Breast tissue regularly undergoes natural changes, which are determined by the specific functioning of the female reproductive system (thelarche, pregnancy, menarche, menopause, lactation). However, some structural changes that occur in the fibrous (fibrous) and glandular breast tissues can be pathological and cause diffuse changes in the mammary glands. Experts say that such disorders are typical for 45% of women during the reproductive period.
View gallery
Causes of this pathology
Diffuse changes in the mammary glands affect:
- Parenchyma is the main functional glandular-epithelial breast tissue with fibrillar fibers of the milk ducts and alveoli.
- Stroma is fibrous connective tissue that surrounds the ducts and divides the lobules.
- Adipose tissue that protects the parenchyma.
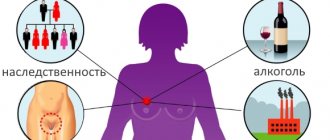
With an increase in the number of tissue cells of the mammary glands or their decrease, as well as with dysplasia (developmental disorder), we can only talk about a hormonal origin. The causes of diffuse changes in the mammary glands may be due to:
It should also be taken into account that diffuse changes in the mammary glands also occur in healthy women. For example, estrogen ensures the development of stroma, the deposition of fat cells and the growth of ducts. Progesterone, with the balance of estrogen, allows the growth of glandular tissue and lobular structures, promotes the formation and alveolar secretory changes. In women of reproductive age, during the menstrual cycle (at the end of the luteal phase), some of the epithelial cells of the alveoli and ducts of the mammary glands, under the influence of progesterone, undergo replication and further apoptosis (physiological natural death). However, increased estrogen levels in women and a lack of progesterone can disrupt this process and cause diffuse fibrotic changes.
During pregnancy, placental lactogen, human chorionic gonadotropin and prolactin stimulate the process of milk secretion and lactation after childbirth. If a hormonal imbalance occurs, the natural processes in women's breast tissue are disrupted. As doctors note, most often there is a pathological proliferation of certain cells, they replace others. Such tissue structural changes in mammology are defined as dishormonal diffuse changes in the mammary glands.
View gallery
About estrogens
This is the collective name of one of the groups of female sex hormones. They are produced in the ovaries in women, in small quantities they are formed in the testes in men, as well as in the liver and adrenal cortex (both men and women). Sex hormones, in general, ensure reproductive function.
Sex hormones are always present in a woman's body. Their level and ratio depend on the period of her life. The main female hormones are estrogens. In the fetus, they are responsible for the formation of female-type genitals; in childhood, they support the growth of the genital organs. During adolescence, the amount of estrogen in the body increases. Due to their influence, secondary sexual characteristics are formed.
The highest level of estrogen is observed in women of reproductive age. At this time, her body undergoes periodic cyclic changes (menstrual cycle).
https://youtu.be/y_hHkA1qLXk
Hormone-releasing hormone agonist Luteinizin (Lupron)
LHRH agonist, blocking the production of hormones in the ovaries. It has many side effects, including hot flashes, depression, decreased libido, myasthenia gravis, vaginal atrophy, bone loss, visual disturbances, and hypertension. It should only be used for short periods of time and should be limited to cases of severe pain.
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs may relieve pain symptoms. It should be taken only for a certain period of time.
Symptoms of breast changes
The very first symptoms of such changes can manifest themselves in the form of increased discomfort in the chest, hypersensitivity before the onset and during menstruation. Many women do not pay attention to this, because after the completion of the next menarche, all unpleasant signs disappear.
However, a consultation with a mammologist will not be superfluous.
Doctors call these most characteristic signs of diffuse changes:
- Tension and heaviness in the mammary glands, which is often accompanied by swelling.
- Burning of the mammary gland, itching in the nipple area, their increased sensitivity.
- Small movable lumps in the form of nodules in the texture of the breast tissue, which can be felt more strongly during menstruation.
- Aching pain of varying strength (intense pain can radiate to the area of the shoulder blades, shoulder or armpit).
- Pain in the mammary glands.
- Clear discharge from the nipples when squeezed.
Many do not feel any of the signs listed above, and a lump in the breast is accidentally discovered, since the manifestations of symptoms of diffuse changes in the mammary glands are predominantly periodic and are caused by the menstrual cycle.
View gallery
Low dietary fat for improvement or resolution of symptoms
Some studies have shown improvement or resolution of symptoms with a low-fat diet. Reducing fat in the diet may improve breast tenderness and pain.
