inflammation of the nasal sinuses and requires complex treatment.
Note! Quite often, otitis media and sinusitis “go hand in hand” with grade 2 and 3 adenoids.
Another common complication is the appearance of speech defects. Since the child cannot breathe through his nose, he does not pronounce some sounds. Also, if nasal breathing is impaired, a noticeable nasal voice is observed.
Hypoxia, or oxygen starvation of tissues, is a complication of grade 3 adenoids. This is due to the fact that when breathing through the mouth, the body lacks oxygen. As a result, metabolic processes deteriorate, sleep quality decreases, and cognitive functions suffer. This is especially noticeable in children of primary school age who have problems concentrating in class due to the fact that the brain does not have enough oxygen.
The most dangerous complication is sleep apnea. This disorder manifests itself as a short-term cessation of breathing during sleep. In severe cases, there is a risk of complete respiratory arrest.
Removal issue
Removal of enlarged tonsils is indicated only in one case - with obvious, true hypertrophy (that is, tissue proliferation). If they are enlarged due to allergic edema or inflammation, then removal of the adenoids is contraindicated. The only solution is to continue conservative treatment. Removal of inflamed tissue is fraught with the development of a number of complications - infections, deep injuries, active bleeding.
When deciding whether surgery is necessary, an ENT specialist must answer the following questions:
- Were there any formations such as mucus and inflammation on the surface of the tonsil? Did they flow down the back of the throat?
- What color was the mucous membrane of the adenoids?
- Was the surface of the tonsil soft or folded in nature?
The answers to these questions will help distinguish hypertrophy of the tonsils from an inflamed area of tissue or the appearance of an allergic reaction in the form of edema.
If the mucous membrane is bright red, unnaturally pale or bluish, this indicates the development of inflammation. A smooth surface also indicates swelling and inflammation. Hypertrophy of the tonsils is indicated by the presence of a healthy pink mucous membrane, as well as a folded surface typical for the normal state of the tonsil. Only in this state of affairs, if necessary, can the child undergo surgery.
Pharyngeal tonsil and its functions
Before treating adenoids and adenoiditis in a child, let’s remember the nature of its occurrence. When pathogenic flora enters the body by airborne droplets, the first barrier of the child’s immunity awaits it in the nasopharynx. This is a Pirogov-Waldeyer ring. It includes several accumulations of lymphoid tissue:
- two palatine tonsils;
- two tubal tonsils;
- one pharyngeal;
- lingual;
- lateral ridges along the posterior wall of the pharynx.
The pharyngeal tonsil is considered an organ of the peripheral immune system. Together with the tonsils, it becomes a defense against antigens entering the oral cavity and upper respiratory tract. In lymphoid tissue, bacteria, viruses, and allergens are captured and inactivated.
Inflammation of the nasopharyngeal tonsil is called adenoiditis, and the growth (hyperplasia) of the organ is called adenoid vegetations.
The pharyngeal tonsil is most active in children under 12 years of age. This is why adenoiditis often occurs in children. The peak progression of adenoid disease in a child is from three to seven years. By the age of 16, involution (reverse development) of this gland occurs. Therefore, the chance of treating her infections increases at this age.
Possible complications
Even if a child does not get sick often, but has difficulty breathing through his nose at night, it is worth understanding where the adenoids are located (photo above). The pathological process at the first stage rarely leads to the development of complications. However, parents should monitor the baby's condition and seek medical help for any unpleasant symptoms.
There can be bad consequences if you do not treat second and third degree adenoids. Chronic inflammation of the upper respiratory tract has already been discussed above. If a child has a weak immune system, a simple sore throat can be fatal. In addition, an “adenoid face” may develop. If you miss the moment, the child’s appearance can no longer be changed. Irreversible deformation of the maxillofacial skeleton occurs. Due to improper breathing, the shape of the chest also changes, and almost all organs suffer from this. The late stage of adenoids can lead to a delay in mental and physical development of the patient. It is not always possible to catch up. Therefore, it is so important to consult a pediatrician already when the baby begins to breathe through his mouth at night and snoring appears.
Prognosis and prevention
If parents do not neglect the health of their children, the prognosis is favorable. In the first stage of adenoid disease, the disease can be maintained with conservative therapy. If the tonsils do not allow you to breathe fully through your nose, an operation is performed, after which the unpleasant symptoms go away within a few days.
