Anatomy Basics
What are women's breasts made of? Glands for milk production form its basis. Interestingly, from an anatomical point of view, they are derivatives of the sweat glands. All mammals have such organs. But at the same time, in the animal world, their number in a female depends on how many cubs are born to representatives of this species on average. Monkeys and humans have only one pair of mammary glands, unlike other species, and in the former they are located on the chest, and not on the stomach.
Breast anatomy is quite complex. For example, if you familiarize yourself with the structure of a simple-looking nipple, you will find out that its top is penetrated by many milky passages. And he himself is surrounded by the areola - that’s what the circle around him is called. The skin in this area appears bumpy. This is due to the fact that large mammary glands pass through it. But around the nipple there are no less large sebaceous glands, and many muscle fibers pass through the skin of this area.
We also recommend reading:
How to correctly find out your breast size Main types of female breasts 2 or another breast size: how to determine Why one breast is larger than the other
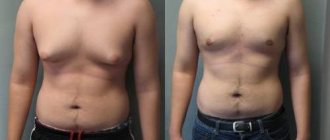
As already mentioned, both men and women have such glands. But among the fairer sex they are always larger. Despite this, their structure is almost the same. The difference lies only in the degree of development. Before puberty, boys and girls' breasts look the same. Then in teenage girls it begins to grow and after some time becomes the most noticeable difference between men and women. But it is still classified as a secondary sexual characteristic. In addition, there are cases when men’s breasts also begin to grow due to disruptions in the endocrine system. Then this phenomenon is called gynecomastia. In these cases, milk production may also occur. Sometimes even the mammary glands of newborns produce secretions, although this is not considered a physiological norm.
Changes in the mammary gland during lactation
The peak of breast growth and changes occurs during pregnancy. During implantation of the embryo into the mucous membrane of the uterus, alveolar ducts gradually grow in the lobules of the gland, at the ends of which alveoli are formed. Before the onset of labor, the cells produce secretions, and before the onset of labor, the mammary glands begin to actively produce colostrum.
Peak growth and changes in the mammary gland occur during pregnancy
The composition of colostrum and breast milk is as follows:
- Colostrum is a thick, yellowish and sticky liquid. Its composition is more similar to blood than to milk. This substance has high energy value. This secretion, consisting of a large amount of easily digestible proteins (albumin, globulins), protective factors (immunoglobulin A, leukocytes, neutrophils) and other important substances, is an important component during the transition from intrauterine nutrition to breastfeeding. Colostrum is produced in the first week after birth.
- A woman's glands begin to produce milk 5-6 days after the birth of the child. Breast milk is not as high in calories and rich in substances as colostrum, but plays a vital role in the development of children in the first years of life. The content of proteins, fats, carbohydrates, enzymes, protective factors, water-soluble vitamins corresponds to the child’s need for nutrients for full development. Vitamin D found in milk prevents the occurrence of rickets. The composition of milk may vary depending on the time of day and the foods that the nursing mother consumes. Therefore, it is necessary to follow a diet and give up bad habits so that the child grows and develops in accordance with the norm.
The structure of the bust is individual at different periods of a woman’s life. This organ plays such an important role as lactation, so it is necessary to take care of its health.
Mammary gland and its structure
Studying the structure of this organ in women begins with a description of the general structure. From this point of view, the mammary gland is a dense body that has the shape of a convex disk. According to the type of its structure, it belongs to the alveolar-tubular glands. Inside, the disk described above consists of cone-shaped slices (there are 15-20 of them). Their tops are directed towards the nipple. In each large lobule, all the ducts are connected into one milky passage. It ends at the nipple with a funnel-shaped hole.
The lobules are separated from each other by layers of loose connective tissue. Inside each large slice there should be even smaller slices. Each of them, in turn, consists of alveoli. They have a diameter of 0.05-0.07 mm.