Studies have shown that women with breast pain have lower levels of an essential fatty acid called gamma-linoleic acid and have a significant proportion of saturated fat. Supplementation with essential fatty acids in the form of evening primrose oil (9% gamma-linoleic acid) may reduce abnormal breast tissue sensitivity. Unfortunately, several large studies have not shown a beneficial effect of evening primrose oil in treating chest pain.
Possible complications
There may be complications such as the formation of benign tumors of different sizes. The most dangerous complication is the malignancy of these tumors.
Although this pathology is benign in nature, if blood relatives have cancer of the reproductive system (breast, ovaries, uterus), serious consequences that require medical intervention cannot be ruled out. In general, with diffuse changes in the mammary gland, the prognosis is positive. However, it is necessary to take into account the possibility of the appearance of a malignant tumor, which occurs against the background of such a pathology much more often than when it is absent.
Prevention
Measures to prevent this pathology are:
- prevention, detection and relief of hormonal changes;
- living in environmentally friendly conditions;
- rejection of bad habits;
- prevention, diagnosis and treatment of psychological, reproductive, endocrine, metabolic, somatic disorders that can become the background for the development of this disease, as well as various pathologies of the mammary gland;
- avoidance of radioactive and ultraviolet radiation;
- selection of the correct bra, corresponding to the size of the mammary glands;
- avoiding injury to the mammary glands;
- when breastfeeding a child - prevention, detection and treatment of cracks, stagnation of milk, inflammation;
- avoiding artificial termination of pregnancy, for this purpose regulating childbirth using various methods of contraception;
- regular preventive examinations by a mammologist and oncologist.
The inspection schedule is as follows:
- all women of childbearing age need to visit a mammologist at least once a year;
- women aged 35 to 50 years should undergo a screening mammogram every 2 years, and after 50 years - once a year;
- if lumps are detected in the mammary gland, this is an indication for a biopsy.
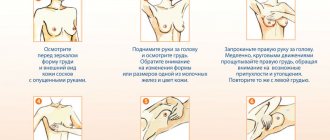
It is important to conduct breast self-examination at least once a month (on days 8-12 of the menstrual cycle). The steps are as follows:
- examine both mammary glands in front of the mirror, evaluate their symmetry, size, shape, contours, skin color;
- palpate all areas of the mammary glands and axillary lymph nodes;
- press on the nipple to identify discharge.
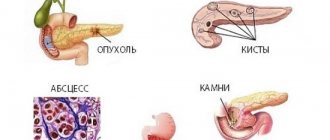
Classification of forms of diffuse mastopathy
In accordance with clinical, x-ray and morphological tissue changes in the mammary glands, diffuse mastopathy is classified as follows:
- Adenosis is a diffuse pathology with a predominance of the glandular component.
- Diffuse mastopathy, in which the cystic component predominates.
- Fibroadenomatosis is a diffuse mastopathy in which the fibrous component predominates.
- Sclerosing type of adenosis.
- Fibrocystic mixed form of mastopathy.
When one or another clinical variant is determined, it is based on the proportion of fatty, glandular and connective tissue elements on mammograms.
Based on the degree of changes present, mild, pronounced and moderate diffuse mastopathy is distinguished.
View gallery
Diagnosis of diffuse changes in the mammary glands
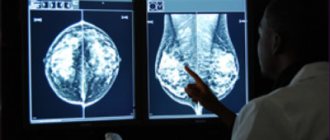
Diffuse mastopathy is diagnosed based on the results of examination of the mammary glands by a mammologist, mammographic examination, ultrasound, laboratory tests, biopsy and MRI of the mammary glands.
With diffuse mastopathy, external changes in the mammary glands are not detected. During palpation examination of the breast, compactions of varying size and extent, painful, without clear boundaries with a lobulated or granular surface are identified. With diffuse mastopathy, seals are most often located in the upper-outer quadrants of the glands.
The standard echographic picture, determined using ultrasound for diffuse changes in the mammary glands, is characterized by thickening of the glandular tissue, fibrous changes in the interlobular septa and ducts, changes in glandular echo density, multiple formation of cysts, discrepancy between the glandular type of structure and age, and ductectasia.
Mammography (survey radiography) for diffuse mastopathy reveals tissue heterogeneity of the glands with small foci of compaction, a dense structure or cystic formations.
Thanks to mammography, it is possible to exclude the presence of tumors in the gland and determine the type of mastopathy.