Prevention is also important. If a child is diagnosed with an early stage of adenoids, parents should work on strengthening the little patient’s immunity. It is worth walking more in the fresh air, eating well, and sleeping at least 10 hours a day. Simple sports such as swimming and gymnastics will also benefit the child.
Is the pathology subject to conservative treatment?
Can a child's adenoid face be corrected through conservative treatment? Most likely, the answer will be negative. In this case, much depends on the age of the child and the degree of completion of the formation of the cranial bones. If it is not completed, then you can try to correct the shape of the face through a specially designed set of gymnastic exercises.
It should be noted that before eliminating such a pathological condition as adenoid face, complex therapy is carried out aimed at curing the nasopharyngeal tonsil. If necessary, surgical intervention is indicated. A deviated nasal septum should also be excluded.
In the later stages of the disease, you can seek the help of a specialist in the field of facial surgery. But you should also constantly work with your child to develop the habit of breathing through the nose, not the mouth, and teach him to keep his mouth closed.
What a child’s adenoid face looks like, photos are presented in this article. The most striking signs can be immediately noted:
- mouth in a slightly open position;
- presence of facial puffiness;
- obvious inhibition in appearance;
- smoothed folds of the nasolabial area;
- due to constant breathing through the mouth, the bones of the face and jaw are deformed;
- the upper jaw is narrowed;
- the face takes on an elongated shape;
- the bite is deformed;
- the upper lip becomes shortened;
- the incisors located on top are constantly visible;
- the skin of the lips becomes dry;
- the chest is deformed;
- teeth may become deformed at the top, acquiring a twisted shape around an axis.
- Secondary complications such as hearing loss and blockage of the Eustachian tube by compacted tonsil tissue near the nasopharynx can also be observed;
- There is severe snoring at night, which often degenerates into apnea.
Approximately half of the children diagnosed with “adenoid face,” the photo of which is presented below, have delayed mental and mental development, pathologies of the respiratory system, and insufficient oxygen supply to the brain tissues.
Adenotomy, is the operation dangerous?
Adenoid removal occurs in a children's hospital under local or general anesthesia. The doctor can perform a classic adenotomy using medical instruments. Then the excess lymphoid tissue is carefully cut off with an adenoid. However, this method is very dangerous, since the cut tissue can get into the respiratory sinuses of the nose and cause complications. There is also a method called endoscopy - the most modern and painless option for surgery. Usually this method is quick and without complications.
After the operation, the doctor gives complete instructions on home regimen. It is worth noting that the postoperative period may be accompanied by nasal and ear congestion, runny nose and otitis media. Although all these factors disappear on the seventh day after removal of the adenoids.
Sometimes the doctor rejects the operation for a number of reasons:
- The baby is not two years old.
- Abnormalities in the nose and throat area.
- Infectious diseases.
- Diseases of the blood and heart.
Surgery can be avoided if you follow the preventive measures prescribed by your doctor.
Preventive actions
To prevent inflammation of the tonsils and the appearance of growths, it is necessary to strengthen the immune system. Moderate hardening is recommended. It is advisable to accustom your child to a contrast shower. Excessive care should be abandoned and the child’s body should be allowed to produce antibodies. This will lead to the rapid formation of the immune system and prevent frequent infectious diseases in kindergarten and school when communicating in a group.
If a child is often sick, it is important to eliminate the cause and symptoms in a timely manner, as well as monitor the condition of the tonsils. Prevention involves treating inflammatory diseases to prevent tissue proliferation.
To prevent the development of diseases of the respiratory system, optimal indoor conditions should be maintained. The humidity level should not fall below 40%. It is advisable to reduce dust concentrations. This can be achieved through wet cleaning and the absence of unnecessary objects in the room. Sources of dust include souvenirs, figurines, and soft toys. In extreme cases, they can be wrapped in plastic wrap to prevent particle penetration.
Existing contraindications for surgery
Contraindications include:
- inflammatory process in an acute state;
- blood rheology disorders.
Many doctors point to the fact that a conservative method of treatment can help cure the disease only in the initial stages of its development.
As for the conservative treatment method for eliminating the adenoid face, much depends on the age of the child and the degree of the disease. The transition from one stage to another causes rapid deformation of the skull bones.