The blood supply to the organ plays an important role. It is carried out through the internal mammary and lateral mammary arteries. These vessels are accompanied by veins. They form a network with wide loops. The venous “pattern” partially located under the skin is visible in the form of blue veins. Lymphatic vessels and nerves from the brachial and cervical plexus pass through here. And along with the vessels, sympathetic nerves also enter the mammary gland.
Breast shape and size are an individual phenomenon. If you know how the female breast is structured, it becomes clear that its size depends not so much on the size of the gland, but on the thickness of the subcutaneous layer of adipose tissue. How erect or saggy the breasts will be also depends on the elasticity of the capsule in which the mammary gland is enclosed. This is a kind of frame consisting of connective tissue.
Those. Neither the shape nor size of the breasts affect a woman's ability to breastfeed, although they are an important part of her image and a component of sexual attractiveness.
Breast anatomy is quite complex
External structure
Women's breasts have a convex shape. Inside it is a mammary gland with lobules and ducts. All existing ducts exit into the elevated nipple. This structure of the ducts ensures the maximum concentration of beneficial components in milk.
The nipple may be cylindrical or conical (depending on whether the woman breastfed). A round areola stands out on the skin around the nipple. The skin of the areola is darker in color and has sebaceous glands on its surface.
Breast size
The shape and size of the mammary gland reflect the hormonal background of the body. Therefore, appearance changes with age and with changes in the phase of the menstrual cycle (fluctuations in size occur
monthly).
Breast size depends on:
- amount of adipose tissue;
- the size of the gland itself;
- filling of the glandular lobes with milk.
In nursing women, breasts reach their maximum size due to the constant flow of milk. During periods of non-pregnancy and lactation, it is noticeably smaller in size.
Breast size (the ratio of glandular and adipose tissue in the gland) does not affect the possibility of lactation and the amount of milk during breastfeeding.
In addition to adipose tissue, the size of the gland itself also affects the appearance. It can become smaller or larger under the influence of hormones. Therefore, changes that occur in the menstrual cycle (menopause or the beginning of menstruation in girls), the period of ovulation (which is accompanied by hormonal changes) affect breast size. It increases before menstruation and while taking hormonal contraceptives. This condition is called mastodynia and is divided into cyclical manifestations (normal for the female body) and non-cyclical (accompanying pregnancy, lactation, menopause or diseases).
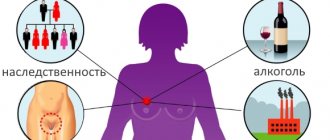
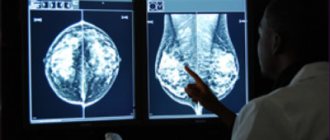
Mastodynia may be accompanied by pain and increased sensitivity. If nipple discharge appears without pregnancy or breastfeeding, you should consult a mammologist.
Breast shape
The shape of the mammary gland depends on the condition of the connective tissue and ligaments (they are called Cooper's ligaments). Sprained ligaments lead to sagging. This condition can occur after breastfeeding.
Indirectly, the appearance and high location of the cones are influenced by the muscle fibers that are located below the chest.
Breast shape is classified into three types:
- Flat or disc-shaped (low, wide chest).
- Hemisphere (equal dimensions of height and base diameter).
- Elongated or conical (height noticeably greater than the base of the chest). If the shape of the breast is lowered and the nipple points downwards, this conical type is called mastoid.
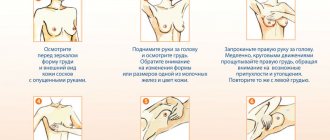
In the video, a mammologist will talk about the structural features of the mammary glands and the harmful factors affecting their health:
Development cycle
Breast development in a girl begins around 9-10 years of age. Before this, the glands and nipples of boys and girls are no different. Hormonal changes increase the growth of glandular tissue and complicate the existing undeveloped ducts. By the age of 12-13 years, the process ends and the first menstruation occurs.
During pregnancy, increased amounts of the hormones estrogen and prolactin increase blood flow around the mammary glands. Additional lobes are formed in the glandular tissue, the milk ducts expand, and the breasts become larger.