If there is discharge from the nipples against the background of diffuse mastopathy, this may indicate the need for ductography, which usually determines the deformation of the milk ducts and cysts of different sizes. Examination of a smear obtained from the nipple makes it possible to differentiate diffuse mastopathy from other lesions - syphilis, actinomycosis, mammary tuberculosis.
If there is a concomitant genital and extragenital background, an analysis of sex hormones and thyroid hormones, liver enzymes, consultation with an endocrinologist-gynecologist, and pelvic ultrasound are prescribed.
If the previous diagnostic data are questionable, then a breast biopsy, cytological analysis of the biopsy specimen, MRI, and determination of the CA 15-3 marker in the blood are performed.
Diagnostics
To make a diagnosis, it is necessary to identify the causes of premature involution and the nature of the changes. At the first consultation, the doctor interviews the patient, examines the mammary glands, and issues a preliminary report.
To confirm or refute pathology, the following may be prescribed:
- mammography;
- Ultrasound of the breast;
- blood test for hormones;
- MRI;
- biopsy (if indicated).
The first two methods are prescribed for any examination of the mammary glands. To describe the results, modern doctors use a special Bi-Rads scale, which takes into account all the signs of possible pathologies. Stage zero, as well as Bi-Rads 1 and Bi-Rads 2 indicate the absence of dangerous changes. The rest (3-6) describe the stages of diseases. The higher the reading, the more severe the disease.
Treatment of pathology
To prescribe a course of therapy, a consultation with a mammologist is required.
View gallery
For diffuse mastopathy, conservative treatment and dynamic observation are prescribed. It is advised to change the diet, include more dairy products and plant fiber, and limit animal fats. If the patient has intestinal dysbiosis, which impairs the absorption of microelements and vitamins, treatment by a gastroenterologist is required. Vitamin complexes, potassium iodide, homeopathy, dietary supplements, adaptogens, and herbal remedies are prescribed. Non-hormonal therapy can include drugs of enzymatic, sedative and diuretic types.
For diffuse mastopathy, it is recommended to increase physical activity, include psychotherapy and exercise therapy. Physiotherapeutic procedures include the use of electrophoresis, laser therapy, galvanization, magnetotherapy, and balneotherapy (mud therapy, climatotherapy, clay therapy, sea and mineral healing baths).
For diffuse mastopathy, regulating hormone therapy is aimed at eliminating hormonal defects and may include prescribing gestagens (dydrogesterone, progesterone, etc.), thyroid hormones to the patient, and the correct selection of contraceptive methods. All these remedies will help level out estrogen levels. What this is is now clear.
To reduce the feeling of tension and soreness in the mammary glands, a gel containing progesterone is applied topically.
Treatment methods: what to choose?
To treat diffuse fibrous mastopathy, a combination of medications and traditional medicine recipes is used.
At an early stage, homeopathic remedies and light preparations with herbal extracts are used: celandine, burdock, burnet, belladonna, hops, sage, yarrow. For more advanced forms, treatment with hormonal drugs is indicated: creams, ointments, tablets and injections.
The latest generation of contraceptives, which are taken orally or implanted under the skin, have proven themselves well.
In severe forms of diffuse fibrous mastopathy with a predominance of the fibrous component, treatment with steroids or testosterone injections is indicated.
Among traditional medicines, compresses made from herbs and vegetables are widely used: cabbage, beets, burdock, hemlock, celandine, plantain.
General strengthening teas and homemade balms based on vegetable oils, propolis, and honey are useful.
The treatment regimen for diffuse mastopathy with a fibrous component includes a diet.
It is necessary to exclude fatty meats, hydrogenated fats, fried, canned, smoked foods, as well as drinks containing caffeine from the diet.
Preference is given to whole grain cereals, fish, poultry, dairy products, fruits and vegetables. Vitamin kits and herbal teas are useful. Quitting alcohol and smoking is mandatory .
Nicotine and tar negatively affect hormonal levels, inhibiting the function of progesterone and causing an increase in the number of fibroids.
In what cases is surgery required?
If drug treatment of diffuse changes in the mammary glands for six months does not produce an effect, then they resort to surgical intervention - the seals are removed. The following techniques can be used during the operation:
- Resection. It involves excision of the inflamed area. The resulting tissue is then sent for histological analysis to rule out breast cancer.
- Sclerosis. Used for cystic form of diffuse changes. This method refers to the introduction of a sclerosing substance, leading to the healing of defects in the mammary gland.