At the initial stages and at an earlier age, a set of gymnastic exercises that are aimed at developing the facial muscles and special therapeutic exercises for the face can correct the adenoid face.
In this regard, it can be stated that existing facial deformation in the later stages can only be eliminated through surgical intervention. In adult patients, correction of the adenoid face is possible only with the use of plastic surgery.
Adenoid grades
Endoscopy allows you to assess the degree of adenoid growths.
Rice. 3. The photo shows the growth of tonsil tissue (view through an endoscope).
Rice. 4. In the first degree of adenoids, the nasal passages are blocked by 1/3 (on the left). With the second, they are blocked by 2/3 (in the center), with the third, they are almost completely blocked (on the right).
Degrees of tonsil enlargement
The lymphoid tissue of the tonsils grows depending on the causes and the state of the immune system. It is customary to divide the inflammatory process into 4 degrees, which is determined by the radiologist when describing the image:
- In the initial stage, the tonsils block about 1/3 of the openings of the nasal passages. During sleep, grade 1 adenoids make breathing difficult. Sometimes snoring or snoring can be heard. Inflammation with such growth must be treated conservatively.
- Grade 2 adenoids cover more than 50% of the lumen in the nasopharynx. When breathing, snoring always appears and difficulty breathing can be heard. With grade 2 adenoid hypertrophy, during a conversation the child inhales air through the mouth, speech is not intelligible. Treatment is conservative.
- The tonsil covers almost the entire nasopharynx. The child has difficulty breathing.
For each grade, treatment options are considered individually depending on the severity of the condition.
Provoking factors for the development of adenoids
Adenoids are provoked by:
- ARVI;
- hypothermia;
- reduced immunity;
- measles;
- whooping cough;
- scarlet fever.
Risk factors for developing a condition such as adenoid vegetation include:
- chronic infections;
- improperly balanced diet;
- monotonous diet with high carbohydrate consumption and lack of vitamins;
- poor ecology in the region in which people live;
- bad habits weaken the body’s immune system and make it vulnerable;
- tendency to allergic reactions, which leads to inflammation of the adenoids.
Symptoms of the disease
Adenoids are a childhood disease that in 95% of cases goes away with age. Typically, tonsil volume loss begins during adolescence. However, in some cases the problem remains in adults.
Symptoms of adenoids in the nose in adults and children are as follows:
- difficult breathing through the nose;
- night snoring;
- sleep apnea (with grade 3 adenoids);
- prostration;
- nasal voice;
- frequent otitis and chronic rhinitis;
- hearing loss;
- frequent headaches.
For nasal adenoids in adults, symptoms include difficult nasal breathing and night snoring. All signs and symptoms of adenoids in the nose are generally the same for adults and children, however, in childhood there is a general decrease in immunity and frequent acute respiratory viral infections.
Quite often, the diagnosis of adenoids in the nose in adults is carried out accidentally, for example, if a person complains of snoring at night. This is explained by the fact that the disease is more typical for young children. Adenoids in an adult can be suspected if there is a chronic runny nose and an increased tendency to otitis media, since these two diseases are typical signs of adenoids.
What do adenoids look like in the nose?
It is impossible to find out on your own what exactly the adenoids in the nose look like, but you can see the proliferation of lymphoid tissue with the help of a special examination. This is due to the fact that the nasopharyngeal tonsil is located deep in the nasopharynx and can only be seen through the nose using a special device.
In general, what exactly the adenoids in a child’s nose look like can be determined using endoscopy. This is an examination during which a thin tube with a camera at the end is inserted into the nasopharynx. With the help of such an examination, the doctor will not only diagnose the extent of the adenoids, but will also show the parents a picture of the growth of the nasopharyngeal tonsil, because the image during endoscopy is displayed on the monitor. The screen will show pink lymphoid tissue of the nasopharyngeal tonsil extending beyond the nasopharynx and overlying part of the vomer.
What is an adenoid face?
How can the face and skull be deformed with adenoids?
Adenoid type of face is a pathological facial expression that is formed due to the presence of adenoid vegetation.
With an adenoid face, a number of main signs are noted, which include:
- keeping the mouth in a half-open position;
- presence of malocclusion;
- the presence of a wedge-shaped lower jaw;
- facial expression devoid of emotion;
- dejected facial expression;
- presence of nasality.