Postpartum processes are accompanied by the replacement of glandular tissue with adipose tissue. This replacement continues during menopause (it is initiated by a decrease in the amount of female sex hormones). Therefore, the breasts become smaller and lose their elasticity.
Nipple structure
In the middle of the breast, formed by gland and connective tissue, there is a protrusion, that is, a nipple. But the shape of the nipple can be different. This depends on several factors. For example, in nulliparous women, the nipples are cone-shaped, and in those who have already given birth, they are cylindrical.
The diameter of the areola can vary: from 3 to 5 cm. The pigmentation of this area is noticeably different from the color of the surrounding skin. The areolas and nipples themselves will always be darker. Here, too, it matters whether the woman managed to become a mother. In nulliparous women, the skin on the nipples is pinkish, less often it is dark red. And in those who give birth, it becomes brownish, since increased pigmentation occurs during pregnancy.
Changes in breast structure over time
Changes occur not only with age, but also with a certain phase of the monthly cycle, as well as during pregnancy. Typically, the size of the mammary gland itself is 10-12 cm in diameter, and its thickness is about 2-3 cm. In young nulliparous women, the weight of the organ is approximately 150-200 g.
During pregnancy, changes begin already in the second month, which are clearly visible even externally. Thus, the isola increases in size and its pigmentation changes - the shade becomes much darker. But all these changes affect not only the external, but also the internal side, since throughout pregnancy the mammary gland will enlarge and undergo restructuring. During the period of breastfeeding, her weight can already be 300-900 g.
The structure of the mammary gland and the effects of hormones
The structure of the mammary gland is complex. All physiological processes that were described above occur under the influence of hormones. Sometimes an organ is even called a hormonal target, since its structure naturally contains receptors for a wide variety of hormones. Scientists have found that the development of this gland in adolescence, its functioning during pregnancy and breastfeeding, as well as the processes occurring in postmenopause, are influenced by at least 15 hormones. And the effect of the rest is simply not yet sufficiently studied.
Estrogens play the most important role. They determine the development of ducts and connective tissue of the glands. Under their influence, lobules of different types are formed. Lobules of the first type are called virgin. They usually develop only before the onset of stable menstruation. Only 6-11 ducts are formed in these lobules. Then, under the influence of estrogens, they evolve into type 2 lobules, in which about 47 ducts are formed. Hormonal stimulation during pregnancy causes them to transform into type 3 lobules, which contain about 80 ducts. There are even more ducts in the lobules of the 4th type, but they are found only in women with lactation. Even if the pregnancy ended in a successful birth, but it was not possible to establish breastfeeding, there simply will not be such lobules in the body.
Natural muscle bra
The beautiful shape and elasticity of the female breast is ensured by well-developed, strong muscles of the chest and back, as well as elastic skin, which support the mammary glands in the correct position.
The main muscles whose tone affects the condition of the female breast are the pectoralis major and minor, deltoid, sternocleidomastoid, scalene, coracobrachialis, trapezius, serratus anterior, latissimus dorsi.
By training these muscle groups with the help of special chest exercises and chest machines, you can add additional breast volume, tighten sagging breasts, and make your breast shape more beautiful.
In addition, exercise improves blood flow and lymph drainage in the tissues of the mammary glands, which means they provide good nutrition to the tissues.
The condition of the breast skin is also an important factor in maintaining and giving a beautiful breast shape. Rapid weight gain and a sharp increase in breast size during pregnancy and breastfeeding can cause stretching of the skin, the appearance of stretch marks, weakening of the interlobular ligamentous apparatus of the mammary glands, which leads to sagging breasts.
Now that you have understood the structure of the female breast, it becomes more clear what affects breast growth, its shape, size, and elasticity. And with knowledge of the matter he treats any advice and means for breast enlargement, for changing its shape.
So, let's figure it out further. What are the reasons why breasts are small? What affects breast growth? What affects the firmness and shape of the breast?
Next, we consciously use available safe methods and methods for strengthening and enlarging the breasts without surgery, at home.