- Surgical (surgical) therapy for multiple formations is not carried out: removal or excision of breast tissue through nucleation is possible only after diagnosing oncology. If there are diffuse changes, then monitoring of the condition of the glands and conservative treatment are prescribed. The patient is registered with a mammologist. She undergoes examinations every six months.
View gallery
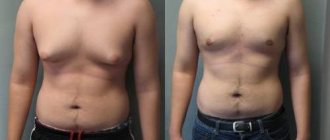
Fibrosis after endoprosthetics
Despite the constant improvement of technology and the professionalism of doctors, fibrosis may well develop after plastic surgery... This condition is called capsular contracture. A thin capsule of fibrosis always forms around the implant, as around a foreign object (we can say that this is mild fibrosis). But, if the stromal tissue becomes rigid, the membrane becomes thick and deforms the endoprosthesis, we talk about contracture and think about a surgical solution to the problem.
Usually the contracture is unilateral and the tissue of the right or left mammary gland is affected.
Any surgical intervention leads to the formation of scar tissue - fibrosis. This means that in the area where a doctor intervenes and opens an abscess, a tumor with fibroadenoma or cancer, you will have local fibrosis. This phenomenon after surgery is normal and is associated with the way our tissues heal.
Post-traumatic fibrosis, like post-operative fibrosis, occurs in both men and women. Women often have larger breasts (anatomy, what can I say). Therefore, ladies involved in contact martial arts are recommended special means of protecting the bust. It is also more often unilateral and usually concerns the left or right breast.
Traditional therapy
Among the folk methods used in the treatment of pathological diffuse fibrotic changes in the mammary gland, one can distinguish external remedies and herbal therapy in the form of decoctions that are taken orally.
The first category includes compresses from infusions of a number of medicinal plants: red clover, sweet clover, St. John's wort, mantle and wormwood. And although the first two plants contain phytoestrogens, it is not entirely clear how they act in the form of compresses.
In addition, folk treatment with compresses made from cabbage leaves, grated raw beets, propolis with lard, aloe with honey has become popular (compresses are usually applied to the chest at night).
Herbal treatment contains recommendations for taking a soothing infusion of valerian (five grams of roots per 200 milliliters of boiling water), a decoction of a mixture of equal amounts of peppermint and motherwort (a tablespoon of the mixture per glass of water), a decoction of cumin and fennel seeds (mix equal amounts of ingredients, take 1 tablespoon per glass of water) – twice a day, 100 milliliters. Fennel is most often used for flatulence and bloating, and its use for diffuse breast pathology can be explained by the presence in the fruits of the plant of essential oils, which consist of unsaturated fatty acids, including oleic and linoleic. The fruits of cumin, related to fennel, are used to improve digestion. They are also rich in terpene compounds, phenolcarboxylic acids and oils.
How dangerous is mastopathy?
Can diffuse changes in mastopathy cause breast cancer? This question is of great concern to women who are faced with a similar problem. Mastopathy itself does not cause malignant transformation and is not considered a precancerous condition. However, the factors that provoke the appearance of this disease are common to oncological pathologies. There is a certain similarity between these diseases in morphology. There are statistics that show the combination of benign formations with malignant tumors in half of all cases, but the probability of transformation of the extraproliferative form of mastopathy into cancer is less than one percent.
But diffuse mastopathy can develop into nodular mastopathy, which in essence is the next stage. With this type, the formation of nodes occurs constantly. It does not depend on the female menstrual cycle. That is why women diagnosed with diffuse mastopathy should undergo examinations by a mammologist every six months. It is necessary to regularly check the level of female hormones estrogen.
View gallery
Prevention and advice for diffuse mastopathy
The key to effective prevention and timely diagnosis of diffuse mastopathy is periodic examinations by a mammologist with a series of instrumental studies. It is necessary to promptly treat gynecological diseases and accompanying genital pathologies.
An important role belongs to regular examination of the condition of the mammary glands by the woman herself. Particular attention should be paid to the appearance of lumps and soreness, spots on the skin of the breast, changes in the shape of the mammary glands, and discharge from the nipples. It is advisable to choose the right bra so that it does not squeeze the breasts and protect the mammary glands from shock, pressure, and injury. During breastfeeding, cracked nipples, mastitis, and lactostasis should not be allowed to appear. To prevent mastopathy, modern contraceptive methods should be used and abortions should not be allowed.
If there is diffuse mastopathy, this is a contraindication for mammoplasty, the use of local wraps and hot compresses on the chest, visiting baths and saunas, tanning in the sun and solarium.