Diagnosis of adenoids
At the moment, in addition to the standard examination by an ENT doctor, there are other methods for recognizing adenoids:
- Endoscopy is the safest and most effective method that allows you to see the condition of the nasopharynx on a computer screen (the condition is that there are no inflammatory processes in the body of the person being examined, otherwise the picture will be unreliable).
- X-ray - allows you to make accurate conclusions about the size of the adenoids, but also has disadvantages: radiation exposure to the body of a small patient and little information content in the presence of inflammation in the nasopharynx.
Previously, the so-called digital research method was also used, but today this very painful examination is not practiced.
General information
Adenoiditis takes a leading position in the structure of ENT diseases in pediatric practice. Adenoids are formed as a result of the proliferation of lymphoid tissue of the nasopharyngeal tonsil. Every person has adenoids, and they perform a protective function if they do not grow or become inflamed. Today, the term “adenoids” refers specifically to inflamed adenoids, which do more harm to the body and immunity than good.
What are adenoids for?
Adenoids are an immune organ whose main function is to protect against infections. Lymphoid tissue produces special immune cells - lymphocytes , which destroy pathogens. During the period of fighting infection, the adenoids increase in size. With chronic adenoiditis, the nasopharyngeal tonsils are constantly inflamed and are the focus of chronic infection. The ICD-10 code is J35.2.
Visual cues
Many people are interested in the question of what adenoids look like and whether they can be identified on their own.
At the initial stage, it is difficult to identify the proliferation of the pharyngeal tonsil. This can only be done by a doctor using a mirror laryngoscope. Normally, the tonsils are ridge-shaped with small, fuzzy nipples covering their surface.
The vomer is a bony structure that makes up the nasal septum.
Choanae are small openings that connect the nasal cavity to the pharynx.
An otolaryngologist should diagnose the pathology and prescribe treatment.
This disease is characterized by a slow and long course. When adenoids appear, the child often begins to get colds. Due to these symptoms, parents are forced to consult a doctor, who subsequently makes a diagnosis based on an examination of the pharyngeal tonsil and nasal passages. For this, a device such as a mirror is used.
There are such signs of adenoids in adults (photo) and children: difficulty breathing through the nose and the presence of discharge from the nasal cavity. This condition is accompanied by permanent or temporary nasal congestion and copious serous discharge. This leads to difficulty in air movement in the upper respiratory tract. As a result, a favorable habitat is created for bacteria and infections, warm and humid.
Thus, polyps and adenoids contribute to the development of various infections. When breathing through the mouth, the air cannot be warmed and moistened to the required degree, as with nasal breathing, which also contributes to the development of a cold and its accompanying complications.
In addition to relapses of sore throat and bronchitis, children with polyps in most cases develop chronic tonsillitis (inflammation of the tonsils of the palate) and pharyngitis (inflammation of the larynx):
- Frequent runny nose. Adenoids cause blood overflow and stagnation in the soft tissues around them. The soft palate and mucous membrane of the nasal passages are affected by these symptoms. This makes breathing even more difficult, and a runny nose can become chronic over time.
- Snore. This pathology is impaired breathing, when vibration of the soft tissues of the nasopharynx and throat produces a low-frequency rattling sound. Snoring occurs solely as a result of mouth breathing.
Adenoids in the nose in adults and children lead to the fact that a person begins to breathe through the mouth, while the soft palate rises and then begins to sag between the nasal cavity and the pharynx. This process is aggravated by the fact that swollen tonsils prevent the free passage of air due to the narrowing of the respiratory passage. In addition, this process progresses due to a decrease in muscle tone of the larynx and pharynx during sleep.
All these symptoms together lead to the occurrence of turbulent air flow (chaotic air movement). In this regard, vibration occurs in the throat, palatal tissue and root of the tongue. This creates a characteristic sound (snoring). Other signs:
- Sleep disorders. Difficulty breathing with adenoids leads to restless sleep. The patient may have nightmares. When the root of the tongue sinks or when soft tissues close during inspiration, suffocation may occur. Poor sleep during the night causes drowsiness and fatigue during the day.
- Nasal and unintelligible speech. When the polyps increase slightly, phonation disturbance occurs. The voice becomes nasal and the timbre decreases. This results in complete or partial closure of the nasopharynx outlet.
In a healthy person, the exit is open, and at the moment of conversation, the sound begins to resonate (intensify) in the sinuses. In the presence of adenoids, this is not possible.
Hearing impairment. The middle ear communicates with the pharynx through the auditory tubes. As the adenoids enlarge, the cavities of these tubes close, which leads to a decrease in the hearing threshold. At the same time, the person often begins to ask again what could be the reason for seeing a doctor.
Open mouth all the time. This occurs due to difficulty breathing. Nasal congestion forces you to breathe through your mouth. When eating, the child often opens his mouth slightly and tries to swallow food as quickly as possible in order to inhale air.
The adenoid face is a type of facial skeleton that is formed under the influence of nasal congestion and a constantly open mouth. The skull in the facial region elongates over time, the upper jaw and nasal passages narrow. Due to impaired development of the hard palate, bite deformation occurs, and the lips no longer close completely.
If this pathology is not recognized and treated in time, this type of face may remain for life.
The disease may be accompanied by the following symptoms:
- rapid fatigue;
- headache;
- apathy;
- lethargy;
- weakness.
Adenoids affect breathing patterns. A healthy person breathes deeply through his nose, while mouth breathing for a long time leads to insufficient ventilation of the lungs. This has a negative impact on your health.
Blood oxygen saturation decreases, and constant oxygen starvation of the brain occurs. This is the reason why children suffering from inflammation of the tonsils become more inattentive and distracted. Their academic performance drops because it is harder for them to remember school material than for healthy children.
With a prolonged course of the disease, due to a decrease in the depth of inspiration, the formation of the chest may be disrupted. One of the most common deformities is chicken breast.
When adenoids grow, an inflammatory process called adenoiditis actively develops. It leads to enlargement of the lymph nodes. In addition, there is a relapse of symptoms of a nonspecific infection (fever, weakness, etc.).
Knowing where the adenoids are located, parents can promptly respond to the deterioration of the child’s condition and seek medical help. Otherwise, such a pathology threatens the development of irreversible changes in the body, which can negatively affect the further life of the individual.
What do grade 1 adenoids look like?
At the first stage, the enlargement of the adenoids cannot be noticed visually, since they increase slightly.
During examination using a mirror, a hyperemic area of lymphoid tissue is revealed, reaching a size of 0.5-2 cm. Its growth occurs unevenly.
Stage 1 overgrowth of adenoids in a person is diagnosed when no more than 1/3 of the choanae and vomer are closed.
Inflamed adenoids of the 1st degree do not create noticeable discomfort for the patient, and therefore it is not often possible to diagnose them at an early stage.
What do grade 2 adenoids look like?
Stage 2 tonsil enlargement can be seen without even using special devices. Externally, an enlarged adenoid looks like a formation with many bulges into which the nipples have turned after inflammation.
To make such a diagnosis, it is necessary to conduct an examination through 2 passages (nose and throat) for a more accurate assessment of the ongoing process.
Grade 2 adenoids are distinguished by the closure of 1/2 of the vomer and choanae.
What do grade 3 adenoids look like in children?
The third degree of adenoids is the last and most advanced. The pharyngeal tonsil can be seen when examined at home using a spatula.
Behind the soft palate are many round structures of varying sizes and colors (crimson, pink and red). The vomer and choanae are closed almost completely or completely.
It will not be difficult to make such a diagnosis.
What do adenoids look like in the nose?
To identify adenoids (photo) in the nose, it is necessary to undergo a thorough examination, collect tests and data from instrumental research methods. The latter include:
- Pharyngoscopy. Such an examination makes it possible to assess the condition of the pharynx and palatine tonsils. The back wall of the pharynx becomes covered with mucopurulent discharge. To examine the adenoids, it is necessary to lift the soft palate using a medical spatula.
- Anterior rhinoscopy. The method consists of the doctor examining the nasal passages. Thus, swelling and the presence of discharge in the nasal cavity can be detected. It is necessary to instill vasoconstrictor drops, after which the adenoids covering the choanae will become visible. The patient must then swallow. During swallowing, the adenoids in the throat vibrate (photo). At this moment, glare of light appears on the tonsils.
- Posterior rhinoscopy. With this type of examination, the doctor, using a mirror, examines the nasal passages through the pharynx. Thus, polyps become visible, similar to a semicircular tumor with grooves on its surface. In some cases, adenoids may look like a cluster of hanging formations located in different parts of the nasopharynx.
This method gives a clear picture of the disease and is the most effective. But conducting such an examination is difficult, especially in young children.
X-ray of the nasopharynx. Pictures are taken in lateral projection. For the most reliable result, the patient needs to open his mouth, allowing air flow from the outside. This method allows you to accurately diagnose enlarged tonsils and determine the stage of adenoids.
Endoscopy of the nasopharynx. Such an examination provides a lot of information and the opportunity to carefully examine the nasopharynx. But there is one caveat. When conducting an examination using this method, young children require anesthesia.
Classification
There are several classifications of inflammation of the nasopharyngeal tonsils depending on the severity of symptoms, duration, clinical and morphological characteristics. This division of the disease into various forms is due to different treatment regimens.
According to the duration of the flow, they are distinguished:
- Spicy. Episodes of inflammation of the adenoids last up to two weeks and are repeated no more than 3 times a year. The duration of the inflammatory process is 5-10 days. The disease develops acutely against the background of childhood infections or acute respiratory viral infections.
- Subacute. Most often it is a consequence of an untreated acute process. It is registered mainly in children with hypertrophied pharyngeal tonsil. On average, the process lasts 20-25 days, and residual effects in the form of low-grade fever can be recorded for up to a month.
- Chronic. The disease lasts more than a month and recurs more than 4 times a year. The causative agents of the inflammatory process are viral units and bacteria. Both initially diagnosed chronic epipharyngitis and adenoiditis that developed against the background of inadequate treatment at the subacute stage are registered.
The main forms of chronic adenoiditis, depending on the morphological changes in the tonsil parenchyma:
- Edema-catarrhal. With an exacerbation of the disease, the tonsil swells greatly, and activation of the inflammatory reaction in the tonsil is observed. The clinical picture is accompanied by catarrhal manifestations and symptoms.
- Serous-exudative. This option is characterized by a large accumulation of pathogenic microflora and purulent masses deep in the parenchyma. All this leads to swelling and enlargement of the tonsil.
- Mucopurulent. There is a continuous secretion of mucus and purulent exudate in huge quantities. At the same time, an increase in the volume of adenoid tissue is recorded.
There are 3 degrees of severity of the disease depending on the existing clinical symptoms and general condition of the patient:
- Compensated. It is considered a normal physiological response of the body to the penetration of infectious agents. The deterioration of the patient's condition may be completely absent or mild. Disturbances in nasal breathing and snoring are periodically recorded.
- Subcompensated. The symptoms of the disease gradually increase, and general systemic intoxication is recorded, which corresponds to acute epipharyngitis. With inadequate therapy or its absence, the disease goes into the stage of decompensation.
- Decompensated. The pharyngeal tonsil is unable to perform its functions and turns into a source of chronic infection. The symptoms of the disease look bright, local immunity is completely absent.
Komarovsky’s opinion on adenoids in a child
Dr. Komarovsky's school has gained popularity among parents due to its information activities, which help parents decide whether it is worth removing the adenoids, or whether it is necessary to continue conservative treatment of the child.
According to E. O. Komarovsky, enlargement of adenoids occurs in almost all children from time to time. But not everyone’s adenoiditis reaches the point where the child cannot do without surgery.
To prevent adenoiditis, Dr. Komarovsky suggests creating conditions for the child in which viral and bacterial infections will occur more easily, that is, increasing immunity. At the same time, limit the entry of microbes into the child’s body. Great importance is attached to air quality in the treatment of adenoiditis. Regular humidification and ventilation of the premises is required.
What are adenoids?
Nowadays, adenoids are a common problem faced by children of different ages. It is noteworthy that the disease is rapidly growing younger, and children aged 2 to 10 years old are faced with it. Only a timely decision on treatment will help prevent dangerous consequences for the child’s body.
The term adenoids refers to the pharyngeal tonsil located in the nasopharynx. It has the most important function - protecting the child’s body from infections. During the period of illness, the tissues grow, and after recovery they return to their original sizes. However, this does not always happen. In people who often experience various inflammatory processes, the tonsils do not return to their original size. In this case, a diagnosis of adenoid hypertrophy is made, and the patient may also receive a diagnosis of adenoiditis.